From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
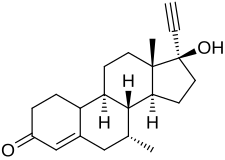
Δ4-Tibolone Other names ORG-OM-38; Delta-4-Tibolone; 7α-Methylnorethisterone; 7α-Methyl-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone; 17α-Ethynyl-17β-hydroxy-7α-methyl-4-estren-3-one
(7R ,8R ,9S ,10R ,13S ,14S ,17R )-17-Ethynyl-17-hydroxy-7,13-dimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a ]phenanthren-3-one
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider UNII Formula C 21 H 28 O 2 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
C[C@@H]1CC2=CC(=O)CC[C@@H]2[C@@H]3[C@@H]1[C@@H]4CC[C@]([C@]4(CC3)C)(C#C)O
InChI=1S/C21H28O2/c1-4-21(23)10-8-18-19-13(2)11-14-12-15(22)5-6-16(14)17(19)7-9-20(18,21)3/h1,12-13,16-19,23H,5-11H2,2-3H3/t13-,16+,17-,18+,19-,20+,21+/m1/s1
Key:WAOKMNBZWBGYIK-KIURNNQRSA-N
Δ4 -Tibolone (developmental code name ORG-OM-38 ), also known as 7α-methylnorethisterone or as 7α-methyl-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone , is a synthetic androgen and progestin which was never marketed.[ 1] [ 2] active metabolite of tibolone , which itself is a prodrug of δ4 -tibolone along with 3α-hydroxytibolone and 3β-hydroxytibolone (which, in contrast to δ4 -tibolone, are estrogens ).[ 1] 4 -tibolone are thought to be responsible for the androgenic and progestogenic activity of tibolone, while 3α-hydroxytibolone and 3β-hydroxytibolone are thought to be responsible for its estrogenic activity.[ 1]
Relative affinities (%) of noretynodrel, tibolone, and metabolites
Compound
Code name
PR Tooltip Progesterone receptor AR Tooltip Androgen receptor ER Tooltip Estrogen receptor GR Tooltip Glucocorticoid receptor MR Tooltip Mineralocorticoid receptor SHBG Tooltip Sex hormone-binding globulin CBG Tooltip Corticosteroid binding globulin
Noretynodrel –
6
0
2
0
0
0
0
Norethisterone (δ4 -NYD )
–
67–75
15
0
0–1
0–3
16
0
3α-Hydroxynoretynodrel
–
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
3β-Hydroxynoretynodrel
–
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
Ethinylestradiol
–
15–25
1–3
112
1–3
<1
0.18
<0.1
Tibolone (7α-Me-NYD )ORG-OD-14
6
6
1
?
?
?
?
Δ4 -Tibolone
ORG-OM-38
90
35
1
0
2
1
0
3α-Hydroxytibolone
ORG-4094
0
3
4–6
0
?
?
?
3β-Hydroxytibolone
ORG-301260
0
4
3–29
0
?
?
?
7α-Methylethinylestradiol
–
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
Notes: Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were promegestone for the PR Tooltip progesterone receptor , metribolone for the AR Tooltip androgen receptor , E2 ER Tooltip estrogen receptor , DEXA Tooltip dexamethasone for the GR Tooltip glucocorticoid receptor , aldosterone for the MR Tooltip mineralocorticoid receptor , DHT Tooltip dihydrotestosterone for SHBG Tooltip sex hormone-binding globulin , and cortisol for CBG Tooltip Corticosteroid-binding globulin . Sources: See template.
Template:Absolute activities of tibolone and metabolites
See also
References
AR Tooltip Androgen receptor
Agonists SARMs Tooltip Selective androgen receptor modulator Antagonists
GPRC6A
PR Tooltip Progesterone receptor
Agonists
Testosterone derivatives: Progestins: 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone acetate 17α-Allyl-19-nortestosterone Allylestrenol Altrenogest Chloroethynylnorgestrel Cingestol Danazol Desogestrel Dienogest Ethinylandrostenediol
Ethisterone Ethynerone Etonogestrel Etynodiol Etynodiol diacetate Gestodene Gestrinone Levonorgestrel Levonorgestrel esters (e.g., levonorgestrel butanoate )Lynestrenol Lynestrenol phenylpropionate Metynodiol Metynodiol diacetate Norelgestromin Norethisterone (norethindrone) Norethisterone esters (e.g., norethisterone acetate , norethisterone enanthate )Noretynodrel Norgesterone Norgestimate Norgestrel Norgestrienone Norvinisterone Oxendolone Quingestanol Quingestanol acetate Tibolone Tigestol Tosagestin ; Anabolic–androgenic steroids: 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone dodecylcarbonate 19-Nor-5-androstenediol 19-Nor-5-androstenedione 19-Nordehydroepiandrosterone Bolandiol Bolandiol dipropionate Bolandione Dimethisterone Dienedione Dienolone Dimethandrolone Dimethandrolone buciclate Dimethandrolone dodecylcarbonate Dimethandrolone undecanoate Dimethyldienolone Dimethyltrienolone Ethyldienolone Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol) Methyldienolone Metribolone (R-1881) Methoxydienone (methoxygonadiene) Mibolerone Nandrolone Nandrolone esters (e.g., nandrolone decanoate , nandrolone phenylpropionate )Norethandrolone Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethandrolone, normethisterone) RU-2309 Tetrahydrogestrinone Trenbolone (trienolone) Trenbolone esters (e.g., trenbolone acetate , trenbolone enanthate )Trendione Trestolone Trestolone acetate MixedSPRMs Tooltip Selective progesterone receptor modulators ) Antagonists
mPR Tooltip Membrane progesterone receptor PAQR Tooltip Progestin and adipoQ receptor )