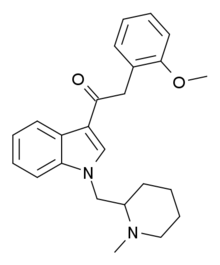
Cannabipiperidiethanone
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Dcirovic (talk | contribs) at 19:44, 28 May 2016 (→top: clean up using AWB). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H28N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 376.490 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cannabipiperidiethanone, (CPE, or 1-(N-methylpiperidin-2-ylmethyl)-3-(2-methoxyphenylacetyl)indole), is a synthetic cannabinoid that has been found as an ingredient of "herbal" synthetic cannabis blends sold in Japan, alongside JWH-122 and JWH-081. Its binding affinity was measured at the CB1 and CB2 receptors and it was found to have an IC50 of 591nM at CB1 and 968nM at CB2, making it 2.3x and 9.4x weaker than JWH-250 at these two targets respectively.[1]
See also
References
- ^ Uchiyama N, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2011). "Identification of a novel cannabimimetic phenylacetylindole, cannabipiperidiethanone, as a designer drug in a herbal product and its affinity for cannabinoid CB₁ and CB₂ receptors". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 59 (9): 1203–5. doi:10.1248/cpb.59.1203. PMID 21881274.
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (modulators) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This cannabinoid related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- Chem-molar-mass both hardcoded and calculated
- Infobox-drug molecular-weight unexpected-character
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- All stub articles
