Clentiazem
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
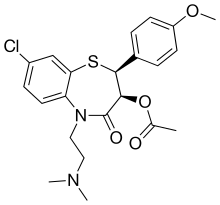
| IUPAC name
acetic acid [(2S,3S)-8-chloro-5-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-yl] ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H25ClN2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 448.9629 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Clentiazem is a calcium channel blocker.[1]
It is a chloride derivative of diltiazem.[2]
References
- ^ Giasson S, Garceau D, Homsy W, Dumont L (October 1995). "Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of clentiazem and diltiazem in closed-chest anesthetized dogs". Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 9 (5): 685–92. doi:10.1007/BF00878551. PMID 8573551.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dagenais F, Hollmann C, Buluran J, Cartier R (October 1995). "Clentiazem and diltiazem preserve endothelium-dependent relaxation following global rat heart ischemia". Can J Cardiol. 11 (9): 816–22. PMID 7585280.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
