Harit Pradesh
Harit Pradesh | |
|---|---|
Proposed state | |
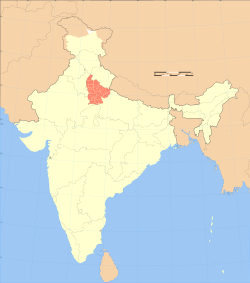 | |
| Country | |
| Region | Northern India |
| Proposed capitals | Meerut |
| Proposed Divisions | |
| Language | Hindi, Khari Boli, Haryanvi, Punjabi, Urdu |
Harit Pradesh (also known as Pashchim Pradesh & Pashchimanchal) is a proposed new state of India comprising the western parts of Uttar Pradesh state.[1] Harit means Green which signifies the agricultural prosperity of the region and Pradesh means state. The region has some demographic, economic and cultural patterns that are distinct from other parts of Uttar Pradesh, and more closely resemble those of Haryana, Punjab and Rajasthan states.
History
In his 1955 critique of the proposed States Reorganisation Act, Thoughts on Linguistic States, B. R. Ambedkar had advocated the division of Uttar Pradesh into three states - Western, Central and Eastern, with capitals at Meerut, Kanpur and Allahabad respectively - in order to prevent excessively large states from dominating politics at the national level.[2] The act was passed in 1956, however, keeping Uttar Pradesh intact as a single state.
Later, socialists like Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia, Jayaprakash Narayan, Acharya Kripalani and others favoured re-drawing of the administrative map of India. But, Jawaharlal Nehru, the then prime minister, supported the States Reorganisation Commission (SRC) recommendation of re-forming states on linguistic basis. Dr K.M. Panikkar, in his dissenting note to the SRC report, however, opposed linguistic states and favoured formation of a state of west Uttar Pradesh.[3]
Later, in 1972, fourteen MLAs in the Uttar Pradesh state assembly moved an unsuccessful resolution to divide the state into three units (Braj Pradesh, Awadh Pradesh and Purvi Pradesh).[4]
- During the 1975-77 Emergency, Sanjay Gandhi almost succeeded in carving out a new state of western Uttar Pradesh with Agra as capital. The new state was to include parts of Haryana too.
- BSP led UP government had on November 23, 2011, passed a resolution in the state assembly for creating Purvanchal, Bundelkhand, Awadh Pradesh and Pashchim Pradesh out of UP. The resolution was forwarded to the UPA government at the Centre but no action was taken.
- After, Congress working committee passed a resolution to recommend formation of a new state of Telangana on 31 July 2013, demand for Harit Pradesh gained momentum. Sh. Jairam Ramesh suggested that UP's reorganisation was necessary as it is difficult to run such a big state effectively. "Purely from an administrative point of view, a state of over 200 million people, 75 districts, over 800 blocks...It's just not governable. It is my personal view...Its politics is a separate issue," he said.[5]
Geography
If created, Harit Pradesh will include three geographic regions:
1. Upper Ganga-Yamuna Doab includes Saharanpur and Meerut Divisions.
2. Middle Ganga-Yamuna Doab (its part of Braj region) includes Aligarh , Agra Divisions and some districts of Kanpur division.
3. Rohilkhand- includes Moradabad and Bareilly Divisions.
It would shares borders with the states of Uttarakhand, Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, as well as a brief international border with Nepal in Pilibhit district. If created, Harit Pradesh, being the only plains state sharing border with Uttarakhand in the Shivalik foothills would serve as the gateway to Uttarakhand.
Soil conditions
Western Uttar Pradesh's soil and relief has marked differences from that of the eastern part of the state.[6] The soil tends to be lighter-textured loam, with some occurrences of sandy soil.[7] Some loess soil is continuously deposited by winds blowing eastwards from Rajasthan's Thar Desert.[8]
Precipitation
Harit Pradesh receives rain through the Indian Monsoon and the Western Disturbances. The Monsoon carries moisture northwards from the Indian Ocean, occurs in late summer and is important to the Kharif or autumn harvest.[9][10] Western Disturbances, on the other hand, are an extratropical weather phenomenon that carry moisture eastwards from the Mediterranean Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Atlantic Ocean.[11][12][13][14] They primarily occur during the winter season and are critically important for the main staple of the region, wheat, which is part of the Rabi or spring harvest.[12]
The proposed state contains Upper Ganga and Yamuna Doab region which is considered one of the most fertile lands in the country. River Yamuna forms a natural border between Harit Pradesh and Haryana.
Administrative divisions

Western Uttar Pradesh includes 29 districts in six divisions:
- Saharanpur division:Districts in this division are Saharanpur, Muzaffarnagar, Shamli.
- Moradabad division:Districts in this division are Moradabad, Bijnor, Rampur, Amroha, Sambhal
- Bareilly division:Districts in this division are Bareilly, Badaun, Pilibhit, Shahjahanpur
- Meerut division:Districts in this division are Meerut, Bulandshahr, Gautam Buddha Nagar, Ghaziabad, Hapur, Baghpat.
- Aligarh division:Districts in this division are Aligarh, Etah, Hathras, Kasganj
- Agra division:Districts in this division are Agra, Firozabad, Mainpuri, Mathura,
- Kanpur Division: Districts of Kanpur division which included in Harit Pradesh are Etawah, Farrukhabad and Auraiya.
Education
The proposed Harit Pradesh has a long tradition of education, although historically it was primarily confined to the elite class and religious schools. Sanskrit-based learning formed the major part of education from the Vedic to the Gupta periods. As cultures traveled through the region they brought their bodies of knowledge with them, adding Pali, Persian, and Arabic scholarship to the community. These formed the core of Hindu-Buddhist-Muslim education until the rise of British colonialism.The present schools-to-university system of education owes its inception and development in the state (as in the rest of the country) to foreign Christian missionaries and the British colonial administration.Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. Hindi is used as a medium of instruction in most of the schools except those affiliated to the CBSE or the Council for ICSE boards. Under the 10+2+3 plan, after completing secondary school, students typically enroll for 2 years in a junior college, also known as pre-university, or in schools with a higher secondary facility affiliated with the Uttar Pradesh Board of High School and Intermediate Education or a central board. Students choose from one of three streams, namely liberal arts, commerce, or science. Upon completing the required coursework, students may enroll in general or professional degree programs.
| School | Location | Established | Comment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aligarh Muslim University | Aligarh | 1920 | Aligarh Muslim University is a public university funded by the Government of India. It was originally established by Sir Syed Ahmad Khan as Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College in 1877. | [15] |
| Chaudhary Charan Singh University | Meerut | 1965 | The university is named after Chaudhary Charan Singh, the fifth Prime Minister of India. | [16] |
| Dr B. R. Ambedkar University | Agra | 1927 | This university was formed as Agra University and renamed in 1996. | [17] |
| Gautam Buddha University | Greater Noida | 2002 | [18] | |
| M. J. P. Rohilkhand University | Bareilly | 1975 | M.J.P. Rohilkhand University was established in 1975 as an affiliating University.The senior faculty members of different disciplines in Humanities, Science and Technology are running research projects funded by various agencies and so far 49 projects funded by UGC, AICTE, DST, CST, ICAR, ICHR, MIF have been completed. | [19] |
| Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel University of Agriculture and Technology | Meerut | 2004 | [20] | |
| Glocal University | Saharanpur | 2012 | Glocal University is a private and coeducational institution located in Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is situated in the foothills of Shivalik mountains. | [21] |
| Shobhit University | Meerut, Saharanpur | 2006, 2011 | Shobhit Institute of Engineering & Technology, Meerut (Shobhit University, Meerut), Shobhit University, Gangoh, Saharanpur. | [22] |
| Invertis University | Bareilly | 2010 | [23] |
Research institutions
Special Economic Zones
Tourism in Harit Pradesh
The tourism is fourth major source of income after Agro Business, Retail sector and IT sector in Harit Pradesh with Agra,Fatehpur Sikri,Mathura,Noida being the tourist hotspots.
-
Prem Mandir in Mathura
-
Vrindavan Chandrodaya Mandir currently under construction would be the tallest Hindu temple in World
-
Jai Gurudev Naam Yog Sadhna Mandir, Mathura
-
Depiction of Vishram Ghat, Mathura in form of painting
-
This is the central column at Martyr's Memorial in Meerut which commemorates the 1857 War of Independence.
-
Paddock Club of Buddh International Circuit at 2013 Airtel Indian Grand Prix in Greater Noida.
Transport networks
The region is a hub of excellent highways, freeways, expressways and touristways. There are further developments going on in these fields. Major State and National highways passing through the proposed Harit Pradesh are:
- DND Flyway
- Noida Greater Noida Expressway
- Yamuna Expressway- Greater Noida to Agra
- Yamnotri Expressway SH-57 [North Delhi-Baghpat-Baraut-Shamli-Saharanpur-Behat-Herbertpur-Vikasnagar-Kalsi-Purola-Harsil-Yamunotri]
- NH-58 [Ghaziabad-Meerut-Muzaffarnagar-Roorkee-Haridwar-Rishikesh-Badrinath]
- NH-24 New Delhi-Lucknow
- NH 709 A Meerut- Karnal Shamli Expressway
- Moradabad-Bareilly Expressway AH 02 also NH 530
- NH-2 New Delhi-Mathura-Agra and
- NH-91 The Bulandshahr-Aligarh-Kanpur connects Delhi with major cities of the region.
The major highways running through intrastate region include
- NH 87, Rampur-Rudrapur-Pantnagar-Haldwani-Nainital-Ranikhet Highway
- NH 73, Roorkee-Saharanpur-Yamunanagar-Saha-Panchkula Highway
- NH 74, Haridwar-Najibabad-Dhampur-Afzalgarh-Jaspur-Kashipur-Rudrapur-Kichha-Pilibhit-Khatima-Tanakpur Highway
- NH 3 The Agra-Gwalior-Indore-Dhule-Nashik-Mumbai Highway
- NH 11, The Agra-Jaipur Touristway
- NH 93, The Internal Highway to Farrukhabad
Upper Ganga Canal Expressway
The Upper Ganga Canal Expressway is an eight-lane access controlled expressway proposed on the right bank of upper Ganga canal from Sanauta bridge (Distt. Bulandshahr) to near Purkazi (Distt.. Muzzafarnagar) before Uttar Pradesh-Uttarakhand border.
Economy
The Western Uttar Pradesh (Harit Pradesh) is agriculturally prosperous. It is relatively industrialised and has seen greater degree of urbanisation as compared to other regions of Uttar Pradesh. Highly fertile land of upper Ganga-Yamuna Doab and its proximity to the National Capital Region play significant role in the economic development of Harit Pradesh.

- Meerut is known as Sports City and is a rich agricultural area. It is the biggest gold market of Asia and biggest exporter of sports related items and music instruments of the country. Meerut has shown healthy numbers in terms of revenue generation. Meerut has started pouring in as Delhi–Mumbai freight corridor and east freight corridor will be intersecting very near to Meerut, making it a cost effective destination for setting up industries.
The real estate, retail business and IT is in boom there.

- Harit Pradesh is 'IT-Hub' of North India. Noida, Greater Noida and Ghaziabad region which lies in NCR has emerged as a key hub for IT and ITeS industries, including software, captive business process outsourcing (BPO) and electronics.Noida is a major hub for multinational firms outsourcing IT services e.g. Sapient, Fiserv, Headstrong, EXL Service, First Flight Courier LTD, Students-Leads, IBM, Miracle, AON Hewitt, Fujitsu, CSC, TCS, WIPRO, Padma Infocom, HCL, Tech Mahindra, Adobe Systems, Ericsson, Dell, Sparta Consulting, Patni Computers, Corbus, Accenture, Samsung etc. Many large software and business process outsourcing companies have their offices in the city.

- Noida is also famous for TV News broadcasters. News channels such as Star News, Zee News, NDTV, Mahua News and several other News channels are located in Film City. Many other companies have their Indian branch offices in Noida, because of many factors, including its Special Economic Zone status, its suburban atmosphere and its proximity to Delhi. Noida also hosts the head office of the Software Technology Park, which was established by the Government of India to promote the software industry. In the Special Economic Zone(SEZ) Sector 135 along the expressway TCS, Accenture, Genpect and Steria have started their offices.

- Muzaffarnagar district is an important hub of Jaggery trading business and is also known as "Sugar Bowl of India". According to Economic Research firm Indicus Analytics, Muzaffarnagar has the highest agricultural GDP in present Uttar Pradesh. It has the largest granary in present UP.Muzaffarnagar lies in what is called the Sugar Belt of Western Uttar Pradesh. The region is one of the important sugarcane producing regions in the world[peacock prose]. Sugar and jaggery (Hindi: गुड़) production are important industries in the Muzaffarnagar district. As a result of the farming activities around, the city is an important hub of jaggery trading business.[24] Naveen Mandi Sthal situated in the eastern outskirts of the city is the trading hub for Jaggery and other agriculture produce. Muzaffarnagar is an important industrial town with sugar, steel and paper being the major industries. District Muzaffarnagar has, 8 sugar mills.

- Saharanpur area, besides being agriculturally rich, is famous for its wooden handicrafts industry and Indian Tobacco Company (ITC Limited). Cherisys Technologies has entered the city as an IT solutions provider after moving to the city from New Delhi. Cherisys Technologies was the first IT solutions provider in the city. Star Paper Mill, Sugar Mill, Hardboard Mill, Textile Mill, and Wood-seasoning Mill are other important industrial enterprises located in the city.

- Aligarh is an important business centre of Uttar Pradesh and is most famous for its lock industry. Aligarh locks are exported across the world. In 1870, Johnson & Co. was the first English lock firm in Aligarh. In 1890, the company initiated production of locks on a small scale here.[25] Aligarh is also a big centre of zinc die casting. There are thousands of pneumatic hot chamber die casting machines here .[citation needed]

- Moradabad is renowned for brass work and has carved a niche for itself in the handicraft industry throughout the world.The modern, attractive, and artistic brass ware, jewelry and trophies made by skilled artisans are the main crafts. The brass ware is exported to countries like the USA, Britain, Canada, Germany and the Middle East. There are about 600 export units and 5000 industries in the district. Moradabad also has an SEZ spread on 450 acres of land.
The retail business, hoteling, real estate are expanding here.

- Agra has a flourishing tourism industry and it is also an important centre of leather and footwear business. Uttar Pradesh's first plant biotech company Harihar Biotech is located near the Taj. It is one of the largest plant tissue culture laboratories in North India with an annual production capacity of 2 million plants.There are about 7,000 small scale industrial units. Agra city is known for leather goods (Taj leather world at sadar bazar agra), carpets (Mughal carpets at fatehabad road agra), handicrafts (Taj handicraft Industries at purani mandi fatehabad road agra), Zari and Zardozi (embroidery work), marble and stone carving and inlay work. Agra is known for its sweets (Petha and Gajak) and snacks (Dalmoth), garment manufacturers and exporters and an automobile industry.
- Mathura Refinery located in Mathura city is one of the biggest oil refineries of Asia. This oil refinery of the Indian Oil Corporation is a highly technologically advanced oil refinery. Mathura Refinery is the first in Asia and third in the world to receive the coveted ISO-14001 certification for Environment Management System in 1996. Textile printing industry that includes both sari-printing and fabric dyeing and silver ornaments manufacturing are major industrial contributors to the region. Apart from these other industries are water tap manufacturing units and other decorative and household items
Demographics
The population of Western Uttar Pradesh is composed of a varied set of communities and tribes, including, Jats, Gujjars, Saini, Mali, Ahir\yadavs, Brahmins / Tyagis, Dalits, Jatavs, Kurmis, Rajputs, Rohilla Pashtuns, Chamars and Balmikis.[28] Tyagi/Brahmans make up around 10% of the population of western Uttar Pradesh followed by Jat 17%, Yadav 5%, Rajput 5% & Gujar 7%.[29][30] These various castes are concentrated in this region and "comprise nearly 40 per cent of the population in Meerut, Muzaffarnagar, Saharanpur, and Bijnor districts" of Western Uttar Pradesh.[28][31]
As per the Census 2011 data, total population of the proposed state is 6.3 Crores. Largest Cities by Population:
| Largest cities in Harit Pradesh | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | District | Population | City | District | Population | |||||
| 1 | Ghaziabad | Ghaziabad | 2,381,452 | 7 | Saharanpur | Saharanpur | 705,478 | |||
| 2 | Agra | Agra | 4,418,797 | 8 | Noida | Gautam Budh Nagar | 637,272 | |||
| 3 | Meerut | Meerut | 1,309,023 | 9 | Muzaffarnagar | Muzaffarnagar | 495,543 | |||
| 4 | Bareilly | Bareilly | 898,167 | 10 | Mathura | Mathura | 601,894 | |||
| 5 | Moradabad | Moradabad | 889,810 | 11 | Budaun | Budaun | 369,221 | |||
| 6 | Aligarh | Aligarh | 874,408 | 12 | Rampur | Rampur | 325,248 | |||
| Source: Census of India 2011[32] | ||||||||||
The region's Rohillas are descended from immigrant groups from centuries ago, and a large subregion of Western Uttar Pradesh, Rohilkhand, takes its name from that Pashtun tribe.[33]
Sikhs from West Punjab, which came from Pakistan after partition, also migrated to the area in large numbers.[34]
Role of specific rural communities
In recent decades, Uttar Pradesh has seen the economic and political rise of the Yadav community, which has a large population and spread in Uttar Pradesh.[35] Jats, who are a dominant agricultural community spread across Pakistan, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh, have found themselves in a "politically disadvantageous position" in Western Uttar Pradesh due to this increasing influence of the Yadavs.[35] A separate Harit Pradesh would likely become a prosperous smaller state similar to Haryana and Punjab.
The most prominent current-day advocate for the creation of the new state is Ajit Singh, the leader of the Rashtriya Lok Dal party and a Jat besides many Gurjar leaders. Pushpendra Singh, former General Secretary of Youth wing of Rashtriya Lok Dal, has also recently launched a political party by the name Harit Pradesh Party for the agenda of creating a separate State of Western UP. Other Jat leaders, such as Om Prakash Chautala of neighboring Haryana state and the leader of the Indian National Lok Dal have also made efforts to involve themselves in the politics of creating a separate state.[36] Since the Muslim population in Western Uttar Pradesh (25%-34%, according to various sources) is higher than in Uttar Pradesh as a whole (17%), the Harit Pradesh proposal has found support from Muslim-affiliated organizations.[37][38][39][40] Of the other main political forces in Uttar Pradesh, the Bahujan Samaj Party has supported the demand in principle, the Samajwadi Party has opposed it, and the Indian National Congress and the Bharatiya Janata Party have adopted a non-committal stance.[41] From the Bahujan Samaj Party, Mayawati and DP Yadav have been vocal about their support.
Rashtriya Lok Dal alleges that "Western UP contributes to a large chunk - nearly 72% - of the state's total income. In turn, what western UP gets is not enough. Just 18% of the state's budget is spent on developing west UP. This anomaly, understandably, makes the people of this area dissatisfied".[42] There are allegations that in most years, funds allocated to west UP were never spent. According to Professor Jates only 20% of the total Government employees, less than 10% of employees in the secretariat, and less than 5% of department heads in the utter pradesh government are from west UP.
The creation of three new states in 2000 (Jharkhand from the division of Bihar, Uttarakhand from the division of Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh from the division of Madhya Pradesh) gave new impetus to the demand for Harit Pradesh.[35]
After coming to power in 2007, in the Bahujan Samaj Party government, Chief Minister Mayawati wrote letters to the prime minister regarding the partitioning of Uttar Pradesh into four different states, in 2007, March 2008, and December 2009.[43][44] Finally on 15 November 2011, Mayawati's cabinet approved partitioning Uttar Pradesh into four different states (Harit Pradesh, Awadh Pradesh, Bundelkhand and Purvanchal) for better administration and governance.[45]
See also
References
- ^ Sajal Basu (2005), Regionalism, ethnicity, and left politics, Rawat Publications, ISBN 81-7033-930-8,
... perhaps only to strengthen his own demand of a separate Harit Pradesh comprising 23 districts from western UP ...A consequent demand for the separation of the more prosperous western districts of UP which have been the bastion of the green revolution, and have variously been named as Pashchim Pradesh or more recently as Harit Pradesh by Ajit Singh ...
- ^ Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar (1955), Thoughts on Linguistic States,
... The only remedy is to break up the Northern States of U.P., Bihar and Madhya Pradesh. How did this solution not strike the Congress Working Committee I am unable to understand ... My proposal with regard to the Uttar Pradesh is to divide it into three States. The three States of the Uttar Pradesh could have as their capitals (1) Meerut (2) Kanpur and (3) Allahabad ...
- ^ "Now demand to divide Uttar Pradesh picks momentum".
- ^ Boris Ivanovich Kluyev (1981), India: National and Language Problem, Sterling,
... For example, in May 1972 fourteen members of the Uttar Pradesh Assembly submitted a resolution for setting up three new States - Braj Pradesh, Awadh Pradesh and Purvi Pradesh. The resolution was defeated. Curiously enough, the arguments of those supporting division were essentially the same, although the representatives hailed from different regions of Uttar Pradesh ...
- ^ http://news.outlookindia.com/items.aspx?artid=805707
- ^ Aijazuddin Ahmad, Geography of the South Asian subcontinent: a critical approach, Concept Publishing Company, 2009, ISBN 9788180695681,
... These differences are caused by the depositional work of rivers, local climates, natural vegetation cover and the soil. Even the difference between the plains of western Uttar Pradesh and eastern Uttar Pradesh is quite well marked ...
- ^ A.K. Kolay, Soil Genesis, Classification Survey And Evaluation, Volume 2, Atlantic Publishers & Distributors, 2007, ISBN 9788126908035,
... ...
- ^ M. Hanif, Encyclopaedia of Agricultural Geography, Anmol Publications Private Limited, 2005, ISBN 9788126124824,
... Loess is the finest particle of sand carried by winds from desert (Thar desert) to the neighbouring areas of Haryana, Punjab, Western Uttar Pradesh and western Madhya Pradesh. Here a thin layer of loess particles ...
- ^ Vidya Sagar Katiyar, "Indian Monsoon and Its Frontiers", Inter-India Publications, 1990, ISBN 81-210-0245-1.
- ^ Ajit Prasad Jain and Shiba Prasad Chatterjee, "Report of the Irrigation Commission, 1972", Ministry of Irrigation and Power, Government of India, 1972.
- ^ "Western disturbances herald winter in Northern India". The Hindu Business Line. 2005-11-17. Retrieved 2008-10-20.
- ^ a b Bin Wang, "The Asian Monsoon", Springer, 2006, ISBN 3-540-40610-7.
- ^ R.K. Datta (Meteorological Office, Dum Dum) and M.G. Gupta (Meteorological Office, Delhi), "Synoptic study of the formation and movements of Western Depressions", Indian Journal of Meteorology & Geophysics, India Meteorological Department, 1968.
- ^ A.P. Dimri, "Models to improve winter minimum surface temperature forecasts, Delhi, India", Meteorological Applications, 11, pp 129-139, Royal Meteorological Society, Cambridge University Press, 2004.
- ^ "Aligarh Muslim University || History". www.amu.ac.in. Retrieved 2016-09-25.
- ^ "Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut | About Us". ccsuniversity.ac.in. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Dr B. R. Ambedkar University". dbrau.ac.in. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "About Us". gbu.ac.in. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "M.J.P. Rohilkhand University". mjpru.ac.in. Archived from the original on 31 July 2011. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Sardar Vallabha Bhai Patel University". svbpmeerut.ac.in. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
- ^ University, Glocal. "Why Glocal | Glocal University". www.glocaluniversity.edu.in. Retrieved 2016-09-25.
- ^ University, Shobhit. "SHOBHIT UNIVERSITY". www.shobhituniversity.ac.in. Retrieved 2016-09-25.
- ^ "Invertis University". UniRank. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- ^ "Muzaffarnagar clashes sour its famed jaggery business". economic times. India Times. Retrieved 10 July 2014.
- ^ Pawan JainPawan Jain (3 June 2003). "Times of India". Timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ "Uttar Pradesh Religion Census 2011". Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 7 September 2015. Retrieved 4 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.census2011.co.in/data/religion/state/9-uttar-pradesh.html/
- ^ a b T. V. Sathyamurthy, Industry and agriculture in India since independence: Social change and political discourse in India Volume 2, Oxford University Press, 1995, ISBN 9780195634570,
... the Jats, Ahirs, Gurjars and Kurmis. These castes comprise nearly 40 per cent of the population in Meerut, Muzaffarnagar, Saharanpur, and Bijnor districts. Rajputs and Tyagis, also cultivate their own land.
- ^ "Maya uses west UP visit to launch 2012 poll campaign - The Times of India". The Times Of India. 2011-09-29.
- ^ Varma, Gyan (12 September 2013). "Communalism gains new ground in rural India".
- ^ Sumit Ganguly; Larry Jay Diamond; Marc F. Plattner, The state of India's democracy, JHU Press, 2007, ISBN 9780801887918,
... Jats represented only 1.6 percent of the state population in 1931, but were concentrated in western Uttar Pradesh ...
- ^ (2011 Census of India estimate)"India: Harit Pradesh". City Population. Thomas Brinkhoff. 25 January 2014. Retrieved 23 February 2015 – via Population Census India.
- ^ Ghaus Ansari, Muslim caste in Uttar Pradesh: a study of culture contact (Volumes 12–13 of The Eastern Anthropologist), Ethnographic and Folk Culture Society, 1960,
... confined primarily to the Rohilkhand and Meerut divisions of Uttar Pradesh. Pathans are generally considered to have come either from Afghanistan or from the Pashto-speaking tribes of the North-West ...
- ^ Bagaulia, Encyclopaedia Of Human Geography (Set Of 3 Vols.), Anmol Publications PVT. LTD., 2005, ISBN 9788126124442,
... Sikhs also settled down in the Terai region of Uttar Pradesh, transforming this once malaria-infested wetland into a granary of northern India ...
- ^ a b c Jagpal Singh (August 4, 2001), "Politics of Harit Pradesh: The Case of Western UP as a Separate State", Economic and Political Weekly, 36 (31): 2961–2967, JSTOR 4410945,
... It is spearheaded by the politicians, especially a section of Jats, belonging to western UP. Ajit Singh has been playing a pivotal role in it ...
- ^ "INLD bid to get foothold in UP", The Tribune, 2001-07-05, retrieved 2009-07-24,
... the move of the Indian National Lok Dal (INLD) supremo and Chief Minister of Haryana, Mr Om Prakash Chautala, to raise the demand of a separate 'kisan pradesh' out of western UP ... Since Mr Ajit Singh has also raised the demand of creating a 'harit pradesh' in the same region, the move by both Mr Chautala and Mr Ajit Singh is seen as only a political strategy to 'outwit' each other ...
- ^ "Minister's demand for Muslim Pradesh condemned", Times of India, 2006-07-19, retrieved 2009-07-24,
... demand is neither feasible nor proper,"said Manzoor Ahmad, former vice-chancellor of Dr B R Ambedkar University, Agra ... Muslim population which is not more than 25% in Western UP. ...
- ^ "Ajit Singh struggling to retain Muslim vote", The Hindu, 2002-02-12, retrieved 2009-07-24,
... the Muslim presence in western U.P. is said to be about 34 per cent ...
- ^ Khan, M.E., Patel, Bella, C., "Reproductive Behaviour of Muslims in Uttar Pradesh", The Journal of Family Welfare, March 1997. 43(1) p. 13-29. Available online at [1]
- ^ "Imams back campaign for 'Harit Pradesh'", The Hindu, 2001-08-18, retrieved 2009-07-24,
... campaign for `Harit Pradesh' ... appears to be gathering momentum with the All-India Imam Association, an influential body of Muslim clerics, today pledging support ...
- ^ "Mayawati joins issue with Paswan, Ajit Singh", The Hindu, 2001-06-26, retrieved 2009-07-24,
... She said the BSP stood for creation of Harit Pradesh ...
- ^ "Ajit Singh reiterates Harit Pradesh demand", The Times of India, 2011-01-10,
...In turn, what western UP gets is not enough ...
- ^ "UP division Mayawati asks Congress, BJP to clarify stand".
- ^ "Chief Minister Mayawati said the Centre's inaction over a 2007 letter forced her government to take the matter to the House".
- ^ "Mayawati wants UP divided into four new states". zeenews.india.com. Zee News Ltd. 15 November 2011. Retrieved 2 July 2013.












