Metaraminol
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous Endotracheal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | ~45% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
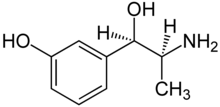
| Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 167.208 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Metaraminol (INN; trade names Aramine, Metaramin, and Pressonex), also known as metaradrine, a stereoisomer of meta-hydroxynorephedrine (3,β-dihydroxyamphetamine), is a potent sympathomimetic amine used in the prevention and treatment of hypotension, particularly as a complication of anesthesia. It is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist with some β effect.[1]
Metaraminol is also used in the treatment of priapism. Although not approved for this use, it appears to be effective.[2][3][4]
See also
References
- ^ Kee VR (Aug 2003). "Hemodynamic pharmacology of intravenous vasopressors". Crit Care Nurse. 23 (4): 79–82. doi:10.4037/ccn2003.23.4.79. PMID 12961786.
- ^ McDonald M, Santucci R (2004). "Successful management of stuttering priapism using home self-injections of the alpha-agonist metaraminol". Int Braz J Urol. 30 (2): 121–2. doi:10.1590/S1677-55382004000200007. PMID 15703094.
- ^ Koga S, Shiraishi K, Saito Y (1990). "Post-traumatic priapism treated with metaraminol bitartrate: case report". J Trauma. 30 (12): 1591–3. doi:10.1097/00005373-199012000-00029. PMID 2258979.
- ^ Block T, Sturm W, Ernst G, Staehler G, Schmiedt E (1988). "[Metaraminol in therapy of various forms of priapism]". Urologe A. 27 (4): 225–9. PMID 3140463.
