Jerusalem: Difference between revisions
→History: more clearing up |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
{{main|History of Jerusalem}} |
{{main|History of Jerusalem}} |
||
{{see also|History of ancient Israel and Judah|History of Palestine|Timeline of Jerusalem}}Some archaeologists, including [[Kathleen Kenyon]], believe Jerusalem as a city was founded by [[West Semitic]] people with organized settlements from around [[26th century BC|2600 BCE]]. |
{{see also|History of ancient Israel and Judah|History of Palestine|Timeline of Jerusalem}} |
||
Some archaeologists, including [[Kathleen Kenyon]], believe Jerusalem as a city was founded by [[West Semitic]] people with organized settlements from around [[26th century BC|2600 BCE]]. According to tradition the city was founded by [[Shem]] and [[Eber]], ancestors of [[Abraham]]. |
|||
| ⚫ | References to Jerusalem<ref>{{cite book|first=James B.|last=Pritchard|year=1968|title=The Ancient Near East|publisher=OUP}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Gerard|last=Herm|year=1975|title=The Phoenicians|publisher=William Morrow|isbn=0-688-02908-6|pages=33,84–106 passim, 123,125,126,145,149,150,154}}</ref><ref>[[Herodotus]]</ref><ref>{{cite book|first=Nelson|last=Glueck|year=1959|title=Rivers in the Desert|publisher=HUC|pages=15, 41, 63, 95, 102, 106, 118, 119, 122, 123, 138, 143, 150–151, 162, 167, 170, 171, 172, 186, 187, 194, 243, 246, 250, 258, 276}}</ref> address the international overseas trade relationship between Jerusalem and its neighbors. Trade with [[Tyre]] in the time of [[Solomon]] and other [[Phoenician]]s for timber, stone, metals and [[juniper]] oil in return for horses, going back to the late bronze age is well documented. |
||
According to tradition the city was founded by [[Shem]] and [[Eber]], ancestors of [[Abraham]]. |
|||
| ⚫ | An extensive trade to the south across the Dead Sea and down the [[Arabah]] to Ezion Geber or [[Elat]] to furnish [[Egypt]] with [[lapis lazuli]], [[carnelian]], [[cobalt]], [[copper]], [[linen]], [[woven]] [[papyrus]], [[purple]] [[dyes]], [[bitumen]], [[naphtha]], joined with cargoes of [[frankincense]] and [[myrrh]] coming north from [[Punt]] is well documented archaeologically.<ref>{{cite book|first=Muhammed Abdul|last=Nayeem|year=1990|title=Prehistory and Protohistory of the Arabian Peninsula|publisher=Hyderabad}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | References to Jerusalem |
||
| ⚫ | All these goods that were provided for the [[mummification]] industry at [[Karnak]], were richly compensated for with [[Nubian]] gold shipped back and forth across the Red Sea from [[Elim]] to [[Elat]]. Overland shipments were made to the Greek [[emporia]] on the coasts following a line of fortified wells through [[Gaza]] as early as the [[Hyskos]] period. The above sources and others document the international overseas trade was ongoing continuously from around 2500 BCE up through the siege by [[Sennacherib]] in 701 BCE but that Jerusalem only expanded from a garrisoned well under the control of the Egyptians to a true city after Egypt's [[18th Dynasty]]. |
||
| ⚫ | An extensive trade to the south across the Dead Sea and down the [[Arabah]] to Ezion Geber or [[Elat]] to furnish [[Egypt]] with [[lapis lazuli]], [[carnelian]], [[cobalt]], [[copper]], [[linen]], [[woven]] [[papyrus]], [[purple |
||
| ⚫ | Archaeological findings indicate the existence of development within present-day Jerusalem as far back as the [[4th millennium BCE]],<ref name="aice" /> but the earliest written records of the city come in the [[Execration Texts]] ([[circa|c.]] [[19th century BCE]]) and the [[Amarna letters]] when its referred to as a garrisoned fortified well used in the manufacture of [[bread]] and [[beer]](c. [[14th century BCE]]). Pritchard<ref>{{cite book|first=James B.|last=Pritchard|year=1968|title=The Ancient Near East|publisher=OUP}}</ref> addresses the relationship with Egypt during the time of the Amarna letters and the wars with Kadesh when Egypt fortified and garrisoned its well, counterbalanced by the [[Assyrian]] campaigns against Syria and [[Palestine]] with Israel and Jerusalem referred to as Mat Hu-um-ri and Bit Humria (''Omri Land'') |
||
| ⚫ | All these goods that were provided for the [[mummification]] industry at [[Karnak]], were richly compensated for with [[Nubian]] gold shipped back and forth across the Red Sea from [[Elim]] to [[Elat]]. Overland shipments were made to the Greek [[emporia]] on the coasts following a line of fortified wells through [[Gaza]] as early as the [[Hyskos]] period. The above sources and others document the international overseas trade was ongoing continuously from |
||
| ⚫ | Archaeological findings indicate the existence of development within present-day Jerusalem as far back as the [[4th millennium BCE]],<ref name="aice" /> but the earliest written records of the city come in the [[Execration Texts]] ([[circa|c.]] [[19th century BCE]]) and the [[Amarna letters]] when its |
||
Pritchards "The Ancient Near East" addresses the relationship with Egypt during the time of the Amarna letters and the wars with Kadesh when Egypt fortified and garrisoned its well, counterbalanced by the [[Assyrian]] campaigns against Syria and [[Palestine]] with Israel and Jerusalem referred to as Mat Hu-um-ri and Bit Humria (Omri Land) |
|||
The [[Bible|Biblical]] account portrays the [[Jebusite]]s as having control of the city, inhabiting the area around the present-day city in the late 11th century BCE when [[David]] is said to have invaded and conquered their city, [[Jebus]], and established it as the capital of the [[United Monarchy|United Kingdom of Israel and Judah]] (c. 1000s BCE).<ref name="promise">{{cite book|title=A Promise Fulfilled: Theodor Herzl, Chaim Weizmann, David Ben-Gurion, and the Creation of the State of Israel |last=Greenfeld |first=Howard |date=[[2005-03-29]] |publisher=Greenwillow |isbn=006051504X |accessdate=2007-01-18 |pages=32}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cityofdavid.org.il/timeline_eng.asp |work=City of David |title=Timeline |publisher=Ir David Foundation |accessdate=2007-01-18}}</ref>{{ref label|bible-david|iv|b}} Recent excavations of a [[Large Stone Structure|large stone structure]] are interpreted by some archaeologists as lending credence to the biblical narrative. |
The [[Bible|Biblical]] account portrays the [[Jebusite]]s as having control of the city, inhabiting the area around the present-day city in the late 11th century BCE when [[David]] is said to have invaded and conquered their city, [[Jebus]], and established it as the capital of the [[United Monarchy|United Kingdom of Israel and Judah]] (c. 1000s BCE).<ref name="promise">{{cite book|title=A Promise Fulfilled: Theodor Herzl, Chaim Weizmann, David Ben-Gurion, and the Creation of the State of Israel |last=Greenfeld |first=Howard |date=[[2005-03-29]] |publisher=Greenwillow |isbn=006051504X |accessdate=2007-01-18 |pages=32}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cityofdavid.org.il/timeline_eng.asp |work=City of David |title=Timeline |publisher=Ir David Foundation |accessdate=2007-01-18}}</ref>{{ref label|bible-david|iv|b}} Recent excavations of a [[Large Stone Structure|large stone structure]] are interpreted by some archaeologists as lending credence to the biblical narrative. |
||
| Line 317: | Line 315: | ||
*''The Holy Cities: Jerusalem'' produced by Danae Film Production, distributed by HDH Communications; 2006 |
*''The Holy Cities: Jerusalem'' produced by Danae Film Production, distributed by HDH Communications; 2006 |
||
*Wasserstein, Bernard (2002) ''Divided Jerusalem: The Struggle for the Holy City'' New Haven and London: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-09730-1 |
*Wasserstein, Bernard (2002) ''Divided Jerusalem: The Struggle for the Holy City'' New Haven and London: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-09730-1 |
||
== Archaeological == |
|||
* Renfrew, Colin and Bahn, Paul {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=2004|Title=Archaeology|Publisher=Thames & Hudson|ID=ISBN 0500 284415 }} Page 515 discusses conflicts between archaeology and Judaism in Jeruselim |
|||
== Near Eastern == |
|||
* Nelson Glueck{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1959|Title=Rivers in the Desert|Publisher=HUC|ID=ISBN}}Discusses Jerusalem pp,15,41,63,95,102,106,118,119,122,123,138,143,150-151,162,167,170,171,172,186,187,194,243,246,250,258,276 |
|||
* William H McNeil and Jean W Sedlar, {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1962|Title=The Ancient Near East|Publisher=OUP|ID=ISBN }} |
|||
* Andrew George, {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=2000|Title=The Epic of Gillgamesh|Publisher=Penguin|ID=ISBN No14-044721-0}} |
|||
* James B. Pritchard, {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1968|Title=The Ancient Near East|Publisher=OUP|ID=ISBN }} Jerusalim, seige and fall |
|||
* Shaika Haya Ali Al Khalifa and Michael Rice, {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1986|Title=Bahrain through the Ages|Publisher=KPI|ID=ISBN 071030112-x}} |
|||
* Dr. Muhammed Abdul Nayeem, {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=Prehistory and Protohistory of the Arabian Peninsula|Publisher=Hyderabad|ID=ISBN }} |
|||
* Michael Roaf{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=Cultural Atlas of Mesopotamia and the Ancient Near East|Publisher=Equinox|ID=ISBN 0-8160-2218-6}} |
|||
* Nicholas Awde and Putros Samano{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1986|Title=The Arabic Alphabet|Publisher=Billing & Sons Ltd.|ID=ISBN 0863560350}} |
|||
* Gerard Herm{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1975|Title=The Phoenicians|Publisher=William Morrow^ Co.Inc.|ID=ISBN 0-688-02908-6}}Jerusalim pp 33,84-106 passim, 123,125,126,145,149,150,154 |
|||
== Marine == |
|||
* Lionel Casson{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1991|Title=The Ancient Mariners|Publisher=PUP|ID=ISBN 06910147879}} |
|||
* George Bass{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=2004|Title=A History of Seafaring|Publisher=Walker and Company|ID=ISBN 08027-0-3909}} |
|||
== Egyptological References == |
|||
* Gardiner{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=Egyptian Grammar|Publisher=Griffith Institute|ID=ISBN 0900416351}} |
|||
* Antonio Loprieno {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1995|Title=Ancient Egyptian|Publisher=CUP|ID=ISBN 0-521-44849-2}} |
|||
* Michael Rice{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=Egypt's Making|Publisher=Routledge|ID=ISBN 0-415-06454-6}} |
|||
* Gillings{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1972|Title=Mathematics in the time of the Pharoahs|Publisher=MIT Press|ID=ISBN 0262070456}} |
|||
* Somers Clarke and R. Englebach{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=Ancient Egyptian Construction and Architecture|Publisher=Dover|ID=ISBN 0486264858}} |
|||
== Linguistic References == |
|||
* Marie-Loise Thomsen, {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1984|Title=Mesopotamia 10 The Sumerian Language |Publisher=Academic Press|ID=ISBN 87-500-3654-8}} |
|||
* Silvia Luraghi{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=Old Hittite Sentence Structure|Publisher=Routledge|ID=ISBN 0415047358}} |
|||
* J. P. Mallory{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1989|Title=In Search of the Indo Europeans |Publisher=Thames and Hudson|ID=ISBN 050027616-1}} |
|||
* Anne H. Groton{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1995|Title=From Alpha to Omega|Publisher=Focus Information group|ID=ISBN 0941051382}} |
|||
* Hines{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1981|Title=Our Latin Heritage|Publisher=Harcourt Brace|ID=ISBN 0153894687}} |
|||
== Classical References == |
|||
* Vitruvius{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1960|Title=The Ten Books on Architecture|Publisher=Dover|ID=}} |
|||
* Claudias Ptolemy{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1991|Title=The Geography|Publisher=Dover|ID=ISBN 048626896}} |
|||
* Herodotus{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1952|Title=The History|Publisher=William Brown|ID=}} War with Judah, Sennacherib, seige of 701 BC |
|||
== Historical References == |
|||
* Michael Grant{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1987|Title=The Rise of the Greeks |Publisher=Charles Scribners Sons|ID=}} |
|||
== Mathematical References == |
|||
* Lucas N. H. Bunt, Phillip S.Jones, Jack D. Bedient {{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1976|Title=The Historical Roots of Elementary Mathematics|Publisher=Dover|ID=ISBN 0486255638}} |
|||
== Mensurational References == |
|||
* H Arthur Klein{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1976|Title=The World of Measurements |Publisher=Simon and Schuster|ID=}} |
|||
* Francis H. Moffitt{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1987|Title=Surveying|Publisher=Harper & Row|ID=ISBN 0060445548}} |
|||
== Architectural References == |
|||
* R. A. Cordingley{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1951|Title=Norman's Parrallel of the Orders of Architecture|Publisher=Alex Trianti Ltd|ID=}} |
|||
== Medieval References == |
|||
* H Johnathan Riley Smith{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1990|Title=The Atlas of the Crusades |
|||
|Publisher=Swanston|ID=ISBN 0723003610}} |
|||
* H.W. Koch{{Section:Book reference after author|Year=1978|Title=Medieval Warfare|Publisher=Prentice Hall|ID=ISBN 0135736005}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
Revision as of 13:07, 9 July 2007
Jerusalem (Hebrew: , Yerushaláyim; Arabic: , al-Quds)[ii] is Israel's capital,[iii] seat of government, and largest city[1] in both population and area,[2] with 732,100 residents in an area of 126 square kilometers (49 sq mi).[3] Located in the Judean Mountains, between the Mediterranean Sea and the northern tip of the Dead Sea, the city has a history that goes back as far as the 4th millennium BCE.[4] Jerusalem has been the holiest city in Judaism and the spiritual center of the Jewish people since the 10th century BCE.[5] The city contains a number of significant ancient Christian sites and is considered the third-holiest city in Islam.[6]
The walled area of Jerusalem, which constituted the entire city until the 1860s, is now called the Old City, and was added to the List of World Heritage Sites in danger in 1982.[7] The Old City has been traditionally divided into four quarters, although the names used today—the Armenian, Christian, Jewish, and Muslim Quarters—were only introduced in the early 19th century.[8] Despite having an area of only 0.9 square kilometer (0.35 square mile),[9] the Old City is home to several sites of key religious importance: the Temple Mount and its Western Wall for Jews, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre for Christians, and the Dome of the Rock and al-Aqsa Mosque for Muslims.
Modern Jerusalem has grown up around the Old City, with its civic and cultural hub extending westward toward the country's urban center in Gush Dan. The Arab population is clustered in the north, east and south. Today, Jerusalem remains a bone of contention in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict: Israel's annexation of East Jerusalem (captured in the 1967 Six-Day War) has been particularly controversial, as Palestinians view this part of the city as the capital of a future Palestinian state.[10][11] The status of a "united Jerusalem" as Israel's "eternal capital"[12][13] has not been officially recognized by most of the international community, and nearly all countries maintain their embassies in Tel Aviv.[14]
Etymology
| Part of a series on |
| Jerusalem |
|---|
 |
Although the precise origin of the name remains uncertain, the Hebrew Yerushalayim may be understood as "Heritage of Peace" — a portmanteau of yerusha (heritage) and shalom (peace), and is cognate with the name "Solomon", the king who built its first temple. [15][16] Alternatively, the second part of the portmanteau may instead be Salem (Shalem literally "whole" or "in harmony"), a city name used prior to Jerusalem[17] and seen in the first book of the Torah, Genesis.[18] Similarly, the Amarna letters call the city the Akkadian Urušalim, a cognate of the Hebrew Ir Shalem (city of Salem). Some consider a connection between the name and Shalim, the beneficent deity known from Ugaritic myths as personifying dusk.[19] The ending -ayim or -im has the appearance of the Hebrew dual, leading some scholars to argue that Jerusalem represents two facets of the city, such as two hills.[20][21]
A Midrashic interpretation comes from Genesis Rabba, which explains that Abraham came to the city that was then called Shalem after rescuing Lot.[22] Upon arrival, he asked the king and high priest Melchizedek to bless him, and Melchizedek did so in the name of God (indicating that he, like Abraham, was a monotheist). According to Biblical exegesis, God immortalizes this encounter between Melchizedek and Abraham by renaming the city in honor of them: the name Yeru (derived from Yireh, the name Abraham gives to the Temple Mount) is placed in front of the contemporary name of Shalem.[22] Yeru-Shalem, meaning "The City of Shalem," or "Founded by Shalem." If used as an adjective, Shalem could mean "complete," or "without defect;" implying either "The Perfect City," or "City of the One Who is Perfect."[23]
History
Some archaeologists, including Kathleen Kenyon, believe Jerusalem as a city was founded by West Semitic people with organized settlements from around 2600 BCE. According to tradition the city was founded by Shem and Eber, ancestors of Abraham.
References to Jerusalem[24][25][26][27] address the international overseas trade relationship between Jerusalem and its neighbors. Trade with Tyre in the time of Solomon and other Phoenicians for timber, stone, metals and juniper oil in return for horses, going back to the late bronze age is well documented.
An extensive trade to the south across the Dead Sea and down the Arabah to Ezion Geber or Elat to furnish Egypt with lapis lazuli, carnelian, cobalt, copper, linen, woven papyrus, purple dyes, bitumen, naphtha, joined with cargoes of frankincense and myrrh coming north from Punt is well documented archaeologically.[28]
All these goods that were provided for the mummification industry at Karnak, were richly compensated for with Nubian gold shipped back and forth across the Red Sea from Elim to Elat. Overland shipments were made to the Greek emporia on the coasts following a line of fortified wells through Gaza as early as the Hyskos period. The above sources and others document the international overseas trade was ongoing continuously from around 2500 BCE up through the siege by Sennacherib in 701 BCE but that Jerusalem only expanded from a garrisoned well under the control of the Egyptians to a true city after Egypt's 18th Dynasty.
Archaeological findings indicate the existence of development within present-day Jerusalem as far back as the 4th millennium BCE,[4] but the earliest written records of the city come in the Execration Texts (c. 19th century BCE) and the Amarna letters when its referred to as a garrisoned fortified well used in the manufacture of bread and beer(c. 14th century BCE). Pritchard[29] addresses the relationship with Egypt during the time of the Amarna letters and the wars with Kadesh when Egypt fortified and garrisoned its well, counterbalanced by the Assyrian campaigns against Syria and Palestine with Israel and Jerusalem referred to as Mat Hu-um-ri and Bit Humria (Omri Land)
The Biblical account portrays the Jebusites as having control of the city, inhabiting the area around the present-day city in the late 11th century BCE when David is said to have invaded and conquered their city, Jebus, and established it as the capital of the United Kingdom of Israel and Judah (c. 1000s BCE).[30][31][iv] Recent excavations of a large stone structure are interpreted by some archaeologists as lending credence to the biblical narrative.
Temple periods
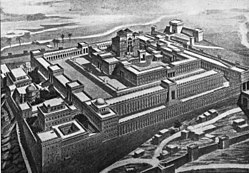
According to the Hebrew Bible, David reigned until 970 BCE, when his son Solomon became king of Israel.[34] Within a decade, Solomon began to build the Holy Temple on Mount Moriah inside the city. Solomon's Temple (later known as the First Temple), went on to play a pivotal role in Jewish and Christian history as the repository of the Ark of the Covenant.[35] The next four centuries, up until the destruction of Solomon's Temple (c. 586 BCE), are known in history as the First Temple Period.[36] Upon Solomon's death (c. 930 BCE), the ten northern tribes split off to form the Kingdom of Israel. Under the leadership of the House of David and Solomon, Jerusalem remained the capital of the Kingdom of Judah.[37] When the Assyrians conquered the Kingdom of Israel in 722 BCE, Jerusalem was strengthened by a great influx of refugees from the northern kingdom. The First Temple period ended around 586 BCE, as the Babylonians conquered Judah and Jerusalem, and laid waste to Solomon's Temple.[37]
In 538 BCE, after fifty years of Babylonian captivity, Persian King Cyrus the Great permitted the Jews to return to Judah to rebuild Jerusalem and their holy temple. Construction of the Second Temple, was completed in 516 BCE, during the reign of Darius the Great, seventy years after the destruction of the First Temple.[38][39] Jerusalem resumed its role as capital of Judah and center of Jewish worship. When Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire, Jerusalem and Judea fell under Hellenistic Greek control, eventually falling to the Ptolemaic dynasty under Ptolemy I. In 198 BCE, Ptolemy V lost Jerusalem and Judea to the Seleucids under Antiochus III. The Seleucid attempt to recast Jerusalem as a Hellenized polis came to a head in 168 BCE with the successful Maccabean revolt of Mattathias the High Priest and his five sons against Antiochus Epiphanes, and their establishment of the Hasmonean Kingdom in 152 BCE with Jerusalem again as its capital.[40]

As Rome became stronger it installed Herod as a Jewish client king. Herod the Great, as he was known, devoted himself to developing and beautifying the city. He built walls, towers and palaces, and expanded the Temple Mount, buttressing the courtyard with blocks of stone weighing up to 100 tons. Under Herod, the area of the Temple Mount doubled in size.[41][42][34] In 6 CE, the city, as well as much of the surrounding area, came under direct Roman rule as the Iudaea Province[43] and Herod's descendants through Agrippa II remained client kings of Judea until 96 CE. Roman rule over Jerusalem and the region began to be challenged with the first Jewish-Roman war, the Great Jewish Revolt, which resulted in the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE. In 130 CE Hadrian attempted to Romanize the city, and renamed it Aelia Capitolina.[44] Jerusalem once again served as the capital of Judea during the three-year rebellion known as the Bar Kochba revolt. The Romans succeeded in recapturing the city in 135 CE and as a punitive measure Hadrian banned the Jews from entering it. Hadrian proceeded to rename the entire Iudaea Province to Syria Palaestina after the Biblical Philistines in an attempt to thwart future rebellion and to de-Judaize Judea.[45][46]
Shifts in control
In the five centuries following the Bar Kokhba revolt, the city remained under Roman then Byzantine rule. During the 4th century, the Roman Emperor Constantine I constructed Christian sites in Jerusalem such as the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. Jerusalem reached a peak in size and population at the end of the Second Temple Period: The city covered two square kilometers (0.8 sq mi.) and had a population of 200,000[47][45] From the days of Constantine until the Arab conquest in 638, Jews were banned from Jerusalem.[48] By the end of the 7th century, an Umayyad caliph Abd al-Malik had commissioned and completed the construction of the Dome of the Rock over the Foundation Stone.[49] In the four hundred years that followed, Jerusalem's prominence diminished as Arab powers in the region jockeyed for control.[50]
In 1099, Jerusalem was besieged by the First Crusaders, who killed most of its Muslim and Jewish inhabitants.[51] That would be the first of several conquests to take place over the next four hundred years. In 1187, the city was taken from the Crusaders by Saladin.[52] Between 1228 and 1244, it was given by Saladin's descendant al-Kamil to the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II. Jerusalem fell again in 1244 to the Khawarizmi Turks, who were later, in 1260, replaced by the Mamelukes. In 1517, Jerusalem and its environs fell to the Ottoman Turks, who would maintain control of the city until the 20th century.[52] This era saw the first expansion outside the Old City walls, as new neighborhoods were established to relieve the overcrowding that had become so prevalent. The first of these new neighborhoods included the Russian Compound and the Jewish Mishkenot Sha'ananim, both founded in 1860.[53]
In 1917 after the Battle of Jerusalem, the British Army, led by General Edmund Allenby, captured the city.[54] The League of Nations, through its 1922 ratification of the Balfour Declaration, entrusted the United Kingdom to administer the Mandate of Palestine and help establish a Jewish state in the region.[55] The period of the Mandate saw the construction of new garden suburbs in the western and northern parts of the city[56][57] and the establishment of institutions of higher learning such as the Hebrew University, founded in 1925.[58]
State of Israel
As the British Mandate of Palestine was expiring, the 1947 UN Partition Plan (Part III) recommended "the creation of a special international regime in the City of Jerusalem, constituting it as a corpus separatum under the administration of the United Nations."[59] However, this plan was never implemented and at the end of the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Jerusalem found itself divided between Israel and Jordan (then known as Transjordan). The ceasefire line established through the Armistice Agreement of 1949 between Israel and Jordan, cut through the center of the city from 1949 until 1967, during which time West Jerusalem was part of Israel and East Jerusalem was part of Jordan. In 1949, Israel designated West Jerusalem as its capital. Contrary to the terms of the Armistice Agreement of 1949 between Jordan and Israel, Israelis were denied access to Jewish holy sites, many of which were desecrated, and only allowed extremely limited access to Christian holy sites.[60]
Following the 1967 Six-Day War Israel captured East Jerusalem, asserted sovereignty over the entire city, and later in 1980 declared Jerusalem, "complete and united", to be the capital of Israel.[61] However, East Jerusalem has been seen by the Palestinian Arabs as a possible capital of a proposed Palestinian state.[62][63] They also refer to Security Council resolution 252, which considers invalid expropriation of land and other actions that tend to change the legal status of Jerusalem.[64] The status of the city and of its holy places remains disputed to this day.
Geography

Jerusalem is situated around 31°47′N 35°13′E / 31.783°N 35.217°E on the southern spur of a plateau in the Judean Mountains, which include the Mount of Olives (East) and Mount Scopus (North East). The altitude of the Old City is approximately 760 metres (2,500 ft).[65] The whole of Jerusalem is surrounded by valleys and dry riverbeds (wadis), although those to the north are less pronounced than those on the other sides.
Three of the most prominent valleys in the region, the Kidron, Hinnom, and Tyropoeon Valleys, intersect in an area just south of the Old City of Jerusalem.[66] The Kidron Valley runs just to the east of the Old City and separates the Mount of Olives from the city proper. Along the southern side of old Jerusalem is the Valley of Hinnom, a steep ravine associated in Biblical eschatology with the concept of Gehenna or hell.[67] A third valley commenced in the northwest near the present-day location of Damascus Gate, ran south-southeasterly through the center of the Old City down to the Pool of Siloam, and divided the lower part into two hills, the Temple Mount to the east, and the rest of the city to the west (the lower and the upper cities described by Josephus). Today, this valley, the Tyropoeon Valley, is mostly hidden from view due to the amount of debris that has accumulated within the ravine over the past few millennia.[66]
Jerusalem is 60 kilometers (37 mi)[68] east of Tel Aviv and the Mediterranean Sea. On the opposite side of the city, approximately 35 kilometers (22 mi)[69] away, is the Dead Sea, the lowest body of water on Earth. Neighboring cities and towns include Bethlehem and Beit Jala to the south, Abu Dis and Ma'ale Adummim to the east, Maoz Zion, Motza and Mevaseret Zion to the west, and Ramallah and Giv'at Ze'ev to the north.[70][71][72]
Climate
Residing at a latitude just north of the Tropic of Cancer and located close to the Mediterranean Sea, Jerusalem is characterized by a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers, and cold and wet winters. Snowfall can occur at least once a year. January is the coldest month of the year, with an average high temperature of 12 °C (54 °F). July and August are the hottest months, with an average high temperature of 29 °C (84 °F).[73] Temperatures vary widely from day to night, and Jerusalem evenings are typically cool even in summer. The average annual precipitation is close to 590 millimetres (23 in) although rain is rare between May and September.[73]
| Climate data for Jerusalem | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: The Weather Channel [74] | |||||||||||||
Most of the air pollution in Jerusalem comes from vehicular traffic, especially in East Jerusalem.[75] Many main streets in Jerusalem were not built to accommodate such a large volume of traffic, leading to traffic congestion and more carbon monoxide released into the air. Industrial pollution inside the city is sparse, but emissions from factories on the Israeli Mediterranean coast can travel eastward and settle over the city.[75]
Demographics
| State of Israel |
|---|
 |
Template:Population of Jerusalem
In May 2006, Jerusalem had a population of 724,000, of whom 65% were Jewish, 32% were Muslim, and 2% were Christian, and a population density of Template:Pop density km2 to mi2.[2][76] In 2005, Jerusalem received 2,450 immigrants, with nearly three quarters of them arriving from the United States, France, and former members of the Soviet Union. Within Israel, emigrants from Jerusalem outnumber immigrants to the city. In 2005, over ten thousand Israelis migrated to Jerusalem while over sixteen thousand left the city.[2] The population of Jerusalem, however, continues to rise due to high birth rates, especially among the Arab and Haredi Jewish communities (whose birth rates are higher than the Israeli national average). Consequently, the total fertility rate in Jerusalem (4.02) is far higher than those of comparable cities in the region such as Tel Aviv (1.98) and well above the national average of 2.90. Similarly, the average size of Jerusalem's 180,000 households is 3.8 people.[2]
In 2005, the total number of residents in Jerusalem grew by approximately thirteen thousand (1.8%) — also well above the Israeli national average. However, as the city has continued to grow, the religious and ethnic composition of Jerusalem has proceeded to shift. Although Jews account for the majority of people in Jerusalem, they only account for thirty-one percent of the children under age fifteen.[2] This recent data corroborates the observation that the Jewish population of Jerusalem has been declining over the past four decades. In 1967, the year of the Six-Day War, Jews accounted for seventy-four percent of the population, which is nine percent more than their share of the population in 2006.[77] Explanations for this decline are the soaring cost of housing in Jerusalem, the smaller job market and the growing religious character of the city. Many young people are moving to the suburbs and coastal cities in search of cheaper housing and the more secular lifestyle offered by other cities.[78]
Demographics and the Jewish-Arab population split continue to play a major role in carving the outcome of the dispute over Jerusalem. In 1998, the chairman of the Jerusalem Development Authority even proposed expanding city limits to the west so as to include more areas heavily populated with Jews.[79]
Local Government
The Jerusalem City Council has thirty-one elected members, one of whom is the mayor. The mayor serves a five-year term and appoints six deputies. The current mayor of Jerusalem, Uri Lupolianski was elected in 2003.[80] Apart from the mayor and his deputies, City Council members receive no salaries and work on a voluntary basis. The longest-serving Jerusalem mayor was Teddy Kollek, who spent twenty-eight years — six consecutive terms — in office. Most of the meetings of the Jerusalem City Council are private, but each month, it holds a session that is open to the public.[80] Within the city council, religious political parties form an especially powerful faction, accounting for the majority of its seats.[81]

The headquarters of the Jerusalem Municipality and the mayor's office are at Safra Square (Kikar Safra) on Jaffa Road. The new municipal complex, comprising two modern buildings and ten renovated historic buildings surrounding a large plaza, opened in 1993.[82] The city falls under the Jerusalem District, with Jerusalem as the district's capital.
Capital of Israel
On December 5, 1949, the State of Israel's first Prime Minister, David Ben-Gurion, proclaimed Jerusalem as Israel's capital[13] and since then all branches of the Israeli government — legislative, judicial, and executive — have resided there.[83] At the time of the proclamation, Jerusalem was divided between Israel and Jordan and thus only West Jerusalem was considered Israel's capital. Immediately after the 1967 Six-Day War, however, Israel annexed East Jerusalem, making it a de facto part of the Israeli capital. Israel enshrined the status of the "complete and united" Jerusalem — west and east — as its capital, in the 1980 Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel.[61]

The non-binding United Nations Security Council Resolution 478, passed on August 20, 1980, declared that this law was "null and void and must be rescinded forthwith." Member states were advised to withdraw their diplomatic representation from the city as a punitive measure. Most of the remaining countries with embassies in Jerusalem complied with the resolution by relocating them to Tel Aviv, where many embassies already resided prior to Resolution 478. Currently there are no embassies located within the city limits of Jerusalem, although there are embassies in Mevasseret Zion, on the outskirts of Jerusalem, and four consulates in the city itself.[84] In 1995, the United States Congress had planned to move its embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem with the passage of the Jerusalem Embassy Act.[85] However, U.S. presidents, including President Bush and President Clinton, have argued that Congressional resolutions regarding the status of Jerusalem are merely "advisory."[86] Israel's most prominent governmental institutions, including the Knesset,[87] the Supreme Court,[88] and the official residences of the President and Prime Minister, are located in Jerusalem.
Palestinian claims
Prior to the creation of the State of Israel, Jerusalem served as the administrative capital of the British Mandate of Palestine, which included present-day Israel and Jordan.[89] From 1949 until 1967, West Jerusalem served as Israel's capital but was not recognized internationally as Israel's capital, because UN General Assembly Resolution 194 ruled Jerusalem an international city. As a result of the Six-Day War in 1967, the whole of Jerusalem came under Israeli control. According to the Oslo Accords, the final status of Jerusalem should be determined by peaceful negotiations, as the Palestinian National Authority sees East Jerusalem as the capital of a future Palestinian state.[10] Orient House was the headquarters of the Palestine Liberation Organization in the 1980s and 1990s, but is currently closed.[90]
Culture


Although Jerusalem is known around the world for its religious significance, the city is also home to many artistic and cultural venues. The Israel Museum, Jerusalem's premier art museum, annually attracts nearly one million visitors, with about a third coming from outside Israel.[91] The twenty-acre (8 ha)[91] Museum complex comprises several artistic institutions that primarily focus on archaeology, sculptures, and traditional artwork from around the world. Among some of the Israel Museum's most notable artifacts are the Dead Sea scrolls, discovered in the mid twentieth century in the Qumran caves near the Dead Sea; they are located in the Museum's Shrine of the Book.[92] The Youth Wing of the museum, which mounts changing exhibits and runs an extensive art education program, is visited by 100,000 children a year.[91] The Israel Museum also owns the Rockefeller Archaeological Museum, Ticho House, and the Paley Center of Art. The Rockefeller Museum, located in East Jerusalem, was the first archeological museum in the Middle East. Built by the British in 1938, it houses findings unearthed in the first half of the twentieth century.[93][94] The Ticho House, located in downtown Jerusalem, houses work by Israeli artist Anna Ticho and the Judaica collections of her husband, an ophthalmologist, who opened Jerusalem's first eye clinic in this building in 1912.[95]
Another prominent cultural institution in Jerusalem is Yad Vashem, Israel's national memorial to the victims of the Holocaust. Yad Vashem houses the world's largest[96] library of Holocaust-related information, with an estimated 100,000 books and articles.[97] The complex contains a state-of-the-art museum that explores the genocide of the Jews through exhibits that focus on the personal stories of individuals and families whose lives were torn asunder, and a gallery displaying permanent and changing exhibits of work by artists who died in the Holocaust.[97] Another memorial at Yad Vashem commemorates the 1.5 million Jewish children who perished at the hands of the Nazis. Yad Vashem operates as both a research and educational institution.

One of the city's foremost orchestras is the Jerusalem Symphony Orchestra, which has been operating since the 1940s.[98] The Orchestra has held performances in cities around the world, including Vienna, Frankfurt, and New York City.[98] Within walking distance of the Old City is a cultural district which includes the Khan Theatre, the only repertoire theater in the city,[99] and the Jerusalem Cinematheque. The Jerusalem Theater, located in the Komemiyut (Talbiya) neighborhood, hosts over 150 concerts a year, as well as theater and dance companies and performing artists from overseas.[100] Other prominent facilities for the performing arts include the International Convention Center (Binyanei Ha'ooma) near the entrance to city, where the Israel Philharmonic Orchestra plays, the Gerard Behar Center in downtown Jerusalem, the Jerusalem Music Center in Yemin Moshe,[101] and the Targ Music Center in Ein Kerem. The Palestinian National Theatre, founded in 1984 and once the only center for art and culture in East Jerusalem,[102] today presents art from the Palestinian perspective.[103] The Israel Festival,[104] featuring local and international vocal artists, concerts, plays and street theater, has been held annually since 1961. For the past 25 years, Jerusalem has been the major organizer of this event, which takes place in May-June, and most of the performances take place at venues around the city.[105]
Religious significance

Jerusalem plays an important role in the three monotheistic religions — Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The 2000 Statistical Yearbook of Jerusalem lists 1204 synagogues, 158 churches, and 73 mosques within the city.[106] Despite efforts to maintain peaceful religious coexistence, some sites, such as the Temple Mount, have been a continuous source of friction and controversy.
Jerusalem has been sacred to the Jews since the 10th century BCE,[5] as the site of Solomon's Temple and the Second Temple. It is mentioned in the Bible 632 times. Today, the Western Wall, a remnant of the Second Temple, is a holy site for Jews, second only to the Temple Mount itself.[107] Synagogues around the world are traditionally built with the Holy Ark facing Jerusalem,[108] and Arks within Jerusalem face the "Holy of Holies".[109] As prescribed in the Mishna and codified in the Shulchan Aruch, daily prayers are recited while facing east, towards Jerusalem. Many Jews have "Mizrach" plaques hung on a wall of their homes to indicate the direction of prayer.[109][110]

Christianity reveres Jerusalem not only for its role in the Old Testament but also for its significance in the life of Jesus. According to Biblical accounts, Jesus was brought to the city of Jerusalem not long after his birth[111] and later in his life cleansed the Second Temple.[112] The Cenacle, believed to be the site of Jesus' Last Supper, is located on Mount Zion in the same building that houses the Tomb of King David.[113][114] Another prominent Christian site in Jerusalem is Golgotha, the site of the crucifixion. The Gospel of John describes it as being located outside Jerusalem,[115] but recent archaeological evidence suggests Golgotha is a short distance from the Old City walls, within the present-day confines of the city.[116] The land currently occupied by the Church of the Holy Sepulchre is considered one of the top candidates for Golgotha and thus has been a Christian pilgrimage site for the past two thousand years.[116][117][118]

According to tradition, Jerusalem is the third-holiest city in Islam.[6] Before it was permanently switched to the Kabaa in Mecca, the qibla (direction of prayer) for Muslims was Jerusalem.[119] The city's lasting place in Islam, however, is primarily due to Muhammad's Night of Ascension (c. 620 CE). Muslims believe Muhammad was miraculously transported one night from Mecca to the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, whereupon he ascended to Heaven to meet previous prophets of Islam.[120][121] The first verse in the Qur'an's Surat al-Isra notes the destination of Muhammad's journey as al-Aqsa (the farthest) mosque,[122] in reference to the location in Jerusalem. Today, the Temple Mount is topped by two Islamic landmarks intended to commemorate the event — al-Aqsa Mosque, derived from the name mentioned in the Qur'an, and the Dome of the Rock, which stands over the Foundation Stone, from which Muslims believe Muhammad ascended to Heaven.[123]
Sports
The two most popular sports in Jerusalem, and Israel as a whole, are football (soccer) and basketball.[124] Beitar Jerusalem Football Club is one of the most popular teams in Israel. Fans include several former and current political figures who make a point of attending its games.[125] Jerusalem's other major football team, and one of Beitar's top rivals, is Hapoel Jerusalem Football Club. Whereas Beitar has been Israel State Cup champion five times,[126] Hapoel has only won the Cup once. Also, Beitar plays in the more prestigious premier league, while Hapoel is in the secondary national league.
In basketball, Hapoel Jerusalem is higher up on the scale. In a league dominated by Maccabi Tel Aviv it has yet to win a championship, but it has won the Israeli Cup three times, and it took the European ULEB Cup in 2004.[127] Since its opening in 1989, Teddy Kollek Stadium has been Jerusalem's primary football stadium, with a capacity of 21,000.[128]
Economy
Historically, Jerusalem's economy was supported almost exclusively by religious pilgrims, as it was located far from the major ports of Jaffa and Gaza.[129] Jerusalem's religious landmarks today remain the top draw for foreign visitors, with the majority of tourists visiting the Western Wall and the Old City,[2] but in the past half-century it has become increasingly clear that Jerusalem's providence cannot solely be sustained by its religious significance.[129]

Although many statistics indicate economic growth in the city, since 1967 East Jerusalem has lagged behind the development of West Jerusalem.[129] Nevertheless, the percentage of households with employed persons is higher for Arab households (76.1%) than for Jewish households (66.8%). The unemployment rate in Jerusalem (8.3%) is slightly better than the national average (9.0%), although the civilian labor force accounted for less than half of all persons fifteen years or older — lower in comparison to that of Tel Aviv (58.0%) and Haifa (52.4%).[2] Poverty in the city has increased dramatically in recent years; between 2001 and 2007, the number of people below the poverty threshold increased by forty percent.[130] In 2006, the average monthly income for a worker in Jerusalem was NIS5,940 (US$1,410), NIS1,350 less than that for a worker in Tel Aviv.[130]
During the British Mandate, a law was passed requiring all buildings to be constructed of Jerusalem stone in order to preserve the unique historic and aesthetic character of the city.[57] Complementing this building code, which is still in force, is the discouragement of heavy industry in Jerusalem; only about 2.2% of Jerusalem's land is zoned for "industry and infrastructure." By comparison, the percentage of land in Tel Aviv zoned for industry and infrastructure is twice as high, and in Haifa, seven times as high.[2] Only 8.5% of the Jerusalem District work force is employed in the manufacturing sector, which is half the national average (15.8%). Higher than average percentages are employed in education (17.9% vs. 12.7%); health and welfare (12.6% vs. 10.7%); community and social services (6.4% vs. 4.7%); hotels and restaurants (6.1% vs. 4.7%); and public administration (8.2% vs. 4.7%).[131] Although Tel Aviv remains Israel's financial center, a growing number of high tech companies are moving to Jerusalem. Northern Jerusalem's Har Hotzvim industrial park is home to some of Israel's major corporations, among them Intel, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, and ECI Telecom. Expansion plans for the park envision one hundred businesses, a fire station, and a school, covering an area of 530,000 m² (130 acres).[132]
Since the establishment of the State of Israel, the national government has remained a major player in Jerusalem's economy. The government, centered in Jerusalem, not only generates a large number of jobs but also offers subsidies and incentives for new business initiatives and start-ups.[129]
Transportation

The airport nearest to Jerusalem is Atarot Airport, which was used for domestic flights only until its closure in 2001. Since then it has been under the control of the Israel Defense Forces due to disturbances in Ramallah and the West Bank. All air traffic from Atarot was rerouted to Ben Gurion International Airport, Israel's largest and busiest airport, which serves nine million passengers annually.[133]
The Egged Bus Cooperative, the second-largest bus company in the world,[134] handles most of the local and intercity bus service out of the city's Central Bus Station on Jaffa Road near the entrance to Jerusalem. Israel Railways, which hopes to transport forty million passengers annually by 2010,[135] runs a limited rail service to Malha train station, at the terminus of an Israel Railways line from Tel Aviv.[136][137]
Begin Expressway is one of Jerusalem's major north-south thoroughfares; it runs on the western side of the city until its northern end merges with Route 443, which continues toward Tel Aviv. Route 60 runs through the center of the city near the Green Line that, de facto, separates East Jerusalem from West Jerusalem. Construction is progressing on parts of a 35-kilometer (22-mile) ring road around the city, fostering faster connection between the suburbs.[138][139] The eastern half of the project was conceptualized decades ago, but reaction to the proposed highway is still mixed.[138]
As of 2007, Egged buses, taxicabs and private cars are the only transportation options in Jerusalem. However, this will change with the completion of the Jerusalem Light Rail, a new rail-based transit system currently under construction. A rail-based system was first envisioned in 1995; since then, a light rail system has been chosen over a subway or monorail design due to its cheaper cost, minimal disruption, and preservation of the city center's aesthetics.[140] The rail system will be capable of transporting an estimated 200,000 people daily. It will have twenty four stops, and is scheduled for completion in January 2009.[141]
In addition,[141] the new high-speed rail line from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem will, when completed in 2011, terminate at an underground station serving the national Convention centre and the Central Bus Station,[142] and is planned to be extended eventually to Malha station.
Education
Jerusalem is home to several prestigious universities, with courses offered in Hebrew, Arabic, and English. Founded in 1925, the Hebrew University of Jerusalem[143] is one of the most respected institutions of higher learning in Israel. The Board of Governors has included such prominent Jewish intellectuals as Albert Einstein and Sigmund Freud.[58] The university has produced several Nobel laureates; recent winners associated with Hebrew University include Avram Hershko,[144] David Gross,[145] and Daniel Kahneman.[146] One of the university's major assets is the Jewish National and University Library, which houses over five million books.[147] The library opened in 1892, over three decades before the university was established, and is one of the world's largest repositories of books on Jewish subjects. Today it is both the central library of the university and the national library of Israel.[148] The Hebrew University operates two campuses in Jerusalem, on Mount Scopus and Givat Ram.
Al-Quds University was established in 1984,[149] to serve as a flagship university for the Arab and Palestinian peoples. It describes itself as the "only Arab university in Jerusalem".[150] Al-Quds University resides southeast of the city proper on a campus encompassing 190,000 square metres (47 acres).[149] Other institutions of higher learning in Jerusalem are the Jerusalem Academy of Music and Dance[151] and Bezalel Academy of Art and Design,[152] whose buildings are located on the campuses of the Hebrew University.
The Jerusalem College of Technology, founded in 1969, combines training in engineering and other high-tech industries with a Jewish studies program.[153] It is one of many schools in Jerusalem, from elementary school and up, that combine secular and religious studies. Numerous religious educational institutions and Yeshivot are based in the city, with the Mir yeshiva claiming to be the largest.[154] There were nearly 8,000 twelfth-grade students in Hebrew-language schools during the 2003–2004 school year.[2] However, due to the large portion of students in Haredi Jewish frameworks, only fifty-five percent of twelfth graders took matriculation exams (Bagrut) and only thirty-seven percent were eligible to graduate. Unlike public schools, many Haredi schools do not prepare students to take standardized tests.[2] To attract more university students to Jerusalem, the city has begaun to offer a special package of financial incentives and housing subsidies to students who rent apartments in downtown Jerusalem.[155]
Schools for Arabs in Jerusalem and other parts of Israel have been criticized for offering a lower quality education than those catering to Israeli Jewish students.[156] While many schools in the heavily Arab East Jerusalem are filled to capacity and there have been complaints of overcrowding, the Jerusalem Municipality is currently building over a dozen new schools within the East Jerusalem neighborhoods of Sheikh Jarrah, Issawiya, Sur Baher, Umm Lison, Beit Hanina, and Wadi Joz. In March 2007, the Israeli government approved a 5-year plan to build 8,000 new classrooms in the city, 40 percent in the Arab sector and 28 percent in the Haredi sector. A budget of 4.6 billion shekels was allocated for this project.[157] Because Arab high school students take the Bagrut matriculation exams, much of their curriculum parallels that of other Israeli high schools, including certain Jewish subjects.[156]
See also
- Jerusalem Day
- List of places in Jerusalem
- Jerusalem Light Rail
- Uri Lupolianski, current mayor of Jerusalem
- International Day of Quds
Sister cities
 New York City, USA (1993)[158]
New York City, USA (1993)[158]
Endnotes
| i. | ^ The website for Jerusalem is available in three languages — Hebrew, English, and Arabic. |
| ii. | ^ Jerusalem in other languages: Arabic Bibles use أورشليم |Ûrshalîm (Ûrushalîm); official Arabic in Israel: أورشليم القدس, Ûrshalîm-al-|Quds (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names) Jerusalem is referred |to in Akkadian in the Amarna letters as URU Uru Šalim KI or the city of peace |
| iii. | ^ Jerusalem is the capital under Israeli law. The presidential residence, government offices, supreme court and parliament (Knesset) are located there. The Palestinian Authority foresees East Jerusalem as the capital of its future state. The United Nations and most countries do not recognize Jerusalem as Israel's capital, arguing that the final status of Jerusalem is pending future negotiations between Israel and the Palestinian Authority. Most countries maintain their embassies in Tel Aviv (see CIA Factbook and Template:PDFlink) See Positions on Jerusalem for more information. |
| iv. | ^ a b Much of the information regarding King David's conquest of Jerusalem comes from Biblical accounts, but modern-day historians have begun to give them credit due to a 1993 excavation.[159] |
| v. | ^ Statistics regarding the demographics of Jerusalem refer to the unified and expanded Israeli municipality, which includes the pre-1967 Israeli and Jordanian municipalities as well as several additional Palestinian villages and neighborhoods to the northeast. Some of the Palestinian villages and neighborhoods have been relinquished to the West Bank de facto by way of the Israeli West Bank barrier,[160] but their legal statuses have not been reverted. |
| vi. | ^ Sources disagree on the timing of the creation of the Pact of Umar (Omar). Whereas some say the Pact originated during Umar's lifetime but was later expanded,[161][162] others say the Pact was created after his death and retroactively attributed to him.[163] Further still, other historians believe the ideas in the Pact pre-date Islam and Umar entirely.[164] |
References
- ^ Largest city:
- "...modern Jerusalem, Israel's largest city..." (Erlanger, Steven. Jerusalem, Now, The New York Times, April 16 2006.)
- "With a population of 701,512 in 2004, Jerusalem is Israel’s largest city. ("Israel (country)", Microsoft Encarta, 2006, p. 3. Retrieved October 18 2006.)
- "Since 1975 unified Jerusalem has been the largest city in Israel." ("Jerusalem", Encyclopædia Britannica Online, 2006. Retrieved October 18, 2006.)
- "Jerusalem is Israel’s largest city." ("Jerusalem", Microsoft Encarta, 2006, p. 1. Retrieved October 18 2006.)
- "Jerusalem is the largest city in the State of Israel. It has the largest population, the most Jews and the most non-Jews of all Israeli cities." (Klein, Menachem. Jerusalem: The Future of a Contested City, New York University Press, March 1 2001, p. 18. ISBN 0-8147-4754-X)
- "In 1967, Tel Aviv was the largest city in Israel. By 1987, more Jews lived in Jerusalem than the total population of Tel Aviv. Jerusalem had become Israel's premier city." (Friedland, Roger and Hecht, Richard. To Rule Jerusalem, University of California Press, September 19 2000, p. 192. ISBN 0-520-22092-7)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Press Release: Jerusalem Day" (pdf). Central Bureau of Statistics. 2006-05-24. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Population of Localities numbering above 1,000 residents and other rural population on 31/12/2006" (pdf). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. 2006-12-31. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)[v] - ^ a b "Timeline for the History of Jerusalem". Jewish Virtual Library. American-Israeli Cooperative Enterprise. Retrieved 2007-04-16.
- ^ a b Since the 10th century BCE:[iv]
- "Israel was first forged into a unified nation from Jerusalem some three thousand years ago, when King David seized the crown and united the twelve tribes from this city... For a thousand years Jerusalem was the seat of Jewish sovereignty, the household site of kings, the location of its legislative councils and courts. In exile, the Jewish nation came to be identified with the city that had been the site of its ancient capital. Jews, wherever they were, prayed for its restoration." Roger Friedland, Richard D. Hecht. To Rule Jerusalem, University of California Press, 2000, p. 8. ISBN 0520220927
- "The Jewish bond to Jerusalem was never broken. For three millennia, Jerusalem has been the center of the Jewish faith, retaining its symbolic value throughout the generations." Jerusalem- the Holy City, Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs, February 23 2003. Accessed March 24, 2007.
- "The centrality of Jerusalem to Judaism is so strong that even secular Jews express their devotion and attachment to the city and cannot conceive of a modern State of Israel without it... For Jews Jerusalem is sacred simply because it exists... Though Jerusalem's sacred character goes back three millennia...". Leslie J. Hoppe. The Holy City:Jerusalem in the theology of the Old Testament, Liturgical Press, 2000, p. 6. ISBN 0814650813
- "Ever since King David made Jerusalem the capital of Israel 3,000 years ago, the city has played a central role in Jewish existence." Mitchell Geoffrey Bard, The Complete Idiot's Guide to the Middle East Conflict, Alpha Books, 2002, p. 330. ISBN 0028644107
- "For Jews the city has been the pre-eminent focus of their spiritual, cultural, and national life throughout three millennia." Yossi Feintuch, U.S. Policy on Jerusalem, Greenwood Publishing Group, 1987, p. 1. ISBN 0313257000
- "Jerusalem became the center of the Jewish people some 3,000 years ago" Moshe Maoz, Sari Nusseibeh, Jerusalem: Points of Friction - And Beyond, Brill Academic Publishers, 2000, p. 1. ISBN 9041188436
- "The Jewish people are inextricably bound to the city of Jerusalem. No other city has played such a dominant role in the history, politics, culture, religion, national life and consciousness of a people as has Jerusalem in the life of Jewry and Judaism. Since King David established the city as the capital of the Jewish state circa 1000 BCE, it has served as the symbol and most profound expression of the Jewish people's identity as a nation." Basic Facts you should know: Jerusalem, Anti-Defamation League, 2007. Accessed March 28 2007.
- ^ a b Third-holiest city in Islam:
- Esposito, John L. (2002-11-02). What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam. Oxford University Press. p. 157. ISBN 0195157133.
The Night Journey made Jerusalem the third holiest city in Islam
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - Brown, Leon Carl (2000-09-15). "Setting the Stage: Islam and Muslims". Religion and State: The Muslim Approach to Politics. Columbia University Press. p. 11. ISBN 0231120389.
The third holiest city of Islam—Jerusalem—is also very much in the center...
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - Hoppe, Leslie J. (2000). The Holy City: Jerusalem in the Theology of the Old Testament. Michael Glazier Books. p. 14. ISBN 0814650813.
Jerusalem has always enjoyed a prominent place in Islam. Jerusalem is often referred to as the third holiest city in Islam...
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
- Esposito, John L. (2002-11-02). What Everyone Needs to Know about Islam. Oxford University Press. p. 157. ISBN 0195157133.
- ^ List of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The site of Jerusalem was nominated in 1981 by Jordan. Old City of Jerusalem and its Walls
- ^ Ben-Arieh, Yehoshua (1984). Jerusalem in the 19th Century, The Old City. Yad Izhak Ben Zvi & St. Martin's Press. p. 14. ISBN 0312441878.
- ^ Kollek, Teddy (1977). "Afterword". In John Phillips (ed.). A Will to Survive - Israel: the Faces of the Terror 1948-the Faces of Hope Today. Dial Press/James Wade.
about 225 acres
- ^ a b Segal, Jerome M. (Fall 1997). "Negotiating Jerusalem". The University of Maryland School of Public Policy. Retrieved 2007-02-25.
- ^ Møller, Bjørn (November 2002). "A Cooperative Structure for Israeli-Palestinian Relations" (pdf). Working Paper No. 1. Centre for European Policy Studies. Retrieved 2007-04-16.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "The Status of Jerusalem". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 1999-03-14. Retrieved 2007-02-12.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Ben-Gurion, David (1949-12-05). "Statements of the Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion Regarding Moving the Capital of Israel to Jerusalem". The Knesset. Retrieved 2007-04-02.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Kellerman, Aharon (1993). Society and Settlement: Jewish Land of Israel in the Twentieth Century. State University of New York Press. p. 140. ISBN 0791412954.
[Tel Aviv] also contains most embassies, given the nonrecognition by many countries of Jerusalem as the capital of Israel.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Bethune, George Washington (1845). The Fruit of the Spirit. Mentz & Rovoudt. p. 93.
is the New Jerusalem, or "heritage of peace."
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Allen, Joseph Henry (1879). Hebrew Men and Times: From the Patriarchs to the Messiah. Roberts Brothers. p. 125.
name it Jerusalem, the "heritage of Peace."
- ^ Elon, Amos (1996-01-08). Jerusalem. HarperCollins Publishers Ltd. ISBN 0006375316. Retrieved 2007-04-26.
The epithet may have originated in the ancient name of Jerusalem—Salem (after the pagan deity of the city), which is etymologically connected in the Semitic languages with the words for peace (shalom in Hebrew, salam in Arabic).
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ From the King James Version of the Bible: "And Melchizedek king of Salem brought forth bread and wine: and he was the priest of the most high God." (Genesis 14:18)
- ^ "Jerusalem, the Old City". al-Quds University. Retrieved 2007-01-12.
- ^ Wallace, Edwin Sherman (1977). Jerusalem the Holy. p. 16. ISBN 0405102984.
A similar view was held by those who give the Hebrew dual to the word
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Smith, George Adam (1907). Jerusalem: The Topography, Economics and History from the Earliest Times to A.D. 70. Hodder and Stoughton. p. 251.
The termination -aim or -ayim used to be taken as the ordinary termination of the dual of nouns, and was explained as signifying the upper and lower cities
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) (see here) - ^ a b Landau, Yehezkel (1996). "Sharing Jerusalem: The Spiritual And Political Challenges". Service International De Documéntation Judéo-Chrétienne. 29 (2–3). Retrieved 2007-01-14.
I will share another meta-midrash...believers in the One Supreme God.
- ^ Sitchin, Zecharia, The Cosmic Code, Avon 1998
- ^ Pritchard, James B. (1968). The Ancient Near East. OUP.
- ^ Herm, Gerard (1975). The Phoenicians. William Morrow. pp. 33, 84–106 passim, 123, 125, 126, 145, 149, 150, 154. ISBN 0-688-02908-6.
- ^ Herodotus
- ^ Glueck, Nelson (1959). Rivers in the Desert. HUC. pp. 15, 41, 63, 95, 102, 106, 118, 119, 122, 123, 138, 143, 150–151, 162, 167, 170, 171, 172, 186, 187, 194, 243, 246, 250, 258, 276.
- ^ Nayeem, Muhammed Abdul (1990). Prehistory and Protohistory of the Arabian Peninsula. Hyderabad.
- ^ Pritchard, James B. (1968). The Ancient Near East. OUP.
- ^ Greenfeld, Howard (2005-03-29). A Promise Fulfilled: Theodor Herzl, Chaim Weizmann, David Ben-Gurion, and the Creation of the State of Israel. Greenwillow. p. 32. ISBN 006051504X.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Timeline". City of David. Ir David Foundation. Retrieved 2007-01-18.
- ^ Vaughn, Andrew G. (2003-08-01). "Jerusalem at the Time of the United Monarchy". Jerusalem in Bible and Archaeology: the First Temple Period. pp. 32–33. ISBN 1589830660.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help); External link in|author=and|coauthors=|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Shalem, Yisrael (1997-03-03). "History of Jerusalem from Its Beginning to David". Jerusalem: Life Throughout the Ages in a Holy City. Bar-Ilan University Ingeborg Rennert Center for Jerusalem Studies. Retrieved 2007-01-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Michael, E. (2005-02-28). The Complete Book of When and Where: In The Bible And Throughout History. Tyndale House Publishers, Inc. pp. 20–1, 67. ISBN 0842355081.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Merling, David (1993-08-26). "Where is the Ark of the Covenant?". Andrew's University. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); External link in|author= - ^ Zank, Michael. "Capital of Judah I (930–722)". Boston University. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ a b Zank, Michael. "Capital of Judah (930–586)". Boston University. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ Sicker, Martin (2001-01-30). Between Rome and Jerusalem: 300 Years of Roman-Judaean Relations. Praeger Publishers. p. 2. ISBN 0275971406.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Zank, Michael. "Center of the Persian Satrapy of Judah (539–323)". Boston University. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ Schiffman, Lawrence H. (1991). From Text to Tradition: A History of Second Temple and Rabbinic Judaism. Ktav Publishing House. pp. 60–79. ISBN 0-88125-371-5.
- ^ Har-el, Menashe. This Is Jerusalem. Canaan Publishing House.
{{cite book}}: Text "1977" ignored (help); Text "pages68-95" ignored (help) - ^ Zank, Michael. "The Temple Mount". Boston University. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ Crossan, John Dominic (1993-02-26). The Historical Jesus: the life of a Mediterranean Jewish peasant (Reprinted ed. ed.). San Francisco: HarperCollins. p. 92. ISBN 0060616296.
from 4 BCE until 6 CE, when Rome, after exiling [Herod Archelaus] to Gaul, assumed direct prefectural control of his territories
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Lehmann, Clayton Miles. "Palestine: People and Places". The On-line Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces. The University of South Dakota. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
- ^ a b Lehmann, Clayton Miles (2007-02-22). "Palestine: History". The On-line Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces. The University of South Dakota. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Cohen, Shaye J. D. (1996). "Judaism to Mishnah: 135–220 C.E". In Hershel Shanks (ed.). Christianity and Rabbinic Judaism: A Parallel History of their Origins and Early Development. Washington DC. p. 196.
{{cite book}}: Text "publisher:Biblical Archaeology Society" ignored (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Har-el, Menashe. This Is Jerusalem. Canaan Publishing House.
{{cite book}}: Text "1977" ignored (help); Text "pages68–95" ignored (help) - ^ Zank, Michael. "Byzantian Jerusalem". Boston University. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ^ Hoppe, Leslie J. (2000). The Holy City: Jerusalem in the Theology of the Old Testament. Michael Glazier Books. p. 15. ISBN 0814650813.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Zank, Michael. "Abbasid Period and Fatimid Rule (750–1099)". Boston University. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ^ Hull, Michael D. (1999). "First Crusade: Siege of Jerusalem". Military History. Retrieved 2007-05-18.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b "Main Events in the History of Jerusalem". Jerusalem: The Endless Crusade. The CenturyOne Foundation. 2003. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ Elyon, Lili (1999). "Jerusalem: Architecture in the Late Ottoman Period". Focus on Israel. Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2007-04-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Fromkin, David (2001-09-01). A Peace to End All Peace: The Fall of the Ottoman Empire and the Creation of the Modern Middle East (2nd reprinted ed.). Owl Books e. pp. 312–3. ISBN 0805068848.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Mendelsson, David. "British Rule". Department for Jewish Zionist Education. The Jewish Agency for Israel. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ Tamari, Salim (1999). "Jerusalem 1948: The Phantom City" (Reprint). Jerusalem Quarterly File (3). Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ a b Eisenstadt, David (2002-08-26). "The British Mandate". Jerusalem: Life Throughout the Ages in a Holy City. Bar-Ilan University Ingeborg Rennert Center for Jerusalem Studies. Retrieved 2007-02-10.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "History". The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-03-18.
- ^ "Considerations Affecting Certain of the Provisions of the General Assembly Resolution on the "Future Government of Palestine": The City of Jerusalem". The United Nations. 1948-01-22. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Mitchell Bard. "Myths & Facts Online: Jerusalem". Jewish Virtual Library.
- ^ a b "Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 1980-07-30. Retrieved 2007-04-02.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "No Mid-East advance at UN summit". BBC. 2000-09-07. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Khaled Abu Toameh (2007-01-11). "Abbas: Aim guns against occupation". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2007-02-03.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "United Nations Security Council Resolution 252". Jewish Virtual Library. 1968-05-21. Retrieved 2007-05-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Cabrera, Enrique (1998-12-31). Drought Management Planning in Water Supply Systems. Springer. p. 304. ISBN 0792352947.
The Old City of Jerusalem (760 m) in the central hills
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Bergsohn, Sam (2006-05-15). "Geography". Cornell University. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Walvoord, John (1996-01-07). "The Metaphorical View". Four Views on Hell. Zondervan. p. 58. ISBN 0310212685.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Rosen-Zvi, Issachar (2004). Taking Space Seriously: Law, Space and Society in Contemporary Israel. Ashgate Publishing. p. 37. ISBN 0754623513.
Thus, for instance, the distance between the four large metropolitan regions are—39 miles
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Federman, Josef (2004-08-18). "Debate flares anew over Dead Sea Scrolls". AP via MSNBC. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Introduction". The Tell es-Safi/Gath Archaeological Expedition. Bar Ilan University. Retrieved 2007-04-24. (Image located here)
- ^ "Map of Israel". Eye On Israel. Retrieved 2007-04-25. (See map 9 for Jerusalem)
- ^ ""One more Obstacle to Peace" – A new Israeli Neighborhood on the lands of Jerusalem city". The Applied Research Institute -- Jerusalem. 2007-03-10. Retrieved 2007-04-24.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) (Image located here) - ^ a b "Monthly Averages for Jerusalem, Israel". The Weather Channel. Retrieved 2007-02-07.
- ^ "Monthly Averages for Jerusalem, Israel". The Weather Channel Interactive, Inc.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Ma'oz, Moshe (2000). Jerusalem: Points of Friction-And Beyond. Brill Academic Publishers. pp. 44–6. ISBN 9041188436.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Population and Density per km² in Localities Numbering Above 5,000 Residents on 31 XII 2005" (pdf). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. 2006. Retrieved 2007-04-11.
- ^ Sel, Neta (2006-05-23). "Jerusalem: More tourists, fewer Jews". YNet. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Hockstader, Lee (1998-08-16). "Jewish Drop In Jerusalem Worries Israel". The Washington Post via Cornell University. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Laub, Karin (2006-12-02). "Jerusalem Barrier Causes Major Upheaval". The Associated Press via The Washington Post. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b Cidor, Peggy (2007-03-15). "Corridors of Power: A tale of two councils". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2007-03-28.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Coker, Margaret (2006-11-11). "Jerusalem Becomes A Battleground Over Gay Rights Vs. Religious Beliefs". Cox Newspapers. Retrieved 2007-03-28.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Safra Square - City Hall". The Municipality of Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-04-24.
- ^ "Jerusalem and Berlin Embassy Relocation Act of 1998". The Library of Congress. 1998-06-25. Retrieved 2007-02-12.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Embassies and Consulates in Israel". Israel Science and Technology Homepage. Retrieved 2007-05-03.
- ^ "Jerusalem Embassy Act of 1995" (PDF). U.S. Government Printing Office. 1995-11-08. Retrieved 2007-02-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Statement on FY 2003 Foreign Relations Authorization Act". Retrieved 2007-05-23.
- ^ "English gateway to the Knesset website". Retrieved 2007-05-18.
- ^ "The State of Israel: The Judicial Authority". Retrieved 2007-05-18.
- ^ Jerusalem as administrative capital of the British Mandate of Palestine:
- Orfali, Jacob G. (1995). Everywhere You Go, People Are the Same. Ronin Publishing. p. 25. ISBN 0914171755.
In the year 1923, [Jerusalem] became the capital of the British Mandate in Palestine
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Oren-Nordheim, Michael (2001). Jerusalem and Its Environs: Quarters, Neighborhoods, Villages, 1800–1948. Wayne State University Press. p. 36. ISBN 0814329098.
The three decades of British rule in Palestine (1917/18–1948) were a highly significant phase in the development, with indelible effects on the urban planning and development of the capital – Jerusalem.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) Ruth Kark is a professor in the Department of Geography at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. - Dumper, Michael (1996-04-15). The Politics of Jerusalem Since 1967. Columbia University Press. p. 59. ISBN 0231106408.
...the city that was to become the administrative capital of Mandate Palestine...
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help)
- Orfali, Jacob G. (1995). Everywhere You Go, People Are the Same. Ronin Publishing. p. 25. ISBN 0914171755.
- ^ Klein, Menachem (2001). "The PLO and the Palestinian Identity of East Jerusalem". Jerusalem: The Future of a Contested City. New York University Press. p. 189. ISBN 081474754X.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c "About the Museum". The Israel Museum, Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ^ "Shrine of the Book". The Israel Museum, Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-02-27.
- ^ "The Rockefeller Archaeological Museum". The Israel Museum, Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ "The Rockefeller Archaeological Museum: About the Museum: The Permanent Exhibition". The Israel Museum, Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ "Ticho House". The Israel Museum, Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ "Yad Vashem". The Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ a b "About Yad Vashem". The Holocaust Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority. Retrieved 2007-02-28.
- ^ a b "History". Jerusalem Orchestra. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- ^ "About Us". The Khan Theatre. 2004. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- ^ "The Jerusalem Centre for the Performing Arts". Jerusalem Theater. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- ^ "Jerusalem Music Center". Retrieved 2007-05-18.
- ^ "History". Palestinian National Theatre. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- ^ "Mission". Palestinian National Theatre. Retrieved 2007-03-04.
- ^ "Israel Festival: Jerusalem 2007". Retrieved 2007-05-18.
- ^ "About". Israel Festival. Retrieved 2007-04-24. The necessary information could be found by clicking the "About" link on the homepage that appears.
- ^ Guinn, David E. (2006-10-02). Protecting Jerusalem's Holy Sites: A Strategy for Negotiating a Sacred Peace (1st ed. ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 142. ISBN 0521866626.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|edition=has extra text (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "What is the Western Wall?". The Kotel. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Goldberg, Monique Susskind. "Synagogues". Ask the Rabbi. Schechter Institute of Jewish Studies. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
- ^ a b Segal, Benjamin J. (1987). Returning: The Land of Israel as Focus in Jewish History. Jerusalem, Israel: Department of Education and Culture of the World Zionist Organization. p. 124. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
- ^ The Jewish injunction to pray toward Jerusalem comes in the Orach Chayim section of Shulchan Aruch (94:1) — "When one rises to pray anywhere in the Diaspora, he should face towards the Land of Israel, directing himself also toward Jerusalem, the Temple, and the Holy of Holies."
- ^ From the King James Version of the Bible: "And when the days of her purification according to the law of Moses were accomplished, they brought [Jesus] to Jerusalem, to present him to the Lord;" (Luke 2:22)
- ^ From the King James Version of the Bible: "And they come to Jerusalem: and Jesus went into the temple, and began to cast out them that sold and bought in the temple, and overthrew the tables of the moneychangers, and the seats of them that sold doves;" (Mark 11:15)
- ^ Boas, Adrian J. (2001-10-12). "Physical Remains of Crusader Jerusalem". Jerusalem in the Time of the Crusades. Routledge. p. 112. ISBN 0415230004.
The interesting, if not reliable illustrations of the church on the round maps of Jerusalem show two distinct buildings on Mount Zion: the church of St Mary and the Cenacle (Chapel of the Last Supper) appear as separate buildings.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Endo, Shusaku (1999). Richard A. Schuchert (ed.). A Life of Jesus. Paulist Press. p. 116. ISBN 0809123193.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ From the King James Version of the Bible: "This title then read many of the Jews: for the place where Jesus was crucified was nigh to the city: and it was written in Hebrew, and Greek, and Latin." (John 19:20)
- ^ a b Stump, Keith W. (1993). "Where Was Golgotha?". Worldwide Church of God. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
- ^ Ray, Stephen K. (2002). St. John's Gospel: A Bible Study Guide and Commentary for Individuals and Groups. p. 340. ISBN 0898708214.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ O'Reilly, Sean (2000-11-30). Pilgrimage: Adventures of the Spirit (1st ed. ed.). Travelers' Tales. p. 14. ISBN 1885211562.
The general consensus is that the Church of the Holy Sepulchre marks the hill called Golgotha, and that the site of the Crucifixion and the last five Stations of the Cross are located under its large black domes.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|edition=has extra text (help); Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthor=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Cordesman, Anthony H. (2005-10-30). "The Final Settlement Issues: Asymmetric Values & Asymmetric Warfare". The Israeli-Palestinian War: Escalating to Nowhere. Praeger Security International. p. 62. ISBN 0275987582.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Peters, Francis E. (2003-10-20). "Muhammad the Prophet of God". The Monotheists: The Peoples of God. Princeton University Press. pp. 95–6. ISBN 0691114609.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Sahih Bukhari". Compendium of Muslim Texts. University of Southern California. Retrieved 2007-03-11. (from an English translation of Sahih Bukhari, Volume IX, Book 93, Number 608)
- ^ From Abdullah Yusuf Ali's English translation of the Qur'an: "Glory to (Allah) Who did take His servant for a Journey by night from the Sacred Mosque to the farthest Mosque, whose precincts We did bless,- in order that We might show him some of Our Signs: for He is the One Who heareth and seeth (all things)." (17:1)
- ^ "The Early Arab Period - 638-1099". Jerusalem: Life Throughout the Ages in a Holy City. Bar-Ilan University Ingeborg Rennert Center for Jerusalem Studies. 1997. Retrieved 2007-04-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Torstrick, Rebecca L. (2004-06-30). Culture and Customs of Israel. Greenwood Press. p. 141. ISBN 0313320918.
The two most popular spectator sports in Israel are soccer (Israeli football) and basketball.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Griver, Simon (1997). "Betar Jerusalem: A Local Sports Legend Exports Talent to Europe's Top Leagues". Israel Magazine via the Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2007-03-07.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Template:He icon "Home". Beitar Jerusalem F.C. Retrieved 2007-03-07. (The listing of championship wins are located on the left side.)
- ^ Template:He icon "Home". Hapoel Migdal Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-03-07. (The listing of championship wins are located at the bottom after the completion of the Flash intro.)
- ^ Eldar, Yishai (2001-12-01). "Jerusalem: Architecture Since 1948". Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2007-03-07.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c d Dumper, Michael (1996-04-15). The Politics of Jerusalem Since 1967. Columbia University Press. pp. 207–10. ISBN 0231106408.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "Study shows poverty level in Jerusalem double that of other Israeli cities". Israel Insider. 2007-01-11. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Employed Persons, by Industry, District and Sub-District of Residence, 2005" (PDF). Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2007-04-11.
- ^ "Har Hotzvim Industrial Park". Har Hotzvim Industrial Park. Retrieved 2007-03-13.
- ^ Smith, Patrick (2006-06-09). "Ask the Pilot". Salon. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Solomon, Shoshanna (2001-11-01). "Facets of the Israeli Economy – Transportation". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "General Information: Railway 2000". Israel Railways. Retrieved 2007-04-01.
- ^ "Jerusalem - Malha". Israel Railways. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
- ^ "Passenger Lines Map". Israel Railways. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
- ^ a b Burstein, Nathan (2006-01-19). "Running rings around us". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2007-03-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Gil Zohar (May 31, 2007). "Their way or the highway?". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2007-06-11.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Solution". Jerusalem Mass Transit System Project. Retrieved 2007-03-17.
- ^ a b Afra, Orit (2007-02-08). "Panacea or pain?". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2007-03-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Life in Jerusalem – Transportation". Rothberg International Station – Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Retrieved 2007-03-14.
- ^ Official site of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem: (Hebrew), (Hebrew)
- ^ Hershko, Avram. "Avram Hershko". The Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2007-03-18.
- ^ Gross, David. "David J. Gross". The Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2007-03-18.
- ^ Kahneman, Daniel. "Daniel Kahneman". The Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2007-03-18.
- ^ "About the Library: Main Collections". Jewish National and University Library. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
- ^ "About the Library: History and Aims". Jewish National and University Library. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
- ^ a b "Science & Technology". al-Quds University. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
- ^ "Urgent Appeal". al-Quds University. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
- ^ Official site of the Jerusalem Academy of Music and Dance: (Hebrew), (English)
- ^ Official site of Bezalel Academy of Art and Design: (Hebrew), (English)
- ^ "About JCT". Jerusalem College of Technology. Retrieved 2007-03-25.
- ^ Wohlgelernter, Elli (2000-12-28). "The village of Mir, where Torah once flowed". Jewish Agency for Israel. Retrieved 2007-03-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Jonathan Lis (May 04, 2005). "The best medicine for Jerusalem".
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b "Summary". Second Class Discrimination Against Palestinian Arab Children in Israel's Schools. Human Rights Watch. 2001. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Or Kashti (March 18, 2007). "8,000 new classrooms to be built in Arab, ultra-Orthodox schools".
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Online Directory: Israel, Middle East". Sister Cities International. Retrieved 2007-04-05.
- ^ Pellegrino, Charles R. (1995-12-01). Return to Sodom & Gomorrah (Second revised ed.). Harper Paperbacks. p. 271. ISBN 0380726335.
[see footnote]
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Laub, Karin (2006-12-02). "Jerusalem Barrier Causes Major Upheaval". The Associated Press via The Washington Post. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Marcus, Jacob Rader (2000). The Jew in the Medieval World: A Source Book, 315–1791 (Revised ed. ed.). Hebrew Union College Press. pp. 13–15. ISBN 087820217X. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Jonsson, David J. (2005-02-19). The Clash of Ideologies. Xulon Press. p. 256. ISBN 1597810398.
During the reign of Umar, the Pact of Umar was established.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Goddard, Hugh (2001-04-25). A History of Christian-Muslim Relations. New Amsterdam Books. p. 46. ISBN 1566633400.
Although the documents are attributed to `Umar, in all probability they actually come from the second Islamic century... The covenant was drawn up in the schools of law, and came to be ascribed, like so much else, to `Umar I
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Goddard, Hugh (2001-04-25). A History of Christian-Muslim Relations. New Amsterdam Books. p. 47. ISBN 1566633400.
It has recently been suggested that many of the detailed regulations concerning what the ahl al-dhimma were and were not permitted to do come from an earlier historical precedent, namely the regulations which existed in the Sassanian Persian Empire with reference to its religious minorities in Iraq.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
Other resources
- Cheshin, Amir S.; Bill Hutman and Avi Melamed (1999). Separate and Unequal: the Inside Story of Israeli Rule in East Jerusalem Harvard University Press
- Cline, Eric (2004) Jerusalem Besieged: From Ancient Canaan to Modern Israel. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press ISBN 0-472-11313-5.
- Collins, Larry, and La Pierre, Dominique (1988). O Jerusalem! Simon and Shuster, N.Y. ISBN 0-671-66241-4
- Gold, Dore (2007) The Fight for Jerusalem: Radical Islam, The West, and the Future of the Holy City Regnery Publishing, Inc. ISBN 978-1-59698-029-7
- Köchler, Hans (1981) The Legal Aspects of the Palestine Problem with Special Regard to the Question of Jerusalem Vienna: Braumüller ISBN 3-7003-0278-9
- The Holy Cities: Jerusalem produced by Danae Film Production, distributed by HDH Communications; 2006
- Wasserstein, Bernard (2002) Divided Jerusalem: The Struggle for the Holy City New Haven and London: Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-09730-1
External links
- Official website of Jerusalem
- Jerusalemp3, offers free virtual tours in mp3 format from the Jerusalem Municipality
- Virtual Tour of Jerusalem @ jerusalem360.com - Interactive Panoramas from Israel
- Template:Wikitravel
- Jerusalem Shots, portal of photographs of Jerusalem
Government
- Template:PDFlink, United Nations document related to the recent dispute over Jerusalem
- Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel, Government of Israel, the Israeli law making Jerusalem the capital of Israel
Culture
- Israel Museum, one of Jerusalem's premier art museums
- Yad Vashem, Israeli memorial to victims of The Holocaust
Education
- Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem's foremost institution of higher learning
- al-Quds University, "the only Arab university in Jerusalem"
Maps
Template:Geolinks-cityscale-no-title
- Modern-day map of Jerusalem, from the Jerusalem Municipality
- Ancient Maps of Jerusalem, from the Jewish National Library at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Media
- The Jerusalem Post, the oldest and largest English-language Israeli newspaper (formerly The Palestine Post)
- Ha'aretz, major source of Israeli news
- Ynetnews, major source of Israeli news
- Arutz Sheva (see also: Arutz Sheva)
31°47′N 35°13′E / 31.783°N 35.217°E

