Languages of Europe: Difference between revisions
Psychonaut (talk | contribs) →Number of speakers: added cleanup templates: most figures are unreferenced; others seem to be original research or nontrivial syntheses of published estimates -- see talk page |
There's a difference between asking for references and claiming original research. False accusations are against Wikipedia policies. |
||
| Line 298: | Line 298: | ||
== Number of speakers == |
== Number of speakers == |
||
The following is a table displaying the number of speakers of a given European language in Europe only. See the languages' individual page for a more detailed summary and for sources. Some figures are approximate and may come from sources that are several years old. Dialects, or languages that have been labelled or contested as dialects by linguists, are not included in the table. |
The following is a table displaying the number of speakers of a given European language in Europe only. See the languages' individual page for a more detailed summary and for sources. Some figures are approximate and may come from sources that are several years old. Dialects, or languages that have been labelled or contested as dialects by linguists, are not included in the table. |
||
{{Original research|table|date=July 2014}}{{Refimprove|table|date=July 2014}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:99%;" |
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:99%;" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Revision as of 09:04, 22 July 2014
Not to be confused with Indo-European languages.

Most of the languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. This family is divided into a number of branches, including Romance, Germanic, Baltic, Slavic, Albanian, Celtic, Armenian and Hellenic (Greek). The Uralic languages, which include Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, also have a significant presence in Europe. The Turkic and Mongolic families also have several European members, while the North Caucasian and Kartvelian families are important in the southeastern extremity of geographical Europe. The Basque language of the western Pyrenees is an isolate unrelated to any other group, while Maltese is the only Semitic language in Europe with national language status.
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European language family descended from Proto-Indo-European, believed to have been spoken thousands of years ago. Indo-European languages are spoken throughout Europe, but particularly dominate Western Europe.

Albanian
Albanian has two major dialects, Gheg and Tosk. It is spoken in Albania, Kosovo (Kosovar Albanians) and parts of Montenegro (Albanians in Montenegro), Serbia (mainly in Preševo Valley), Turkey, southern Italy (Arbëresh), western parts of Macedonia, Greece (Arvanitika and Cham Albanians) and Albanian diaspora.
Armenian
Armenian has two major dialects, Western Armenian and Eastern Armenian. It is spoken in Armenia, where it has sole official status, and is also spoken in neighboring Georgia, Iran, and Azerbaijan (mainly in Nagorno-Karabakh Republic). It is also spoken in Turkey by a very small minority (Western Armenian and Homshetsi), and by small minorities in many other countries where members of the widely dispersed Armenian diaspora reside.
Baltic languages
The Baltic languages are spoken in Lithuania (Lithuanian, Samogitian) and Latvia (Latvian, Latgalian). Samogitian and Latgalian are usually considered to be dialects of Lithuanian and Latvian respectively.
New Curonian[citation needed] is nearly extinct: it was spoken in the Curonian Spit which is now divided between Lithuania and the Kaliningrad Oblast. There are also several extinct Baltic languages, including Old Prussian and Sudovian.
Celtic

There are six more or less living Celtic languages, spoken in areas of northwestern Europe dubbed the "Celtic nations". All six are members of the Insular Celtic family, which in turn is divided into:
- Brythonic family: Welsh (Wales), Cornish (Cornwall) and Breton (Brittany)
- Goidelic family: Irish (Ireland), Scottish Gaelic (Scotland), and Manx (Isle of Man)
Continental Celtic languages had previously been spoken across Europe from Iberia and Gaul to Asia Minor, but became extinct in the first millennium AD.
Germanic
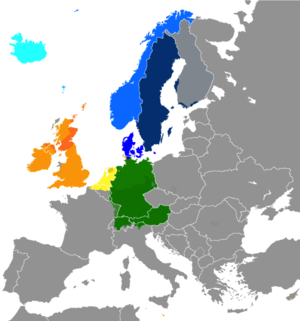
North Germanic languages West Germanic languages Dots indicate areas where multilingualism is common.
The Germanic languages make up the predominant language family in northwestern Europe, reaching from Iceland to Sweden and from parts of the United Kingdom and Ireland to Austria. There are two extant major sub-divisions: West Germanic and North Germanic. A third group, East Germanic, is now extinct; the only known surviving East Germanic texts are written in the Gothic language.
West Germanic
There are three major groupings of West Germanic languages: Anglo-Frisian, Low Franconian (now primarily modern Dutch) and High German.
Anglo-Frisian
The Anglo-Frisian language family has two major groups:
- The English languages are descended from the Old English language of the Anglo-Saxons and include:
- English, the main language of the United Kingdom, also used in English-speaking Europe
- Modern Scots, spoken in Scotland and Ulster.
- The Frisian languages are spoken by about 500,000 Frisians, who live on the southern coast of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. These languages include West Frisian, Saterlandic, and North Frisian.
High German
German is spoken throughout Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, the East Cantons of Belgium, much of Switzerland (including the northeast areas bordering on Germany and Austria) and northern Italy (South Tyrol).
There are several groups of German dialects:
- High German include several dialect families:
- Standard German
- Central German dialects, spoken in central Germany and include Luxembourgish
- High Franconian, a family of transitional dialects between Central and Upper High German
- Upper German, including Austro-Bavarian and Swiss German
Low German
Low German is a separate language group from High German, but is still considered a dialect. It is spoken in various regions throughout Northern Germany, but has no official status, as the official language is Standard German.
Low Franconian
- Dutch is spoken throughout the Netherlands, northern Belgium, as well as the Nord-Pas de Calais region of France, and around Düsseldorf in Germany. In Belgian and French contexts, Dutch is sometimes referred to as Flemish. Dutch dialects are varied and cut across national borders. In Germany it is called East Bergish.
- Afrikaans is spoken by South African emigrant communities in Europe, most notably in the Netherlands, Belgium, and the United Kingdom.
North Germanic
The North Germanic languages are spoken in Scandinavian countries and include Danish (Denmark, Greenland and the Faroe Islands), Norwegian (Norway), Swedish (Sweden and parts of Finland), Elfdalian or Övdalian (in a small part of central Sweden), Faroese (Faroe Islands), and Icelandic (Iceland).
Greek
- Greek is the official language of Greece and Cyprus, and there are Greek-speaking enclaves in Albania, Bulgaria, Italy, the Republic of Macedonia[citation needed], Romania, Georgia, Ukraine, Lebanon, Egypt, Israel, Jordan and Turkey, and in Greek communities around the world. Dialects of modern Greek that originate from Attic Greek (through Koine and then Medieval Greek) are Cappadocian, Pontic, Cretan, Cypriot, Katharevousa, and Yevanic
- Griko is, debatably, a Doric dialect of Greek. It is spoken in the lower Calabria region and in the Salento region of Southern Italy.
- Tsakonian is a Doric dialect of the Greek language spoken in the lower Arcadia region of the Peloponnese around the village of Leonidio
Indo-Iranian languages
The Indo-Iranian languages have two major groupings, Indo-Aryan languages including Romani, and Iranian languages, which include Kurdish, Persian, and Ossetian.
Romance languages

The Romance languages descended from the Vulgar Latin spoken across most of the lands of the Roman Empire. Some of the Romance languages are official in the European Union and the Latin Union and the more prominent ones are studied in many educational institutions worldwide. Three of the Romance languages (Spanish, French, and Portuguese) are spoken by one billion speakers worldwide. Many other Romance languages and their local varieties are spoken throughout Europe, and some are recognized as regional languages.
The list below is a summary of Romance languages commonly encountered in Europe:
- Aragonese is recognized, but not official, in Aragon (Spain).
- Asturian is recognized, but not official, in the Spanish region of Asturias.
- Catalan is official in Andorra; co‑official in the Spanish regions of Catalonia, Valencian Community (as Valencian) and Balearic Islands; and recognized, but not official, in La Franja of Aragon. It is also natively spoken in Northern Catalonia, France, in the Languedoc-Roussillon region (Llengadoc-Rosselló) and in the city of Alghero, Sardinia, Italy (as Alguerese).
- Corsican is spoken on the French island of Corsica and in the extreme north of Sardinia. Traditionally split up into three differents dialects pertaining to the northern and southern halves of Corsica, in addition to the Sardinian subregion of Gallura, the origins of the language date back to the Middle Ages and are closely related to Tuscan. Its prospects of survival are better than most French minority languages, but it still suffers from the lack of promotion.
- Franco-Provençal, sometimes called "Arpitan", protected by statutes in the Aosta Valley Autonomous Region of Italy, also spoken alpine valleys of the province of Turin, two communities in province of Foggia, Romandy region of western Switzerland, and in east central France (i.e., between standard French and Occitan domains). It is in serious danger of extinction.
- French is official in France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Monaco, Switzerland and the Channel Islands. It is also official in Canada, in many African countries and in overseas departments and territories of France.
- Galician, akin to Portuguese, is co‑official in Galicia, Spain. It is also spoken by Galician diaspora.
- Italian is official in Italy, San Marino, Switzerland, Vatican City and Istria (in Croatia and Slovenia). It is also widely spoken in Malta and Monaco.
- Latin is usually classified as an Italic language of which the Romance languages are a subgroup. It is extinct as a spoken language, but it is widely used as a liturgical language by the Roman Catholic Church and studied in many educational institutions. It is also the official language of the Holy See (but not of the Vatican City State). Latin was the main language of literature, sciences, and arts for many centuries and greatly influenced all European languages.
- Leonese is recognized in Spain's autonomous Castile and León region
- Mirandese is officially recognized by the Portuguese Parliament.
- Norman has been debatedly referred to as a language in its own right or a dialect of standard French with its own regional character. Its use is recognized in the Channel Islands, remnants of the historical Duchy of Normandy, and since 2008 it is among the regional languages recognised in the French constitution.
- Occitan is spoken principally in France, but is only officially recognized in Spain as one of the three official languages of Catalonia (termed there Aranese), and in Italy as a minority language. Its use was severely reduced due to the once de jure and currently de facto promotion of French.
- Picard is spoken in two regions in the far north of France – Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy – and in parts of the Belgian region of Wallonia. Belgium's French Community gave full official recognition to Picard as a regional language.
- Portuguese is official in Portugal. It is also official in several former Portuguese colonies in Africa, Eastern Asia as well as in America (see Geographic distribution of Portuguese and Community of Portuguese Language Countries).
- Romanian is official in Romania, Moldova (as Moldovan), and Vojvodina (Serbia).
- Romansh is an official language of Switzerland.
- Sardinian is a language spoken on the Italian island of Sardinia. Traditionally subdivided into two main dialectal varieties, it is considered to be one of the most conservative languages in terms of phonology, when compared to other Romance languages. Sardinian enjoys the same dignity and standing of Italian by the regional law,[1] in spite of the fact that, in practice, it still suffers from a lack of promotion at institutional level and is put under heavy pressure by Italian.
- Spanish (also termed "Castilian") is official in Spain. It is also official in most Latin American countries with the exception of Brazil, French Guyana and Haiti.
Slavic
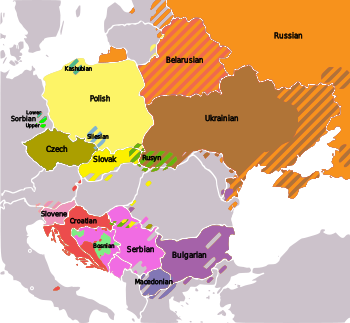
Slavic languages are spoken in large areas of Central Europe, Southern Europe and Eastern Europe including Russia.
- East Slavic languages include Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, and Rusyn.
- West Slavic languages include Czech, Polish, Slovak, Sorbian and Kashubian. Silesian has also been called a separate language.
- South Slavic languages include Bosnian, Bulgarian, Croatian, Macedonian, Montenegrin, Old Church Slavonic (a liturgical language), Serbian, and Slovene.
Languages not from the Indo-European family
Basque
The Basque language (or Euskara) is a language isolate and the ancestral language of the Basque people who inhabit the Basque Country, a region in the western Pyrenees mountains mostly in northeastern Spain and partly in southwestern France of about 3 million inhabitants, where it is spoken fluently by about 750,000 and understood by more than 1.5 million people.
Basque is directly related to ancient Aquitanian, and it is likely that an early form of the Basque language was present in Western Europe before the arrival of the Indo-European languages in the area. The language may have been spoken since Paleolithic times.
Basque is also spoken by immigrants in Australia, Costa Rica, Mexico, the Philippines and the United States, especially in the states of Nevada, Idaho, and California.[2]
Kartvelian languages

The Kartvelian language family consists of Georgian and the related languages of Svan, Mingrelian, and Laz. Proto-Kartvelian is believed to be a common ancestor language of all Kartvelian languages, with the earliest split occurring in the second millennium BC or earlier when Svan was separated. Megrelian and Laz split from Georgian roughly a thousand years later, roughly at the beginning of the first millennium BC (e.g., Klimov, T. Gamkrelidze, G. Machavariani).
The group is considered as isolated, and although for simplicity it is at times grouped with North Caucasian languages, no linguistic relationship exists between the two language families.
North Caucasian
North Caucasian languages (sometimes called simply "Caucasic", as opposed to Kartvelian, and to avoid confusion with the concept of the "Caucasian race") is a blanket term for two language families spoken chiefly in the north Caucasus and Turkey—the Northwest Caucasian family (including Abkhaz, spoken in Abkhazia, and Circassian) and the Northeast Caucasian family, spoken mainly in the border area of the southern Russian Federation (including Dagestan, Chechnya, and Ingushetia).
Many linguists, notably Sergei Starostin and Sergei Nikolayev, believe that the two groups sprang from a common ancestor about 5,000 years ago.[3] However this view is difficult to evaluate, and remains controversial.
Uralic

Europe has a number of Uralic languages and language families, including Estonian, Finnish, and Hungarian.
Turkic

- Oghuz languages in Europe include Turkish, which is spoken in Turkey, Northern Cyprus and Kosovo; Azerbaijani, which is spoken in Azerbaijan and Dagestan; and Gagauz, which is spoken in Gagauzia.
- Kypchak languages in Europe include Crimean Tatar, which is spoken in Crimea; Tatar, which is spoken in Tatarstan; Bashkir, which is spoken in Bashkortostan; and Kazakh, which is spoken in Kazakhstan. Other Kypchak languages include Karaim, Krymchak and Kumyk language.
- Oghur languages were historically indigenous to much of Eastern Europe, however most of them are extinct today, with the exception of Chuvash, which is spoken in Chuvashia.
Mongolic
The Mongolic languages originated in Asia, and most did not proliferate west to Europe. Kalmyk is spoken in the Republic of Kalmykia, part of the Russian Federation, and is thus the only native Mongolic language spoken in Europe.
Semitic
Cypriot Maronite Arabic
Cypriot Maronite Arabic (also known as Cypriot Arabic) is a variety of Arabic spoken by Maronites in Cyprus. Most speakers live in Nicosia, but others are in the communities of Kormakiti and Lemesos. Brought to the island by Maronites fleeing Lebanon over 700 years ago, this variety of Arabic has been influenced by Greek in both phonology and vocabulary, while retaining certain unusually archaic features in other respects.
Hebrew
Hebrew has been written and spoken by the Jewish communities of all of Europe in liturgical, educational, and often conversational contexts since the entry of the Jews into Europe some time during the late antiquity. Its restoration as the official language of Israel has accelerated its secular use. It also has been used in educational and liturgical contexts by some segments of the Christian population. Hebrew has its own consonantal alphabet, in which the vowels may be marked by diacritical marks termed pointing in English and Niqqud in Hebrew. The Hebrew alphabet was also used to write Yiddish, a West Germanic language, and Ladino, a Romance language, formerly spoken by Jews in northern and southern Europe respectively, but now nearly extinct in Europe itself.
Maltese
Maltese is a Semitic language with Romance and Germanic influences, spoken in Malta.[4][5][6][7] It is based on Sicilian Arabic, with influences from Italian (particularly Sicilian), French, and, more recently, English.
It is unique in that it is the only Semitic language whose standard form is written in the Latin alphabet. It is also the smallest official language of the EU in terms of speakers, and the only official Semitic language within the EU.
General issues
Lingua Franca—past and present
Europe has had a number of languages that were considered linguae francae over some ranges for some periods according to some historians. Typically in the rise of a national language the new language becomes a lingua franca to peoples in the range of the future nation until the consolidation and unification phases. If the nation becomes internationally influential, its language may become a lingua franca among nations that speak their own national languages. Europe has had no lingua franca ranging over its entire territory spoken by all or most of its populations during any historical period. Some linguae francae of past and present over some of its regions for some of its populations are:
- Classical Greek and then Koine Greek in the Mediterranean Basin from the Athenian empire to the eastern Roman Empire, being replaced by Modern Greek.
- Koine Greek and Modern Greek, in the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire and other parts of the Balkans south of the Jireček Line.[8]
- Vulgar Latin and Late Latin among the uneducated and educated populations respectively of the Roman empire and the states that followed it in the same range no later than 900 AD; medieval Latin and Renaissance Latin among the educated populations of western, northern, central and part of eastern Europe until the rise of the national languages in that range, beginning with the first language academy in Italy in 1582/83; new Latin written only in scholarly and scientific contexts by a small minority of the educated population at scattered locations over all of Europe; ecclesiastical Latin, in spoken and written contexts of liturgy and church administration only, over the range of the Roman Catholic Church.
- Lingua Franca or Sabir, the original of the name, an Italian-based pidgin language of mixed origins used by maritime commercial interests around the Mediterranean in the Middle Ages and early Modern Age.[9]
- Old French in continental western European countries and in the Crusader states.[10]
- Czech, mainly during the reign of Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV (14th century) but also during other periods of Bohemian control over the Holy Roman Empire.
- Middle Low German (14th–16th century, during the heyday of the Hanseatic League).
- Spanish as Castilian in Spain and New Spain from the times of the Catholic Monarchs and Columbus, c. 1492; that is, after the Reconquista, until established as a national language in the times of Louis XIV, c. 1648; subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the Spanish Empire.[11]
- Polish, due to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (16th-18th centuries).
- French from the golden age under Cardinal Richelieu and Louis XIV c. 1648; i.e., after the Thirty Years' War, in France and the French colonial empire, until established as the national language during the French Revolution of 1789 and subsequently multinational in all nations in or formerly in the various French Empires.[10]
- German in Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe.[12]
- English in Great Britain until its consolidation as a national language in the Renaissance and the rise of Modern English; subsequently internationally under the various states in or formerly in the British Empire; globally since the victories of the predominantly English speaking countries (United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and others) and their allies in the two world wars ending in 1918 (World War I) and 1945 (World War II) and the subsequent rise of the United States as a superpower and major cultural influence.
- Russian in Eastern Europe, Northern and Central Asia from the World War II to the break‑up of the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact.
First dictionaries and grammars
The earliest dictionaries were glossaries, i.e., more or less structured lists of lexical pairs (in alphabetical order or according to conceptual fields). The Latin-German (Latin-Bavarian) Abrogans was among the first. A new wave of lexicography can be seen from the late 15th century onwards (after the introduction of the printing press, with the growing interest in standardizing languages).
Language and identity, standardization processes
In the Middle Ages the two most important defining elements of Europe were Christianitas and Latinitas. Thus language—at least the supranational language—played an elementary role[clarification needed]. The concept of the nation state became increasingly important. Nations adopted particular dialects as their national language. This, together with improved communications, led to official efforts to standardise the national language, and a number of language academies were established (e.g., 1582 Accademia della Crusca in Florence, 1617 Fruchtbringende Gesellschaft in Weimar, 1635 Académie française in Paris, 1713 Real Academia Española in Madrid). Language became increasingly linked to nation as opposed to culture, and was also used to promote religious and ethnic identity (e.g., different Bible translations in the same language for Catholics and Protestants).
The first languages for which standardisation was promoted included Italian (questione della lingua: Modern Tuscan/Florentine vs. Old Tuscan/Florentine vs. Venetian → Modern Florentine + archaic Tuscan + Upper Italian), French (the standard is based on Parisian), English (the standard is based on the London dialect) and (High) German (based on the dialects of the chancellery of Meissen in Saxony, Middle German, and the chancellery of Prague in Bohemia ("Common German")). But several other nations also began to develop a standard variety in the 16th century.
Scripts


This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (April 2011) |
The main scripts used in Europe today are the Latin and Cyrillic; Greek also has its own script. All of the aforementioned are alphabets.
History
The Greek alphabet was derived from the Phoenician and Latin was derived from the Greek via the Old Italic alphabet.
In the Early Middle Ages, Ogham was used in Ireland and runes (derived the Old Italic script) in Scandinavia. Both were replaced in general use by the Latin alphabet by the Late Middle Ages. The Cyrillic script was derived from the Greek with the first texts appearing around 940 AD.
Around 1900 there were mainly two typeface variants of the Latin alphabet used in Europe: Antiqua and Fraktur. Fraktur was used most for German, Estonian, Latvian, Norwegian and Danish whereas Antiqua was used for Italian, Spanish, French, Portuguese, English, Romanian, Swedish and Finnish. The Fraktur variant was banned by Hitler in 1941, having been described as "Schwabacher Jewish letters".[13] Other scripts have historically been in use in Europe, including Arabic during the era of the Ottoman Empire, Phoenician, from which modern Latin letters descend, Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs on Egyptian artefacts traded during Antiquity, and various runic systems used in Northern Europe preceding Christianisation.
Language and the Council of Europe
The most ancient historical social structure of Europe is that of politically independent tribes, each with its own ethnic identity, based among other cultural factors on its language. For example, the Latini speaking Latin in Latium. A Linguistic conflict has been important in European history. Historical attitudes towards linguistic diversity are illustrated by two French laws: the Ordonnance de Villers-Cotterêts (1539), which said that every document in France should be written in French (i.e., neither in Latin nor in Occitan) and the Loi Toubon (1994), which aimed to eliminate Anglicisms from official documents. States and populations within a state have often resorted to war to settle their differences. Attempts have been made to prevent such hostilities: one such initiative was the Council of Europe, founded in 1949, whose membership is affirms the right of minority language speakers to use their language fully and freely.[14] The Council of Europe is committed to protecting linguistic diversity. Currently all European countries except France, Andorra and Turkey have signed the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, while Greece, Iceland and Luxembourg have signed it, but have not ratified it. This framework entered into force in 1998.
Language and the European Union
Official status
The European Union designates one or more languages as "official and working" with regard to any member state if they are the official languages of that state. The decision as to whether they are and their use by the EU as such is entirely up to the laws and policies of the member states. In the case of multiple official languages the member state must designate which one is to be the working language.[15]
As the EU is an entirely voluntary association established by treaty — a member state may withdraw at any time — each member retains its sovereignty in deciding what use to make of its own languages; it must agree to legislate any EU acceptance criteria before membership. The EU designation as official and working is only an agreement concerning the languages to be used in transacting official business between the member state and the EU, especially in the translation of documents passed between the EU and the member state. The EU does not attempt in any way to govern language use in a member state.
Currently the EU has designated by agreement with the member states 24 languages as "official and working:" Bulgarian, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Irish, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish and Swedish.[15] This designation provides member states with two "entitlements:" the member state may communicate with the EU in the designated one of those languages and view "EU regulations and other legislative documents" in that language.[16]
Proficiency
The European Union and the Council of Europe have been collaborating in a number of tasks, among which is the education of member populations in languages for "the promotion of plurilingualism" among EU member states,[17] The joint document, "Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment (CEFR)", is an educational standard defining "the competencies necessary for communication" and related knowledge for the benefit of educators in setting up educational programs. That document defines three general levels of knowledge: A Basic User, B Independent User and C Proficient User.[18] The ability to speak the language falls under competencies B and C ranging from "can keep going comprehensibly" to "can express him/herself at length with a natural, effortless, unhesitating flow."[19]
These distinctions were simplified in a 2005 independent survey requested by the EU's Directorate-General for Education and Culture regarding the extent to which major European languages were spoken in member states. The results were published in a 2006 document, "Europeans and Their Languages", or "Eurobarometer 243", which is disavowed as official by the European Commission, but does supply some scientific data concerning language use in the EU. In this study, statistically relevant samples of the population in each country were asked to fill out a survey form concerning the languages that they spoke with sufficient competency "to be able to have a conversation".[20] Some of the results showing the distribution of major languages are shown in the maps below. The darkest colors report the highest proportion of speakers. Only EU members were studied. Thus data on Russian speakers were gathered, but Russia is not an EU member and so Russian does not appear in Russia on the maps. It does appear as spoken to the greatest extent in the Baltic countries, which are EU members that were formerly under Soviet rule; followed by former Eastern bloc countries such as Poland, the Czech Republic, and the northeastern part of Germany (former socialist East Germany).
Number of speakers
The following is a table displaying the number of speakers of a given European language in Europe only. See the languages' individual page for a more detailed summary and for sources. Some figures are approximate and may come from sources that are several years old. Dialects, or languages that have been labelled or contested as dialects by linguists, are not included in the table.
See also
Notes
- ^ Both native and second language speakers residing in Europe only.
- ^ Country is defined as being one of the 193 members of the United Nations. 'Recognised minority language' status is not included.
- ^ Region is defined as being a subordinate constituent of a country, where a legitimate political entity has granted the language official status in that region.
References
- ^ Legge Regionale 15 ottobre 1997, n. 26
- ^ "Basque". UCLA Language Materials Project, UCLA International Institute. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
- ^ Nikolayev, S., and S. Starostin. 1994 North Caucasian Etymological Dictionary. Moscow: Asterisk Press. Available online.
- ^ Marie Alexander; et al. (2009). "2nd International Conference of Maltese Linguistics: Saturday, September 19 – Monday, September 21, 2009". International Association of Maltese Linguistics. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
{{cite web}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Aquilina, J. (1958). "Maltese as a Mixed Language". Journal of Semitic Studies. 3 (1): 58–79. doi:10.1093/jss/3.1.58.
- ^ Aquilina, Joseph (July–September 1960). "The Structure of Maltese". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 80 (3): 267–68.
- ^ Werner, Louis; Calleja, Alan (November–December 2004). "Europe's New Arabic Connection". Saudi Aramco World.
- ^ Counelis, James Steve (March 1976). "Review [untitled] of Ariadna Camariano-Cioran, Les Academies Princieres de Bucarest et de Jassy et leur Professeurs". Church History. 45 (1): 115–116. doi:10.2307/3164593.
...Greek, the lingua franca of commerce and religion, provided a cultural unity to the Balkans...Greek penetrated Moldavian and Wallachian territories as early as the fourteenth century.... The heavy influence of Greek culture upon the intellectual and academic life of Bucharest and Jassy was longer termed than historians once believed.
- ^ Wansbrough, John E. (1996). "Chapter 3: Lingua Franca". Lingua Franca in the Mediterranean. Routledge.
- ^ a b Calvet, Louis Jean (1998). Language wars and linguistic politics. Oxford [England]; New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 175–76.
- ^ Jones, Branwen Gruffydd (2006). Decolonizing international relations. Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 98.
- ^ Darquennes, Jeroen; Nelde, Peter (2006). "German as a Lingua Franca". Annual Review of Applied Linguistics. 26: 61–77. doi:10.1017/s0267190506000043.
- ^ Facsimile of Bormann's Memorandum (in German)
The memorandum itself is typed in Antiqua, but the NSDAP letterhead is printed in Fraktur.
"For general attention, on behalf of the Führer, I make the following announcement:
It is wrong to regard or to describe the so‑called Gothic script as a German script. In reality, the so‑called Gothic script consists of Schwabach Jew letters. Just as they later took control of the newspapers, upon the introduction of printing the Jews residing in Germany took control of the printing presses and thus in Germany the Schwabach Jew letters were forcefully introduced.
Today the Führer, talking with Herr Reichsleiter Amann and Herr Book Publisher Adolf Müller, has decided that in the future the Antiqua script is to be described as normal script. All printed materials are to be gradually converted to this normal script. As soon as is feasible in terms of textbooks, only the normal script will be taught in village and state schools.
The use of the Schwabach Jew letters by officials will in future cease; appointment certifications for functionaries, street signs, and so forth will in future be produced only in normal script.
On behalf of the Führer, Herr Reichsleiter Amann will in future convert those newspapers and periodicals that already have foreign distribution, or whose foreign distribution is desired, to normal script". - ^ "European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages: Strasbourg, 5.XI.1992". Council of Europe. 1992.
- ^ a b "Regulation No. 1 determining the languages to be used by the European Economic Community" (PDF). European Commission, European Union. 2009. Retrieved 5 November 2009.
- ^ "Languages of Europe: Official EU languages". European Commission, European Union. 2009. Retrieved 5 November 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment (CEFR)". Council of Europe. Retrieved 5 November 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Page 23.
- ^ Page 29.
- ^ "Europeans and Their Languages" (PDF). European Commission. 2006. p. 8. Retrieved November 5, 2009.
- ^ Le Statut spécial de la Vallée d'Aoste, Article 38, Title VI. Region Vallée d'Aoste. Retrieved 5-11-2012.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ [1]
External links
- Everson, Michael (2001). "The Alphabets of Europe" (in English). evertype.com. Retrieved 19 March 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - Haarmann, Harald (2011). "Europe's Mosaic of Languages" (in English and others). Institute of European History. Retrieved 2 November 2, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - Reissmann, Stefan; Argador, Urion (2006). "Luingoi in Europa" (in Esperanto, English, and German). Reissmann & Argador. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - Zikin, Mutur (2005–06). "Europako Mapa linguistikoa" (in Basque and others). muturzikin.com. Retrieved 2 November 2009.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)







