Geography of Albania
 | |
| Continent | Europe |
|---|---|
| Region | Southern Europe |
| Coordinates | 41°00′N 20°00′E / 41.000°N 20.000°E |
| Area | Ranked 145 |
| • Total | 28,748 km2 (11,100 sq mi) |
| • Land | 97,70% |
| • Water | 2,30% |
| Coastline | 427 km (265 mi) |
| Borders | Greece 212 km (132 mi), Montenegro 186 km (116 mi), Macedonia 181 km (112 mi), Kosovo[a] 112 km (70 mi) |
| Highest point | Mount Korab, 2,764 m (9,068 ft) |
| Lowest point | Adriatic Sea, 0 m |
| Longest river | Drin, 335 km (208 mi) |
| Largest lake | Shkodër 530 km2 (200 sq mi) |
The Geography of Albania is defined by its location. Albania is a small predominantly mountainous country in Southeastern Europe, on facing the Adriatic and Ionian seas within the Mediterranean Sea. About 20% of the country's teritorry consist of coastal plains, while the remaining by a mass of high rugged mountain ranges. Albania covers a territory of 28,748 km2 (11,100 sq mi), making it the 145th largest country in the world.[1][2] It lies mostly between latitudes 42° and 39° N, and longitudes 21° and 19° E. The country shares borders with Montenegro in the northwest, Kosovo in the northeast, Macedonia in the east and Greece in the south.[3] It's coastline length on the Adriatic and the Ionian Seas is 476 km (296 mi).[4] The lowlands of the west face the Adriatic Sea and the strategically important Strait of Otranto, which puts less than 72 km (45 mi) of water between Albania and the heel of the Italian coast.
Topographically, the country encompasses coastal plains in the west to the Albanian Alps in the north, the Sharr Mountains in the northeast, Skanderbeg Mountains in the center, Korab Mountains in the east, Pindus Mountains in the southeast and Ceraunian Mountains in the southwest along the Albanian Riviera. The hydrographic network of Albania includes several of the largest and most ancient bodies of freshwater in Southern Europe. Lake Shkodër is located on the border between Albania and Montenegro, with an area that seasonally can vary between 370 km2 (140 sq mi) to 600 km2 (230 sq mi).[5] However, the Lake Ohrid is the deepest lake 288 m (945 ft) in the Balkans, the ancient lake in Europe and one of the most ancient in the world.[6][7].
Albania is distinguished for its rich biological diversity.[8] Due to its climatic, hydrological, geological and topographical conditions, Albania is host to 30% of the entire flora and 42% of fauna of Europe.[9][10] There are 799 Albanian protected areas covering a surface of 5,216.96 square kilometres.[11] These include 2 strict nature reserves, 14 national parks, 1 marine park, 8 archaeological parks, 750 natural monuments, 22 habitat/species management areas, 5 protected landscapes, 4 protected landscapes, 4 managed resources areas and 4 ramsar wetlands.[12][13] The national parks covers a surface area of 210,668.48 hectares (2,106.6848 km2) or roughly 13.65% of the overall territory.[14]
The northern border is 287 kilometres (178 mi) long, of them 173 kilometres (107 mi) are with Montenegro and 114 kilometres (71 mi) with Kosovo.[15] In the north and the northeast mountainous sections, the border connects high points and follows mountain ridges through the largely inaccessible Albanian Alps. For the most part, there is no natural boundary from the highlands to the Adriatics, although Lake of Shkodër and a portion of the Buna River south of it were used to mark the northwest border with Montenegro. The eastern border with the Republic of Macedonia is 151 kilometres (94 mi) long. The frontier runs from the Dibër valley in the east; to the north it is the Korab mountain range, containing Mount Korab at 2,764 metres (9,068 ft) above sea level the highest point in both countries, through the Elbasan County, crosses the Lake of Ohrid and ends at the Lake of Prespa in the Korçë County. In addition to the Mount Korab, it is the highest mountain of the European Green Belt.[16] The southern and southeastern border with Greece is 282 kilometres (175 mi).[17] The Gramos mountain range forms the border with Greece. The western border 446 kilometres (277 mi) is maritime and encompasses the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast from Buna River in the north near the city of Shkodër up to the Bay of Vlorë and the Albanian Riviera, where the Ionian sea to the border with Greece.[18]
In 2016, Albania had a population of 2.87 million (1,46 million males and 1,42 million females), ranking 136th in the world by population. The population density was 101 inhabitants per square kilometre.[19] The overall life expectancy in Albania at birth is 78 years.[20] The total fertility rate of 1.80 children per mother is one of the lowest in the world. In 2016, the population of Albania was about 2,89 million, comprising 1,447 million male and 1,443 female persons.[21] There were 38,003 live births and 20,737 deaths in Albania. The natural increase of the population was positive, as the number of births exceeded the number of deaths by 17,266. Due to external migration, the population declined by 18,307. The total dependency ratio of population in Albania is 46.8 %.
Territory

With a surface of 28.748 square kilometres (11.100 sq mi), Albania is placed along the eastern part of the Adriatic Sea and the Ionian Sea inside the Mediterranean sea. It has a length of borders about 1,094 kilometres (680 mi), 657 kilometres (408 mi) of which are terrestrial, 316 kilometres (196 mi) of shore border, 48 kilometres (30 mi) river borders and 73 kilometres (45 mi) of lake borders.[22] Inland water surface is 1,350 square kilometres (520 sq mi), composed by natural lakes 325 square kilometres (125 sq mi), coastal lagoons 130 square kilometres (50 sq mi), artificial lakes 174 square kilometres (67 sq mi) and rivers 721 kilometres (448 mi).[23] With the exception of the coastline, all Albanian borders are artificial. They were established at the 1912-1913 Conference London. The country was occupied by several forces during first World War, but the 1913 boundaries were essentially reaffirmed by the victorious states in 1921. Division of the lake district among three states required that each of them have a share of the lowlands in the vicinity. Such an artificial distribution, once made, necessarily affected the borderlines to the north and south. The border that runs generally north from the lakes, although it follows the ridges of the eastern highlands, stays sixteen to 32 kilometres (20 mi) west of the watershed divide. Due to negotiators at the Conference of London declined to use the watershed divide as the northeast boundary of the new state of Albania, the Albanian population of Kosovo was incorporated into Serbia.
Adriatic Coast

Albania's Adriatic Sea Coast is 274 kilometres (170 mi) long, covering most of the western bound of Albania, stretching from the mouth of Buna River close to Lake Shkodër in the north down to Bay of Vlorë in the south, where the Ionian Sea and the Albanian Riviera begins.[24] Almost 74% is coastal lowland marked by sandy beaches and river mouth deposits or marshlands. The coastline has wide and long sandy beaches with various capes, bays and lagoons. The shores are largely alluvial or terraced, built by the quaternary deposits of the Drin, Mat, Ishëm, Seman, Shkumbin, Erzen, and Vjosa Rivers. The sediments which has been discharged by Shkumbin, Seman and Vjosa has formed up the Myzeqe Plain with Karavasta and Narta in the immediate proximity of the sea. From Durrës to Bay of Vlorë, the coastline is relative low with no rocky shores related to the vast Myzeqe Plain.
The largest Albanian cities on the Adriatic Sea Coast are Durrës, Shëngjin and Vlorë. The country has 10 islands on the Adriatic Sea, with Sazan and Kunë, being larger than one square kilometres. Sazan is strategically located between the Strait of Otranto and the entrance to the Bay of Vlorë; it is the country's westernmost point. The climate is not Mediterranean but rather subtropical on account of its warm winters and hot summers. The climate and vegetation resemble those of the south of Crete, Tunisia and even parts of Egypt.
Ionian Coast

The Ionian Sea Coast is 172 kilometres (107 mi) long, extending from Bay of Vlorë until the border with Greece.[25] Although, most of the coastline represents the renowned Albanian Riviera. The Ionian littoral is represented western edge of the Maja e Çikës anticline in Ionian tectonic zone. 80% of the Ionian litoral is rocky high coast.[26] The mountains along the coast rises up to approximately 2,045 metres (6,709 ft). The Ceraunian Mountains extend nearly 100 kilometres (62 mi) along the Albanian Riviera in a north-west direction from the Albanian-Greek border to the Llogara Pass, on the eastern shore of Strait of Otranto. In addition, the Llogara Pass 1,027 metres (3,369 ft) divides the mountains into a western and an eastern range.
The coastline continues down along the coast through the villages of Borsh, Dhermi, Himara, Qeparo, and Piqeras, and ends at Lukovë.[27] Sarandë is ahead with Vlorë, the largest city along the Albanian Ionian coastline. It is also home to 2 islands, with Ksamil being the largest with an area of 71,000 square metres (760,000 sq ft), followed by the rocky Tongo Island.
Albanian Alps

The composition of the great tectonic units reflects the history of the formation of the Albanian Alps. They are the southernmost geological continuation of the Dinaric Alps, forming a section of the Alpine-Himalayan orogenic belt, which extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Himalaya Mountains. The Albanian Alps extend more than 64 kilometres (40 mi) from Lake Shkodër along the border with Montenegro in the southwest, towards to Kosovo in the northeast. Albania encompasses the significant portion of the Alps with a surface area of 2,240 square kilometres (860 sq mi).[28] The ice ages had relatively little direct geologic influence on the Albanian Alps. No permanent ice caps existed, and there is a little evidence of extensive glaciation. Further, the southernmost glaciers in Europe were recently discovered on the Albanian portion of the Alps.[29]

Maja Jezercë is the highest mountain of the Dinaric Alps with an altitude of 2,694 metres (8,839 ft) above sea level.[30] However, it is the second highest mountain in Albania. Other high mountains within the Albanian Alps includes Maja Radohimës 2,570 metres (8,430 ft), Maja Kollatës 2,554 metres (8,379 ft), Maja Gjallica 2,489 metres (8,166 ft), Maja Bogiçaj 2,405 metres (7,890 ft), Maja Koritnik 2,393 metres (7,851 ft), Maja Shkëlzen 2,404 metres (7,887 ft) and Maja e Thatë 2,404 metres (7,887 ft).
The Albanian Alps are home to many important rivers of Western Balkans. The main drainage basins of the Alps are those of the Drin and Danube Rivers.[31] Rivers on the Alps fall roughly into two categories, those that flow into the Lim and those that enter the White Drin and meet the Black Drin downstream at the Drin confluence. However, Drin dominates, draining most of the Alps with its tributaries and when measured from the source of the White Drin to the mouth of the Drin near Lezhë. But not all of the Drin flows near or parallel to the Alps. One Drin tributary is the Valbona River, which drains into the Adriatic Sea, and its eastern tributary the Gashi River.
Korab Mountains

The Korab Mountains are the most defining feature of eastern Albania. They stretch in north-south direction along the tripoint of Albania, Macedonia and Kosovo up to Lake Ohrid. They mountain chain is part of the inner Albanides within the Dinarido-Albanido-Hellenides organic belt. The composition of the mountains is of mainly with Paleozoic limestones and dolomites, including numerous fossils.[32] Located about 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) above sea level, the mountains are characterized by an extremely fragmented, rugged alpine landscape hosting a great diversity of ecosystems and biodiversity. The Mount Korab is the highest summit on the range as well one of the highest in the Balkans standing at 2,764 metres (9,068 ft).[33]
Other high mountains are Maja Gjallica 2,489 metres (8,166 ft), Maja Koritnik 2,393 metres (7,851 ft), Maja e Pikellimes 2,392 metres (7,848 ft), Mali i Gramës 2,345 metres (7,694 ft) and Maja e Velivarit 2,375 metres (7,792 ft).[34]
Korab is renowned for its 39 glacial lakes situated between 2,300 metres (7,500 ft) elevation above sea level with Gramë Lake being the largest and the deepest.[35]
Ceraunian Mountains

The Ceraunian Mountains, a coastal mountain range in southwestern Albania, stretches about 100 kilometres (62 mi) one the Ionian Sea from Sarandë in south-east-northwest direction along the Albanian Riviera Orikum. The relief is varied, with many mountain passes, canyons, gorges, hills and other landforms. The mountains are characterized by housing Black pines, Bulgarian firs, Bosnian pines and Ash trees. The mountain chain is home to many large mammals, including brown bears, grey wolves, lynx, golden eagles and others. The highest point on the chain is Maja e Çikës, that rises to an elevation of 2,045 metres (6,709 ft) above the Adriatic. From the peak, there is a magnificent view of the Albanian Riviera, the northern Ionian Islands as well as the Italian coast of Apulia and Otranto. The section has wide and long beaches, with a number of bays and headlands.
Streching until the Llogara Pass at 1,027 metres (3,369 ft), the mountain chain gets separatet into the Ceraunians in the west and the Akroceraunians (or Reza e Kanalit) in the east within the Karaburun Peninsula.[36] The villages of Palasë, Dhërmi, Vuno, Himarë, Qeparo, Borsh, Pilur, Kudhës and Ilias are located on the Ceraunian range. The Llogara National Park covers an area of 10,100 square metres (109,000 sq ft) and
Karaburun Peninsula

The Karaburun Peninsula is situated at the eastern side of Strait of Otranto, where the Adriatic Sea meets the Ionian Sea. Its area is 62 square kilometres (24 sq mi), having a length of 16 kilometres (9.9 mi), and a width of only 5 kilometres (3.1 mi).[37] The Mesokanali is the narrow channel, that separates the peninsula from the Sazan Island. Geologically, it is made up of carbonic limestone, dating back to the Mesozoic period, while in the northewestern it is composed of terrigenous sediment.[38] Furthermore, these formations have been continuously under the effect of Karst and are exploited as marble. The relief of the peninsula comprises a number of hills with a average altitude of about 800 metres (2,600 ft) above sea level. The highest summits are Maja e Ilqës 733 metres (2,405 ft), Maja e Flamurit 826 metres (2,710 ft) and Maja Çadëri 839 metres (2,753 ft).[39]
The coastal landscape is characterized by a rough relief, that dips vertically into the Ionian Sea, it features several solitary peaks, large canyons, bays, caves and gulfs. Examples of typicall landforms include Gjipe Canyon, Gjiri i Arushës, Gjiri i Dafinës, Gjiri i Gramës and so on. The geological evolution has formed also capes such as Haxhi Aliu, Galloveci and Kepi i Gjuhëzës, and other of 20 caves along the entire shoreline.
The climate is mediterranean, having hot summers and generally warm to cool, dry winters. Due to its climatic, hydrological and geological conditions, the area is characterized by its unique flora and fauna. Most of the territory consists of forests and is relatively well preserved, it include many types of trees, such as Mediterranean oak, Manna ash, Kermes oak and Field maple.[40]
Topography and Hydrography

In the relatively small territory, Albania has extensive lowlands, plains, hills, low and high mountains, many valleys, caves and deep gorges. Albania is predominantly mountainous country with an average elevation of about 708 metres (2,323 ft) of which mountains occupy about two thirds of the territory. Most of the mountains were formed during the Jurassic and Cenozoic periods. From north to south, the largest mountain ranges are the Albanian Alps, Korab Mountains, Skanderbeg Mountains, Ceraunian Mountains and Pindus Mountains. The Albanian Alps in the north, Skanderbeg Mountains in the center and Ceraunian Mountains in the south, separates the interior of Albania from the coastal plain. Along the Western Lowlands there is a alluvial plain that extends from southern Vlorë across the Albanian Adriatic mainland coast to Lake Shkodër on the Albanian and Montenegrin borders. The Albanian Adriatic coast is characterized by numerous lagoons and wetlands, while the Albanian Ionian coast rises steeply to the Ceraunian Mountains.
Biogeographically, Albania falls within the Alpine and Mediterranean Basin. The Albanian Mediterranean Basin is home to 68 percent of Albania's population.[41] Albania belongs to the Dinarides that forms the southern section of the Alpide belt, extending south from the Southern Alps in Central Europe along the east coast of the Adriatic and Ionian Seas towards the Aegean Sea. The Albanian Alps are the southernmost section of the Dinaric Alps,
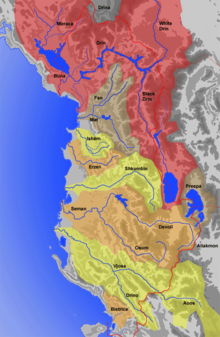

The territory of Albania covers about 65% of a total water area of 43,905 square kilometres (16,952 sq mi).[42] River mouths and deltas, lagoons, abandoned riverbeds, marsh labyrinths, sandy or rocky beaches, dunes covered with vegetation, dense forests represents the littoral of Albania. Albania has around 247 natural lakes, mostly of karstic or glacial origin.[43] It's largest lakes are Shkodër in the northwest, Ohrid, Prespa and Small Prespa in the southeast and Butrint in the southwest. Albania is also home to many lagoons, such as Karavasta, Patoku, Narta, Kunë-Vain and Butrint.[44]
The northern, central and southern mountain ranges divide Albania into nearly equal drainage systems. It has a dense network of about 152 rivers and streams, forming at least 10 large rivers flowing from east to west, mainly discharging towards the Adriatic sea. The rivers of Albania are characterized by a high flow rate.[45] There are two catchment basins such as the Adriatic Sea and the Ionian Sea basins. The eight rivers are the Drin 285 kilometres (177 mi), Vjosë 192 kilometres (119 mi), Shkumbin 181 kilometres (112 mi), Mat 115 kilometres (71 mi), Erzen 108 kilometres (67 mi), Seman 85 kilometres (53 mi), Ishëm 74 kilometres (46 mi), and the Buna 74 kilometres (46 mi).

Nearly all of the precipitation that falls on Albania, drains into the rivers and reaches the coast on the west without even leaving the country. In the north, only one small stream escapes Albania. In the south, an even smaller rivulet drains into Greece. Due to the topographical divide is east of the border with the Republic of Macedonia. An extensive portion of the basin of the White Drin, basin is in the Dukagjin region, across the northeastern border with Kosovo. The Lake of Ohrid, Lake of Prespa and the Small Lake of Prespa on the southeast, as well as the streams that flow into them, drain into the Black Drin. The watershed divide in the south also dips nearly 75 km (47 mi) into Greece at one point. Several tributaries of the Vjosa River rise in that area.
The longest river located in the Albanian territory is the Drin, with a length of 285 kilometres (177 mi) and a catchment area of 5,957 km2 (2,300 sq mi). It is fed by melting snows from the northern Albanian Alps and the eastern Korab Mountains and by the more evenly distributed seasonal precipitation of that area. Its flow does not have the extreme variations characteristic of nearly all other rivers in Albania. As it collects from the Adriatic portion of Kosovo's watersheds and the Lake Prespa and Small Prespa Lake drains to the Lake Ohrid along an underground stream, its total basin encompasses about 15,540 km2 (6,000 sq mi). The Seman and Vjosa Rivers are the only other rivers that are longer than 160 km (99 mi) and having basins larger than 2,600 km2 (1,004 sq mi).
Climate and Biodiversity

Considering its relatively small area, Albania has variable and complex climate. The country's diverse regions has a remarkable range of microclimates, with the weather system on the coasts contrasting with that prevailing in the interior. However, the weather in Albania varies from the north to the south and the west to the east. Albania occupies The climate ranges from Temperate climate on the coasts to Continental climate in the interior.[47] The warmest areas of the country are at the coasts, which are characterized by a Mediterranean climate (Csa, Csb and Cfa) as defined by the Köppen climate classification. The highlands experiences a Oceanic climate. Winters in Albania are characteristically mild and wet while summers are warm and dry. The northern areas of country such as the Albanian Alps experiences Subarctic climate with frequently very cold winters, and short, mild summers.

The lowlands of Albania have mild winters, averaging about 7 °C (45 °F). The summer temperatures average 32 °C (90 °F), however, humidity is low. In the southern lowlands specifically the areas on the Ionian sea, temperatures average about 5 °C (41 °F) in the winter and 30 °C (86 °F) during the summer.
Although a small territory, Albania can be subdivided between a number of ecoregions, due to its climatic, hydrological, geological and topographical conditions, which makes the country one of the richest in Europe in terms of biodiversity. 30% of the entire flora and 42% of fauna in Europe is found in the country.[48] Albania is part of the Boreal Kingdom specifically, part of the Illyrian province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal kingdom. The country is divided into four ecoregions, among them are the Illyrian deciduous forests, Dinaric Alpine mixed forests, Balkan mixed forests and Pindus Mountains mixed forests. Further, Biomes in Albania include Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest and Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub, forming part of the Palearctic ecozone. Within the country's territory, there are 799 protected areas covering a surface of 5,216.96 square kilometres.[49][50][51][52]
See also
Notes
| a. | ^ Template:Kosovo-note |
Further readings
- Dako, Alba; Mirela Lika, and Hysen Mankolli. "Monitoring Aspects of Air Quality in Urban Areas of Tirana and Durrës, Albania". Natura Montenegrina 7, no. 2 (2008): 549–557.
- Floqi, Tania; Daut Vezi and Ilirian Malollari. "Identification and Evaluation of Water Pollution from Albanian Tanneries", Desalination 213, no. 1-3 (2007): 56–64.
- Muller, Daniel; and Thomas Sikor. "Effects of Post-Socialist Reforms on Land Cover and Land Use in South-Eastern Albania". Applied Geography 26, no. 3-4 (2006):175–191.
References
- ^ "Introduction" (PDF). dspace.epoka.edu.al.
Albania has 28.748 square kilometers area and the length of the borderline of the Republic of Albania is 1094 km, of which 657 km land border, 316 km of coastline, 48 km and 73 km through rivers dividing line through the lakes.
- ^ "ALBANIA". cia.gov.
Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and Ionian Sea, between Greece to the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north
- ^ "Albania country profile". bbc.com. Europe. 19 June 2017.
Albania is a small, mountainous country in the Balkan peninsula, with a long Adriatic and Ionian coastline.
- ^ R. Eftimi. "SOME CONSIDERATIONS ON SEAWATER-FRESHWATER RELATIONSHIP IN ALBANIAN COASTAL AREA" (PDF). ITA Consult.
- ^ "IBAC 2012 vol.2" (PDF). dspace.epoka.edu.al. p. 253.
In the North-Western part of the country, there is the Shkoder Lake, which is the largest in the Balkan Peninsula.
- ^ "Natural and Cultural Heritage of the Ohrid region". whc.unesco.org. pp. UNESCO.
Situated on the shores of Lake Ohrid, the town of Ohrid is one of the oldest human settlements in Europe; Lake Ohrid is a superlative natural phenomenon, providing refuge for numerous endemic and relict freshwater species of flora and fauna dating from the tertiary period. As a deep and ancient lake of tectonic origin, Lake Ohrid has existed continuously for approximately two to three million years.
- ^ "Lake Ohrid; Invest in Macedonia – Agency for Foreign Investments of the Republic of Macedonia". InvestInMacedonia.com. Archived from the original on 14 September 2008. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Introduction" (PDF). dspace.epoka.edu.al. p. 252.
Although a small country, Albania has rich physical geography features. The variation of geomorphology, climate, biological diversity, rivers and lakes create favorable conditions. These features affected on human and their activities.
- ^ "Biodiversity Albania". climatechangepost.com.
Some of the 30% of the European plant species, and 42% of the European mammals can be found in the country. Albania's variety of wetlands, lagoons and large lakes also provide critical winter habitat for migratory birds (1).
- ^ "BIODIVERSITY IN ALBANIA REPORT ON NATIONAL SITUATION OF BIODIVERSITY IN ALBANIA" (PDF). macfungi.webs.com. p. 2.
Approximately 30% of all European floras occur in Albania.
- ^ "Albania, Europe". protectedplanet.net.
- ^ "Protected Areas System in Albania" (PDF). tap-ag.com. p. 5.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-01-12. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Përshkrimi i Rrjetit aktual të zonave të mbrojtura
- ^ "Geografie - Albanien". uni-koblenz.de (in German).
Angrenzende Länder - Griechenland 282 km
- ^ The Green Belt of Europe: From Vision to Reality (Andrew Terry, Karin Ullrich, Uwe Riecken ed.). IUCN. 2006. p. 68. ISBN 9782831709451.
- ^ "Geografie - Albanien". uni-koblenz.de (in German).
Angrenzende Länder - Griechenland 282 km
- ^ Sustainable Development of Sea-Corridors and Coastal Waters: The TEN ECOPORT project in South East Europe (Chrysostomos Stylios, Tania Floqi, Jordan Marinski, Leonardo Damiani ed.). Springer. 2015-04-07. p. 85. ISBN 9783319113852.
- ^ "Population of Albania" (PDF). instat.gov.al. p. 1.
The population of Albania on January 1st is 2,886,026 inhabitants, compared to the population of 2015 there is a decrease of 6,276 inhabitants. The sex ratio of this population is 102.6 males for 100 females. The median age of the population of Albania on January the 1st 2015 is 34.7 years.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth (years) 2000-2015". gamapserver.who.int.
- ^ "Demographics of Albania 2016". countrymeters.info. 30 June 2017.
- ^ "THE INFLUENCE OF PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHIC FEATURES IN ALBANIA ON HUMAN, CULTURE AND SPATIAL" (PDF). dspace.epoka.edu.al. p. 2.
- ^ Assessing the Comparative Advantage of Wheat Produced in Albania (Luce Agraja ed.). Cuvillier Verlag. 2006. p. 7. ISBN 9783867279994.
- ^ Sustainable Development of Sea-Corridors and Coastal Waters: The TEN ECOPORT project in South East Europe (Chrysostomos Stylios, Tania Floqi, Jordan Marinski, Leonardo Damiani ed.). Springer. 2015-04-07. p. 85. ISBN 9783319113852.
- ^ Sustainable Development of Sea-Corridors and Coastal Waters: The TEN ECOPORT project in South East Europe (Chrysostomos Stylios, Tania Floqi, Jordan Marinski, Leonardo Damiani ed.). Springer. 2015-04-07. p. 85. ISBN 9783319113852.
- ^ Sustainable Development of Sea-Corridors and Coastal Waters: The TEN ECOPORT project in South East Europe (Chrysostomos Stylios, Tania Floqi, Jordan Marinski, Leonardo Damiani ed.). Springer. 2015-04-07. p. 85. ISBN 9783319113852.
- ^ Gloyer, Gillian (2008). The Bradt Travel Guide Albania. Bradt Publications UK. p. 199. ISBN 1-84162-246-X.
- ^ "ALBANIAN ALPS GEOTOPES" (PDF). lib.icimod.org. p. 1.
The Alps have a width of 60 km and a length of 64 km and occupy an area of about 2020 km2 .
- ^ "FEASIBILITY STUDY ON ESTABLISHING A TRANSBOUNDARY PROTECTED AREA PROKLETIJE / BJESHKËT E NEMUNA MOUNTAINS" (PDf). condesan.org. p. 4.
The number of glacial ponds in this area is rare for the European mainland and can only be compared to the Alps.
- ^ "FEASIBILITY STUDY ON ESTABLISHING A TRANSBOUNDARY PROTECTED AREA PROKLETIJE / BJESHKËT E NEMUNA MOUNTAINS" (PDF). condesan.org. p. 37.
The highest peaks of Prokletije / Bjeshkët e Nemuna mountains are Maja Jezercë/ Jezerski Vrh (2694 m) in Albania.
- ^ "General Overview of the Transboundary Waters of Rivers, Lakes, Groundwater and Trend of them, in Albania". researchgate.net. January 2016.
Vermoshi river is located in the northern tip of Albania, and it is the only river that flows into the Danube, therefore, the Vermoshi River is only tributary of Danube River in Albania.
- ^ "The King of the Mountains" (PDF). dmwcorg.tk. p. 24.
Korab is a very rugged mountain massif that consists mainly of shale and limestone of the Palaeozoic era with bloc structures.
- ^ "The King of the Mountains" (PDF). dmwcorg.tk. p. 24.
At 2764 meters Korab peak is one of only two summits in Europe which are the highest point for more than one country.
- ^ "Korab - Koritnik Natural Park Management Plan". researchgate.net. p. 25.
The main mountains in the area are Maja e Pikellimes (2,392m), Gjallica Mountain (2,484m), and Korab Mountain (2,751m), which is the highest mountain on Albanian territory.
- ^ "FEASIBILITY STUDY ON ESTABLISHING A TRANSBOUNDARY PROTECTED AREA SHARR/ŠAR PLANINA – KORAB – DEŠAT/DESHAT" (PDF). envsec.org. p. 4.
- ^ "Management Plan Llogora-Rreza e Kanalit-Dukat -Orikum-TragjasRadhime-Karaburun Complex Site" (PDF). vinc.s.free.fr (in Albanian). p. 23.
- ^ "Llogora-Rreza e Kanalit-Dukat -Orikum-TragjasRadhime-Karaburun Complex Site" (PDF). vinc.s.free.fr. p. 24.
The Karaburun Peninsula covers a surface of 62 km2; It is 16 km long and 3-5 km wide
- ^ "Llogora-Rreza e Kanalit-Dukat -Orikum-TragjasRadhime-Karaburun Complex Site" (PDF). vinc.s.free.fr. p. 24.
From the geological point of view it is made up of carbonic limestone of Kretac era, while in the northewestern part of it, Bay of Shën Jani, it is composed of terigenic deposits.
- ^ "Llogora-Rreza e Kanalit-Dukat -Orikum-TragjasRadhime-Karaburun Complex Site" (PDF). vinc.s.free.fr.
The relief comprises a number of hills. The average altitude from the sea levels 800 m with a number of peaks. The highest peaks are the so-called Maja e Ilqes (733 m), Maja e Flamurit (826 m) and Çadëri (839 m).
- ^ "Llogora-Rreza e Kanalit-Dukat -Orikum-TragjasRadhime-Karaburun Complex Site" (PDF). vinc.s.free.fr. p. 43.
The most important trees in this type of forest are Quercus ilex, Fraxinus ornus, Quercus coccifera, Acer campestre, which form dense tree layer (cover 80 – 90 % in very well developed stands, height 8-10 m ).
- ^ [Mediterranean-Basin-2017-ecosystem-profile-English.pdf "Mediterranean Basin Biodiversity Hotspot"] (PDF). cepf.net. p. 127.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ "The quality of Albanian natural waters and the human impact". researchgate.net. p. 2. Retrieved 21 August 2004.
- ^ "The quality of Albanian natural waters and the human impact". researchgate.net. p. 134.
- ^ "The quality of Albanian natural waters and the human impact". researchgate.net. p. 138.
Karavasta lagoon represents the largest lagoon inAlbania and is among the biggest of the Adriatic basin; - Lezha lagoons extend on both sides of the Drini delta,Ceka lagoon in the southern part of river delta, Merxhanilagoon and Kenalla pond on its northern side; - Narta lagoon (Vlora) is situated at the southern Adriaticcoast; it is 42 km2in size and has a depth of 0.3 to 1.0 m.: - Butrinti lagoon is 16.3 km2in size with a mean depth of14 m and a maximal depth of 21 m. It is situated in thesouthern part at the Ionian Sea.
- ^ "nces See all › 7 FiguresShare Download full-text PDF The quality of Albanian natural waters and the human impact". researchgate.net. p. 137.
Albanian rivers are characterized by ahigh flow rate; the total annual mean flow is 1308 m3s1,which corresponds to an annual water volume of 41,250 km3.
- ^ Fred Pearce. "Scientists demand halt to damming of Europe's last wild river". newscientist.com. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- ^ Inland Fisheries of Europe. Food & Agriculture Org. p. 3. ISBN 9789251033586.
- ^ "Biodiversity Albania". climatechangepost.com.
Some of the 30% of the European plant species, and 42% of the European mammals can be found in the country. Albania's variety of wetlands, lagoons and large lakes also provide critical winter habitat for migratory birds (1).
- ^ "Albania, Europe". protectedplanet.net.
- ^ "Protected Areas System in Albania" (PDF). tap-ag.com. p. 5.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-01-12. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Përshkrimi i Rrjetit aktual të zonave të mbrojtura

