Classes of United States senators
| This article is part of a series on the |
| United States Senate |
|---|
 |
| History of the United States Senate |
| Members |
|
|
| Politics and procedure |
| Places |
The 100 seats in the United States Senate are divided into three classes for the purpose of determining which seats will be up for election in any two-year cycle, with only one class being up for election at a time. With senators being elected to fixed terms of six years, the classes allow about a third of the seats to be up for election in any presidential or midterm election year instead of having all 100 be up for election at the same time every six years. The seats are also divided in such a way that any given state's two senators are in different classes so that each seat's term ends in different years. Class 1 and class 2 consist of 33 seats each, while class 3 consists of 34 seats. Elections for class 1 seats took place in 2024, and elections for classes 2 and 3 will take place in 2026 and 2028, respectively.
The three classes were established by Article I, Section 3, Clause 2 of the U.S. Constitution. The actual division was originally performed by the Senate of the 1st Congress in May 1789 by lot.[1] Whenever a new state subsequently joined the union, its two Senate seats were assigned to two different classes by a random draw, while keeping the three classes as close to the same number as possible.[2]
The classes only apply to the regular fixed-term elections of the Senate. A special election to fill a vacancy, usually either due to the incumbent resigning or dying while in office, may happen in any given year regardless of the seat's class.[3]
A senator's description as junior or senior senator is also not related to their class. Rather, a state's senior U.S. senator is the one with the greater seniority in the Senate, which is mostly based on length of service.
History
[edit]Constitutional footing
[edit]The U. S. Constitution sets the fixed term of senators to six years and staggers their elections into three cycles, so that a third of the Senate was up for election every two years. This allows at least some Senate elections to be held during any presidential or midterm election year, as the U.S. President is elected to a fixed term of four years and members of the U.S. House of Representatives are elected to fixed terms of two years. The objective is to promote stability in the Senate, and encourage senators to deliberate measures over time, rather than risk a rapid turnover of the entire chamber every six years. At the same time, it provided for more frequent elections as opposed to waiting every six years, to prevent senators from permanently combining for "sinister purposes".[1]
The three classes of the Senate are specified by Article I, Section 3 of the U.S. Constitution:
Immediately after they shall be assembled in Consequence of the first Election, they shall be divided as equally as may be into three Classes. The Seats of the Senators of the first Class shall be vacated at the Expiration of the second Year, of the second Class at the Expiration of the fourth Year, and of the third Class at the Expiration of the sixth Year, so that one third may be chosen every second Year.
The allocation took place in May 1789, several weeks after the first Senate assembled. Only twenty senators from ten states were present; North Carolina and Rhode Island had not yet ratified the U.S. Constitution, and New York, because of its late ratification, had not yet selected its senators.[4] To decide on how to implement the division into classes, on May 11 the Senate appointed a committee consisting of Senators Ellsworth, Carroll, and Few.[5] In accordance with their recommendation, on May 14 the Senate divided the members into three classes:[6]
Thursday, May 14, 1789. The committee appointed to consider and report a mode of carrying into effect the provision in the second clause of the third section of the first article of the Constitution, reported:
Whereupon, Resolved, That the Senators be divided into three classes:
- The first to consist of Mr. Langdon [of New Hamphire], Mr. Johnson [Connecticut], Mr. Morris [Pennsylvania], Mr. Henry [Maryland], Mr. Izard [South Carolina], and Mr. Gunn [Georgia];
- The second of Mr. Wingate [of New Hamphire], Mr. Strong [Massachusetts], Mr. Paterson [New Jersey], Mr. Bassett [Delaware], Mr. Lee [Virginia], Mr. Butler [South Carolina], and Mr. Few [Georgia];
- And the third of Mr. Dalton [of Massachusetts], Mr. Ellsworth [Connecticut], Mr. Elmer [New Jersey], Mr. Maclay [Pennsylvania], Mr. Read [Delaware], Mr. Carroll [Maryland], and Mr. Grayson [Virginia].
That three papers of an equal size, numbered 1, 2, and 3, be, by the Secretary, rolled up and put into a box, and drawn by Mr. Langdon, Mr. Wingate, and Mr. Dalton, in behalf of the respective classes in which each of them are placed; and that the classes shall vacate their seats in the Senate according to the order of numbers drawn for them, beginning with number one: And that, when Senators shall take their seats from States that have not yet appointed Senators, they shall be placed by lot in the foregoing classes, but in such manner as shall keep the classes as nearly equal as may be in numbers.
On the next day, May 15, the term expiration of each class was determined by drawing lots.[6] Lot 1 was drawn by Dalton, 2 by Wingate, and 3 by Langdon.
Upon the expiration of a senator's term of any length, someone starts a new six-year term as senator (based on election by the state legislatures until the Seventeenth Amendment required direct popular election of senators).
Addition of new states to the Union
[edit]When a new state is admitted to the Union, its two senators are placed into separate classes. Which two classes are determined by a scheme that keeps the three classes as close to the same size as possible, so that the largest class never differs by more than one senator from the smallest class.[2] A random draw determined which new senator enters which of the classes selected to be expanded.[2] This means at least one of any new state's first pair of senators had a term of more than 2 and up to 6 years and the other had a term that was 2 or 4 years shorter.
New York, which held its first Senate elections in July 1789, was the first state to undergo this process after the original May 1789 draw by the Senate of the 1st Congress. Among the new senators, Philip Schuyler drew the lot for class 1 (whose term would end in 1791) while Rufus King drew class 3 (whose term would end in 1795).[7] This made class 1 have 8 senators while classes 2 and 3 had 7 senators each. North Carolina was then assigned classes 2 and 3 after holding its first Senate elections in November 1789, making all three classes have 8 seats each.
When the newest state, Hawaii, was admitted in 1959, its first Senate elections had candidates run either for "seat A" or "B". The new senators, Hiram Fong and Oren E. Long, in a process managed by the Secretary of the Senate, drew lots to determine which of the two would join class 1 (whose term would end in five-and-a-half years), and which would join class 3 (whose term would end in three-and-a-half years).[4][8][9] If a 51st state is admitted, it will receive senators in classes 1 and 2, at which point all three classes would have 34 senators.[2]
Because each state is represented by 2 senators, regardless of population, each class varies in electorate and populace. Since the early 19th century, it so happens class 2 senators cumulatively co-represent 50–60% of the population; senators from each of the other 2 classes: 70–75% of the U.S. population. [10] Because each state has 2 senators, the sum of these figures is 200%, not 100%. Several of the most populous states, such as California, Florida, New York, Pennsylvania, and Ohio, have their senators in classes 1 and 3, provoking this imbalance.
The only times when both of a state's Senate seats are up for election in the same year are either when a new state joins the union (as mentioned above), or when there is a special election to fill a vacant seat. Special elections have no bearing on when the term for that seat ends, and a senator elected in a special election will serve the remainder of the term, until the next regularly scheduled election, not affecting which class that seat falls within.[3]
Class 1
[edit]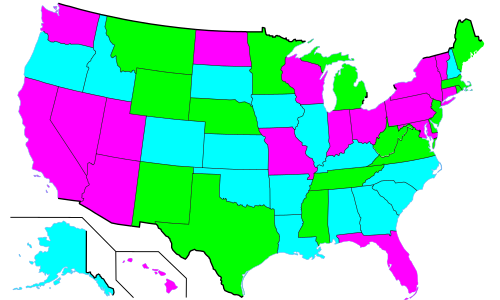
Class 1 consists of:
- the 33 current senators whose seats are scheduled for re-election in November 2024, and whose terms end January 3, 2025; and
- earlier senators with terms that ended in 1791, 1797, 1803, 1809, 1815, 1821, 1827, 1833, 1839, 1845, 1851, 1857, 1863, 1869, 1875, 1881, 1887, 1893, 1899, 1905, 1911, 1917, 1923, 1929, 1935, 1941, 1947, 1953, 1959, 1965, 1971, 1977, 1983, 1989, 1995, 2001, 2007, 2013, and 2019.
States with a class 1 senator: Arizona, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Hawaii, Indiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
Class 2
[edit]Class 2 consists of:
- the 33 current senators whose seats are scheduled for re-election in November 2026, and whose terms end January 3, 2027; and
- earlier senators with terms that ended in 1793, 1799, 1805, 1811, 1817, 1823, 1829, 1835, 1841, 1847, 1853, 1859, 1865, 1871, 1877, 1883, 1889, 1895, 1901, 1907, 1913, 1919, 1925, 1931, 1937, 1943, 1949, 1955, 1961, 1967, 1973, 1979, 1985, 1991, 1997, 2003, 2009, 2015, and 2021.
States with a class 2 senator: Alabama, Alaska, Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, West Virginia, and Wyoming.
Class 3
[edit]Class 3 consists of:
- the 34 current senators whose seats are scheduled for re-election in November 2028, and whose terms end January 3, 2029; and
- earlier senators with terms that ended in 1795, 1801, 1807, 1813, 1819, 1825, 1831, 1837, 1843, 1849, 1855, 1861, 1867, 1873, 1879, 1885, 1891, 1897, 1903, 1909, 1915, 1921, 1927, 1933, 1939, 1945, 1951, 1957, 1963, 1969, 1975, 1981, 1987, 1993, 1999, 2005, 2011, 2017, and 2023.
States with a class 3 senator: Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, South Dakota, Utah, Vermont, Washington, and Wisconsin.
Election cycle years
[edit]This table is re-sorted every two years so that the next scheduled election year appears at the top.
| Class | Most recent election year |
Next scheduled election year |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | 2018 | 2024 |
| Class 2 | 2020 | 2026 |
| Class 3 | 2022 | 2028 |
Comparison with other United States general elections
[edit]| Year | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Presidential | Off-year | Midterm | Off-year | Presidential |
| President | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Senate | Class I (33 seats) | No | Class II (33 seats) | No | Class III (34 seats) |
| House | All 435 seats[3] | No | All 435 seats[2] | No | All 435 seats[3] |
| Gubernatorial | 11 states, 2 territories DE, IN, MO, MT, NH, NC, ND, UT, VT, WA, WV, AS, PR |
2 states NJ, VA |
36 states, DC, & 3 territories[4] AL, AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IA, KS, ME, MD, MA, MI, MN, NE, NV, NH, NM, NY, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, VT, WI, WY, DC (Mayor), GU, MP, VI |
3 states KY, LA, MS |
11 states, 2 territories DE, IN, MO, MT, NH, NC, ND, UT, VT, WA, WV, AS, PR |
| Lieutenant gubernatorial[5] | 5 states, 1 territory DE, MO, NC, VT, WA, AS |
1 state VA |
10 states[6] AL, AR, CA, GA, ID, NV, OK, RI, TX, VT |
2 states LA, MS |
5 states, 1 territory DE, MO, NC, VT, WA, AS |
| Secretary of state | 7 states MO, MT, NC, OR, VT, WA, WV |
None | 26 states AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, GA, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, MA, MI, MN, NE, NV, NM, ND, OH, RI, SC, TX, VT, WI, WY |
3 states KY, LA, MS |
7 states MO, MT, NC, OR, VT, WA, WV |
| Attorney general | 10 states IN, MO, MT, NC, OR, PA, UT, VT, WA, WV |
1 state VA |
30 states, DC, & 2 territories AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, ID, IL, IA, KS, MD, MA, MI, MN, NE, NV, NM, NY, ND, OH, OK, RI, SC, SD, TX, VT, WI, DC, GU, MP |
3 states KY, LA, MS |
10 states IN, MO, MT, NC, OR, PA, UT, VT, WA, WV |
| State treasurer[7] | 9 states MO, NC, ND, OR, PA, UT, VT, WA, WV |
None | 23 states AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, FL (CFO), ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, MA, NE, NV, NM, OH, OK, RI, SC, VT, WI, WY |
2 states KY, MS |
9 states MO, NC, ND, OR, PA, UT, VT, WA, WV |
| State comptroller/controller | None | None | 7 states CA, CT, IL, MD, NV, NY, SC |
None | None |
| State auditor | 9 states MT, NC, ND, PA, UT, VT, WA, WV, GU |
None | 15 states AL, AR, DE, IN, IA, MA, MN, MO, NE, NM, OH, OK, SD, VT, WY |
1 state KY |
9 states MT, NC, ND, PA, UT, VT, WA, WV, GU |
| Superintendent of public instruction | 4 states MT, NC, ND, WA |
1 state WI |
8 states AZ, CA, GA, ID, OK, SC, SD (incl. Land), WY |
None | 4 states MT, NC, ND, WA |
| Agriculture commissioner | 2 states NC, WV |
None | 6 states AL, FL, GA, IA, ND, SC |
2 states KY, MS |
2 states NC, WV |
| Insurance commissioner | 3 states NC, ND, WA, |
None | 5 states DE, CA GA, KS, OK, |
2 states LA, MS |
3 states NC, ND, WA, |
| Other commissioners & elected officials | 1 state NC (Labor) |
None | 8 states AZ (Mine Inspector), AR (Land), GA (Land), NM (Land), ND (Tax), OK (Labor), OR (Labor), TX (Land) |
None | 1 state NC (Labor) |
| State legislatures[8] | 44 states, DC, & 5 territories AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, ME, MA, MI, MN, MO, MN, NE, NV, NH, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WA, WV, WI, WY, DC, AS, GU, MP, PR, VI |
2 states VA, NJ |
46 states, DC, & 4 territories AK, AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, ME, MA, MD, MI, MN, MO, MN, NE, NV, NH, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WA, WV, WI, WY, DC, AS, GU, MP, VI |
4 states LA, MS, NJ, VA |
44 states, DC, & 5 territories AK, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, HI, ID, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, ME, MA, MI, MN, MO, MN, NE, NV, NH, NM, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, SD, TN, TX, UT, VT, WA, WV, WI, WY, DC, AS, GU, MP, PR, VI |
| State boards of education [9] | 8 states, DC, & 3 territories AL, CO, KS, MI, NE, OH, TX, UT, DC, GU, MP, VI |
None | 8 states, DC, & 3 territories AL, CO, KS, MI, NE, OH, TX, UT, DC, GU, MP, VI |
None | 8 states, DC, & 3 territories AL, CO, KS, MI, NE, OH, TX, UT, DC, GU, MP, VI |
| Other state, local, and tribal offices | Varies | ||||
- 1 This table does not include special elections, which may be held to fill political offices that have become vacant between the regularly scheduled elections.
- 2 As well as all six non-voting delegates of the U.S. House.
- 3 As well as five non-voting delegates of the U.S. House. The resident commissioner of Puerto Rico instead serves a four-year term that coincides with the presidential term.
- 4 The governors of New Hampshire and Vermont are each elected to two-year terms. The other 48 state governors and all five territorial governors serve four-year terms.
- 5 In 26 states and 3 territories the lieutenant governor is elected on the same ticket as the governor: AK, CO, CT, FL, HI, IL, IN, IA, KS, KY, MD, MA, MI, MN, MT, NE, NJ, NM, NY, ND, OH, PA, SC, SD, UT, WI, GU, MP, VI.
- 6 Like the governor, Vermont's other officials are each elected to two-year terms. All other state officers for all other states listed serve four-year terms.
- 7 In some states, the comptroller or controller has the duties equivalent to a treasurer. There are some states with both positions, so both have been included separately.
- 8 This list does not differentiate chambers of each legislature. Forty-nine state legislatures are bicameral; Nebraska is unicameral. Additionally, Washington, DC, Guam, and the US Virgin Islands are unicameral; the other territories are bicameral. All legislatures have varying terms for their members. Many have two-year terms for the lower house and four-year terms for the upper house. Some have all two-year terms and some all four-year terms. Arkansas has a combination of both two- and four-year terms in the same chamber.
- 9 Most states not listed here have a board appointed by the governor and legislature. All boards listed here have members that serve four-year staggered terms, except Colorado, which has six-year terms, and Guam, which has two-year terms. Most are elected statewide, some are elected from districts. Louisiana, Ohio, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands have additional members who are appointed.
List of current senators by class
[edit]The following table lists the senators by party by class.
|
Democrat
Independent who caucuses with Democrats
Republican
Not up for election
The following table lists the senators by state and by class, including the states' Cook Partisan Voting Index ratings, which indicate the party direction in which a state tends to lean and the extent of that lean.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "The Senate and the United States Constitution". senate.gov. Retrieved October 23, 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Frequently Asked Questions about a New Congress". United States Senate. Retrieved June 11, 2013.
- ^ a b Pittman, Travis (October 16, 2018). "The US Senate is divided into classes: What that means". ABC 10. KXTV. Retrieved November 12, 2022.
- ^ a b "Senators Receive Class Assignments". Senate History. United States Senate. Retrieved May 1, 2022.
- ^ "Annals of Congress". Constitution Society. Retrieved August 4, 2016.
- ^ a b "Journal of the Senate of the United States of America". Journal of the Senate of the United States of America, 1789–1793. Library of Congress. May 14, 1789. Retrieved June 11, 2013.
- ^ Power, Nicholas (August 4, 1789). "New-York, July 29". Poughkeepsie Journal. Poughkeepsie, NY. p. 2 – via newspapers.com.
- ^ Davies, Lawrence E. (July 30, 1959). "G.O.P. Wins Governorship in Hawaii's First State Vote". The New York Times.
- ^ Trussell, C. P. (August 25, 1959). "Congress Hails Three New Members from 50th State". The New York Times.
- ^ Skelley, Geoffrey (May 29, 2014). "Senate Class Population Imbalance". Sabato's Crystal Ball. Retrieved May 30, 2014.



