Hispanic and Latino Americans: Difference between revisions
Made several correction to the original paragraph. Latino, Hispanic and Spanish are completely different definitions. Latino: From any culture derived from the Roman Empire or the Latin language, which includes France and Romania for example. Hispanic: |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Redirect4|Latino|Latina}} |
|||
{{distinguish2|[[Latin Americans]] or the inhabitants of [[Hispanic America]]}} |
{{distinguish2|[[Latin Americans]] or the inhabitants of [[Hispanic America]]}} |
||
{{Infobox ethnic group |
{{Infobox ethnic group |
||
Revision as of 05:56, 9 April 2014
 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| All areas of the United States | |
| Languages | |
| Spanish • American English • Portuguese • Indigenous languages | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Roman Catholicism;[1] large minority of Protestantism[1] · Indigenous beliefs · Jehovah's Witnesses · Mormonism Judiasm, Islam, also rapidly growing Atheism · Agnosticism[1][2] | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Latin Americans, Native Americans, Haitian Americans, Belizean Americans, Brazilian Americans, White Latin Americans, Afro-Latin Americans, Asian Latin Americans, Mestizos, Métis, Mulattoes, Pardos, Castizos and others. It is important to note that some of the prior groups are not officially considered Hispanic or Latinos by the U.S. Government and are not included in any Hispanic or Latino surveys[3] |
Hispanics (Spanish: hispanos [isˈpanos], [hispánicos] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) [isˈpanikos], or Latinos [latinos] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) [laˈtinos], Portuguese: latinos [lɐˈtʃĩnus]) are an ethnolinguistic group of Americans with origins in the countries of Latin America, Spain or Portugal.[5][6][7] More generally it includes all persons in the United States who self-identify as Hispanic or Latino.[8][9][10][11][12][13][14]
Latin American population has origins in all the continents and has ancestries including many Native American cultures,[15] Hispanic and Latino Americans are separate terms that are racially diverse, and as a result form an ethnic category, rather than a race.[13][16][17][18] In the 2010 Census, 53% Hispanics in the US are properly self-identified as white since Hispanics by definition are Caucasians.
While the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, Hispanic is a narrower term and refers mostly to persons of Spanish-speaking ancestry, while Latino is more frequently used to refer more generally to anyone of Latin American origin or ancestry, including Brazilians.[19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30] Hispanic thus includes Spanish speaking Latin Americans countries and Spain, excluding both Portuguese and Brazilians (who speak Portuguese) while Latino includes both Spanish-speaking and Portuguese-speaking Latin Americans, but excluding Spain. The choice between the terms Latino and Hispanic among those of Spanish speaking ancestry is also associated with location: persons of Spanish speaking ancestry residing in the eastern United States tend to prefer the term Hispanic, whereas those in the West tend to prefer Latino.[12]
Hispanics or Latinos constitute 16.9% of the total United States population, or 53 million people,[31] making it home to the largest community of Spanish speakers outside of Mexico according to the Pew Research Hispanic Center, surpassing Argentina, Colombia, and Spain within the last decade.[32] Latinos overall are the second largest ethnic group, after non-Hispanic White Americans (a group composed of dozens of sub-groups, as is Hispanic and Latino Americans).[33] Hispanic and Latino Americans are the largest of all the minority groups, but Black Americans are the largest minority among the races, after White Americans in general (non-Hispanic and Hispanic).[34] Mexican Americans, Cuban Americans, Colombian Americans, Dominican Americans, Puerto Rican Americans, Spanish Americans, and Salvadoran Americans are some of the Hispanic and Latino American national origin groups.[35]
There have been people of Hispanic or Latino heritage in the territory of the present-day United States continuously[36][37][38][39] since the 1565 founding of St. Augustine, Florida, by the Spanish, the longest among European American ethnic groups and second-longest of all U.S. ethnic groups, after Native Americans to inhabit what is today the United States. Hispanics have also lived continuously in the Southwest since near the end of the 16th century, with settlements in New Mexico that began in 1598, and which were transferred to the area of El Paso, Texas, in 1680.[40] Spanish settlement of New Mexico resumed in 1692, and new ones were established in Arizona and California in the 18th century.[41][42] The Hispanic presence can even be said to date from half a century earlier than St. Augustine, if San Juan, Puerto Rico is considered to be the oldest Spanish settlement, and the oldest city, in the U.S.[43]
Terminology
| Part of a series on |
| Hispanic and Latino Americans |
|---|
The term Hispanic was adopted by the United States government in the early 1970s during the administration of Richard Nixon[44] after the Hispanic members of an interdepartmental Ad Hoc Committee to develop racial and ethnic definitions recommended that a universal term encompassing all Hispanic subgroups—including Central and South Americans—be adopted.[45] As the 1970 census did not include a question on Hispanic origin on all census forms—instead relying on a sample of the population via an extended form ("Is this person's origin or descent: Mexican; Puerto Rican; Cuban; Central or South American; Other Spanish; or None of these")[46]—the members of the Ad Hoc Committee wanted a common designation to better track the social and economic progress of the group vis-à-vis the general population.[45] The designation has since been used in local and federal employment, mass media, academia, and business market research. It has been used in the U.S. Census since 1980.[47] Because of the popularity of "Latino" in the western portion of the United States, the government adopted this term as well in 1997, and used it in the 2000 census.[12][13]
Previously, Hispanic and Latino Americans were categorized as "Spanish-Americans", "Spanish speaking Americans", and "Spanish surnamed Americans". However:
- Although a large majority of Hispanic and Latino Americans have Spanish ancestry, most are not of direct, "from-Spain-to-the-U.S."[48][49] Spanish descent; many are not primarily of Spanish or descent; and some are not of Spanish descent at all. People whose ancestors or who themselves arrived in the United States directly from Spain or are a tiny minority of the Hispanic or Latino population (see figures in this article), and there are Hispanic/Latino Americans who are of other European ancestries in addition to Spanish (e.g. Portuguese, Italian, German, and Middle Eastern, such as the Lebanese).[50]
- Most Hispanic and Latino Americans can speak Spanish, not all; and most Spanish speaking and speaking Americans are Hispanic or Latino, not all. E.g., Hispanic/Latino Americans often do not speak Spanish or by the third generation, and some Americans who are Spanish speaking or may not identify themselves with Spanish speaking Americans as an ethnic group.
- Not all Hispanic and Latino Americans have Spanish surnames, and most Spanish-surnamed Americans are Hispanic or Latino, not all. For example, non-Spanish surnamed Bill Richardson (former governor, Congressman, etc.), former National Football League (NFL) star Jim Plunkett, and Salma Hayek (actress) have Hispanic or Latino origin. Filipino Americans, and Pacific Islander Americans of Chamorro (Guamanians and Northern Mariana Islanders), Palauan, Micronesian (FSM), and Marshallese origin often have Spanish surnames, but have their own, non-Hispanic/Latino ethnic identities and origin. Likewise, while many Louisiana Creole people have Spanish surnames, they identify with the mostly French—though partially Spanish—culture of their region.
Neither term refers to race, as a person of Latino or Hispanic origin can be of any race.[13][51]
The U.S. government has defined Hispanic or Latino persons as being "persons who trace their origin [to] …Central and South America, and other Spanish cultures".[12] The Census Bureau's 2010 census does provide a definition of the terms Latino or Hispanic and is as follows: “Hispanic or Latino” refers to a person of Cuban, Mexican, Puerto Rican, South or Central American, or other Spanish culture or origin regardless of race. It allows respondents to self-define whether they were Latino or Hispanic and then identify their specific country or place of origin.[52] On its website, the Census Bureau defines "Hispanic" or "Latino" persons as being "persons who trace their origin [to]... Spanish speaking Central and South America countries, and other Spanish cultures".[12][13][53]
These definitions thus arguably does not include Brazilian Americans,[12][13][54] especially since the Census Bureau classifies Brazilian Americans as a separate ancestry group from Hispanic or Latino.[55] The 28 Hispanic or Latino American groups in the Census Bureau's reports are the following:[13][35][56] Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Dominican; Central American: Costa Rican, Guatemalan, Honduran, Nicaraguan, Panamanian, Salvadoran, Other Central American; South American: Argentinian, Bolivian, Chilean, Colombian, Ecuadorian, Paraguayan, Peruvian, Uruguayan, Venezuelan, Other South American; Other Hispanic or Latino: Spaniard, Spanish, Spanish American, All other Hispanic.
One dictionary of American English maintains a distinction between the terms "Hispanic" and "Latino":
Though often used interchangeably in American English, Hispanic and Latino are not identical terms, and in certain contexts the choice between them can be significant. Hispanic, from the Latin word for "Spain," …potentially encompass[es] all Spanish speaking peoples in both hemispheres and emphasiz[es] the common denominator of language among communities that sometimes have little else in common. Latino—which in Spanish means "Latin" but which as an English word is probably a shortening of the Spanish and Portuguese word latinoamericano—refers …to persons or communities of Latin American origin. Of the two, only Latino can be used to refer to Brazilians, who are Latin American, but who do not speak Spanish, and only Hispanic can be used in referring to Spain and its history and culture; a native of Spain residing in the United States is a Hispanic, not a Latino, and one cannot substitute Latino in the phrase the Hispanic influence on native Mexican cultures without garbling the meaning. In practice, however, this distinction is of little significance when referring to residents of the United States, most of whom are of Latin American origin and can theoretically be called by either word.[57]
The AP Stylebook states that Latino is often the preferred term for a person from - or whose ancestors were from - a Spanish speaking land or culture or from Latin America. Latina is the feminine form. Follow the person's preference. Use a more specific identification when possible, such as Cuban, Puerto Rican, Brazilian or Mexican-American. Of Hispanic the AP Stylebook states: Hispanic - A person from - or whose ancestors were from - a Spanish speaking land or culture. Latino and Latina are sometimes preferred. Follow the person’s preference.[30] Some federal and local government agencies and non-profit organizations may include Brazilians and Portuguese in their definition of Hispanic. The U.S. Department of Transportation defines Hispanic as, "persons of Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Dominican, Central or South American, or other Spanish or Portuguese culture or origin, regardless of race".[8] This definition has been adopted by the Small Business Administration as well as by many federal, state, and municipal agencies for the purposes of awarding government contracts to minority owned businesses.[9]
The Congressional Hispanic Caucus, which was founded by Hispanic Puerto Rican Herman Badillo, and the Congressional Hispanic Conference include representatives of Spanish and Portuguese descent and Hispanic and Latino Americans. The Hispanic Society of America is dedicated to the study of the arts and cultures of Spain, Portugal, and Latin America. The Hispanic Association of Colleges and Universities, which proclaims itself the champion of Hispanic success in higher education, has member institutions in the US, Puerto Rico, Latin America, Spain, and Portugal. Even though the term "Hispanic" is related to "Spanish," many Hispanic Americans do not speak Spanish.
History
This section needs expansion with: more about the 19th and 20th centuries. You can help by adding to it. (January 2010) |

A continuous Hispanic/Latino presence in the territory of the United States has existed since the 16th century,[36][37][38][39] earlier than any other group after the Native Americans. Spaniards pioneered the present-day United States. The first confirmed European landing in the continental U.S. was by Juan Ponce de León, who landed in 1513 at a lush shore he christened La Florida.
Within three decades of Ponce de León's landing, the Spanish became the first Europeans to reach the Appalachian Mountains, the Mississippi River, the Grand Canyon and the Great Plains. Spanish ships sailed along the East Coast, penetrating to present-day Bangor, Maine, and up the Pacific Coast as far as Oregon. From 1528 to 1536, Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca and three other castaways from a Spanish expedition (including an African named Estevanico) journeyed all the way from Florida to the Gulf of California, 267 years before the Lewis and Clark Expedition.
In 1540 Hernando de Soto undertook an extensive exploration of the present U.S., and in the same year Francisco Vásquez de Coronado led 2,000 Spaniards and Mexican Indians across today's Arizona–Mexico border and traveled as far as central Kansas, close to the exact geographic center of what is now the continental United States. Other Spanish explorers of the US make up a long list that includes, among others: Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón, Pánfilo de Narváez, Sebastián Vizcaíno, Gaspar de Portolà, Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca, Tristán de Luna y Arellano and Juan de Oñate, but also non-Spanish explorers working for the Spanish Crown like Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo. In all, Spaniards probed half of today's lower 48 states before the first English colonization attempt at Roanoke Island in 1585.
The Spanish created the first permanent European settlement in the continental United States, at St. Augustine, Florida, in 1565. Santa Fe, New Mexico also predates Jamestown, Virginia (founded in 1607) and Plymouth Colony (of Mayflower and Pilgrims fame; founded in 1620). Later came Spanish settlements in San Antonio, Texas, Tucson, Arizona, San Diego, California, Los Angeles, California and San Francisco, California, to name just a few.

Two iconic American stories have Spanish antecedents, too. Almost 80 years before John Smith's alleged rescue by Pocahontas, a man by the name of Juan Ortiz told of his remarkably similar rescue from execution by an Indian girl. Spaniards also held a thanksgiving—56 years before the famous Pilgrims festival—when they feasted near St. Augustine with Florida Indians, probably on stewed pork and garbanzo beans. As late as 1783, at the end of the American Revolutionary War (a conflict in which Spain aided and fought alongside the United States), Spain held claim to roughly half of today's continental United States. From 1819 to 1848, the United States (through treaties, purchase, diplomacy, and the Mexican-American War) increased its area by roughly a third at Spanish and Mexican expense, acquiring three of today's four most populous states—California, Texas and Florida.
The Hispanic and Latino role in the history and present of the United States is addressed in more detail below (See Notables and their contributions). On September 17, 1968, President Lyndon B. Johnson designated a week in mid-September as National Hispanic Heritage Week, with Congress's authorization. In 1988, President Ronald Reagan extended the observance to a month, designated Hispanic Heritage Month.[58]
Demographics
| Hispanic Group | Population | % |
|---|---|---|
| 31,798,258 | 63.0 | |
| 4,623,716 | 9.2 | |
| 1,785,547 | 3.5 | |
| 1,648,968 | 3.3 | |
| 1,414,703 | 2.8 | |
| 1,044,209 | 2.1 | |
| 908,734 | 1.8 | |
| 635,253 | 1.3 | |
| 633,401 | 1.3 | |
| 564,631 | 1.1 | |
| 531,358 | 1.1 | |
| 348,202 | 0.7 | |
| 224,952 | 0.4 | |
| 215,023 | 0.4 | |
| 165,456 | 0.3 | |
| 126,810 | 0.3 | |
| 126,418 | 0.3 | |
| 99,210 | 0.2 | |
| 56,884 | 0.1 | |
| 20,023 | - | |
| All other | 3,505,838 | 6.9 |
| Total | 50,477,594 | 100 |
As of 2011, Hispanics accounted for 16.7% of the national population, or around 52 million people.[31] The Hispanic growth rate over the April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2007 period was 28.7%—about four times the rate of the nation's total population (at 7.2%).[60] The growth rate from July 1, 2005 to July 1, 2006 alone was 3.4%[61]—about three and a half times the rate of the nation's total population (at 1.0%).[60] Based on the 2010 census, Hispanics are now the largest minority group in 191 out of 366 metropolitan areas in the US.[62] The projected Hispanic population of the United States for July 1, 2050 is 132.8 million people, or 30.2% of the nation's total projected population on that date.[63]
Of the nation's total Hispanic or Latino population, 49% (21.5 million) lives in California or Texas. Not counting Puerto Rico, which is a Commonwealth of the United States, New Mexico is the state with the highest ratio of Hispanics, 44.7%. Next are California and Texas, with 35.9% and 35.6%, respectively.[64]

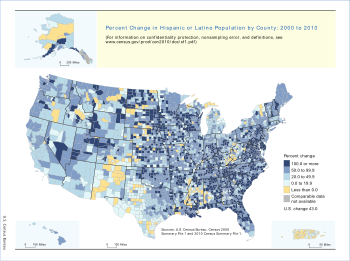
The overwhelming majority of Mexican Americans are concentrated in the Southwest and the West Coast/West, primarily in California, Texas, Arizona, Nevada, New Mexico, Colorado, and Utah. The majority of the Hispanic population in the Southeast and Great Plains (Plains States), concentrated in Florida, are of Cuban origin; However, the Mexican, Dominican and Puerto Rican populations have risen significantly in this region since the mid-1990s.
The Hispanic population in the Northeast, concentrated in New York, New Jersey, and Southeastern Pennsylvania, is composed mostly of Hispanics of Dominican and Puerto Rican origin. The remainder of Hispanics and Latinos may be found throughout the country, though South Americans tend to concentrate on the East Coast and Central Americans on the West Coast. Nevertheless, since the 1990s, several cities on the East Coast have seen often impressive increases in their Mexican population, namely Miami and Philadelphia.
The Hispanic population of Los Angeles County, California, numbering 4.7 million, is the largest of any county in the nation,[65] comprising 47 percent of the county's ten million residents.[66]
As of 2000, the ten most populous places with Hispanic majorities were East Los Angeles (97% Hispanic), Laredo, Texas (94%), Brownsville, Texas (91%) Hialeah, Florida (90%), McAllen, Texas (80%), El Paso, Texas (77%), Santa Ana, California (76%), El Monte, California (72%) Oxnard, California (66%), and Miami (66%).[67]
Some 64% of the nation's Hispanic population are of Mexican origin (see table). Another 9% are of Puerto Rican origin, with about 3% each of Cuban, Salvadoran and Dominican origins. The remainder are of other Central American or South American origin, or of origin directly from Spain. About 7% are of unspecified national origins. It should be noted that these figures pertain to ethnic self-identification; the same dataset (abstracted from the 2007 American Community Survey) indicates that 60.2% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans were born in the United States.[68]
There are few recent immigrants directly from Spain. In the 2000 Census, 299,948 Americans, of whom 83% were native-born,[69] specifically reported their ancestry as Spaniard.[70][71]
In northern New Mexico and southern Colorado live peoples who trace their ancestry to Spanish settlers of the late 16th century through the 17th century. People from this background often self-identify as "Hispanos", "Spanish", or "Hispanic". Many of these settlers also intermarried with local Amerindians, creating a Mestizo population.[72] Likewise, southern Louisiana is home to communities of people of Canary Islands descent, known as Isleños, in addition to other people of Spanish ancestry.
Hispanics are almost uniformly Christian, with Catholicism the majority confession and an increasing Protestant community.
Race

As shown below, the largest number of White Hispanics come from within the Mexican community, the highest percentage of White Hispanics among major Hispanic groups comes from the Cuban American community, also high percentages of White Hispanics from Hispanic groups come from within the Argentine, Colombian and also Spanish communities. The largest number of Black Hispanics come from within the Puerto Rican community, while the highest percentage of Black Hispanics among major Hispanic groups come from the Dominican community. Significant numbers of Black Hispanics can also be found among the Central American communities.[75]
The largest number of Asian Hispanics come from within the Mexican community, while the highest percentage of Asian Hispanics come from the Peruvian community. The largest population of Native American Hispanic come from within the Mexican community and the highest percentage of Native American Hispanics among major Hispanic groups come from within the Guatemalan community.
Although half of the US Hispanic self-identifies as "white", most of the US Hispanic population is actually racially mixed. Most of the Multiracial population in the Mexican, Salvadoran, and Guatemalan communities are of Mestizo descent (European and Native American), while most of the multiracial population in the Puerto Rican, Dominican, and Cuban communities are of Mulatto descent (European and African).
Hispanic or Latino origin is independent of race and is termed "ethnicity" by the United States Census Bureau. The racial categories are: American Indian and Alaska Native, White, Black or African American, Asian, Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander, Some other race, and Two or more races. The distinction made by government agencies for those within the population of each race category is between those of Hispanic or Latino origin, and all others of Non-Hispanic or Latino origin.
The majority of Hispanic and Latino Americans are considered white by both sets of government estimates: 54% are white per the American Community Survey,"B03002. Hispanic or Latino origin by race". 2007 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. while the ratio rises to 92% in the Population Estimates Program, which are the official estimates."T4-2007. Hispanic or Latino By Race [15]". 2007 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau.
The much larger official figure is due to the absence of the Some other race category from these estimates, which instead reallocate that category among the five standard, minimum, single-race categories, mostly the white category."Technical Documentation for the Census 2000 Modified Race Data Summary File". United States Census Bureau. The complete 2007 Hispanic or Latino racial breakdown is as follows: White 92% (official) or 54% (ACS); Black or African American 3.8% (official) or 1.5% (ACS); American Indian and Alaska Native 1.4% (official) or 0.8% (ACS); Asian 0.6% (official) or 0.3% (ACS); Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander 0.3% (official) or 0.07% (ACS); Some other race 40% (ACS only; not an official race); Two or more races 0.6% (official) or 3.8% (ACS).
Though comprising very small percentages of the Hispanic and Latino American population, and even smaller percentages of the total U.S. population, some of the preceding racial subgroups make up large minorities among the respective racial groups, overall. For instance, Hispanics and Latinos who are American Indian or Alaska Native compose 15% of all American Indians and Alaska Natives (per the ACS estimates). Meanwhile, the 120,000 Hispanics and Latinos who are of Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander race compose 22% of this entire race nationally (per the Population Estimates). Again, nearly a third of the overall 'Two or more race' population is Hispanic or Latino (ACS).
| Race | Population | % of all Hispanic and Latino Americans |
|---|---|---|
| White | 26,735,713 | 53.0 |
| Some other race (Mestizo, Mulatto, etc.) | 18,503,103 | 36.7 |
| Two or more races | 3,042,592 | 6.0 |
| Black | 1,243,471 | 2.5 |
| American Indian and Alaska Native | 685,150 | 1.4 |
| Asian | 209,128 | 0.4 |
| Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander | 58,437 | 0.1 |
| Total | 50,477,594 | 100.0 |
| Hispanic Group | Total | White | Black | American Indian and Alaska Native |
Asian | Other (Some Other Race or Two or More Races or Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31,798,258 100% |
16,794,111 52.8% |
296,778 0.9% |
460,098 1.4% |
101,654 0.3% |
14,145,617 44.6% | |
| 4,623,716 100% |
2,455,534 53.1% |
403,372 8.7% |
42,504 0.9% |
24,312 0.5% |
1,697,994 36.7% | |
| 1,785,547 100% |
1,525,521 85.4% |
82,398 4.6% |
3,002 0.2% |
4,391 0.2% |
170,235 9.6% | |
| 1,648,968 100% |
663,224 40.2% |
16,150 1.0% |
17,682 1.1% |
4,737 0.3% |
947,175 57.4% | |
| 1,414,703 100% |
419,016 29.6% |
182,005 12.9% |
19,183 1.4% |
4,056 0.3% |
790,443 55.8% | |
| 1,044,209 100% |
401,763 38.5% |
11,471 1.1% |
31,197 3.0% |
2,386 0.2% |
597,392 57.2% | |
| All other | 4,087,656 100% |
2,018,397 49.4% |
112,521 2.8% |
75,976 1.9% |
50,299 1.2% |
1,830,463 44.9% |
| Total | 50,477,594 100% |
26,735,713 53.0% |
1,243,471 2.5% |
685,150 1.4% |
209,128 0.4% |
21,604,132 42.8% |
Population by state or territory

| less than 2 % 2 - 5 % 5 - 10 % 10 - 15 % 15 - 20 % 20 - 25 % | 25 - 30 % 30 - 35 % 35 - 40 % 40 - 45 % 45 - 50 % |
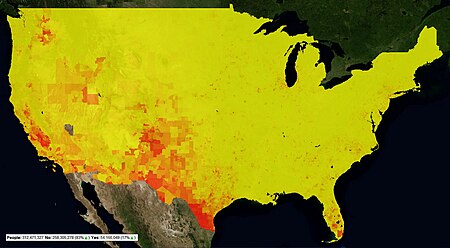
| State/Territory | Pop 2000 | % pop 2000 | Pop 2010 | % pop 2010 | % growth 2000-2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75,830 | 1.7% | 185,602 | 3.9% | +144.8% | |
| 25,852 | 4.1% | 39,250 | 5.5% | +51.8% | |
| 1,295,617 | 25.3% | 1,895,149 | 29.6% | +46.3% | |
| 86,866 | 3.2% | 186,050 | 6.4% | +114.2% | |
| 10,966,556 | 32.4% | 14,013,719 | 37.6% | +27.8% | |
| 735,801 | 17.1% | 1,038,687 | 20.7% | +41.2% | |
| 320,323 | 9.4% | 479,087 | 13.4% | +49.6% | |
| 37,277 | 4.8% | 73,221 | 8.2% | +96.4% | |
| 44,953 | 7.9% | 54,749 | 9.1% | +21.8% | |
| 2,682,715 | 16.8% | 4,223,806 | 22.5% | +57.4% | |
| 435,227 | 5.3% | 853,689 | 8.8% | +96.1% | |
| 87,699 | 7.2% | 120,842 | 8.9% | +37.8% | |
| 101,690 | 7.9% | 175,901 | 11.2% | +73.0% | |
| 1,530,262 | 12.3% | 2,027,578 | 15.8% | +32.5% | |
| 214,536 | 3.5% | 389,707 | 6.0% | +81.7% | |
| 82,473 | 2.8% | 151,544 | 5.0% | +83.7% | |
| 188,252 | 7.0% | 300,042 | 10.5% | +59.4% | |
| 59,939 | 1.5% | 132,836 | 3.1% | +121.6% | |
| 107,738 | 2.4% | 192,560 | 4.2% | +78.7% | |
| 9,360 | 0.7% | 16,935 | 1.3% | +80.9% | |
| 227,916 | 4.3% | 470,632 | 8.2% | +106.5% | |
| 428,729 | 6.8% | 627,654 | 9.6% | +46.4% | |
| 323,877 | 3.3% | 436,358 | 4.4% | +34.7% | |
| 143,382 | 2.9% | 250,258 | 4.7% | +74.5% | |
| 39,569 | 1.4% | 81,481 | 2.7% | +105.9% | |
| 118,592 | 2.1% | 212,470 | 3.5% | +79.2% | |
| 18,081 | 2.0% | 28,565 | 2.9% | +58.0% | |
| 94,425 | 5.5% | 167,405 | 9.2% | +77.3% | |
| 393,970 | 19.7% | 716,501 | 26.5% | +81.9% | |
| 20,489 | 1.7% | 36,704 | 2.8% | +79.1% | |
| 1,117,191 | 13.3% | 1,555,144 | 17.7% | +39.2% | |
| 765,386 | 42.1% | 953,403 | 46.3% | +24.6% | |
| 2,867,583 | 15.1% | 3,416,922 | 17.6% | +19.2% | |
| 378,963 | 4.7% | 800,120 | 8.4% | +111.1% | |
| 7,786 | 1.2% | 13,467 | 2.0% | +73.0% | |
| 217,123 | 1.9% | 354,674 | 3.1% | +63.4% | |
| 179,304 | 5.2% | 332,007 | 8.9% | +85.2% | |
| 275,314 | 8.0% | 450,062 | 11.7% | +63.5% | |
| 394,088 | 3.2% | 719,660 | 5.7% | +82.6% | |
| 90,820 | 8.7% | 130,655 | 12.4% | +43.9% | |
| 95,076 | 2.4% | 235,682 | 5.1% | +147.9% | |
| 10,903 | 1.4% | 22,119 | 2.7% | +102.9% | |
| 123,838 | 2.2% | 290,059 | 4.6% | +134.2% | |
| 6,669,666 | 32.0% | 9,460,921 | 37.6% | +41.8% | |
| 201,559 | 9.0% | 358,340 | 13.0% | +77.8% | |
| 5,504 | 0.9% | 9,208 | 1.5% | +67.3% | |
| 329,540 | 4.7% | 631,825 | 7.9% | +91.7% | |
| 441,509 | 7.5% | 755,790 | 11.2% | +71.2% | |
| 12,279 | 0.7% | 22,268 | 1.2% | +81.4% | |
| 192,921 | 3.6% | 336,056 | 5.9% | +74.2% | |
| 31,669 | 6.4% | 50,231 | 8.9% | +58.6% | |
| 3,762,746 | 98.8% | 3,688,455 | 99.0% | -2.0% | |
| 15,196 | 14.0% | 18,504 | 17.4% | +21.8% | |
| 35,305,818 | 12.5% | 50,477,594 | 16.3% | +43.0% |
Sexuality
According to a Gallup survey conducted from June to September 2012, it found that 4 percent of Hispanic and Latino Americans self identify as LGBT; this is greater than the estimated 3.4 percent of American adults that self identify as LGBT in the total population.[78]
Socioeconomics
Education

The high school graduation rate for Hispanics, according to the 2010, is 62.2 percent. It is highest among Cuban Americans (68.7 percent) and lowest among Mexican Americans (47.7 percent). The Puerto Rican rate is 63.2 percent, Central and South American Americans' is 60.4 percent, and the Dominican American is 51.7 percent.
According to the 2010 census, South Americans had the highest college graduation rates, from 49.7 percent of Venezuelan-Americans compared to 7.8 percent for Salvadoran-Americans 25 years and older. On the other hand, only 9.1 percent of Mexican Americans, 15.9 percent of Puerto Ricans and 15.2 percent of Dominican Americans had achieved a 4-year degree. Over 21% of all second-generation Dominican Americans have college degrees, slightly below the national average (27.9%) but significantly higher than U.S.-born Mexican Americans (13%) and U.S.-born Puerto Rican Americans (12%).[80]
In comparison non-Hispanic Asian Americans (50.2 percent) and non-Hispanic White Americans (30.9 percent) had higher rates than any Hispanic American group. Non-Hispanic Black Americans (17.7 percent) had a lower graduation rate than Cuban Americans and Central and South Americans, but had a higher rate than Mexican Americans, Puerto Ricans, and Dominican Americans.[81]
Health
Hispanic and Latino Americans are the longest-living Americans, according to official data. Their life expectancy is more than two years longer than for non-Hispanic whites and almost eight years longer than for African Americans.[82]
Workforce and average income


In 2002, the average individual income among Hispanic and Latino Americans was highest for Cuban Americans ($38,733), and lowest for Dominican Americans ($26,467) and Puerto Rican Americans ($27,877). For Mexican Americans it was $33,927, and $30,444 for Central and South Americans. In comparison, the income of the average Hispanic American is lower than the national average.
Among Hispanics, Cuban Americans (28.5 percent) had the highest percentage in professional–managerial occupations. The percentage for Mexican Americans was 20.7, Central and South Americans' was 8.8 percent, and Puerto Ricans was 7.2 percent. All these are lower than the average for non-Hispanics (36.2 percent).[citation needed]
Poverty
According to the ACS, the poverty rate among Hispanic groups is highest among Dominican Americans (28.1 percent), Mexican Americans (23.9 percent), and Honduran Americans and Puerto Ricans (23.7 percent both). It is lowest among South Americans, such as Colombian Americans (10.6 percent) and Peruvian Americans (13.6 percent), and relatively low poverty rates are also found among Salvadoran Americans (15.0 percent) and Cuban Americans (15.2 percent).[85]
In comparison, the average poverty rates for non-Hispanic White Americans (8.8 percent)[85] and Asian Americans (7.1 percent) were lower than those of any Hispanic group. African Americans (21.3 percent) had a higher poverty rate than Cuban Americans and Central and South Americans, but had a lower poverty rate than Mexican Americans, Puerto Ricans, and Dominican Americans.[85]
Hispanophobia
Hispanophobia has existed in various degrees throughout U.S. history, based largely on ethnicity, race, culture, Anti-Catholicism, economic and social conditions in Latin America, and use of the Spanish language.[86][87][88][89] In 2006, Time Magazine reported that the number of hate groups in the United States increased by 33 percent since 2000, primarily due to anti-illegal immigrant and anti-Mexican sentiment.[90] According to Federal Bureau of Investigation statistics, the number of anti-Latino hate crimes increased by 35 percent since 2003 (albeit from a low level). In California, the state with the largest Latino population, the number of hate crimes against Latinos almost doubled.[91]
For the year 2009, the FBI reported that 483 of the 6,604 hate crimes committed in the United States were anti-Hispanic comprising 7.3% of all hate crimes. This compares to 34.6% of hate crimes being anti-Black, 17.9% being anti-Homosexual, 14.1% being anti-Jewish, and 8.3% being anti-White.[92]
Relations with other minority groups
As a result of the rapid growth of the Hispanic population, there has been some tension with other minority populations,[93] especially the African American population, as Hispanics have increasingly moved into once exclusively Black areas.[94][95][96][97][98][99][100][101][102][103][104] There has also been increasing cooperation between minority groups to work together to attain political influence.[105][106][107][108][109]
- A 2007 UCLA study reported that 51% of Blacks felt that Hispanics were taking jobs and political power from them and 44% of Hispanics said they feared African-Americans identifying them with high crime rates. That said, large majorities of Hispanics credited American blacks and the civil rights movement with making life easier for them in the US.[110][111]
- A Pew Research Center poll from 2006 showed that Blacks overwhelmingly felt that Hispanic immigrants were hard working (78%) and had strong family values (81%) but also that they believed that immigrants took jobs from Americans (34%) with a significant minority of Blacks (22%) believing that they had directly lost a job to an immigrant and 34% of Blacks wanting immigration to be curtailed. The report also surveyed three cities: Chicago (with its well-established Latino community); Washington DC (with a less-established but quickly growing Hispanic community); and Raleigh-Durham (with a very new but rapidly growing Hispanic community). The results showed that a significant proportion of Blacks in those cities wanted immigration to be curtailed: Chicago (46%), Raleigh-Durham (57%), and Washington DC (48%).[112]
- Per a 2008 University of California, Berkeley Law School research brief, a recurring theme to Black / Hispanic tensions is the growth in "contingent, flexible, or contractor labor," which is increasingly replacing long term steady employment for jobs on the lower-rung of the pay scale (which had been disproportionately filled by Blacks). The transition to this employment arrangement corresponds directly with the growth in the Latino immigrant population. The perception is that this new labor arrangement has driven down wages, removed benefits, and rendered temporary, jobs that once were stable (but also benefiting consumers who receive lower-cost services) while passing the costs of labor (healthcare and indirectly education) onto the community at large.[113]
- A 2008 Gallup poll indicated that 60% of Hispanics and 67% of blacks believe that good relations exist between US blacks and Hispanics[114] while only 29% of blacks, 36% of Hispanics, and 43% of whites, say Black - Hispanic relations are bad.[114]
- In 2009, in Los Angeles County, Latinos committed 77% of the hate crimes against black victims and blacks committed half of the hate crimes against Latinos.[115]
Political trends

Hispanics and Latinos differ on their political views depending on their location and background, but the majority (57%)[116] either identify themselves as or support the Democrats, and 23% identify themselves as Republicans.[116] This 34 point gap as of December, 2007 was an increase from the gap of 21 points 16 months earlier. Cuban Americans and Colombian Americans tend to favor conservative political ideologies and support the Republicans, while Mexican Americans, Puerto Ricans, and Dominican Americans tend to favor liberal views and support the Democrats. However, because the latter groups are far more numerous—as, again, Mexican Americans alone are 64% of Hispanics and Latinos—the Democratic Party is considered to be in a far stronger position with the group overall.
The Presidency of George W. Bush had a significant impact on the political leanings of Hispanics and Latinos. As a former Governor of Texas, Bush regarded this growing community as a potential source of growth for the conservative movement and the Republican Party,[citation needed] and he made some gains for the Republicans among the group.

In the 1996 presidential election, 72% of Hispanics and Latinos backed President Bill Clinton, but in 2000 the Democratic total fell to 62%, and went down again in 2004, with Democrat John Kerry winning Hispanics 58–40 against Bush.[117] Hispanics in the West, especially in California, were much stronger for the Democratic Party than in Texas and Florida. California Latinos voted 63–32 for Kerry in 2004, and both Arizona and New Mexico Latinos by a smaller 56–43 margin; but Texas Latinos were split nearly evenly, favoring Kerry 50–49, and Florida Latinos (mostly being Cuban American) backed Bush, by a 54–45 margin.
In the 2006 midterm election, however, due to the unpopularity of the Iraq War, the heated debate concerning illegal immigration, and Republican-related Congressional scandals, Hispanics and Latinos went as strongly Democratic as they have since the Clinton years. Exit polls showed the group voting for Democrats by a lopsided 69–30 margin, with Florida Latinos for the first time split evenly. The runoff election in Texas' 23rd congressional district was seen as a bellwether of Latino politics, and Democrat Ciro Rodriguez's unexpected (and unexpectedly decisive) defeat of Republican incumbent Henry Bonilla was seen as proof of a leftward lurch among Latino voters, as heavily Latino counties overwhelmingly backed Rodriguez, and heavily Anglo counties overwhelmingly backed Bonilla.
Although during 2008 the economy and employment were top concerns for Hispanics and Latinos, immigration was "never far from their minds": almost 90% of Latino voters rated immigration as "somewhat important" or "very important" in a poll taken after the election.[118] There is "abundant evidence" that the heated Republican opposition to the Comprehensive Immigration Reform Act of 2007 has done significant damage to the party's appeal to Hispanics and Latinos in the years to come, especially in the swing states such as Florida, Nevada, and New Mexico.[118] In a Gallup poll of 4,604 registered Hispanic voters taken in the final days of June 2008, only 18% of participants identified themselves as Republicans.[119]
2008 election
In the 2008 Presidential election's Democratic primary Hispanics and Latinos participated in larger numbers than before, with Hillary Clinton receiving most of the group's support.[120] Pundits discussed whether a large percentage of Hispanics and Latinos would vote for an African American candidate, in this case Barack Obama, Clinton's opponent.[121] Hispanics/Latinos voted 2 to 1 for Mrs. Clinton, even among the younger demographic, which in the case of other groups was an Obama stronghold.[122] Among Hispanics, 28% said race was involved in their decision, as opposed to 13% for (non-Hispanic) whites.[122]
Obama defeated Clinton. In the matchup between Obama and Republican candidate John McCain for the presidency, Hispanics and Latinos supported Obama with 59% to McCain's 29% in the Gallup tracking poll as of June 30, 2008.[119] This surprised some analysts, since a higher than expected percentage of Latinos and Hispanics favored Obama over McCain, who had been a leader of the comprehensive immigration reform effort.[123] However, McCain had retracted during the Republican primary, stating that he would not support the bill if it came up again. Some analysts believed that this move hurt his chances among Hispanics and Latinos.[124] Obama took advantage of the situation by running ads aimed at the ethnic group, in Spanish, in which he mentioned McCain's about-face.[125]
In the general election, 67% of Hispanics and Latinos voted for Obama[126] and 31% voted for McCain,[127] with a relatively stronger turnout than in previous elections in states such as Colorado, New Mexico, Nevada, and Virginia helping Obama carry those formerly Republican states. Obama won 70% of non-Cuban Hispanics and 35% of the traditionally Republican Cuban Americans that have a strong presence in Florida, while the changing state demographics towards a more non-Cuban Hispanic community also contributed to his carrying Florida's Latinos with 57% of the vote.[126][128] Hispanics and Latinos also supplanted Republican gains in traditional red states, for example Obama carried 63% of Texas Latinos, despite that the overall state voted for McCain by 55%.[129]
Some political organizations associated with Hispanic and Latino Americans are LULAC, the NCLR, the United Farm Workers, the Cuban American National Foundation, and the National Institute for Latino Policy.
2012 election
Hispanic and Latinos went even more heavily for Democrats in the 2012 election with the Democratic incumbent Barack Obama receiving 71% and the Republican challenger Mitt Romney receiving about 27% of the vote.[130][131]
Culture
The geographic, political, social, economic, and racial other diversity of Hispanic and Latino Americans extends to culture, as well. Yet several features tend to unite Hispanics and Latinos from these diverse backgrounds.
Language

With 40% of Hispanic and Latino Americans being immigrants,[132] and with many of the 60% who are U.S.-born being the children or grandchildren of immigrants, bilingualism is the norm in the community at large: at home, at least 69% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans over age five are bilingual in English and Spanish, whereas up to 22% are monolingual English-speakers, and 9% are monolingual Spanish-speakers; another 0.4% speak a language other than English and Spanish at home.[133]
In all, a full 90% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans speak English, and at least 78% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans speak Spanish.[133] Spanish is the oldest European language in the United States, spoken uninterruptedly for four and a half centuries, since the foundation of St. Augustine.[36][37][38][39]
The usual pattern is monolingual Spanish use among new migrants or older foreign-born Hispanics, complete bilingualism among long-settled immigrants and the children of immigrants, and the sole use of English, or both English and either Spanglish or colloquial Spanish by the third generation and beyond.
Religion

The most methodologically rigorous study of Hispanic or Latino religious affiliation to date was the Hispanic Churches in American Public Life (HCAPL) National Survey, conducted between August and October 2000. This survey found that 70% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans are Catholic, 20% are Protestant, 3% are "alternative Christians" (such as Mormon or Jehovah's Witnesses), 1% identify with a non-Christian religion (including Muslims), and 6% have no religious preference (with only 0.37% claiming to be atheist or agnostic). This suggests that Hispanics/Latinos are not only a highly religious, but also a highly Christian constituency.
It also suggests that Hispanic/Latino Protestants are a more sizable minority than sometimes realized. Catholic affiliation is much higher among first-generation than second- or third-generation Hispanic or Latino immigrants, who exhibit a fairly high rate of defection to Protestantism. Also Hispanics and Latinos in the Bible Belt, which is mostly located in the South, are more likely to defect to Protestantism than those in other regions. Examples of Protestant denominations that experiencing an inflow of Hispanic/Latino converts are Pentecostalism[134][135] and the Episcopal Church.[136][137] Hispanic or Latino Catholics are also increasingly working to enhance member retention through youth and social programs and through the spread of the Catholic Charismatic Renewal.[138]
Media

The United States is home to thousands of Spanish-language media outlets, which range in size from giant commercial and some non-commercial broadcasting networks and major magazines with circulations numbering in the millions, to low-power AM radio stations with listeners numbering in the hundreds. There are hundreds of Internet media outlets targeting U.S. Hispanic consumers. Some of the outlets are online versions of their printed counterparts and some online exclusively.
Among the most noteworthy Hispanic/Latino-oriented media outlets are:
- Univisión, the largest Spanish-language television network[disambiguation needed] in the United States, with affiliates in nearly every major U.S. market, and numerous affiliates internationally;
- Telemundo, the second-largest Spanish-language television network in the United States, with affiliates in nearly every major U.S. market, and numerous affiliates internationally;
- Azteca América, a Spanish-language television network in the United States, with affiliates in nearly every major U.S. market, and numerous affiliates internationally;
- La Opinión, a Spanish-language daily newspaper published in Los Angeles, California and distributed throughout the six counties of Southern California. It is the largest Spanish-language newspaper in the United States;
- El Nuevo Herald and Diario Las Américas, both Spanish-language daily newspapers serving the greater Miami, Florida market;
- La Voz de Indiana, a bilingual (English and Spanish) publication based in Indianapolis, Indiana;
- Hispanic Business, an English-language business magazine about Hispanics;
- mun2, a cable network that produces content for U.S.-born Hispanic and Latino audiences;
- People en Español, a Spanish-language magazine counterpart of People;
- ConSentido TV, a television, radio, and newspaper network in North Texas;
- TBN Enlace USA, a Spanish-language Christian television network based in Tustin, California;
- 3ABN Latino, a Spanish-language Christian television network based in West Frankfort, Illinois;
- CNN en Español, a Spanish-language all-news television network based in Atlanta, Georgia;
- Vida Latina, a Spanish-language entertainment magazine distributed throughout the Southern United States.
- ESPN Deportes and Fox Deportes, two Spanish-language sports television networks.
Intermarriage
Hispanic Americans, like immigrant groups before them, are out-marrying at very high rates comprising 17.4% of all existing Hispanic marriages in 2008.[140] The rate is higher for newlyweds (which excludes immigrants who are already married): Among all newlyweds in 2010, 25.7% of all Hispanics married a non-Hispanic (this compares to out-marriage rates of 9.4% of whites, 17.1% of blacks, and 27.7% of Asians). The rate was even more profound for native-born Hispanics with 36.2% of native-born Hispanics (both men and women) out-marrying compared to 14.2% of foreign-born Hispanics.[141] The difference is attributed to the fact that recent immigrants tend to marry within their immediate immigrant community due to commonality of language, proximity, familial connections, and familiarity.[140]
In 2008, 81% of Hispanics who intermarried married non-Hispanic Whites, 9% married non-Hispanic Blacks, 5% non-Hispanic Asians, and the remainder married non-Hispanic, multi-racial partners.[140]
Of the 275,500 new intermarried pairings in 2010, 43.3% were White-Hispanic (compared to White-Asian at 14.4%, White-Black at 11.9%, and Other Combinations at 30.4%; other combinations consists of pairings between different minority groups, multi-racial people, and American Indians).[141] Unlike blacks and Asians, intermarriage rates between White and Hispanic newlyweds do not vary by gender. The combined median earnings of White/Hispanic couples are lower than those of White/White couples but higher than those of Hispanic/Hispanic couples. 23% of Hispanic men who married White women have a college degree compared to only 10% of Hispanic men who married a Hispanic woman. 33% of Hispanic women who married a White husband are college-educated compared to 13% of Hispanic women who married a Hispanic man.[141]
Attitudes amongst non-Hispanics toward intermarriage with Hispanics are mostly favorable with 81% of Whites, 76% of Asians, and 73% of Blacks "being fine" with a member of their family marrying a Hispanic and an additional 13% of Whites, 19% of Asians, and 16% of Blacks "being bothered but accepting of the marriage." Only 2% of Whites, 4% of Asians, and 5% of Blacks would not accept a marriage of their family member to a Hispanic.[140]
Hispanic attitudes toward intermarriage with non-Hispanics are likewise favorable with 71% "being fine" with marriages to Whites and 81% "being fine" with marriages to Blacks. A further 22% admitted to "being bothered but accepting" of a marriage of a family member to a White and 16% admitted to "being bothered but accepting" of a marriage of a family member to a Black. Only 3% of Hispanics objected outright marriage of a family member to a non-Hispanic Black and 3% to a non-Hispanic White.[140]
Notables and their contributions
Hispanic and Latino Americans have made distinguished contributions to the United States in all major fields, such as politics, the military, music, literature, philosophy, sports, business and economy, and science.[142]
Business

The total number of Hispanic-owned businesses in 2002 was 1.6 million, having grown at triple the national rate for the preceding five years.[58]

Hispanic and Latino business leaders include Cuban immigrant Roberto Goizueta, who rose to head of The Coca-Cola Company.[144] Advertising magnate Arte Moreno became the first Hispanic to own a major league team in the United States when he purchased the Los Angeles Angels baseball club.[145] Also a major sports team owner is Linda G. Alvarado, president and CEO of Alvarado Construction, Inc and co-owner of the Colorado Rockies baseball team.
The largest Hispanic-owned food company in the US is Goya Foods, because of World War II hero Joseph A. Unanue, the son of the company's founders.[146] Angel Ramos was the founder of Telemundo, Puerto Rico's first television station[147] and now the second largest Spanish-language television network in the United States, with an average viewership over one million in primetime. Samuel A. Ramirez, Sr. made Wall Street history by becoming the first Hispanic to launch a successful investment banking firm, Ramirez & Co.[148][149] Nina Tassler is president of CBS Entertainment since September 2004. She is the highest-profile Latina in network television and one of the few executives who has the power to approve the airing or renewal of series.
Government and politics

As of 2007 there were more than five thousand elected officeholders in the United States who were of Latino origin.[150]
In the House of Representatives, Hispanic and Latino representatives have included Ladislas Lazaro, Antonio M. Fernández, Henry B. Gonzalez, Kika de la Garza, Herman Badillo, Romualdo Pacheco, and Manuel Lujan, Jr., out of almost two dozen former Representatives. Current Representatives include Luis Gutiérrez, Ileana Ros-Lehtinen, Nydia Velázquez, Joe Baca, Loretta Sanchez, Silvestre Reyes, Rubén Hinojosa, Linda Sánchez, and John Salazar—in all, they number twenty-three. Former senators are Octaviano Ambrosio Larrazolo, Mel Martinez, Dennis Chavez, Joseph Montoya, and Ken Salazar. As of January 2011, the U.S. Senate includes Hispanic members Bob Menendez, a Democrat, and Marco Rubio, a Republican.[151]
Numerous Hispanics and Latinos hold elective and appointed office in state and local government throughout the United States.[152] Current Hispanic Governors include Republican Nevada Governor Brian Sandoval and Republican New Mexico Governor Susana Martinez; upon taking office in 2011, Martinez became the first Latina governor in the history of the United States.[153] Former Hispanic governors include Democrats Jerry Apodaca, Raul Hector Castro, and Bill Richardson, as well as Republicans Octaviano Ambrosio Larrazolo, Romualdo Pacheco, and Bob Martinez.
Since 1988,[154] when Ronald Reagan appointed Lauro Cavazos the Secretary of Education, the first Hispanic United States Cabinet member, Hispanic Americans have had an increasing presence in presidential administrations. Hispanics serving in subsequent cabinets include Ken Salazar, current Secretary of the Interior; Hilda Solis, current United States Secretary of Labor; Alberto Gonzales, former United States Attorney General; Carlos Gutierrez, Secretary of Commerce; Federico Peña, former Secretary of Energy; Henry Cisneros, former Secretary of Housing and Urban Development; Manuel Lujan, Jr., former Secretary of the Interior; and Bill Richardson, former Secretary of Energy and Ambassador to the United Nations. Six of the last ten US Treasurers, including the latest three, are Hispanic women.
In 2009, Sonia Sotomayor became the first Supreme Court Associate Justice of Hispanic or Latino origin.
The Congressional Hispanic Caucus (CHC), founded in December 1976, and the Congressional Hispanic Conference (CHC), founded on March 19, 2003, are two organizations that promote policy of importance to Americans of Hispanic descent. They are divided into the two major American political parties: The Congressional Hispanic Caucus is composed entirely of Democratic representatives, whereas the Congressional Hispanic Conference is composed entirely of Republican representatives.
Literature and journalism
Among the distinguished Hispanic and Latino authors and their works may be noted:
- Isabel Allende (The House of the Spirits and City of the Beasts)
- Sandra Cisneros (The House on Mango Street and Woman Hollering Creek and Other Stories)
- Julia Alvarez ("How the García Girls Lost Their Accents")
- Jorge Majfud Crisis
- Rudolfo Anaya (Bless Me, Ultima and Heart of Aztlan)
- Giannina Braschi (Empire of Dreams, Yo-Yo Boing!, and United States of Banana)
- Junot Díaz (The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao)
- Frank X Gaspar (Leaving Pico)
- Rigoberto González (Butterfly Boy: Memories of a Chicano Mariposa)
- Jovita González de Mireles (Caballero, cowritten with Eve Raleigh, and Dew On The Thorn)
- Oscar Hijuelos (The Mambo Kings Play Songs of Love)
- Micol Ostow ("Mind Your Manners, Dick and Jane", "Emily Goldberg Learns to Salsa")[155]
- Benito Pastoriza Iyodo (A Matter of Men and September Elegies)
- Tomas Rivera (...And the Earth did Not Devour Him)
- Richard Rodriguez (Hunger of Memory)
- Rubén Salazar (journalist)
- George Santayana (novelist and philosopher: "Those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it")
- Sergio Troncoso (From This Wicked Patch of Dust and The Last Tortilla and Other Stories)
- Alisa Valdes-Rodriguez (Haters)
- Victor Villaseñor (Rain of Gold)
- Oscar Zeta Acosta (The Revolt of the Cockroach People)
- Guadalupe Baca-Vaughn (The Souls in Purgatory)
Military and intelligence







Hispanics and Latinos have participated in the military of the United States and in every major military conflict from the American Revolution onward.[156] Tens of thousands of Latinos are deployed in the Iraq War, the Afghanistan War, and U.S. military missions and bases elsewhere. Hispanics and Latinos have not only distinguished themselves in the battlefields but also reached the high echelons of the military, serving their country in sensitive leadership positions on domestic and foreign posts.Up to now, 43 Hispanics and Latinos have been awarded the nation's highest military distinction, the Medal of Honor (also known as the Congressional Medal of Honor). The following is a list of some notable Hispanics/Latinos in the military:
- American Revolution
- Lieutenant Jorge Farragut Mesquida (1755–1817)-Participated in the American Revolution as a lieutenant in the South Carolina Navy.
- American Civil War
- Admiral David Farragut- Farragut was promoted to vice admiral on December 21, 1864, and to full admiral on July 25, 1866, after the war, thereby becoming the first person to be named full admiral in the Navy's history.[157]
- Colonel Ambrosio José Gonzales - Gonzales was active during the bombardment of Fort Sumter and because of his actions was appointed Colonel of artillery and assigned to duty as Chief of Artillery in the department of South Carolina, Georgia and Florida.
- Brigadier General Diego Archuleta (1814–1884) - was a member of the Mexican Army who fought against the United States in the Mexican American War. During the American Civil War he joined the Union Army (US Army) and became the first Hispanic to reach the military rank of Brigadier General. He commanded The First New Mexico Volunteer Infantry in the Battle of Valverde.He was later appointed an Indian (Native Americans) Agent by Abraham Lincoln.[158]
- Colonel Carlos de la Mesa - Grandfather of Major General Terry de la Mesa Allen, Sr. commanding general of the First Infantry Division in North Africa and Sicily, and later the commander of the 104th Infantry Division during World War II. Colonel Carlos de la Mesa was a Spanish national who fought at Gettysburg for the Union Army in the Spanish Company of the "Garibaldi Guard" of the 39th New York State Volunteers.[159]
- Colonel Federico Fernández Cavada - Commanded the 114th Pennsylvania Volunteer infantry regiment when it took the field in the Peach Orchard at Gettysburg.[160]
- Colonel Miguel E. Pino - Commanded the 2nd Regiment of New Mexico Volunteers, which fought at the Battle of Valverde in February and the Battle of Glorieta Pass and helped defeat the attempted invasion of New Mexico by the Confederate Army.[161]
- Colonel Santos Benavides - Commanded his own regiment, the "Benavides Regiment." He was the highest ranking Mexican-American in the Confederate Army.[160]
- Major Salvador Vallejo - Officer in one of the California units that served with the Union Army in the West.[161]
- Captain Adolfo Fernández Cavada - Cavada served in the 114th Pennsylvania Volunteers at Gettysburg with his brother, Colonel Federico Fernandez Cavada. He served with distinction in the Army of the Potomac from Fredericksburg to Gettysburg and was a "special aide-de-camp" to General Andrew A. Humphreys.[160][162]
- Captain Roman Anthony Baca - Member of the Union forces in the New Mexico Volunteers. He also served as a spy for the Union Army in Texas.[161]
- Lieutenant Augusto Rodriguez - A Puerto Rican native who served as an officer in the 15th Connecticut Volunteer Infantry, of the Union Army. Rodríguez served in the defenses of Washington, D.C. and led his men in the Battles of Fredericksburg and Wyse Fork.[163]
- Lola Sánchez - Sánchez was a Cuban born woman who became a Confederate spy who helped the Confederates obtain a victory against the Union Forces in the "Battle of Horse Landing".
- Loreta Janeta Velazquez as known as "Lieutenant Harry Buford"- She was a Cuban woman who donned Confederate garb and served as a Confederate officer and spy during the American Civil War.
- World War I
- Major General Luis R. Esteves, U.S. Army- In 1915, Esteves became the first Hispanic to graduate from the United States Military Academy ("West Point"). Esteves also organized the Puerto Rican National Guard.
- First Lieutenant Félix Rigau Carrera, known as "El Aguila de Sabana Grande" (The Eagle from Sabana Grande)-Was the first Hispanic fighter pilot in the United States Marine Corps.[164]
- Private Marcelino Serna- Was an undocumented Mexican immigrant who joined the United States Army and became the most decorated soldier from Texas in World War I. Serna was the first Hispanic to be awarded the Distinguished Service Cross.
- World War II
- Lieutenant General Pedro del Valle- the first Hispanic to reach the rank of Lieutenant General. He played an instrumental role in the seizure of Guadalcanal and Okinawa as Commanding General of the U.S. 1st Marine Division during World War II.
- Lieutenant General Elwood R. Quesada (1904–1993) - Commanding general of the 9th Fighter Command, where he established advanced headquarters on the Normandy beachhead on D-Day plus one, and directed his planes in aerial cover and air support for the Allied invasion of the European continent during World War II. He was the foremost proponent of "the inherent flexibility of air power", a principle he helped prove during the war.
- Major General Terry de la Mesa Allen, Sr. (1888–1969) - was the commanding general of the 1st Infantry Division in North Africa and Sicily during World War II, and was made commander of the 104th Infantry Division.
- Colonel Virgil R. Miller - was the Regimental Commander of the 442d Regimental Combat Team, a unit that was composed of "Nisei" (second generation Americans of Japanese descent), during World War II. He led the 442nd in its rescue of the Lost Texas Battalion of the 36th Infantry Division, in the forests of the Vosges Mountains in northeastern France.[165][166]
- Captain Marion Frederic Ramírez de Arellano (1913–1980) - served in World War II and was the first Hispanic submarine commander.
- First Lieutenant Oscar Francis Perdomo, of the 464th Fighter Squadron, 507th Fighter Group was the last "Ace in a Day" for the United States in World War II.
- CWO2 Joseph B. Aviles, Sr.- a member of the United States Coast Guard and the first Hispanic-American to be promoted to Chief Petty Officer, received a war-time promotion to Chief Warrant Officer (November 27, 1944), thus becoming the first Hispanic American to reach that level as well.[167]
- Sergeant First Class Agustín Ramos Calero- was the most decorated Hispanic soldier in the European Theatre of World War II.
- PFC Guy Gabaldon, USMC - captured over a thousand prisoners during the World War II Battle of Saipan.
- Tech4 Carmen Contreras-Bozak - the first Hispanic to serve in the U.S. Women's Army Corps where she served as an interpreter and in numerous administrative positions.[168]
- Korean War
- Major General Salvador E. Felices, U.S. Air Force - In 1953, Felices flew in 19 combat missions over North Korea, during the Korean War. In 1957, he participated in "Operation Power Flite", a historic project that was given to the Fifteenth Air Force by the Strategic Air Command headquarters. Operation Power Flite was the first around the world non-stop flight by an all-jet aircraft.
- First Lieutenant Baldomero Lopez- is the only Hispanic graduate of the United States Naval Academy ("Annapolis") to be awarded the Medal of Honor.
- Sergeant First Class Modesto Cartagena- was a member of the 65th Infantry Regiment, an all-Puerto Rican regiment also known as "The Borinqueneers", during World War II and the Korean War. He was the most decorated Puerto Rican soldier in history.[169]
- Cuban Missile Crisis
- Admiral Horacio Rivero, Jr.- second Hispanic four-star Admiral, was the commander of the American fleet sent by President John F. Kennedy to set up a quarantine (blockade) of the Soviet ships during the Cuban Missile Crisis.
- Vietnam War
- Sergeant First Class Jorge Otero Barreto a.k.a. "The Puerto Rican Rambo"- was the most decorated Hispanic American soldier in the Vietnam War[170]
- Post-Vietnam
- Lieutenant General Ricardo Sanchez- top commander of the Coalition forces during the first year of the occupation of Iraq, 2003–2004, during the Iraq War
- Lieutenant General Edward D. Baca- In 1994, Baca became the first Hispanic Chief of the National Guard Bureau.
- Vice Admiral Antonia Novello, M.D., Public Health Service Commissioned Corps- In 1990, Novello became the first Hispanic (and first female) U.S. Surgeon General.
- Vice Admiral Richard Carmona, M.D., Public Health Service Commissioned Corps- Carmona served as the 17th Surgeon General of the United States, under President George W. Bush.
- Brigadier General Joseph V. Medina, USMC -made history by becoming the first Marine Corps officer to take command of a Naval flotilla.
- Rear Admiral Ronald J. Rábago is the first person of Hispanic American descent to be promoted to Rear Admiral (lower half) in the United States Coast Guard.[171]
- Captain Linda Garcia Cubero, United States Air Force- in 1980 became the first Hispanic woman graduate of the United States Air Force.
- Major General Erneido Oliva. He was appointed to the position of Deputy Commanding General of the D.C. National Guard.
- Brigadier General Carmelita Vigil-Schimmenti, United States Air Force- in 1985 became the first Hispanic female to attain the rank of Brigadier General in the Air Force.[172][173]
- On August 2, 2006, Brigadier General Angela Salinas, made history when she became the first Hispanic female to obtain a general rank in the Marines.[174]
- Chief Master Sergeant Ramón Colón-López is pararescueman who in 2007, was the only Hispanic among the first six airmen to be awarded the newly created Air Force Combat Action Medal.
Medal of Honor
The following 43 Hispanics were awarded the Medal of Honor:
Philip Bazaar, Joseph H. De Castro, John Ortega, France Silva, David B. Barkley, Lucian Adams, Rudolph B. Davila, Marcario Garcia, Harold Gonsalves, David M. Gonzales, Silvestre S. Herrera, Jose M. Lopez, Joe P. Martinez, Manuel Perez Jr., Cleto L. Rodriguez, Alejandro R. Ruiz, Jose F. Valdez, Ysmael R. Villegas, Fernando Luis García, Edward Gomez, Ambrosio Guillen, Rodolfo P. Hernandez, Baldomero Lopez, Benito Martinez, Eugene Arnold Obregon, Joseph C. Rodriguez, John P. Baca, Roy P. Benavidez, Emilio A. De La Garza, Ralph E. Dias, Daniel Fernandez, Alfredo Cantu "Freddy" Gonzalez, Jose Francisco Jimenez, Miguel Keith, Carlos James Lozada, Alfred V. Rascon, Louis R. Rocco, Euripides Rubio, Hector Santiago-Colon, Elmelindo Rodrigues Smith, Jay R. Vargas, Humbert Roque Versace, and Maximo Yabes.
National intelligence
- In the spy arena, Jose Rodriguez, a native of Puerto Rico, was the Deputy Director of Operations and subsequently Director of the National Clandestine Service (D/NCS), two senior positions in the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), between 2004 and 2007.[175]
- Lieutenant Colonel Mercedes O. Cubria (1903–1980), a.k.a. La Tia (The Aunt), was the first Cuban-born female officer in the U.S. Army. She served in the Women's Army Corps during World War II, in the U.S. Army during the Korean War, and was recalled into service during the Cuban Missile Crisis. In 1988, she was posthumously inducted into the Military Intelligence Hall of Fame.[176]
Performing arts
In 1995, the American Latino Media Arts Award, or ALMA Award was created. It's a distinction given to Latino performers (actors, film and television directors, and musicians) by the National Council of La Raza.
Music

There are many Hispanic American musicians that have achieved international fame, such as Jennifer López, Joan Baez, Linda Ronstadt, Zack de la Rocha, Fergie, Gloria Estefan, Kat DeLuna, Selena, Ricky Martin, Marc Anthony, Carlos Santana, Christina Aguilera, Los Lonely Boys, Frankie J, Jerry García, Robert Trujillo, Aventura and Tom Araya.
Among the Hispanic American musicians who were pioneers in the early stages of rock and roll were Ritchie Valens, who scored several hits, most notably "La Bamba" and Herman Santiago wrote the lyrics to the iconic rock and roll song "Why Do Fools Fall in Love". Another song that became popular in the United States and is heard during the Holiday/Christmas season is "Feliz Navidad" by José Feliciano.
The most prestigious Latin music awards are the Latin Grammy Awards, launched in 2000. Billboard Magazine also honors these artists, with the Billboard Latin Music Awards. The latter's nominees and winners are a result of performance on Billboard's sales and radio charts, while the Latin Grammy Awards nominees and winners are selected by the Latin Academy of Recording Arts & Sciences (LARAS).
Film, radio, stage, and television
Hispanics and Latinos have also contributed some prominent actors and others in the film industry, a few of whom includes actors José Ferrer, the first Hispanic actor to win an Academy Award for his role in Cyrano de Bergerac, Anthony Quinn, Cameron Diaz, Martin Sheen, Cheech Marín, Salma Hayek, Dolores del Río, Anita Page, Rita Hayworth, Antonio Banderas, Raquel Welch, Benicio del Toro, Eva Mendes, Zoe Saldana, Edward James Olmos, Maria Montez, Ramón Novarro, Ricardo Montalbán, Cesar Romero, Rosie Perez, Katy Jurado, Rita Moreno, Lupe Vélez, Esai Morales, Andy García, Rosario Dawson, John Leguizamo, and, behind the camera, directors Robert Rodriguez, Guillermo del Toro, Alfonso Cuarón and Brett Ratner (also producers and cinematographers) and Luis Valdez.
In standup comedy, Paul Rodríguez, Greg Giraldo, Cheech Marin, George Lopez, Freddie Prinze, Carlos Mencia, John Mendoza, and others are prominent.
Some of the Hispanic or Latino actors who achieved notable success in U.S. television include Desi Arnaz, Lynda Carter, Jimmy Smits, Selena Gómez, Carlos Pena, Jr., Eva Longoria, George Lopez, Benjamin Bratt, Ricardo Montalbán, America Ferrera, Erik Estrada, Cote de Pablo, Freddie Prinze, Lauren Vélez, and Charlie Sheen. Kenny Ortega is an Emmy Award-winning producer, director, and choreographer who has choreographed many major television events such as Super Bowl XXX, the 72nd Academy Awards, and Michael Jacksons memorial service.
Hispanics and Latinos are underrepresented in U.S. television, radio, and film. This is combatted by organizations such as the Hispanic Organization of Latin Actors (HOLA), founded in 1975; and National Hispanic Media Coalition (NHMC), founded in 1986.[177] Together with numerous Latino civil rights organizations, the NHMC led a "brownout" of the national television networks in 1999, after discovering that there were no Latinos in any of their new prime time shows that year.[178] This resulted in the signing of historic diversity agreements with ABC, CBS, Fox, and NBC that have since increased the hiring of Hispanic and Latino talent and other staff in all of the networks.
Latino Public Broadcasting (LPB) funds programs of educational and cultural significance to Hispanic Americans. These programs are distributed to various public television stations throughout the United States.
-
Robert Rodriguez is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, cinematographer, editor and musician.
-
Myrtle González is considered the first female Latin star in Hollywood.[179]
-
Anita Page, who is of Salvadoran ancestry, was referred to as "the girl with the most beautiful face in Hollywood" in the 1920s.
-
In 2010, Forbes ranked Cameron Diaz as the richest Hispanic female celebrity, ranking number 60 among the top 100.[180][181]
Fashion
In the world of fashion, notable Hispanic and Latino designers include Oscar de la Renta, Carolina Herrera, and Narciso Rodríguez among others. Christy Turlington and Lea T achieved international fame as models.
Science and technology

Among Hispanic Americans who have excelled in science are Luis Walter Álvarez, Nobel Prize–winning physicist, and his son Walter Alvarez, a geologist. They first proposed that an asteroid impact on the Yucatán Peninsula caused the extinction of the dinosaurs. Dr. Victor Manuel Blanco is an astronomer who in 1959 discovered "Blanco 1", a galactic cluster.[182] F. J. Duarte is a laser physicist and author; he received the Engineering Excellence Award from the prestigious Optical Society of America for the invention of the N-slit laser interferometer.[183] Francisco J. Ayala is a biologist and philosopher, former president of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, and has been awarded the National Medal of Science and the Templeton Prize.

Dr. Fernando E. Rodríguez Vargas discovered the bacteria that cause dental cavity. Dr. Gualberto Ruaño is a biotechnology pioneer in the field of personalized medicine and the inventor of molecular diagnostic systems, Coupled Amplification and Sequencing (CAS) System, used worldwide for the management of viral diseases.[184] Fermín Tangüis was an agriculturist and scientist who developed the Tangüis Cotton in Peru and saved that nation's cotton industry.[185] Severo Ochoa, born in Spain, was a co-winner of the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Some Hispanics and Latinos have made their names in astronautics, including several NASA astronauts:[186] Franklin Chang-Diaz, the first Latin American NASA astronaut, is co-recordholder for the most flights in outer space, and is the leading researcher on the plasma engine for rockets; France A. Córdova, former NASA chief scientist; Juan R. Cruz, NASA aerospace engineer; Lieutenant Carlos I. Noriega, NASA mission specialist and computer scientist; Dr. Orlando Figueroa, mechanical engineer and Director of Mars Exploration in NASA; Amri Hernández-Pellerano, engineer who designs, builds and tests the electronics that will regulate the solar array power in order to charge the spacecraft battery and distribute power to the different loads or users inside various spacecraft at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center.
Mercedes Reaves, research engineer and scientist who is responsible for the design of a viable full-scale solar sail and the development and testing of a scale model solar sail at NASA Langley Research Center. Dr. Pedro Rodríguez, inventor and mechanical engineer who is the director of a test laboratory at NASA and of a portable, battery-operated lift seat for people suffering from knee arthritis. Dr. Felix Soto Toro, electrical engineer and astronaut applicant who developed the Advanced Payload Transfer Measurement System (ASPTMS) (Electronic 3D measuring system); Ellen Ochoa, a pioneer of spacecraft technology and astronaut; Joseph Acaba, Fernando Caldeiro, Sidney Gutierrez, Jose Hernández, Michael López-Alegría, John Olivas, and George Zamka, who are current or former astronauts.
Sports

The large number of Hispanic and Latino American stars in Major League Baseball (MLB) includes players like Ted Williams (considered by many to be the greatest hitter of all time), Miguel Cabrera, Lefty Gómez, Iván Rodríguez, Carlos Gonzalez, Roberto Clemente, Adrian Gonzalez, David Ortiz, Fernando Valenzuela, Nomar Garciaparra, Albert Pujols, Omar Vizquel, managers Al López, Ozzie Guillén, and Felipe Alou, and General Manager Omar Minaya.
There have been far fewer football and basketball players, let alone star players, but Tom Flores was the first Hispanic head coach and the first Hispanic quarterback in American professional football, and won Super Bowls as a player, as assistant coach and as head coach for the Oakland Raiders. Anthony Múñoz is enshrined in the Pro Football Hall of Fame, ranked #17 on Sporting News's 1999 list of the 100 greatest football players, and was the highest-ranked offensive lineman. Jim Plunkett won the Heisman Trophy and was inducted into the College Football Hall of Fame, and Joe Kapp is inducted into the Canadian Football Hall of Fame and College Football Hall of Fame. Steve Van Buren, Martin Gramatica, Victor Cruz, Tony Gonzalez, Marc Bulger, Tony Romo and Mark Sanchez can also be cited among successful Hispanics and Latinos in the National Football League (NFL).
Trevor Ariza, Mark Aguirre, Carmelo Anthony, Manu Ginobili, Carlos Arroyo, Gilbert Arenas, Rolando Blackman, Pau Gasol, Jose Calderon, José Juan Barea and Charlie Villanueva can be cited in the National Basketball Association (NBA). Dick Versace made history when he became the first person of Hispanic heritage to coach an NBA team. Rebecca Lobo was a major star and champion of collegiate (National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA)) and Olympic basketball and played professionally in the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA). Diana Taurasi became just the seventh player ever to win an NCAA title, a WNBA title, and as well an Olympic gold medal. Orlando Antigua became in 1995 the first Hispanic and the first non-black in 52 years to play for the Harlem Globetrotters.
Boxing's first Hispanic world champion was Panama Al Brown. Some other champions include Oscar De La Hoya, Miguel Cotto, Bobby Chacon, Joel Casamayor, Michael Carbajal, John Ruiz, and Carlos Ortiz.
Ricco Rodriguez, Tito Ortiz, Diego Sanchez, Nick Diaz, Nathan Diaz' Dominick Cruz, Frank Shamrock, Gilbert Melendez, Roger Huerta, Carlos Condit, Kelvin Gastelum, and UFC Heavy Weight Champion Cain Velasquez have been competitors in the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) of mixed martial arts.
In 1991 Bill Guerin whose mother is Nicaraguan became the first Hispanic player in the National Hockey League (NHL). He was also selected to four NHL All-Star Games. In 1999 Scott Gomez won the NHL Rookie of the Year Award.[187]
Tennis legend Pancho Gonzales and Olympic tennis champions and professional players Mary Joe Fernández and Gigi Fernández; soccer players in the Major League Soccer (MLS) Tab Ramos, Claudio Reyna, Marcelo Balboa and Carlos Bocanegra; figure skater Rudy Galindo; golfers Chi Chi Rodríguez, Nancy López, and Lee Trevino; softball player Lisa Fernández; and Paul Rodríguez Jr., X Games professional skateboarder, are all Hispanic or Latino Americans who have distinguished themselves in their sports.
In sports entertainment we find the professional wrestlers Alberto Del Rio, Rey Mysterio, Eddie Guerrero, Tyler Black and Melina Pérez, and executive Vickie Guerrero.
See also
Places of settlement in United States:
- List of U.S. communities with Hispanic majority populations in the 2010 census
- List of U.S. cities with large Hispanic population
- List of U.S. cities by Spanish-speaking population
- Hispanic and Latino Americans in California
- Hispanic and Latino Americans in Arizona
- Hispanic and Latino Americans in New Mexico
- Hispanic and Latino Americans in Texas
- Hispanic and Latino Americans in Nevada
- Hispanic and Latino Americans in Florida
- National Alliance for Hispanic Health
Diaspora:
Individuals:
- List of Hispanic and Latino Americans
General:
Footnotes
- ^ a b c U.S. Catholic Hispanic Population Less Religious, Shrinking
- ^ Growing number of Latinos have no religious affiliation
- ^ http://www.census.gov/prod/cen2010/briefs/c2010br-02.pdf
- ^ a b US Census Bureau 2012 American Community Survey B03001 1-Year Estimates HISPANIC OR LATINO ORIGIN BY SPECIFIC ORIGIN retrieved September 20, 2013
- ^ Luis Fraga; John A. Garcia (2010). Latino Lives in America: Making It Home. Temple University Press. p. 145. ISBN 978-1-4399-0050-5.
- ^ Nancy L. Fisher (1996). Cultural and Ethnic Diversity: A Guide for Genetics Professionals. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-8018-5346-3.
- ^ Robert H. Holden; Rina Villars (2012). Contemporary Latin America: 1970 to the Present. John Wiley & Sons. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-118-27487-3.
- ^ a b "49 CFR Part 26". Retrieved 2012-10-22.
'Hispanic Americans,' which includes persons of Mexican, Puerto Rican, Cuban, Dominican, Central or South American, or other Spanish or Portuguese national, culture or origin, regardless of race;
- ^ a b "US Small Business Administration 8(a) Program Standard Operating Procedure" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-10-22.
SBA has defined 'Hispanic American' as an individual whose ancestry and culture are rooted in South America, Central America, Mexico, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, or the Iberian Peninsula, including Spain and Portugal.
- ^ Humes, Karen R.; Jones, Nicholas A.; Ramirez, Roberto R. "Overview of Race and Hispanic Origin: 2010" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-03-28.
"Hispanic or Latino" refers to a person of Cuban, Mexican, Puerto Rican, South or Central American, or other Spanish or Portuguese culture or origin regardless of race.
- ^ "American FactFinder Help: Hispanic or Latino origin". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
For Census 2000, American Community Survey: People who identify with the terms "Hispanic" or "Latino" are those who classify themselves in one of the specific Hispanic or Latino categories listed on the Census 2000 or ACS questionnaire - "Mexican," "Puerto Rican," or "Cuban" - as well as those who indicate that they are "other Spanish, Hispanic, or Latino." Origin can be viewed as the heritage, nationality group, lineage, or country of birth of the person or the person's parents or ancestors before their arrival in the United States. People who identify their origin as Spanish, Hispanic, or Latino may be of any "race".
1990 Census of Population and Housing: A self-designated classification for people whose origins are from Spain, the Spanish speaking countries of Central or South America, the Caribbean, or those identifying themselves generally as Spanish, Spanish-American, etc. Origin can be viewed as ancestry, nationality, or country of birth of the person or person's parents or ancestors prior to their arrival in the United States. - ^ a b c d e f Office of Management and Budget. "Revisions to the Standards for the Classification of Federal Data on Race and Ethnicity. Federal Register Notice October 30, 1997". Retrieved 2012-06-01.
- ^ a b c d e f g Grieco, Elizabeth M. "Overview of Race and Hispanic Origin: 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-04-27.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "B03001. Hispanic or Latino origin by specific origin". 2009 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-10-17.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Field Listing :: Ethnic groups". Retrieved 2010-11-18.
- ^ "T4-2007. Hispanic or Latino By Race [15]". 2007 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "B03002. Hispanic or Latino origin by race". 2007 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau.
- ^ Tafoya, Sonya (2004-12-06). "Shades of Belonging" (PDF). Pew Hispanic Center. Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- ^ Carlos Dejud (2007). The Relationship Among Ethnic Identity, Psychological Well-being, Academic Achievement, and Intergroup Competence of School-age Hispanic/Latino Youth. ProQuest. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-549-29853-3.
- ^ Timothy Ready (1991). Latino Immigrant Youth: Passages from Adolescence to Adulthood. Taylor & Francis. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-8153-0057-1.
- ^ "Latino: People with roots in the Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking Americas. This broader term, mostly used in the United States, is sometimes used as a replacement for Hispanic. http://csuchico-dspace.calstate.edu/handle/10211.4/222
- ^ http://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/mexicanamerica/glossary.html (Defining "Hispanic" as meaning those with Spanish speaking roots in the Americas and Spain, and "Latino" as meaning those with both Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking roots in Latin America.)
- ^ "'Latino' . . . 'is more inclusive and descriptive'" than Hispanic. "'Latino' is short for 'latinoamericano,' which of course means Latin American in Spanish. Like its English counterpart, the term 'latinoamericano' strictly refers to the people who come from the territory in the Americas colonized by Latin nations, such as Portugal, Spain, and France, whose languages are derived from Latin. People from Brazil, Mexico, and even Haiti are thus all 'latinoamericanos.' Individuals who are decendants of the former British or Dutch colonies are excluded. . . . Finally, 'hispanoamericanos' are persons from the former colonies of Spain in the 'New World.' The expression 'Hispanic' probably derives from 'hispanoamericanos.'" Angel R. Oquendo, Re-Imagining the Latino/a Race, 12 Harvard BlackLetter L.J. 93, 96 -97 (1995)
- ^ "[T]he term 'Latino' . . . is more inclusive and descriptive than the term 'Hispanic.'" Deborah A. Ramirez, Excluded Voices: The Disenfranchisement of Ethnic Groups From Jury Service, 1993 Wis. L. Rev. 761, 806 (1993).
- ^ http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0825/is_n3_v62/ai_18771519/.
{{cite news}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Anderson, Kevin (2008-10-18). "The complexity of race in New Mexico". The Guardian. London.
- ^ http://etd.auburn.edu/etd/bitstream/handle/10415/88/VITALE_MICHELE_14.pdf?sequence=1
- ^ "AP Stylebook Twitter". Retrieved 2012-04-06.
- ^ "Herald Style Guide". Retrieved 2012-04-06.
- ^ a b "Newsroom 101: Recent Changes to AP Style". Newsroom 101. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012. Retrieved 2012-04-06.
- ^ a b http://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12-90.html
- ^ http://www.rawstory.com/rs/2013/06/15/u-s-now-has-most-spanish-speakers-outside-mexico/
- ^ "Hispanics or Latinos: A Culture - Not a Race!". The Writing of F. Lennox Campello. Tripod.com. Retrieved 01-06-2009.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ United States - QT-P4. Race, Combinations of Two Races, and Not Hispanic or Latino: 2000
- ^ a b "American FactFinder Help; Spanish/Hispanic/Latino". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- ^ a b c Small, Lawrence M (2002-08-01). "Latino Legacies". Smithsonian Magazine. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2008-04-28.
There was a Hispanic presence on the continent for more than 200 years before 13 colonies on the eastern coast declared their independence from England.... By 1607, when the British established their first successful settlement, at Jamestown, Virginia, writes historian Bernard Bailyn, "Spain's American dominion extended nearly 8,000 miles, from Southern California to the Straits of Magellan...
- ^ a b c "A Brief History of St. Augustine". City of St. Augustine. Retrieved 2008-04-28.
Founded in 1565, St. Augustine is the oldest continuously occupied settlement of European origin in the United States. Forty-two years before the English colonized Jamestown and fifty-five years before the Pilgrims landed at Plymouth Rock, the Spanish established at St. Augustine this nation's first enduring settlement.
- ^ a b c "A Spanish Expedition Established St. Augustine in Florida". America's Library. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on May 24, 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-28.
On September 8, 1565, Pedro Menéndez de Avilés landed on the shore of what is now called Matanzas Bay and began the founding of the Presidio of San Agustin. Later the settlement would be called St. Augustine, Florida. Built on the site of an ancient Native American village, and near the place where Ponce de León, the European discoverer of Florida, landed in 1513 in search of the legendary Fountain of Youth, it has been continually inhabited since its founding.
- ^ a b c Francisco Lopez de Mendoza Grajales. "The Founding of St. Augustine, 1565". Modern History Sourcebook. Fordham University. Retrieved 2008-04-28.
- ^ The Encyclopedia Americana. Encyclopedia Americana Corp. 1919. p. 151.
- ^ "Documents in Mexican American History". University of Houston. Retrieved 2008-06-11.
- ^ "Cuartocentennial of Colonization of New Mexico". New Mexico State University. Retrieved 2008-06-11.
- ^ "Oldest U.S. City — Infoplease.com". Retrieved 2008-11-21.
- ^ "A Cultural Identity". 1997-06-18. Retrieved 2006-12-27.
- ^ a b Huffington Post: "Latino Or Hispanic? How The Federal Government Decided" By Grace Flores-Hughes September 19, 2013
- ^ U.S. Census website: US Census History - 1970 (Population): retrieved September 25, 2013
- ^
Gibson, Campbell (2002). "Historical Census Statistics on Population Totals By Race, 1790 to 1990, and By Hispanic Origin, 1970 to 1990, For The United States, Regions, Divisions, and States". Working Paper Series No. 56. Retrieved 2006-12-07.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Nicolás Kanellos; Thomas Weaver; Claudio Esteva Fabregat (1994). Handbook of Hispanic Cultures in the United States: Anthropology. Arte Publico Press. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-61192-161-8.
- ^ Jamie Martinez Wood (2007). Latino Writers and Journalists. Infobase Publishing. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-4381-0785-1.
- ^ Rochin, Refugio I. "U.S. Latino Patriots: From the American Revolution to Afghanistan, An Overview" (PDF). Pew Research Hispanic Center. Retrieved 2013-09-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) Latino denotes "the inclusion of the non-Spanish cultures of Latin America that have contributed immensely to the development and structure of present-day Latino cultural groups. These groups may include people of Latin American descent whose cultural heritage may be African, Asian, American Indian or indigenous, Middle Eastern and/or European." - ^ United States Census Bureau. "U.S. Census Bureau Guidance on the Presentation and Comparison of Race and Hispanic Origin Data". Retrieved 2007-03-18.
Race and Hispanic origin are two separate concepts in the federal statistical system. People who are Hispanic may be of any race. People in each race group may be either Hispanic or Not Hispanic. Each person has two attributes, their race (or races) and whether or not they are Hispanic.
- ^ http://2010.census.gov/2010census/about/interactive-form.php
- ^ http://www.census.gov/population/www/socdemo/hispanic/about.html
- ^ In contrast, some dictionary definitions may include Brazilian Americans or Brazilian people, or both in general.
- ^ "Select Population Groups". 2009 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates, Selected Population Profile. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-12-07.
- ^ "B03001. Hispanic or Latino Origin by Specific Origin". 2009 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-12-07.
- ^ "American Heritage Dictionary". Retrieved 2012-04-06.
- ^ a b "US Census Press Releases; Hispanic Heritage Month 2009: Sept. 15 – Oct. 15". Retrieved 2010-01-26. [dead link]
- ^ United States Census Bureau: "The Hispanic Population 2010 Census Brief: Table 1. "Hispanic or Latino Origin Population by Type: 2000 and 2010" May 2011
- ^ a b "T1. Population Estimates [10]; Data Set: 2007 Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-04-30.
- ^ "US Census Press Releases". United States Census Bureau. 2008-07-16. Archived from the original on March 23, 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-30.
- ^ USA Today: "Census: Hispanics surpass blacks in most U.S. metros" April 14, 2011
- ^ "Table 4. Projections of the Population by Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: 2010 to 2050" (Excel). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ^ "Hispanic Population by State: 2006" (PDF). Pew Hispanic Center. Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- ^ "US Census Press Releases; More Than 300 Counties Now "Majority-Minority"". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on April 19, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-18.
- ^ "Los Angeles County, California - ACS Demographic and Housing Estimates: 2006". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-05-18.
- ^ "Ten Places with Highest Percent Hispanic: 2000". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2009-04-05.
- ^ "Detailed Hispanic Origin: 2007" (PDF). Pew Hispanic Center. Retrieved 2009-05-30.
- ^ "United States - Selected Population Profile in the United States (Spaniard)". 2007 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2009-04-05.
- ^ Brittingham, Angela (June 2004). "Ancestry: 2000. Census 2000 Brief" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-05-13.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Additionally, in the 2000 Census some 2,187,144 Americans reported "Spanish" as their ancestry. For more about this group, see Spanish American.
- ^ "New Mexico CultureNet - Cuartocentenario". New Mexico CultureNet. Retrieved 2008-05-13.
- ^ Latina Magazine "A native of Phoenix, Nanette moved with her family at age 8 to Guadalajara (and later to Mexico City), where she developed "a Mexican soul," she says... It's a legacy Alexis feels strongly connected to—and proud of. "In general I think Latinos know how to live and eat and sleep and spend time with their families," she says."
- ^ "A Chat With Alexis Bledel" February 19, 2003, DVDTown.com
- ^ http://www.census.gov/prod/cen2010/briefs/c2010br-04.pdf
- ^ US Census Bureau: "Redistricting Data, First Look at Local 2010 Census Results"
- ^ US Census Bureau: "Population by Race and Hispanic or Latino Origin, for the United States, Regions, Divisions, and States, and for Puerto Rico: 2000"
- ^ David Crary (18 October 2012). "Gallup study: 3.4 percent of US adults are LGBT". WTOP. Associated Press. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ http://weblogs.sun-sentinel.com/educationblog/2011/06/fiu_nova_produce_most_degrees.html
- ^ Castro, Max J. (2002). The Dominican Diaspora Revisited, Dominicans and Dominican-Americans in a New Century.
- ^ "The Population With a Bachelor's Degree or Higher by Race and Hispanic Origin: 2006–2010" (PDF). American Community Survey Briefs. American Community Survey Briefs. 10 (19). U.S. Census Bureau. May 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Arias, E. United States life tables by Hispanic origin. National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat 2(152). 2010. Page 1.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, homeownership by race". Retrieved 2006-10-06.
- ^ DeNavas-Walt, Carmen; Proctor, Bernadette D.; Smith, Jessica C. (September 2012). "Real Median Household Income by Race and Hispanic Origin: 1967 to 2010". Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2011 (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. p. 8.
- ^ a b c "The American Community-Hispanics: 2004" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. February 2007. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ^ Lynching and Violence in America: Migrant Workers
- ^ press3b
- ^ Steven H. Wilson | Brown over "Other White": Mexican Americans' Legal Arguments and Litigation Strategy in School Desegregation Lawsuits | Law and History Review, 21.1 | The History Cooperative
- ^ Digital History
- ^ How Immigration is Rousing the Zealots - TIME
- ^ Democracy Now! | FBI Statistics Show Anti-Latino Hate Crimes on the Rise December 5, 2007
- ^ FBI: "Incidents, Offenses, Victims, and Known Offenders by Bias Motivation, 2009"
- ^ New York Times: "Survey Points to Tensions Among Chief Minorities" by JULIA PRESTON December 13, 2007
- ^ Christian Science Monitor: "Rising black-Latino clash on jobs" May 25, 2006
- ^ New York Times: "In Obama’s Pursuit of Latinos, Race Plays Role" January 15, 2008
- ^ Los Angeles Times: "Roots of anger Longtime prejudices, not economic rivalry, fuel Latino-black tensions" January 07, 2007
- ^ The Economist:"Where black and brown collide: The struggle for political dominance" August 2, 2007
- ^ The Daily Press: "Hispanic Influx Causes Tensions with Blacks" February 27, 2011
- ^ FoxNews: "Alleged Bias Attacks Inflame Tensions in New York City" August 16, 2010
- ^ Washington Post: "Jail Riots Illustrate Racial Divide in California" February 21, 2006
- ^ National Public Radio: "Racial Tension at Los Angeles High School" May 16, 2005.
- ^ USA Today: "Blacks, Latinos in the South: Cooperation or confrontation?" November 4, 2006
- ^ Los Angeles Times: "Attack on family in Compton latest incident in wave of anti-black violence - A Latino gang is intimidating blacks into leaving the city that was once an African American enclave. It's part of a violent trend seen in other parts of the L.A. area" By Sam Quinones, Richard Winton and Joe Mozingo January 25, 2013
- ^ Los Angeles Times: "A Southern accent on day laborers Stereotypes, language skills and the lowest price come into play as black Americans and Latino immigrants compete on an Atlanta street" By Richard Fausset December 28, 2007
- ^ New York Times: "A Black-Latino Coalition Emerges in Los Angeles" by JOHN M. BRODER April 24, 2005
- ^ Southern Regional Council: "Building Black - Brown Coalitions in the Southeast: Four Case Studies of African American-Latino Collaborations" by Joel Alvarado and Charles Jaret 2009
- ^ Carnegie reporter: "Blacks and Latinos in the U.S" by Roberto Suro Spring 2009
- ^ Nagourney, Adam; Jennifer Steinhauer (January 15, 2008). "In Obama's Pursuit of Latinos, Race Plays Role". New York Times.
- ^ Southern Poverty Law Center Intelligence Report: "Latino Gang Members in Southern California are Terrorizing and Killing Blacks" Winter 2006, Issue Number: 124
- ^ New York Times: "Survey Points to Tensions Among Chief Minorities" December 13, 2007
- ^ UCLA Center for Communications & Community December 13, 2007
- ^ Pew Research Center: "Attitudes Toward Immigration: In Black and White" April 26, 2006
- ^ University of Berkeley Law School: Research Brief "Labor arrangement corresponds with the growth in the Latino immigrant population" July 2008
- ^ a b Gallup: "Whites May Exaggerate Black-Hispanic Tensions" by Lydia Saad July 17, 2008
- ^ Los Angeles Times: "Hate crimes in L.A. County down overall, but anti-Jewish vandalism rises" December 21, 2010
- ^ a b Levenson, Michael (2007-12-10). "GOP hopefuls beckon Hispanics in debate - The Boston Globe". The Boston Globe. The New York Times Company. Retrieved 2008-06-08.
- ^ "The Hispanic Vote in Presidential Elections, 1980-2012" (PDF). Pew Research Center. Retrieved 2013-05-11.
- ^ a b Ewers, Justin. "Republicans and Latino Voters: Has the GOP Shifted on Immigration Reform? - US News and World Report". US News. Retrieved 2009-04-08. Page 1
- ^ a b "AFP: Obama dominates McCain among Hispanics: poll". Retrieved 2009-04-09.
- ^ Daniel Dombey (2008-03-22). "Obama gets another ally - Politics - United States - United Kingdom - International - Obama running for the White House - Africa". Retrieved 2008-06-08.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ In Obama’s Pursuit of Latinos, Race Plays Role By Adam Nagourney and Jennifer Steinhauer, Published: January 15, 2008, New York Times.
- ^ a b The Hispanic Vote in the 2008 Democratic Presidential Primaries Report, Original Publication Date: February 21, 2008, Pew Hispanic Center
- ^ Hispanictips.com
- ^ Alternet.org
- ^ Video on YouTube
- ^ a b Lawrence, Jill (2008-11-06). "Hispanic vote grows, shifts to Democrats - USATODAY.com". USA Today. Retrieved 2009-04-11.
- ^ "Local Exit Polls - Election Center 2008 - Elections & Politics from CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved 2010-05-04.
- ^ Carroll, Susan (2008-11-06). "In record turnout, Latino voters flip red states to blue". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved 2009-04-11.
- ^ "Local Exit Polls - Election Center 2008 - Elections & Politics from CNN.com". CNN.
- ^ http://njtoday.net/2012/11/27/opinion-the-latino-vote-in-2012-and-the-depth-of-the-gop-problem/
- ^ Are Republican immigration reform opponents losing clout?
- ^ "United States - Selected Population Profile in the United States (Hispanic or Latino (of any race))". 2006 American Community Survey. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-06-11.
- ^ a b "B16006. Language spoken at home by ability to speak English for the population 5 years and over (Hispanic or Latino)". 2006 American Community Survey. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-06-12. [There were 39.5 million Hispanic and Latino Americans aged 5 or more in 2006. 8.5 million of them, or 22%, spoke only English at home, and another 156,000, or 0.4%, spoke neither English nor Spanish at home. The other 30.8 million, or 78%, spoke Spanish at home. Of these, 3.7 million spoke no English, while the overwhelming majority, 27.2 million, did, at these levels: 15.5 million "very well", 5.8 million "well", and 5.9 million "not well". These 27.2 million bilingual speakers represented 69% of all (39.5 million) Hispanic and Latino Americans aged five or over in 2006, while the 3.7 million monolingual Spanish-speakers represented 9%.]
- ^ Kunerth, Jeff (2010-01-02). "Hispanics flock to Pentecostal churches". The Orlando Sentinel. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ^ Bradley Hagerty, Barbara (2011-10-19). "U.S. Hispanics Choose Churches Outside Catholicism". NPR. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ^ Carrasquillo, Adrian (2012-07-09). "Latinos fueling growth within an Episcopal Church they feel embraces women, gays and immigrants". NBC Latino. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ^ Lehman, Chris (2012-09-11). "Episcopal Church Woos Latinos To Congregations". NPR. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ^ Gaston Espinosa, "Latinos, Religion, and the American Presidency," in Religion, Race, and the American Presidency, ed. Gaston Espinosa (Lanham, Md.: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers), 242-44.
- ^ http://www.adweek.com/news/television/hispanic-tv-market-grows-univision-reshuffles-execs-137594
- ^ a b c d e Pew Social Trends: "Marrying Out" June 15, 2010
- ^ a b c Pew Research Social & Demographic Trends: "The Rise of Intermarriage - Rates, Characteristics Vary by Race and Gender" by Wendy Wang February 16, 2012
- ^ Suzanne Oboler and Deena J. González, eds. The Oxford Encyclopedia Of Latinos & Latinas In The United States (4 vol. 2006)
- ^ http://www.hispanicbusiness.com/research/500/list.asp?ListYear=2012&States=All&City=&RawText=&Conjunction=AND&Submit1=Find+companies
- ^ "04/13/1998 I'd like the world to by a coke". The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ^ "Arturo Moreno - TIME". Time Inc. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ^ "Joseph Unanue". Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ^ "Biografía de Ángel Ramos Torres". Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- ^ "Samuel A. Ramirez & Company, Inc. Introduces The Ramirez Hispanic Index Equally-Weighted Portfolio". Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- ^ "Making Wall Street History" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-04-16. [dead link] Scan of cover story in Hispanic Trends, issue of December, 2005 – January 2006.
- ^ "Directory of Latino Elected Officials". Retrieved 2010-01-27.
- ^ [1]
- ^ "History of NALEO". Retrieved 2010-01-27.
- ^ "First Latina Governor's Historic Inauguration Gets Little National News Coverage". Fox News. 2011-01-11.
- ^ http://www.lib.utexas.edu/taro/ttusw/00035/tsw-00035.html
- ^ Princeton's Children's Book Festival
- ^ Army.mil, Senate.gov, Houstonculture.org
- ^ "David Farragut". NNDB. Retrieved 2007-04-14.
- ^ "Hispanics Firsts"; by: Nicolas Kanellos; pgs. 210-211; Publisher: Visible Ink Press; ISBN 0-7876-0519-0
- ^ Arlington National Cemetery
- ^ a b c "The Civil War, 1840s-1890s"; by Roger E. Hernandez, Roger E. Hernndez; ISBN 978-0-7614-2939-5; ISBN 0-7614-2939-5
- ^ a b c "Hispanics in America's Defense"; Office of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Military Manpower and Personnel Policy
- ^ Cavada Brothers
- ^ "The Puerto Rican Diaspora: historical perspectives"; By Carmen Teresa Whalen, Víctor Vázquez-Hernandez; page 176; Publisher: Temple University Press; ISBN 978-1-59213-413-7; ISBN 1-59213-413-0
- ^ "The Puerto Ricans: A Documentary History"; by Kal Wagenheim (Editor), Olga Jimenez de Wagenheim (Editor); page 355- 56; Publisher: Markus Wiener Publishers; Revised edition; ISBN 1-55876-476-3; ISBN 978-1-55876-476-7
- ^ Collection of the U.S. Military Academy Library, Pages 132–133; Publication: Assembly; Summer 1969
- ^ Template:Wayback
- ^ site United States Coast Guard
- ^ Young woman's life defined by service in Women's Army Corp
- ^ "Outpost Kelly". Retrieved October 10, 2006.
- ^ Univision
- ^ HISPANIC AMERICANS IN THE COAST GUARD
- ^ Hispanic Military history
- ^ Notable Hispanics
- ^ "Enlisted Commissioning Program (ECP)". United States Marine Corps. Retrieved 2006-08-05.
- ^ "HPSCI Chairman Reyes Honors D/NCS Jose Rodriguez — Central Intelligence Agency". Retrieved 2010-03-09.
- ^ "Diversity, the MI Tradition" (PDF). Fort Huachuca, United States Army. Retrieved October 27, 2011.
- ^ "National Hispanic Media Coalition: About Us". Retrieved 2008-06-12.
- ^ Noriega, Chon. "Politics and Culture: Making a Difference". Connecticut College. Retrieved 2008-06-12.
- ^ From bananas to buttocks: the Latina body in popular film and culture
- ^ Richest Hispanic Celebrities According to Forbes.
- ^ Cameron Diaz Forbes 100 Celebrity list.
- ^ El Escultor de las Galaxias
- ^ Optics & Photonics News 6(10), 12 (1995).
- ^ Genetic Roadmap Targets Drug Therapies from Hartford Business Review 30 November 2009
- ^ Un Modelo de Vida (A role model in his lifetime)[dead link]
- ^ "HEP@NASA LaRC; NASA Hispanic Astronauts". NASA. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "NHL.com - Trophies". Retrieved 2009-04-06.
Further reading
Surveys and historiography
- Bean, Frank D., and Marta Tienda. The Hispanic Population of the United States (1987), statistical analysis of demography and social structure
- Miguel A. De La Torre. Encyclopedia on Hispanic American Religious Culture (2 vol. ABC-CLIO Publishers, 2009).
- De Leon, Arnoldo, and Richard Griswold Del Castillo. North to Aztlan: A History of Mexican Americans in the United States (2006)
- Garcia, Richard A. "Changing Chicano Historiography," Reviews in American History 34.4 (2006) 521-528 in Project Muse
- Gomez-Quiñones, Juan. Mexican American Labor, 1790-1990. (1994).
- Gutiérrez, David G. ed. The Columbia History of Latinos in the United States Since 1960 (2004) 512pp excerpt and text search
- Gutiérrez, David G. "Migration, Emergent Ethnicity, and the 'Third Space'": The Shifting Politics of Nationalism in Greater Mexico" Journal of American History 1999 86(2): 481-517. in JSTOR covers 1800 to the 1980s
- Leonard, David J. Latino History and Culture: An Encyclopedia (Sharpe Reference 2009)
- Oboler, Suzanne, and Deena J. González, eds. The Oxford Encyclopedia Of Latinos & Latinas In The United States (4 vol. 2006) excerpt and text search
- Rochín, Refugio I., and Denis N. Valdés, eds. Voices of a New Chicana/o History. (2000). 307 pp.
- Ruiz, Vicki L. “Nuestra América: Latino History as United States History,” Journal of American History, 93 (2006), 655–72. in JSTOR
- Ruiz, Vicki L. From Out of the Shadows: Mexican Women in Twentieth-Century America (1998)
Pre 1965
- Bogardus, Emory S. The Mexican in the United States (1934), sociological
- Gamio, Manuel. The Life Story of the Mexican Immigrant (1931)
- Gamio, Manuel. Mexican Immigration to the United States (1939)
- García, Mario T. Mexican Americans: Leadership, Ideology and Identity, 1930–1960 (1989)
- García, Mario T. Desert Immigrants. The Mexicans of El Paso, 1880-1920 (1982) 348 pp; excerpt and text search
- Gomez-Quinones, Juan. Roots of Chicano Politics, 1600-1940 (1994)
- Grebler, Leo, Joan Moore, and Ralph Guzmán. The Mexican American People: The Nation's Second Largest Minority (1970), emphasis on census data and statistics
- Rivas-Rodríguez, Maggie ed. Mexican Americans and World War II (2005)
- Sanchez, George J. Becoming Mexican American: Ethnicity, Culture, and Identity in Chicano Los Angeles, 1900-1945 (1995) excerpt and text search
Culture and politics, post 1965
- Abrajano, Marisa A., and R. Michael Alvarez, eds. New Faces, New Voices: The Hispanic Electorate in America (Princeton University Press; 2010) 219 pages. Documents the generational and other diversity of the Hispanic electorate and challenges myths about voter behavior.
- Aranda, José, Jr. When We Arrive: A New Literary History of Mexican America. U. of Arizona Press, 2003. 256 pp.
- Arreola, Daniel D., ed. Hispanic Spaces, Latino Places: Community and Cultural Diversity in Contemporary America. 2004. 334 pp.
- Badillo, David A. Latinos and the New Immigrant Church. 2006. 275 pp. excerpt and text search
- Berg, Charles Ramírez. Latino Images in Film: Stereotypes, Subversion, and Resistance. 2002. 314 pp.
- Branton, Regina. "Latino Attitudes toward Various Areas of Public Policy: The Importance of Acculturation," Political Research Quarterly, Vol. 60, No. 2, 293-303 (2007) Abstract
- Cepeda, Raquel. Bird of Paradise: How I Became Latina Atria Books. 2013. ISBN 978-1-4516-3586-7. A personal exploration of Dominican American identity via family interviews, travel and genetic genealogy. Synopsis and Excerpt
- DeGenova, Nicholas and Ramos-Zayas, Ana Y. Latino Crossings: Mexicans, Puerto Ricans, and the Politics of Race and Citizenship. 2003. 257 pp.
- Dolan, Jay P. and Gilberto M. Hinojosa; Mexican Americans and the Catholic Church, 1900-1965 (1994)
- Fregoso, Rosa Linda. The Bronze Screen: Chicana and Chicano Film Culture. (1993) excerpt and text search
- García, Mario T. Mexican Americans: Leadership, Ideology and Identity, 1930–1960 (1989)
- García, María Cristina. Seeking Refuge: Central American Migration to Mexico, The United States, and Canada. (2006) 290pp
- Gomez-Quinones, Juan. Chicano Politics: Reality and Promise, 1940-1990 (1990)
- Gutiérrez, David G. Walls and Mirrors: Mexican Americans, Mexican Immigrants, and the Politics of Ethnicity in the Southwest, 1910-1986 1995. excerpt and text search
- Hammerback, John C., Richard J. Jensen, and Jose Angel Gutierrez. A War of Words: Chicano Protest in the 1960s and 1970s 1985.
- Herrera-Sobek, Maria. Celebrating Latino Folklore: An Encyclopedia of Cultural Traditions (3 vol., 2012) excerpt and text search
- Kanellos, Nicolás, ed. The Greenwood Encyclopedia of Latino Literature (3 vol. 2008) excerpt and text search
- Kenski, Kate and Tisinger, Russell. "Hispanic Voters in the 2000 and 2004 Presidential General Elections." Presidential Studies Quarterly 2006 36(2): 189-202. Issn: 0360-4918
- López-Calvo, Ignacio. Latino Los Angeles in Film and Fiction: The Cultural Production of Social Anxiety. University of Arizona Press, 2011. ISBN 0-8165-2926-4
- Martinez, Juan Francisco. Sea La Luz: The Making of Mexican Protestantism in the American Southwest, 1829-1900 (2006)
- Matovina, Timothy. Guadalupe and Her Faithful: Latino Catholics in San Antonio, from Colonial Origins to the Present. 2005. 232 pp. excerpt and text search
- Meier, Matt S., and Margo Gutierrez, ed. Encyclopedia of the Mexican American Civil Rights Movement (2000) excerpt and text search
- Nuno, S. A. "Latino Mobilization and Vote Choice in the 2000 Presidential Election" American Politics Research, (2007); 35(2): 273 - 293. Abstract
- Saldívar-Hull, Sonia. Feminism on the Border: Chicana Gender Politics and Literature 2000. excerpt and text search
- Wegner, Kyle David, “Children of Aztlán: Mexican American Popular Culture and the Post-Chicano Aesthetic” (PhD dissertation State University of New York, Buffalo, 2006). Order No. DA3213898.
Regional and Local
- Overmyer-Velazquez, Mark. Latino America: A State-by-State Encyclopedia (2 vol. 2008) excerpt and text search
California
- Hubert Howe Bancroft. The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft,
- Bedolla, Lisa García. Fluid Borders: Latino Power, Identity, and Politics in Los Angeles. 2005. 279 pp.
- Burt, Kenneth C. The Search for a Civic Voice: California Latino Politics (2007) excerpt and text search
- Camarillo, Albert. Chicanos in a Changing Society: From Mexican Pueblos to American Barrios in Santa Barbara and Southern California, 1848–1930 (1979)
- Camarillo, Albert M., “Cities of Color: The New Racial Frontier in California’s Minority-Majority Cities,” Pacific Historical Review, 76 (Feb. 2007), 1–28; looks at cities of Compton, East Palo Alto, and Seaside
- Daniel, Cletus E. Bitter Harvest: A History of California Farmworkers, 1870-1941 1981.
- García, Matt. A World of Its Own: Race, Labor, and Citrus in the Making of Greater Los Angeles, 1900-1970 (2001),
- Hayes-Bautista, David E. La Nueva California: Latinos in the Golden State. U. of California Press, 2004. 263 pp. excerpt and text search
- Hughes, Charles. "The Decline of the Californios: The Case of San Diego, 1846-1856" The Journal of San Diego History Summer 1975, Volume 21, Number 3 online at [2]
- McWilliams, Carey. North from Mexico. (1949), farm workers in California
- Pitt, Leonard. The Decline of the Californios: A Social History of the Spanish speaking Californians, 1846-1890 (ISBN 0-520-01637-8)
- Sánchez; George J. Becoming Mexican American: Ethnicity, Culture, and Identity in Chicano Los Angeles, 1900-1945 (1993) excerpt and text search
- Valle, Victor M. and Torres, Rodolfo D. Latino Metropolis. 2000. 249 pp. on Los Angeles
Texas and Southwest
- Alonzo, Armando C. Tejano Legacy: Rancheros and Settlers in South Texas, 1734-1900 (1998)
- Hubert Howe Bancroft. The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft,
- Blackwelder, Julia Kirk. Women of the Depression: Caste and Culture in San Antonio 1984. excerpt and text search
- Buitron Jr., Richard A. The Quest for Tejano Identity in San Antonio, Texas, 1913-2000 (2004) excerpt and text search
- Chávez, John R. The Lost Land: The Chicano Image of the Southwest (Albuquerque, 1984)
- Chávez-García, Miroslava. Negotiating Conquest: Gender and Power in California, 1770s to 1880s (2004).
- De León, Arnoldo. They Called Them Greasers: Anglo Attitudes toward Mexicans in Texas, 1821–1900 (Austin, 1983)
- De León, Arnoldo. Mexican Americans in Texas: A Brief History, 2nd ed. (1999)
- Deutsch, Sarah No Separate Refuge: Culture, Class, and Gender on the Anglo-Hispanic Frontier in the American Southwest, 1880-1940 1987
- Dysart, Jane. "Mexican Women in San Antonio, 1830-1860: The Assimilation Process" Western Historical Quarterly 7 (October 1976): 365-375. in JSTOR
- Echeverría, Darius V., “Aztlán Arizona: Abuses, Awareness, Animosity, and Activism amid Mexican-Americans, 1968–1978” PhD dissertation (Temple University, 2006). Order No. DA3211867.
- Fregoso; Rosa Linda. Mexicana Encounters: The Making of Social Identities on the Borderlands (2003)
- Garcia, Ignacio M. Viva Kennedy: Mexican Americans in Search of Camelot, Texas A&M University Press, 2000. 227pp and online search from Amazon.com.
- García, Richard A. Rise of the Mexican American Middle Class: San Antonio, 1929-1941 1991
- Getz; Lynne Marie. Schools of Their Own: The Education of Hispanos in New Mexico, 1850-1940 (1997)
- Gómez-Quiñones, Juan. Roots of Chicano Politics, 1600-1940 (1994)
- Gonzales-Berry, Erlinda, David R. Maciel, editors, The Contested Homeland: A Chicano History of New Mexico, 314 pages (2000), ISBN 0-8263-2199-2
- González; Nancie L. The Spanish-Americans of New Mexico: A Heritage of Pride (1969)
- Guglielmo, Thomas A. "Fighting for Caucasian Rights: Mexicans, Mexican Americans, and the Transnational Struggle for Civil Rights in World War II Texas," Journal of American History, 92 (March 2006) in History Cooperative
- Gutiérrez; Ramón A. When Jesus Came, the Corn Mothers Went Away: Marriage, Sexuality, and Power in New Mexico, 1500-1846 (1991)
- Márquez, Benjamin. LULAC: The Evolution of a Mexican American Political Organization (1993)
- Matovina, Timothy M. Tejano Religion and Ethnicity, San Antonio, 1821-1860 (1995)
- Montejano, David. Anglos and Mexicans in the Making of Texas, 1836-1986 (1987)
- Muñoz, Laura K., “Desert Dreams: Mexican American Education in Arizona, 1870–1930” (PhD dissertation Arizona State University, 2006). Order No. DA3210182.
- Quintanilla, Linda J., “Chicana Activists of Austin and Houston, Texas: A Historical Analysis” (University of Houston, 2005). Order No. DA3195964.
- Sánchez; George I. Forgotten People: A Study of New Mexicans (1940; reprint 1996) on New Mexico
- Taylor, Paul S. Mexican Labor in the United States. 2 vols. 1930-1932, on Texas
- Stewart, Kenneth L., and Arnoldo De León. Not Room Enough: Mexicans, Anglos, and Socioeconomic Change in Texas, 1850-1900 (1993)
- de la Teja, Jesús F. San Antonio de Béxar: A Community on New Spain's Northern Frontier (1995).
- Tijerina, Andrés. Tejanos and Texas under the Mexican Flag, 1821-1836 (1994),
- Tijerina, Andrés. Tejano Empire: Life on the South Texas Ranchos (1998).
- Timmons, W. H. El Paso: A Borderlands History (1990).
- Trevino, Roberto R. The Church in the Barrio: Mexican American Ethno-Catholicism in Houston. (2006). 308pp.
- Weber, David J. The Mexican Frontier, 1821-1846: The American Southwest under Mexico (1982)
- Garcia, Richard A. "Changing Chicano Historiography," Reviews in American History 34.4 (2006) 521-528 in Project Muse
Other regions
- Bullock, Charles S., III and Hood, M. V., III. "A Mile-wide Gap: the Evolution of Hispanic Political Emergence in the Deep South." Social Science Quarterly 2006 87(special Issue): 1117-1135. Issn: 0038-4941 Fulltext: in Blackwell Synergy
- García, María Cristina. Havana, USA: Cuban Exiles and Cuban Americans in South Florida, 1959–1994 (1996); excerpt and text search
- Korrol, Virginia Sánchez. From Colonia to Community: The History of Puerto Ricans in New York City, 1917–1948 (1994)
- Millard, Ann V. and Chapa, Jorge. Apple Pie and Enchiladas: Latino Newcomers in the Rural Midwest. 2004. 276 pp. excerpt and text search
- Murphy, Arthur D., Colleen Blanchard, and Jennifer A. Hill, eds. Latino Workers in the Contemporary South. 2001. 224 pp.
- Padilla, Felix M. Puerto Rican Chicago. (1987). 277 pp.
- Sãnchez Korrol, Virginia E. From Colonia to Community: The History of Puerto Ricans in New York City. (1994) complete text online free in California; excerpt and text search
- Vargas, Zaragosa. Proletarians of the North: A History of Mexican Industrial Workers in Detroit and the Midwest, 1917-1933 (1993) complete text online free in California; excerpt and text search
- Whalen, Carmen Teresa, and Victor Vásquez-Hernández, eds. The Puerto Rican Diaspora: Historical Perspectives (2005),
Primary sources
- Richard Ellis, ed. New Mexico Past and Present: A Historical Reader. 1971.
- David J. Weber; Foreigners in Their Native Land: Historical Roots of the Mexican Americans (1973), primary sources to 1912


![Myrtle González is considered the first female Latin star in Hollywood.[179]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/ba/Myrtle-Gonzalez.jpg/137px-Myrtle-Gonzalez.jpg)

![In 2010, Forbes ranked Cameron Diaz as the richest Hispanic female celebrity, ranking number 60 among the top 100.[180][181]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/23/CameronDiazByCarolineRenouard2010.jpg/133px-CameronDiazByCarolineRenouard2010.jpg)