German submarine U-255
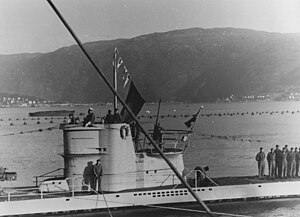 U-255 at Narvik flying four victory pennants and the flag of the merchant ship SS Paulus Potter after the attack on the ships of Convoy PQ 17
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | U-255 |
| Ordered | 23 September 1939[1] |
| Builder | Bremer Vulkan, Bremen-Vegesack[1] |
| Yard number | 20[1] |
| Laid down | 21 December 1940[1] |
| Launched | 8 October 1941[1] |
| Commissioned | 29 November 1941[1] |
| Decommissioned | 1 September 1944[1] |
| Recommissioned | 2 March 1945[1] |
| Fate | list error: <br /> list (help) Surrendered, 19 May 1945 Sunk in Operation Deadlight on 13 December 1945[1] |
| General characteristics [2][3] | |
| Type | Type VIIC submarine |
| Displacement | list error: <br /> list (help) 769 long tons (781 t) surfaced 871 long tons (885 t) submerged |
| Length | list error: <br /> list (help) 67.1 m (220 ft 2 in) o/a 50.5 m (165 ft 8 in) pressure hull |
| Beam | list error: <br /> list (help) 6.2 m (20 ft 4 in) o/a 4.7 m (15 ft 5 in) pressure hull |
| Draft | 4.74 m (15 ft 7 in) |
| Propulsion | list error: <br /> list (help) 2 × supercharged Germaniawerft 6-cylinder 4-stroke M6V 40/46 diesel engines, totalling 2,800–3,200 bhp (2,100–2,400 kW). Max rpm: 470-490 2 × electric motors, totalling 750 shp (560 kW) and max rpm: 296. |
| Speed | list error: <br /> list (help) 17.7 knots (20.4 mph; 32.8 km/h) surfaced 7.6 knots (8.7 mph; 14.1 km/h) submerged |
| Range | list error: <br /> list (help) 15,170 km (8,190 nmi) at 10 kn (19 km/h) surfaced 150 km (81 nmi) at 4 kn (7.4 km/h) submerged |
| Test depth | list error: <br /> list (help) 230 m (750 ft) Crush depth: 250–295 m (820–968 ft) |
| Complement | 44–52 officers & ratings |
| Armament | list error: <br /> list (help) • 5 × 533 mm (21 in) torpedo tubes (4 bow, 1 stern) • 14 × G7e torpedoes or 26 TMA mines • 1 × C35 88mm/L45 deck gun (220 rounds) • AA guns (2 cm FlaK 30) |
| Service record[1][4] | |
| Part of: |
list error: <br /> list (help) 8th U-boat Flotilla (29 November 1941–30 June 1942) 11th U-boat Flotilla (1 July 1942–31 May 1943) 13th U-boat Flotilla (1 June–30 November 1943) 7th U-boat Flotilla (1 December 1943–1 September 1944) 13th U-boat Flotilla (1 March–8 May 1945) |
| Commanders: |
list error: <br /> list (help) Kapitänleutnant Reinhart Reche (29 November 1941–6 June 1943) Oberleutnant zur See Erich Harms (7 June 1943–August 1944) Oberleutnant zur See Helmuth Heinrich (2 March–19 May 1945) |
| Operations: |
list error: <br /> list (help) 1st patrol: 23 June–15 July 1942 2nd patrol: 4 August–9 September 1942 3rd patrol: 13–25 September 1942 4th patrol: 23 January–9 February 1943 5th patrol: 22 February–15 March 1943 6th patrol: 29 March–29 April 1943 7th patrol: 19 July–19 September 1943 8th patrol: 26 February–11 April 1944 9th patrol: 6–8 May 1944 10th patrol: 6–15 June 1944 11th patrol: 22–24 April 1945 12th patrol: 28–30 April 1945 13th patrol: 2–3 May 1945 14th patrol: 5–7 May 1945 15th patrol: 8–19 May 1945 |
| Victories: |
list error: <br /> list (help) 10 commercial ships sunk (47,640 GRT GRT uses unsupported parameter (help)) 1 warship sunk (1,200 GRT) 1 commercial ship a total loss (7,191 GRT) |
German submarine U-255 was a Type VIIC U-boat that served in the German Kriegsmarine during World War II. The submarine was laid down on 21 December 1940 at the Bremer Vulkan yard at Bremen-Vegesack, launched on 8 October 1941, and commissioned on 29 November 1941 under the command of Kapitänleutnant Reinhart Reche.[1]
One of the most successful U-boats to operate in Arctic waters,[5] she operated from Norway during 1942–1943, and then from France in 1944–1945, sailing on 15 combat patrols, and sinking ten merchant ships totalling 47,640 GRT GRT uses unsupported parameter (help), and damaging another of 7,191 GRT enough for it to be written off as a total loss.[6] She also sank the 1,200 GRT Edsall-class destroyer escort USS Leopold (DE-319).[6] At the end of the war U-255 surrendered to the British, and was sunk during Operation Deadlight on 13 December 1945.[1]
Construction
U-255 was ordered by the Kriegsmarine on 23 September 1939 and laid down more than a year later on 21 December 1940 at the Bremer Vulkan yard at Bremen-Vegesack as Werk 20. U-255 was launched 8 October 1941, and commissioned on 29 November that same year with Kapitänleutnant Reinhart Reche in command of the U-boat.[1] U-255 carried 5 × 533 mm (21 in) torpedo tubes (4 located in the bow, 1 in the stern) and had one C35 88mm/L45 deck gun with 220 rounds. She could also carry 14 G7e torpedoes or 26 TMA mines and had a crew of 44-52 men.[2]
Service record
After a period of training with the 8. Unterseebootsflottille, based at Königsberg in the Baltic Sea, U-255 was transferred to the 11. Unterseebootsflottille, based at Bergen, Norway, for front-line service on 1 July 1942.
1st patrol
On 15 June 1942, U-255 sailed from Kiel, under the command of Kapitänleutnant Reinhart Reche, arriving at Narvik on the 20th. She then departed on her first patrol on 23 June, sailing into the Barents Sea, north of Russia.[7]
She made her first kill on 6 July, sinking the 7,191 ton American Liberty ship John Witherspoon about 20 miles off Novaya Zemlya. The ship, en route from Baltimore to Arkhangelsk with 8,575 tons of ammunition and tanks aboard, had been a part of Convoy PQ 17 which had dispersed on Admiralty orders in the Barents Sea on 4 July. After being hit by four torpedoes, the ship broke in two, and sank within minutes. The crew abandoned ship, and one seaman fell overboard and drowned. U-255 questioned the survivors, offered food and water, gave directions to the nearest land, and left. The crew were picked up by Royal Navy ships on 9 July.[8]
The next day, 7 July, she sank the 5,116 ton American Hog Islander Alcoa Ranger, also from Convoy PQ 17. A single torpedo struck the ship, causing the vessel to list heavily to starboard. The crew abandoned ship in three lifeboats within 15 minutes. After she questioned the crew, she began to shell the ship from a distance of about 100 metres (330 ft), firing at least 60 shells (some survivors said as many as 150) until the ship sank. The crewmen were rescued by Soviet patrol boats later that day.[9]
Early on 8 July, U-255 caught another ship from Convoy PQ 17, the 6,069 ton American merchant ship Olopana, loaded with 6,000 tons of explosives, gasoline, and trucks as deck cargo. A single torpedo hit the ship, blowing out all the bulkheads, and killing seven of the crew. The surviving crewmen abandoned ship on four rafts, as U-255 surfaced and fired 20 shells at the ship, which sank after 20 minutes. U-255 questioned the survivors, gave them a course to land, and asked if they had enough food and water before leaving. The survivors landed at Moller Bay, Novaya Zemlya, two days later.[10]
On 13 July U-255 found the 7,168 ton Dutch merchant ship Paulus Potter abandoned and drifting, with 2,250 tons of general goods, ammunition, 34 tanks, 15 aircraft and 103 trucks aboard. The ship had been attacked by Ju 88 dive bombers of III./KG 30 east-north-east of Bear Island on 5 July, the day after Convoy PQ 17 dispersed, and the crew had abandoned the badly damaged ship believing it was about to sink. All 76 of the crew had taken five days to reach land at Novaya Zemlya, eventually being rescued by a Soviet whaling vessel. After finding her the II.WO and two mates from U-255 boarded, and attempted to start the engines, but the engine room was flooded. They then searched the ship, taking blankets, cigarettes, and other useful materials, including confidential documents found on the bridge, and the ship's ensign as prize, before the ship was sunk with a single torpedo.[11] U-255 returned to Narvik on 15 July.[4]
2nd patrol
U-255 left Narvik on 18 July 1942, arriving at Bergen on the 20th.[4] She sailed from Bergen on 4 August for her second combat patrol, heading deep into Soviet waters, but had no successes,[12] though she shelled two Soviet wireless stations[5], as part of Operation Wunderland, before arriving at Neidenfjord on the Norwegian/Finnish border on 9 September.[12]
3rd patrol
U-255 sailed from Neidenfjord on 13 September 1942, patrolling the Barents Sea, with no result, before heading out into the Greenland Sea.[13] There, on 20 September, she sank the 4,937 ton American merchant ship Silver Sword, returning from Arkhangelsk to New York with 5,000 tons of hides and chrome ore and a deck cargo of wood pulp. Hit by two torpedoes, which blew off the stern post, propeller and rudder, and caused the after magazine to explode, the 48 crew and 16 passengers (survivors from PQ 17) abandoned ship in two lifeboats and one raft. The ship was then shelled by HMS Worcester and sank. The crew were later picked up by British ships, with one man dying of wounds later.[14]
Three days later, on 23 September, U-255 was attacked by a Catalina patrol aircraft of No. 210 Squadron RAF south of Jan Mayen. After being heavily damaged by two depth charges, she was forced to return to Bergen, arriving on the 25th.[13]
Refitting and 4th patrol
On 29 September 1942 U-255 sailed from Bergen, arriving back at Kiel on 3 October.[4] There the submarine was fitted with a Schnorchel underwater-breathing apparatus[1] before sailing again on 7 January 1943, and arriving at Hammerfest in northern Norway on the 18th.[4]
Returning to her old hunting grounds north of Norway, U-255 sailed from Hammerfest on 23 January 1943,[15] and on the 26th, U-255 likely sank the 2,418 ton Soviet merchant ship Krasnyj Partizan with two torpedoes west of Bear Island. The Russian ship had just evaded the pursuing U-625 when it went missing. She was probably sunk by U-255 due to the fact that the submarine recorded a loss the same day. After the sinking of the unknown merchant ship tht was likely the Krasnyj Partizan, U-255 surfaced and tried to question the survivors. They only spoke Russian and could not be understood. As a result, the crew of U-255 were unable to confirm the identity of the vessel.[16] On 29 January, she sank another Russian freighter, the 1,892 ton Ufa, south of Bear Island.[17] Both the Krasnyj Partizan and the Ufa were loaded with timber destined for the United States, and no survivors were found from either ship unless the survivors from the unknown Russian merchant vessel that was sunk by U-255 were indeed crew members of the Krasnyj Partizan.[17][16]
On the afternoon of 3 February, about 600 miles north-east of Iceland, U-255 fired a salvo of torpedoes at Convoy RA-52, in route from Murmansk to New York, and hit the 7,460 ton American merchant ship Greylock. The ship attempted to evade the attack, but was holed below the waterline, immediately flooded, and began to list to starboard. Within fifteen minutes the crew of 61 and nine passengers abandoned ship in four lifeboats. A British escort then shelled and sank the crippled ship.[18] U-255 then arrived back at Narvik on 9 February.[4]
5th patrol
U-255 sailed from Narvik on 22 February 1943 out into the northern seas once more.[19] On 5 March she fired a spread of three torpedoes at Convoy RA-53, sailing from Murmansk to Scotland, and hit two American merchant ships; the 4,978 ton Hog Islander Executive, loaded with 1,500 tons of potassium chloride, and the 7,191 ton Liberty ship Richard Bland, carrying 4,000 tons of lumber.
The Executive was struck on the starboard side, and the explosion demolished the booms, engine, dynamos and all the equipment in the immediate area. One hold rapidly flooded and the ship began to settle by the stern. Nine of the crew were killed, and the remaining 53 abandoned ship in three lifeboats and a raft. The ship was scuttled by gunfire from a destroyer about an hour after the attack.[20]
The Richard Bland was struck by a torpedo which did not explode, but passed through the ship, making 8-foot (2.4 m) holes on either side. The ship remained with the convoy with only a slightly reduced speed, but on the night of 6 March lost contact in gale force winds and rough seas, and proceeded alone towards Iceland. Five days later, on 10 March, U-255 found the ship about 35 miles off Langanes, Iceland, and hit her with two more torpedoes, breaking the ship in two just forward of the bridge. The crew abandoned ship, and of the 69 crew, the master, five officers, 13 crewmen and 15 armed guards were lost, when their lifeboats swamped in heavy seas. The stern section was torpedoed by U-255 again and sank, but the forward section was towed to Akureyri, Iceland, where the ship was declared a total loss.[21] U-255 then returned to Narvik, arriving on 15 March.[4]
6th patrol
U-255 sailed from Narvik on 29 March 1943 to patrol the Barents Sea, but had no successes, arriving at Bergen on 29 April.[22] On 1 June 1943, U-255 was transferred to the newly-created 13. Unterseebootsflottille based at the DORA 1 submarine base at Trondheim.[1]
7th patrol
Under the command of Oberleutnant zur See Erich Harms (the U-boat's former I.WO) from 7 June 1943,[1] U-255 sailed from Bergen on 9 July, arriving at Narvik on the 16th.[4] She left Narvik on 19 July and sailed into Soviet waters,[23] where on 27 July she sank the 411 ton Russian survey ship Akademik Shokalskij with her deck gun and small arms fire.[24] U-255 established a secret seaplane base on Novaya Zemlya,[5] and returned to Narvik on 19 September after 63 days at sea.
On 1 December 1943 U-255 was transferred again, this time to the 7. Unterseebootsflottille, based at Saint-Nazaire.[1]
8th patrol
U-255 departed Bergen on 26 February 1944 sailing out into the northern Atlantic between Greenland and Iceland.[25] On 10 March, about 400 miles south of Iceland, U-255 located Convoy CU 16, but was detected by sonar by the US Navy destroyer escort Leopold.[26] The ship turned to investigate the contact, but was hit by a acoustic torpedo. The crew abandoned ship, and she sank after several hours. Only 28 survivors were picked up by her sister ship Joyce from her crew of 199. U-255 was hunted by other escorts for three hours, but managed to slip away.[25][27] On 11 April the inbound U-boat was caught on the surface with its escort by 15 British Mosquito aircraft.[28] These were in turn attacked by German Ju 88 aircraft. U-255 reached its new home port of St. Nazaire later that day on with only minor damage.[1]
9th and 10th patrols
U-255 made two short patrols in the Bay of Biscay on the 6–9 May and 6–15 June 1944, but had no successes. U-255 began ninth patrol on 6 May 1944 when she left St. Nazaire. However she was recalled back to home port after only 2 days fully at sea on 8 May.[29] U-255's Tenth patrol was to suffer the same fate as her ninth. She left St. Nazaire on 6 June 1944, (the day of the Normandy landings) and was recalled back home on 15 June afer only 10 days at sea.[30]
11th-14th patrols
Damaged in an air raid in August 1944 U-255 was decommissioned for repairs.[5] U-255 was transferred back to the 13. Unterseebootsflottille on 1 March 1945, and recommissioned on 2 March with Oberleutnant zur See Helmuth Heinrich in command.[1] U-255 made a series of four short patrols between St. Nazaire and La Pallice in April and early May 1945[4] laying mines.[5]
15th patrol
U-255 began her final voyage under the command of Oberleutnant zur See Helmuth Heinrich on the day of the German surrender, sailing from St. Nazaire on 8 May 1945 to Loch Alsh in Scotland, arriving there on 19 May to make her formal surrender.[5][4]
Post war fate
U-255 was transferred to Loch Eriboll, and then Loch Ryan on 14 May 1945 for "Operation Deadlight".[1] She was towed out to sea by HMS Cubitt and on 13 December was sunk by Beaufighter aircraft of No. 254 Squadron RAF with RP-3 rockets[31] in position 51°16′N 13°38′W / 51.267°N 13.633°W.[1]
Raiding career
During her service in the German Kriegsmarine, U-255 sank 10 commercial ships for 47,640 GRT, one warship of 1,200 GRT, and sank another commercial ship for a total loss of 7,191 GRT.[6]
| Date[6] | Ship[6] | Nationality[6] | Tonnage[6] | Fate[6] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 July 1942 | John Witherspoon | 7,191 | sunk at 72°05′N 40°30′E / 72.083°N 40.500°E | |
| 7 July 1942 | Alcoa Ranger | 5,116 | sunk at 71°38′N 49°35′E / 71.633°N 49.583°E | |
| 8 July 1942 | Olopana | 6,069 | sunk at 72°10′N 51°00′E / 72.167°N 51.000°E | |
| 13 July 1942 | Paulus Potter | 7,168 | sunk at 70°00′N 52°00′E / 70.000°N 52.000°E | |
| 20 September 1942 | Silver Sword | 4,937 | sunk at 75°52′N 00°20′W / 75.867°N 0.333°W | |
| 26 January 1943 | Krasnyj Partizan | 2,418 | sunk at 73°45′N 17°30′E / 73.750°N 17.500°E | |
| 29 January 1943 | Ufa | 1,892 | sunk at 73°40′N 24°30′E / 73.667°N 24.500°E | |
| 3 February 1943 | Greylock | 7,460 | sunk at 70°52′N 00°21′W / 70.867°N 0.350°W | |
| 5 March 1943 | Executive | 4,978 | sunk at 72°44′N 11°27′E / 72.733°N 11.450°E | |
| 10 March 1943 | Richard Bland | 7,191 | total loss at 66°53′N 14°10′W / 66.883°N 14.167°W | |
| 27 July 1943 | Akademik Shokalskij | 411 | sunk | |
| 9 March 1944 | USS Leopold (DE 319) | 1,200 | sunk at 58°44′N 25°50′W / 58.733°N 25.833°W |
References
- Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Helgason, Guðmundur. "U-255". German U-boats of WWII. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Helgason, Guðmundur. "Type VIIC". U-Boat War in World War II. Uboat.net. Retrieved 14 March 2010.
- ^ "Type VII U-Boat". German U-boat. Uboataces.com. Retrieved 10 April 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Helgason, Guðmundur. "War Patrols by German U-boat U-255". Boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f Bishop, C. (2006). Kriegsmarine U-Boats, 1939-45. Amber Books.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ a b c d e f g h Helgason, Guðmundur. "Ships hit by U-255". WWII U-boat successes. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (First patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "John Witherspoon (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Alcoa Ranger (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Olopana (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Paulus Potter (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Second patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Third patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Silver Sword (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Fourth patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Helgason, Guðmundur. "Krasnyj Partizan (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Helgason, Guðmundur. "Ufa (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Greylock (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Fith patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Executive (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Richard Bland (Steam merchant)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Sixth patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Seventh patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Akademik Shokalskij (Survey ship)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ a b Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Eighth patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ "Lost DE's". Lost and Damaged DE's in WWII. Desausa.org. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "USS Leopold (DE 319) (Destroyer escort)". Ships hit by U-boats. Uboat.net. Retrieved 1 April 2010.
- ^ Wynn, Kenneth (March 1998). U-boat Operations of the Second World War: Career histories, U1-U510. Naval Institute Press. p. 179. ISBN 978-1557508607. Retrieved 8 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Ninth patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 7 April 2010.
- ^ Helgason, Guðmundur. "Patrol info for U-255 (Tenth patrol)". U-boat patrols. Uboat.net. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- ^ "Deutsche U-Boote 1935-1945: U-255". u-boot-archiv.de. Retrieved 1 April 2010. Template:De icon
- Further reading
- Bishop, C., Kriegsmarine U-Boats, 1939-45, Amber Books. 2006.
External links
See also
