Demographics of Nepal
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2007) |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 27 million | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 29,519,114 | |
| 4,100,000 | |
| 400,000 | |
| 350,000 | |
| 300,000 | |
| 110,616 | |
| 100,000 | |
| 100,000 | |
| 50,000 | |
| 50,000 | |
| 20,348 | |
| 15,950 | |
| 11,000 | |
| 10,000 | |
| 7,000 | |
| 3,780 | |
| 1,000[1] | |
| Languages | |
| Nepali language, English | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Hinduism and significantly Buddhism | |
The population of Nepal is estimated at 26,630,809 people in census of 2011, with a population growth rate of 1.596% and a median age of 21.6 years. Female median age is estimated at 22.5 years, and male median age at 20.7 years. Only 4.4% of the population are estimated to be more than 65 years old, comprising 681,252 females and 597,628 males, whereas 61.1% of the population is between 15 and 64 years old, and 34.6% is estimated at younger than 14 years. Birth rate is estimated at 22.17 births/1,000 population with an infant mortality rate at 44.54 deaths per 1,000 live births. Life expectancy at birth is estimated at 67.44 years for females and 64.94 years for males. Death rate is estimated at 681 deaths per 100,000 people. Net migration rate is estimated at 61 migrants per 100,000 people. According to the 2001 census, only 48.6% of the total population is literate, of which 62.7% are male and 34.9% are female.[2]
The words "Nepali" and "Nepalis" are gaining widespread popularity in English usage as opposed to Nepalese, which is an Anglicized version.Nepal has the largest amount of illegal immigrants in any country in the world mainly from India due to the open border between two countries, Nepal government has issued high time alert of this illegal Indian immigrants. Indian Government sending them from bordering states of Bihar and UP helping economically to get benefits from the ongoing political crisis of Nepal.
Demographic history
Nepali or Nepalese are descendants of migrants from parts of Kashmir, earlier Greater Nepal, Tibet, India, and parts of Burma and Yunnan, along with native tribal populations.
Indo-Aryans and East Asian looking mixed people live in the hill region. The mountainous region is sparsely populated above 3,000 m (9,800 ft), but in central and western Nepal ethnic Tibetans inhabit even higher semi-arid valleys north of the Himalaya. Kathmandu Valley, in the middle hill region, constitutes a small fraction of the nation's area but is the most densely populated, with almost 5 percent of the nation's population. Nepali society is multilingual, multireligious and multiethnic.
Population growth


A significantly high universal marriage rate, particularly among reformed Hindus drives Nepal's annual population growth rate in excess of two percent. The result of this is that the marriage rate has caused the population to double about every 30 years. This severely strains the country's underdeveloped economy and finite natural resources. Deforestation is exceedingly widespread. A large amount of marginal land is cleared for agriculture, trees are cut down for firewood and leaves are harvested for fodder. Deforestation causes erosion in the hills, in turn causing alluvial buildup down on the Gangetic Plain that interferes with flood control structures.
Population in the hills greatly exceeds agricultural productivity. Thus, chronic food deficits drive resettlement into the Inner Terai to the detriment of indigenous Tharu people and eastward into Sikkim and Bhutan, where traditional practices of delayed marriage and diversion of significant population into monasteries and nunneries otherwise checked population growth. Seeing the demographic writing on the wall after a population census in 1988, Bhutan expelled some 100,000 ethnic Nepalese who became Bhutanese refugees in camps in southeastern Nepal. Overpopulation also drives export of manpower to India, the Middle East, Europe, Australia and North America in search of employment, the so-called Nepalese Diaspora.
Refugees comprise 107,803 people from Bhutan and 20,153 Tibetan people.[2]
Most refugees live in seven camps established by the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. Presence and activity of Tibetan refugees in Nepal also raise sporadic diplomatic conflicts with the People's Republic of China.
Vital statistics
UN estimates[3]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR1 | CDR1 | NC1 | TFR1 | IMR1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 368 000 | 218 000 | 150 000 | 42.9 | 25. | |||
| 1955–1960 | 406 000 | 230 000 | 176 000 | 43.4 | 24.6 | 18.8 | 6.10 | 199.3 |
| 1960–1965 | 448 000 | 241 000 | 207 000 | 43.9 | 23.6 | 20.3 | 6.10 | 186.9 |
| 1965–1970 | 496 000 | 249 000 | 246 000 | 43.8 | 22.0 | 21.8 | 6.08 | 172.5 |
| 1970–1975 | 546 000 | 253 000 | 292 000 | 43.1 | 20.0 | 23.1 | 6.04 | 156.0 |
| 1975–1980 | 597 000 | 254 000 | 343 000 | 42.0 | 17.9 | 24.1 | 5.92 | 139.2 |
| 1980–1985 | 651 000 | 253 000 | 398 000 | 40.7 | 15.8 | 24.9 | 5.72 | 122.9 |
| 1985–1990 | 707 000 | 249 000 | 458 000 | 39.3 | 13.8 | 25.5 | 5.39 | 106.8 |
| 1990–1995 | 767 000 | 244 000 | 523 000 | 37.7 | 12.0 | 25.7 | 4.96 | 91.5 |
| 1995–2000 | 805 000 | 224 000 | 581 000 | 35.0 | 9.7 | 25.3 | 4.41 | 72.3 |
| 2000–2005 | 797 000 | 201 000 | 596 000 | 30.9 | 7.8 | 23.1 | 3.74 | 54.9 |
| 2005–2010 | 732 000 | 177 000 | 555 000 | 25.6 | 6.2 | 19.4 | 2.95 | 38.7 |
| 1 CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births | ||||||||
Ethnic groups
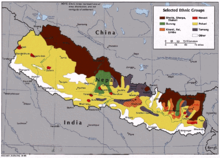
Bhotia, Sherpa, Thakali, Gurung, Kiranti, Rai, Limbu, Newari, Pahari, Tamang

Nepal's 2001 census enumerated 102 castes and ethnic groups.[4]
Recent studies derives 90% people being Nepali Origin and 10% Indian origin. Nepali origin are divide into two groups Khas and Mongoloids. Khas origin has further subgroups and they account for 50% of Nepal's total population, while Mongoloids group account for 40% of populations. Famous Khas origins are Chhetri, Thakuri, Bharamin etc. and famous Mongoloids origin are Gurung, Magar,Newar, Tamang, Sherpa, Rai, Limbu etc.
The following table is based on endogamous ethnicity, not language. Madheshi groups in the following table would need to be re-arranged or grouped together if a linguistic ethnic categorization is preferred instead and could reveal significantly different picture. References are according to the 2001 census.
| Caste/ethnic group | Population | % of total |
|---|---|---|
| Khas - Chhetri (Kshatriya) | 3,593,496 | 15.5[2] |
| Khas - Brahman | 2,896,477 | 12.5[2] |
| Magar | 1,622,421 | 7.0[2] |
| Madheshi Tharu | 1,533,879 | 6.6[2] |
| Tamang | 1,282,304 | 5.5[2] |
| Newar | 1,245,232 | 5.4[2] |
| Madheshi Muslim | 971,056 | 4.2[2] |
| Khas & - Kami | 895,954 | 3.9[2] |
| Madhesi Yadav | 895,423 | 3.9[2] |
| Rai | 635,151 | 2.79 |
| Gurung | 686,000 | 2.39 |
| Khas - Damai/Dholi | 390,305 | 1.72 |
| Limbu | 359,379 | 1.58 |
| Khas - Thakuri | 334,120 | 1.47 |
| Khas - Sarki | 318,989 | 1.40 |
| Madheshi Teli | 304,536 | 1.34 |
| Madheshi Chamar, Harijan, Ram | 269,661 | 1.19 |
| Madheshi Koiri | 251,274 | 1.11 |
| Madheshi Kurmi | 212,842 | 0.94 |
| Khas - Sanyasi | 199,127 | 0.88 |
| Madheshi Dhanuk | 188,150 | 0.83 |
| Madheshi Musahar | 172,434 | 0.76 |
| Madheshi Dusad/Paswan/Pasi | 158,525 | 0.70 |
| Sherpa | 154,622 | 0.68 |
| Madheshi Sunar | 145,088 | 0.64 |
| Madheshi Kewat | 136,953 | 0.60 |
| Madheshi Brahmin | 134,496 | 0.59 |
| Madheshi Baniya | 126,971 | 0.56 |
| Gharti/Bhujel[5][6] | 117,568 | 0.52 |
| Madheshi Mallah | 115,986 | 0.51 |
| Khas - Kalwar | 115,606 | 0.51 |
| Madheshi Kumal | 99,389 | 0.44 |
| Madheshi Hajam/Thakur | 98,169 | 0.43 |
| Madheshi Kanu | 95,826 | 0.42 |
| Madheshi Rajbansi | 95,812 | 0.42 |
| Sunuwar | 95,254 | 0.42 |
| Madheshi Sudhi | 89,846 | 0.40 |
| Madheshi Lohar | 82,637 | 0.36 |
| Tatma | 76,512 | 0.34 |
| Khatwe[7][8] | 74,972 | 0.33 |
| Madheshi Dhobi | 73,413 | 0.32 |
| Madheshi Majhi[9][10] | 72,614 | 0.32 |
| Madheshi Nuniya[11] | 66,873 | 0.29 |
| Madheshi Kumhar | 54,413 | 0.24 |
| Danuwar | 53,229 | 0.23 |
| Chepang | 52,237 | 0.23 |
| Madheshi Haluwai | 50,583 | 0.22 |
| Madheshi Rajput | 48,454 | 0.21 |
| Madheshi Kayastha | 46,071 | 0.20 |
| Madheshi Badhai | 45,975 | 0.20 |
| Marwadi | 43,971 | 0.19 |
| Madheshi Santhal/Satar | 42,698 | 0.19 |
| Madheshi Dhagar/Jhagar[12] | 41,764 | 0.18 |
| Bantar[13] | 35,839 | 0.16 |
| Khas & Madhesi - Barai | 35,434 | 0.16 |
| Madheshi Kahar | 34,531 | 0.15 |
| Gangai[14] | 31,318 | 0.14 |
| Madheshi Lodha | 24,738 | 0.11 |
| Madheshi Rajbhar | 24,263 | 0.11 |
| Thami | 22,999 | 0.10 |
| Dhimal | 19,537 | 0.09 |
| Bhote | 19,261 | 0.08 |
| Binga/Binda | 18,720 | 0.08 |
| Madheshi Bhediyar/Gaderi | 17,729 | 0.08 |
| Nurang | 17,522 | 0.08 |
| Yakkha | 17,003 | 0.07 |
| Darai[15][16] | 14,859 | 0.07 |
| Madheshi Tajpuriya[17] | 13,250 | 0.06 |
| Thakali | 12,973 | 0.06 |
| Madheshi Chidimar | 12,296 | 0.05 |
| Non-Khas Pahari peoples | 11,505 | 0.05 |
| Khas - Mali | 11,390 | 0.05 |
| Madheshi Bangali | 9,860 | 0.04 |
| Chhantyal | 9,814 | 0.04 |
| Madheshi Dom | 8,931 | 0.04 |
| Kamar | 8,761 | 0.04 |
| Bote[18][19] | 7,969 | 0.04 |
| Brahmu/Baramu[20][21] | 7,383 | 0.03 |
| Khas & Madhesi - Gaine/Gandarbha | 5,887 | 0.03 |
| Jirel | 5,316 | 0.02 |
| Adivasi/Janajati | 5,259 | 0.02 |
| Dura | 5,169 | 0.02 |
| Churaute[22][23] | 4,893 | 0.02 |
| Badi | 4,442 | 0.02 |
| Meche[24][25] | 3,763 | 0.02 |
| Lepcha | 3,660 | 0.02 |
| Madheshi Halkhor | 3,621 | 0.02 |
| Punjabi/Sikh | 3,054 | 0.01 |
| Kisan | 2,876 | 0.01 |
| Raji | 2,399 | 0.01 |
| Byangsi[26][27] | 2,103 | 0.01 |
| Hayu | 1,821 | 0.01 |
| Madheshi Koche | 1,429 | 0.01 |
| Madheshi Dhunia | 1,231 | 0.01 |
| Walung | 1,148 | 0.01 |
| Jain | 1,015 | 0.00 |
| Munda | 660 | 0.00 |
| Raute | 658 | 0.00 |
| Hyolmo[28][29] | 579 | 0.00 |
| Madheshi Pattharkatta/Kuswariya[30][31] | 552 | 0.00 |
| Kusunda | 164 | 0.00 |
| Unspecified Khas Dalit | 173,401 | 0.76 |
| Caste/Ethnicity not stated | 231,641 | 1.02 |
| Total | 22,736,934 | 100.00 |
Demographic statistics
Nepal Demographic and Health Survey
The following demographic statistics are from the 2011 Nepal Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS).[32]
Median birth intervals (Median number of months since preceding birth)
- Total: 36.2
- Rural: 35.9
- Urban: 40.3 (2011)
Median age at first birth
- Median age: 20.1 (2011)
Fertility rate - past trend and present
- Total fertility rate: 4.6 children born/woman (1996)
- Total fertility rate: 4.1 children born/woman (2001)
- Total fertility rate: 3.1 children born/woman (2006)
- Total fertiltiy rate: 2.6 children born/woman
- Rural fertility rate: 2.8 children born/woman
- Urban fertility rate: 1.6 children born/woman (2011)
Ideal family size - Mean ideal number of children
- Overall (female/male): 2.1 / 2.3
- Currently married (female/male): 2.2 / 2.3
- Urban (female/male): 1.9 / 2.0
- Rural (female/male): 2.2 / 2.3 (2011)
Ideal family size by gender and age group
- Below is a table of the ideal family size by gender and age for 2011.
| Age | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| 15-19 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| 20-24 | 1.9 | 2.1 |
| 25-29 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| 30-34 | 2.2 | 2.3 |
| 35-39 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
| 40-44 | 2.5 | 2.4 |
| 45-49 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
CIA World Factbook
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Nationality
- noun: Nepali (singular and plural)
- adjective: Nepali
Religions
- Hindu 80.6%, Buddhist 10.7%, Muslim 4.2%, Kirant 3.6%, other 0.9% (2001 census)
Literacy
- definition: age 15 and over can read and write
- total population: 48.6%
- male: 62.7%
- female: 34.9% (2001 census)
Population
- 29,890,686 (July 2012 est.)
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 34.6% (male 5,177,264/female 4,983,864)
- 15-64 years: 61.1% (male 8,607,338/female 9,344,537)
- 65 years and over: 4.4% (male 597,628/female 681,252) (2011 est.)
Median age
- total: 21.6 years
- male: 20.7 years
- female: 22.5 years (2011 est.)
Population growth rate
- 1.768% (2012 est.)
Birth rate
- 21.85 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Death rate
- 6.75 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
Net migration rate
- 2.58 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 2.41 children born/woman (2012 est.)
Urbanization
- urban population: 19% of total population (2010)
- rate of urbanization: 4.7% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Sex ratio
- at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2012 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 66.51 years
- male: 65.26 years
- female: 67.82 years (2012 est.)
Languages
Nepal's diverse linguistic heritage evolved from four major language groups: Indo-Aryan, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolian, and various indigenous language isolates. According to the 2001 national census, 92 different living languages are spoken in Nepal (a 93rd category was "unidentified"). The major languages of Nepal (percent spoken as mother tongue) are Nepali (80%)(2011 est.), Tharu (3%), Tamang (2%), Gurung (1.5%), Maithili (2%), Bhojpuri (2%) Newari/Nepal Bhasa (1%), Magar (1%), Awadhi (1%), Rai (1%), Limbu (1%) and Bajjika (1%). The remaining 81 languages are each spoken as mother tongue by less than one percent of the population.
Derived from Khas bhasa, Nepali is considered to be a member of Indo-European language and is written in Devanagari script. Nepali was the language of the country's unifiers in the late 18th century and became the official, national language that serves as the lingua franca among Nepalese of different ethnolinguistic groups. Hindi—along with regional dialects Awadhi, Bhojpuri and Maithili—is spoken in the southern Terai Region. Other than those, most of the Nepali can also understand and speak Neighbouring country's language . Many Nepali in government and business uses English as well.
Other languages, particularly in the Inner Terai, hill and mountain regions are remnants of the country's pre-unification history of dozens of political entities isolated by mountains and gorges. These languages typically are limited to an area spanning about one day's walk. Beyond that distance dialects and languages lose mutual intelligibility.
Religion
Hinduism 80.2%, Buddhism 10.7%, Islam 4.2%, Yuma Samyo or Yumaism 3.6% other 1.2% (2006). Religion is important in Nepal; the Kathmandu Valley alone has more than 2,700 religious shrines. The constitution of Nepal describes the country as a "Hindu kingdom", although it does not establish Hinduism as the state religion. Nepal's constitution continues long-standing legal provisions prohibiting discrimination against other religions (but also proselytization). The king was deified as the earthly manifestation of the Hindu god Vishnu. Then on May 19, 2006, the government facing a constitutional crisis, the House of Representatives which had been just reformed, having been previously dissolved, declared Nepal a "secular state".
The 2001 census identified 80.6% of the population as Hindu and 10.7% as Buddhist (although many people labeled Hindu or Buddhist often practice a syncretic blend of Hinduism, Buddhism, or animist traditions). 4.2% of the population is Muslim and 3.6% of the population follows the indigenous Kirant Mundhum religion. Christianity is practiced by less than 0.5% of the population. [1]
Buddhist and Hindu shrines and festivals are respected and celebrated by most Nepalese. Certain animist practices of old indigenous religions survive.
Ethnic and regional equity
Pahari Hill Hindus of the Khas tribe (Bahun and Chhetri castes) and the Newar ethnicity dominated the civil service, the judiciary and upper ranks of the army throughout the Shah regime (1768–2008). Nepali was the national language and Sanskrit became a required school subject. Children who spoke Nepali natively and who were exposed to Sanskrit had much better chances of passing the national examinations at the end of high school, which meant they had better employment prospects and could continue into higher education. Children who natively spoke local languages of the Terai and Hills, or Tibetan dialects prevailing in the high mountains were at a considerable disadvantage. This history of exclusion coupled with poor prospects for improvement created grievances that encouraged many in ethnic communities such as Madhesi and Tharu in the Terai and Kham Magar in the mid-western hills to support the Unified Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist) and various other armed Maoist opposition groups such as the JTMM during and after the Nepalese Civil War. The negotiated end to this war forced King Gyanendra to abdicate in 2008. Issues of ethnic and regional equity have tended to dominate the agenda of the new republican government and continue to be divisive.[33][34][35][36][37]
Nepali in the U.K.
According to latest figure from Office for National Statistics estimates that 35,000 Nepali-born people are currently resident in the UK .[38]
Nepali in Hong Kong
Nepali people in Hong Kong are mainly the children of ex-Gurkhas born in Hong Kong during their parents' service with the British Army's Brigade of Gurkhas, which was based in Hong Kong from the 1970s until the handover. Large groups can be found in Shek Kong, Yuen Long District, of the main bases of the British army. Many ex-Gurkhas remained in Hong Kong after the end of their service under the sponsorship of their Hong Kong-born children, who held right of abode.
Nepalis of middle age or older generations in Hong Kong are predominantly found in security, while those of younger generations are predominantly found in the business industry.
Nepali overseas
| Country | Articles | Overseas Nepali Population |
|---|---|---|
| India | Nepali Indian | 4,100,000 |
| Burma | Burmese Gurkha | 400,000 |
| Saudi Arabia | Nepalis in Saudi Arabia | 350,000 |
| Malaysia | Nepalese people in Malaysia | 300,000 |
| United States | Nepalese American | 110,616 |
| Bhutan | Lhotshampa | 110,000 |
| Qatar | Nepalis in Qatar | 100,000 |
| Japan | Nepalis in Japan | 100,000 |
| United Arab Emirates | Nepalis in the United Arab Emirates | 50,000 |
| United Kingdom | Nepalis in the United Kingdom | 35,000[38] |
| Iraq | 30,000[39] | |
| China | Nepalis in China | 21,000 |
| Continental Europe | 20,000 | |
| Hong Kong | Nepalis in Hong Kong | 16,000 |
| Australia | Nepalese Australian | 10,000 |
| South Korea | Nepalis in South Korea | 100,000 |
| Canada | Nepalese Canadian | 6,000 |
| Total Overseas Nepal Population | ~5,643,000 |
References
- ^ International Nepal Fellowship - Nepali diaspora
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k CIA (2011) The World Factbook : Nepal.
- ^ World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision
- ^ Government of Nepal. Central Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Year Book of Nepal, 2009 (PDF). Kathmandu.
- ^ "Nationalities of Nepal, #36: Bhujels/Ghartis". Friedrich-Ebert-Stifting (FES). Retrieved 2011-04-06.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Lewis, M. Paul (2009). "Bhujel, a language of Nepal". Ethnologue: Languages of the World. Dallas: SIL International. Retrieved 2011-04-06.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Anon. (April, 2006), Social Inclusion: What really achieved? (PDF), Kishore, Nepal: Centre for Professional Journalism Studies, Nepal
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Jha, Shrawan Kumar (1997), "The Khatbe of North Bihar, an Anthropological Perspective", Scheduled Castes Today (Makhan Jha, ed.), New Delhi: M D Publications, pp. 161 ff.
- ^ "#40: Majhis". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Majhi, a language of Nepal".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "Call to uplift ethnic Nunia community". The Rising Nepal. Kathmandu: Gorkhapatra. June 13. Retrieved April 8, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "#12: Jhangads". FES, op. cit.
- ^ "Bantar Community in Nepal". BlogSpot: Mahesh Paudyal Prarambha. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- ^ "#5: Gangais". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Darai, a language of Nepal".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "#24: Darais". FES, op. cit.
- ^ "#16: Tajpurias". FES, op. cit.
- ^ "#34: Botes". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Bote-Majhi, a language of Nepal".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "#32: Baramos". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Baraamu, a language of Nepal".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Sharma, Sudhindra. "How the crescent fares in Nepal". Himal, May 1995. Retrieved April 7, 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help) - ^ Siddique, Muhammad (2001). "Muslim Population in the Kingdom of Nepal: Some Outstanding Features" (PDF). Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs. 21 (2). Retrieved April 7, 2011.
- ^ "#43: Meches". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Bodo, a language of India".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "#35: Byasis". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Byangsi, a language of India".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "#61: Hyolmos". FES, op. cit.
- ^ Lewis, op. cit. "Helabu Sherpa, a language of Nepal".
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|title=(help); Unknown parameter|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "#3: Kushbadias". FES, op. cit.
- ^ National Coalition Against Racism. "Janajati: Kushbadia". Retrieved April 8, 2011.
- ^ "Nepal Demographic and Health Survey 2011" (PDF). Retrieved 2011-05-07.
- ^ "OCHA Nepal – Situation Overview" (PDF). Issue 12. OCHA. 2007. Retrieved 2011-05-07.
{{cite journal}}:|volume=has extra text (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "OCHA Nepal – Situation Overview" (PDF). Issue 16. OCHA. 2007. Retrieved 2011-05-07.
{{cite journal}}:|volume=has extra text (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "OCHA Nepal – Situation Overview" (PDF). Issue 30. OCHA. 2008. Retrieved 2011-05-07.
{{cite journal}}:|volume=has extra text (help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Sharma, Hari (2010-11-18). "Body of murder victim found in Gulmi". Gulmi: The Himalayan Times online. Retrieved 2011-05-07.
- ^ Hatlebakk, Magnus (2007). "Economic and social structures that may explain the recent conflicts in the Terai of Nepal" (PDF). Kathmandu: Norwegian Embassy. Retrieved 2011-05-08.
- ^ a b "Population by Country of birth and nationality Jan10-Dec10". Office for National Statistics. September 2011. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ Nepal government lifts Iraq working ban
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2024 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2003 edition.)
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook (2024 ed.). CIA. (Archived 2003 edition.)




