Czechs
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c. 10–12 million | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
6,732,104[1][nb 1]–9 246 784[2] | |
| Significant diasporic populations in: | |
| 1,462,000[3] | |
| 94,805[4] | |
| 60,000 | |
| 50,000 | |
| 45,000 | |
| 45,000[5] | |
| 40,324[6] | |
| 40,000 | |
| 38,000 | |
| 30,367[7] | |
| 21,196[8] | |
| 20,000 | |
| 9,641 (2011) | |
| 8,600 | |
| 11,000 | |
| 7,175 (2001) | |
| 5,451[9] | |
| 5,622 (2006) | |
| 5,000–6,000 | |
| 5,000[citation needed] | |
| 3,500 | |
| 3,339 (2002) | |
| 3,000 | |
| 2,300 | |
| 2,000 | |
| 2,000 | |
| 1,824 (2011)[10] | |
| 1,200 | |
| 1,083 | |
| 1,000[11] | |
| 600–1,000[12] | |
| Languages | |
| Czech | |
| Religion | |
| Christianity: Roman Catholic, Hussite, Lutheran Irreligion and other | |
The Czechs (Czech: Češi, pronounced [ˈtʃɛʃɪ]; singular masculine: Čech [ˈtʃɛx], singular feminine: Češka [ˈtʃɛʃka]) or the Czech people (Český národ), are a West Slavic ethnic group native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and are native speakers of the Czech language.
Ethnic Czechs were called Bohemians in English until the early 20th century, referring to the late Iron Age tribe of Celtic Boii and the land Bohemia. During the Migration Period, West Slavic tribes of Bohemians settled in the area, "assimilated the remaining Celtic and Germanic populations", and formed an principality in the 9th century, which was part of great Moravia, in form of Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia, the predecessors of the modern republic.
The Czech diaspora is found in notable numbers in the United States, Canada, Israel, Austria, Germany, Slovakia, Switzerland, Italy, the United Kingdom, Australia, Argentina and Brazil among others.
Ethnology
The Czech ethnic group is part of the West Slavic subgroup of the larger Slavic ethno-linguistical group. The West Slavs have origin in early Slavic tribes which settled in Central Europe after East Germanic tribes had left this area during the migration period.[13] The West Slavic tribe of Bohemians settled in the area of Bohemia during the migration period, and assimilated the remaining Celtic and Germanic populations.[14] They formed a principality in the 9th century, the Duchy of Bohemia, under the Přemyslid dynasty which was part of the Great Moravia under Svatopluk I. According to mythology, the founding father of the Czech people were Forefather Čech, who according to legend brought the tribe of Czechs into its land.
The Czech are closely related to the neighbouring Slovaks (with whom they constituted Czechoslovakia 1918–1993). The Czech–Slovak languages form a dialect continuum rather than being two clearly distinct languages.[15] Czech cultural influence in Slovak culture is noted as having been much higher than the other way around.[16] Czech (Slavic) people have a long history of coexistence with Germanic people. In the 17th century, German replaced Czech in central and local administration; upper classes in Bohemia and Moravia were Germanized, and espoused a political identity (landespatriotismus), while Czech ethnic identity survived among the lower and lower-middle classes.[17] The Czech National Revival took place in the 18th and 19th centuries aiming to revive Czech language, culture and national identity. The Czech were the initiators of Pan-Slavism.[18]
The Czech ethnonym (archaic Čechové) was the name of a Slavic tribe in central Bohemia that subdued the surrounding tribes in the late 9th century and created the Czech/Bohemian state. The origin of the name of the tribe itself is unknown. According to legend, it comes from their leader Čech, who brought them to Bohemia. Research regards Čech as a derivative of the root čel- (member of the people, kinsman).[19] The Czech ethnonym was adopted by the Moravians in the 19th century.[20] The name "Bohemia" (and "Bohemians") is Germanic; English used that name until after the establishment of Czechoslovakia.
Genetics

The population of the Czech lands has been influenced by different human migrations that wide-crossed Europe over time. In their Y-DNA haplogroups, which are inherited along the male line, Czechs have shown a mix of Eastern and Western European traits. 34.2% of Czech males belong to R1a, which is particularly common in a large region extending from South Asia and Southern Siberia to Central Europe and Scandinavia. Within the Czech Republic, the proportion of R1a seems to gradually increase from west to east [22] According to a 2000 study, 35.6% of Czech males have haplogroup R1b, which is very common in Western Europe among Germanic and Celtic nations, but rare among Slavic nations.[23] A mtDNA study of 179 individuals from Western Bohemia showed that 3% had East Eurasian lineages that perhaps entered the gene pool through admixture with Central Asian nomadic tribes in the early Middle Ages.[24] A group of scientists suggested that the high frequency of a gene mutation causing cystic fibrosis in Central European (including Czech R.) and Celtic populations proves a proto-Celtic population origin, besides the Slavic, in the Czech population.[25]
| Population | n | R1b | R1a | I | E1b1b | J | G | N | T | Others | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Czech R. | 257 | — | 34.2 | 18.3 | 5.8 | 4.7 | 5.1 | 1.6 | — | — | Luca et al. 2007[21] |
| Czech R. | ? | 35.6 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | Semino et al. 2000[23] |
History
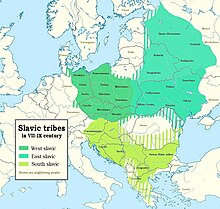


The population of the Czech Republic descends from diverse peoples of Slavic, Celtic and Germanic origin.[14][26][27] Presence of West Slavs in the 6th century during the Migration Period has been documented on the Czech territory.[14] Slavs settled in Bohemia, Moravia and Austria sometime during the 6th or 7th centuries,[28] and "assimilated the remaining Celtic and Germanic populations".[14][29] According to a popular myth, the Slavs came with Forefather Čech who settled at the Říp Mountain.
During the 7th century, the Frankish merchant Samo, supporting the Slavs fighting against nearby settled Avars, became the ruler of the first known Slav state in Central Europe, the Samo's Empire. The principality Great Moravia, controlled by Moymir dynasty, arose in the 8th century and reached its zenith in the 9th (during the reign of Svatopluk I of Moravia) when it held off the influence of the Franks. Great Moravia was Christianized, the crucial role played Byzantine mission of Cyril and Methodius. The Duchy of Bohemia emerged in the late 9th century. In 880, Prague Castle was constructed by Prince Bořivoj, founder of the Přemyslid dynasty and the city of Prague was established. Vratislav II was the first Czech king in 1085 and the duchy was raised to a hereditary kingdom under Ottokar I in 1198.
The second half of the 13th century was a period of advancing German immigration into the Czech lands. The number of Czechs who have at least partly German ancestry today probably runs into hundreds of thousands.[30] The Habsburg Monarchy focused much of its power on religious wars against the Protestants. While these religious wars were taking place, the Czech estates revolted against Habsburg from 1546 to 1547 but were ultimately defeated.[31]
| Part of a series on |
| Czechs |
|---|
 |
Defenestrations of Prague in 1618, signaled an open revolt by the Bohemian estates against the Habsburgs and started the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of White Mountain in 1620, all Czech lands were declared hereditary property of the Habsburg family. The German language was made equal to the Czech language.
Czech patriotic authors tend to call the following period, from 1620 to 1648 until the late 18th century, the "Dark Age". It is characterized by devastation by foreign troops; Germanization; and economic and political decline. It is estimated that the population of the Czech lands declined by a third.[32]
The 18th and 19th century is characterized by the Czech National Revival, focusing to revive Czech culture and national identity.
Since the turn of the 20th century, Chicago is the city with the third largest Czech population, after Prague and Vienna.[33][34]
During World War I, Czechoslovak Legions fought in France, Italy and Russia against the Central Powers and in 1918 was proclaimed independent Czechoslovakia. Czechs formed the leading class in the new state from the remnants of the Austrian-Hungarian Monarchy. After 1933, Czechoslovakia remained the only democracy in central and eastern Europe.
In 1938 the Munich Agreement severed the Sudetenland, with a considerable Czech minority, from Czechoslovakia, and in 1939 the German Nazi regime established the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia for Resttschechei (the rump Czech state[35][36][37]). Emil Hácha became president of the protectorate under Nazi domination, which only allowed pro-Nazi Czech associations and tended to stress ties of the Czechs with the Bohemian Germans and other parts of the German people, in order to facilitate assimilation by Germanization. In Lidice, Ležáky and Javoříčko the Nazi authorities committed war crimes against the local Czech population. On May 2, 1945, the Prague Uprising reached its peak, supported by the Russian Liberation Army. The post-war expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia and the immediate reprisals against Germans and Nazi collaborators by Czech resistance and the Czechoslovak state authorities, made Czechs—especially in the early 1950s—settle alongside Slovaks and Romani people in the former lands of the Sudeten Germans, who had been deported to East Germany, West Germany and Austria according to the Potsdam Conference and Yalta Conference.
The Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968 was followed by a wave of emigration, unseen before and stopped shortly after (estimate: 70,000 immediately, 300,000 in total),[38] typically of highly qualified people.
Tens of thousands of Czechs had repatriated from Volhynia and Banat after World War II. Since the 1990s, the Czech Republic has been working to repatriate Romania and Kazakhstan's ethnic Czechs.[39][40]
Following the Czech Republic's entry into the European Union in May 2004, Czechs gradually gained the right to work in EU countries without a work permit.[41]
Notable people
Historical figures
The last five Přemyslids were kings: Ottokar I of Bohemia, Wenceslaus I of Bohemia, Ottokar II of Bohemia, Wenceslaus II of Bohemia and Wenceslaus III of Bohemia. The most successful and influential of all Czech kings was Charles IV, who also became the Holy Roman Emperor.[42] The Luxembourg dynasty represents the heights of Czech (Bohemian) statehood territorial and influence as well as advancement in many areas of human endeavors.[43]
Many people are considered national heroes and cultural icons, many national stories concern their lives. Jan Hus was a religious reformist from the 15th century and spiritual father of the Hussite Movement.[44] Jan Žižka was a leader of hussite army, George of Poděbrady was a hussite king. Albrecht von Wallenstein was a notable military leader during the Thirty Years' War. The teacher of nations Jan Amos Komenský is also considered a notable figure in Czech history.[45] Joseph Radetzky von Radetz was an Austrian general staff during the later period of the Napoleonic Wars. Josef Jungmann is often credited for expanding the modern Czech language, and preventing its extinction.[46] The first modern Czech politician was František Palacký, often called "father of nation".
Modern politicians
One of the most notable figures are founders of Czechoslovakia, modern state of independence of Czech and Slovak nations, Presidents Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk and Edvard Beneš, who was also leader of exile government in World War II. Ludvík Svoboda was a head of the Czechoslovak military units on the Eastern Front during the World War II (later president of Czechoslovakia). Jan Palach committed self-immolation as a political protest against the end of the Prague Spring resulting from the 1968 invasion of Czechoslovakia by the Warsaw Pact armies.
Another notable politician after the fall of the communist regime is Václav Havel, last President of Czechoslovakia and first President of the Czech Republic.[47] The current first directly elected president is Miloš Zeman.[48]
The Czech Republic has had multiple Prime Ministers the first of which was latter Presidents Václav Klaus and Miloš Zeman.[49] Another Prime Ministers of the Czech Republic were conservative politicians such as Mirek Topolánek, Petr Nečas and social democratic such as Vladimír Špidla, Jiří Paroubek, Bohuslav Sobotka.[50]
Madeleine Albright is of Czech origin and fluent in Czech.
Science
Czechs established themselves mainly in Biology, Chemistry, Philology or Egyptology.
- Chemistry – Jaroslav Heyrovský (Nobel Prize 1959), Zdenko Hans Skraup
- Biology – Jan Evangelista Purkyně, Carl Borivoj Presl, Jan Svatopluk Presl, Karel Domin, Kaspar Maria von Sternberg, Friedrich von Berchtold, Ferdinand Stoliczka, Wenceslas Bojer, Jan Janský, Alberto Vojtěch Frič, August Carl Joseph Corda
- Mathematics – Eduard Čech, Miroslav Katětov, Petr Vopěnka
- Physics and Engineering – Ignaz von Born, Otto Wichterle, František Běhounek, Jan Marek Marci, Josef Ressel, František Křižík, Vincenc Strouhal, Prokop Diviš, František Josef Gerstner
- Astronomy – Antonín Mrkos, Antonín Bečvář
- Philology – Bedřich Hrozný, Josef Dobrovský, Josef Jungmann, Vilém Mathesius, Julius Pokorny, René Wellek, Jan Mukařovský
- Medicine – Carl von Rokitansky, Joseph Škoda
- Archeology – Pavel Pavel, Lubor Niederle, Karel Absolon, Miroslav Verner
- Anthropology and Ethnography – Aleš Hrdlička, Emil Holub, Alois Musil
- History – František Palacký, Bohuslav Balbín, Konstantin Jireček, Max Dvořák, Miroslav Hroch
- Philosophy – Jan Patočka, Karel Kosík, Egon Bondy, Ladislav Klíma
- Psychology – Stanislav Grof
- Theology – Jan Hus, Jerome of Prague, Petr Chelčický, Jan Rokycana, Tomáš Špidlík, Tomáš Halík
- Modern occultism – Franz Bardon
- Pedagogy – Jan Amos Komenský
- Folklorists – František Ladislav Čelakovský, Karel Jaromír Erben
- Literary theory – Karel Teige, Pavel Janáček
Sports
Sports have also been a contributor to famous Czechs especially tennis, football, hockey, and athletics:
- Tennis – Jaroslav Drobný, Jan Kodeš, Martina Navratilová, Ivan Lendl, Hana Mandlíková, Jana Novotná, Petr Korda, Petra Kvitová,[51] Tomáš Berdych, Karolína Plíšková
- Football – Oldřich Nejedlý, Antonín Puč, František Plánička, Josef Bican, Josef Masopust, Ivo Viktor, Antonín Panenka, Zdeněk Nehoda, Pavel Nedvěd, Karel Poborský, Jan Koller, Milan Baroš, Marek Jankulovski, Vladimír Šmicer, Tomáš Rosický,[52][53] Petr Čech
- Hockey – Jaromír Jágr, Dominik Hašek, Vladimír Růžička, Jiří Šlégr, Ivan Hlinka, Jiří Holeček, Jaroslav Pouzar, Jiří Hrdina, Petr Sýkora, Patrik Eliáš, Bobby Holík, Michal Rozsíval, Milan Hejduk, Petr Nedvěd, Martin Straka, Václav Prospal, Jakub Voráček, Tomáš Plekanec, František Kaberle, David Výborný, Pavel Patera, Martin Procházka
- Athletics – Emil Zátopek, Dana Zátopková, Jarmila Kratochvílová, Roman Šebrle, Jan Železný, Barbora Špotáková
- Chess – Wilhelm Steinitz, Věra Menčíková, Richard Réti, Salo Flohr, David Navara
- Others – Věra Čáslavská, Martina Sáblíková, Martin Doktor, Štěpánka Hilgertová, Josef Holeček, Filip Jícha, Jiří Zídek Sr., Jan Veselý
The arts
Music

Czech music had its first significant pieces created in the 11th century.[54] The great progress of Czech artificial music began with the end of the Renaissance and the early Baroque era, concretely in works of Adam Václav Michna z Otradovic, where the specific character of Czech music was rising up by using the influence of genuine folk music. This tradition determined the development of Czech music and has remained the main sign in the works of great Czech composers of almost all eras – Jan Dismas Zelenka and Josef Mysliveček in Baroque, Bedřich Smetana and Antonín Dvořák in Romanticism, Leoš Janáček, Bohuslav Martinů and Josef Suk in modern classical or Petr Eben and Miloslav Kabeláč in contemporary classical music.
Czech musicians also played an important role in the development of European music. Jan Václav Antonín Stamic in 18th-century contributed to the creation of Classicism in music[55] by innovations of compositional forms and the founding of the Mannheim school. Similarly, Antonín Rejcha's experiments prefigured new compositional techniques in the 19th century.[56] The influence of Czech musicians expanded beyond the borders of the European continent, when Antonín Dvořák created a new American classical music style, using the richness of ethnic music of that country during his mission in the US. The contribution of Alois Hába to microtonal music in the 20th century must be also mentioned.
Czech music reached as far as Qing China. Karel Slavíček was a Jesuit missionary, scientist and sinologist who was introduced to the Kangxi Emperor on February 3, 1717, in Beijing. The emperor favored him and employed him as court musician. (Slavíček was a Spinet player).[57]
Some notable modern Czech musicians are US-based composer and guitarist Ivan Král, musician and composer Jan Hammer and the rock band The Plastic People of the Universe which played an important part in the underground movement during the communist regime.
Other important names: Franz Benda, Rafael Kubelík, Jan Ladislav Dussek, Vítězslav Novák, Zdeněk Fibich, Jan Kubelík, Jiří Antonín Benda, Julius Fučík, Karel Svoboda, Karel Kryl, Václav Neumann, Václav Talich, František Xaver Richter, Jan Křtitel Vaňhal, Vojtěch Živný, Josef Bohuslav Foerster, Magdalena Kožená, Karel Ančerl, Ema Destinnová, Maria Jeritza, František Xaver Brixi, Jiří Bělohlávek, Oskar Nedbal, Karel Gott.[58]
Literature
Jaroslav Seifert was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature for his poetry.[51] Božena Němcová has become a cultural icon and gained much fame for her book Babička.[59] Other important Czech writers include Milan Kundera, Karel Čapek, Jaroslav Hašek, Jan Neruda, Franz Kafka, Bohumil Hrabal, Viktor Dyk, Kosmas, Pavel Kohout, Alois Jirásek, Josef Škvorecký, Karel Jaromír Erben, Jiří Wolker, Karel Hynek Mácha, Vítězslav Nezval, Arnošt Lustig, Jaroslav Vrchlický, Karel Havlíček Borovský, Ivan Klíma, Egon Erwin Kisch, Vladimír Holan or Svatopluk Čech. From contemporary Czech writers can be mentioned Jáchym Topol, Patrik Ouředník, Michal Viewegh or Daniela Hodrová. Important playwrights were Karel Čapek, František Langer or Josef Kajetán Tyl. Strong was also the theatrical avant-garde (Jan Werich, Jiří Voskovec, Emil František Burian). Known journalists were Julius Fučík, Milena Jesenská or Ferdinand Peroutka.
Visual Arts

Mikoláš Aleš was a painter, known for redesigning the Prague National Theatre.[60] Alphonse Mucha was an influential artist in the Art Nouveau movement of the Edwardian period. František Kupka was a pioneer and co-founder of the abstract art movement. Other well-known painters are Josef Čapek, Josef Lada, Theodoric of Prague, Wenceslaus Hollar, Toyen, Jan Kupecký, Petr Brandl, Vladimír Vašíček, Václav Brožík, Josef Mánes, Karel Škréta or Max Švabinský. Renowned sculptors were Josef Václav Myslbek or Matyáš Bernard Braun, photographers Jan Saudek, Josef Sudek, František Drtikol or Josef Koudelka, illustrators Zdeněk Burian or Adolf Born, architects Jan Kotěra or Josef Gočár. Jiří Kylián was an important ballet choreographer.
Film
Film director Miloš Forman, known best for his movie, One Flew over the Cuckoo's Nest is of Czech origin and started his career in Czechoslovakia.[61] Forman was a member of the so-called Czech New Wave. Other members included Jiří Menzel (Oscar 1967), Věra Chytilová and Elmar Klos (Oscar 1965). Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film has also Jan Svěrák (1996). The influential surrealist filmmaker and animator Jan Švankmajer was born in Prague and has resided in the Czech Republic throughout his life. In the field of animation and puppet film made famous Zdeněk Miler, Karel Zeman and Jiří Trnka.
Actors Zdeněk Svěrák, Vlastimil Brodský,[62] Vladimír Menšík,[63] Libuše Šafránková or Karel Roden have also made a mark in modern Czech history. The most successful Czech erotic actress is Silvia Saint.
Modeling
The first Czech models have made a breakthrough in the international modeling were Paulina Porizkova or Ivana Trump. After the fall of communism in Czechoslovakia many other models succeeded: Karolína Kurková, Eva Herzigová, Taťána Kuchařová, Petra Němcová or Daniela Peštová.
Saints
Czech culture involves many saints,[64] most notably St. Wenceslaus (Václav), patron of the Czech nation,[65] St. John of Nepomuk (Jan Nepomucký),[66] St. Adalbert (Vojtěch),[67] Saint Procopius or St. Agnes of Bohemia (Anežka Česká).[68]
Natives
Modern Czech nation was formed in process of Czech national revival. In it, he pushed linguistic concept of the nation (particularly promoted by Jungmann), i.e. "Czech = one who has Czech language as their first language - naturally or by choice." (That is why they are often considered the Czechs, Slovaks who have chosen the Czech language as their literary language, such as Ján Kollár or Pavel Jozef Šafařík). Like other nations, the Czechs also discuss two alternative concepts - land concept (Czech is one who is born in the historic Czech territory), which in times of Jungmann success primarily nobility, and ethnic concept. Definition by the territory is still discussed alternative,[69][70] from time to time is indicated for Czechs number of natives (speaking mostly German, English or otherwise) - these include US Secretary of State Madeleine Albright, film director Karel Reisz, actor Herbert Lom, the founder of psychoanalysis Sigmund Freud, the founder of genetics Gregor Mendel, logician and mathematician Kurt Gödel, the philosopher Edmund Husserl, scientists Gerty Cori, Carl Cori and Peter Grünberg (all Nobel Prize winners) and Ernst Mach, economists Joseph Schumpeter and Eugen Böhm von Bawerk, philosophers Bernard Bolzano, Ernest Gellner, Vilém Flusser and Herbert Feigl, Marxist theoretician Karl Kautsky, astronomer Johann Palisa, legal theorist Hans Kelsen, inventors Alois Senefelder and Viktor Kaplan, automotive designer Ferdinand Porsche, psychologist Max Wertheimer, a geologist Karl von Terzaghi, musicologists Eduard Hanslick and Guido Adler, chemist Johann Josef Loschmidt, biologists Heinrich Wilhelm Schott and Georg Joseph Kamel, the founder of the dermatology Ferdinand Ritter von Hebra, peace activist Bertha von Suttner (Nobel Peace Prize), the composers Gustav Mahler, Heinrich Biber, Viktor Ullmann, Ervin Schulhoff, Pavel Haas, Erich Wolfgang Korngold and Ralph Benatzky, writers Franz Kafka, Reiner Maria Rilke, Max Brod, Karl Kraus, Franz Werfel, Marie von Ebner-Eschenbach, Leo Perutz, Tom Stoppard and Egon Erwin Kisch, painters Anton Raphael Mengs and Emil Orlik, architects Adolf Loos, Peter Parler, Josef Hoffmann, Jan Santini Aichel and Kilian Ignaz Dientzenhofer, cellist David Popper, violist Heinrich Wilhelm Ernst, pianists Alice Herz-Sommer and Rudolf Serkin, president of Austria Karl Renner, Prime Minister of Poland Jerzy Buzek, industrialist Oskar Schindler, or chess player Wilhelm Steinitz.
Czech ancestry
Czech ancestry have astronauts Eugene Cernan and Jim Lovell, film directors Chris Columbus and Jim Jarmusch, swimmer Katie Ledecky, politicians John Forbes Kerry, Caspar Weinberger and John Kasich, chemist and Nobel Prize laureate Thomas Cech, physicist Karl Guthe Jansky, economist Friedrich Hayek, painters Jan Matejko, Gustav Klimt, Egon Schiele and Oskar Kokoschka, actors Ashton Kutcher, Sissy Spacek and Kim Novak, tennis players Richard Krajicek, Jakob Hlasek and Stan Wawrinka, singer Jason Mraz, Brazil president Juscelino Kubitschek, founder of McDonald's company Ray Kroc, writers Georg Trakl and Robert Musil, mayor of Chicago Anton Cermak or Ivanka Trump and her brother Donald Trump Jr.
Geography

The Czechs live in three historical lands: Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia;[71] these regions make up the modern Czech Republic. However, the country is now divided into 14 administrative regions.[72] The local culture varies somewhat in each of the historical regions.[73] Moravians are usually more nationalistic regional patriots of Moravia, but they also speak Czech. Local dialects (such as Central Bohemian, the Chod dialect, Moravian, Cieszyn Silesian, etc.) are found in various parts of the country.[74]
Czech language
The Czech language is spoken by approximately 12 million people around the world, but the vast majority are in the Czech Republic.[75] It developed from the Proto-Slavic language in the 10th century[75][76] and is mutually intelligible with the Slovak language.[77]
Religion
Richard Felix Staar described Czechs as "tolerant and even indifferent towards religion as a rule".[78]
After the Bohemian Reformation, most Czechs (about 85%) became followers of Jan Hus, Petr Chelcicky and other regional Protestant Reformers. Bohemian Estates' defeat in the Battle of White Mountain brought radical religious changes and started a series of intense actions taken by the Habsburgs in order to bring the Czech population back to the Roman Catholic Church. After the Habsburgs regained control of Bohemia, Czech people were forcibly converted to Roman Catholicism. All kinds of Protestant communities including the various branches of Hussites, Lutherans and Reformed were either expelled, killed, or converted to Catholicism. The Catholic Church lost the bulk of its adherents during the Communist era and continues to lose in the modern, ongoing secularization.
According to the 2011 census, 34.5% of the population stated they had no religion, 10.5% were Catholics, 1% Protestants, 0.9% members of other Christian churches, 6.8% were believers but not members of religions, while 0.7% were believers and members of other certain religions. 44.7 of the population did not answer the question about religion.[79]
Demographics
In the Czech Republic, the nation state of the Czech people, 6,732,104 (63.7%) declared as ethnic Czech according to the 2011 census. Notably, another 2,742,669 (26%) were undeclared, and 522,474 (4.9%) declared as Moravians.[80] There is a large Czech diaspora, which includes 1,703,930 Americans of Czech/Czechoslovak ancestry,[81] 94,805 Canadians of Czech ancestry,[82] an estimated 45,000 Czech-born residents in the United Kingdom,[5] and ca. 31,000 in Australia.[83] There are smaller communities throughout Europe.
See also
References
Footnotes
- ^ This number is a lower estimate, as 2,742,669 people opted out declaring ethnicity in 2011.
Notes
- ^ "Tab. 6.2 Obyvatelstvo podle národnosti podle krajů: výsledky podle trvalého bydliště" [Tab. 6.2 Population by nationality by regions: results for permanent residence] (PDF). Czech Statistical Office (CZSO) (in Czech). 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Czech Republic". CIA - The World Factbook. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "2004 survey". United States Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "Ethnic Origin (264), Single and Multiple Ethnic Origin Responses (3), Generation Status (4), Age Groups (10) and Sex (3) for the Population in Private Households of Canada, Provinces, Territories, Census Metropolitan Areas and Census Agglomerations, 2011 National Household Survey".
- ^ a b "Table 1.3: Overseas-born population in the United Kingdom, excluding some residents in communal establishments, by sex, by country of birth, January 2013 to December 2013". Office for National Statistics. 2 July 2015. Retrieved 20 July 2015. Figure given is the central estimate. See the source for 95 per cent confidence intervals.
- ^ "Bevölkerung nach Staatsangehörigkeit und Geburtsland".
- ^ Štatistický úrad SR Archived 29 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Data & analysis". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "CSO Emigration" (PDF). Census Office Ireland. Retrieved 29 January 2013.
- ^ Попис становништва, домаћинстава и станова 2011. у Републици Србији: Становништво према националној припадности - "Oстали" етничке заједнице са мање од 2000 припадника и двојако изјашњени
- ^ Joshua Project. "People Groups". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "webzdarma - Soubor nenalezen / File not found". Archived from the original on 14 October 2007. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Kobyliński, Zbigniew (1995). "The Slavs". In McKitterick, Rosamond (ed.). The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 1, C.500-c.700. The New Cambridge Medieval History. Vol. 1, C.500–c.700. Cambridge University Press. p. 531. ISBN 9780521362917.
- ^ a b c d Rick Fawn, Jiří Hochman. Historical Dictionary of the Czech State. Page xix. Rowman & Littlefield. 2010. ISBN 978-0810856486. ISBN 0810856484.
- ^ Tomasz Kamusella; Motoki Nomachi; Catherine Gibson (29 April 2016). The Palgrave Handbook of Slavic Languages, Identities and Borders. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 140–. ISBN 978-1-137-34839-5.
- ^ Berger 2003.
- ^ Joshua A. Fishman (25 January 2001). Handbook of Language & Ethnic Identity. Oxford University Press. pp. 320–. ISBN 978-0-19-976139-5.
- ^ Hans Kohn (1953). Pan-Slavism: its history and ideology. University of Notre Dame Press.
- ^ Spal, Jaromír (1953). "Původ jména Čech" [Origin of the name Čech]. Naše řeč (Our Speech) (in Czech). 36 (9–10). The Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic: 263–267. Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- ^ T. Kamusella (16 December 2008). The Politics of Language and Nationalism in Modern Central Europe. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 501–. ISBN 978-0-230-58347-4.
- ^ a b Luca F, Di Giacomo F, Benincasa T, Popa LO, Banyko J, Kracmarova A, Malaspina P, Novelletto A, Brdicka R (2007). "Y-chromosomal variation in the Czech Republic". Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 132 (1): 132–9. doi:10.1002/ajpa.20500. PMID 17078035.
- ^ F. Luca, F. Di Giacomo, T. Benincasa et al., "Y-Chromosomal Variation in the Czech Republic," American Journal of Physical Anthropology 132:132–139 (2007).
- ^ a b O. Semino et al, The genetic legacy of paleolithic Homo sapiens sapiens in extant Europeans: a Y chromosome perspective, Science, vol. 290 (2000), pp. 1155–59.
- ^ Malyarchuk; et al. "Mitochondrial DNA Variability in the Czech Population, with Application to the Ethnic History of Slavs". Human Biology. 78 (6). doi:10.1353/hub.2007.0014.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Macek; et al. "Relativně vysoký výskyt mutací G551D a CFTRdel21kb CFTR genu v České republice u pacientů s cystickou fibrózou objektivně prokazuje, že naše populace je slovanského a keltského původu" (Document). Centrum pro diagnostiku a léčbu cystické fibrosy.
{{cite document}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|archive-date=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|archive-url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help) - ^ Horáková, Pavla (10 May 2007). "In search of 'Forefather Czech' - DNA tests disclose remote ancestors". Radio Prague. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- ^ Bohemia and Poland. Chapter 20.pp 512-513. [in:] Timothy Reuter. The New Cambridge Medieval History: c. 900 – c. 1024. 2000
- ^ The exact dating of Slavic settlement is a matter of dispute amongst scholars. See e.g. Curta ("The Slavs in Bohemia: A Response to my critics; 2009") who favours a 7th-century settlement versus Nada Profantova, who argues a 6th-century settlement
- ^ Jaroslav Jirik "Bohemian Barbarians. Bohemia in late Antiquity", in Neglected Barbarians Brepols 2010[page needed]
- ^ "Ethnic German Minorities in the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovakia". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "The Habsburg Monarchy and Rudolph II". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ Agnew 2004, p. 72.
- ^ Cozine, Alicia (2005). "Czechs and Bohemians". The Electronic Encyclopedia of Chicago. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Czech and Slovak roots in Vienna, wieninternational.at
- ^ Gruner, Wolf. 2015. Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. In: Wolf Grüner & Jörg Osterloh (eds.), The Greater German Reich and the Jews: Nazi Persecution Policies in the Annexed Territories 1935–1945, pp. 99–135. Transl. Bernard Heise. New York: Berghahn, p. 103.
- ^ Ramsden, John. 2002. The Oxford Companion to Twentieth-Century British Politics. Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 450.
- ^ Rothschild, Joseph. 1974. East Central Europe between the Two World Wars. Seattle: University of Washington Press, p. 366.
- ^ ""Day when tanks destroyed Czech dreams of Prague Spring" (Den, kdy tanky zlikvidovaly české sny Pražského jara) at Britské Listy (British Letters)". Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ The Czech ethnic minority in Romania, 29-12-2004 - Radio Prague
- ^ Government completes 13-year program to integrate Kazakh Czechs, The Prague Post, 31 October 2007
- ^ "Práce v Evropské unii: jaké máme možnosti? penize.cz". 23 February 2007. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ "Charles IV (Karel IV.) - Czech king and Holy Roman Emperor". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Travel guide - Luxembourg dynasty (1310–1378) - accommodation in hotels and apartments - Travel.cz". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Jan Hus". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Jan Amos Comenius Archived 15 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Josef Jungmann (1773–1847)[permanent dead link]
- ^ Liukkonen, Petri. "Václav Havel". Books and Writers (kirjasto.sci.fi). Finland: Kuusankoski Public Library. Archived from the original on 4 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|website=(help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "VACLAV HAVEL". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Rejstřík předsedů vlád". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Radio Prague - Milos Zeman - outgoing prime minister". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ a b "CzechSite: Famous Czechs". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Radio Prague - Antonin Panenka - the footballer Pele described as "either a genius or a madman"". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Josef, Ladislav. "Masopust's memory lingers on". Archived from the original on 22 December 2007. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.eu2009.cz/en/czech-republic/music/history/history-of-czech-music-2374 History of Czech music
- ^ http://www.czechmusic.net/klasika/stamic_jv.htm Jan Václav Antonín Stamic (in Czech)
- ^ http://www.classical.net/music/comp.lst/reicha.php Antonín Rejcha
- ^ "Český jezuita na čínském dvoře". cinsky.cz. 26 February 2009. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- ^ "Karel Gott". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic. Archived from the original on 1 January 2008. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ Partridge, James. "Book Review: The Grandmother". Central Europe Review. Retrieved 10 February 2008.
- ^ Tyman, Jaroslav. "Mikoláš Aleš". Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ^ Erickson, Hal. "Milos Forman, biography". Allmovie. Archived from the original on 23 February 2008. Retrieved 10 February 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Vlastimil Brodsky - Czech Film - Worldpress.org". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Czech-Slovak film Database, Vladimír Menšík". POMO Media Group. Retrieved 11 February 2008.
- ^ Maurice, Edmund (1908). The story of Bohemia from the earliest times to the fall of national independence in 1620;: With a short summary of later events. Fisher, Unwin.
- ^ Mershman, Francis. "St. Wenceslaus". Kevin Knight. Retrieved 10 February 2008.
- ^ Krčmář, Luděk. "St. John of Nepomuk - life". MultiMedia Activity. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 10 February 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Attwater, Donald and Catherine Rachel John. The Penguin Dictionary of Saints. 3rd edition. New York: Penguin Books, 1993. ISBN 0-14-051312-4.
- ^ "Order of the Knights of the Cross with the Red Star". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ http://blisty.cz/art/44512.html
- ^ http://www.cs-magazin.com/index.php?a=a2011121kdo
- ^ "Political subdivision of Bohemia, Moravia and Silesia". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "The Area of the Czech Republic". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Czech regions - Czech republic Archived 4 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Czech
- ^ a b "Czech Language". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Czech Republic. Archived from the original on 18 January 2008. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ http://www.kortlandt.nl/publications/art066e.pdf
- ^ "The Czech Language on WWW". Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Richard Felix Staar, Communist regimes in Eastern Europe, Issue 269, p. 90
- ^ "Úvodní stránka - SLDB 2011". czso.cz. Retrieved 19 November 2013.
- ^ "Tab. 6.2 Obyvatelstvo podle národnosti podle krajů: výsledky podle trvalého bydliště" [Tab. 6.2 Population by nationality by regions: results for permanent residence] (PDF). Czech Statistical Office (CZSO) (in Czech). 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "US Census Bureau, American FactFinder, Decennial Programs, Census 2000, Data Set Census 2000 Summary File 3 (SF 3) – Sample Data, Table: PCT18 ANCESTRY (TOTAL CATEGORIES TALLIED) FOR PEOPLE WITH ONE OR MORE ANCESTRY CATEGORIES REPORTED [109] Universe".
- ^ Statistics Canada. "2011 National Household Survey: Data tables". Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ "The People of Australia – Statistics from the 2011 Census" (PDF). Australian Government.
Sources
- Agnew, Hugh (2004). The Czechs and the Lands of the Bohemian Crown. Hoover Press. ISBN 978-0-8179-4492-6.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Berger, Tilman (July 2003). "Slovaks in Czechia—Czechs in Slovakia". International Journal of the Sociology of Language. 2003 (162).
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) - Pánek, Jaroslav (2009). A History of the Czech Lands. Charles University. ISBN 978-80-246-1645-2.
- King, Jeremy (2005). Budweisers Into Czechs and Germans: A Local History of Bohemian Politics, 1848-1948. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-12234-2.
- Wiskemann, Elizabeth (1967). Czechs & Germans: a study of the struggle in the historic provinces of Bohemia and Moravia. Royal Institute of International Affairs; Macmillan.
- Mastny, Vojtech (1971). The Czechs under Nazi Rule. Columbia University Press.
- Hermann, Adolf Hanus (1975). A History of the Czechs. Lane, Allen.
- Vyšný, Paul (1977). Neo-Slavism and the Czechs 1898-1914. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-21230-4.
Further reading
- Hroch, Miroslav (2004). "From ethnic group toward the modern nation: the Czech case". Nations and Nationalism. 10 (1–2). Wiley-Blackwell: 95–107. doi:10.1111/j.1354-5078.2004.00157.x.
- Holy, Ladislav (1996). The Little Czech and the Great Czech Nation: National Identity and the Post-Communist Social Transformation. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-55469-5.