Commonwealth realm: Difference between revisions
Miesianiacal (talk | contribs) Undid revision 568600689 by The Four Deuces (talk) read the source |
Miesianiacal (talk | contribs) →Post-war evolution: quote Salmond per Wikipedia:No original research/Noticeboard#Scottish independence; + |
||
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
Several non-African realms have also become republics within the Commonwealth, starting with India in 1950 and Pakistan in 1957. The most recent change is Mauritius, which became a republic in 1992. In a number of Commonwealth realms, including the United Kingdom, movements have emerged advocating a [[republic]]an government in place of [[constitutional monarchy]]; they were, and continue to be, countered by monarchist leagues that support the existing system and/or celebrate the historical and modern connections the shared monarchy provides. Unsuccessful referenda on proposed models of republics have taken place in Australia, Tuvalu, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. |
Several non-African realms have also become republics within the Commonwealth, starting with India in 1950 and Pakistan in 1957. The most recent change is Mauritius, which became a republic in 1992. In a number of Commonwealth realms, including the United Kingdom, movements have emerged advocating a [[republic]]an government in place of [[constitutional monarchy]]; they were, and continue to be, countered by monarchist leagues that support the existing system and/or celebrate the historical and modern connections the shared monarchy provides. Unsuccessful referenda on proposed models of republics have taken place in Australia, Tuvalu, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. |
||
On 6 July 2010, Queen Elizabeth II addressed the [[United Nations]] in [[New York City]] as queen of all 16 Commonwealth realms.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.royal.gov.uk/LatestNewsandDiary/Speechesandarticles/2010/AddresstotheUnitedNationsGeneralAssembly6July2010.aspx| last=Royal Household| title=Address to the United Nations General Assembly| date=6 July 2010| publisher=Queen's Printer| accessdate=6 July 2010}}</ref> The following year, [[Portia Simpson-Miller]], the [[Prime Minister of Jamaica]], spoke of a desire to make that country a republic,<ref>{{cite news|title=Jamaica plans to become a republic|url=http://www.skynews.com.au/world/article.aspx?id=702384&vId=|accessdate=31 December 2011|newspaper=Sky News Australia|date=31 December 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Jamaica to break links with Queen, says Prime Minister Simpson Miller|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-16449969|accessdate=8 January 2012|newspaper=BBC News|date=6 January 2012}}</ref> while [[Alex Salmond]], the [[First Minister of Scotland]] and leader of the [[Scottish National Party]] (which favours [[Scottish independence]]) stated |
On 6 July 2010, Queen Elizabeth II addressed the [[United Nations]] in [[New York City]] as queen of all 16 Commonwealth realms.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.royal.gov.uk/LatestNewsandDiary/Speechesandarticles/2010/AddresstotheUnitedNationsGeneralAssembly6July2010.aspx| last=Royal Household| title=Address to the United Nations General Assembly| date=6 July 2010| publisher=Queen's Printer| accessdate=6 July 2010}}</ref> The following year, [[Portia Simpson-Miller]], the [[Prime Minister of Jamaica]], spoke of a desire to make that country a republic,<ref>{{cite news|title=Jamaica plans to become a republic|url=http://www.skynews.com.au/world/article.aspx?id=702384&vId=|accessdate=31 December 2011|newspaper=Sky News Australia|date=31 December 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Jamaica to break links with Queen, says Prime Minister Simpson Miller|url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-latin-america-16449969|accessdate=8 January 2012|newspaper=BBC News|date=6 January 2012}}</ref> while [[Alex Salmond]], the [[First Minister of Scotland]] and leader of the [[Scottish National Party]] (which favours [[Scottish independence]]), stated an independent Scotland "would still share a monarchy with... the UK, just as... 16 [sic] other Commonwealth countries do now."<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.snp.org/blog/post/2012/feb/scottish-independence-good-england| last=Salmond| first=Alex| authorlink=Alex Salmond| title=Scottish independence "good" for England| publisher=Scottish National Party| accessdate=16 February 2012}}</ref> [[Dennis Canavan]], leader of [[Yes Scotland]], disagreed and said a separate, post-independence referendum should be held on the matter.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.scotsman.com/news/scottish-independence-call-for-vote-on-monarchy-1-3018623| last=Barnes| first=Eddie| title=Scottish independence: Call for vote on monarchy| date=29 July 2013| newspaper=The Scotsman| accessdate=16 August 2013}}</ref> |
||
Following the [[Perth Agreement]] of 2011, the Commonwealth realms, in accordance with the Statute of Westminster, collectively engaged in a process of amending the parallel lines or shared line of succession to the respective throne of each country. In legislative debates in the United Kingdom, the term ''Commonwealth realm'' was employed.<ref>{{cite hansard |jurisdiction=United Kingdom | url=http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmhansrd/cm130122/debtext/130122-0001.htm| house=House of Commons| date=22 January 2013| column-188| speaker=Chloe Smith| position=Parliamentary Secretary, Cabinet Office}}</ref><ref>{{cite hansard |jurisdiction=United Kingdom | url=http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmhansrd/cm130122/debtext/130122-0001.htm| house=House of Commons| date=22 January 2013| column=211| speaker=Nick Clegg| position=Deputy Prime Minister}}</ref> |
Following the [[Perth Agreement]] of 2011, the Commonwealth realms, in accordance with the Statute of Westminster, collectively engaged in a process of amending the parallel lines or shared line of succession to the respective throne of each country. In legislative debates in the United Kingdom, the term ''Commonwealth realm'' was employed.<ref>{{cite hansard |jurisdiction=United Kingdom | url=http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmhansrd/cm130122/debtext/130122-0001.htm| house=House of Commons| date=22 January 2013| column-188| speaker=Chloe Smith| position=Parliamentary Secretary, Cabinet Office}}</ref><ref>{{cite hansard |jurisdiction=United Kingdom | url=http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmhansrd/cm130122/debtext/130122-0001.htm| house=House of Commons| date=22 January 2013| column=211| speaker=Nick Clegg| position=Deputy Prime Minister}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 16:56, 16 August 2013
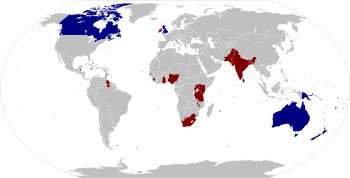
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state that is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, has Elizabeth II as its reigning constitutional monarch, and has a royal line of succession in common with the other realms.[1][2] Since 1992, there are sixteen Commonwealth realms.
The Statute of Westminster 1931 provided for the then Dominions—named therein as Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the Union of South Africa, the Irish Free State, and Newfoundland—to have full or nearly full legislative independence as equal members of the British Commonwealth of Nations sharing with the United Kingdom one person as the respective sovereign of each. Thereafter, India and Pakistan in 1947 and Ceylon in 1948 became Dominions. By the early 1950s, in order to reflect the equality between the countries in that group, each, including the United Kingdom, but without Ireland and India, which had by that time become republics, came to be known as a realm. The term was formally used with Britain's proclamation of Elizabeth II as queen in 1952 and was adopted for the modern royal styles and titles under the legislation enacted by the individual countries, though the phrase Commonwealth realm is only an informal description, not an official term. The sovereign status of other Commonwealth realms was later granted directly.
Current Commonwealth realms
The number of independent countries in the Commonwealth of Nations that shared the same person as monarch rose from the number at the time of the Statute of Westminster in 1931 up to 18 between 1983 and 1987. There have been 16 realms since 1992. As of 2010[update], they have a combined area (excluding Antarctic claims) of 18.7 million km² (7.2 million mi²) and a population of 134 million,[3] of which all but about two million live in the six most populous: the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Papua New Guinea, New Zealand, and Jamaica.
| Country[* 1] | Pop.[* 2] | Monarchy | Date[* 3] | Queen's Title (differences shown here bolded) | Sovereign's Royal Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.09 | Monarchy of Antigua and Barbuda | 1981 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Antigua and Barbuda and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth. | None | |
| 23.25 | Monarchy of Australia | 1942[* 4] | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Australia and Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth. | ||
| 0.34 | Monarchy of the Bahamas | 1973 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of the Commonwealth of the Bahamas and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth. | None | |
| 0.27 | Monarchy of Barbados | 1966 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Barbados and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | ||
| 0.31 | Monarchy of Belize | 1981 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Belize and of Her Other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 34.02 | Monarchy of Canada | 1931 | English: Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God of the United Kingdom, Canada and of Her other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith French: Elizabeth Deux, par la grâce de Dieu Reine du Royaume-Uni, du Canada et de ses autres royaumes et territoires, Chef du Commonwealth, Défenseur de la Foi[4] |
||
| 0.10 | Monarchy of Grenada | 1974 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and of Grenada and Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 2.74 | Monarchy of Jamaica | 1962 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Jamaica and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | ||
| 4.37 | Monarchy of New Zealand | 1947 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of New Zealand and Her Other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith | File:Royal Standard of New Zealand.svg | |
| 6.86 | Monarchy of Papua New Guinea | 1975 | Elizabeth the Second, Queen of Papua New Guinea and Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth[5] | None | |
| 0.05 | Monarchy of Saint Kitts and Nevis | 1983 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Saint Christopher and Nevis and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 0.17 | Monarchy of Saint Lucia | 1979 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Saint Lucia and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 0.11 | Monarchy of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 1979 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 0.54 | Monarchy of Solomon Islands | 1978 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Solomon Islands and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 0.01 | Monarchy of Tuvalu | 1978 | Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, Queen of Tuvalu and of Her other Realms and Territories, Head of the Commonwealth | None | |
| 62.04 | Monarchy of the United Kingdom | n/a[* 5] | English: Elizabeth the Second, by the Grace of God, of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and of Her other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth, Defender of the Faith Latin: Elizabeth Secunda Dei Gratia Britanniarum Regnorumque Suorum Ceterorum Regina Consortionis Populorum Princeps Fidei Defensor[6] |
||
| |||||
Relationship of the realms
The Commonwealth realms are sovereign states, united only in the voluntary and symmetric sharing of the institution of the monarchy,[7] the succession, and the Queen herself; the person of the sovereign and the Crown were said in 1936 to be "the most important and vital link" between the realms.[8] Political scientist Peter Boyce called this grouping of countries associated in this manner, "an achievement without parallel in the history of international relations or constitutional law."[9] Terms such as personal union,[10][11][12][13][14][15] a form of personal union,[† 1][17] and shared monarchy,[7] amongst others,[† 2][20] have all been advanced as definitions since the beginning of the Commonwealth itself, though there has been no agreement on which term is most accurate,[19][20] or even whether personal union is applicable at all.[† 3][22] The United Kingdom no longer holds any legislative power over any country besides itself, although some countries continue to use, by their own volition, the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council as part of their own judiciary; usually as the highest court of appeal.
Since each realm has the same person as its monarch, the diplomatic practice of exchanging ambassadors with letters of credence and recall from one head of state to another is redundant. Diplomatic relations between the Commonwealth realms are thus at a cabinet level only and high commissioners are exchanged between realms (though all other countries in the Commonwealth of Nations also follow this same practice, but for traditional reasons). A high commissioner's full title will thus be High Commissioner for Her Majesty's Government in [Country].
Conflicts of interest have arisen from this relationship amongst independent states, ranging from minor diplomatic matters—such as the monarch expressing on the advice of one of her cabinets views that counter those of another of her cabinets[† 4]—to more serious conflicts regarding matters of armed conflict, wherein the monarch, as head of state of two different realms, may be simultaneously at war and at peace with a third country, or even at war with himself as head of two hostile nations.[† 5] In such cases, viceroys have tended to avoid placing the sovereign directly in the centre of the conflict, meaning that a governor-general may have to take controversial actions entirely on his or her own initiative through the exercise of the reserve powers.[† 6]
The Crown in the Commonwealth realms
The evolution of the Commonwealth realms has led to the scenario wherein the Crown has both a separate and a shared character; it is a singular institution with one sovereign, but also simultaneously operates separately within each country, with the Queen being equally a part of each state and acting in right of a particular realm as a distinct legal person guided only by the advice of the cabinet of that jurisdiction.[7][25][26][27][28][29][30] This means that in different contexts the term Crown may refer to the extra-national institution shared amongst all 16 countries, or to the Crown in each realm considered separately.[† 8] However, though the monarchy is therefore no longer an exclusively British institution,[25][30] having become "domesticated" in each of the realms,[31] it may in the media and legal fields often still be elaborated as the British Crown for reasons historical, of convenience, or political, regardless of the different, specific, and official national titles and terms used when addressing the Queen of the citizenry in each jurisdiction; for example, in Barbados the Queen is titled as Elizabeth II, Queen of Barbados, or simply the Queen of Barbados, with her full title making mention of her position as queen of the other Commonwealth realms.
To guarantee the continuity of this arrangement after the first realms were established in 1931, the preamble of the Statute of Westminster laid out a convention that any alteration to the line of succession in any one country must be voluntarily approved by the parliaments of all the realms.[† 9][33][34] This convention was first applied to the abdication of Edward VIII in 1936 and was reasserted by the Perth Agreement of 2011, in which all 16 realms agreed in principle to change the succession rule to absolute primogeniture of non-Catholics. Alternatively, a realm may choose to end its participation in the shared monarchy.
From a cultural standpoint, the shared nature of the Crown is less clear. In all realms, the sovereign's name and image and other royal symbols unique to each nation are visible in the emblems and insignia of governmental institutions and militia, leading to the argument that the Crown is a shared link between the Commonwealth realms, with the Crown in right of each country having unique domestic characteristics. The Queen's effigy, for example, appears on coins and banknotes in some countries, and an oath of allegiance to the Queen is usually required from politicians, judges, military members and new citizens. It is also asserted, however, that the Crown throughout the realms remains essentially British and primarily of the United Kingdom, despite the legal and cultural evolution of the Commonwealth since the 1930s. Indeed, by 1959 it was being asserted by Buckingham Palace officials that the Queen was "equally at home in all her realms."[35]
Monarch's role in the realms
The monarch is, in theory, the supreme governor of each of the Commonwealth realms, charged with issuing executive orders, commanding the military forces, and creating and administering laws. However, each country now operates under the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy and the concept of responsible government, meaning that the monarch only exercises her powers on the advice of her Crown ministers, who are usually drawn from, and thus responsible to, the elected chamber of the relevant parliament.
While this remains the case for all the Commonwealth realms, their sovereign resides predominantly in her oldest realm, the United Kingdom, and thus carries out her duties there mostly in person. The Queen appoints viceroys to perform most of the royal constitutional and ceremonial duties on her behalf in the other realms: in each, a governor-general as her personal national representative, as well as a governor as her representative in each of the Australian states. These appointments are all made on the advice of the prime minister of the country or the premier of the state concerned, though this process may have additional requirements.[† 10] In certain other cases, the extent to which varies from realm to realm, specific additional powers are reserved exclusively for the monarch—such as the appointment of extra senators to the Canadian Senate, the creation of honours, or the issuance of letters patent—and on occasions of national importance, the Queen may be advised to perform in person her constitutional duties, such as granting Royal Assent or issuing a royal proclamation. Otherwise, all royal powers, including the Royal Prerogative, are carried out on behalf of the sovereign by the relevant viceroy, which, apart from those already mentioned, include a lieutenant governor in each province of Canada (appointed by the Governor General of Canada). In the United Kingdom, the Queen appoints Counsellors of State to perform her constitutional duties in her absence.
Similarly, the monarch will perform ceremonial duties in the Commonwealth realms to mark historically significant events.[36] He or she does so most frequently in the United Kingdom and, in the other countries, during tours at least once every five or six years, meaning the Queen is present in a number of her dominions outside the UK, or acting on behalf of those realms abroad, approximately every other year. For this work, the sovereign receives no salary from any state; instead, only the expenses incurred for each event (security, transportation, venue, etc.) are, due to the nature of the Crown in the realms, funded by the relevant state individually through the ordinary legislative budgeting process and, if called for, by the organisation that invited the sovereign's attendance. These engagements are organised in order for the Crown to honour, encourage, and learn about the achievements or endeavours of individuals, institutions, and enterprises in a variety of areas of the lives of the Queen's subjects.
Citizens in Commonwealth realms or British Overseas Territories may request birthday or wedding anniversary messages to be sent from the sovereign. This is available for 100th, 105th, and beyond for birthdays; and 60th ("Diamond"), 65th, 70th ("Platinum"), and beyond for wedding anniversaries.[37]
Religious role of the monarch
The sovereign's religious role differs from country to country. In all realms except Papua New Guinea the Queen is sovereign "By the Grace of God", a phrase that forms a part of her official title within those states. In Canada, the United Kingdom, and New Zealand, "Defender of the Faith" (in Latin: fidei defensor)—the ancient phrase first granted in 1521 by Pope Leo X to King Henry VIII—is also included as a part of the royal title and the sovereign is anointed as such in the only coronation that takes place in any of the realms,[38] a ceremony in the context of a church service imbued with theological and constitutional symbolism and meaning, held at Westminster Abbey in London, United Kingdom.
However, it is solely in the United Kingdom that the Queen actually plays a role in organised religion. In England, she acts as the Supreme Governor of the Church of England and appoints its bishops and archbishops who thereafter act as her Lords Spiritual. In Scotland, she swears an oath to uphold and protect the Church of Scotland and sends to meetings of the church's General Assembly a Lord High Commissioner as her representative, when she is not personally in attendance.[39]
Royal family
The Royal Family of the Commonwealth realms |
|---|
 |
| Badge of the House of Windsor |
Members of the Royal Family HM The Queen
|
As with the sovereign, a single royal family is shared by the Commonwealth realms, similarly being most frequently referred to in a casual fashion as the British Royal Family, sometimes causing conflict with official national titles, such as in Canada. Though there is no strict legal or formal definition of who is or is not a member of the Royal Family, the group is loosely defined as the extended family of the monarch and these persons constitute the apex of a modern royal court.
These persons, either as representatives of the monarch or as part of their own charitable endeavours, regularly perform public duties at hundreds of events throughout the 16 realms each year, funded in the same way as the monarch's similar execution of his or her ceremonial role. Their work, which is all formally recorded in the Court Circular, draws public attention to amicable relations within and between the nations of the Commonwealth and beyond; the members of the Royal Family draw enormous media coverage in the form of photographic, written, and televised commentary on not only their activities and public roles, but also family relationships, rites of passage, personalities, attire, and behaviour.
Flags
The sharing of one royal family among different countries is illustrated in the different heraldic standards held by some members of the family for use in the appropriate realm.
The Queen employs various royal standards to mark her presence, the particular one used depending on which realm she is in or acting on behalf of at the time. There are currently unique flags for Australia, Barbados, Canada, Jamaica, New Zealand, and two variations for the United Kingdom—one for Scotland and another for the rest of the country. All are heraldic banners displaying the shield of the sovereign's coat of arms for that state, and each, save for those of the UK, are defaced in the centre with the Queen's Personal Flag, a crowned E for Elizabeth surrounded by a garland of roses representing the countries of the Commonwealth. This latter flag on its own is used for realms that do not have a unique personal standard for the monarch, as well as for general use in representing the Queen as Head of the Commonwealth. The monarch previously held royal standards for Sierra Leone, Mauritius, Malta, and Trinidad and Tobago, but these banners became obsolete when the countries became republics.
Other members of the Royal Family have their own personal standards. In the United Kingdom, most have their own distinctive banner or banners. The Prince of Wales and the Duke of Cambridge also have one each for Canada. Those who do not possess a standard for an individual realm will use their British standard to identify themselves when touring other Commonwealth realms and foreign countries.
The governors-general throughout the Commonwealth realms also each use a personal flag, which, like that of the sovereign, passes to each successive occupant of the office. Most feature a lion passant atop a St. Edward's royal crown with the name of the country across a scroll underneath, all on a blue background. The two exceptions are those of, since 1981, Canada (bearing on a blue background the crest of the Royal Coat of Arms of Canada) and, since 2008, New Zealand (a St. Edward's Crown above the shield of the Coat of Arms of New Zealand). The lieutenant governors of the Canadian provinces each have their own personal standards, as do the governors of the Australian states.
Historical development
Dominions emerge
The possibility that a colony within the British Empire might become a new kingdom was first mooted in the 1860s, when it was proposed that the British North American territories of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and the Province of Canada unite as a confederation that might be known as the Kingdom of Canada.[40][41][42] In light of geo-political circumstances at the time, however, the name was abandoned in favour of the Dominion of Canada.[† 11] As more British colonies followed Canada in gaining legislative independence from the United Kingdom, Prime Minister of Canada Wilfrid Laurier insisted at the 1907 Imperial Conference that a formula be created to differentiate between the Crown and the self-governing colonies. For the latter the Canadian precedent was followed, and the term Dominion was extended to apply to Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, and the colonies of the Cape, Natal, and Transvaal, before and after they merged in 1910 with the Orange River Colony to form the Union of South Africa. These countries were joined in 1921 by the Irish Free State.


Although the Dominions were capable of governing themselves internally, they technically remained—especially in regard to foreign policy and defence—subject to British authority, wherein the governor-general of each Dominion represented the British monarch-in-Council reigning over these territories as a single imperial domain. It was commonly held in some circles that the Crown was a monolithic element throughout all the monarch's territories; A.H. Lefroy wrote in 1918 that "the Crown is to be considered as one and indivisible throughout the Empire; and cannot be severed into as many kingships as there are Dominions, and self-governing colonies."[43] This unitary model began to erode, however, when the Dominions gained more international prominence as a result of their participation and sacrifice in the First World War, in 1919 prompting Canadian prime minister Robert Borden and South African minister of defence Jan Smuts to demand that the Dominions be given at the Versailles Conference full recognition as "autonomous nations of an Imperial Commonwealth." The immediate result was that, though the King signed as High Contracting Party for the empire as a whole,[44] the Dominions were also separate signatories to the Treaty of Versailles, as well as, together with India, founding members of the League of Nations. In 1921 the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom David Lloyd George stated that the "British Dominions have now been accepted fully into the community of nations."[45]
Between the wars
The pace of independence increased in the 1920s, led by Canada, which exchanged envoys with the United States in 1920 and concluded the Halibut Fisheries Treaty in its own right in 1923.[44] In the Chanak crisis of 1922, the Canadian government insisted that its course of action would be determined by the Canadian parliament,[46] not the British government, and, by 1925, the Dominions felt confident enough to refuse to be bound by Britain's adherence to the Treaty of Locarno.[47] These developments, combined with a realisation that the Crown was already operating distinctly and separately within each of the jurisdictions of the Canadian provinces and Australian states,[† 14][49][44] appeared to put to rest previous assertions that the Crown could never be divided amongst the Dominions.
Another catalyst for change came in 1926, when then Governor General of Canada the Lord Byng of Vimy refused the advice of his prime minister (William Lyon Mackenzie King) in what came to be known colloquially as the King–Byng Affair.[50] Mackenzie King, after resigning and then being reappointed as prime minister some months later, pushed at the Imperial Conference of 1926 for a reorganisation of the way the Dominions related to the British government, resulting in the Balfour Declaration, which declared formally that the Dominions were fully autonomous and equal in status to the United Kingdom.[51] What this meant in practice was not at the time worked out; conflicting views existed, some in the United Kingdom not wishing to see a fracturing of the sacred unity of the Crown throughout the empire, and some in the Dominions not wishing to see their jurisdiction have to take on the full brunt of diplomatic and military responsibilities.[31]
What did follow was that the Dominion governments gained an equal status with the United Kingdom, a separate and direct relationship with the monarch, without the British Cabinet acting as an intermediary, and the governors-general now acted solely as a personal representative of the sovereign in right of that Dominion.[† 15][53] Though no formal mechanism for tendering advice to the monarch had yet been established—former Prime Minister of Australia William Morris Hughes theorised that the Dominion cabinets would provide informal direction and the British Cabinet would offer formal advice[54]—the concepts were first put into legal practice with the passage in 1927 of the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act, which implicitly recognised the Irish Free State as separate from the UK, and the King as king of each Dominion uniquely, rather than as the British king in each Dominion. At the same time, terminology in foreign relations was altered to demonstrate the independent status of the Dominions, such as the dropping of the term "Britannic" from the King's style outside of the United Kingdom.[55] Then, in 1930 George V's Australian ministers employed a practice adopted by resolution at that year's Imperial Conference,[44] directly advising the King to appoint Sir Isaac Isaacs as his Australian governor-general, against the preferences of the British government and the King himself.
These new developments were explicitly codified in 1931 with the passage of the Statute of Westminster, through which Canada, the Union of South Africa, and the Irish Free State all immediately obtained formal legislative independence from the UK, while in the other Dominions adoption of the statute was subject to ratification by the Dominion's parliament. Australia and New Zealand did so in 1942 and 1947, respectively, with the former's ratification back-dated to 1939, while Newfoundland never ratified the bill and reverted to direct British rule in 1934. As a result, the parliament at Westminster was unable to legislate for any Dominion unless requested to do so,[44] although the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council was left available as the last court of appeal for some Dominions.[56] Specific attention was given in the statute's preamble to royal succession, outlining that no changes to that line could be made by the parliament of the United Kingdom or that of any Dominion without the assent of all the other parliaments of the UK and Dominions, an arrangement a justice of the Ontario Superior Court in 2003 likened to "a treaty among the Commonwealth countries to share the monarchy under the existing rules and not to change the rules without the agreement of all signatories."[57]
This was all met with only minor trepidation either before or at the time,[† 16] and the government of Ireland was confident that the relationship of these independent countries under the Crown would function as a personal union,[17] akin to that which had earlier existed between the United Kingdom and Hanover (1801 to 1837), or between England and Scotland (1603 to 1707). The civil division of the Court of Appeal of England and Wales later found in 1982 that the British parliament could have legislated for a Dominion simply by including in any new law a clause claiming the Dominion cabinet had requested and approved of the act, whether that was true or not.[59] Further, the British parliament was not obliged to fulfill a Dominion's request for legislative change. Regardless, in 1935 the British Parliament refused to consider the result of the Western Australian secession referendum of 1933 without the approval of the Australian federal parliament. In 1937, the Appeal Division of the Supreme Court of South Africa ruled unanimously that a repeal of the Statute of Westminster in the United Kingdom would have no effect in South Africa, stating: "We cannot take this argument seriously. Freedom once conferred cannot be revoked."[60] Others in Canada upheld the same position.[44]
The first prominent example of this arrangement working in practice came with the abdication of King Edward VIII in 1936,[44] for which it was necessary to gain the approval of all the Dominions of the Commonwealth before the resignation could take place;[61] Canada, the Union of South Africa, and the Irish Free State even passed unique legislation to solidify the changes in succession within their jurisdictions.[† 17] Following the accession of Edward's brother, George VI, to the throne, the United Kingdom created legislation that would provide for a regency in the event of the incapacitation of the monarch. Though input was sought from the Dominions on this matter, all declined to make themselves bound by the British legislation, feeling instead that the governors-general could carry out royal functions in place of a debilitated sovereign.[63]

During his tenure as Governor General of Canada, Lord Tweedsmuir urged the organisation of a royal tour of the country by King George VI, so that he might not only appear in person before his people, but also personally perform constitutional duties and pay a state visit to the United States as king of Canada.[64] While the idea was embraced in Canada as a way to "translate the Statute of Westminster into the actualities of a tour," throughout the planning of the trip that took place in 1939, the British authorities resisted at numerous points the idea that the King be attended by his Canadian ministers instead of his British ones.[65] The Canadian prime minister (still Mackenzie King) was ultimately successful, however, in being the minister in attendance, and the King did in public throughout the trip ultimately act solely in his capacity as the Canadian monarch. Yet, the international status of the Crown was also illustrated by George VI simultaneously bolstering from both Canada and the United States support for the United Kingdom in the looming war with Nazi Germany.[64]
When this threat became reality, there was some uncertainty in the Dominions about the ramifications of Britain's declaration of war against Adolf Hitler. Australia and New Zealand had not yet ratified the Statute of Westminster; the Australian prime minister, Robert Menzies, considered the government bound by the British declaration of war,[66][67][68] while New Zealand coordinated a declaration of war to be made simultaneously with Britain's.[69] As late as 1937, some scholars were still of the mind that, when it came to declarations of war, if the King signed, he did so as king of the empire as a whole; at that time, W. Kennedy wrote: "in the final test of sovereignty—that of war—Canada is not a sovereign state... and it remains as true in 1937 as it was in 1914 that when the Crown is at war, Canada is legally at war,"[70] and, one year later, A. Berriedale Keith argued that "issues of war or neutrality still are decided on the final authority of the British Cabinet."[71] In 1939, however, Canada and South Africa made separate proclamations of war against Germany a few days after the UK's. Their example was followed more consistently by the other realms as further war was declared against Italy, Rumania, Hungary, Finland, and Japan.[44] Ireland remained neutral.[68] At the war's end, it was said by F.R. Scott that "it is firmly established as a basic constitutional principle that, so far as relates to Canada, the King is regulated by Canadian law and must act only on the advice and responsibility of Canadian ministers."[72]
Post-war evolution
Once the Second World War was over, India, Pakistan, and Ceylon became independent realms within the Commonwealth (then still called Dominions), though it was made clear at the time that India would soon move to a republican form of government. Unlike Ireland and Burma at the time of their becoming republics, however, there was no desire on the part of India to give up its membership in the British Commonwealth, prompting a Commonwealth Conference and the issuance of the London Declaration in April 1949, which entrenched the idea of Canadian prime minister Louis St. Laurent that different royal houses and republics be allowed in the Commonwealth so long as they recognised as the international organisation's symbolic head the shared sovereign of the United Kingdom and the Dominions.[73] Shortly before the London Declaration, Newfoundland, which had remained a Dominion in name only, had become a province of Canada.
At approximately the same time, the tabling in 1946 of the Canadian parliament's Canadian Citizenship Act had brought into question the homogeneity of the King's subjects, which, prior to that year, was uniformly defined in terms of allegiance to the sovereign, without regard to the individual's country of residence. Following negotiations, it was decided in 1947 that each Commonwealth member was free to pass its own citizenship legislation, so that its citizens owed allegiance only to the monarch in right of that country.
As these constitutional developments were taking place, the Dominion and British governments became increasingly concerned with how to represent the more commonly accepted notion that there was no distinction between the sovereign's role in the United Kingdom and his or her position in any of the Dominions. Thus, at the 1948 Prime Ministers' Conference the term Dominion was avoided in favour of Commonwealth country, in order to avoid the subordination implied by the older designation.[74] Then, with the British proclamation of Elizabeth II's accession to the throne in 1952, the phrases Commonwealth realm and Head of the Commonwealth became established, deriving from the words that declared the monarch as "of this Realm, and of her other Realms and Territories Queen, Head of the Commonwealth." Previously, the term realm in its singular form was understood to refer to the entire British Empire, rather than a "separate kingdom" under a shared crown.[75]
The Commonwealth realms' prime ministers thereafter discussed the matter of the new monarch's title, with St. Laurent stating at the 1953 Commonwealth Conference that it was important to agree on a format that would "emphasise the fact that the Queen is Queen of Canada, regardless of her sovereignty over other Commonwealth countries."[26] The result was a new Royal Style and Titles Act being passed in each of the seven realms then existing (excluding Pakistan), which all identically gave formal recognition to the separateness and equality of the countries involved, and replaced the phrase "British Dominions Beyond the Seas" with "Her Other Realms and Territories", the latter using the medieval French word realm (from royaume) in place of dominion. Further, at her coronation, Elizabeth II's oath contained a provision requiring her to promise to govern according to the rules and customs of the realms, naming each one separately. The change in perspective was summed up by Patrick Gordon Walker's statement in the British House of Commons: "We in this country have to abandon... any sense of property in the Crown. The Queen, now, clearly, explicitly and according to title, belongs equally to all her realms and to the Commonwealth as a whole."[25]
In the same period, Walker also suggested to the British parliament that the Queen should annually spend an equal amount of time in each of her realms. The Lord Altrincham, who in 1957 criticised Queen Elizabeth II for having a court that encompassed mostly Britain and not the Commonwealth as a whole,[76] was in favour of the idea, but it did not attract wide support.[77] Another thought raised was that viceregal appointments should become trans-Commonwealth; the Governor-General of Australia would be someone from South Africa, the Governor-General of Ceylon would come from New Zealand, and so on. The prime ministers of Canada and Australia, John Diefenbaker and Robert Menzies, respectively, were sympathetic to the concept, but, again, it was never put into practice.[78]
The principle of complete separation and equality was followed in all future grants of independence to countries which became realms, including those that came through the winds of change that swept through Africa in the 1960s, the collapse of the Federation of the West Indies in 1962, and at later dates. The most recently created Commonwealth realm is Saint Kitts and Nevis, which achieved the status in 1983. The process of separation was completed when the residual rights of the British parliament in the affairs of Canada, Australia and New Zealand established by the Statute of Westminster were repealed in the 1980s, through the Constitution Act of 1982 for Canada, the Australia Act of 1986 and the Constitution Act of 1986 for New Zealand, and corresponding legislation in Britain.
Within a few years of gaining independence, the African realms drafted new constitutions in order to become republics within the Commonwealth; South Africa, having been a Dominion and then a realm for 51 years, also became a republic in 1961. The white minority government of Rhodesia in 1965 issued its unilateral declaration of independence, and its members affirmed their loyalty to Elizabeth II as "Queen of Rhodesia", a title to which she had not consented, did not accept, and was not recognised internationally. Her representative in the colony, Sir Humphrey Gibbs, immediately dismissed his prime minister, Ian Smith, but this action was ignored by Smith and he appointed, without the Queen's consent, an Officer Administrating the Government to perform the governor's constitutional duties until 1970, when Smith's government declared Rhodesia a republic.
Several non-African realms have also become republics within the Commonwealth, starting with India in 1950 and Pakistan in 1957. The most recent change is Mauritius, which became a republic in 1992. In a number of Commonwealth realms, including the United Kingdom, movements have emerged advocating a republican government in place of constitutional monarchy; they were, and continue to be, countered by monarchist leagues that support the existing system and/or celebrate the historical and modern connections the shared monarchy provides. Unsuccessful referenda on proposed models of republics have taken place in Australia, Tuvalu, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
On 6 July 2010, Queen Elizabeth II addressed the United Nations in New York City as queen of all 16 Commonwealth realms.[79] The following year, Portia Simpson-Miller, the Prime Minister of Jamaica, spoke of a desire to make that country a republic,[80][81] while Alex Salmond, the First Minister of Scotland and leader of the Scottish National Party (which favours Scottish independence), stated an independent Scotland "would still share a monarchy with... the UK, just as... 16 [sic] other Commonwealth countries do now."[82] Dennis Canavan, leader of Yes Scotland, disagreed and said a separate, post-independence referendum should be held on the matter.[83]
Following the Perth Agreement of 2011, the Commonwealth realms, in accordance with the Statute of Westminster, collectively engaged in a process of amending the parallel lines or shared line of succession to the respective throne of each country. In legislative debates in the United Kingdom, the term Commonwealth realm was employed.[84][85]
Former Commonwealth realms
| Country[‡ 1] | From | To | Original republican system | Method of transition | Royal Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948 | 1972 | Parliamentary republic | New constitution | ||
| 1970 | 1987 | Parliamentary republic | Military coup | ||
| 1965 | 1970 | Presidential republic | Referendum | ||
| 1957 | 1960 | Presidential republic | Referendum | ||
| 1966 | 1970 | Parliamentary republic | Constitutional amendment | ||
| 1947 | 1950 | Parliamentary republic | New constitution | ||
| 1931 | 1949[‡ 4] | Parliamentary republic | Act of parliament | ||
| 1963 | 1964 | Presidential republic | New constitution | ||
| 1964 | 1966 | Single-party republic | New constitution | ||
| 1964 | 1974 | Parliamentary republic | Constitutional amendment | ||
| 1968 | 1992 | Parliamentary republic | Constitutional amendment | ||
| 1960 | 1963 | Parliamentary republic | Constitutional amendment | ||
| 1947 | 1956 | Parliamentary republic | New constitution | ||
| 1961 | 1971 | Presidential republic | New constitution | ||
| 1931 | 1961 | Parliamentary republic | Referendum and new constitution | ||
| 1961 | 1962 | Presidential republic | New constitution | ||
| 1962 | 1976 | Parliamentary republic | New constitution | ||
| 1962 | 1963 | Parliamentary republic | Constitutional amendment | ||
| |||||
Republican referendums
A number of Commonwealth realms have held referendums to consider whether they should become a republic. As of July 2013, of the eight referendums held, only three have been successful in Ghana, South Africa and Gambia (on the second referendum). Those that were rejected were held in Australia, twice in Tuvalu and in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
There are currently no planned referendums, but interest in holding a referendum has been noted in Australia (despite it being rejected in 1999) and Jamaica.[86][87]
| Year held | Country | Yes | No | Majority (%) | Republic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 1,008,740 | 131,145 | 877,595 (77%) | ||
| 1960 | 850,458 | 775,878 | 74,580 (5%) | ||
| 1965 | 61,563 | 31,921 | —1 | ||
| 1970 | 84,968 | 35,638 | 49,330 (41%) | ||
| 1986 | 121 | 2,144 | 2,023 (86%) | ||
| 1999 | 5,273,024 | 6,410,787 | 1,137,763 (10%) | ||
| 2008 | 679 | 1,260 | 581 (30%) | ||
| 2009 | 22,646 | 29,167 | 6,521 (12%) |
- Notes
- ^ This referendum failed to have one side of the vote clearing a two-thirds (66%) total, therefore it was rejected.
See also
- States headed by Elizabeth II
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Commonwealth Family
- African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States
- British Empire
Notes
- ^ F.R. Scott stated: "The common kinship within the British group today establishes a form of personal union, the members of which are legally capable of following different international policies even in time of war."[16]
- ^ W.Y Elliott stated: If a personal union be chosen, the Crown will be forced to act on the king's own discretion [and] since personal discretion is a modern monarch is unthinkable, the only alternative would be a league of states with a common but symbolic crown",[18] and Alexander N. Sack stated: "Whatever the future development of the British Commonwealth may be [it] can be described as a that of associations or unions of States, as distinguished from 'personal' unions, on the one hand, and federal States, on the other.[19]
- ^ J. D. B. Miller stated:[T]he survey concludes with an attempt to classify the Commonwealth. It is no longer a federation, nor a military alliance, nor a personal union.[21]
- ^ During a British state visit to Jordan in 1984, Queen Elizabeth II made a speech expressing opinions of her British Cabinet that countered the views of her Australian Cabinet,[23] though the Queen was evidently not representing Australia at that time. Similarly, Elizabeth II undertook a visit to Latin America to promote British goods at the same time a Canadian ministerial trip was underway in the same region in order to promote Canadian products.[24]
- ^ On 3 September 1939, the United Kingdom declared war on Nazi Germany, but it was only on 6 September that, under the articles of the Statute of Westminster, the Union of South Africa did same, followed by Canada on 10 September. Therefore, from 3 to 10 September, King George VI, as king of the United Kingdom, South Africa and Canada, was both at war and at peace with Germany. Similarly, as he was still technically monarch of Ireland, it was George VI's duty to validate the credentials of the German consul to Ireland, which remained neutral throughout the war.
A more extreme example was the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947, in which George VI, as head of state of both warring nations, was, in a legal sense, at war with himself. Similarly, in 1983 Queen Elizabeth II was monarch of Grenada when her governor-general there requested the invasion of the country by a number of other Caribbean states, including some that were also realms of the Queen; an undertaking that was opposed by a number of Elizabeth's other governments, such as those of the United Kingdom, Canada, and Belize. - ^ In the example of the 1983 invasion of Grenada, the Governor-General, Sir Paul Scoon, invited the intervention of foreign troops deliberately without ever having informed the Queen. Also, when Sir John Kerr dismissed the Australian government in 1975, he did not inform the Queen of his intent to do so.
- ^ The figures in the image are, from left to right, back row: Ivy Dumont, Governor-General of the Bahamas; Silvia Cartwright, Governor-General of New Zealand; Tomasi Puapua, Governor-General of Tuvalu; Pearlette Louisy, Governor-General of Saint Lucia; Charles Antrobus, Governor-General of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines; Silas Atopare, Governor-General of Papua New Guinea; Adrienne Clarkson, Governor General of Canada; Peter Hollingworth, Governor-General of Australia; John Lapli, Governor-General of the Solomon Islands; front row: Clifford Husbands, Governor-General of Barbados; Colville Young, Governor-General of Belize; Howard Cooke, Governor-General of Jamaica; Queen Elizabeth II; The Duke of Edinburgh; James Carlisle, Governor-General of Antigua and Barbuda; Cuthbert Sebastian, Governor-General of Saint Kitts and Nevis; and Daniel Williams, Governor-General of Grenada.
- ^ One Canadian constitutional scholar, Dr. Richard Toporoski, stated on this: "I am perfectly prepared to concede, even happily affirm, that the British Crown no longer exists in Canada, but that is because legal reality indicates to me that in one sense, the British Crown no longer exists in Britain: the Crown transcends Britain just as much as it does Canada. One can therefore speak of 'the British Crown' or 'the Canadian Crown' or indeed the 'Barbadian' or 'Tuvaluan' Crown, but what one will mean by the term is the Crown acting or expressing itself within the context of that particular jurisdiction".[30]
- ^ Monarchist League of New Zealand Chairman Professor Noel Cox stated: "Any alteration by the United Kingdom Parliament in the law touching the succession to the throne would, except perhaps in the case of Papua New Guinea, be ineffective to alter the succession to the throne in respect of, and in accordance with the law of, any other independent member of the Commonwealth which was within the Queen's realms at the time of such alteration. Therefore it is more than mere constitutional convention that requires that the assent of the Parliament of each member of the Commonwealth within the Queen's realms be obtained in respect of any such alteration in the law."[32]
- ^ In the Solomon Islands and Tuvalu, the prime minister must consult the legislature in confidence; in Papua New Guinea, the governor-general is nominated to the Queen by a parliamentary vote.
- ^ The Colonial Office in London opposed this potentially "premature" and "pretentious" reference for a new country, and were also wary of antagonising the United States, which had emerged from its Civil War as a formidable military power with unsettled grievances because of British support for the Confederate cause. See also: Name of Canada > Adoption of Dominion.
- ^ The Australian and South African prime ministers, Billy Hughes and Louis Botha, stand first and second from the right; the Canadian delegate, Sir George Foster, stands fourth from left. The representatives of New Zealand and Newfoundland are not shown.
- ^ The figures in the photo are, back row, left to right: Walter Stanley Monroe, Prime Minister of Newfoundland; Gordon Coates, Prime Minister of New Zealand; Stanley Bruce, Prime Minister of Australia; James Hertzog, Prime Minister of South Africa, and W.T. Cosgrave, President of the Executive Council of the Irish Free State; front row, left to right: Stanley Baldwin, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom; the King; and William Lyon Mackenzie King, Prime Minister of Canada.
- ^ The Viscount Haldane said in 1919 that in Australia the Crown "acts in self-governing States on the initiative and advice of its own ministers in these States."[48]
- ^ The ministers in attendance at the Imperial Conference agreed that: "In our opinion it is an essential consequence of the equality of status existing among the members of the British Commonwealth of Nations that the Governor General of a Dominion is the representative of the Crown, holding in all essential respects the same position in relation to the administration of public affairs in the Dominion as is held by His Majesty the King in great Britain, and that he is not the representative or agent of His Majesty's Government in Great Britain or of any Department of that Government.[52]
- ^ P.E. Corbett in 1940 questioned whether there were any existing terms that could be used to describe any or all of the "possessions of the British Crown,"[20] while Scottish constitutional lawyer Arthur Berriedale Keith warned before 1930 that "the suggestion that the King can act directly on the advice of Dominion Ministers is a constitutional monstrosity, which would be fatal to the security of the position of the Crown."[58]
- ^ The Oireachtas of the Irish Free State passed the External Relation Act on 12 December 1936,[62] the parliament of the Union of South Africa passed an act declaring that the abdication had taken place on 10 December, and the parliament of Canada passed the Succession to the Throne Act in 1937.[44]
References
- ^ "What is a Commonwealth Realm?". Royal Household. Retrieved 6 October 2009.
- ^ Royal Household. "Her Majesty the Queen". Queen's Printer. Retrieved 23 January 2011.
- ^ Figures totaled from Member state profiles at the Commonwealth of Nations secretariat, area rounded to the nearest 100,000, population to the nearest million.
- ^ Elizabeth II (1985). Loi sur les titres royaux. Ottawa: Queen's Printer for Canada. R.S., 1985, c. R-12. Retrieved 3 May 2009.
- ^ "Article 85. Royal Title and Styles" (PDF). Constitution of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea. Ministry of Inter Government Relations. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ^ Velde, François. "Royal Arms, Styles and Titles of Great Britain". Heraldica. François R Velde. Retrieved 24 January 2012.
- ^ a b c Trepanier, Peter (2004). "Some Visual Aspects of the Monarchical Tradition". Canadian Parliamentary Review. 27 (2). Ottawa: Commonwealth Parliamentary Association. Retrieved 2 May 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Berriedale, Kieth (1936), "The King and the Imperial Crown: The Powers and Duties of His Majesty", in Coates, Colin MacMillan (ed.), Majesty in Canada: essays on the role of royalty, Toronto: Dundurn Press Ltd. (published 2006), p. 12, ISBN 978-1-55002-586-6, retrieved 16 January 2011
- ^ Boyce, Peter (2008). The Queen's Other Realms. Annandale: Federation Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-86287-700-9.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Oppenheim, Lassa (1952). Lauterpacht, Hersch (ed.). International law: a treatise. Vol. 1. London: Longmans. p. 163. ISBN 1-58477-609-9. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ^ Clerk of the House of Commons (1947). Debates: official report. Vol. 1. Ottawa: King's Printer for Canada. p. 591. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ^ Coolidge, Archibald Cary (1927). Foreign affairs, Volume 6. New York: Council on Foreign Relations. pp. 124–125, 127. Retrieved 7 November 2009.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Library of Parliament (1947). Special war session, Volume 1. Ottawa: Queen's Printer for Canada. p. 591. Retrieved 7 November 2009.
- ^ "Personal Union". Crowned Republic. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ^ Hudson, Wayne (2004). Restructuring Australia: Regionalism, Republicanism and Reform of the Nation-State. Sydney: Federation Press. p. 86. ISBN 9781862874923.
- ^ Scott, F. R. (January 1944). "The End of Dominion Status". The American Journal of International Law. 38 (1). American Society of International Law: 34–49. doi:10.2307/2192530. JSTOR 2192530.
- ^ a b "Black v Chrétien: Suing a Minister of the Crown for Abuse of Power, Misfeasance in Public Office and Negligence". Murdoch University Electronic Journal of Law. 9 (3). September 2002. Retrieved 2 October 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Elliott, W.Y (November 1930). "The Sovereignty of the British Dominions: Law Overtakes Practice". The American Political Science Review. 24 (4). American Political Science Association: 971–989. doi:10.2307/1946754. JSTOR 1946754.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ a b Sack, Alexander N.; Stewart, Robert B. (March 1940). "Treaty Relations of the British Commonwealth of Nations". University of Pennsylvania Law Review and American Law Register. 88 (5). The University of Pennsylvania Law Review: 637–640. doi:10.2307/3308937. JSTOR 3308937.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ a b c Corbett, P. E. (1940). "The Status of the British Commonwealth in International Law". The University of Toronto Law Journal. 3 (2). University of Toronto Press: 348–359. doi:10.2307/824318. JSTOR 824318.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Miller, J.D.B (October 1959). "The Commonwealth in the World". The American Historical Review. 65 (1). Washington, DC: American Historical Association.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Keith, Arthur Berriedale (1929). The sovereignty of the British dominions. New York: Macmillan and Co. Ltd. p. xvii. ISBN 0-8371-8668-4. Retrieved 7 November 2009.
- ^ Cohen, Zelman (1995). "Further Reflections on an Australian Republic" (Lecture). Sir Robert Menzies Lecture Trust. Retrieved 3 May 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Sharp, Mitchell (1994). Which Reminds Me..., A Memoir. Toronto: University of Toronto Press. p. 223. ISBN 978-0-8020-0545-8.
- ^ a b c Bogdanor, Vernon (12 February 1998). The Monarchy and the Constitution. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 288. ISBN 978-0-19-829334-7.
- ^ a b High Commissioner in United Kingdom (24 November 1952). "Royal Style and Titles". Documents on Canadian External Relations > Royal Style and Titles. 18 (2). DEA/50121-B-40.
- ^ Smy, William A. (2008). "Royal titles and styles". The Loyalist Gazette. XLVI (1). Toronto: United Empire Loyalists Association of Canada. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- ^ Cox, Noel (19 October 2003), The Development of a Separate Crown in New Zealand (PDF), Auckland University of Technology, p. 18, retrieved 3 January 2011
- ^ Michie, Allan Andrew (1952). The Crown and the People. London: Secker and Warburg. p. 52. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- ^ a b c Toporoski, Richard. "The Invisible Crown". Monarchy Canada. Archived from the original on 2 October 2008. Retrieved 20 April 2008.
{{cite web}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch; 9 February 2008 suggested (help) - ^ a b Mallory, J.R. (August 1956). "Seals and Symbols: From Substance to Form in Commonwealth Equality". The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science. 22 (3). Montreal: Blackwell Publishing: 281–291. ISSN 0008-4085. JSTOR 138434.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Cox, Noel (1998). Written at Auckland University of Technology. School of Law, Macquarie University (ed.). Australian Journal of Law and Society. Vol. 14, no. 1998/1999. North Ryde: Macquarie University Press (published 23 August 2003). ISSN 0729-3356. Retrieved 13 July 2009.
{{cite news}}:|contribution=ignored (help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ See Sue v Hill [1999] HCA 30 at 93
- ^ George V (11 December 1931). Statute of Westminster, 1931. Westminster: Queen's Printer. c. 4 (U.K.). Retrieved 2 May 2009.
- ^ Buckner, Phillip (2005). "The Last Great Royal Tour: Queen Elizabeth's 1959 Tour to Canada". In Buckner, Phillip (ed.). Canada and the End of Empire. Vancouver: UBC Press. p. 66. ISBN 0-7748-0915-9. Retrieved 24 October 2009.
- ^ The Royal Household. "The current Royal Family". Queen's Printer. Retrieved 2 July 2009.
- ^ Royal Household. "Queen and anniversary messages – Who is entitled?". Queen's Printer. Retrieved 22 February 2011.
- ^ "World Who's Who > Reigning Royal Families > United Kingdom". Routledge Taylor & Francis Group. Retrieved 3 May 2009.
- ^ "The Monarchy Today > Queen and State > Queen and Church > Queen and Church of Scotland". Queen's Printer. Retrieved 25 October 2008.
- ^ Farthing, John (1985). Freedom Wears a Crown. Toronto: Veritas Paperback. ISBN 978-0-949667-03-8.
- ^ Pope, Joseph (2009). Confederation: Being a Series of Hitherto Unpublished Documents Bearing on the British North America Act. Whitefish: Kessinger Publishing. p. 177. ISBN 978-1-104-08654-1.
- ^ Hubbard, R.H. (1977). Rideau Hall. Montreal and London: McGill-Queen's University Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7735-0310-6.
- ^ Lefroy, A. H. (1918). A Short Treatise on Canadian Constitutional Law. Toronto: Carswell. pp. 59–60. ISBN 0-665-85163-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Heard, Andrew (1990). Canadian Independence. Vancouver: Simon Fraser University. Retrieved 6 May 2009. Cite error: The named reference "Heard" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Dale, W. (1983). The Modern Commonwealth. London: Butterworths. p. 24. ISBN 0-406-17404-0.
- ^ Phillip Alfred Buckner (2008). Canada and the British Empire. Oxford University Press. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-19-927164-1.
- ^ John F. Hilliker (1990). Canada's Department of External Affairs: The Early Years, 1909-1946. McGill-Queen's Press - MQUP. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-7735-6233-2.
- ^ Theodore v. Duncan, 696, p.706 (Judicial Committee of the Privy Council 1919).
- ^ Clement, W.H.P. (1916). The Law of the Canadian Constitution (3 ed.). Toronto: Carswell. pp. 14–15. ISBN 0-665-00684-5.
- ^ Williams, Jeffery (1983). Byng of Vimy: General and Governor General. Barnsley, S. Yorkshire: Leo Cooper in association with Secker & Warburg. pp. 314–317. ISBN 0-8020-6935-5.
- ^ Marshall, Peter (September 2001). "The Balfour Formula and the Evolution of the Commonwealth". The Round Table. 90 (361): 541–53. doi:10.1080/00358530120082823.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Balfour, Arthur (November 1926). "Imperial Conference 1926" (PDF). Balfour Declaration. London: King's Printer. p. 4. E (I.R./26) Series. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Twomey, Anne (2006). The Chameleon Crown. Sydney: Federation Press. p. 111. ISBN 9781862876293.
- ^ Jenks, Edward (1927). "Imperial Conference and the Constitution". Cambridge Law Journal. 3 (13). Cambridge: Cambridge University Law Society: 21. ISSN 0008-1973.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Walshe, Joseph P. (29 August 1927). Documents on Irish Foreign Policy > Despatch from Joseph P. Walshe (for Patrick McGilligan) to L.S. Amery (London) (D.5507) (Confidential) (Copy). Royal Irish Academy. Retrieved 24 October 2009.
- ^ Baker, Philip Noel (1929). The Present Juridical Status of the British Dominions in International Law. London: Longmans. p. 231.
- ^ O'Donohue v. Canada, J. Rouleau, 33 (Ontario Superior Court of Justice 17 April 20013).
- ^ Keith, Arthur Berriedale (1928). Responsible Government in the Dominions. Vol. 1 (2 ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press. p. xviii. ISBN 0-665-82054-2.
- ^ Manuel et al. v. Attorney General, 822, p. 830 (Court of Appeal of England and Wales 1982).
- ^ Ndlwana v. Hofmeyer, 229, p.237 (Supreme Court of South Africa 1937).
- ^ Williams, Susan (2003). The People's King: The True Story of the Abdication. London: Penguin Books Ltd. p. 130. ISBN 0-7139-9573-4.
- ^ Edward VIII (12 December 1936). Executive Authority (External Relations) Act, 1936. Dublin: King's Printer for the Irish Free State. 3.2. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- ^ Mallory, J. R. (1984). The Structure and Function of Canadian Government (2 ed.). Toronto: Gage. pp. 36–37.
- ^ a b Library and Archives Canada. "The Royal Tour of 1939". Queen's Printer for Canada. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- ^ Galbraith, William (1989). "Fiftieth Anniversary of the 1939 Royal Visit". Canadian Parliamentary Review. 12 (3). Ottawa: Commonwealth Parliamentary Association. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Hasluck, Paul (1952). The Government and the People, 1939–1941. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. pp. 149–151.
- ^ "Menzies' announcement of the declaration of war". Department of Veterans Affairs. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ a b Boyce 2008, p. 27
- ^ Monckton-Arundell, George (1949). "Documents Relating to New Zealand's Participation in the Second World War 1939–45 > 9 – The Governor-General of New Zealand to the Secretary of State for Dominion Affairs". In Historical Publications Branch (ed.). The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945. Vol. 1. Wellington: Victoria University of Wellington (published 4 September 1939). Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- ^ William Paul McClure Kennedy (1938). The Constitution of Canada, 1534-1937: An Introduction to Its Development, Law and Custom. Oxford University Press. pp. 540–541.
- ^ Keith, A. Berriedale (1938). The Dominions as Sovereign States. London: Macmillan. p. 203.
- ^ Scott 1944, p. 152
- ^ de Smith, S. A. (1949). "The London Declaration of the Commonwealth Prime Ministers, April 28, 1949". The Modern Law Review. 12 (3): 351–354. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2230.1949.tb00131.x. JSTOR 1090506.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Statistics New Zealand. New Zealand Official Yearbook 2000. Auckland: David Bateman. p. 55.
- ^ Powell, Enoch (3 March 1953). "Speech on the Royal Titles Bill". enochpowell.net. Retrieved 6 January 2013.
- ^ Pimlott, Ben (5 June 2002). The Queen. New York: HarperCollins Publishers Ltd. p. 280. ISBN 978-0-00-711436-8.
- ^ Boyce 2008, pp. 9–10
- ^ Boyce 2008, p. 11
- ^ Royal Household (6 July 2010). "Address to the United Nations General Assembly". Queen's Printer. Retrieved 6 July 2010.
- ^ "Jamaica plans to become a republic". Sky News Australia. 31 December 2011. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ^ "Jamaica to break links with Queen, says Prime Minister Simpson Miller". BBC News. 6 January 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2012.
- ^ Salmond, Alex. "Scottish independence "good" for England". Scottish National Party. Retrieved 16 February 2012.
- ^ Barnes, Eddie (29 July 2013). "Scottish independence: Call for vote on monarchy". The Scotsman. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Chloe Smith, Parliamentary Secretary, Cabinet Office (22 January 2013). http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmhansrd/cm130122/debtext/130122-0001.htm. Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). United Kingdom: House of Commons.
{{cite book}}:|chapter-url=missing title (help) - ^ Nick Clegg, Deputy Prime Minister (22 January 2013). http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm201213/cmhansrd/cm130122/debtext/130122-0001.htm. Parliamentary Debates (Hansard). United Kingdom: House of Commons. col. 211.
{{cite book}}:|chapter-url=missing title (help) - ^ BBC News - Australia's Gillard backs republic after Queen's death. Bbc.co.uk (2010-08-17). Retrieved on 2013-07-17.
- ^ Jamaica 'to cut ties with British monarchy' - Americas. Al Jazeera English. Retrieved on 2013-07-17.
Bibliography
- Bogdanor, V.; The Monarchy and the Constitution; Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995
- Cox, Noel; "The Theory of Sovereignty and the Importance of the Crown in the Realms of The Queen"; Oxford University Commonwealth Law Journal; Vol. 2, No. 2; 2002
- Forsey, Eugene; Royal Power of Dissolution on Parliament in the British Commonwealth; Toronto: Oxford University Press; 1968 [1943]
- Maitland, F; "The Crown as a Corporation"; Law Quarterly Review; Vol. 17, No. 131; 1901
- McIntyre; P.; "The Strange Death of Dominion Status", Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History; Vol. 27, No. 2; 1999; 193–212


