Thiobutabarbital
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Boghog (talk | contribs) at 06:00, 2 September 2020 (templated cites). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Thiobutabarbital, Inactin, Brevinarcon, 5-sec-Butyl-5-ethyl-2-thiobarbituric acid |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.600 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H16N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 228.31 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Thiobutabarbital (Inactin, Brevinarcon) is a short-acting barbiturate derivative invented in the 1950s. It has sedative, anticonvulsant and hypnotic effects, and is still used in veterinary medicine for induction in surgical anaesthesia.[1]
Stereochemistry
Thiobutabarbital contains a stereocenter and consists of two enantiomers. This is a racemate, ie a 1: 1 mixture of ( R ) - and the ( S ) - form:[2]
| Enantiomers of Thiobutabarbital | |
|---|---|
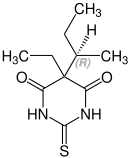 (R)-Form |
 (S)-Form |
References
- ^ Rieg T, Richter K, Osswald H, Vallon V (October 2004). "Kidney function in mice: thiobutabarbital versus alpha-chloralose anesthesia". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 370 (4): 320–3. doi:10.1007/s00210-004-0982-x. PMID 15549274. S2CID 25580831.
- ^ Entry on Thiobutabarbital. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 15. Juni 2014.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
