Basava
Jagajyoti Basava | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Personal life | |
| Born | 1131[1] |
| Died | 1167[1] (aged 36–37) |
| Known for | Socio-religious reforms, Anubhava Mantapa, Vachana literature, Women empowerment movement in South India, Founder of Lingayatism |
| Religious life | |
| Religion | Hinduism |
| Sect | Lingayat Shaivism (Sharana)[2][3] |
| Religious career | |
| Part of a series on |
| Hinduism |
|---|
 |
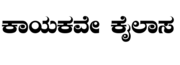 |
| Part of a series on |
| Lingayatism |
|---|
| Saints |
| Beliefs and practices |
| Scriptures |
| Pilgrim centers |
| Related topics |
| Representative Body |
|
|
Basava (1131–1167), also called Basavēśvara and Basavaṇṇa, was an Indian philosopher, poet, Lingayat social reformer in the Shiva-focused bhakti movement, and a Hindu Shaivite[4] social reformer during the reign of the Kalyani Chalukya/Kalachuri dynasty. Basava was active during the rule of both dynasties but reached the peak of his influence during the rule of King Bijjala II in Karnataka, India.[2][5][6]
Basava spread social awareness through his poetry, popularly known as Vachanaas. He rejected gender or social discrimination, superstitions and rituals[1] but introduced Ishtalinga necklace, with an image of the lingam,[7] to every person regardless of their birth, to be a constant reminder of one's bhakti (devotion) to Shiva. A strong promoter of ahimsa, he also condemned human and animal sacrifices. As the chief minister of his kingdom, he introduced new public institutions such as the Anubhava Mantapa (or, the "hall of spiritual experience"),[8] which welcomed men and women from all socio-economic backgrounds to discuss spiritual and mundane questions of life, in open.[9]
The traditional legends and hagiographic texts state Basava to be the founder of the Lingayats. However, modern scholarship relying on historical evidence such as the Kalachuri inscriptions state that Basava was the poet philosopher who revived, refined and energized an already existing tradition.[1][2][10] The Basavarajadevara Ragale (13 out of 25 sections are available) by the Kannada poet Harihara (c. 1180) is the earliest available account on the life of the social reformer and is considered important because the author was a near contemporary of his protagonist.[11] A full account of Basava's life and ideas are narrated in a 13th-century sacred Telugu text, the Basava Purana by Palkuriki Somanatha.[12]
Basava literary works include the Vachana Sahitya in Kannada Language. He is also known as Bhaktibhandari (lit. 'the treasurer of devotion')[13] and Basavanna.
Early life
[edit]
Basava was born in 1131 CE[1] in the town of Basavana Bagewadi in the northern part of Karnataka, to Maadhavarasa and Madalambike, a Kannada Orthodox Brahmin family[14] devoted to the Hindu deity Shiva.[10][13][15] He was named Basava, a Kannada form of the Sanskrit Vrishabha in honor of Nandi bull (carrier of Shiva) and the local Shaivism tradition.[15]
Basava grew up in Kudalasangama (northwest Karnataka), near the banks of rivers Krishna and its tributary Malaprabha.[10][13] Basava spent twelve years studying in the Hindu temple in the town of Kudalasangama,[13] at Sangameshwara then a Shaivite school of learning, probably of the Lakulisha-Pashupata tradition.[15]
Basava married Gangambike,[13] a cousin from his mother's side. Her father was the provincial prime minister of Bijjala, the Kalachuri king.[10][15] He began working as an accountant to the court of the king.[13] When his maternal uncle died, the king invited him to be the chief minister. The king also married Basava's sister named Nagamma.[10]
As chief minister of the kingdom, Basava used the state treasury to initiate social reforms and religious movement focussed on reviving Shaivism, recognizing and empowering ascetics who were called Jangamas.[10] One of the innovative institutions he launched in the 12th century was the Anubhava Mantapa, a public assembly and gathering that attracted men and women across various walks of life from distant lands to openly discuss spiritual, economic and social issues of life.[9] He composed poetry in local language, and spread his message to the masses. His teachings and verses such as Káyakavé Kailása (Work is the path to Kailasa [bliss, heaven], or work is worship) became popular.[16]
Literary works
[edit]Several works are attributed to Basava, which are revered in the Veerashaiva Lingayat community. These include various Vachana[1] such as the Shat-sthala-vachana (discourses of the six stages of salvation), Kala-jnana-vachana (forecasts of the future), Mantra-gopya, Ghatachakra-vachana and Raja-yoga-vachana.[17]
Hagiography
[edit]The Basava Purana, a Telugu biographical epic poem, first written by Palkuriki Somanatha in 13th-century,[18] and an updated 14th century Kannada version, written by Bhima Kavi in 1369, are sacred texts in Veerashaiva Lingayat.[2][19]
Other hagiographic works include the 15th-century Mala Basava-raja-charitre and the 17th-century Vrishabhendra Vijaya, both in Kannada.[10]
Authenticity
[edit]Scholars state that the poems and legends about Basava were written down long after his death.[18] This has raised questions about the accuracy and creative interpolation by authors who were not direct witness but derived their work relying on memory, legends, and hearsay of others. Michael states, "All 'Vachana'collections as they exist at present are probably much later than the 15th-century [300 years post-Basava]. Much critical labor needs to be spent in determining the authenticity of portions of these collections".[20]
Philosophy
[edit]Basava grew up in a Shaivite family.[10][13] As a leader, he developed and inspired a new devotional movement named Virashaivas, or "ardent, heroic worshippers of Shiva". This movement shared its roots in the ongoing Tamil Bhakti movement, particularly the Shaiva Nayanars traditions, over the 7th- to 11th-century. However, Basava championed devotional worship that rejected temple worship and rituals led by Brahmins and replaced it with personalized direct worship of Shiva through practices such as individually worn icons and symbols like a small linga. This approach brought Shiva's presence to everyone and at all times, without gender, class or caste discrimination.[8][21] Basava's poem, such as Basavanna 703, speak of strong sense of gender equality and community bond, willing to wage war for the right cause, yet being a fellow "devotees' bride" at the time of their need.[22]
A recurring contrast in his poems and ideas is of Sthavara and Jangama, that is, of "what is static, standing" and "what is moving, seeking" respectively. Temples, ancient books represented the former, while work and discussion represented the latter.[23]
The rich
will make temples for Shiva,
What shall I,
a poor man do?
My legs are pillars,
the body the shrine,
the head a cupola of gold.
Listen, O lord of the meeting rivers,
things standing shall fall,
but the moving ever shall stay.— Basavanna 820, Translated by Ramanujan[24]
Basava emphasized constant personal spiritual development as the path to profound enlightenment. He championed the use of vernacular language, Kannada, in all spiritual discussions so that translation and interpretation by the elite is unnecessary, and everyone can understand the spiritual ideas.[8] His approach is akin to the protestant movement, states Ramanuja.[23] His philosophy revolves around treating one's own body and soul as a temple; instead of making a temple, he suggests being the temple.[23] His trinity consisted of guru (teacher), linga (personal symbol of Shiva) and jangama (constantly moving and learning).
Basava established, in 12th-century, Anubhava Mantapa, a hall for gathering and discussion of spiritual ideas by any member of the society from both genders, where ardent devotees of Shiva shared their achievements and spiritual poems in the local language.[8] He questioned rituals, dualism, and externalization of god, and stated that the true God is "one with himself, self-born".
How can I feel right
about a god who eats up lacquer and melts,
who wilts when he sees a fire?
How can I feel right
about gods you sell in your need,
and gods you bury for fear of thieves?
The lord Kudalasangama,
self-born, one with himself,
he alone is the true god.— Basavanna 558, Translated by Ramanujan[25]
While Basava rejected rituals, he encouraged icons and symbols such as the wearing of Istalinga (necklace with personal linga, symbol of Shiva), of Rudraksha seeds or beads on parts of one body, and apply Vibhuti (sacred ash on forehead) as a constant reminder of one's devotion and principles of faith.[26] Another aid to faith, he encouraged was the six-syllable mantra, Shivaya Namah, or the shadhakshara mantra which is Om Namah Shivaya.[26]
Bhakti marga as the path to liberation
[edit]The Basava Purana, in Chapter 1, presents a series of impassioned debates between Basava and his father.[27] Both declare Hindu Sruti and Smriti to be sources of valid knowledge, but they disagree on the marga (path) to liberated, righteous life. Basava's father favors the tradition of rituals, while Basava favors the path of direct, personal devotion (bhakti).[28]
According to Velcheru Rao and Gene Roghair,[28] Basava calls the path of devotion as "beyond six systems of philosophy. Sruti has commended it as the all-seeing. the beginning of the beginning. The form of that divine linga is the true God. The guru [teacher] of the creed is an embodiment of kindness and compassion. He places God in your soul, and he also places God in your hand. The six-syllabled mantra,[29] the supreme mantra, is its mantra. The dress – locks of hair, ashes and rudrashaka beads – place a man beyond the cycle of birth and death. It follows the path of liberation. (...) This path offers nothing less than liberation in this lifetime."[28]
Roots in the Vedanta philosophy
[edit]Sripati, a Virasaiva scholar, explained Basava's philosophy in Srikara Bhasya, using the Vedanta Sutra, suggesting Basava's Lingayat theology to be a form of qualified nondualism, wherein the individual Atma (soul) is the body of God, and that there is no difference between Shiva and Atma(self, soul), Shiva is one's Atma, one's Atma is Shiva.[26] Sripati's analysis places Basava's views in Vedanta school, in a form closer to the 11th century Vishishtadvaita philosopher Ramanuja, than to Advaita philosopher Adi Shankara. However, Sripati's analysis has been contested in the Virasaiva community.[26]
Legacy and influence
[edit]
Modern scholarship relying on historical evidence such as the Kalachuri inscriptions state that Basava was the 12th-century poet-philosopher who revived and energized an already existing tradition.[1][2][10] The community he helped form is also known as the Sharanas. The community is largely concentrated in Karnataka, but has migrated into other states of India as well as overseas. Towards the end of the 20th century, Michael estimates, one-sixth of the population of the state of Karnataka, or about 10 million people, were Veerashaiva Lingayat or of the tradition championed by Basava.[16] Veerashaiva Lingayat constitutes around 17% of Karnataka's population and has dominance over 100 out of 223 constituencies. Among the total of 23 chief ministers that Karnataka had since 1952, 10 were from Lingayat community.[30]
Social reform
[edit]
Basava taught that every human being was equal, irrespective of caste, and that all forms of manual labor was equally important.[31] Michael states that it wasn't birth but behavior that determined a true saint and Shaiva bhakta in the view of Basava and the Sharanas community.[3] This, writes Michael, was also the position of south Indian man, that it was "behavior, not birth" that determines the true man.[3] One difference between the two was that Sharanas welcomed anyone, whatever occupation he or she might have been born in, to convert and be reborn into the larger family of Shiva devotees and then adopt any occupation he or she wanted.[3] Basava insisted on ahimsa or non-violence and vehemently condemned all forms of sacrifices, human or animal.[32][33]
Synthesis of diverse Hindu traditions
[edit]Basava is credited with uniting diverse spiritual trends during his era. Jan Peter Schouten states that Virashaivism, the movement championed by Basava, tends towards monotheism with Shiva as the godhead, but with a strong awareness of the unity of the Ultimate Reality.[34] Schouten calls this as a synthesis of Ramanuja's Vishishtadvaita and Shankara's Advaita traditions, naming it Shakti-Vishishtadvaita, that is monism fused with Shakti beliefs.[34] An individual's spiritual progress is viewed by Basava's tradition as a six-stage Satsthalasiddhanta, which progressively evolves the individual through phase of the devotee, to phase of the master, then phase of the receiver of grace, thereafter Linga in life-breath (god dwells in their soul), the phase of surrender (awareness of no distinction in god and soul, self), to the last stage of complete union of soul and god (liberation, mukti).[34] Basava's approach is different from Adi Shankara, states Schouten, in that Basava emphasizes the path of devotion, compared to Shankara's emphasis on the path of knowledge – a system of monistic Advaita philosophy widely discussed in Karnataka in the time of Basava.[35][36]
Jessica Frazier et al. state that Basava laid the foundations of a movement that united "Vedic with Tantric practice, and Advaitic monism with effusive Bhakti devotionalism."[37]
Icons and symbols
[edit]
Basava advocated the wearing of Ishtalinga, a necklace with pendant that contains a small Shiva linga.[31] He was driven by his realization; in one of his Vachanas he says Arive Guru, which means one's own awareness is his/her teacher. Many contemporary Vachanakaras (people who have scripted Vachanas) have described him as Swayankrita Sahaja, which means "self-made".
Monuments and recognition
[edit]- The then President of India Abdul Kalam inaugurated Basaveshwara's statue on 28 April 2003 in the Parliament of India.[38][39]
- Basaveshwara is the first Kannadiga in whose honour a commemorative coin has been minted in recognition of his social reforms. The former Prime Minister of India, Dr Manmohan Singh was in Bengaluru, the capital of Karnataka to release the coins.[40][41][42]
- On 14 November 2015 The Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi inaugurated the statue of Basaveshwara along the bank of the river Thames at Lambeth in London.[43][44][45]
- Basava Dharma Peetha has constructed 108 ft (33 m) tall statue of Basava in Basavakalyana.[46]
- Vishwaguru Basaveshwara Statue is constructed in the year 2015 next to the lake in Gadag district of Karnataka. This is the tallest standing basaveshwara statue with the height of 111ft.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g Carl Olson (2007), The Many Colors of Hinduism: A Thematic-historical Introduction, Rutgers University Press, ISBN 978-0813540689, pages 239–240
- ^ a b c d e Basava Encyclopædia Britannica (2012), Quote: "Basava, (flourished 12th century, South India), Hindu religious reformer, teacher, theologian, and administrator of the royal treasury of the Kalachuri-dynasty king Bijjala I (reigned 1156–67)."
- ^ a b c d R Blake Michael (1992), The Origins of Vīraśaiva Sects, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120807761, pages 7–9
- ^ Jestice, Phyllis G. (2004). Holy People of the World: A Cross-cultural Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 107. ISBN 978-1-57607-355-1.
- ^ A. K. Ramanujan (1973). Speaking of Śiva. Penguin. pp. 175–177. ISBN 978-0-14-044270-0.
- ^ Gene Roghair (2014). Siva's Warriors: The Basava Purana of Palkuriki Somanatha. Princeton University Press. pp. 11–14. ISBN 978-1-4008-6090-6.
- ^ Fredrick Bunce (2010), Hindu deities, demi-gods, godlings, demons, and heroes, ISBN 9788124601457, page 983
- ^ a b c d Jan Peter Schouten (1995), Revolution of the Mystics: On the Social Aspects of Vīraśaivism, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120812383, page 4
- ^ a b SK Das (2005), A History of Indian Literature, 500–1399: From Courtly to the Popular, Sahitya Akademi, ISBN 978-8126021710, page 163
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Edward Rice (1982), A History of Kannada Literature, Asian Educational Services, ISBN 978-8120600638, pages 52–53
- ^ Shiva Prakash (1997), p. 179
- ^ Velchuri Rao and Gene Roghair (2014), Siva's Warriors: The Basava Purana of Palkuriki Somanatha, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691604879, pp. 1–14
- ^ a b c d e f g Jan Peter Schouten (1995), Revolution of the Mystics: On the Social Aspects of Vīraśaivism, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120812383, pages 2–3
- ^ "Basavanna, the Immortal, Being Invoked by the Mortals to Achieve Political Goals". News18. Retrieved 18 April 2018.
- ^ a b c d SK Das (2005), A History of Indian Literature, 500–1399: From Courtly to the Popular, Sahitya Akademi, ISBN 978-8126021710, pages 161–162
- ^ a b R Blake Michael (1982), Work as Worship in Vīraśaiva Tradition, Journal of the American Academy of Religion, Vol. 50, No. 4, pages 605–606
- ^ Edward Rice (1982), A History of Kannada Literature, Asian Educational Services, ISBN 978-8120600638, pages 53–54
- ^ a b Velchuri Rao and Gene Roghair (2014), Siva's Warriors: The Basava Purana of Palkuriki Somanatha, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691604879, pages 21–23
- ^ "Basava in Literature". Lingayatreligion.com. Archived from the original on 27 May 2013. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ^ R Blake Michael (1992), The Origins of Vīraśaiva Sects, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120807761, page 64 footnote 19
- ^ R Blake Michael (1992), The Origins of Vīraśaiva Sects, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120807761, pages 1–5
- ^ AK Ramanujan (1973), Speaking of Śiva, Penguin Classics, ISBN 978-0140442700, page 29
- ^ a b c AK Ramanujan (1973), Speaking of Śiva, Penguin Classics, ISBN 978-0140442700, pages 19–22
- ^ AK Ramanujan (1973), Speaking of Śiva, Penguin Classics, ISBN 978-0140442700, page 19
- ^ AK Ramanujan (1973), Speaking of Śiva, Penguin Classics, ISBN 978-0140442700, page 28
- ^ a b c d e Carl Olson (2007), The Many Colors of Hinduism: A Thematic-historical Introduction, Rutgers University Press, ISBN 978-0813540689, pages 243–244
- ^ Velcheru Rao and Gene Roghair (2014), Siva's Warriors: The Basava Purana of Palkuriki Somanatha, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691604879, pages 55–58
- ^ a b c Velcheru Rao and Gene Roghair (2014), Siva's Warriors: The Basava Purana of Palkuriki Somanatha, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0691604879, pages 57–58
- ^ Om Namah Shivaya, see: Carl Olson (2007), The Many Colors of Hinduism: A Thematic-historical Introduction, Rutgers University Press, ISBN 978-0813540689, pages 243–244
- ^ "Lingayats hold key to electoral outcome in poll-bound Karnataka". The Economic Times. 31 March 2023. ISSN 0013-0389. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ a b MN Srinivas (1980), The Remembered Village, University of California Press, ISBN 978-0520039483, pages 307–308
- ^ Uppar, Ravindra (8 October 2016). "'Prevent sacrificing thousands of animals at Kakkeri fair-seer'". The Times of India. Belagavi: The Times Group. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ Lankesh, Gauri (9 May 2016). "Basavanna: India's first free thinker". Bangalore Mirror. Bangalore: IndiaTimes.com. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Jan Peter Schouten (1995), Revolution of the Mystics: On the Social Aspects of Vīraśaivism, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120812383, pages 9–10
- ^ Jan Peter Schouten (1995), Revolution of the Mystics: On the Social Aspects of Vīraśaivism, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120812383, pages 111–112
- ^ サイ (2005). Sai. [Sai]. OCLC 852251154.
- ^ Jessica Frazier et al. (2014), The Bloomsbury Companion to Hindu Studies, Bloomsbury Academic, ISBN 978-1472511515, page 281
- ^ "Basava, Shivaji statues for Parliament | India News - Times of India". The Times of India. 19 April 2003. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- ^ "Kalam to unveil statues of Shivaji, Basaveshwara in Parliament | India News". Zee News. 28 April 2003. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- ^ "PM's address on the occasion of release of Commemorative Coin in honour of Mahatma Basaveshwara". archivepmo.nic.in. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ Ataulla, Naheed (14 November 2015). "PM Modi unveils 12th century social reformer Basavanna's statue in London". The Times of India. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ Staff (23 June 2006). "Manmohan arrives in Bangalore ahead of schedule". Oneindia. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ T.V. Sivanandan (11 February 2011). "Basaveshwara's statue may come up in London". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 7 September 2013. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- ^ "Lambeth Basaveshwara - Home". www.lambethbasaveshwara.co.uk.
- ^ Image of the Prime Minister paying homage to Basaveshwara statue in London The Hindu (14 November 2015)
- ^ "Basavakalyan to get 108-ft statue of Basaveshwara". The Hindu. 26 October 2012. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Speaking of Siva, by A. K. Ramanujan. Penguin. 1973. ISBN 978-0-14044-270-0
- Dr. J. P. Dodamani (1996). Research essay. Kannada. "Sharanara Kurita Kannada Kadambari galu". p.52-194.
- Shiva Prakash, H.S. (1997). "Kannada". In Ayyappapanicker (ed.). Medieval Indian Literature:An Anthology. Sahitya Akademi. ISBN 978-81-260-0365-5.
- Understanding Basavana: history, hagiography and a modern Kannada drama, Julia Leslie (1998), Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, Volume 61, Issue 2, pages 228–261
- "Linga" as Lord Supreme in the Vacancies of Basava, R Blake Michael (1982), Numen, Volume 29, Issue 2, pages 202–219
- Lingayats as a Sect, William McCormack (1963), The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, Vol. 93, No. 1, pages 59–71
- Work as Worship in Vīraśaiva Tradition, R Blake Michael (1982), Journal of the American Academy of Religion, Vol. 50, No. 4, pages 605–619
External links
[edit]- 1131 births
- 1196 deaths
- 12th-century Hindus
- 12th-century Indian philosophers
- 12th-century Indian poets
- Activists from Karnataka
- Anti-caste activists
- Bhakti movement
- Brahmins who fought against discrimination
- Hindu philosophers and theologians
- History of Karnataka
- Indian male poets
- Indian social reformers
- Kannada poets
- Lingayat poets
- Lingayat saints
- Lingayatism
- People from Bijapur district, Karnataka
- Poets from Karnataka
- Scholars from Karnataka
- Shaivite religious leaders
