Lidocaine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Lidocaine /ˈlaɪdəˌkeɪn/[1][2] lignocaine /ˈlɪɡnəˌkeɪn/ |
| Trade names | Xylocaine |
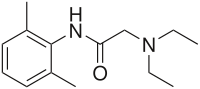
| Other names | N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Local Monograph Injectable Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | intravenous, subcutaneous, topical, oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 35% (oral) 3% (topical) |
| Metabolism | Liver,[3] 90% CYP3A4-mediated |
| Onset of action | within 1.5 min (IV)[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5–2 h |
| Duration of action | 10 to 20 min(IV),[3] 0.5 to 3 h (injection)[4][5] |
| Excretion | Kidney[3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.821 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 234.34 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 68 °C (154 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Lidocaine, also known as xylocaine and lignocaine, is a medication used to numb tissue in a specific area and to treat ventricular tachycardia.[3][4] It can also be used for nerve blocks. Lidocaine mixed with a small amount of epinephrine is available to allow larger doses to be used as numbing and to make it last longer.[4] When used as an injectable it typically begins working within four minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours.[4][5] Lidocaine may also be applied directly to the skin for numbing.[4]
Common side effects with intravenous use include sleepiness, muscle twitching, confusion, changes in vision, numbness, tingling, and vomiting. It can cause low blood pressure and an irregular heart rate.[3] There are concerns that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage.[4] It appears to be generally safe for use in pregnancy.[3] A lower dose may be required in those with liver problems.[3] It is generally safe to use in those allergic to tetracaine or benzocaine.[4] Lidocaine is an antiarrhythmic medication of the class Ib type. Lidocaine works by blocking sodium channels and thus decreasing the rate of contractions of the heart.[3] When used locally as a numbing agent, local neurons cannot signal the brain.[4]
Lidocaine was discovered in 1946 and went on sale in 1948.[6] It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic healthcare system.[7] It is available as a generic medication and is not very expensive.[4][8] In 2014, lidocaine was US$0.45 to $1.05 wholesale per 20ml vial of medication.[9]
Medical uses
Local numbing agent
The efficacy profile of lidocaine as a local anesthetic is characterized by a rapid onset of action and intermediate duration of efficacy. Therefore, lidocaine is suitable for infiltration, block, and surface anesthesia. Longer-acting substances such as bupivacaine are sometimes given preference for subdural and epidural anesthesias; lidocaine, though, has the advantage of a rapid onset of action. Epinephrine (adrenaline) vasoconstricts arteries, reducing bleeding and also delays the resorption of lidocaine, almost doubling the duration of anaesthesia. For surface anesthesia, several available formulations can be used for endoscopies, before intubations, etc. Buffering the pH of lidocaine makes local numbing less painful.[10] Lidocaine drops can be used on the eyes for short ophthalmic procedures.
There is tentative evidence for topical lidocaine for neuropathic pain.[11]
Heart arrhythmia
Lidocaine is also the most important class-1b antiarrhythmic drug; it is used intravenously for the treatment of ventricular arrhythmias (for acute myocardial infarction, digoxin poisoning, cardioversion, or cardiac catheterization) if amiodarone is not available or contraindicated. Lidocaine should be given for this indication after defibrillation, CPR, and vasopressors have been initiated. A routine preventative dose is no longer recommended after a myocardial infarction as the overall benefit is not convincing.[12]
Other
Inhaled lidocaine can be used as an antitussive (cough suppressor) acting peripherally to reduce the cough reflex. This application can be implemented as a safety and comfort measure for patients who have to be intubated, as it reduces the incidence of coughing and any tracheal damage it might cause when emerging from anesthesia.[13]
Lidocaine, along with ethanol, ammonia, and acetic acid, may also help in treating jellyfish stings, both numbing the affected area and preventing further nematocyst discharge.[14][15]
Insensitivity
Relative insensitivity to lidocaine is genetic. In hypokalemic sensory overstimulation, relative insensitivity to lidocaine has been described in people who also have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.[16] In dental anesthesia, a relative insensitivity to lidocaine can occur for anatomical reasons due to unexpected positions of nerves. Some people with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are insensitive to lidocaine.[17]
Dosage forms



Lidocaine, usually in the form of lidocaine hydrochloride, is available in various forms including:
- Injected local anesthetic (sometimes combined with epinephrine to reduce bleeding)
- Dermal patch (sometimes combined with prilocaine in a eutectic mixture)
- Intravenous injection
- Intravenous infusion
- Intraosseous infusion
- Nasal instillation/spray (combined with phenylephrine)
- Oral gel (often referred to as "viscous lidocaine" or abbreviated "lidocaine visc" or "lidocaine HCl visc" in pharmacology; used as teething gel)
- Oral liquid
- Oral and topical ointments, with and without flavoring, respectively[18][19]
- Topical gel (as with aloe vera gels that include lidocaine)[20]
- Topical liquid
- Lidocaine HCl 2% jelly, combined with hypromellose, to anesthetize and lubricate the urethra, etc., for inserting a catheter or instrument
- Topical patch (lidocaine 5%), marketed since 1999 in the US by Endo Pharmaceuticals[21] as "Lidoderm" - and since 2007 in the UK by Grünenthal as "Versatis".
- Topical ointment (lidocaine 5%) as a temporary reliever of discomfort associated anorectal disorders, such as hemorrhoids, marketed as an over-the-counter product in the US as RectiCare since 2012 by Ferndale Healthcare, Inc
- Topical aerosol spray
- Inhaled by nebulizer
- As a component of a GI cocktail used in emergency rooms
- Ophthalmic solution
Adverse effects
Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are rare when lidocaine is used as a local anesthetic and is administered correctly. Most ADRs associated with lidocaine for anesthesia relate to administration technique (resulting in systemic exposure) or pharmacological effects of anesthesia, and allergic reactions only rarely occur.[22] Systemic exposure to excessive quantities of lidocaine mainly result in central nervous system (CNS) and cardiovascular effects – CNS effects usually occur at lower blood plasma concentrations and additional cardiovascular effects present at higher concentrations, though cardiovascular collapse may also occur with low concentrations. ADRs by system are:
- CNS excitation: nervousness, agitation, anxiety, apprehension, tingling around the mouth (circumoral paraesthesia), headache, hyperesthesia, tremor, dizziness, pupillary changes, psychosis, euphoria, hallucinations, and seizures
- CNS depression with increasingly heavier exposure: drowsiness, lethargy, slurred speech, hypoesthesia, confusion, disorientation, loss of consciousness, respiratory depression and apnoea.
- Cardiovascular: hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias, flushing, venous insufficiency, increased defibrillator threshold, edema, and/or cardiac arrest – some of which may be due to hypoxemia secondary to respiratory depression.[23]
- Respiratory: Bronchospasm, dyspnea, respiratory depression or arrest
- Gastrointestinal: metallic taste, nausea, vomiting
- Ears: tinnitus
- Eyes: local burning, Conjunctival hyperemia, corneal epithelial changes/ulceration, diplopia, visual changes (opacification)
- Skin: itching, depigmentation, rash, urticaria, edema, angioedema, bruising, inflammation of the vein at the injection site, irritation of the skin when applied topically
- Blood: methemoglobinemia
- Allergy
ADRs associated with the use of intravenous lidocaine are similar to toxic effects from systemic exposure above. These are dose-related and more frequent at high infusion rates (≥3 mg/min). Common ADRs include: headache, dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, visual disturbances, tinnitus, tremor, and/or paraesthesia. Infrequent ADRs associated with the use of lidocaine include: hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, muscle twitching, seizures, coma, and/or respiratory depression.[23]
It is generally safe to use lidocaine with vasoconstrictor such as epinephrine including in regions such as the nose, ears, fingers and toes.[24] While concerns of tissue death if used in these areas have been raised evidence does not support these concerns.[24]
Interactions
Any drugs that are also ligands of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 can potentially increase serum levels and potential for toxicity or decrease serum levels and the efficacy, depending on whether they induce or inhibit the enzymes, respectively. Drugs that may increase the chance of methemoglobinemia should also be considered carefully. Dronedarone and liposomal morphine are both absolutely contraindicated, as they may increase the serum levels, but hundreds of other drugs require monitoring for interaction.[25]
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications for the use of lidocaine include:
- Heart block, second or third degree (without pacemaker)
- Severe sinoatrial block (without pacemaker)
- Serious adverse drug reaction to lidocaine or amide local anesthetics
- Hypersensitivity to corn and corn-related products (corn-derived dextrose is used in the mixed injections)
- Concurrent treatment with quinidine, flecainide, disopyramide, procainamide (class I antiarrhythmic agents)
- Prior use of amiodarone hydrochloride
- Adams-Stokes syndrome[26]
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome[26]
- Lidocaine viscous is not recommended by the FDA to treat tooth pain in children and infants.[27]
Exercise caution in patients with any of these:
- Hypotension not due to arrhythmia
- Bradycardia
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
- Elderly patients
- Pseudocholinesterase deficiency
- Intra-articular infusion (this is not an approved indication and can cause chondrolysis)
- Porphyria, especially acute intermittent porphyria; lidocaine has been classified as porphyrogenic because of the hepatic enzymes it induces,[28] although clinical evidence suggests it is not.[29] Bupivacaine is a safe alternative in this case.
- Impaired liver function - people with lowered hepatic function may have an adverse reaction with repeated administration of lidocaine because the drug is metabolized by the liver. Adverse reactions may include neurological symptoms (e.g. dizziness, nausea, muscle twitches, vomiting, or seizures).[30]
Overdosage
Overdoses with lidocaine can be a result of excessive administration by topical or parenteral routes, accidental oral ingestion of topical preparations by children who are more susceptible to overdose, accidental intravenous (rather than subcutaneous, intrathecal, or paracervical) injection, or prolonged use of subcutaneous infiltration anesthesia during cosmetic surgical procedures. These occurrences have often led to severe toxicity or death in both children and adults. Lidocaine and its two major metabolites may be quantified in blood, plasma, or serum to confirm the diagnosis in potential poisoning victims or to assist in the forensic investigation in a case of fatal overdose. It is important in the interpretation of analytical results to recognize that lidocaine is often routinely administered intravenously as an antiarrhythmic agent in critical cardiac-care situations.[31] Treatment with intravenous lipid emulsions (used for parental feeding) to reverse the effects of local anaesthetic toxicity is becoming more commonplace.[32]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Lidocaine alters signal conduction in neurons by blocking the fast voltage-gated Na+ channels in the neuronal cell membrane responsible for signal propagation.[33] With sufficient blockage, the membrane of the postsynaptic neuron will not depolarize and will thus fail to transmit an action potential. This creates the anaesthetic effect by not merely preventing pain signals from propagating to the brain, but by stopping them before they begin. Careful titration allows for a high degree of selectivity in the blockage of sensory neurons, whereas higher concentrations also affect other modalities of neuron signaling.
The same principle applies for this drug's actions in the heart. Blocking sodium channels in the conduction system, as well as the muscle cells of the heart, raises the depolarization threshold, making the heart less likely to initiate or conduct early action potentials that may cause an arrhythmia.[34]
Pharmacokinetics
The onset of action of lidocaine is about 45 to 90 seconds and its duration is 10 to 20 minutes.[citation needed] It is about 95% metabolized (dealkylated) in the liver mainly by CYP3A4 to the pharmacologically active metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and then subsequently to the inactive glycine xylidide. MEGX has a longer half-life than lidocaine, but also is a less potent sodium channel blocker.[35] The volume of distribution is 1.1-2.1 l/kg, but congestive heart failure can decrease it. About 60-80% circulates bound to the protein alpha1 acid glycoprotein. The oral bioavailability is 35% and the topical bioavailability is 3%.
The elimination half-life of lidocaine is biphasic and around 90–120 minutes in most patients. This may be prolonged in patients with hepatic impairment (average 343 min) or congestive heart failure (average 136 min).[36] Lidocaine is excreted in the urine (90% as metabolites and 10% as unchanged drug).[37]
History
Lidocaine, the first amino amide–type local anesthetic, was first synthesized under the name 'xylocaine' by Swedish chemist Nils Löfgren in 1943.[38][39][40] His colleague Bengt Lundqvist performed the first injection anesthesia experiments on himself.[38] It was first marketed in 1949.
Society and culture
Names
Lidocaine is the INN and BAN while lignocaine is the AAN and former BAN.
Xylocaine is a brandname.
Recreational use
Lidocaine is not currently listed by the World Anti-Doping Agency as an illegal substance.[41] It is used as an adjuvant, adulterant, and diluent to street drugs such as cocaine and heroin.[42]
Adulterant in cocaine
Lidocaine is often added to cocaine as a diluent.[43][44] Cocaine numbs the gums when applied, and since lidocaine causes stronger numbness,[45][failed verification] a user gets the impression of high-quality cocaine when in actuality, the user is receiving a diluted product.[citation needed]
Compendial status
Veterinary use
It is a component of the veterinary drug Tributame along with embutramide and chloroquine used to carry out euthanasia on horses and dogs.[47][48]
See also
- Lidocaine/prilocaine
- Dimethocaine (has some DRI activity)
- Procaine
References
- ^ "Lidocaine". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ "Lidocaine". Dictionary.com Unabridged (Online). n.d.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lidocaine Hydrochloride (Antiarrhythmic)". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved Aug 26, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lidocaine Hydrochloride (Local)". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved Aug 26, 2015.
- ^ a b "Analgesia and anaesthesia". Cambridge Textbook of Accident and Emergency Medicine. Project co-ordinator, Fiona Whinster. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. 1997. p. 194. ISBN 9780521433792.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Scriabine, Alexander (1999). "Discovery and development of major drugs currently in use". Pharmaceutical Innovation: Revolutionizing Human Health. Philadelphia: Chemical Heritage Press. p. 211. ISBN 9780941901215.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ^ Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 22. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ "Lidocaine HCL". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 27 August 2015.
- ^ Cepeda MS, Tzortzopoulou A, Thackrey M, Hudcova J, Arora Gandhi P, Schumann R (2010). "Adjusting the pH of lidocaine for reducing pain on injection". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (12): CD006581. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006581.pub2. PMID 21154371.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Derry, S; Wiffen, PJ; Moore, RA; Quinlan, J (24 July 2014). "Topical lidocaine for neuropathic pain in adults". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 7: CD010958. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010958.pub2. PMID 25058164.
- ^ Martí-Carvajal, AJ; Simancas-Racines, D; Anand, V; Bangdiwala, S (21 August 2015). "Prophylactic lidocaine for myocardial infarction". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 8: CD008553. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008553.pub2. PMID 26295202.
- ^ Biller JA (2007). "Airway obstruction, bronchospasm, and cough". In Berger AM, Shuster JL, Von Roenn JH (ed.). Principles and practice of palliative care and supportive oncology. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 297–307. ISBN 978-0-7817-9595-1.
Inhaled lidocaine is used to suppress cough during bronchoscopy. Animal studies and a few human studies suggest that lidocaine has an antitussive effect…
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Birsa LM, Verity PG, Lee RF (May 2010). "Evaluation of the effects of various chemicals on discharge of and pain caused by jellyfish nematocysts". Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 151 (4): 426–30. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.01.007. PMID 20116454.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Morabito R, Marino A, Dossena S, La Spada G (Jun 2014). "Nematocyst discharge in Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) oral arms can be affected by lidocaine, ethanol, ammonia and acetic acid". Toxicon : official journal of the International Society on Toxinology. 83: 52–8. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.03.002. PMID 24637105.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Segal MM, Rogers GF, Needleman HL, Chapman CA (Dec 2007). "Hypokalemic sensory overstimulation". Journal of child neurology. 22 (12): 1408–10. doi:10.1177/0883073807307095. PMID 18174562.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hakim AJ, Grahame R, Norris P, Hopper C (February 2005). "Local anaesthetic failure in joint hypermobility syndrome". J R Soc Med. 98 (2): 84–5. doi:10.1258/jrsm.98.2.84. PMC 1079398. PMID 15684369.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Product information for lidocaine ointment, USP 5%, spearmint flavored" (PDF). Product Insert. Taro Pharmaceuticals Industries Ltd. Retrieved July 27, 2009.
- ^ "Lidocaine Ointment Prescribing Information". Drugs.com. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- ^ "Solarcaine". Schering-Plough Healthcare Products, Inc. Retrieved July 27, 2009.
- ^ "Lidoderm (Lidocaine Patch 5%)". Our Products. Endo Pharmaceuticals. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- ^ Jackson D, Chen AH, Bennett CR (October 1994). "Identifying true lidocaine allergy". J Am Dent Assoc. 125 (10): 1362–6. PMID 7844301.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Australian Medicines Handbook. Adelaide, S. Aust: Australian Medicines Handbook Pty Ltd. 2006. ISBN 0-9757919-2-3.[page needed]
- ^ a b Nielsen, LJ; Lumholt, P; Hölmich, LR (27 October 2014). "[Local anaesthesia with vasoconstrictor is safe to use in areas with end-arteries in fingers, toes, noses and ears.]". Ugeskrift for laeger. 176 (44). PMID 25354008.
- ^ "Lidocaine". Epocrates. Retrieved April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Lidocaine Hydrochloride and 5% Dextrose Injection". Safety Labeling Changes. FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). January 2014.
- ^ "Lidocaine Viscous: Drug Safety Communication - Boxed Warning Required - Should Not Be Used to Treat Teething Pain". FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). June 2014.
- ^ "Table 96–4. Drugs and Porphyria" (PDF). Merck Manual. Merck & Company, Inc. 2011.
- ^ "Lidocaine - N01BB02". Drug porphyrinogenicity monograph. The Norwegian Porphyria Centre and the Swedish Porphyria Centre.
strong clinical evidence points to lidocaine as probably not porphyrinogenic
- ^ Khan, M. Gabriel (2007). Cardiac Drug Therapy (7th ed.). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. ISBN 9781597452380.
- ^ Baselt R (2008). Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man (8th ed.). Foster City, CA: Biomedical Publications. pp. 840–4. ISBN 0-9626523-7-7.
- ^ Picard J, Ward SC, Zumpe R, Meek T, Barlow J, Harrop-Griffiths W (February 2009). "Guidelines and the adoption of 'lipid rescue' therapy for local anaesthetic toxicity". Anaesthesia. 64 (2): 122–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05816.x. PMID 19143686.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Carterall, William A. (2001). "Molecular mechanisms of gating and drug block of sodium channels". Sodium Channels and Neuronal Hyperexcitability. Novartis Foundation Symposia. Vol. 241. pp. 206–225. doi:10.1002/0470846682.ch14. ISBN 9780470846681.
- ^ Sheu SS, Lederer WJ (Oct 1985). "Lidocaine's negative inotropic and antiarrhythmic actions. Dependence on shortening of action potential duration and reduction of intracellular sodium activity". Circulation Research. 57 (4): 578–90. doi:10.1161/01.res.57.4.578. PMID 2412723.
- ^ Lewin NA, Nelson LH (2006). "Chapter 61: Antidysrhythmics". In Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA, Nelson LH (ed.). Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies (8th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 963–4. ISBN 0-07-143763-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Thomson PD, Melmon KL, Richardson JA, Cohn K, Steinbrunn W, Cudihee R, Rowland M (April 1973). "Lidocaine pharmacokinetics in advanced heart failure, liver disease, and renal failure in humans". Ann. Intern. Med. 78 (4): 499–508. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-78-4-499. PMID 4694036.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Collinsworth KA, Kalman SM, Harrison DC (1974). "The clinical pharmacology of lidocaine as an antiarrhythymic drug". Circulation. 50 (6): 1217–30. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.50.6.1217. PMID 4609637.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Löfgren N (1948). Studies on local anesthetics: Xylocaine: a new synthetic drug (Inaugural dissertation). Stockholm, Sweden: Ivar Heggstroms. OCLC 646046738.[page needed]
- ^ Löfgren N, Lundqvist B (1946). "Studies on local anaesthetics II". Svensk Kemisk Tidskrift. 58: 206–17.
- ^ Wildsmith JAW (2011). "Lidocaine: A more complex story than 'simple' chemistry suggests" (PDF). The Proceedings of the History of Anaesthesia Society. 43: 9–16.
- ^ "The 2010 Prohibited List International Standard" (PDF). The World Anti-Doping Code. World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). 19 September 2009.
- ^ "New York Drug Threat Assessment". National Drug Intelligence Center. November 2002.
- ^ Bernardo NP, Siqueira MEPB, De Paiva MJN, Maia PP (2003). "Caffeine and other adulterants in seizures of street cocaine in Brazil". International Journal of Drug Policy. 14 (4): 331–4. doi:10.1016/S0955-3959(03)00083-5.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "UNITED STATES of America, Plaintiff-Appellee, v. Luis A. CUELLO, Alvaro Bastides-Benitez, John Doe, a/k/a Hugo Hurtado, and Alvaro Carvajal, Defendants-Appellants". Docket No. 78-5314. United States Court of Appeals, Fifth Circuit. 1979-07-25.
- ^ Kimberly H (1997-12-15). "Take a big-picture approach when dealing with corneal sensation". Retrieved 2009-04-23.
Lidocaine is more potent, with rapid diffusion and penetration.
- ^ "Revision Bulletin: Lidocaine and Prilocaine Cream–Revision to Related Compounds Test". The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. November 30, 2007.
- ^ Peterson, Michael E.; Talcott, Patricia A. (2013-08-07). Small Animal Toxicology. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 0323241980.
- ^ "FDA Freedom of Information Summary - TRIBUTAME" (PDF).
