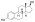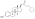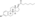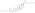Estradiol dipropionate
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Agofollin, Di-Ovocylin, Progynon DP, others |
| Other names | EDP; Estradiol dipropionate; Estradiol 3,17β-dipropionate; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 3,17β-dipropanoate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| Drug class | Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | IM: High[1] |
| Protein binding | Estradiol: ~98% (to albumin and SHBG)[2][3] |
| Metabolism | Cleavage via esterases in the liver, blood, and tissues[4][5] |
| Metabolites | Estradiol, benzoic acid, and metabolites of estradiol[4][5] |
| Elimination half-life | Unknown |
| Duration of action | IM (5 mg): 5–8 days[6][7] |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.660 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H32O4 |
| Molar mass | 384.516 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Estradiol dipropionate (EDP), sold under the brand names Agofollin, Di-Ovocylin, and Progynon DP among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women and in the treatment of gynecological disorders.[8][9][10][11][12][13] It has also been used in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men.[14][8] Although widely used in the past, estradiol dipropionate has largely been discontinued and is mostly no longer available today.[15][13][11] It appears to remain in use only in Japan, Macedonia, and Australia.[13] Estradiol dipropionate is given by injection into muscle at intervals ranging from once or twice a week to once every week and a half to two weeks.[8][16][14]
Side effects of estradiol dipropionate include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, nausea, headache, and fluid retention.[17] Estradiol dipropionate is an estrogen and hence is an agonist of the estrogen receptor, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol.[5][4] It is an estrogen ester and a prodrug of estradiol in the body.[4][5] Because of this, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of estrogen.[4]
Estradiol dipropionate was patented in 1937[18] and was introduced for medical use by 1940.[19][20] It was one of the earliest estradiol esters to be used.[8] Along with estradiol benzoate, estradiol dipropionate was among the most widely used esters of estradiol for many years following its introduction.[15]
Medical uses
[edit]The medical uses of estradiol dipropionate are the same as those of estradiol and other estrogens.[8][9] Estradiol dipropionate is used in hormone therapy for the treatment of menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal atrophy and in the treatment of hypoestrogenism and delayed puberty due to hypogonadism or other causes in women.[8][9] It is also used in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women.[14] Aside from hormone therapy, estradiol dipropionate is used in the treatment of gynecological disorders such as menstrual disorders, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and breast engorgement.[8][9] In addition, it is used as a form of high-dose estrogen therapy in the palliative treatment of prostate cancer in men.[8]
Estradiol dipropionate has typically been used at a dosage of 1 to 5 mg once or twice per week by intramuscular injection for relevant indications.[8][16] It has been used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms at a dosage of 1 to 5 mg initially for two to three injections and 1 to 2.5 mg for maintenance once every 10 to 14 days, and in the treatment of hypoestrogenism and delayed puberty at a dosage of 2.5 to 5 mg once per week.[8][21] As a component of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women, estradiol dipropionate has been used at dosages of 2 to 10 mg once per week or 5 to 20 mg once every 2 weeks.[14] In the treatment of prostate cancer, estradiol dipropionate has been used at a dosage of 5 mg once per week.[8]
Available forms
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate was previously available by itself as an oil solution for intramuscular injection provided as vials and ampoules at concentrations of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2.5, and 5 mg/mL.[8][22][23][24][25] The medication has largely been discontinued, with most of these formulations no longer being available.[11][13] Estradiol dipropionate remains available at a concentration of 1 mg/mL in combination with 50 mg/mL hydroxyprogesterone caproate under the brand name EP Hormone Depot (Teikoku Zoki Pharmaceutical Company) in Japan.[26][27][28][29][30][31][32]
Contraindications
[edit]Contraindications of estrogens include coagulation problems, cardiovascular diseases, liver disease, and certain hormone-sensitive cancers such as breast cancer and endometrial cancer, among others.[33][34][35][36]
Side effects
[edit]The side effects of estradiol dipropionate are the same as those of estradiol. Examples of such side effects include breast tenderness and enlargement, nausea, bloating, edema, headache, and melasma.[17]
Overdose
[edit]Symptoms of estrogen overdosage may include nausea, vomiting, bloating, increased weight, water retention, breast tenderness, vaginal discharge, heavy legs, and leg cramps.[33] These side effects can be diminished by reducing the estrogen dosage.[33]
Interactions
[edit]Inhibitors and inducers of cytochrome P450 may influence the metabolism of estradiol and by extension circulating estradiol levels.[37]
Pharmacology
[edit]
Pharmacodynamics
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate is an estradiol ester, or a prodrug of estradiol.[4][5] As such, it is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors.[4][5] Estradiol dipropionate is of about 41% higher molecular weight than estradiol due to the presence of its C3 and C17β propionate esters.[10][11] Because estradiol dipropionate is a prodrug of estradiol, it is considered to be a natural and bioidentical form of estrogen.[4]
| Estrogen | Form | Dose (mg) | Duration by dose (mg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPD | CICD | ||||
| Estradiol | Aq. soln. | ? | – | <1 d | |
| Oil soln. | 40–60 | – | 1–2 ≈ 1–2 d | ||
| Aq. susp. | ? | 3.5 | 0.5–2 ≈ 2–7 d; 3.5 ≈ >5 d | ||
| Microsph. | ? | – | 1 ≈ 30 d | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | Oil soln. | 25–35 | – | 1.66 ≈ 2–3 d; 5 ≈ 3–6 d | |
| Aq. susp. | 20 | – | 10 ≈ 16–21 d | ||
| Emulsion | ? | – | 10 ≈ 14–21 d | ||
| Estradiol dipropionate | Oil soln. | 25–30 | – | 5 ≈ 5–8 d | |
| Estradiol valerate | Oil soln. | 20–30 | 5 | 5 ≈ 7–8 d; 10 ≈ 10–14 d; 40 ≈ 14–21 d; 100 ≈ 21–28 d | |
| Estradiol benz. butyrate | Oil soln. | ? | 10 | 10 ≈ 21 d | |
| Estradiol cypionate | Oil soln. | 20–30 | – | 5 ≈ 11–14 d | |
| Aq. susp. | ? | 5 | 5 ≈ 14–24 d | ||
| Estradiol enanthate | Oil soln. | ? | 5–10 | 10 ≈ 20–30 d | |
| Estradiol dienanthate | Oil soln. | ? | – | 7.5 ≈ >40 d | |
| Estradiol undecylate | Oil soln. | ? | – | 10–20 ≈ 40–60 d; 25–50 ≈ 60–120 d | |
| Polyestradiol phosphate | Aq. soln. | 40–60 | – | 40 ≈ 30 d; 80 ≈ 60 d; 160 ≈ 120 d | |
| Estrone | Oil soln. | ? | – | 1–2 ≈ 2–3 d | |
| Aq. susp. | ? | – | 0.1–2 ≈ 2–7 d | ||
| Estriol | Oil soln. | ? | – | 1–2 ≈ 1–4 d | |
| Polyestriol phosphate | Aq. soln. | ? | – | 50 ≈ 30 d; 80 ≈ 60 d | |
Notes and sources
Notes: All aqueous suspensions are of microcrystalline particle size. Estradiol production during the menstrual cycle is 30–640 µg/d (6.4–8.6 mg total per month or cycle). The vaginal epithelium maturation dosage of estradiol benzoate or estradiol valerate has been reported as 5 to 7 mg/week. An effective ovulation-inhibiting dose of estradiol undecylate is 20–30 mg/month. Sources: See template. | |||||
Pharmacokinetics
[edit]Compared to estradiol benzoate, a related estradiol ester, estradiol dipropionate has enhanced and prolonged effects.[38][16] Whereas the duration of action of estradiol benzoate is said to be 2 to 3 days, the duration of estradiol dipropionate has been said to be 1 to 2 weeks.[39] However, newer estradiol esters have longer durations than either estradiol benzoate or estradiol dipropionate; the duration of estradiol valerate has been said to be 1 to 3 weeks, and the duration of estradiol cypionate has been said to be 3 to 4 weeks.[39][16] A single intramuscular injection of 5 mg estradiol dipropionate has a duration of about 5 to 8 days.[6][7]
A single intramuscular injection of 50 μg/kg estradiol dipropionate in oil in 15 pubertal girls (about 1 mg for a 50-kg (110-lb) girl) was found to produce peak estradiol levels of about 215 pg/mL after 1.5 days.[40] Estradiol levels declined to about 90 pg/mL after 4 days.[40]
-
Vaginal cornification with a single intramuscular injection of different estradiol esters in oil solution in women.[41] Source was Schwartz & Soule (1955).[41]
Chemistry
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate, also known as estradiol 3,17β-dipropionate, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of estradiol.[10][11] It is an estrogen ester; specifically, it is the C3,17β dipropionate ester of estradiol.[10][11]
The experimental octanol/water partition coefficient (logP) of estradiol dipropionate is 4.9.[42]
| Estrogen | Structure | Ester(s) | Relative mol. weight |
Relative E2 contentb |
log Pc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position(s) | Moiet(ies) | Type | Lengtha | ||||||
| Estradiol | – | – | – | – | 1.00 | 1.00 | 4.0 | ||
| Estradiol acetate | C3 | Ethanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 2 | 1.15 | 0.87 | 4.2 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate | C3 | Benzoic acid | Aromatic fatty acid | – (~4–5) | 1.38 | 0.72 | 4.7 | ||
| Estradiol dipropionate | C3, C17β | Propanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 3 (×2) | 1.41 | 0.71 | 4.9 | ||
| Estradiol valerate | C17β | Pentanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 5 | 1.31 | 0.76 | 5.6–6.3 | ||
| Estradiol benzoate butyrate | C3, C17β | Benzoic acid, butyric acid | Mixed fatty acid | – (~6, 2) | 1.64 | 0.61 | 6.3 | ||
| Estradiol cypionate | C17β | Cyclopentylpropanoic acid | Cyclic fatty acid | – (~6) | 1.46 | 0.69 | 6.9 | ||
| Estradiol enanthate | C17β | Heptanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 | 1.41 | 0.71 | 6.7–7.3 | ||
| Estradiol dienanthate | C3, C17β | Heptanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 7 (×2) | 1.82 | 0.55 | 8.1–10.4 | ||
| Estradiol undecylate | C17β | Undecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 11 | 1.62 | 0.62 | 9.2–9.8 | ||
| Estradiol stearate | C17β | Octadecanoic acid | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 | 1.98 | 0.51 | 12.2–12.4 | ||
| Estradiol distearate | C3, C17β | Octadecanoic acid (×2) | Straight-chain fatty acid | 18 (×2) | 2.96 | 0.34 | 20.2 | ||
| Estradiol sulfate | C3 | Sulfuric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.29 | 0.77 | 0.3–3.8 | ||
| Estradiol glucuronide | C17β | Glucuronic acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.65 | 0.61 | 2.1–2.7 | ||
| Estramustine phosphated | C3, C17β | Normustine, phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.91 | 0.52 | 2.9–5.0 | ||
| Polyestradiol phosphatee | C3–C17β | Phosphoric acid | Water-soluble conjugate | – | 1.23f | 0.81f | 2.9g | ||
| Footnotes: a = Length of ester in carbon atoms for straight-chain fatty acids or approximate length of ester in carbon atoms for aromatic or cyclic fatty acids. b = Relative estradiol content by weight (i.e., relative estrogenic exposure). c = Experimental or predicted octanol/water partition coefficient (i.e., lipophilicity/hydrophobicity). Retrieved from PubChem, ChemSpider, and DrugBank. d = Also known as estradiol normustine phosphate. e = Polymer of estradiol phosphate (~13 repeat units). f = Relative molecular weight or estradiol content per repeat unit. g = log P of repeat unit (i.e., estradiol phosphate). Sources: See individual articles. | |||||||||
History
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate was first synthesized and patented in 1937.[43][18] It was assessed in clinical studies by 1939 and was introduced by Ciba as an oil solution for use by intramuscular injection under the brand name Di-Ovocylin by the same year.[43][38][19] Other formulations such as Ovocyclin P by Ciba, Progynon DP by Schering and Dimenformon Dipropionate by Roche-Organon were also marketed by the early 1940s.[44][45][20][46] Later in the 1940s the brand name Di-Ovocylin was changed by Ciba to Ovocylin Dipropionate.[22] Along with estradiol benzoate, which was introduced in 1933,[47] estradiol dipropionate was one of the first estradiol esters to be introduced for medical use.[48][45] Prior to the development and introduction of longer-acting estradiol esters like estradiol valerate and estradiol cypionate in the 1950s, estradiol dipropionate and estradiol benzoate were the most widely used estradiol esters.[15][49]
Society and culture
[edit]Generic names
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate is the generic name of the drug and its INNM, BANM, and JAN.[10][11][12][13]
Brand names
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate has been marketed under a variety of brand names, including Agofollin, Akrofolline, Dihidrofolina "Kével", Dimenformon, Dimenformon Dipropionate, Diovocylin, Di-Ovocylin, Diprostron, Diprovex, Endofollicolina D.P., EP Hormone Depot (in combination with hydroxyprogesterone caproate), Estroici, Estronex, Follicyclin, Follicyclin P, Follikelmon Depot, Horiken-Depot, Nacyclyl, Oestradiol Galenika, Oestradiol Streuli, Orofollina, Ovacrin, Ovahormon Depot, Ovocylin, Ovocylin Dipropionate, Ovocylin P, and Progynon DP, among others.[50][10][11][12][51][52][13] Agofollin was an oil solution of estradiol dipropionate that was previously marketed in the Czech Republic and Slovakia.[53]
Availability
[edit]Estradiol dipropionate has been discontinued in most countries, but remains available in Japan and Macedonia alone under the brand names Ovahormon and Oestradiol Galenika and/or in combination with hydroxyprogesterone caproate under the brand name EP Hormone Depot.[11][13] It is also marketed for use in veterinary medicine in combination with hydroxyprogesterone caproate and nandrolone decanoate under the brand name Reepair in Australia.[13]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Düsterberg B, Nishino Y (December 1982). "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacological features of oestradiol valerate". Maturitas. 4 (4): 315–324. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(82)90064-0. PMID 7169965.
- ^ Stanczyk FZ, Archer DF, Bhavnani BR (June 2013). "Ethinyl estradiol and 17β-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment". Contraception. 87 (6): 706–727. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2012.12.011. PMID 23375353.
- ^ Gupta MK, Chia SY (2007). "Ovarian hormones: structure, biosynthesis, function, mechanism of action, and laboratory diagnosis". In Falcone T, Hurd WW (eds.). Clinical Reproductive Medicine and Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 22, 362, 388. ISBN 978-0-323-03309-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Oettel M, Schillinger E, Kuhnz W, Blode H, Zimmermann H (6 December 2012). "Pharmacokinetics of exogenous natural and synthetic estrogens and antiestrogens". In Oettel M, Schillinger E (eds.). Estrogens and Antiestrogens II: Pharmacology and Clinical Application of Estrogens and Antiestrogen. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 261. ISBN 978-3-642-60107-1.
Natural estrogens considered here include: [...] Esters of 17β-estradiol, such as estradiol valerate, estradiol benzoate and estradiol cypionate. Esterification aims at either better absorption after oral administration or a sustained release from the depot after intramuscular administration. During absorption, the esters are cleaved by endogenous esterases and the pharmacologically active 17β-estradiol is released; therefore, the esters are considered as natural estrogens.
- ^ a b c d e f Kuhl H (August 2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration". Climacteric. 8 (Suppl 1): 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947. S2CID 24616324.
- ^ a b Knörr K, Knörr-Gärtner H, Beller FK, Lauritzen C (8 March 2013). Lehrbuch der Geburtshilfe und Gynäkologie: Physiologie und Pathologie der Reproduktion. Springer-Verlag. pp. 508–. ISBN 978-3-662-00526-2.
- ^ a b Knörr K, Beller FK, Lauritzen C (17 April 2013). Lehrbuch der Gynäkologie. Springer-Verlag. pp. 212–213. ISBN 978-3-662-00942-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "NNR: Products Recently Accepted by the A. M. A. Council on Pharmacy and Chemistry". Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association (Practical Pharmacy Ed.). 10 (11): 692–694. 1949. doi:10.1016/S0095-9561(16)31995-8. ISSN 0095-9561.
- ^ a b c d Swyer GI (April 1959). "The oestrogens". British Medical Journal. 1 (5128): 1029–1031. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.5128.1029. PMC 1993181. PMID 13638626.
- ^ a b c d e f Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 898–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 406–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b c Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 206–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Estradiol: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects". Drugs.com.
- ^ a b c d Nakatsuka M (May 2010). "Endocrine treatment of transsexuals: assessment of cardiovascular risk factors". Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism. 5 (3): 319–322. doi:10.1586/eem.10.18. PMID 30861686. S2CID 73253356.
- ^ a b c Schwartz MM, Soule SD (July 1955). "Estradiol 17-beta-cyclopentylpropionate, a longacting estrogen". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 70 (1): 44–50. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(55)90286-6. PMID 14388061.
- ^ a b c d Huhnstock KH, Kutscha W, Dehmel H (12 March 2013). Diagnose und Therapie in der Praxis. Springer-Verlag. pp. 1053–. ISBN 978-3-642-68385-5.
- ^ a b McIver B, Tebben PJ, Shas P (23 September 2010). "Endocrinology". In Ghosh AK (ed.). Mayo Clinic Internal Medicine Board Review. OUP USA. pp. 222–. ISBN 978-0-19-975569-1.
- ^ a b US patent 2233025, Miescher K, Scholz C, "Estradiol-17-monoesters", published 1941-02-25, assigned to Ciba Pharmaceutical Products, Inc.
- ^ a b Escamilla RF, Lisserf H (1940). "Induction of menarche and development of secondary sexual characteristics in a woman aged 34 by injections of estradiol dipropionate". Endocrinology. 27 (1): 153. doi:10.1210/endo-27-1-153. ISSN 0013-7227.
The estradiol dipropionate used in this case was furnished by the Ciba Co. Their trade name for this product is Di-Ovocylin.
- ^ a b Shorr E (1940). "Effect of Concomitant Administration of Estroens and Proesterone on Vainal Smear in Man". Experimental Biology and Medicine. 43 (3): 501–506. doi:10.3181/00379727-43-11244. ISSN 1535-3702. S2CID 75787837.
Grateful acknowledgment is made to Dr. Erwin Schwenk of the Schering Corporation for the estradiol benzoate (Progynon B), estradiol dipropionate (Progynon DP), progesterone (Proluton), and pregneninolone (Pranone) used in these experiments;
- ^ American Medical Association. Dept. of Drugs; Council on Drugs (American Medical Association); American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (1 February 1977). "Estrogens, Progestagens, Oral Contraceptives, and Ovulatory Agents". AMA drug evaluations. Publishing Sciences Group. pp. 540–572. ISBN 978-0-88416-175-2.
Intramuscular: For replacement therapy, (Estradiol, Estradiol Benzoate) 0.5 to 1.5 mg two or three times weekly; (Estradiol Cypionate) 1 to 5 mg weekly for two or three weeks; (Estradiol Dipropionate) 1 to 5 mg every one to two weeks; (Estradiol Valerate) 10 to 40 mg every one to four weeks.
- ^ a b "New Prescription Products". Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association (Practical Pharmacy Ed.). 10 (4): 198–206. 1949. doi:10.1016/S0095-9561(16)31795-9. ISSN 0095-9561.
- ^ Indian Pharmaceutical Guide. Pamposh Publications. 1968.
- ^ Modell W (21 November 2013). Drugs in Current Use 1958. Springer. pp. 51–. ISBN 978-3-662-40303-7.
- ^ Hospital Formulary and Compendium of Useful Information. University of California Press. 1952. pp. 49–. GGKEY:2UAAZRZ5LN0.
- ^ Kawamura I, Mizota T, Lacey E, Tanaka Y, Manda T, Shimomura K, Kohsaka M (September 1993). "The estrogenic and antiestrogenic activities of droloxifene in human breast cancers". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 63 (1): 27–34. doi:10.1254/jjp.63.27. PMID 8271528.
- ^ Asanuma F, Yamada Y, Kawamura E, Lee K, Kobayashi H, Yamada T, et al. (1998). "Antitumor activity of paclitaxel and epirubicin in human breast carcinoma, R-27". Folia Microbiologica. 43 (5): 473–474. doi:10.1007/BF02820793. PMID 9821299. S2CID 22732235.
- ^ Noguchi M, Tajiri K, Taniya T, Kumaki T, Ashikari A, Miyazaki I (1990). "Influence of hormones on proliferation of ER-positive cells and ER-negative cells of human breast cancer (MCF-7)". Oncology. 47 (1): 19–24. doi:10.1159/000226779. PMID 2137212.
- ^ Kubota T, Oka S, Utsumi T, Inoue S, Kuzuoka M, Suto A, et al. (July 1989). "Human breast carcinoma (ZR-75-1) serially transplanted into nude mice--with reference to estradiol dependency and sensitivity to tamoxifen". The Japanese Journal of Surgery. 19 (4): 446–451. doi:10.1007/BF02471626. PMID 2810959. S2CID 23267652.
- ^ Ueda H, Nakajima H, Hori Y, Fujita T, Nishimura M, Goto T, Okuhara M (March 1994). "FR901228, a novel antitumor bicyclic depsipeptide produced by Chromobacterium violaceum No. 968. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical and biological properties, and antitumor activity". The Journal of Antibiotics. 47 (3): 301–310. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.47.301. PMID 7513682.
- ^ Hori Y, Abe Y, Nishimura M, Goto T, Okuhara M, Kohsaka M (July 1993). "R1128 substances, novel non-steroidal estrogen-receptor antagonists produced by a Streptomyces. III. Pharmacological properties and antitumor activities". The Journal of Antibiotics. 46 (7): 1069–1075. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.46.1055. PMID 8360101.
- ^ Noguchi M, Koyasaki N, Miyazaki I, Mizukami Y (November 1991). "Effects of hormones on tumor growth and immunoreactive insulin-like growth factor-1 of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer (MCF-7) transplanted in nude mice". Japanese Journal of Cancer Research. 82 (11): 1199–1202. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01780.x. PMC 5918318. PMID 1752778.
- ^ a b c Lauritzen C (September 1990). "Clinical use of oestrogens and progestogens". Maturitas. 12 (3): 199–214. doi:10.1016/0378-5122(90)90004-P. PMID 2215269.
- ^ Lauritzen C (22 June 2005). "Practice of Hormone Substitution". In Lauritzen C, Studd JW (eds.). Current Management of the Menopause. CRC Press. pp. 95–98, 488. ISBN 978-0-203-48612-2.
- ^ Laurtizen C (2001). "Hormone Substitution Before, During and After Menopause" (PDF). In Fisch FH (ed.). Menopause – Andropause: Hormone Replacement Therapy Through the Ages. Krause & Pachernegg: Gablitz. pp. 67–88. ISBN 978-3-901299-34-6.
- ^ Midwinter A (1976). "Contraindications to estrogen therapy and management of the menopausal syndrome in these cases". In S (ed.). The Management of the Menopause & Post-Menopausal Years: The Proceedings of the International Symposium held in London 24–26 November 1975 Arranged by the Institute of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, The University of London. MTP Press Limited. pp. 377–382. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-6165-7_33. ISBN 978-94-011-6167-1.
- ^ Cheng ZN, Shu Y, Liu ZQ, Wang LS, Ou-Yang DS, Zhou HH (February 2001). "Role of cytochrome P450 in estradiol metabolism in vitro". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 22 (2): 148–154. PMID 11741520.
- ^ a b Greene RR, Dorr EM (1939). "Clinical use of a new estrogen". Endocrinology. 24 (4): 577–578. doi:10.1210/endo-24-4-577. ISSN 0013-7227.
- ^ a b Quirk Jr GJ, Wendell Jr GD (6 December 2012). "The Biological Effects of Natural and Synthetic Estrogens". In Buchsbaum HJ (ed.). The Menopause. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 62–. ISBN 978-1-4612-5525-3.
- ^ a b c d e Presl J, Hořejší J, Štroufová A, Herzmann J (1976). "Sexual maturation in girls and the development of estrogen induced gonadotropic hormone release". Annales de Biologie Animale, Biochimie, et Biophysique. 16 (3): 377–383. doi:10.1051/rnd:19760314. ISSN 0003-388X.
- ^ a b Schwartz MM, Soule SD (July 1955). "Estradiol 17-beta-cyclopentylpropionate, a longacting estrogen". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 70 (1): 44–50. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(55)90286-6. PMID 14388061.
- ^ "Estradiol Dipropionate | C24H32O4". ChemSpider.
- ^ a b Dorr EM, Greene RR (1939). "Treatment of the menopause with estradiol dipropionate". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 38 (3): 458–464. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(39)90763-5. ISSN 0002-9378.
- ^ Reilly WA (November 1941). "Estrogens: Their Use in Pediatrics". California and Western Medicine. 55 (5): 237–239. PMC 1634235. PMID 18746057.
- ^ a b Fluhmann CF (1944). "Clinical Use of Extracts from the Ovaries". Journal of the American Medical Association. 125 (1): 1. doi:10.1001/jama.1944.02850190003001. ISSN 0002-9955.
- ^ Macpherson AI (June 1940). "The Use of Œstrogens in Obstetrics and Gynæcology". Edinburgh Medical Journal. 47 (6): 406–424. PMC 5306594. PMID 29646930.
- ^ Buschbeck H (1934). "Neue Wege der Hormontherapie in der Gynäkologie" [New ways of hormonal therapy in gynecology]. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift. 60 (11): 389–393. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1129842. ISSN 0012-0472. S2CID 72668930.
- ^ Greene RR (1941). "Endocrine Therapy for Gynecologic Disorders". Medical Clinics of North America. 25 (1): 155–168. doi:10.1016/S0025-7125(16)36624-X. ISSN 0025-7125.
- ^ Oriowo MA, Landgren BM, Stenström B, Diczfalusy E (April 1980). "A comparison of the pharmacokinetic properties of three estradiol esters". Contraception. 21 (4): 415–424. doi:10.1016/S0010-7824(80)80018-7. PMID 7389356.
- ^ Negwer M (1987). Organic-chemical Drugs and Their Synonyms: (an International Survey). VCH Publishers. p. 1272. ISBN 978-0-89573-552-2.
- ^ International Agency for Research on Cancer (1979). Sex Hormones (II). International Agency for Research on Cancer. ISBN 978-92-832-1221-8.
- ^ Lewis RJ (13 June 2008). Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 594–. ISBN 978-0-470-18024-2.
- ^ Lissak K (6 December 2012). Hormones and Brain Function. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 145–. ISBN 978-1-4684-2007-4.

![Estradiol levels after a single intramuscular injection of 50 μg/kg estradiol dipropionate in oil in pubertal girls.[40] This dose would be 1 mg in a 50-kg (110-lb) girl.[40] Source was Presl et al. (1976).[40]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/db/Estradiol_levels_after_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_50_%CE%BCg_per_kg_estradiol_dipropionate_in_pubertal_girls.png/323px-Estradiol_levels_after_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_50_%CE%BCg_per_kg_estradiol_dipropionate_in_pubertal_girls.png)
![Vaginal cornification with a single intramuscular injection of different estradiol esters in oil solution in women.[41] Source was Schwartz & Soule (1955).[41]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/23/Vaginal_cornification_with_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_different_estradiol_esters_in_women.png/395px-Vaginal_cornification_with_a_single_intramuscular_injection_of_different_estradiol_esters_in_women.png)