Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, Utah | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top: The skyline in July 2011, Utah State Capitol, TRAX, Union Pacific Depot, the Block U, the City and County Building, and the Salt Lake Temple | |
| Nickname: "The Crossroads of the West" | |
 Location in Salt Lake County and the state of Utah | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Salt Lake |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jackie Biskupski (D) |
| Area | |
• City | 285.9 km2 (110.4 sq mi) |
| • Land | 282.5 km2 (109.1 sq mi) |
| • Water | 3.3 km2 (1.3 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,288 m (4,226 ft) |
| Population | |
• City | 186,440 |
• Estimate (2013)[2] | 191,180 |
| • Rank | US: 124th |
| • Density | 643.3/km2 (1,666/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,021,243 (US: 42nd) |
| • Metro | 1,153,340 (US: 48th) |
| • CSA | 2,467,709 (US: 23rd) |
| Demonym | Salt Laker[3] |
| Time zone | UTC-7 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-6 (Mountain) |
| ZIP Codes | Zip codes[4] |
| Area code(s) | 385, 801 |
| FIPS code | 49-67000[5] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1454997[6] |
| Website | Salt Lake City |
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and the most populous municipality of the U.S. state of Utah. With an estimated population of 190,884 in 2014,[7] the city lies at the core of the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, which has a total population of 1,153,340 (2014 estimate). Salt Lake City is further situated within a larger metropolis known as the Salt Lake City-Ogden-Provo Combined Statistical Area. This region is a corridor of contiguous urban and suburban development stretched along an approximately 120-mile (190 km) segment of the Wasatch Front, comprising a total population of 2,423,912 as of 2014[update].[8] It is one of only two major urban areas in the Great Basin (the other is Reno, Nevada), and the largest in the Intermountain West.
The city was founded in 1847 by Brigham Young, Isaac Morley, George Washington Bradley and numerous other Mormon followers, who extensively irrigated and cultivated the arid valley. Due to its proximity to the Great Salt Lake, the city was originally named "Great Salt Lake City"—the word "great" was dropped from the official name in 1868 by the 17th Utah Territorial Legislature.[9] Home to the headquarters of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and Temple Square, Salt Lake City was historically considered a holy city by members of the LDS church; Brigham Young called it a "Kingdom of Heaven on Earth".[10] Today, however, less than half the population of Salt Lake City proper are members of the LDS Church.[11]
Immigration of international LDS members, mining booms, and the construction of the first transcontinental railroad initially brought economic growth, and the city was nicknamed the Crossroads of the West. It was traversed by the Lincoln Highway, the first transcontinental highway, in 1913, and presently two major cross-country freeways, I-15 and I-80, intersect in the city. Salt Lake City has since developed a strong outdoor recreation tourist industry based primarily on skiing, and hosted the 2002 Winter Olympics. It is the industrial banking center of the United States.[12]
History
| External videos | |
|---|---|
 | |

Source: Britannica 7th Ed.
Before Mormon settlement, the Shoshone, Ute, and Paiute had dwelt in the Salt Lake Valley for thousands of years. At the time of the founding of Salt Lake City, the valley was within the territory of the Northwestern Shoshone;[14] however, occupation was seasonal, near streams emptying from Canyons into the Salt Lake Valley. The land was treated by the United States as public domain; no aboriginal title by the Northwestern Shoshone was ever recognized by the United States or extinguished by treaty with the United States.[15] The first U.S. explorer in the Salt Lake area is believed to be Jim Bridger in 1825, although others had been in Utah earlier, some as far north as the nearby Utah Valley (the Dominguez-Escalante expedition of 1776 were undoubtedly aware of Salt Lake Valley's existence). U.S. Army officer John C. Frémont surveyed the Great Salt Lake and the Salt Lake Valley in 1843 and 1845.[16] The Donner Party, a group of ill-fated pioneers, had traveled through the Great Salt Lake Valley in August 1846.

The first permanent settlements in the valley date to the arrival of the Latter-day Saints on July 24, 1847.[17] They had traveled beyond the boundaries of the United States into Mexican Territory [18] seeking a secluded area to safely practice their religion, far away from the violence and the persecution they experienced in the East. Upon arrival at the Salt Lake Valley, president of the church Brigham Young is recorded as stating, "This is the right place, drive on." Brigham Young claimed to have seen the area in a vision prior to the wagon train's arrival. They found the broad valley empty of any human settlement.

Four days after arriving in the Salt Lake Valley, Brigham Young designated the building site for the Salt Lake Temple, which would eventually become a famous Mormon and Salt Lake City landmark.
The Salt Lake Temple, constructed on the block that would later be called Temple Square, took 40 years to complete. Construction started in 1853, and the temple was dedicated on 6 April 1893. The temple has become an icon for the city and serves as its centerpiece. In fact, the southeast corner of Temple Square is the initial point of reference for the Salt Lake Meridian, and for all addresses in the Salt Lake Valley.
The Mormon pioneers organized a new state called Deseret and petitioned for its recognition in 1849. The United States Congress rebuffed the settlers in 1850 and established the Utah Territory, vastly reducing its size, and designated Fillmore as its capital city. Great Salt Lake City replaced Fillmore as the territorial capital in 1858, and the name was subsequently abbreviated to Salt Lake City. The city's population continued to swell with an influx of Mormon converts and Gold Rush gold seekers, making it one of the most populous cities in the American Old West.
Explorer, ethnologist, and author Richard Francis Burton traveled by coach in the summer of 1860 to document life in Great Salt Lake City. He was granted unprecedented access during his three-week visit, including audiences with President Brigham Young and other contemporaries of Joseph Smith. The records of his visit include sketches of the early city buildings, a description of local geography and agriculture, commentary on its politics and social order, essays, speeches, and sermons from Brigham Young, Isaac Morley, George Washington Bradley and other prominent leaders, and snapshots of everyday life such as newspaper clippings and the menu from a high-society ball.[19]

Disputes with the federal government ensued over the Mormon practice of polygamy. A climax occurred in 1857 when President James Buchanan declared the area in rebellion after Brigham Young refused to step down as governor, beginning the Utah War. A division of the United States Army, commanded by Albert Sidney Johnston, later a general in the army of the Confederate States of America, marched through the city and found it had been evacuated. This division set up Camp Floyd approximately 40 mi (64 km) southwest of the city. Another military installation, Fort Douglas, was established in 1862 to maintain Union allegiance during the American Civil War. Many area leaders were incarcerated at the territorial prison in Sugar House in the 1880s for violation of anti-polygamy laws. The LDS Church began their eventual abandonment of polygamy in 1890, releasing "The Manifesto", which officially suggested members obey the law of the land (which was equivalent to forbidding new polygamous marriages inside the U.S. and its territories, but not in Mormon settlements in Canada and Mexico). This paved the way for statehood in 1896, when Salt Lake City became the state capital.
The First Transcontinental Railroad was completed in 1869 at Promontory Summit on the north side of the Great Salt Lake.[20] A railroad was connected to the city from the Transcontinental Railroad in 1870, making travel less burdensome. Mass migration of different groups followed. Ethnic Chinese (who laid most of the Central Pacific railway) established a flourishing Chinatown in Salt Lake City nicknamed "Plum Alley", which housed around 1,800 Chinese during the early 20th century. The Chinese businesses and residences were demolished in 1952 although a historical marker has been erected near the parking ramp which has replaced Plum Alley. Immigrants also found economic opportunities in the booming mining industries. Remnants of a once-thriving Japantown – namely a Buddhist temple and Japanese Christian chapel – still remain in downtown Salt Lake City. European ethnic groups and East Coast missionary groups constructed St. Mark's Episcopal Cathedral in 1874, the Roman Catholic Cathedral of the Madeleine in 1909 and the Greek Orthodox Holy Trinity Cathedral in 1923. This time period also saw the creation of Salt Lake City's now defunct red-light district that employed 300 courtesans at its height before being closed down in 1911.[21]

During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, an extensive streetcar system was constructed throughout the city with the first streetcar running in 1872 and electrification of the system in 1889. As in the rest of the country, the automobile usurped the streetcar, and the last trolley was approved for conversion in 1941, yet ran until 1945, due to WWII. Trolley buses ran until 1946. Light rail transit returned to the city when UTA's TRAX opened in 1999.[22] The S Line (formerly known as Sugar House Streetcar) opened for service in December 2013 on an old D&RGW right-of-way.[23][24]
The city's population began to stagnate during the 20th century as population growth shifted to suburban areas north and south of the city. Few of these areas were annexed to the city, while nearby towns incorporated and expanded themselves. As a result, the population of the surrounding metropolitan area greatly outnumbers Salt Lake City. A major concern of recent government officials has been combating inner-city commercial decay. The city lost population from the 1960s through the 1980s, but experienced some recovery in the 1990s. Presently, the city has gained an estimated 5 percent of its population since the year 2000.[2]
The city has experienced significant demographic shifts in recent years.[25] Hispanics now account for approximately 22% of residents and the city has a significant gay community.[26] There is also a large Pacific Islander population, mainly made up of Samoans and Tongans; they compose roughly 2% of the population of the Salt Lake Valley area.
Salt Lake City was selected to host the 2002 Winter Olympics in 1995. The games were plagued with controversy. A bid scandal surfaced in 1998 alleging bribes had been offered to secure the city for the 2002 games location. During the games, other scandals erupted over contested judging scores and illegal drug use. Despite the controversies, the games were heralded as a financial success, being one of the few in recent history to profit. In preparation major construction projects were initiated. Local freeways were expanded and repaired, and a light rail system was constructed. Olympic venues are now used for local, national, and international sporting events and Olympic athlete training.[27] Tourism has increased since the Olympic games,[28][failed verification] but business did not pick up immediately following them.[29] Salt Lake City expressed interest in bidding for the 2022 Winter Olympics.[30][31] However, Beijing was selected to host the 2022 Winter Olympics.[32]
Salt Lake City hosted the 16th Winter Deaflympic games in 2007, taking place in the venues in Salt Lake City and Park City,[33] and Rotary International chose the city as the host site of their 2007 convention, which was the single largest gathering in Salt Lake City since the 2002 Winter Olympics.[34] The U.S. Volleyball Association convention in 2005 drew 39,500 attendees.
Geography


Salt Lake City has a total area of 110.4 square miles (286 km2) and an average elevation of 4,327 feet (1,319 m) above sea level. The lowest point within the boundaries of the city is 4,210 feet (1,280 m) near the Jordan River and the Great Salt Lake, and the highest is Grandview Peak, at 9,410 feet (2,868 m).[35]
The city is located in the northeast corner of the Salt Lake Valley surrounded by the Great Salt Lake to the northwest and the steep Wasatch and Oquirrh mountain ranges on the eastern and southwestern borders, respectively. Its encircling mountains contain several narrow glacial and stream carved canyons. Among these canyons, City Creek, Emigration, Millcreek, and Parley's border the eastern city limits.
The burgeoning population of Salt Lake City and the surrounding metropolitan area, combined with its geographical situation, has led to air quality becoming a top concern for the populace. The Wasatch Front is subject to strong temperature inversions during the winter, which trap pollutants and lower air quality.[36] The Utah Division of Air Quality closely monitors air quality and issues alerts for voluntary and mandatory actions when pollution exceeds federal safety standards.[citation needed] Protests have been held at the Utah State Capitol and Democratic lawmakers have introduced legislation in the Utah State Legislature to make public transportation free during January and July, when air quality is usually at its worst.[36] The population of the Salt Lake City metropolitan area is projected to double by 2040, putting further pressure on the region's air quality.[citation needed]
The Great Salt Lake is separated from Salt Lake City by extensive marshlands and mudflats. The metabolic activities of bacteria in the lake result in a phenomenon known as "lake stink", a scent reminiscent of foul poultry eggs, two to three times per year for a few hours.[37] The Jordan River flows through the city and is a drainage of Utah Lake that empties into the Great Salt Lake.
The highest mountaintop visible from Salt Lake City is Twin Peaks, which reaches 11,330 feet (3454 m).[38] Twin Peaks is southeast of Salt Lake City in the Wasatch Range. The Wasatch Fault is found along the western base of the Wasatch and is considered at high risk of producing an earthquake as large as 7.5. Catastrophic damage is predicted in the event of an earthquake with major damage resulting from the liquefaction of the clay- and sand-based soil and the possible permanent flooding of portions of the city by the Great Salt Lake.[39]
The second-highest mountain range is the Oquirrhs, reaching a maximum height of 10,620 feet (3,237 m) at Flat Top. The Traverse Mountains to the south extend to 6,000 feet (1,830 m), nearly connecting the Wasatch and Oquirrh Mountains. The mountains near Salt Lake City are easily visible from the city and have sharp vertical relief caused by massive ancient earthquakes, with a maximum difference of 7,099 feet (2164 m) being achieved with the rise of Twin Peaks from the Salt Lake Valley floor.[38]
The Salt Lake Valley floor is the ancient lakebed of Lake Bonneville which existed at the end of the last Ice Age. Several Lake Bonneville shorelines can be distinctly seen on the foothills or benches of nearby mountains.
Layout
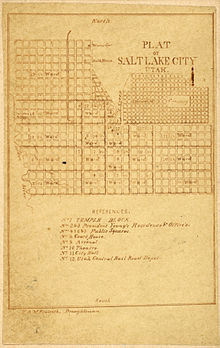
The city, as well as the county, is laid out on a grid plan.[40] Most major streets run very nearly north-south and east-west. The grid's origin is the southeast corner of Temple Square, the block containing the Salt Lake Temple; the north-south axis is Main Street; and the east-west axis is South Temple Street. Addresses are coordinates within the system (similarly to latitude and longitude). Odd and even address numbering depends on the quadrant of the grid in which an address is located. The rule is: When traveling away from the grid center (Temple Square) or its axes (Main Street, South Temple Street), odd numbers will be on the left side of the street.
The streets are relatively wide, at the direction of Brigham Young, who wanted them wide enough a wagon team could turn around without "resorting to profanity".[41] These wide streets and grid pattern are typical of other Mormon towns of the pioneer era throughout the West.
Though the nomenclature may initially confuse new arrivals and visitors, most consider the grid system an aid to navigation.[citation needed] Some streets have names, such as State Street, which would otherwise be known as 100 East. Other streets have honorary names, such as the western portion of 300 South, named "Adam Galvez Street" (in honor of a local Marine corporal killed in action) or others honoring Rosa Parks, Martin Luther King, Jr., César Chávez, and John Stockton. These honorary names appear only on street signs and cannot be used in postal addresses.

In the Avenues neighborhood, north-south streets are given letters of the alphabet, and east-west streets are numbered in 2.5-acre (1.0 ha) blocks, smaller than those in the rest of the city.
Joseph Smith, founder of the Latter-day Saint movement, planned the layout in the "Plat of the City of Zion" (intended as a template for Mormon towns wherever they might be built). In his plan the city was to be developed into 135 10-acre (4.0 ha) lots. However, the blocks in Salt Lake City became irregular during the late 19th century when the LDS Church lost authority over growth and before the adoption of zoning ordinances in the 1920s. The original 10-acre (4.0 ha) blocks allowed for large garden plots, and many were supplied with irrigation water from ditches that ran approximately where modern curbs and gutters would be laid. The original water supply was from City Creek. Subsequent development of water resources was from successively more southern streams flowing from the mountains to the east of the city. Some of the old irrigation ditches are still visible in the eastern suburbs, or are still marked on maps, years after they were gone. There are still some canals that deliver water as required by water rights. There are many lots, in Salt Lake City and surrounding areas, that have irrigation water rights attached to them. Local water systems, in particular Salt Lake City Public Utilities, have a tendency to acquire or trade for these water rights. These can then be traded for culinary water rights to water imported into the valley. At its peak, irrigation in the valley comprised over one hundred distinct canal systems, many originating at the Jordan Narrows at the south end of the valley. Water and water rights were very important in the 19th and early 20th centuries. As heavy agricultural usage changed into a more urban and suburban pattern, canal water companies were gradually replaced by culinary water systems.
Neighborhoods
Salt Lake City has many informal neighborhoods. The eastern portion of the city is less affordable than its western counterpart. This is a result of the railroad being built in the western half as well as panoramic views from inclined ground in the eastern portion. Housing is more economically diverse on the west side, which results in demographic differences. Interstate 15 was also built in a north-south line, further dividing east and west sides of the city.
The west side of the city has historically been more culturally diverse. People of many faiths, races, and backgrounds live in the neighborhoods of Rose Park, Westpointe, Poplar Grove, and Glendale. It has always been considered a classic and diverse area, although recently its affordability has attracted many professionals and the more youthful generation. For example, the small, increasingly trendy Marmalade District on the west side of Capitol Hill was heavily gentrified and is now an eclectic and desirable location.[citation needed] For example, Rose Park has a lower crime rate than the average of the rest of Salt Lake City.[citation needed]

Sugar House, in southeastern Salt Lake City, has a reputation as an older neighborhood with lots of small shops in the center.[42] Sugar House is a friendly area which has been the focus of redevelopment efforts such as the UTA S-Line Streetcar. In late 2015 there were approximately 900 apartment units either recently built or under construction in the Sugar House area, with an additional 492 units proposed.[43]
Just northeast of Downtown is The Avenues, a neighborhood outside of the regular grid system on much smaller blocks. The area from South Temple North to 6th Avenue is a Historical District that is nearly entirely residential, and contains many historical Victorian era homes. Recently the Avenues is becoming known for intimate restaurants and shops opening in old retail space mixed within the community like Hatch Family Chocolates, Avenues Bistro on Third. The Avenues are situated on the upward-sloping bench in the foothills of the Wasatch Range, with the earlier built homes in the lower elevation. The Avenues, along with Federal Heights, just to the east and north of the University of Utah, and the Foothill area, south of the university, contain gated communities, large, multimillion-dollar houses, and fantastic views of the valley. Many consider this some of the most desirable real estate in the valley.
In addition to larger centers like Sugar House and Downtown, Salt Lake City contains several smaller neighborhoods, each named after the closest major intersection. Two examples are the 9th and 9th (located at the intersection of 900 East and 900 South Streets) and 15th & 15th (located at the intersection of 1500 East and 1500 South Streets) neighborhoods. These areas are home to foot-traffic friendly, amenities-based businesses such as art galleries, clothing retail, salons, restaurants and coffee shops. During the summer of 2007, 9th and 9th saw sidewalk and street improvements as well as an art installation by Troy Pillow of Seattle, Washington inspired by the 9 Muses of Greek myth, thanks in part to a monetary grant from Salt Lake City.
Many of the homes in the valley date from pre–World War II times, and only a select few areas, such as Federal Heights and the East Bench, as well as the far west side, including parts of Rose Park and Glendale, have seen new home construction since the 1970s.
Climate
The climate of Salt Lake City is commonly claimed to be semi-arid, but under the Köppen climate classification, Salt Lake City has a hot-summer humid continental climate (Dfa) with hot summers and cold, snowy winters.
The primary source of precipitation in Salt Lake City is massive storms that move in from the Pacific Ocean along the jet stream from October to May. In mid-to-late summer, when the jet stream retreats far to the north, precipitation mainly comes from afternoon thunderstorms caused by monsoon moisture moving up from the Gulf of California. Although rainfall can be heavy, these storms are usually scattered in coverage and rarely severe. However, downtown was hit by an F2 tornado on 11 August 1999, killing 1 person, injuring 60, and causing $170 million in damage. The remnants of tropical cyclones from the East Pacific can rarely reach the city during Fall. The remnants of Hurricane Olivia helped bring the record monthly precipitation of 7.04 inches (179 mm) in September 1982.[44][45] 1983 was the wettest year on record, with 24.26 inches (616 mm), while 1979 was the driest, when 8.70 inches (221 mm) were recorded.[46] Spring snowmelt from the surrounding mountains can cause localized stream flooding during late spring and early summer, the worst examples being in 1952 and especially 1983, when City Creek burst its banks, forcing city engineers to convert several downtown streets into waterways.[47]
Snow falls on average from 6 November to 18 April, producing a total average of 60 inches (152 cm), although measurable snow has fallen as early as 17 September and as late as 28 May.[48][49][50] The snowiest season was 1951–52, with 117.3 inches (298 cm), while the least snowy season was 16.6 inches (42 cm) in 1933–34.[51] The snowiest month on record was January 1993, in which 50.3 inches (128 cm) were recorded.[52]
The nearby Great Salt Lake is a significant contributor to precipitation in the city. The lake effect can help enhance rain from summer thunderstorms and produces lake-effect snow approximately 6 to 8 times per year, some of which can drop excessive snowfalls. It is estimated about 10% of the annual precipitation in the city can be attributed to the lake effect.[53]
Salt Lake City features large variations in temperatures between seasons. During summer, there are an average of 56 days per year with temperatures of at least 90 °F (32.2 °C), 23 days of at least 95 °F (35 °C), and 5 days of 100 °F (37.8 °C).[54] However, average daytime July humidity is only 22%.[55] Winters are quite cold but rarely frigid. While an average of 127 days drop to or below freezing,[56] and 26 days with high temperatures that fail to rise above freezing,[56] the city only averages 2.3 days at or below 0 °F (−17.8 °C).[56] The record high temperature is 107 °F (42 °C), which occurred first on 26 July 1960 and again on 13 July 2002, while the record low is −30 °F (−34 °C), which occurred on 9 February 1933.
During mid-winter, strong areas of high pressure often situate themselves over the Great Basin, leading to strong temperature inversions. This causes air stagnation and thick smog in the valley from several days to weeks at a time and can result in the worst air-pollution levels in the U.S., reducing air quality to unhealthy levels.[57][58] This same effect will also occasionally play a role in the summer months, causing tropospheric ozone to peak in July & August, but in 2015 it started at the beginning of June.[59]
| Climate data for Salt Lake City International Airport (1991–2020 normals,[a] extremes 1874–present)[b] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 63 (17) |
69 (21) |
80 (27) |
89 (32) |
99 (37) |
107 (42) |
107 (42) |
106 (41) |
107 (42) |
92 (33) |
75 (24) |
69 (21) |
107 (42) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 51.8 (11.0) |
58.8 (14.9) |
70.4 (21.3) |
80.2 (26.8) |
88.9 (31.6) |
97.9 (36.6) |
101.9 (38.8) |
99.6 (37.6) |
93.9 (34.4) |
82.0 (27.8) |
67.1 (19.5) |
54.3 (12.4) |
102.3 (39.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 38.6 (3.7) |
44.7 (7.1) |
55.3 (12.9) |
61.9 (16.6) |
72.6 (22.6) |
84.1 (28.9) |
94.0 (34.4) |
91.7 (33.2) |
80.6 (27.0) |
65.5 (18.6) |
50.7 (10.4) |
39.0 (3.9) |
64.9 (18.3) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 31.4 (−0.3) |
36.6 (2.6) |
45.8 (7.7) |
51.8 (11.0) |
61.5 (16.4) |
71.6 (22.0) |
81.1 (27.3) |
79.1 (26.2) |
68.4 (20.2) |
54.6 (12.6) |
41.7 (5.4) |
32.2 (0.1) |
54.7 (12.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 24.2 (−4.3) |
28.6 (−1.9) |
36.3 (2.4) |
41.8 (5.4) |
50.4 (10.2) |
59.1 (15.1) |
68.2 (20.1) |
66.6 (19.2) |
56.3 (13.5) |
43.6 (6.4) |
32.8 (0.4) |
25.3 (−3.7) |
44.4 (6.9) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 6.5 (−14.2) |
9.2 (−12.7) |
21.0 (−6.1) |
28.7 (−1.8) |
34.8 (1.6) |
43.5 (6.4) |
54.9 (12.7) |
52.4 (11.3) |
39.7 (4.3) |
29.5 (−1.4) |
16.9 (−8.4) |
7.3 (−13.7) |
0.9 (−17.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −22 (−30) |
−30 (−34) |
0 (−18) |
14 (−10) |
25 (−4) |
32 (0) |
40 (4) |
37 (3) |
27 (−3) |
14 (−10) |
−14 (−26) |
−21 (−29) |
−30 (−34) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 1.43 (36) |
1.30 (33) |
1.75 (44) |
2.16 (55) |
1.82 (46) |
0.95 (24) |
0.49 (12) |
0.58 (15) |
1.06 (27) |
1.26 (32) |
1.32 (34) |
1.40 (36) |
15.52 (394) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 12.7 (32) |
10.7 (27) |
5.9 (15) |
2.9 (7.4) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.5 (1.3) |
7.0 (18) |
12.1 (31) |
51.9 (132) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.3 | 9.5 | 9.2 | 10.4 | 8.9 | 4.8 | 3.9 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 6.5 | 8.3 | 9.6 | 91.5 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 7.6 | 6.0 | 4.0 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 3.6 | 7.1 | 31.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74.0 | 69.8 | 60.2 | 53.2 | 48.7 | 41.4 | 35.9 | 38.5 | 45.6 | 55.7 | 66.3 | 74.3 | 55.3 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 19.9 (−6.7) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
27.1 (−2.7) |
31.1 (−0.5) |
36.9 (2.7) |
41.4 (5.2) |
45.7 (7.6) |
45.1 (7.3) |
39.9 (4.4) |
34.5 (1.4) |
28.4 (−2.0) |
21.7 (−5.7) |
33.0 (0.5) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 127.4 | 163.1 | 241.9 | 269.1 | 321.7 | 360.5 | 380.5 | 352.5 | 301.1 | 248.1 | 150.4 | 113.1 | 3,029.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 43 | 55 | 65 | 67 | 72 | 80 | 83 | 83 | 81 | 72 | 50 | 39 | 68 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1.7 | 2.7 | 4.6 | 6.6 | 8.4 | 9.8 | 10.4 | 9.0 | 6.6 | 4.0 | 2.2 | 1.4 | 5.6 |
| Source 1: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990)[56][60][61][62][63] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: UV Index Today (1995 to 2022)[64] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1850 | 6,157 | — | |
| 1860 | 8,236 | 33.8% | |
| 1870 | 12,854 | 56.1% | |
| 1880 | 20,768 | 61.6% | |
| 1890 | 44,843 | 115.9% | |
| 1900 | 53,531 | 19.4% | |
| 1910 | 92,777 | 73.3% | |
| 1920 | 116,110 | 25.1% | |
| 1930 | 140,267 | 20.8% | |
| 1940 | 149,934 | 6.9% | |
| 1950 | 182,121 | 21.5% | |
| 1960 | 189,454 | 4.0% | |
| 1970 | 175,885 | −7.2% | |
| 1980 | 163,034 | −7.3% | |
| 1990 | 159,936 | −1.9% | |
| 2000 | 181,743 | 13.6% | |
| 2010 | 186,440 | 2.6% | |
| 2015 (est.) | 192,672 | [65] | 3.3% |
| Source:[66] | |||
| Racial composition | 2010[68] | 1990[69] | 1970[69] | 1950[69] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 75.1% | 87.0% | 96.8% | 98.3% |
| —Non-Hispanic | 65.6% | 82.6% | 90.6%[70] | n/a |
| Black or African American | 2.7% | 1.7% | 1.2% | 0.6% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 22.3% | 9.7% | 6.4%[70] | n/a |
| Asian | 4.4% | 4.7% | 1.1% | 1.0% |
At the 2010 census, the city's population was 75.1% White, 2.7% African American, 1.2% American Indian and Alaska Native, 4.4% Asian, 2.0% Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander, 10.7% from other races and 3.7% of mixed descent. 22.3% of the total population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.[71]
Salt Lake City's population has historically been predominantly white.[69] Between 1860 and 1950 whites represented about 99% of the city's population.[69]
37.0% of the population had a bachelor's degree or higher. 18.5% of the population was foreign born and another 1.1% was born in Puerto Rico, U.S. insular territories, or born abroad to American parent(s). 27.0% spoke a language other than English at home.
As of the census of 2010,[5] there are 186,440 people (up from 181,743 in 2000), 75,177 households, and 57,543 families residing in the city. This amounts to 6.75% of Utah's population, 18.11% of Salt Lake County's population, and 16.58% of the new Salt Lake metropolitan population. The area within the city limits covers 14.2% of Salt Lake County. Salt Lake City is more densely populated than the surrounding metro area with a population density of 1,688.77/sq mi (1,049.36/km²). There are 80,724 housing units at an average density of 731.2 per square mile (454.35/km²).
The Salt Lake City-Ogden metropolitan area, which included Salt Lake, Davis, and Weber counties, had a population of 1,333,914 in 2000, a 24.4% increase over the 1990 figure of 1,072,227. Since the 2000 Census, the Census Bureau has added Summit and Tooele counties to the Salt Lake City metropolitan area, but removed Davis and Weber counties and designated them as the separate Ogden-Clearfield metropolitan area. The Salt Lake City-Ogden-Clearfield combined statistical area, together with the Provo-Orem metropolitan area, which lies to the south, have a combined population of 2,094,035 as of 1 July 2008.
There are 75,177 households, out of which 27.0% have children under the age of 18 living with them, 41.1% are married couples living together, 10.2% have a female householder with no husband present, and 44.3% are other types of households. Of the 75,177 households, 3,904 were reported to be unmarried partner households: 3,047 heterosexual, 458 same-sex male, and 399 same-sex female. 33.2% of all households are made up of individuals, and 9.7% have someone living alone who is 65 years of age or older. The average household size is 2.48, and the average family size is 3.24.
The city's age distribution was (as of 2000):
- 23.6% under 18
- 15.2% from 18 to 24
- 33.4% from 25 to 44
- 16.7% from 45 to 64
- 11.0% 65 or older
The median age is 30 years. For every 100 females there are 102.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there are 101.2 males. The median income for a household in the city is $36,944, and the median income for a family is $45,140. Males have a median income of $31,511 versus $26,403 for females. The per capita income for the city is $20,752. 15.3% of the population and 10.4% of families are below the poverty line. Out of the total population, 18.7% of those under the age of 18 and 8.5% of those 65 and older are living below the poverty line.
Large family sizes and low housing vacancy rates, which have inflated housing costs along the Wasatch Front, have led to one out of every six residents living below the poverty line.
Fewer than 50% of Salt Lake City's residents are members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. This is a much lower proportion than in Utah's more rural municipalities; altogether, LDS members make up about 62% of Utah's population.[72]
The Rose Park and Glendale sections are predominantly Spanish-speaking with Hispanic and Latino Americans accounting for 60% of public school-children.[73] The Centro Civico Mexicano acts as a community gathering point for the Wasatch Front's estimated 300,000 Latinos,[74] Mexican President Vicente Fox began his U.S. tour in the city in 2006.
Salt Lake City is home to a sizeable Bosnian American community of more than 8,000 residents. Most of them came to Salt Lake City during the Bosnian War in the 1990s.[75] The large Pacific Islander population, mainly Samoan and Tongan, is also centered in the Rose Park, Glendale, and Poplar Grove sectors. Most of Salt Lake City's ethnic Pacific Islanders are members of the LDS Church[76] though various Samoan and Tongan-speaking congregations are situated throughout the Salt Lake area including Samoan Congregational, Tongan Wesleyan Methodist, and Roman Catholic. Just outside Salt Lake City limits, newer immigrant communities include Nepalis, and refugees of Karen origin from Myanmar (formerly Burma). Salt Lake City also has the third largest Sri Lankan community in the United States.[77]
Salt Lake City has been considered one of the top 51 "gay-friendly places to live" in the U.S.[78] The city is home to a large, business savvy, organized, and politically supported gay community. Leaders of the Episcopal Church's Diocese of Utah,[79][80] as well as leaders of Utah's largest Jewish congregation, the Salt Lake Kol Ami,[81] along with three elected representatives of the city identify themselves as gay. These developments have attracted controversy from socially conservative officials representing other regions of the state. A 2006 study by UCLA estimates approximately 7.6% of the city's population, or almost 14,000 people, are openly gay or bisexual, compared to just 3.7%, or just over 60,000 people, for the metropolitan area as a whole.[82]
In 2007 Salt Lake City was ranked by Forbes as the most vain city in America, based on the number of plastic surgeons per 100,000 and their spending habits on cosmetics, which exceed cities of similar size.[83] However, this likely reflects a concentration of plastic surgeons within the city limits but whose client base includes the entire metropolitan area. Forbes also found the city to be the 8th most stressful. In contrast to the 2007 ranking by Forbes, a 2010 study conducted by Portfolio.com and bizjournals concluded Salt Lake City was the least stressful city in the United States.[84] In 2014, CNN deemed Salt Lake City to be the least stressed-out city in the United States, citing the low cost of living and abundance of jobs.[85]
A 2008 study by the magazines Men's Health and Women's Health found Salt Lake City to be the healthiest city for women by looking at 38 different factors, including cancer rates, air quality, and the number of gym memberships.[86]
Economy


This section needs to be updated. (July 2014) |
Historically known as the "Crossroads of the West" for its railroads, when nearby steel, mining and railroad operations provided a strong source of income with Silver King Coalition Mines, Geneva Steel, Bingham Canyon Mine, and oil refineries, Salt Lake City's modern economy is service-oriented. Today the city's major sectors are government, trade, transportation, utilities, and professional and business services. The daytime population of Salt Lake City proper swells to over 315,000 people, not including tourists or students.[87]
Local, state, and federal governments have a large presence in the city, and trade, transportation, and utilities also take up a significant portion of employment, with the major employer being the Delta hub at Salt Lake City International Airport. Equally significant are the professional and business services, while health services and health educational services are significant areas of employment, including the largest health care provider in the Intermountain West, Intermountain Healthcare. Other major employers include the University of Utah, Sinclair Oil Corporation, and The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Besides its central offices, the LDS Church owns and operates a for-profit division, Deseret Management Corporation and its subsidiaries, which are headquartered in the city.
Salt Lake City is home to one Fortune 500 company, Huntsman Corporation, and two Fortune 1000 companies, Zions Bancorporation and Questar Corporation.[88] Other notable firms headquartered in the city include AlphaGraphics, Sinclair Oil Corporation, Smith's Food and Drug (owned by national grocer Kroger), MonaVie, Myriad Genetics, and Vehix.com.[89] Notable firms based in nearby cities within the metropolitan area include Arctic Circle Restaurants, FranklinCovey, and Overstock.com. Metropolitan Salt Lake was also once the headquarters of American Stores, the Skaggs Companies, and ZCMI, one of the first department stores; it is currently owned by Macy's, Inc. Former ZCMI stores now operate under the Macy's label. High-tech firms with a large presence in the suburbs include Adobe, ColcaSac, eBay, Unisys, Siebel, Micron, L-3 Communications, Telarus, and 3M. Goldman Sachs has its second biggest presence in Salt Lake City.
Other economic activities include tourism, conventions, and major suburban call centers. Tourism has increased since the 2002 Olympic Winter Games,[28] and many hotels and restaurants were built for the events. The convention industry has expanded since the construction of the Salt Palace convention center in the late 1990s, which hosts trade shows and conventions, including the annual Outdoor Retailers meeting and Novell's annual BrainShare convention.
Downtown Salt Lake City continues to modernize its commercial real estate. 111 Main, a 440,542 sq. ft. Class A office tower is expected to finish construction during the 4th quarter of 2016. Other projects in the downtown area include the 2,500-seat George S. and Dolores Dore Eccles Theater, and a mixed use retail and boutique hotel planned along Regent Street.[90]
Law and government

The Salt Lake City and County Building has been the seat of city government since 1894. It also served as Utah's first statehouse from 1896 until the current Utah State Capitol was dedicated on 9 October 1916.[91]
Since 1979 Salt Lake City has had a non-partisan mayor-council form of government. The mayor and the seven councillors are elected to four-year terms. Mayoral elections are held the same year as three of the councilors. The other four councilors are staggered two years from the mayoral. Council seats are defined by geographic population boundaries. Each councillor represents approximately 26,000 citizens. Officials are not subject to term limits.
Municipal elections throughout Utah are non-partisan. The most recent election was held in November 2013. Stan Penfold was re-elected to a second term on the city council, while James Rogers, Erin Mendenhall and Lisa Ramsey Adams were elected to fill vacancies. Council members were sworn in to office on 6 January 2014. Charlie Luke was elected by his peers to serve as the Council Chair for 2014. By state statute, members of the city council also serve as the governing board of the Redevelopment Agency of Salt Lake City.
| Elected officials of Salt Lake City as of 2016[update] | |||
| Official | Position | Assumed office | Term ends |
| Jackie Biskupski (D) | Mayor | 2016 | 2020 |
| City Council | |||
| James Rogers (R) | District 1 | 2014 | 2018 |
| Andrew Johnson (D) | District 2 | 2016 | 2020 |
| Stan Penfold (D) | District 3 | 2010 | 2018 |
| Derek Kitchen (D) | District 4 | 2016 | 2020 |
| Erin Mendenhall (D) | District 5 | 2014 | 2018 |
| Charlie Luke, Chair (D) | District 6 | 2012 | 2020 |
| Lisa Ramsey Adams (R) | District 7 | 2014 | 2018 |
Elections are held in odd-numbered years. Candidates take office in January of the following year.
The separation of church and state was the most heated topic in the days of the Liberal Party and People's Party of Utah, when many candidates were also would-be LDS Church bishops. This tension is still reflected today with the Bridging the Religious Divide campaign.[92] This campaign was initiated when some city residents complained the Utah political establishment was unfair in its dealings with non-LDS residents by giving the LDS Church preferential treatment, while LDS residents perceived a growing anti-Mormon bias in city politics.
The city's political demographics are liberal and Democratic, not having had a Republican mayor in over forty years.This stands in stark contrast to the majority of Utah where conservative and Republican views generally dominate.
The city is home to several non-governmental think-tanks and advocacy groups such as the conservative Sutherland Institute, the gay-rights group Equality Utah, and the quality-growth advocates Envision Utah. Salt Lake hosted many foreign dignitaries during the 2002 Winter Olympics, and in 2006 the President of Mexico began his U.S. tour in the city and Israel's ambassador to the United States opened a cultural center.[93] President George W. Bush visited in 2005 and again in 2006 for national veterans' conventions; both visits were protested by then-Mayor Rocky Anderson. Other political leaders such as Howard Dean and Harry Reid gave speeches in the city in 2005.
In July 2013, a new Public Safety Building housing police, fire, and emergency dispatch employees opened. It was billed as the largest net zero energy building in the nation at opening, and is expected to be certified LEED Platinum.[94]
The Salt Lake City Fire Department currently operates out of 14 fire stations.
Education


In 1847 pioneer Jane Dillworth held the first classes in her tent for the children of the first LDS families. In the last part of the 19th century, there was much controversy over how children in the area should be educated. LDS and non-LDS could not agree on the level of religious influence in schools. Today, many LDS youths in grades 9 through 12 attend some form of religious instruction, referred to as seminary. Students are released from public schools at various times of the day to attend seminary.[95][96] LDS seminaries are usually located on church-owned property adjacent to the public school and within walking distance.[97]
Because of high birth rates and large classrooms, Utah spends less per student than any other state yet simultaneously spends more per capita than any state with the exception of Alaska. Money is always a challenge, and many businesses donate to support schools. Several districts have set up foundations to raise money. Recently, money was approved for the reconstruction of more than half of the elementary schools and one of the middle schools in the Salt Lake City School District, which serves most of the area within the city limits. There are twenty-three K-6 elementary schools, five 7-8 middle schools, three 9-12 high schools (Highland, East, and West, with the former South High being converted to the South City campus of the Salt Lake Community College), and an alternative high school (Horizonte) located within the school district. In addition, Highland has recently been selected as the site for the charter school Salt Lake School for the Performing Arts (SPA). Many Catholic schools are located in the city, including Judge Memorial Catholic High School. Rowland Hall-St. Mark's School, established in 1867 by Episcopal Bishop Daniel Tuttle,[98] is the area's premier independent school.
The Salt Lake City Public Library system consists of the main library downtown, and five branches in various neighborhoods. The main library, designed by renowned architect Moshe Safdie, opened in 2003. In 2006, the Salt Lake City Public Library was named "Library of the Year" by the American Library Association.[99]
Postsecondary educational options in Salt Lake City include the University of Utah, Westminster College, Salt Lake Community College, Stevens-Henager College, Eagle Gate College, The Art Institute of Salt Lake City, Violin Making School of America, and LDS Business College. Utah State University, Neumont University and Brigham Young University also operate education centers in the city. There are also many trade and technical schools such as Healing Mountain Massage School and the Utah College of Massage Therapy. The University of Utah is noted for its research and medical programs. It was one of the original four universities to be connected to ARPANET, the predecessor to the Internet,[100] in 1969, and was also the site of the first artificial heart transplant in 1982.[101]
Culture
Museums and the arts

Salt Lake City is home to several museums. Near Temple Square is the Church History Museum; operated by The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the museum contains collections of artifacts, documents, art, photographs, tools, clothing and furniture from the history of the LDS Church, which spans nearly two centuries. West of Temple Square, at the Gateway District, is the Clark Planetarium, which houses an IMAX theater, and Discovery Gateway, a children's museum. The University of Utah campus is home to the Utah Museum of Fine Arts as well as the Natural History Museum of Utah. Other museums in the area include the Utah State Historical Society, Daughters of Utah Pioneers Memorial Museum, Fort Douglas Military Museum, the Social Hall Heritage Museum, and The Leonardo, a new art, science and technology museum.
Salt Lake also is home to several classic movie theaters including the Tower Theatre and the Broadway Theater. Both of these iconic theaters host the Salt Lake Film Society members and shows. The Salt Lake Film Society also puts on free shows at the Rose Wagner Theater and the Salt Lake Public Library. Theaters that are now closed are Trolley Corners and Villa Theatre.
On 5 December 2007, the Salt Lake Chamber and Downtown Alliance announced a two-block section of downtown south of the planned City Creek Center is planned to become a new arts hub. This will include renovations to two theaters located in the area and a new theater with a seating capacity of 2,400 and increased space for galleries and artists. The opening of the new facilities were anticipated to coincide with the opening of the City Creek Center in 2011, but have yet to be completed.[102] The site of the $81.5 million theater was officially revealed and attempts to secure funding began.[103] The theater plans have come under criticism, however, especially from nearby smaller theaters which host Off-Broadway tours and claim such a theater cannot be supported and will hurt their business.[104]
Performing arts

Salt Lake City provides many venues for both professional and amateur theatre. The city attracts many traveling Broadway and Off-Broadway performances which perform in the historic Capitol Theatre. Local professional acting companies include the Pioneer Theatre Company, Salt Lake Acting Company and Plan-B Theatre Company, which is the only theatre company in Utah fully devoted to developing new plays by Utah playwrights. The Off-Broadway Theatre, located in Salt Lake's historic Clift Building, features comedy plays and Utah's longest-running improv comedy troupe, Laughing Stock.
Salt Lake City is the home of the Mormon Tabernacle Choir, founded in 1847. The choir's weekly program, called Music and the Spoken Word, is the longest-running continuous network broadcast in the world.[105] Salt Lake City is also the home to the Utah Symphony Orchestra, which was founded in 1940 by Maurice Abravanel and has become widely renowned. Its current music director is Thierry Fischer. The orchestra's original home was the Salt Lake Tabernacle, but since 1979 has performed at Abravanel Hall in the western downtown area. In 2002, Utah Symphony merged with Utah Opera, which was founded in 1978 by Glade Peterson and under current Artistic Director Christopher McBeth presents four opera productions at Capitol Theatre in downtown Salt Lake City. Salt Lake City area is also home to the internationally renowned children's choir from The Madeleine Choir School and the Salt Lake Children's Choir (established in 1979).
The University of Utah is home to two highly ranked dance departments, the Ballet Department and the Department of Modern Dance. Professional dance companies in Salt Lake City include Ballet West, Ririe-Woodbury Dance Company (which celebrated its 45th anniversary season in 2008/2009) and Repertory Dance Theatre. RWDC and RDT both call the Rose Wagner Performing Arts Center home.
Music
The city has a local music scene dominated by hip hop, blues, rock and roll, punk, Deathcore, horrorcore and indie groups. There are also many clubs which offer musical venues. Popular groups or persons who started in the Wasatch Front area or were raised and influenced by it, including Iceburn, Eagle Twin, The Almost, The Brobecks, Meg and Dia, Royal Bliss, The Artificial Flower Company, Shedaisy, The Summer Obsession, The Used and Chelsea Grin. Salt Lake also has an underground metal scene, which includes bands such as Gaza and Bird Eater. In 2004 over 200 bands submitted tracks for a compilation by a local music zine, SLUG Magazine. The zine trimmed the submissions to 59 selections featuring diverse music types such as hip-hop, jazz, jazz-rock, punk and a variety of rock and roll. In the summer, Salt Lake City also hosts the Twilight Concert series which is a free summer concert series for all the residents in the city. The series has been a part of the Salt Lake City music scene for 23 years. In year 2010, crowds peaked at 40,000 attendees in downtown's Pioneer Park.[106]
Films and television
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2016) |
Many films, music videos, commercials, and TV shows have been recorded in the Salt Lake metropolitan area. They include: SLC Punk!, Touched by an Angel, Everwood, Big Love, Bonneville, Dawn of the Dead, Drive Me Crazy, Forever Strong, High School Musical, High School Musical 2, High School Musical 3: Senior Year, Legally Blonde 2: Red, White & Blonde, Unaccompanied Minors, Dumb and Dumber, The Stand, Halloween 4: The Return of Michael Myers, Halloween 5: The Revenge of Michael Myers, Halloween: The Curse of Michael Myers, Independence Day, Poolhall Junkies, The Brown Bunny, The World's Fastest Indian, The Way of the Gun, Joy Ride, The Wizard, Carnival of Souls, The Amazing Race 8, Denizen, The Postal Service's Such Great Heights, Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End, The Sandlot, Revenge of the Ninja, A Life Less Ordinary, and 127 Hours.
Festivals
Salt Lake City has a thriving and vibrant festival culture. Various festivals happen throughout the year, celebrating the diversity of the communities in the Salt Lake Valley. From culture, food, religion and spirituality, to dance, music, spoken word, and film, almost any type of festival can be found. Many of the festivals have been ongoing for decades.

The Utah Pride Festival is an LGBTQ festival which is held in June each year. Since 1983, it has grown dramatically to a three-day festival with attendance having exceeded 20,000 people. The Utah Pride Festival is sponsored by the Utah Pride Center. It is the second largest festival behind Days of '47 and is one of the biggest festivals in the USA.[107][108][109] The festival includes hundreds of vendors, food, music stars, a 5k run, a dyke and trans march, as well as an interfaith service by the Utah Pride Interfaith Coalition.[110]
The Utah Arts Festival has been held annually since 1977 with an average attendance of 80,000. About 130 booths are available for visual artists and there are five performance venues for musicians.[111]
The Dark Arts Festival is an annual 3-day festival dedicated to the goth and industrial subcultures. The festival started in 1993, and is hosted at the local goth club Area 51.[112][113][114] The festival is centered around the bands who are contracted to play during the event. 2015's lineup included Tragic Black, The Gothsicles, Adrian H & the Wounds, and Hocico.[115]

The Utah Arts Alliance puts on an Urban Arts Festival annually. The free festival draws over 20,000 attendees and features artists displaying and selling paintings, sculpture, photography, and jewelry. The live music is different genres and bands from rock, hip hop, R&B, funk, and jazz. Demonstrations and workshops for various interests such as skateboarding and gardening take place. The festival also hosts the Voice of the City film festival which allows local filmmakers to show their version of Salt Lake.[116]
The Jewish Arts Festival, hosted by the IJ and Jeanné Wagner JCC of Salt Lake City, showcases Jewish culture through workshops, theater, food, film, art, and contemporary music from the local and global Jewish communities.[117][118]
The Sugar House neighborhood holds an annual arts festival on 4 July. The festival features local artists, performances, music, food, and vendors. The festival coincides with the fireworks show at Sugar House Park that takes place in the evening.[119][120]
Salt Lake City also hosts portions of the Sundance Film Festival. The festival, which is held each year, brings many cultural icons, movie stars, celebrities, and thousands of film buffs to see the largest independent film festival in the United States. The headquarters of the event is in nearby Park City.
Several other film festivals take place in Salt Lake City: FilmQuest, Salty Horror Con & Film, Damn These Heels, and the Voice of the City film festivals. FilmQuest began in 2014 and centers around genres, usually fantasy and science fiction.[121] Salty Horror, which began in 2010, is a competition based horror film festival which showcases general horror, science fiction horror, and physiological thriller horror films.[122] Damn These Heels Film Festival is part of the Utah Film center. It celebrated its 10th anniversary in 2013. The festival focuses on independent, documentary, and foreign feature-length films surrounding LGBTQ issues, ideas, and art.[123][124] Voice of the City is part of the Urban Arts Festival and allows local filmmakers to show their version of Salt Lake.
The 2015 Great Salt Lake Fringe Festival was the first performance festival in Salt Lake City. The 4-day festival included various performances involving music, dance, theatre, spoken word, circus arts, magic, and puppetry.[125][126]
The Living Traditions Festival is a 3-day multicultural arts festival hosted by the Salt Lake City Arts Council. The festival celebrates traditional dance, music, crafts and food from the various contemporary ethnic communities of Salt Lake City.[127] The festival celebrated its 30th anniversary in 2015.[128]
Earth Jam is an annual festival celebrated in Salt Lake's Liberty Park to celebrate Earth Day through music. The free festival hosts speakers, vendors, food, performing art, a Goddess pageant, and children's garden. The music is the heart of the celebration.[129]
The Live Green SLC! Festival aims to showcase sustainable products, ideas, and solutions from renewable technologies for the everyday household.[130] The festival promotes education, sustainability, and accessibility to green and organic products and services.[131]
Craft Lake City DIY (Do-It-Yourself) festival is an artisan festival that promotes the use of science and technology to help local artists produce their crafts such as silk screens, jewelry, and other mediums. The festival promotes education through workshops, galleries, and demonstrations which includes various vendors and food.[132]
The 9th and 9th Street Festival is a neighborhood festival celebration of art, music, crafts, antiques, collectibles and people held annual at the intersection of the streets 900 E and 900 S, which is a neighborhood with shops and restaurants.[133]

The Catholic Nuns of Carmelite Monastery hold an annual fair each fall in Holladay, a suburb of Salt Lake City. The festival includes music, food, a live auction, Golf for the Nuns tournament, a prize giveaway, and a 5k Run for the Nuns marathon.[134][135]
The Sri Sri Ganesh Hindu Temple of Utah, located in Salt Lake City, has an annual Ganesh Festival called Ganesh Chathurthi.[136] The 10-day festival is devoted to rites of worship of the Hindu God Ganesh. In 2014 the festival was hosted at the Krishna Temple of Salt Lake since the Ganesh temple's exterior was under construction, which made the inner temple inaccessible.[137]
India Fest is hosted by the Krishna Temples of Salt Lake City and Spanish Fork, Utah. The festival includes food, dances, drama and a pageant of the Ramayana.[138] Since 2011 the Krishna Temple of Salt Lake City has held an annual Festival of Colors, similar to the famous festival at the Krishna Temple in Spanish Fork, Utah.[139]
The Great Salt Lake City Yoga Festival is in its fifth year as of 2015[update]. 2015 saw the first Downtown Yoga festival in Salt Lake City. Both festivals are intended to inspire yogis in the community by teaching about yoga, healthy living, raw food, and traditional yoga music.[140][141]

The local Pagan community has enjoyed the annual Salt Lake City Pagan Pride Day since 2001. The festival features rituals, workshops, dancers, bards, vendors, and requires only a can of food donation for admission.[142][143][144][145][146][147][148][149][150]

Members of the steampunk subculture have an annual 2-day festival called "Steamfest" in Salt Lake City. The Salt City Steamfest hosts various vendors, panels, and cosplayers dressed in the fashion of various punk cultures, mostly around steam, deco, and diesel punk.[151][152]
The Rose Park (a suburb of Salt Lake) Community puts on a festival in the spring. The festival celebrates the diversity of that community and includes dancers, music, a 5k run, silent auction and food.[153] Westfest is a festival that celebrates the establishment of West Valley and the suburb's various diverse cultures and community.[154]
Sandy, another suburb of Salt Lake City, holds a Hot Air Balloon Festival at the end of summer. The main event includes several waves of hot air balloons which rise into the sky for an afternoon and evening show. The festival includes food and entertainment.[155]
The suburb of Holladay hosts a Blue Moon Festival in August. The free festival has dancing, live bands, art and food vendors.[156]

The Greek Festival, held the weekend after Labor Day, celebrates Utah's Greek heritage and is located at the downtown Greek Orthodox Church. The 3-day event includes Greek music, dance groups, cathedral tours, booths and a large buffet. Attendance ranges from 35,000 to 50,000. It celebrated its 40th anniversary in 2015.
The Utah Asian Festival, approaching its 40th anniversary in 2017, celebrates various Asian cultures around Utah and is held in Salt Lake City. Vendors, food, music, and performances representing the cultures of China, Cambodia, Japan, Korea, Laos, Thailand, Indonesian, Filipino, Vietnamese, Hawaiian, and Tibetan are all present at the event.[157][158]
The Italian cultural street festival Ferragosto celebrates Italian food and culture from Italian communities in Salt Lake City.[159] Festa Italian is a 2-day festival that highlights various regions of Italy with live music, food, wine, beer and entertainment. The proceeds go to local charities.[160]
Other cultural festivals in Salt Lake City include the Peruvian Festival,[161] the Utah Brazilian Festival,[162] the Polynesian Cultural Festival,[163] the Nihon Matsuri Japanese Festival,[164] and the Buddhist Obon Japanese Festival.[165]
Conventions
Salt Lake City is host to a number of conventions that come to the Crossroads of the West. With several large venues, including the Salt Palace and Vivint Smart Home Arena in downtown, Salt Lake is capable of accommodating conventions upwards of 100,000 or more people.

Salt Lake Comic Con, which started in 2013, has grown to over 100,000 people in just over two years. Because of this, Salt Lake Comic Con started having a second event, FanX (Fan Experience) to give those who were not able to come to the fall Comic Con an opportunity in the spring. The convention broke inaugural records in 2013, hosting the largest crowd of any inaugural comic convention.[166] The second event, FanX of 2014, and the fall event of 2014 both broke attendance records for the event, surpassing 120,000 people.[167] The convention was sued[168][169] by San Diego Comic Con, but won the right to use the trademark of comic con in its name.[170][171] In 2014, Stan Lee called the Salt Lake Comic Con "the greatest comic con in the world".[172] On 25 September 2015 at 6 pm, the Con broke the world record for the most costumed comic book cosplay characters in one location. At 1784 people, this beat the previous record by about 250,[173] surpassing the International Animation CCJOY LAND in Changzhou City, China, which had gathered 1530 people on 29 April 2011.
A My Little Pony convention called Crystal Mountain Pony Con takes place annually downtown, with many cosplayers, vendors, and panels. 2015 saw more than 800 bronies in attendance.[174][175]
Salt Lake hosts its own International Tattoo Convention in the spring. The Salt Lake City International Tattoo Convention brings in various artists from around the United States and world. A select few local shops are allowed to attend, but the highlights of the convention are well-known artists who are booked for the convention.[176][177]
Fantasy Con hosted its first convention, the first of its kind, in Salt Lake City in 2014. After a successful run, the convention reorganized to better serve the needs of the fantasy community. Intended to be annual, it did not host one for 2015 but will have another convention in 2016. 2014 saw over 30,000 attend.[178][179]

2015 saw the first Gaming Convention come to Salt Lake City. The convention included contests, cosplay, panels, and was centered around console, computer, card, and tabletop gaming.[180][181][182]
The furry community had its own convention in Salt Lake from 2012 to 2015 .[183][184][185]
Events

Although the LDS church holds a large influence, the city is still very culturally and religiously diverse. The city is the location of many cultural activities.[186]
A major state holiday is Pioneer Day, 24 July, the anniversary of the Mormon pioneers' entry into the Salt Lake Valley. It is celebrated each year with a week's worth of activities, including a children parade, a horse parade, the featured Days of '47 Parade (one of the largest parades in the United States), a rodeo, and a large fireworks show at Liberty Park. Fireworks can be legally sold and set off around 24 July.
First Night on New Year's Eve, a celebration emphasizing family-friendly entertainment and activities held at Rice-Eccles Stadium at the University of Utah, culminates with a fireworks display at midnight.
Beginning in 2004, Salt Lake City has been the host of the international Salt Lake City Marathon. In 2006, Real Madrid and many of the nation's best cyclist had engagements.[187]
Salt Lake City has begun to host its own events in the last few years, most notably the Friday Night Flicks,[188] free movies in the city's parks, as well as the Mayor's health and fitness awareness program, Salt Lake City Gets Fit.[189]
Salt Lake City was host to the 2002 Winter Olympics. At the time of the 2002 Olympics, Salt Lake City was the most populated area to hold a Winter Olympic Games. The event put Salt Lake City in the international spotlight and is regarded by many as one of the most successful Winter Olympics ever.[190]
In February 2002, Torino, Italy was granted an Olympic Sister City relationship with Salt Lake City, which became a Friendship City relationship in October 2003. On 13 January 2007 an agreement was signed, where Salt Lake City and Torino officially became Olympic Sister Cities.[191]
On the third Friday of every month, the Salt Lake Gallery Stroll presents a free evening of visual art; many galleries and other art-related businesses stay open late, allowing enthusiasts to tour various exhibits after hours. Sidewalk artists, street performers and musicians also sometimes participate in these monthly events.
Media


Salt Lake City has many diverse media outlets. Most of the major television and radio stations are based in or near the city. The Salt Lake City metropolitan area is ranked as the 31st largest radio[192] and 33rd largest television[193] market in the United States.
Print media include two major daily newspapers, The Salt Lake Tribune and the Deseret News (previously the Deseret Morning News). Other more specialized publications include Now Salt Lake, Salt Lake City Weekly, Nuestro Mundo of the Spanish-speaking community, QSaltLake and The Pillar for the LBGT community. Other Spanish-language newspapers include El Estandar, Amigo Hispano (online only), and El Observador de Utah, which offers free residential delivery. There are a number of local magazines, such as Wasatch Journal (a quarterly magazine covering Utah's arts, culture, and outdoors), Utah Homes & Garden, Salt Lake Magazine (a bimonthly lifestyle magazine), CATALYST Magazine (a monthly environmental, health, arts and politics magazine), SLUG Magazine, an alternative underground music magazine. Utah Stories is a magazine that covers local issues, primarily focused on the Salt Lake Valley.
KTVX signed on the air as Utah's first television station in 1947 under the experimental callsign W6SIX. KTVX is the oldest TV station in the Mountain Time Zone and the third oldest west of the Mississippi. It is Salt Lake City's current ABC affiliate. KSL-TV, the local NBC affiliate, has downtown studios at "Broadcast House" in the Triad Center office complex. KSL is operated by Deseret Media Companies, a company owned by the LDS Church. KUTV is Salt Lake City's CBS affiliate. KSTU is the area's Fox affiliate. KUCW is the CW affiliate and part of a duopoly with KTVX. KJZZ-TV is an independent station owned by the family of late Utah Jazz owner Larry H. Miller.
Because television and radio stations serve a larger area (usually the entire state of Utah, as well as parts of western Wyoming, southern Idaho, parts of Montana, and eastern Nevada), ratings returns tend to be higher than those in similar-sized cities. Some Salt Lake radio stations are carried on broadcast translator networks throughout the state.
Salt Lake City has become a case of market saturation on the FM dial; one cannot go through more than about two frequencies on an FM radio tuner before encountering another broadcasting station. A variety of companies, most notably Millcreek Broadcasting and Simmons Media, have constructed broadcast towers on Humpy Peak in the Uinta Mountains to the east. These towers allow frequencies allocated to nearby mountain communities to be boosted by smaller, low-powered FM transmitters along the Wasatch Front.
Main sights

Salt Lake City is the headquarters for The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and has many LDS-related sites open to visitors. The most popular is Temple Square, which includes the Salt Lake Temple (not open to the general public) and visitors' centers open to the public, free of charge. Temple Square also includes the historic Tabernacle, home of the world-famous Mormon Tabernacle Choir. The modern LDS Conference Center is across the street to the north. The Family History Library, the largest genealogical library in the world, is just west of Temple Square. It is run by the LDS Church and is open to the public and free of charge. Adjacent to Temple Square is also the Eagle Gate Monument.
In 2004, the Salt Lake City main library received an Institute Honor Award for Architecture by the American Institute of Architects[194] and features a distinctive architectural style. The roof of the building serves as a viewpoint for the Salt Lake Valley. The Utah State Capitol Building offers marble floors and a dome similar to the building that houses the U.S. Congress. Other notable historical buildings include the Thomas Kearns Mansion (now the Governor's Mansion), City and County Building, built in 1894, the Kearns Building on Main Street, St. Mark's Episcopal Cathedral, built in 1874, and the Roman Catholic Cathedral of the Madeleine, built in 1909.

Near the mouth of Emigration Canyon lies This Is The Place Heritage Park, which re-creates typical 19th century LDS pioneer life. Hogle Zoo is located across the street from the park. The city's largest public park, at over 100 acres (0.40 km2), Liberty Park features a lake with two islands in the middle and the Tracy Aviary. The park is home to a large number of birds, both wild and in the aviary. Red Butte Garden and Arboretum, located in the foothills of Salt Lake City, features many different exhibits and also hosts many musical concerts. Jordan Park is home to the International Peace Gardens. The Bonneville Shoreline Trail is a popular hiking and biking nature trail which spans ninety mi through the foothills of the Wasatch Front.
The Olympic Cauldron Park at Rice-Eccles Stadium, features the Olympic Cauldron from the games, a visitor's center, and the Hoberman Arch. The Olympic Legacy Plaza, located at the Gateway District, features a dancing fountain set to music and the names of 30,000 Olympic volunteers carved in stone. The Utah Olympic Park, located near Park City, features the Olympic ski jumps, as well as bobsleigh, luge, and skeleton runs. Today, the Olympic Park is used for year-round training and competitions. Visitors to the park can watch the various events and even ride a bobsled. The Utah Olympic Oval, located in nearby Kearns, was home to the speed skating events and is now open to the public. Other popular Olympic venues include Soldier Hollow, the site of cross-country skiing events, located southeast of Salt Lake near Heber City.
Salt Lake City is close to several world-class ski and summer resorts, including Snowbird, Alta, Brighton, Solitude, Park City Mountain Resort, and Deer Valley. The resorts cater to millions of visitors each year and offer year-round activities.
Salt Lake City is also home to a few major shopping centers. Trolley Square is an indoor and outdoor mall with many independent art boutiques, restaurants, and national retailers. The buildings housing the shops are renovated trolley barns with cobblestone streets. The Gateway District, an outdoor shopping mall, has many national restaurants, clothing retailers, a movie theater, the Clark Planetarium, the Discovery Gateway (formerly The Children's Museum of Utah), a music venue called The Depot, and the Olympic Legacy Plaza. City Creek Center is the city's newest major shopping center and features many high-end retailers not found anywhere else in Utah.

On 3 October 2006, the LDS Church, who owned the ZCMI Center Mall and Crossroads Mall, both on Main Street, announced plans to demolish the malls, a skyscraper, and several other buildings to make way for the $1.5 billion City Creek Center redevelopment. It combined several new office and residential buildings (one of which is the third-tallest building in the city) around an outdoor shopping center featuring a stream, fountain, and other outdoor amenities;[195] it opened on 22 March 2012. Sugar House is a neighborhood with a small town main street shopping area and numerous old parks, which will soon be served by the S Line (formerly known as Sugar House Streetcar). Sugar House Park is the second largest park in the city, and is host to frequent outdoor events and the primary Fourth of July fireworks in the city.
Other attractions in or within close proximity to Salt Lake City include Timpanogos Cave National Monument, the Golden Spike National Historic Site (where the world's first transcontinental railroad was joined), the Lagoon (amusement park), the Great Salt Lake, the Bonneville Salt Flats, Gardner Historic Village, one of the largest dinosaur museums in the U.S. at Thanksgiving Point in Lehi, and the world's largest man-made excavation at Bingham Canyon Mine.
Sports and recreation
Winter sports, such as skiing and snowboarding, are popular activities in the Wasatch Mountains east of Salt Lake City. Eight ski resorts lie within 50 miles (80 km) of the city. Alta, Brighton, Solitude, and Snowbird all lie directly to the southeast in the Wasatch Mountains, while nearby Park City contains three more resorts. The popularity of the ski resorts has increased nearly 29 percent since the 2002 Winter Olympics.[196] Summer activities such as hiking, camping, rock climbing, mountain biking, and other related outdoor activities are popular in the mountains, as well. The many small reservoirs and rivers in the Wasatch Mountains are popular for boating, fishing, and other water-related activities.
Professional sports

Salt Lake City is home to the Utah Jazz of the National Basketball Association (NBA), who moved from New Orleans in 1979 and play their home games in Vivint Smart Home Arena (formerly known as the Delta Center and later known as EnergySolutions Arena). They are the only team from one of the four top-level professional sports leagues in the state. They have been to the playoffs in 22 of the last 25 seasons, making them among the most successful in the NBA in that time span, but have yet to win a championship. Salt Lake City was previously home to a professional basketball team, the Utah Stars of the American Basketball Association (ABA), between 1970-75. They won one championship in the city (in 1971) and enjoyed some of the strongest support of any ABA team, but they folded just months before the ABA–NBA merger, thus preventing them from being absorbed by the NBA. The success of the Stars may have had a hand in the decision by the struggling Jazz to relocate to Salt Lake City in 1979.
Real Salt Lake of Major League Soccer was founded in 2004, initially playing at Rice-Eccles Stadium at the University of Utah before the soccer-specific Rio Tinto Stadium was completed in 2008 in neighboring Sandy.[197] The team won their first MLS championship by defeating the Los Angeles Galaxy at the 2009 MLS Cup. RSL advanced to the finals of the CONCACAF Champions League in 2011 but lost 3-2 on aggregate, and also advanced to the 2013 MLS Cup Final. The city has also played host to several international soccer games.

Arena football expanded into the city in 2006 with the Utah Blaze of the Arena Football League. They recorded the highest average attendance in the league in their first season.[198] After the original AFL folded in 2009, the future of the Blaze was unclear. However, a new league branded as the Arena Football League began play in 2010. The Blaze franchise was restored and is playing in the new league.[199]
There are also two minor league teams located in the city. The Salt Lake Bees, a Pacific Coast League Triple A affiliate of the Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim, play at Smith's Ballpark and were established in 1994 as the Buzz. Their name was changed to the Stingers in 2002 and to the Bees, a historical Salt Lake City baseball team name, in 2006. The Utah Grizzlies hockey team of the ECHL were established in 2005, replacing the previous Grizzlies team that existed from when they relocated from Denver in 1995 to 2005 in the International Hockey League (IHL) and, later, the American Hockey League (AHL). They play at the Maverik Center in neighboring West Valley City.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue | Established | Titles | Attendance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Salt Lake | Soccer | Major League Soccer | Rio Tinto Stadium (in Sandy) | 2004 | 1 | 20,160 |
| Utah Jazz | Basketball | National Basketball Association | Vivint Smart Home Arena | 1979 | 0 | 18,185 |
| Salt Lake Bees | Baseball | Pacific Coast League | Smith's Ballpark | 1994 | 0 | 6,722 |
| Utah Grizzlies | Hockey | ECHL | Maverik Center (in West Valley City) | 2005 | 0 | 4,622 |
| Real Monarchs SLC | Soccer | United Soccer League | Rio Tinto Stadium (in Sandy) | 2014 | 0 | 4,698 |
Amateur sports
Utah lacks a professional football team of its own, and college football is very popular in the state. The University of Utah and Brigham Young University both maintain large followings in the city, and the rivalry between the two colleges has a long and storied history. Despite the fact Utah is a secular university, the rivalry is sometimes referred to as the Holy War because of BYU's status as an LDS university. Until the 2011–12 season, they both played in the Mountain West Conference of the NCAA's Division I and have played each other 90 times since 1896 (continuously since 1922). The University of Utah was the first school from a non-BCS conference to win two BCS bowl games (and was the first from outside the BCS affiliated conferences to be invited to one) since the system was introduced in 1998.
The University of Utah was a part of the controversy surrounding the fairness of the Bowl Championship Series (BCS) of college football. Despite undefeated seasons in both 2004 and 2008, Utah was not invited to participate in the national championship in either season because it was a member of the Mountain West Conference, a non-BCS conference.[200]
The Utah Avalanche, formed in January 2011, were a development rugby league team for the now defunct American National Rugby League.[201] The Utah Warriors were a rugby union team that competed in the Rugby Super League in 2011, playing their home games at Rio Tinto Stadium.[202] In June 2012, Salt Lake City hosted the IRB Junior World Rugby Trophy, a major international rugby union tournament for under-20 national teams from "second-tier" nations.[203]
Utah became the first state outside Minnesota where bandy exists when Olympic Bandy Club was formed in Salt Lake City.[204] Salt Lake is also home to two roller derby leagues: the Salt City Derby Girls[205] and Wasatch Roller Derby,[206] both of which field travel teams.[207]
Transportation
Roads

Salt Lake City lies at the convergence of two cross-country freeways; I-15, which runs north-to-south just west of downtown, and I-80, which connects downtown with Salt Lake City International Airport just to the west and exits to the east through Parley's Canyon. I-215 forms a 270-degree loop around the city. SR-201 extends to the western Salt Lake City suburbs. The Legacy Parkway (SR-67), a controversial and oft-delayed freeway, opened September 2008, heading north from I-215 into Davis County along the east shore of the Great Salt Lake. Travel to and from Davis County is complicated by geography as roads have to squeeze through the narrow opening between the Great Salt Lake to the west and the Wasatch Mountains to the east. Only four roads run between the two counties to carry the load of rush hour traffic from Davis County.
Salt Lake City's surface street system is laid out on a simple grid pattern. Road names are numbered with a north, south, east, or west designation, with the grid originating at the southeast corner of Temple Square downtown. One of the visions of Brigham Young and the early settlers was to create wide, spacious streets, which characterizes downtown. The grid pattern remains fairly intact in the city, except on the East Bench, where geography makes it impossible. The entire Salt Lake Valley is laid out on the same numbered grid system, although it becomes increasingly irregular further into the suburbs. Many streets carry both a name and a grid coordinate. Usually both can be used as an address. US-89 enters the city from the northwest and travels the length of the valley as State Street (with the exception of northern Salt Lake City).
Public transportation

Salt Lake City's mass transit service is operated by the Utah Transit Authority (UTA) and includes a bus system, light rail, and a commuter rail line. Intercity services are provided by Amtrak and various intercity bus lines. These services are all interconnected at the Salt Lake City Intermodal Hub (Salt Lake Central Station) located a short distance west of the city center. The Brookings Institution in 2011 rated Salt Lake City's mass transit system as the third-best in the nation at connecting people to jobs, providing access to 59% of the jobs in the valley.[208]
Transit bus service
UTA's bus system extends throughout the Wasatch Front from Brigham City in the north to Santaquin in the south and as far west as Grantsville, as well as east to Park City. UTA also operates routes to the ski resorts in Big and Little Cottonwood Canyons, as well as Sundance in Provo Canyon, during the ski season (typically November to April). Approximately 60,000 people ride the bus daily, although ridership has reportedly declined since TRAX was constructed.[209]
Light rail

The 44.8-mile (72.1 km)[210] light rail system, called TRAX, consists of three lines. The Blue Line, which opened in 1999 and was expanded in 2008, travels from the Salt Lake City Intermodal Hub (Salt Lake Central Station), south to the nearby city of Draper. The Red Line, which originally opened in 2001 and was expanded in 2011, runs from the University of Utah, south-west through Salt Lake to the community of Daybreak in South Jordan. A third line, known as the Green Line, opened in 2011 and runs from the Salt Lake City International Airport to West Valley City (via Downtown Salt Lake City), with the extension to the airport having opened in April 2013. The system has a total of 50 stations of which 23 are within the city limits.[211] Daily ridership averaged 60,600 as of the fourth quarter of 2012,[212] making TRAX the ninth most-ridden light rail system in the country.
Commuter rail

The commuter rail system, FrontRunner, opened on 26 April 2008 and extends from the Intermodal Hub north through Davis County to Pleasant View on the northern border of Weber County.[213] Daily ridership on the line averages 7,800, as of the fourth quarter of 2012.[212] An expansion called "FrontRunner South", which extended FrontRunner south to Provo in central Utah County, was completed in December 2012 as part of UTA's FrontLines 2015 project.[211][214][215] These extensions were made possible by a sales tax hike for road improvements, light rail, and commuter rail approved by voters on 7 November 2006.[216] In addition, a $500 million letter of intent was signed by the Federal Transit Administration for all four of the planned TRAX extensions in addition to the FrontRunner extension to Provo.[217]
Intercity bus and rail services
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides service to Salt Lake City operating its California Zephyr daily in both directions between Chicago and Emeryville, California. Greyhound Lines serves Salt Lake City as well. Their nine daily buses provide service to Denver, Reno, Las Vegas, and Portland. Both of these stations are located at the Salt Lake City Intermodal Hub.
Air transportation

Salt Lake City International Airport is approximately 4 miles (6 km) west of downtown. Delta Air Lines operates a hub at the airport, serving over 100 non-stop destinations in the United States, Mexico, and Canada, as well as Paris and Amsterdam.[218] SkyWest Airlines operates its largest hub at the airport as Delta Connection, and serves 243 cities as Delta Connection and United Express. The airport is served by 4 UTA bus routes, and a UTA operated light rail line (TRAX) opened services on 14 April 2013. A total of 22,029,488 passengers flew through Salt Lake City International Airport in 2007, representing a 2.19% increase over 2006.[219] The airport ranks as the 21st busiest airport in the United States in total passengers, is consistently rated first in the country in on-time arrivals and departures, and has the second-lowest number of cancellations.[220] There are two general aviation airports nearby; South Valley Regional Airport in West Jordan and Skypark Airport in Woods Cross.
Cycling
This article may contain an excessive amount of intricate detail that may interest only a particular audience. (August 2016) |
Salt Lake City is widely considered a bicycle-friendly city. In 2010, Salt Lake City was designated as a Silver-level Bicycle Friendly Community[221] by the League of American Bicyclists, placing the city in the top 18 bicycling cities in the U.S. with a population of at least 100,000. Many streets in the city have bike lanes, and the city has published a bicycle map.[222] However, off-road biking in the valley has suffered significantly as access to trails and paths has declined with the increase of housing developments and land privatization. In 2012, the Salt Lake Transportation Division launched BikeSLC.com, which consolidates the city's information about bicycle routes, safety, and promotions. The website includes a form for business owners to request bicycle racks to be installed on public property free of charge close to their businesses, a service that has a months-long waiting list.[223]
Salt Lake City was the first city in the United States to use the "Green Shared Lane", also known as a "super sharrow",[224] a 4-foot (1.2 m) wide green band down the middle of a travel lane where adding a dedicated bike lane is unfeasible. Other cities such as Long Beach, California, Oakland, California, and Edina, Minnesota, have since introduced similar designs. These four cities are currently participating in a study by the Federal Highway Administration to measure the effect of the design on automobile speed and passing distance when overtaking bicycles, crashes between automobiles and bicycles, and whether it encourages more bicycle ridership, along with other metrics.[225]
On 25 September 2010, UTA in partnership with Salt Lake City, the Utah Department of Transportation, the Wasatch Front Regional Council, and the Mayor's Bicycle Advisory Committee, opened a Bicycle Transit Center (BTC) at the Intermodal Hub. The BTC is anticipated to serve multi-modal commuters from TRAX and FrontRunner, as well as providing a secure bicycle parking space for bicycle tourists who want to tour the city on foot or transit.
In April 2013, Salt Lake City launched a bike share program known as GREENbike. The program allows users to pay $5 per day to access bicycles, with the option of purchasing a weekly or annual pass.[226] As of the launch of the program, there were 10 stations located in the downtown core.[227] By October 2014, the number of stations had expanded to 20.[228] In addition to the bike sharing program, eighty businesses in the city participate in the Bicycle Benefits program,[229] which provides discounts to customers who arrive by bicycle. The city is also home to the Salt Lake City Bicycle Collective.
As a result of this increasing support, Salt Lake City's on-road bikeway network has grown to encompass 200 lane miles. In July 2014, the city began construction of a protected bicycle lane on a 1.35 miles (2.17 km) segment of 300 South between 300 West and 600 East. The project received significant opposition from business owners and residents along the route because of concerns about the 30% reduction in car parking spaces and disruptions resulting from construction. The construction preceded in stages, with the last stage completed in late October 2014. The performance of the protected bicycle lane (specifically, its role in encouraging more bicycle ridership) will influence future plans for making the city more bicycle-friendly.[230]
One popular example of the city's cycling and walking routes is the loop around City Creek Canyon on Bonneville Boulevard.[231] The city has designated the road as one lane only (one-way) for motor vehicles, turning the other lane over to two-way cyclists and pedestrians. From the last Monday in May to the last weekend in September, City Creek Canyon Road itself is closed to motor vehicles on odd-numbered days, while bicycles are prohibited on even-numbered days and holidays. Bicycles are allowed every day for the rest of the year.
Sister cities
Salt Lake City has several sister cities/towns,[232][233] including:
See also
- List of people from Salt Lake City
- List of tallest buildings in Salt Lake City
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Salt Lake City, Utah
- Trolley Square shooting
- USS Salt Lake City (Ships of the United States Navy named "Salt Lake City").
Notes
- ^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the expected highest and lowest temperature readings at any point during the year or given month) calculated based on data at said location from 1991 to 2020.
- ^ The official Salt Lake City climatology station was located in downtown from March 1874 to April 30, 1928 and at Salt Lake City Int'l since May 1, 1928. For further information, see ThreadEx.
References
- ^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ a b "Population Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ "Definition for "Salt Laker"". Merriam-Webster. 16 July 2014. Retrieved 29 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Zip Code Lookup". USPS. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ a b "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ^ "U.S. Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 25 October 2007. Retrieved 31 January 2008.
- ^ Division, US Census Bureau, Data Integration. "Population Estimates". www.census.gov. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2014 - United States - Combined Statistical Area; and for Puerto Rico". Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ^ Van Cott, John W. (1990). Utah place names: a comprehensive guide to the origins of geographic names : a compilation. University of Utah Press. p. 327. ISBN 978-0-87480-345-7. Accessed 25 July 2011.
- ^ "Mormon Pioneers". BBC Religion. BBC. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- ^ "PBS American Experience. "The Mormons"". pbs.org. 30 April 2007. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
- ^ "FDIC Industrial Banks". Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. 25 June 2004. Retrieved 6 March 2007.
- ^ "10 Towns that Changed America". WTTW. 19 April 2016. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ Madsen, Brigham (1985). The Shoshoni Frontier and the Bear River Massacre. University of Utah Press. p. 6. ISBN 0-87480-494-9.
- ^ "89 L.Ed. 985; 65 S.Ct. 690; 324 U.S. 335" (PDF). United States Supreme Court. 9 April 1945. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
- ^ Alexander, Thomas G. "Utah History to Go - Fremont's Exploration". Utah State Historical Society. Retrieved 15 December 2006.
- ^ Alexander, Thomas G.; Allen, James B. (1984). Mormons & Gentiles: A History of Salt Lake City (First ed.). Boulder, Colorado: Pruett Publishing Company. p. 24. ISBN 0-87108-664-6.
By the time Brigham Young caught his first glimpse of the valley...Salt Lake City was already begun. Two days earlier an advance party...entered the valley...The next day they explored further, and on July 23 began plowing the hard, dry ground.
- ^ Mexico (Map).
- ^ Burton, Sir Richard Francis (1862). The City of the Saints: Across the Rocky Mountains to California. New York City: Harper & brothers (reprinted by University of Michigan Library). Accessed 13 September 2006.
- ^ "Ceremony at "Wedding of the Rails", May 10, 1869 at Promontory Point, Utah". World Digital Library. 10 May 1869. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
- ^ Stilltoe, Linda. A History of Salt Lake County. p. 138.
- ^ Money, Marti. "Utah Street Tramways - History of trams in Salt Lake City". Archived from the original on 28 September 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Davidson, Lee (28 August 2013). "Sugar House streetcar testing begins next week". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "Salt Lake City welcomes S-Line". Railway Gazette International. Sutton, London: Railway Gazette Group. 9 December 2013. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ^ El Nasser, Haya (15 September 2006). "Immigrants turn Utah into mini-melting pot". USA Today. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ Reed, Travis (11 June 2005). "Salt Lake City Has High Gay Population". Associated Press.
- ^ Roche, Lisa Riley (5 October 2006). "Big incentive helps lure speed skating group". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ a b Gorrell, Mike (30 June 2006). "Convention numbers best since Olympics; S.L. County conventions post big year". The Salt Lake Tribune.
- ^ Gorrell, Mike (15 February 2004). "Olympic windfall unseen". The Salt Lake Tribune. Salt Lake City.
- ^ Gorrell, Mike (15 January 2012). "Salt Lake City in the hunt for 2022 Olympics?". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Hula, Ed (11 July 2011). "Ukraine, Swiss, Quebec City Winter Olympic Bids; Salt Lake Bid Rumblings". Around the Rings. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Beijing to host 2022 Winter Olympics and Paralympics". BBC Sport. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ "Games · International Committee of Sports for the Deaf". Deaflympics.com. Retrieved 29 July 2014.
- ^ Beebe, Paul (9 November 2005). "SLC to land Rotarians in '07". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "Area Information - Frequently Asked Questions". Salt Lake City Corporation. Archived from the original on 24 October 2006. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Frosch, Dan (23 February 2013). "Seen as Nature Lovers' Paradise, Utah Struggles With Air Quality". The New York Times. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Utah's Infamous "Lake Stink"". Utah Department of Environmental Quality. Archived from the original on 23 September 2006. Retrieved 11 March 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Arave, Lynn (6 March 2005). "Mountains High: Utah abounds with high peaks in all counties". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ Davidson, Lee (19 April 2006). "It's 2008 — and 'the big one' slams Utah". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ Husarik, Theresa. "Navigating Utah's Streets". About.com. Archived from the original on 1 January 2007. Retrieved 11 March 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Hill, William E. (1996). The Mormon Trail: yesterday and today. Logan, Utah: Utah State University Press. p. 26. ISBN 0-87421-202-2.
- ^ Balaz, Christine. "Find the Best Things to Do in Sugarhouse". 10 Best. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- ^ Smart, Christopher (29 October 2015). "Sugar House apartment project would bring impacts — not impact fees". Salt Lake Tribune.
- ^ "Remnants of Hurricane Olivia - September 23-28, 1982". Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Record high and low precipitation for each month". National Weather Service. Retrieved 11 March 2007.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Maximum and Minimum Calendar Year Precipitation". National Weather Service. Retrieved 2 December 2010.
- ^ Smart, Christopher (4 May 2011). "Utah snowpack, weather revive memories of '83 floods". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Average snowfall". National Weather Service. Retrieved 11 March 2007.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Earliest and latest measurable snowfall". National Weather Service. Retrieved 11 March 2007.
- ^ "Late spring snowstorm surprises Utahns". ksl.com. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. 24 May 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Maximum and minimum seasonal snowfall". National Weather Service. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Top 5 Snowiest, Top 5 Driest, and Normal Monthly Mean Snowfall". National Weather Service. Retrieved 2 December 2010.
- ^ Bauman, Joe (5 August 1999). "Lake has great impact on storms, weather". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ "NWS Salt Lake City - Average number of days per month of 90, 95, and 100 degrees or more". National Weather Service.
- ^ "National Weather Service Salt Lake City - Relative humidity averages by month/hour". National Weather Service. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ a b c d "Summary of Monthly Normals 1991-2020, Station Name: UT SALT LAKE CITY INTL ARPT". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ Fahys, Judy (7 March 2007). "Winter's bad air still choking Utah". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Frosch, Dan (23 February 2013). "Seen as Nature Lovers' Paradise, Utah Struggles With Air Quality". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 July 2014.
- ^ Maffly, Brian (29 June 2015). "Summer ozone blast threatening Utahns' health, thanks to sunshine and car exhaust". Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ^ "xmACIS". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- ^ "Highest and Lowest Daily Maximum Temperature for Each Month with Day and Year of Occurrence, Plus Normal Monthly Maximum Temperature". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 26 June 2007. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- ^ "Highest and Lowest Daily Minumum [sic] Temperature for Each Month with Day and Year of Occurrence, Plus Normal Monthly Minimum Temperature". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 17 December 2004. Retrieved 11 May 2010.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for SALT LAKE CITY/INTL, UT 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 19 July 2020.
- ^ "Historical UV Index Data - Salt Lake City, UT". UV Index Today. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Retrieved 2 July 2016.
- ^ Moffatt, Riley (1996). Population History of Western U.S. Cities & Towns, 1850-1990. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow. p. 310.
- ^ United States Census Bureau. "Census of Population and Housing". Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ "State & County QuickFacts: Salt Lake City (city), Utah". U.S. Census Bureau. 8 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d e "Race and Hispanic Origin for Selected Cities and Other Places: Earliest Census to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- ^ a b From 15% sample
- ^ American FactFinder, United States Census Bureau. "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 - 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ^ Canham, Matt (22 June 2005). "Mormon portion of Utah population steadily shrinking". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Lyon, Julia (1 May 2006). "Update: School ranks thinned by 'Day Without Immigrants'". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "Latinos eye Utah for 2009 meeting". The Salt Lake Tribune. 1 August 2006. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Johnson, Kirk (15 February 2007). "Anti-Bosnian Backlash Feared in Utah". The New York Times.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Lattin, Don (10 April 1996). "New Mormon Melting Pot/Church transcends its racist history". San Francisco Chronicle. San Francisco. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ "The Utah Community Data Project". The Utah Community Data Project. The Bureau of Economic and Business Research. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ Stewart, Erin (9 November 2005). "Travel book to highlight Salt Lake as 'gay-friendly place to live'". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Perkins, Nancy (26 October 2003). "Utah Episcopalians support gay bishop". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ "Bishop explains ousting of gay Episcopal bishop". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Associated Press. 22 May 2004. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Davis, Kristy (11 June 2007). "Eye on the Rabbi". Salt Lake City Weekly. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ "Same-sex Couples and the Gay, Lesbian, Bisexual Population: New Estimates from the American Community Survey" (PDF). Los Angeles: The Williams Institute. October 2006. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Ruiz, Rebecca (29 November 2007). "In Pictures: America's Vainest Cities". Forbes. forbes.com. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Thomas, G. Scott (7 September 2010). "A Stress Test for America". Portfolio.com. Archived from the original on 5 January 2011. Retrieved 16 May 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Hicken, Melanie (25 June 2014). "10 Least Stressed Out Cities". CNN Money. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Nichols, Michelle (19 December 2008). "Salt Lake City, Madison healthiest U.S. cities: study | Lifestyle". Reuters. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ "Salt Lake City 2011 Mayor's recommended budget" (PDF). p. A-11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2012. Retrieved 22 February 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Fortune 500". Fortune. 4 May 2009. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|work=(help) - ^ "Vehix". Vehix. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Marketbeat Office Snapshot Q1 2016, Salt Lake City" (PDF). Cushman & Wakefield Commerce. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ "Official Utah State Capitol history page". Archived from the original on 4 January 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Stack, Peggy Fletcher (21 January 2006). "Mormons, non-Mormons clear the air". The Salt Lake Tribune. Salt Lake City. Accessed 14 April 2013.
- ^ Kalev, Gol. "Let's be partners, Israel's ambassador urges governor" (PDF). America–Israel Friendship League. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Dalrymple, Jim, II (19 July 2013). "Salt Lake City Public Safety Building opens to fanfare". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "LDS Seminary in Public Schools". American Civil Liberties Union. August 2007. Archived from the original on 17 January 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Gehrke, Robert (27 August 2010). "Guv claims Corroon could eliminate LDS seminary". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "Seminary". The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ Quinn, Frederick (2004). "1". Building the "Goodly Fellowship of Faith" - A History of the Episcopal Church in Utah - 1867-1996. Logan, Utah: Utah State University Press.
- ^ Berry, John N. (15 June 2006). "Gale/LJ Library of the Year 2006: Salt Lake City Public Library-Where Democracy Happens". Library Journal. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Leiner, Barry M.; Robert E. Kahn; Jon Postel. "A Brief History of the Internet". Internet Society. Retrieved 18 May 2009.
- ^ "University Health Care Milestones". University of Utah Health Care. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Page, Jared (6 December 2007). "2 Salt Lake City blocks may become arts hub". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Page, Jared (15 October 2008). "New theater is coming to Regent Street". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ Hansen, Erica Hansen (17 October 2008). "Many are questioning necessity of Salt Lake theater". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ^ "Music & the Spoken Word — History". Bonneville Communications. Archived from the original on 24 December 2012. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Pioneer packed as nearly 40K jam Twilight Concert opening". Fox13. 8 July 2010. Archived from the original on 6 October 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Surprise! Utah Pride Festival Among Nations Biggest and Best Pride Weekends". Visit Salt Lake. 5 May 2015. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah Pride Festival 2012 - History of the Utah Pride Festival". Utahpride.org. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ Albo, Mike. "Gayest Cities in America". The Advocate. Archived from the original on 7 January 2012. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Pride Interfaith Service". Utah Pride Center. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah Arts Festival". Utah Arts Festival. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ^ "Uniquely Utah: Dark Arts Festival". Fox 13 News. 9 June 2013. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Dark Arts Festival @ Area 51 06. 20-22". Slug Magazine. 27 June 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Dark Arts Festival". City Weekly. 12 June 2009. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Dark Arts of Utah 2015". Songkick. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Urban Arts Festival". Urban Arts Festival. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Jewish Arts Festival". IJ and Jeanné Wagner JCC. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Jewish Arts Festival". City Weekly. 11 November 2010. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Sugar House Arts Festival". City Weekly. 1 July 2010. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Sugar House Arts Festival". Sugar House Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "FilmQuest Film Festival". City Weekly. 17 June 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Film Festival". Salty Horror Con & Film Festival. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Damn These Heels Film Festival". Utah Film Center. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "Damn These Heels Film Festival". City Weekly. 9 July 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "Great Salt Lake Fringe Festival". Great Salt Lake Fringe. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Great Salt Lake Fringe Festival Taking Over Sugar House". Good 4 Utah. 6 August 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Living Traditions Festival". Salt Lake City Arts Council. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake City's Living Traditions Festival Celebrates 30 years of Ethnic Food, Music, and Dance". Salt Lake Tribune. 6 August 2015. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
- ^ "Earth Jam". Earth Jam. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Live Green SLC! Festival". Live Green SLC. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Festival Shows Environmentally Green Products, Services". Salt Lake Tribune. 5 May 2012. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "DIY Festival". Craft Lake City. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "9th and 9th Street Festival". 9th and 9th Street Festival. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Carmel of the Immaculate Heart of Mary". Carmelite Monastery. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Mormon Neighbors help Catholic Nuns with Annual Carmelite Fair". Deseret News. 16 September 2014. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Ganesh Chathurthi Celebrations 2015". Sri Sri Ganesh Hindu Temple of Utah. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Gurukul Have Been Invited for Ganehs Festival on Sunday at 10:30 am See the Details Below". SLC Gurukul. 15 September 2014. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "26th Annual India Fest this Saturday & Sunday". Utah Krishnas. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake City Krishna Temple Celebrates with Festival of Colors". Salt Lake Tribune. 9 May 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Downtown Yoga Festivals". Great Salt Lake City Yoga Festival. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Yoga Festival in Downtown Salt Lake City Kicks Off its First Year". Fox 13 News. 23 May 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake City Pagan Pride Day". Salt Lake City Pagan Pride Day. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah's Pagan Community Grows". Salt Lake Tribune. 10 September 2012. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Pagan Pride Days Kasey Conder". City Weekly. 6 September 2010. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Pagan Pride Day 2010 Successful". Salt Lake Pagan Society. 12 September 2010. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Pagan Pride Day 2011". Salt Lake Pagan Society. 10 September 2011. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Pagan Pride Day 2012~ A Blast!". Salt Lake Pagan Society. 10 September 2012. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Pagan Pride Day 2013 Full of Fun!". Salt Lake Pagan Society. 16 September 2013. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "13th Annual Salt Lake City Pagan Pride Day 2014". Salt Lake Pagan Society. 6 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "14th Annual Salt Lake City Pagan Pride Day 2015- Harvest Blessings!". Salt Lake Pagan Society. 14 September 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt City Steamfest". Salt City Steamfest. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt City Steamfest: a Look into the SLC Steampunk Fest Happening July 17–18". City Weekly. 17 July 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Rose Park Community Festival". Rose Park Community Council. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ "Westfest". Westfest. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Balloon Festival". Sandy City Corporation. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Blue Moon Festival August 30". City of Hollady, Utah. 26 August 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah Asian Festival". Utah Asian Festival. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah Asian Festival Celebrates States Cultural Diversity". Salt lake Tribune. 13 June 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Ferragosto Italian Cultural Street Fair in "Little Italy"". Ferragosto. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Festa Italiana". Festa Italiana. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ "Event Organizers Invite Utah Community To Saturday's Peruvian Festival". Fox 13 News. 25 July 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah Brazilian Festival". Utah Brazilian Festival. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "North Salt Lake to Host Polynesian Cultural Festival Next Weekend". Deseret News. 17 August 2015. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Nihon Matsuri Japanese Festival Salt Lake City, Utah". Nihon Matsuri Japanese Festival. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Utah Buddhists to Celebrate Japanese Festival of Joy". KSL. 11 July 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Shatner, Lee and Record Breaking Crowds Inaugural Salt Lake Comic Con Ends with a Bang". Deseret News. 9 September 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Despite Growing Pains Salt Lake Comic Con Nets Another Record Breaking Event". Deseret News. 6 September 2014. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake, San Diego Comic-Con Lawsuit Headed to Trial". Salt Lake Tribune. 2 July 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "Trademark Battle: Salt Lake Covention Cites Other Events Named "Comic Con" in Latest Court Filing". Deseret News. 23 September 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Scores Win With Trademark Office Amid Sand Diego Comic-Con Lawsuit". Salt Lake Tribune. 23 July 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "San Diego Comic-Con International Vs. Salt Lake Comic Con Court Documents". Salt Lake Comic Con. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ "Stan Lee Declares Salt Lake Comic Con "Greatest" in the World". Salt Lake Tribune. 6 September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2015.
- ^ "SL Comic Con Sets World Records for Costumed Comic Book Gathering". KSL. 26 September 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2015.
- ^ "Crystal Mountain Pony Con". Crystal Mountain Pony Con. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "My Little Pony Convention Welcomes 800 "Bronies" to Downtown SLC". Fox 13 News. 17 July 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake City International Tattoo Convention". Salt Lake City International Tattoo Convention. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Ink Enthusiasts Gather for Salt Lake City International Tattoo Convention". Fox 13 News. 28 March 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Fantasy Con". Fantasy Con. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Are Three Cons too Many for Salt Lake? FantasyCon Fans Say No". Salt Lake Tribune. 6 July 2014. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Gaming Con". Salt Lake Gaming Con. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Gaming Con: Giant Gaming Convention Planned in Salt Lake City". Salt Lake Tribune. 31 March 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Salt Lake Gaming Con Kicks Off Inaugural Event". Salt Lake Tribune. 2 August 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Furry Unlocked". Furry Unlocked. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Furry Unlocked". WikiFur. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Closing Furry Unlocked". Furry Unlocked. 16 January 2016. Retrieved 9 April 2016.
- ^ "Greater Salt Lake City Annual Events (2005)". Metroguide.com, Inc. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ^ Eborn, Jared (6 October 2006). "Tour of Utah takes step forward". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 15 April 2013.
- ^ "SLC Events - Friday Night Flicks". Salt Lake City. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Salt Lake City Gets Fit". Salt Lake City. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "The Salt Lake City Games were by all accounts the most successful Winter Olympics ever." — Fantin, Linda (11 September 2002). "Games Helped to Heal a Nation". The Salt Lake Tribune. NewsBank Article Archive ID: 100DF5198ADF1309.
"Controversies aside, the 2002 Salt Lake games may prove to be the most successful Winter Olympics in recent history." — Steisand, Betsy (17 February 2002). "Hey, baby, it's gold outside: Skeptics thought the '02 Olympics would be boredom on ice. Were they ever wrong". U.S. News & World Report. p. 1. Retrieved 16 April 2013.[dead link] - ^ Jensen, Brittany (11 January 2007), "Torino Named SLC Sister City", The Daily Universe, Provo, Utah: Brigham Young University
- ^ "Arbitron Radio Market Rankings: Spring 2013". Arbitron. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Markets & Stations: DMA: Salt Lake City, UT". Television Bureau of Advertising. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "American Institute of Architects Institute Honor Award". American Institute of Architects. Archived from the original on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Smeath, Doug (4 October 2006). "Downtown rebound: LDS Church unveils plans for 20-acre development". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Gorrell, Mike; Knight Ridder (16 May 2006). "Utah's ski industry chalks up another record year for visitors". The Salt Lake Tribune. Archived from the original on 12 February 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Dethman, Leigh (16 August 2006). "Salt Lake County plays ball, OKs a deal with Real: Corroon, Checketts still must iron out some final details". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Jorgensen, Loren (28 May 2006). "Blaze burn bright with optimism". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Jewkes, Wade (18 February 2010). "Arena Football League: AFL will return this season with 15 teams". Deseret News. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Utah AG: BCS may violate antitrust laws". ESPN. 7 January 2009. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Utah Avalanche | American National Rugby League". Amnrl.com. Archived from the original on 4 December 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "New Team Joins Super League". We Are Rugby. 13 December 2010. Archived from the original on 27 July 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "USA to host Junior World Rugby Trophy 2012" (Press release). International Rugby Board. 29 January 2012. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Google Oversetter: About American Bandy Association" (in Norwegian). Translate.google.no. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "Salt City Derby Girls". Archived from the original on 22 October 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Wasatch Roller Derby". Wasatch Roller Derby. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Means, Sean P. (4 October 2010). "Roller derby update: Big in Boise". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Davidson, Lee (12 May 2011). "Utah transit among best to connect people and jobs". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ Loomis, Brandon (22 March 2008). "Bus riders press for probe of UTA". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "FrontLines 2015 Project" (PDF) (Map). rideuta.com. Utah Transit Authority. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ a b "UTA setting end dates on TRAX construction". Deseret Morning News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. 9 August 2007. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ a b "Public Transportation Ridership Report Fourth Quarter 2012" (PDF). American Public Transportation Association. 1 March 2013. p. 27. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ Raymond, Arthur (26 April 2008). "UTA FrontRunner up and running today". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Thomas, Ethan (12 August 2008). "Ground broken for FrontRunner line to Utah County". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ "UTA FrontRunner South Project Update". Utah Transit Authority. 2 November 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Warburton, Nicole (8 November 2006). "Transit measures approved". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ Warburton, Nicole (25 September 2007). "UTA on track for U.S. funds". Deseret News. Salt Lake City: Deseret Digital Media. Retrieved 13 April 2013.
- ^ Beebe, Paul (22 July 2009). "Swine flu, economy prompt Delta to trim SLC-Tokyo route". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "Salt Lake City International Airport Statistics" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Research and Innovative Technology Administration". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- ^ http://bikeleague.org/content/league-announces-spring-2010-bicycle-friendly-communities
- ^ "Salt Lake City Bike Map". BikeSLC.com. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ "Bike Racks and Corrals". BikeSLC.com website. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ "Mea Culpa: Long Beach Not First to Have Colored Shared Lane". Streetsblog. 6 July 2009. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Green-Colored Pavement with the Shared-Lane Marking". Federal Highway Administration website. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Salt Lake to Launch Bike Share Program". Associated Press. Retrieved 21 May 2013.
- ^ "Salt Lake City launches GREENbike bicycle sharing". The Salt Lake Tribune. 8 April 2013. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "GREENbikeSLC". GREENbikeSLC website. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ http://www.bicyclebenefits.org/index.php?option=com_sobi2&catid=5&Itemid=54
- ^ Smart, Christopher (31 August 2014). "New downtown Salt Lake City bicycle track worries small businesses". The Salt Lake Tribune. Retrieved 20 October 2014.
- ^ "City Creek Canyon/Memory Grove". BikeSLC.com website. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ Sister Cities International (SCI). Sister Cities International.
- ^ "Our Sister Cities". Saltlakesistercities.com. Retrieved 6 February 2013.
- ^ Pessotto, Lorenzo. "International Affairs - Twinnings and Agreements". International Affairs Service in cooperation with Servizio Telematico Pubblico. City of Torino. Archived from the original on 18 June 2013. Retrieved 6 August 2013.
- ^ "Sister cities, Trujillo, Salt Lake City". Archived from the original on 12 March 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
Literature
- Alexander, Thomas G. (2001). Grace & Grandeur: A History of Salt Lake City. Heritage Media Corp. ISBN 1-886483-60-4.
- Alexander, Thomas G.; Allen, James B. (1984). Mormons & Gentiles: A History of Salt Lake City. Pruett Publishing Co. ISBN 0-87108-664-6.
- Bagley, Will (2004). World Book Encyclopedia (S-Sn ed.). World Book Inc. pp. 76–76a. ISBN 0-7166-0104-4.
- McCormick, John S. (2000). The Gathering Place: An Illustrated History of Salt Lake City. Signature Books. ISBN 1-56085-132-5.
- Rainey, Virginia (2004). Insiders' Guide: Salt Lake City (4th ed.). Globe Pequot Press. ISBN 0-7627-2836-1.
- Stober, Daniel (2004). "Utah Street Names". Archived from the original on 21 August 2008. Retrieved 2004.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - McCarthy, Terry (3 February 2002). "The New Utah". Time.com.
- "Area Information – Salt Lake City's Climate". Salt Lake City. 1991. Archived from the original on 3 May 2005. Retrieved March 2005.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Area Information – Employment". Salt Lake City. 2002. Archived from the original on 6 March 2005. Retrieved March 2005.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Area Information – FAQ". Salt Lake City. 2005. Archived from the original on 24 October 2006. Retrieved March 2005.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Cities and Counties of Utah Census Brief" (PDF). May 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 April 2005. Retrieved 15 April 2005.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "NOAA Satellites and Information". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- "Salt Lake City History". Salt Lake City. 2004. Archived from the original on 17 August 2004. Retrieved September 2004.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Salt Lake City. 2005. Archived from the original on 2 March 2005. Retrieved March 2005.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|work=ignored (help); Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Mormon Tabernacle Choir [official website]". Intellectual Reserve, Inc. Retrieved 16 April 2013.
- Tullidge, Edward W. (1886). History of Salt Lake City. Salt Lake City: Star Printing Co. pp. 140–44.
External links
 Media related to Salt Lake City at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Salt Lake City at Wikimedia Commons Salt Lake City travel guide from Wikivoyage
Salt Lake City travel guide from Wikivoyage- . The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
- Official website
- "Salt Lake City". U.S. City Open Data Census. UK: Open Knowledge Foundation.
- Official Salt Lake City Convention and Visitors Bureau
- Articles with trivia sections from September 2016
- Salt Lake City
- Cities in Utah
- Holy cities
- County seats in Utah
- Planned cities in the United States
- Populated lakeshore places in the United States
- Populated places established in 1847
- Cities in Salt Lake City metropolitan area
- Wasatch Front
- 1847 establishments in the United States




