Baghlan Province: Difference between revisions
Updated population per Afghan Central Statistics Organization numbers |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.2.5) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
In the mid-20th Century, as Afghanistan became the target of international development from both the Western and Soviet world, agricultural-industrial projects were initiated in Baghlan. These included factories for the production of sugar from sugar beets (initiated by Czech experts in the 1940s<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bv4hzxpo424C&pg=PA38&dq=sugar+czech+baghlan&hl=en#v=onepage&q=sugar%20czech%20baghlan&f=false |title=Conflict in Afghanistan: A Historical Encyclopedia - Frank Clements |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref>) and for vegetable oil.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ITsMAQAAIAAJ&q=sugar+czech+baghlan&dq=sugar+czech+baghlan&hl=en |title=Asian Annual: The "Eastern World" Handbook |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> Czech expertise also figured heavily into the development of Baghlans' coal-mining industry,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LclscNCTz9oC&pg=PA85&dq=baghlan+coal+mine&hl=en#v=snippet&q=baghlan%20coal&f=false |title=The Far East and Australasia 2003 - Eur |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> centred at Baghlan's [[Karkar Valley]], the only coal mine in Afghanistan to remain operational up through 1992.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7LKS93lbSM0C&pg=PA42&dq=baghlan+karkar+coal&hl=en#v=onepage&q=baghlan%20karkar%20coal&f=false |title=Aiding Afghanistan: The Background and Prospects for Reconstruction in a ... - Asger Christensen |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> |
In the mid-20th Century, as Afghanistan became the target of international development from both the Western and Soviet world, agricultural-industrial projects were initiated in Baghlan. These included factories for the production of sugar from sugar beets (initiated by Czech experts in the 1940s<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bv4hzxpo424C&pg=PA38&dq=sugar+czech+baghlan&hl=en#v=onepage&q=sugar%20czech%20baghlan&f=false |title=Conflict in Afghanistan: A Historical Encyclopedia - Frank Clements |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref>) and for vegetable oil.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ITsMAQAAIAAJ&q=sugar+czech+baghlan&dq=sugar+czech+baghlan&hl=en |title=Asian Annual: The "Eastern World" Handbook |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> Czech expertise also figured heavily into the development of Baghlans' coal-mining industry,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LclscNCTz9oC&pg=PA85&dq=baghlan+coal+mine&hl=en#v=snippet&q=baghlan%20coal&f=false |title=The Far East and Australasia 2003 - Eur |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> centred at Baghlan's [[Karkar Valley]], the only coal mine in Afghanistan to remain operational up through 1992.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7LKS93lbSM0C&pg=PA42&dq=baghlan+karkar+coal&hl=en#v=onepage&q=baghlan%20karkar%20coal&f=false |title=Aiding Afghanistan: The Background and Prospects for Reconstruction in a ... - Asger Christensen |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> |
||
The modern Baghlan Province was created out of the former [[Qataghan Province]] in 1964.<ref name=Iranica>{{cite encyclopedia |
The modern Baghlan Province was created out of the former [[Qataghan Province]] in 1964.<ref name=Iranica>{{cite encyclopedia|author=D. Balland |author2=X. de Planhol |editor=[[Ehsan Yarshater]] |encyclopedia=[[Encyclopædia Iranica]] |title=BAGÚLAÚN |url=http://www.iranica.com/newsite/articles/v3f4/v3f4a082.html |accessdate=2007-12-19 |edition= |date= |year= |month= |publisher=[[Columbia University]] |volume= |location=[[United States]] |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20090102205056/http://www.iranica.com:80/newsite/articles/v3f4/v3f4a082.html |archivedate=2009-01-02 |df= }}</ref> |
||
During the [[Soviet–Afghan War]], the Soviets in 1982 established the Kayan military zone in southern Baghlan. The area was defended by 10,000 Ismaili militiamen, increasing to 18,000 by 1992, who sided with the Soviets due to differences with the Islamist opposition.<ref name="BhatiaSedra2008">{{cite book|author1=Michael V. Bhatia|author2=Mark Sedra|title=Afghanistan, arms and conflict: armed groups, disarmament and security in a post-war society|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YghqI97M56kC&pg=PA252|accessdate=30 March 2011|year=2008|publisher=Psychology Press|isbn=978-0-415-45308-0|pages=252–}}</ref> Afghan Ismailis overall were inclined to support the Communists, though a local Ismaili leader, [[Sayed Manuchehr]], lead a partisan movement against the Communists until Ismaili leader [[Sayed Mansur Naderi]] accepted Soviet support.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bY8ck6iktikC&pg=PA73&dq=manuchehr+baghlan&hl=en&ei=ktDoTqu-CqL50gGHlrHsCQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=manuchehr%20baghlan&f=false |title=Culture and Customs of Afghanistan - Hafizullah Emadi |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> |
During the [[Soviet–Afghan War]], the Soviets in 1982 established the Kayan military zone in southern Baghlan. The area was defended by 10,000 Ismaili militiamen, increasing to 18,000 by 1992, who sided with the Soviets due to differences with the Islamist opposition.<ref name="BhatiaSedra2008">{{cite book|author1=Michael V. Bhatia|author2=Mark Sedra|title=Afghanistan, arms and conflict: armed groups, disarmament and security in a post-war society|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YghqI97M56kC&pg=PA252|accessdate=30 March 2011|year=2008|publisher=Psychology Press|isbn=978-0-415-45308-0|pages=252–}}</ref> Afghan Ismailis overall were inclined to support the Communists, though a local Ismaili leader, [[Sayed Manuchehr]], lead a partisan movement against the Communists until Ismaili leader [[Sayed Mansur Naderi]] accepted Soviet support.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bY8ck6iktikC&pg=PA73&dq=manuchehr+baghlan&hl=en&ei=ktDoTqu-CqL50gGHlrHsCQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=manuchehr%20baghlan&f=false |title=Culture and Customs of Afghanistan - Hafizullah Emadi |publisher=Books.google.com |date= |accessdate=2015-06-18}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 03:42, 24 October 2016
Baghlan
بغلان | |
|---|---|
 Afghan National Army in Baghlan province | |
 Map of Afghanistan with Baghlan highlighted | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Puli Khumri |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Sultan Mohammad Ebadi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 21,118 km2 (8,154 sq mi) |
| Population (2013)[1] | |
| • Total | 863,700 |
| • Density | 41/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+4:30 |
| ISO 3166 code | AF-BGL |
| Main languages | Dari (Afghan Persian) Pashto |
Baghlan (Pashto/Persian: بغلان Baġlān) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. It is in the north of the country. As of 2013, the province has a population of about 910,700.[1]
Its capital is Puli Khumri, but its name comes from the other major town in the province, Baghlan. The ruins of a Zoroastrian fire temple, the Surkh Kotal, are located in Baghlan. The lead nation of the local Provincial Reconstruction Team (PRT) was Hungary, which operated from 2006 to 2015.
History
| History of Afghanistan |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
Early history
The name Baghlan is derived from Bagolango or "image-temple", inscribed on the temple of Surkh Kotal during the reign of the Kushan emperor, Kanishka in the early 2nd century CE. The Chinese Buddhist monk Xuanzang traveled through Baghlan in the mid-7th Century CE, and referred to it as the "kingdom of Fo-kia-lang".[2]
In the 13th Century CE, a permanent garrison of Mongol troops was quartered in the Kunduz-Baghlan area, and in 1253 fell under the jurisdiction of Sali Noyan Tatar, appointed there by Möngke Khan. Sali Noyan's positiion was later inherited by his son Uladu, and grandson Baktut.[3] These Turco-Mongol garrison troops (tamma) formed the Qara'unas faction, and by the 14th Century had allied with the Chaghataite Khanate. Under the rule of Temür the Qara'unas were given to Chekü Barlas, and then to his son Jahānshāh. Forbes Manz notes that these Kunduz-Baghlan forces appear to have remained cohesive and influential throughout the Timurid period, though under different leaders and different names, up until the Uzbek invasion.[when?][4] By the Islamic year 900 (1494-1495 CE), the area was noted in the Baburnama as ruled by a Qipchaq emir.[4]
20th century
In the mid-20th Century, as Afghanistan became the target of international development from both the Western and Soviet world, agricultural-industrial projects were initiated in Baghlan. These included factories for the production of sugar from sugar beets (initiated by Czech experts in the 1940s[5]) and for vegetable oil.[6] Czech expertise also figured heavily into the development of Baghlans' coal-mining industry,[7] centred at Baghlan's Karkar Valley, the only coal mine in Afghanistan to remain operational up through 1992.[8]
The modern Baghlan Province was created out of the former Qataghan Province in 1964.[9]
During the Soviet–Afghan War, the Soviets in 1982 established the Kayan military zone in southern Baghlan. The area was defended by 10,000 Ismaili militiamen, increasing to 18,000 by 1992, who sided with the Soviets due to differences with the Islamist opposition.[10] Afghan Ismailis overall were inclined to support the Communists, though a local Ismaili leader, Sayed Manuchehr, lead a partisan movement against the Communists until Ismaili leader Sayed Mansur Naderi accepted Soviet support.[11]
Large portions of Baghlan and neighbouring Samangan Province were under the sway of the Soviet-aligned Naderi clan, the hereditary Ismaili Sayeds (spiritual leaders) of Kayan. Under their jurisdiction, was largely quiet and societally functional throughout the 1980s, with hospitals, schools, and administrative services, funded by the communist central government. Despite the Naderi's alliance with the Communists, they also maintained positive relations with the Mujahideen as well, permitting them to move through the area provided they refrained from attacks.[12]
One of the Soviets' three primary bases in Afghanistan, Kiligai, was located in Baghlan Province, and served as the "largest military supply and armoury centre of the Soviet troops in Afghanistan."[13]
Recent history
As the 2001 Afghan War commenced, Ismaili spiritual leader Sayed Mansoor Naderi attempted to retake Baghlan from the Taliban. Naderi was aligned with Uzbek warlord Abdul Rashid Dostum and his Jumbesh-e Milli party, and the competing Tajik-dominated Jamiat-e Islami party was also keen to seize control of Baghlan as Taliban power eroded. The Jamiat were able to seize the capital of Pul-i Khumri before Naderi, who despite his strong backing among the Afghan Ismailis and Shia Hazaras, was unable to rally enough supporters to control the province. Naderi failed to retake the capital in 2001 and 2003, in the latter event he was forced by the dominant Andarabi militias to fall back to the Ismaili bastion of the Kayan Valley, and then to flee the region.[14]
On 13 June 2012, two earthquakes hit Afghanistan and there was a major landslide in Burka District of Baghlan Province. The village of Sayi Hazara was buried under up to 30 meters of rock, killing an estimated 71 people.
Politics and governance
The current governor of the province is Sultan Mohammad Ebadi. The town of Puli Khumri serves as the capital of the province. All law enforcement activities throughout the province are handled by the Afghan National Police (ANP). The provincial police chief represents the Ministry of the Interior in Kabul. The ANP is backed by other Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF), including the NATO-led forces.
Demographics
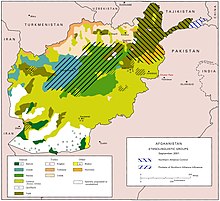
The population of Baghlan province was reported at 863,700 in the year 2013.[1] Tajiks make up 55% of the population, followed by 20% Pashtuns, 15% Hazaras, 9% Uzbeks, and the remainder are Tatar.[15] In another source Tajiks along their sub-groups like Aimaks and Sayyid-Tajiks make more than 70% of the provincial population. In addition, a significant number of Hazaras are also counted as part of the Persian-speaking people which stating Persian language as overwhelming speaking language, followed by Pashhtu-speaking Pashtuns, Uzbeks and some Tatars.[16] Baghlan is also home to a small community of Ismaili Muslims led by the Sayeds of Kayan.
Healthcare
The percentage of households with clean drinking water increased from 19% in 2005 to 25% in 2011.[17] The percentage of births attended to by a skilled birth attendant increased from 5.5% in 2005 to 22% in 2011.[17]
Education
The overall literacy rate (6+ years of age) increased from 21% in 2005 to 24% in 2011.[17] The overall net enrolment rate (6–13 years of age) increased from 29% in 2005 to 62% in 2011.[17]
Economy
Agriculture
Baghlan's primary crops (as of 1974) were cotton and sugar beets, industrial sugar production having begun under Czech supervision in the 1940s. The area also produced grapes, pistachios, and pommegranates. The primary livestock are Karakul sheep.[18]
Other products
The province also produces silk, and coal is mined in the Karkar Valley.[18]
Districts

| District | Capital | Population[1] | Area | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andarab | 24,800 | Sub-divided in 2005 | ||
| Baghlani Jadid | 167,200 | |||
| Burka | 52,200 | |||
| Dahana-I-Ghuri | 57,300 | |||
| Dih Salah | 31,100 | Created in 2005 within Andarab District | ||
| Dushi | 65,000 | |||
| Farang Wa Gharu | 16,100 | Created in 2005 within Khost Wa Fereng District | ||
| Guzargahi Nur | 9,900 | Created in 2005 within Khost Wa Fereng District | ||
| Khinjan | 29,600 | |||
| Khost Wa Fereng | 61,300 | Sub-divided in 2005 | ||
| Khwaja Hijran | 23,200 | Created in 2005 within Andarab District | ||
| Nahrin | 67,200 | |||
| Puli Hisar | 26,800 | Created in 2005 within Andarab District | ||
| Puli Khumri | Puli Khumri | 203,600 | ||
| Tala wa Barfak | 29,400 |
See also
References
- ^ a b c d "Settled Population of Baghlan province by Civil Division, Urban, Rural and Sex-2015-16". Islamic Republic of Afghanistan: Central Statistics Organization. Retrieved September 6, 2015.
- ^ Xuanzang. Record of the Western Regions. translated by Samuel Beal (1884) in Buddhist Records of the Western World, London: Trubner & Co. Ltd., 1884
- ^ "The Rise and Rule of Tamerlane - Beatrice Forbes Manz". Books.google.com. 1999-03-25. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ a b "The Rise and Rule of Tamerlane - Beatrice Forbes Manz". Books.google.com. 1999-03-25. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "Conflict in Afghanistan: A Historical Encyclopedia - Frank Clements". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "Asian Annual: The "Eastern World" Handbook". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "The Far East and Australasia 2003 - Eur". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "Aiding Afghanistan: The Background and Prospects for Reconstruction in a ... - Asger Christensen". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ D. Balland; X. de Planhol. "BAGÚLAÚN". In Ehsan Yarshater (ed.). Encyclopædia Iranica. United States: Columbia University. Archived from the original on 2009-01-02. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Michael V. Bhatia; Mark Sedra (2008). Afghanistan, arms and conflict: armed groups, disarmament and security in a post-war society. Psychology Press. pp. 252–. ISBN 978-0-415-45308-0. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- ^ "Culture and Customs of Afghanistan - Hafizullah Emadi". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "Empires of Mud: The Neo-Taliban Insurgency in Afghanistan 2002-2007 - Antonio Giustozzi". Books.google.com. 2011-02-10. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "Summary of World Broadcasts: Far East". Books.google.com. 2009-05-11. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ "Empires of Mud: The Neo-Taliban Insurgency in Afghanistan 2002-2007 - Antonio Giustozzi". Books.google.com. 2011-02-10. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ^ Baghlan province on NPS
- ^ http://www.mrrd.gov.af/nabdp/Provincial%20Profiles/Baghlan%20PDP%20Provincial%20profile.pdf
- ^ a b c d [1] Archived 2014-05-31 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "Conflict in Afghanistan: A Historical Encyclopedia - Frank Clements". Books.google.com. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
