From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
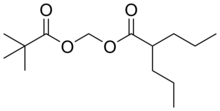
Valproate pivoxil (Pivadin, Valproxen) is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy.[1] It is the pivaloyloxymethyl ester derivative of valproic acid.[2] It is likely a prodrug of valproic acid, as pivoxil esters are commonly employed to make prodrugs in medicinal chemistry.
See also
References
|
|---|
| Transporter | | GATTooltip GABA transporter | |
|---|
| VIAATTooltip Vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Enzyme | | GADTooltip Glutamate decarboxylase | |
|---|
| GABA-TTooltip γ-Aminobutyrate aminotransferase | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Other | |
|---|
|
|
|---|
| Calcium | | VDCCsTooltip Voltage-dependent calcium channels | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Potassium | | VGKCsTooltip Voltage-gated potassium channels | |
|---|
| IRKsTooltip Inwardly rectifying potassium channel | |
|---|
| KCaTooltip Calcium-activated potassium channel | |
|---|
| K2PsTooltip Tandem pore domain potassium channel | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Sodium | | VGSCsTooltip Voltage-gated sodium channels | |
|---|
| ENaCTooltip Epithelial sodium channel | |
|---|
| ASICsTooltip Acid-sensing ion channel | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Chloride | | CaCCsTooltip Calcium-activated chloride channel | |
|---|
| CFTRTooltip Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | |
|---|
| Unsorted | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Others | | TRPsTooltip Transient receptor potential channels | |
|---|
| LGICsTooltip Ligand gated ion channels | |
|---|
|
|---|
|