From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Pharmaceutical compound
Aprobarbital Other names aprobarbital, Oramon, allylpropymal, Alurate, 5-isopropyl- 5-allylbarbituric acid AHFS /Drugs.com Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information ATC code Legal status
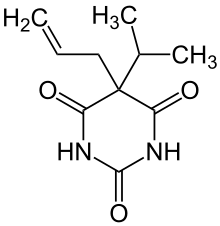
5-propan-2-yl-5-prop-2-enyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione
CAS Number PubChem CID DrugBank ChemSpider UNII KEGG ChEBI ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) ECHA InfoCard 100.000.908 Formula C 10 H 14 N 2 O 3 Molar mass 210.23 g/mol g·mol−1 3D model (JSmol )
O=C1NC(=O)NC(=O)C1(C(C)C)C\C=C
InChI=1S/C10H14N2O3/c1-4-5-10(6(2)3)7(13)11-9(15)12-8(10)14/h4,6H,1,5H2,2-3H3,(H2,11,12,13,14,15)
Y Key:UORJNBVJVRLXMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Y (verify)
Aprobarbital (as known in the United States , or aprobarbitone (as known elsewhere), sold as Oramon , Somnifaine , and Allonal , is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s by Ernst Preiswerk. It has sedative , hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily for the treatment of insomnia .[ 1] phenobarbital and is now rarely prescribed as it has been replaced by newer drugs with a better safety margin.
See also: Alphenal
References
^ Reddemann H, Turk E. Oramon poisoning in infancy and childhood. Observations on 12 aprobarbital poisonings (German). Das Deutsche Gesundheitswesen. 1966 May 12;21(19):878-81.
Alcohols Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Carbamates Flavonoids Imidazoles Kava constituentsMonoureides Neuroactive steroids Nonbenzodiazepines Phenols Piperidinediones Pyrazolopyridines Quinazolinones Volatiles /gases Others/unsorted
3-Hydroxybutanal α-EMTBL AA-29504 Alogabat Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide , potassium bromide , sodium bromide )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole Darigabat DEABL Deuterated etifoxine Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine , dihydroergosine , dihydroergotamine , ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )DS2 Efavirenz Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid , mefenamic acid , niflumic acid , tolfenamic acid )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Hopantenic acid KRM-II-81 Lanthanum Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol , honokiol , magnolol , obovatol )Loreclezole Menthyl isovalerate (validolum) Monastrol Niacin Niacinamide Org 25,435 Phenytoin Propanidid Retigabine (ezogabine) Safranal Seproxetine Stiripentol Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) , tetronal , trional )Terpenoids (e.g., borneol )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid , isovaleramide , valerenic acid , valerenol )
Alcohols Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Carbamates Flavonoids Imidazoles Kava constituentsMonoureides Neuroactive steroids Nonbenzodiazepines Phenols Piperidinediones Pyrazolopyridines Quinazolinones Volatiles /gases Others/unsorted
3-Hydroxybutanal α-EMTBL AA-29504 Alogabat Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide , potassium bromide , sodium bromide )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole Darigabat DEABL Deuterated etifoxine Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine , dihydroergosine , dihydroergotamine , ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )DS2 Efavirenz Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid , mefenamic acid , niflumic acid , tolfenamic acid )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Hopantenic acid KRM-II-81 Lanthanum Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol , honokiol , magnolol , obovatol )Loreclezole Menthyl isovalerate (validolum) Monastrol Niacin Niacinamide Org 25,435 Phenytoin Propanidid Retigabine (ezogabine) Safranal Seproxetine Stiripentol Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) , tetronal , trional )Terpenoids (e.g., borneol )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid , isovaleramide , valerenic acid , valerenol )