Economy of the European Union
 London is the largest city in the EU | |
| Currency | € (EUR) - Euro/Ευρώ/Евро = 1.05USD |
|---|---|
Trade organisations | WTO, G-20, G7 |
| Statistics | |
| GDP | $16.97 trillion (nominal, 2017)[1] $20.75 trillion (PPP, 2017)[1] |
GDP growth | 0.3% (Q2 2016)[2] |
GDP per capita | $33,300 $40,600 |
GDP by sector | 71.3% services 24.4% industry 1.6% agriculture (2015)[1] |
Population below poverty line | 9.8%[1] |
| 31 (2015)[3] | |
Labour force | 232 million (2015)[1] 20.973 million unemployed (August 2016)[4] |
Labour force by occupation | agriculture: 5% industry: 21,9% services: 73.1% (2014)[1] |
| Unemployment | |
| $20,000, annual(2015) | |
Main industries | List
|
| External | |
| Exports | €1,790.7 billion (goods, 2015)[5] €684.4 billion (services, 2013)[6] |
Export goods | List
|
Main export partners |
|
| Imports | €1,756.5 billion (goods, 2015)[5] €511.2 billion (services, 2013)[6] |
Import goods | List
|
Main import partners |
|
FDI stock | €4 trillion (inward, 2012)[7] € 5.206 trillion (outward, 2012)[8] |
| Public finances | |
| Revenues | 45.0% of GDP (2015)[12] |
| Expenses | 47.4% of GDP (2015)[13] |
| Economic aid | €15 billion (2013)[14] |
| $0.6 trillion (2010).[16] | |
The European Union is the second largest economy in the world (if treated as a single country) in nominal terms and according to purchasing power parity (PPP). The European Union's GDP was estimated to be €16.5 trillion (nominal) in 2016 according to the International Monetary Fund, representing 22,8% of nominal global GDP.[17]
The euro, used by 19 of its 28 members, is the second largest reserve currency as well as the second most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar.[18][19][20] The euro is the official currency in the eurozone and in six other European countries, officially or de facto. All the members of the European Union are obliged to join the eurozone, except the United Kingdom and Denmark who have negotiated opt-outs.
The European Union (EU) economy consists of an internal market of mixed economies based on free market and advanced social models. The GDP per capita (PPP) was $37,800 in 2015,[1] compared to $57,084 in the United States and $14,340 in China.[21] With a low Gini coefficient of 31, the European Union has a more egalitarian repartition of incomes than the world average.[22][23]
Euronext is the main stock exchange of the Eurozone and the 7th world largest by market capitalisation.[24] Foreign investments made in the European Union total $5.1 trillion in 2012, while the E.U's investments in foreign countries total 9.1 trillion, by far the highest domestic and foreign investments in the world.[25][26]
Since the beginning of the public debt crisis in 2009, opposite economic situations have emerged between Southern Europe on one hand, and Central and Northern Europe on the other hand : a high unemployment rate and public debt in the Mediterranean countries, and a low unemployment rate with higher GDP growth rate in the former Eastern communist countries and in the Northern countries. In 2015, public debt in the European Union was slightly above 85% of GDP, with important disparities between the lowest rate, Estonia with 9,7%, and the highest, Greece with 176%.[27]
The seven largest trading partners of the European Union are the United States, China, Switzerland, Russia, Japan, Turkey and Norway. The EU is represented as a unified entity in the World Trade Organization (WTO), the G-20 and G7, alongside with the EU's member countries participating.
Currency
Beginning in the year 1999 with some EU member states, now 19 out of 28 EU states use the euro as official currency in a currency union. The remaining 9 states continued to use their own currency with the possibility to join the euro later. The euro is also the most widely used currency in the EU.
Since 1992 the Maastricht treaty sets out rigid economic and fiscal convergence criteria for the states joining the euro. Starting 1997, the Stability and Growth Pact has been started to ensure continuing economic and fiscal stability and convergence.
Denmark and the United Kingdom, not members of the eurozone, have special opt-outs concerning the later joining of the euro. Also, Sweden can effectively opt out by choosing when or whether to join the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, which is the preliminary step towards joining. The remaining states are committed to join the euro through their Treaties of Accession.
Starting with Greece in 2009, five of the 19 eurozone states have been struggling with a sovereign debt crisis, by many called the European debt crisis. All these states started reforms and got bailout packages (Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Spain, Cyprus). As of May 2015, all countries but Greece have recovered from their debt crisis (Greece is recovering as of April 2016, though[citation needed]). Other non-eurozone states also experienced a debt crisis and also went through successful bailout programmes, i.e. Hungary, Romania and Latvia (the latter before it joined the eurozone).[28]
Budget
The operation of the EU has an agreed budget of €141 billion for the year 2011, and €862 billion for the period 2007–2013,[29] this represents around 1% of the EU's GDP.
Industries
The services sector is by far the most important sector in the European Union, making up 74.7% of GDP, compared to the manufacturing industry with 23.8% of GDP and agriculture with only 1.5% of GDP.[30]
Agriculture
The agricultural sector is supported by subsidies from the European Union in the form of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP). In 2013 this represented approximately €45billion (less than 33% of the overall budget of €148billion) of the EU's total spending.[31] It was used originally to guarantee a minimum price for farmers in the EU. This is criticised as a form of protectionism, inhibiting trade, and damaging developing countries; one of the most vocal opponents is the UK, the second largest economy within the bloc, which has repeatedly refused to give up the annual UK rebate unless the CAP undergoes significant reform; France, the biggest beneficiary of the CAP and the bloc's third largest economy, is its most vocal proponent. The CAP is however witnessing substantial reform. In 1985, around 70% of the EU budget was spent on agriculture. In 2011, direct aid to farmers and market-related expenditure amount to just 30% of the budget, and rural development spending to 11%. By 2011, 90% of direct support had become non-trade-distorting (not linked to production) as reforms have continued to be made to the CAP, its funding and its design.[32]
Tourism
The European Union is a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from outside of the Union and citizens travelling inside it. Internal tourism is made more convenient by the Schengen treaty and the euro. All citizens of the European Union are entitled to travel to any member state without the need of a visa.
France is the world's number one tourist destination for international visitors, followed by Spain, Italy, Germany and the United Kingdom. It is worth noting, however, that a significant proportion of international visitors to EU countries are from other member states.
London, the capital of the United Kingdom is also the world's most visited city (16.9 million visitors in 2012) and the highest in tourism receipts, shortly followed by Paris with 16 million visitors.[33]
Companies
The European Union's member states are the birthplace of many of the world's largest leading multinational companies, and home to its global headquarters. Among these are distinguished companies ranked first in the world within their industry/sector, like Allianz, which is the largest financial service provider in the world by revenue; WPP plc which is the world's largest advertising agency by revenue; Airbus, which is the world's largest aircraft manufacturer;[34] Air France-KLM, which is the largest airline company in the world in terms of total operating revenues; Amorim, which is the world's largest cork-processing and cork producer company; ArcelorMittal, which is the largest steel company in the world; Inditex which is the biggest fashion group in the world; Groupe Danone, which has the world leadership in the dairy products market.[citation needed]
Anheuser-Busch InBev is the largest beer company in the world; L'Oréal Group, which is the world's largest cosmetics and beauty company; LVMH, which is the world's largest luxury goods conglomerate; Nokia Corporation, which is the world's largest manufacturer of mobile telephones; Royal Dutch Shell, which is one of the largest energy corporations in the world; and Stora Enso, which is the world's largest pulp and paper manufacturer in terms of production capacity, in terms of banking and finance the EU has some of the worlds largest notably HSBC and Grupo Santander, the largest bank in Europe in terms of Market Capitalisation.[citation needed]
Many other European companies rank among the world's largest companies in terms of turnover, profit, market share, number of employees or other major indicators. A considerable number of EU-based companies are ranked among the worlds' top-ten within their sector of activity. Europe is also home to many prestigious car companies such as BMW, Ferrari, Jaguar, Land Rover, Maserati, Mercedes, Porsche, as well as volume manufacturers such as Fiat, PSA group, Renault and Volkswagen.[citation needed]
Economies of member states
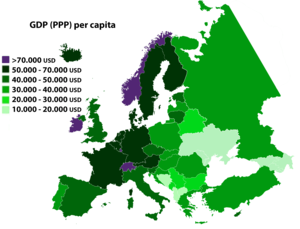

Below is a table showing, respectively, the GDP and the GDP (PPP) per capita for the European Union and for each of its member states, ordered according to the 'Size' of their economies. The table can also be used as a rough gauge to the relative standards of living among member states, with Luxembourg the highest and Bulgaria the lowest. Eurostat, based in Luxembourg, is the Official Statistical Office of the European Communities releasing yearly GDP figures for the member states as well as the EU as a whole, which are regularly updated, supporting this way a measure of wealth and a base for the European Union's budgetary and economic policies. Figures are stated in euros.
Economic performance varies from state to state. The Growth and Stability Pact governs fiscal policy with the European Union. It applies to all member states, with specific rules which apply to the eurozone members that stipulate that each state's deficit must not exceed 3% of GDP and its public debt must not exceed 60% of GDP. Many larger members have consistently run deficits substantially in excess of 3%, and the eurozone as a whole has a debt percentage exceeding 60% (see below).
| Member state sorted by GDP |
GDP (Nominal) in billions of euro (2015)[35] |
GDP (Nominal) per capita 2015 euro[35] |
GDP (PPS) per capita 2015 euro[36] |
Public debt[37] % of GDP (2015) |
Deficit (-)/ Surplus (+)[38] % of GDP (2015) |
Inflation % Annual[39] (2015) |
Unemp.[40] % 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14,702.1 | 28,800 | 28,800 | 85.2 | −2.4 | 0.0 | 9.4 | |
| 3,032.8 | 37,100 | 36,000 | 71.2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 4.6 | |
| 2,577.3 | 39,600 | 31,600 | 89.2 | −4.4 | 0.0 | 5.3 | |
| 2,181.1 | 32,800 | 30,300 | 95.8 | −3.5 | 0.1 | 10.4 | |
| 1,642.4 | 27,000 | 27,500 | 132.7 | −2.6 | 0.1 | 11.9 | |
| 1,075.6 | 23,200 | 26,200 | 99.2 | −5.1 | -0.6 | 22.1 | |
| 676.5 | 40,000 | 36,800 | 65.1 | −1.8 | 0.2 | 6.9 | |
| 447.0 | 45,600 | 35,600 | 43.4 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 7.4 | |
| 429.8 | 11,200 | 19,800 | 51.3 | −2.6 | -0.7 | 7.5 | |
| 410.4 | 36,600 | 33,800 | 106.0 | −2.6 | 0.6 | 8.5 | |
| 339.9 | 39,400 | 36,600 | 86.2 | -1.2 | 0.8 | 5.7 | |
| 271.8 | 47,800 | 36,200 | 40.2 | -2.1 | 0.2 | 6.2 | |
| 255.8 | 55,100 | 49,600 | 93.8 | −2.3 | 0.0 | 9.4 | |
| 209.2 | 38,200 | 31,200 | 63.1 | −2.7 | -0.2 | 9.4 | |
| 179.5 | 17,300 | 22,300 | 129.0 | −4.4 | 0.5 | 12.6 | |
| 176.0 | 16,200 | 20,300 | 176.9 | −7.2 | −1.1 | 24.9 | |
| 167.0 | 15,800 | 25,000 | 41.1 | −0.4 | 0.3 | 5.1 | |
| 160.4 | 8,100 | 16,300 | 38.4 | −0.7 | -0.4 | 6.8 | |
| 109.7 | 11,100 | 19,700 | 75.3 | −2.0 | 0.1 | 6.8 | |
| 78.7 | 14,500 | 22,200 | 52.9 | -3.0 | −0.3 | 11.5 | |
| 51.2 | 89,900 | 76,400 | 21.4 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 6.1 | |
| 45.3 | 6,300 | 13,300 | 26.7 | −2.1 | −1.1 | 9.2 | |
| 43.8 | 10,400 | 16,700 | 86.7 | −3.2 | -0.3 | 16.3 | |
| 38.6 | 18,700 | 23,700 | 83.2 | −2.9 | -0.8 | 9.0 | |
| 37.3 | 12,900 | 21,300 | 42.7 | −0.2 | -0.7 | 9.1 | |
| 24.4 | 12,300 | 18,500 | 36.4 | −1.3 | 0.2 | 9.9 | |
| 20.3 | 15,400 | 21,200 | 9.7 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 6.2 | |
| 17.6 | 20,800 | 23,500 | 108.9 | −1.0 | −1.6 | 15.1 | |
| 8.8 | 20,300 | 25,400 | 63.9 | −1.5 | 1.2 | 5.4 |
Economic growth


The EU's share of gross world product (GWP) is stable at around one fifth.[41]
The twelve new member states of the European Union have enjoyed a higher average percentage growth rate than their elder members of the EU. Slovakia has the highest GDP growth in the period 2005–2011 among all countries of the European Union (See Tatra Tiger). Notably the Baltic states have achieved high GDP growth, with Latvia topping 11%, close to China, the world leader at 9% on average for the past 25 years (though these gains have been in great part cancelled by the late-2000s recession).
Reasons for this growth include government commitments to stable monetary policy, export-oriented trade policies, low flat-tax rates and the utilisation of relatively cheap labour. In 2015 Ireland had the highest GDP growth of all the states in EU (5.2%). The current map of EU growth is one of huge regional variation, with the larger economies suffering from stagnant growth and the new nations enjoying sustained, robust economic growth.
Although EU28 GDP is on the increase, the percentage of gross world product is decreasing because of the emergence of economic powers such as China, India and Brazil.
| Member state | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Growth (base year 2004)[43] | Yearly average since 2004
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 1.5 | −3.8 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 14.5 | 1.3 | |
| 2.1 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 0.7 | −2.3 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 0.1 | -0.1 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 14.5 | 1.3 | |
| 7.1 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 6.0 | −3.6 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 3.6 | 34.6 | 2.8 | |
| 4.2 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 2.1 | −7.4 | −1.7 | −0.3 | −2.2 | −1.1 | −0.5 | 1.6 | 4.1 | 0.4 | |
| 3.7 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 3.9 | −1.8 | 1.3 | 0.3 | −3.2 | −6.0 | −1.5 | 1.7 | 7.2 | 0.7 | |
| 6.4 | 6.9 | 5.5 | 2.7 | −4.8 | 2.3 | 2.0 | −0.8 | −0.5 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 29.7 | 2.4 | |
| 2.3 | 3.9 | 0.9 | −0.5 | −4.9 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 6.1 | 0.6 | |
| 9.4 | 10.3 | 7.7 | −5.4 | −14.7 | 2.3 | 7.6 | 4.3 | 1.4 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 28.6 | 2.6 | |
| 2.8 | 4.1 | 5.2 | 0.7 | −8.3 | 3.0 | 2.6 | −1.4 | −0.8 | −0.7 | 0.2 | 7.7 | 0.7 | |
| 1.6 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 0.2 | −2.9 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 10.4 | 0.9 | |
| 0.7 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 1.1 | −5.6 | 4.1 | 3.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 15.6 | 1.4 | |
| 0.6 | 5.7 | 3.3 | −0.3 | −4.3 | −5.5 | −9.1 | −7.3 | −3.2 | 0.4 | −0.2 | −18.8 | −1.8 | |
| 4.4 | 3.9 | 0.4 | 0.9 | −6.6 | 0.7 | 1.7 | −1.6 | 2.1 | 4.0 | 3.1 | 12.2 | 1.1 | |
| 5.8 | 5.9 | 3.8 | −4.4 | −4.6 | 2.0 | 0.0 | -1.1 | 1.1 | 8.5 | 26.3 | 30.6 | 2.5 | |
| 0.9 | 2.0 | 1.5 | −1.1 | −5.5 | 1.7 | 0.6 | −2.8 | −1.7 | 0.1 | 0.7 | −3.9 | −0.3 | |
| 10.7 | 11.9 | 9.9 | −3.6 | −14.3 | −3.8 | 6.2 | 4.0 | 2.9 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 29.5 | 2.7 | |
| 7.7 | 7.4 | 11.1 | 2.6 | −14.8 | 1.6 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 36.1 | 3.1 | |
| 3.2 | 5.1 | 8.4 | −0.8 | −5.4 | 5.8 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 4.2 | 4.7 | 3.5 | 33.6 | 2.8 | |
| 3.8 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 3.3 | −2.5 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 6.2 | 37.7 | 3.0 | |
| 2.2 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 1.7 | −3.8 | 1.4 | 1.7 | −1.1 | −0.2 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 12.0 | 1.1 | |
| 3.5 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 3.6 | 5.0 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 50.6 | 3.8 | |
| 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 0.2 | −3.0 | 1.9 | −1.8 | −4.0 | −1.1 | 0.9 | 1.6 | -0.7 | 0.0 | |
| 4.2 | 8.1 | 6.9 | 8.5 | −7.1 | −0.8 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 3.5 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 35.5 | 2.9 | |
| 6.8 | 8.5 | 10.8 | 5.6 | −5.4 | 5.0 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 2.6 | 3.8 | 50.8 | 3.9 | |
| 4.0 | 5.7 | 6.9 | 3.3 | −7.8 | 1.2 | 0.6 | −2.7 | −1.1 | 3.1 | 2.3 | 16.2 | 1.5 | |
| 3.7 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 1.1 | −3.6 | 0.0 | −1.0 | −2.9 | −1.7 | 1.4 | 3.2 | 8.4 | 0.8 | |
| 2.8 | 4.7 | 3.4 | −0.6 | −5.2 | 6.0 | 2.7 | −0.3 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 22.6 | 1.9 | |
| 3.0 | 2.5 | 2.6 | −0.6 | −4.3 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 2.2 | 16.4 | 1.4 | |
| 2.1 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 0.4 | −4.4 | 2.1 | 1.7 | −0.5 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 10.6 | 1.0 | |
| Eurozone | 1.6 | 3.2 | 3.0 | 0.4 | −4.5 | 2.1 | 1.5 | −0.9 | −0.3 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 8.9 | 0.8 |
Energy resources

The European Union has uranium, coal, oil, and natural gas reserves. There are six oil producers in the European Union, primarily in North Sea oilfields. The United Kingdom is by far the largest producer; Denmark, Germany, Italy, Romania and the Netherlands all produce oil. If it is treated as a single unit, which is not conventional in the oil markets, the European Union is the 19th largest producer of oil in the world, producing 1,241,370 (2013) barrels a day.[citation needed]
It is the world's second largest consumer of oil, consuming much more than it can produce, at 12,790,000 (2013) barrels a day. Much of the difference comes from Russia and the Caspian Sea basin. All countries in the EU have committed to the Kyoto Protocol, and the European Union is one of its biggest proponents. The European Commission published proposals for the first comprehensive EU energy policy on 10 January 2007.[citation needed]
Trade



The European Union is the largest exporter in the world[44] and as of 2008 the largest importer of goods and services.[45] Internal trade between the member states is aided by the removal of barriers to trade such as tariffs and border controls. In the eurozone, trade is helped by not having any currency differences to deal with amongst most members.[46]
The European Union Association Agreement does something similar for a much larger range of countries, partly as a so-called soft approach ('a carrot instead of a stick') to influence the politics in those countries. The European Union represents all its members at the World Trade Organization (WTO), and acts on behalf of member states in any disputes. When the EU negotiates trade related agreement outside the WTO framework, the subsequent agreement must be approved by each individual EU member.[46]
| Main trading partners (2015)[47] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Trade with partner country groupings(2012)[47] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Main trade partners[48] | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exports (million euro) | Imports (million euro) | Total Trade (million euro) | Exports | Imports | Total Trade | Exports | Imports | Total Trade | Exports | Imports | Total Trade | |
| Total EU | 1,319,819 | 1,582,932 | 2,902,751 | 1,101,746 | 1,234,317 | 2,336,063 | 1,360,059 | 1,531,043 | 2,891,102 | 1,561,890 | 1,726,514 | 3,288,404 |
| 247,818 | 182,351 | 430,169 | 203,587 | 154,862 | 358,449 | 242,451 | 173,067 | 415,518 | 263,791 | 191,555 | 455,346 | |
| 78,276 | 247,815 | 326,091 | 82,391 | 214,238 | 296,629 | 113,426 | 282,509 | 395,935 | 136,372 | 293,693 | 430,065 | |
| 104,843 | 178,294 | 283,137 | 65,587 | 118,122 | 183,709 | 86,134 | 160,709 | 246,843 | 108,355 | 199,922 | 308,277 | |
| 100,537 | 82,348 | 182,885 | 88,693 | 80,570 | 169,263 | 110,401 | 85,228 | 195,629 | 142,022 | 93,202 | 235,224 | |
| 43,698 | 95,888 | 139,586 | 37,476 | 68,864 | 106,340 | 41,914 | 78,981 | 120,895 | 46,678 | 93,813 | 140,491 | |
| 42,347 | 76,177 | 118,524 | 35,932 | 58,233 | 94,165 | 43,948 | 67,258 | 111,206 | 49,018 | 69,549 | 118,567 | |
| 54,415 | 45,963 | 100,378 | 44,385 | 36,228 | 80,613 | 61,747 | 42,397 | 104,144 | 73,096 | 48,143 | 121,239 | |
| 31,349 | 29,540 | 60,889 | 27,477 | 25,414 | 52,891 | 34,866 | 33,308 | 68,112 | 40,558 | 39,906 | 80,464 | |
| 25,491 | 39,565 | 65,056 | 21,596 | 32,370 | 53,966 | 27,957 | 39,391 | 67,348 | 32,510 | 36,175 | 68,685 | |
| 26,302 | 35,855 | 62,157 | 21,574 | 25,926 | 47,500 | 31,466 | 33,238 | 64,704 | 35,752 | 38,939 | 74,691 | |
| 25,468 | 25,043 | 50,511 | 21,934 | 19,285 | 41,219 | 26,758 | 24,697 | 51,455 | 29,885 | 30,708 | 60,593 | |
| 22,213 | 16,137 | 38,350 | 20,404 | 14,579 | 34,983 | 24,550 | 18,760 | 43,310 | 27,256 | 19,184 | 46,440 | |
| 20,800 | 24,597 | 45,397 | 16,083 | 19,229 | 35,312 | 21,755 | 20,406 | 42,161 | 26,212 | 21,807 | 48,019 | |
| 21,081 | 22,001 | 43,082 | 19,068 | 11,766 | 30,834 | 23,216 | 16,300 | 39,516 | 26,401 | 28,440 | 54,841 | |
| 11,595 | 24,069 | 35,660 | 10,021 | 17,875 | 27,896 | 14,782 | 24,138 | 38,920 | 16,212 | 24,230 | 40,532 | |
| 21,786 | 12,258 | 34,044 | 19,667 | 13,277 | 32,944 | 27,250 | 14,302 | 41,552 | 30,763 | 10,969 | 41,732 | |
| 26,689 | 13,785 | 40,474 | 21,930 | 9,923 | 31,853 | 26,955 | 12,454 | 39,409 | 31,159 | 14,944 | 46,103 | |
| 15,391 | 28,259 | 43,650 | 14,807 | 17,410 | 32,217 | 15,584 | 21,069 | 36,653 | 17,279 | 27,844 | 45,123 | |
| 5,836 | 35,308 | 41,144 | 6,484 | 20,870 | 27,354 | 7,087 | 29,230 | 36,317 | 2,093 | 10,444 | 12,537 | |
| 21,976 | 13,981 | 35,597 | 15,988 | 10,135 | 26,123 | 21,342 | 13,748 | 35,090 | 23,908 | 16,985 | 40,893 | |
Unemployment

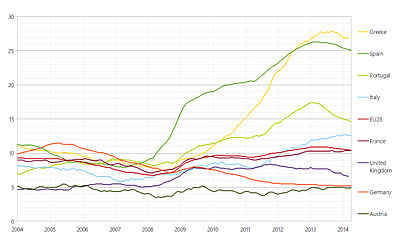
The EU seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was 8.6% in May 2016. The euro area unemployment rate was 10.1%.[49]
Among the member states, the lowest unemployment rates were recorded in the Czech Republic (4.0%), Malta (4.1%) and Germany (4.2%), and the highest in Spain (19.8%) and Greece (23.3% in April 2016).[49]
The following table shows the history of the unemployment rate for all European Union member states:
| Unemployment[50] | 2005-03 | 2006-03 | 2007-03 | 2008-03 | 2009-03 | 2010-03 | 2011-03 | 2012-03 | 2013-03 | 2014-03 | 2015-03 | 2016-03 | 2016-08[51] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.5 | 5.7 | 4.9 | 4.1 | 5.0 | 4.9 | 4.7 | 4.6 | 5.4 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 6.2 | |
| 8.6 | 8.6 | 7.9 | 6.7 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 6.9 | 7.1 | 8.3 | 8.5 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.2 | |
| 5.2 | 4.2 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 5.3 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.7 | 7.1 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 5.8 | 6.2 | |
| 8.5 | 7.9 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 7.6 | 8.5 | 7.9 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 8.4 | 9.2 | 9.3 | ||
| 8.6 | 9.1 | 8.4 | 7.2 | 8.9 | 9.3 | 9.1 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 10.5 | |
| 10.9 | 10.4 | 8.9 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 5.4 | 5.3 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 4.2 | |
| 10.0 | 9.3 | 8.9 | 8.2 | 9.1 | 11.6 | 16.0 | 22.7 | 27.1 | 26.9 | 26.0 | 23.7 | 23.3 | |
| 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 5.2 | 11.1 | 13.2 | 14.3 | 15.0 | 13.6 | 12.0 | 9.8 | 8.6 | 8.3 | |
| 7.8 | 7.1 | 5.9 | 6.4 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 8.0 | 10.5 | 11.9 | 12.7 | 12.4 | 11.4 | 11.4 | |
| 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 5.4 | 4.6 | 4.7 | 5.1 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 6.3 | 6.2 | |
| 6.0 | 5.3 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 5.1 | 4.8 | 5.5 | 6.9 | 7.8 | 7.0 | 6.4 | 5.8 | |
| 8.5 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 8.6 | 10.1 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 15.0 | 17.2 | 14.7 | 13.2 | 12.1 | 11.0 | |
| 9.7 | 8.7 | 8.1 | 9.4 | 17.4 | 19.5 | 20.7 | 23.9 | 26.3 | 25.2 | 23.0 | 20.4 | 19.5 | |
| 7.3 | 7.4 | 6.5 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 8.8 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 7.2 | 7.0 | |
| 4.6 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 5.2 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 7.7 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 6.6 | 5.4 | 5.1 | ||
| 10.5 | 9.0 | 7.2 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 9.9 | 11.2 | 12.1 | 13.0 | 11.9 | 10.0 | 7.3 | 7.7 | |
| 13.2 | 12.3 | 10.5 | 9.1 | 8.9 | 10.8 | 13.7 | 15.5 | 16.5 | 17.7 | 16.6 | 14.9 | 12.9 | |
| 5.2 | 5.1 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 4.6 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 10.7 | 14.9 | 16.2 | 16.2 | 12.1 | 12.1 | |
| 8.0 | 7.6 | 5.6 | 4.4 | 5.9 | 7.7 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 7.2 | 6.5 | 5.6 | 4.1 | 3.9 | |
| 8.6 | 6.3 | 5.1 | 4.3 | 11.9 | 19.2 | 14.0 | 11.1 | 9.1 | 7.9 | 6.7 | 6.8 | 6.8 | |
| 6.9 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.5 | 9.6 | 11.4 | 11.1 | 11.3 | 10.6 | 7.9 | 7.3 | 5.6 | 5.1 | |
| 10.7 | 7.9 | 6.6 | 6.4 | 14.8 | 20.4 | 16.7 | 15.9 | 11.9 | 11.1 | 9.8 | 9.9 | 9.3 | |
| 9.3 | 6.2 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 11.6 | 17.8 | 16.5 | 14.0 | 12.1 | 11.5 | 9.3 | 8.5 | 8.6 | |
| 7.2 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 5.9 | 6.6 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.2 | 5.9 | 5.7 | 4.7 | 4.8 | |
| 18.2 | 14.9 | 10.3 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 10.0 | 9.4 | 9.8 | 10.6 | 9.7 | 7.8 | 6.8 | 5.9 | |
| 7.7 | 7.1 | 6.7 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 7.3 | 6.8 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 6.0 | |
| 17.0 | 14.3 | 11.3 | 10.2 | 10.7 | 14.9 | 13.6 | 13.7 | 14.1 | 13.6 | 11.9 | 10.2 | 9.5 | |
| 6.4 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 6.9 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 9.2 | 8.1 | 7.8 | |
| 9.0 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 6.8 | 8.6 | 9.7 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 10.5 | 9.7 | 8.8 | 8,6 |
Evolution of unemployment ranking within the European Union (from lower to higher rates):[50]
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 18 | |
| 2 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 4 | |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 17 | 24 | 25 | 24 | 24 | |
| 6 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 6 | |
| 7 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 9 | |
| 8 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 15 | 12 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 15 | |
| 9 | 13 | 17 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 18 | 19 | 15 | 10 | 11 | 5 | |
| 10 | 14 | 17 | 14 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | |
| 11 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 12 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 13 | |
| 12 | 11 | 15 | 12 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 9 | |
| 13 | 12 | 12 | 17 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 22 | 23 | 23 | |
| 14 | 16 | 11 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| 15 | 17 | 16 | 16 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 19 | |
| 16 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 24 | 24 | 24 | |
| 17 | 19 | 20 | 19 | 17 | 13 | 8 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 16 | |
| 18 | 23 | 22 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 21 | 21 | |
| 19 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 26 | 26 | 23 | 18 | 13 | 10 | 8 | 11 | |
| 20 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 22 | 20 | 19 | 17 | 16 | |
| 21 | 21 | 21 | 27 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 28 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| 22 | 24 | 23 | 24 | 20 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 | |
| 23 | 22 | 17 | 15 | 9 | 17 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 20 | 20 | 14 | |
| 24 | 18 | 14 | 17 | 27 | 28 | 26 | 26 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 20 | |
| 25 | 25 | 23 | 23 | 12 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 26 | 26 | 27 | 26 | 18 | 19 | 22 | 25 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 26 | |
| 27 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 23 | 24 | 21 | 21 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 22 | |
| 28 | 28 | 26 | 20 | 16 | 18 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 11 |
Regional variation
Comparing the richest areas of the EU can be a difficult task. This is because the NUTS 1 & 2 regions are not homogenous, some of them being very large regions, such as NUTS-1 Hesse (21,100 km²) or NUTS-1 Île-de-France (12,011 km²), whilst other NUTS regions are much smaller, for example NUTS-1 Hamburg (755 km²) or NUTS-1 Greater London (1,580 km²). An extreme example is Finland, which is divided for historical reasons into mainland Finland with 5.3 million inhabitants and Åland, an autonomous archipelago with a population of 27,000, or about the population of a small Finnish city.
One problem with this data is that some areas, including Greater London, are subject to a large number of commuters coming into the area, thereby artificially inflating the figures. It has the effect of raising GDP but not altering the number of people living in the area, inflating the GDP per capita figure. Similar problems can be produced by a large number of tourists visiting the area. The data is used to define regions that are supported with financial aid in programs such as the European Regional Development Fund. The decision to delineate a Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) region is to a large extent arbitrary (i.e. not based on objective and uniform criteria across Europe), and is decided at European level (See also: Regions of the European Union).
Top 10: economically strongest NUTS-1 and NUTS-2 regions
The 10 NUTS-1 and NUTS-2 regions with the highest GDP per capita are almost all, except two, in the first fifteen-member states: Prague and Bratislava are the only ones in the 13 new member states that joined in May 2004, January 2007 and July 2013. The leading regions in the ranking of NUTS-2 regional GDP per inhabitant in 2014 were Inner London-West in the United Kingdom (539% of the average), the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (266%) and Brussels in Belgium (207%). Figures for these three regions, however, are artificially inflated by the commuters who do not reside in these regions ("Net commuter inflows in these regions push up production to a level that could not be achieved by the resident active population on its own. The result is that GDP per inhabitant appears to be overestimated in these regions and underestimated in regions with commuter outflows."[52]).
Another example of artificial inflation is Groningen. The calculated GDP per capita is very high because of the large natural gas reserves in this region, but Groningen is one of the poorest parts in the Netherlands. Among the 46 NUTS-2 regions exceeding the 125% level, fourteen were in Germany, five in the Netherlands and in Austria, four each in Belgium and the United Kingdom, three in Italy, two in Finland and one in Czech Republic, Denmark, Ireland, France, Romania, Slovakia, Spain and Sweden, as well as in the single region Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The NUTS Regulation lays down a minimum population size of 3 million and a maximum size of 7 million for the average NUTS-1 region, whereas a minimum of 800,000 and a maximum of 3 million for NUTS-2 regions ¹ [1]. This definition, however, is not respected by Eurostat. E.g.: the région of Île-de-France, with 11.6 million inhabitants, is treated as a NUTS-2 region, while the state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, with only 664,000 inhabitants, is treated as a NUTS-1 region.
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Eurostat[52]
Economically weakest NUTS-2 regions
Among the ten lowest regions in the ranking in 2014 most were in Bulgaria and Romania, with the lowest figure recorded in Severozapaden in Bulgaria. Among the 76 regions below the 75% level, fourteen were in Poland, eleven in Greece, seven in Romania, six each in Hungary and Italy, five each in Bulgaria, Portugal and Spain, four each in the Czech Republic and France, three in Slovakia, two each in Croatia and the United Kingdom, one in Slovenia as well as Latvia.[52]
Source: Eurostat[52]
See also
- Currencies of the European Union
- European Investment Bank
- European Union value added tax
- List of largest European companies by revenue
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3217494/7641722/KS-BJ-16-009-EN-N.pdf/323706aa-88ee-4811-98bd-9e2ca8b0b3fc
- ^ http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/tgm/table.do?tab=table&plugin=0&language=en&pcode=tessi190
- ^ a b "Harmonised unemployment rate by sex - Total". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- ^ a b http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/International_trade_in_goods
- ^ a b http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/International_trade_in_services
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "Balance of payment statistics - Statistics Explained". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/International_investment_position_statistics#EU-28_turned_from_a_net_borrower_to_a_net_lender_of_other_investment_in_2015
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ https://europa.eu/eyd2015/en/content/eu-development-aid
- ^ a b c "The EU as a borrower - European Commission". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ Bank, European Central. "Foreign reserves and own funds". European Central Bank. Retrieved 15 October 2016.
- ^ "Report for Selected Country Groups and Subjects". www.imf.org. Retrieved 12 October 2016.
- ^ "Triennial Central Bank Survey 2007" (PDF). BIS. 19 December 2007. Retrieved 25 July 2009.
- ^ Aristovnik, Aleksander; Čeč, Tanja (30 March 2010). "Compositional Analysis of Foreign Currency Reserves in the 1999–2007 Period. The Euro vs. The Dollar As Leading Reserve Currency" (PDF). Munich Personal RePEc Archive, Paper No. 14350. Retrieved 27 December 2010.
- ^ Boesler, Matthew (11 November 2013). "There Are Only Two Real Threats To The US Dollar's Status As The International Reserve Currency". Business Insider. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.imf.org. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
- ^ "GINI index (World Bank estimate) | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 14 October 2016.
- ^ "Monthly Reports". www.world-exchanges.org. Retrieved 12 October 2016.
- ^ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 12 October 2016.
- ^ "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 12 October 2016.
- ^ "Eurostat - Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ "Romania becomes third eastern European EU country to be bailed out". The Guardian. 25 March 2009.
- ^ "EU budget at a glance". Europa, EU information website. Retrieved 6 November 2007.
- ^ "Europäische Union: Anteile der Wirtschaftssektoren am Bruttoinlandsprodukt (BIP) von 2004 bis 2014". statista.de (in German). World Bank. Retrieved 22 March 2016.
- ^ "EU expenditure and revenue". Financial Programming and Budget. European Commission. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- ^ "EU budget myths". EC Europa. European Commission. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- ^ http://newsroom.mastercard.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/06/MasterCard_Global_Destination_Cities_Index_2012.pdf
- ^ "Airbus beats Boeing in 2010". News.ninemsn.com.au. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ a b "Gross domestic product at market prices (Current prices and per capita)". Eurostat. Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ "Gross domestic product at market prices (Current prices, PPS per capita)". Eurostat. 7 June 2016. Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ "General government gross debt - annual data". Eurostat. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ "Government deficit, excluding support for financial institutions". Eurostat. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
- ^ "Annual Inflation". Eurostat. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- ^ "Total unemployment rate". Eurostat. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ "2020_REPORT" (PDF). Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Eurostat – Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- ^ "Eurostat – Tables, Graphs and Maps Interface (TGM) table". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 29 June 2015. Retrieved 24 November 2015.
- ^ "Central Intelligence Agency". Cia.gov. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "World trade report 2009" (PDF). WTO information website.
- ^ a b Se-jeong, Kim (19 July 2009). "EU-Korea FTA Will Be a Long Process: Greek Ambassador". The Korea Times. Retrieved 15 August 2009.
- ^ a b http://trade.ec.europa.eu/doclib/docs/2006/september/tradoc_122530.pdf
- ^ "Extra-EU27 trade, by main partners, total product". Epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. 17 October 2013. Retrieved 20 May 2014.
- ^ a b Eurostat - Harmonised unemployment rate by sex
- ^ a b "Unemployment rate by sex and age - monthly average, %". europa.eu. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ^ "File:Unemployment rates, seasonally adjusted, August 2016.png - Statistics Explained". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ a b c d Eurostat (26 February 2016). "Twenty-one regions below half of the EU average…". Europa web portal. Retrieved 26 February 2016.
- ^ Cells shaded in green indicate forecast figure
- ^ One region may be classified by Eurostat as a NUTS-1, NUTS-2 as well as a NUTS-3 region. Several NUTS-1 regions are also classified as NUTS-2 regions such as Brussels-Capital or Ile-de-France. Many countries are only classified as a single NUTS-1 and a single NUTS-2 region such as Latvia, Lithuania, Luxemburg and (although over 3 million inhabitants) Denmark.
- "Euro-indicators News release" (PDF). June 2005 inflation data. Retrieved 18 July 2005.
- "Euro-indicators News release" (PDF). May 2005 unemployment data. Retrieved 18 July 2005.
- "World Bank". GNI data (July 2005). Retrieved 4 August 2005.
The following links are used for the GDP growth and GDP totals (IMF):
- Link to 10 new memberstates Growth Rates
- Link to Growth Rates for the Eurozone
- Link to non-Eurozone EU15 countries Growth Rates
