North Carolina: Difference between revisions
Steve Quinn (talk | contribs) →Geography: copy edit |
|||
| Line 538: | Line 538: | ||
;History |
;History |
||
*[http://library.uncg.edu/dp/ University of North Carolina at Greensboro Libraries Digital Collections] |
|||
*[http://www.loc.gov/rr/program/bib/states/northcarolina/ North Carolina State Guide, from the Library of Congress] |
*[http://www.loc.gov/rr/program/bib/states/northcarolina/ North Carolina State Guide, from the Library of Congress] |
||
Revision as of 15:28, 15 August 2011
North Carolina | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Province of North Carolina |
| Admitted to the Union | November 21, 1789 (12th) |
| Capital | Raleigh |
| Largest city | Charlotte |
| Largest county or equivalent | Wake |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Charlotte metropolitan area |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Bev Perdue (D) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Walter H. Dalton (D) |
| Legislature | General Assembly |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | House of Representatives |
| U.S. senators | Richard Burr (R) Kay Hagan (D) |
| U.S. House delegation | 7 Democrats, 6 Republicans (list) |
| Population | |
| • Total | (2,010) 9,535,483[1] |
| • Density | 165.24/sq mi (63.80/km2) |
| • Median household income | $44,670[2] |
| • Income rank | 38th[2] |
| Language | |
| Latitude | 33° 50′ N to 36° 35′ N |
| Longitude | 75° 28′ W to 84° 19′ W |
North Carolina (/[invalid input: 'en-us-North Carolina.ogg']ˌnɔːrθ kærəˈlaɪnə/) is a state located in the Southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties.[5] Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte. In the past five decades, North Carolina's economy has undergone a transition from reliance upon tobacco and furniture to a more diversified economy with an emphasis on engineering, biotechnology, and finance.[6][7]
North Carolina has a wide range of elevations, from sea level on the coast to 6,684 feet (2,037 m) at Mt. Mitchell, the highest point in the Eastern US.[8] The coastal plains are strongly influenced by the Atlantic Ocean. Most of the state falls in the humid subtropical climate zone. More than 300 miles (500 km) from the coast, the western, mountainous part of the state has a subtropical highland climate.
Between 2008 and 2009, North Carolina was the eighth-fastest growing state by population in the United States, and the fastest growing state east of the Mississippi River.[9]
Geography



North Carolina borders South Carolina on the south, Georgia on the southwest, Tennessee on the west, Virginia on the north, and the Atlantic Ocean on the east. The United States Census Bureau classifies North Carolina as a southern state in the subcategory of being one of the South Atlantic States.
North Carolina consists of three main geographic sections: the coastal plain, which occupies the eastern 45% of the state; the Piedmont region, which contains the middle 35%; and the Appalachian Mountains and foothills. The extreme eastern section of the state contains the Outer Banks, a string of sandy, narrow islands which form a barrier between the Atlantic Ocean and two inland waterways or "sounds": Albemarle Sound in the north and Pamlico Sound in the south. They are the two largest landlocked sounds in the United States. So many ships have been lost off Cape Hatteras that the area is known as the "Graveyard of the Atlantic". More than 1,000 ships have sunk in these waters since records began in 1526.
Immediately inland, the coastal plain is relatively flat, with rich soils ideal for growing tobacco, soybeans, melons, and cotton. The coastal plain is North Carolina's most rural section, with few large towns or cities. Agriculture remains an important industry. The major rivers of the coastal plain: the Neuse, Tar, Pamlico, and Cape Fear, tend to be slow-moving and wide.
The coastal plain transitions to the Piedmont region along the "fall line", a line which marks the elevation at which waterfalls first appear on streams and rivers. The Piedmont region of central North Carolina is the state's most urbanized and densely populated section. It consists of gently rolling countryside frequently broken by hills or low mountain ridges. A number of small, isolated, and deeply eroded mountain ranges and peaks are located in the Piedmont, including the Sauratown Mountains, Pilot Mountain, the Uwharrie Mountains, Crowder's Mountain, King's Pinnacle, the Brushy Mountains, and the South Mountains. The Piedmont ranges from about 300–400 feet (90–120 m) elevation in the east to over 1,000 feet (300 m) in the west. Due to the rapid population growth of the Piedmont, many of the farms and much of the rural countryside in this region is being replaced by suburbanization: shopping centers, housing, and corporation offices. Agriculture is steadily declining in importance in this region. The major rivers of the Piedmont, such as the Yadkin and Catawba, tend to be fast-flowing, shallow, and narrow.
The western section of the state is part of the Appalachian Mountain range. Among the subranges of the Appalachians located in the state are the Great Smoky Mountains, Blue Ridge Mountains, Great Balsam Mountains, and the Black Mountains. The Black Mountains are the highest in the Eastern United States, and culminate in Mount Mitchell at 6,684 feet (2,037 m).[4] It is the highest point east of the Mississippi River. Although agriculture remains important, tourism has become the dominant industry in the mountains. One agricultural pursuit which has prospered and grown in recent decades is the growing and selling of Christmas Trees. Due to the higher altitude of the mountains, the climate often differs markedly from the rest of the state. Winters in western North Carolina typically feature significant snowfall and subfreezing temperatures more akin to a midwestern state than a southern one.

North Carolina has 17 major river basins. Those west of the Blue Ridge Mountains flow to the Gulf of Mexico (via the Ohio and then the Mississippi River). All the others flow to the Atlantic Ocean. Of the 17 basins, 11 originate within the state of North Carolina, but only four are contained entirely within the state's borders - the Cape Fear, Neuse, White Oak and Tar-Pamlico.[10]
Climate
The geographical divisions of North Carolina are useful when discussing the climate of the state.
The Coastal Plain is influenced by the Atlantic Ocean which keeps temperatures mild in winter and moderate in the summer. Daytime high temperatures on the coast average less than 89 °F (31.6 °C) during the summer. In the winter, the coast has the mildest temperatures in the state, with daytime temperatures rarely dropping below 40 °F (4.4 °C); the average daytime winter temperature in the coastal plain is usually in the mid-60's. Temperatures in the coastal plain rarely drop below freezing even at night. The coastal plain usually receives only one inch (2.5 cm) of snow and/or ice annually, and in some years there may be no snow or ice at all.


The Atlantic Ocean has less influence on the Piedmont region, and as a result the Piedmont has hotter summers and colder winters than the coast. Daytime highs in the Piedmont often average over 90 °F (32.2 °C) in the summer. While it is not common for temperatures to reach over 100 °F (37.8 °C) in North Carolina, when it happens, the highest temperatures are to be found in the lower areas of the Piedmont. Additionally, the weaker influence of the Atlantic Ocean means that temperatures in the Piedmont often fluctuate more widely than the coast.
In the winter, the Piedmont is colder than the coast, with daytime temperatures that are usually in the 40s, and temperatures that often drop below freezing at night. The region averages from 3–5 inches of snowfall annually in the Charlotte area to 6–8 inches in the Raleigh–Durham area. The Piedmont is especially notorious for sleet and freezing rain. It can be heavy enough in some storms to snarl traffic and collapse trees and power lines. Annual precipitation and humidity is lower in the Piedmont than either the mountains or the coast, but even at its lowest, the precipitation is a generous 40 in (102 cm) per year.
The Appalachian Mountains are the coolest area of the state, with daytime temperatures averaging in the low 40's and upper 30's for highs in the winter and often falling into the teens (−9 °C) or lower on winter nights. Relatively cool summers have temperatures rarely rising above 80 °F (26.7 °C). Snowfall in the mountains is usually 14–30 in (36–51 cm) per year, but it is often greater in the higher elevations. For example, during the Blizzard of 1993 more than 60 inches (150 cm) of snow fell on Mount Mitchell over a period of three days. Additionally, Mount Mitchell has received snow in every month of the year.

Severe weather occurs regularly in North Carolina. On average, the state receives a direct hit from a hurricane once a decade. Some destructive hurricanes that have hit the state include: Hurricane Hazel, Hurricane Fran, and Hurricane Floyd. In recent years, Hurricane Isabel stands out as the most damaging of the 21st century.[11] Tropical storms arrive every 3 or 4 years. In addition, many hurricanes and tropical storms graze the state. In some years, several hurricanes or tropical storms can directly strike the state or brush across the coastal areas. Only Florida and Louisiana are hit by hurricanes more often. Although many people believe that hurricanes menace only coastal areas, the rare hurricane which moves inland quickly enough can cause severe damage. In 1989 Hurricane Hugo caused heavy damage in Charlotte and even as far inland as the Blue Ridge Mountains in the northwestern part of the state. On average, North Carolina has 50 days of thunderstorm activity per year, with some storms becoming severe enough to produce hail], flash floods, and damaging winds.
North Carolina averages fewer than 20 tornadoes per year. Many of these are produced by hurricanes or tropical storms along the coastal plain. Tornadoes from thunderstorms are a risk, especially in the eastern part of the state. The western Piedmont is often protected by the mountains breaking storms up as they try to cross over them. The storms will often reform farther east. Also a weather feature known as "cold air damming" occurs in the western part of the state. This can also weaken storms but can also lead to major ice events in winter."[12]
In April of 2011, one of the worst tornado outbreaks in North Carolina's history occurred. 25 confirmed tornadoes touched down, mainly in the Eastern Piedmont, killing at least 24 people. Damages in the capital of Raleigh alone were over $115 million.[13][14]
| Monthly normal high and low temperatures (Fahrenheit) for various North Carolina cities. | ||||||||||||
| City | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asheville | 46/26 | 50/28 | 58/35 | 66/42 | 74/51 | 80/58 | 83/63 | 82/62 | 76/55 | 67/43 | 57/35 | 49/29 |
| Boone | 39/20 | 43/22 | 50/29 | 59/38 | 67/47 | 73/55 | 77/59 | 75/57 | 70/50 | 62/38 | 52/30 | 44/22 |
| Cape Hatteras | 54/39 | 55/39 | 60/44 | 68/52 | 75/60 | 82/68 | 85/73 | 85/72 | 81/68 | 73/59 | 65/50 | 57/43 |
| Charlotte | 51/32 | 56/34 | 64/42 | 73/49 | 80/58 | 87/66 | 90/71 | 88/69 | 82/63 | 73/51 | 63/42 | 54/35 |
| Fayetteville | 52/31 | 56/33 | 64/39 | 73/47 | 80/56 | 87/65 | 90/70 | 89/69 | 83/63 | 74/49 | 65/41 | 56/34 |
| Greensboro | 47/28 | 52/31 | 60/38 | 70/46 | 77/55 | 84/64 | 88/68 | 86/67 | 79/60 | 70/48 | 60/39 | 51/31 |
| Greenville | 51/30 | 54/32 | 63/38 | 72/46 | 79/55 | 85/65 | 90/70 | 89/67 | 82/61 | 71/49 | 63/40 | 54/33 |
| Raleigh | 50/30 | 54/32 | 62/39 | 72/46 | 79/55 | 86/64 | 89/68 | 87/67 | 81/61 | 72/48 | 62/40 | 53/33 |
| Wilmington | 56/36 | 60/38 | 66/44 | 74/51 | 81/60 | 86/68 | 90/72 | 88/71 | 84/66 | 76/54 | 68/45 | 60/38 |
| [1]|[15] | ||||||||||||
History
Spanish colonial forces were the first Europeans to make a permanent settlement in the area, when the Juan Pardo-led Expedition built Fort San Juan in 1567. This was sited at Joara, a Mississippian culture regional chiefdom near present-day Morganton in the western interior. It lasted only 18 months as the natives killed all but one of the 120 men Pardo had stationed at a total of six forts in area.[16]
North Carolina became one of the English Thirteen Colonies, and was originally known as Province of Carolina, along with South Carolina. The nothern and southern parts of the original Province separated in 1729. Originally settled by small farmers, sometimes having a few slaves, who were oriented toward subsistence agriculture, the colony lacked cities or even towns. Pirates menaced the seacoast settlements, but by 1718 the pirates had been captured and executed. Growth was strong in the middle of the 18th century, as the economy attracted Scotch-Irish, Quaker, English and German immigrants. The colonists supported the American Revolution, as the Loyalists were weak. North Carolina made the smallest per-capita contribution to the war on any state, as only 7800 men joined the Continental Army under General George Washington; an additional 10,000 served in local militia units under such leaders as General Nathanael Greene.[17] There was some military action, especially in 1780-81. Many Carolinian frontiersmen had moved over the mountains into Tennessee, but the state relinquished its claims on Tennessee to the national government in 1789. After 1800, cotton and tobacco became important export crops, and the eastern half of the state developed a plantation system based on slavery, while the western areas were dominated by white families who operated small farms. In the early national period, the state became a center of Jeffersonian Democracy and Jacksonian Democracy with a strong Whig presence especially in the West.
On May 20, 1861, North Carolina was the second to last (after Tennessee) of the Confederate states to declare secession from the Union. Some 125,000 North Carolinians saw military service; 20,000 were killed in battle and 21,000 died of disease. The state government was reluctant to support the demands of the national government in Richmond, and the state was the scene of only small battles. With the end of the war in 1865, the Reconstruction Era began, slavery was abolished without any compensation to the slave-holders, or reparations to the freedmen. A coalition of black Freedmen, northern Carpetbaggers, and local Scalawags controlled state government for three years but the white conservatives were back in control by 1871. The system of Jim Crow and legal segregation made the blacks into second-class citizens from the 1880s until 1964. Angry memories of Reconstruction helped make the Democratic Party dominant in state and national elections. By the 1960s, changing party politics, and the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, significantly reversed the role of Democrat and Republican parties in the South.
North Carolina was impoverished by the Civil War, and became increasingly locked into a cotton economy. Towns and cities remained few in the east, but a major industrial base emerged in the late 19th century in the western counties based on cotton mills. The state was the site of the first successful controlled, powered and sustained heavier-than-air flight, by the Wright brothers, near Kitty Hawk on December 17, 1903. North Carolina was hard hit by the Great Depression, but the New Deal's farm programs for cotton and tobacco significantly helped the farmers. After World War II, the state's economy grew rapidly, highlighted by the growth of such cities as Charlotte, Raleigh, and Durham. In the 1990s, Charlotte became a major regional and national banking center.
Native Americans, lost colonies, and permanent settlement
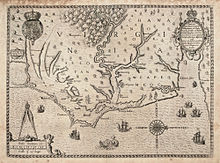
North Carolina was originally inhabited by many different prehistoric native cultures. Before 200 AD, they were building earthwork mounds, which were used for ceremonial and religious purposes. Succeeding peoples, including those of the ancient Mississippian culture established by 1000 AD in the Piedmont, continued to build or add on to such mounds. In the 500–700 years preceding European contact, the Mississippian culture built large, complex cities and maintained far flung regional trading networks. Historically documented tribes in the North Carolina region included the Carolina Algonquian-speaking tribes of the coastal areas, such as the Chowanoke, Roanoke, Pamlico, Machapunga, Coree, Cape Fear Indians, and others, who were the first encountered by the English; Iroquoian-speaking Meherrin, Cherokee and Tuscarora of the interior; and Southeastern Siouan tribes, such as the Cheraw, Waxhaw, Saponi, Waccamaw, and Catawba.
Spanish explorers traveling inland in the 16th century met the Mississippian culture people at Joara, a regional chiefdom near present-day Morganton. Records of Hernando de Soto attested to his meeting with them in 1540. In 1567 Captain Juan Pardo led an expedition into the interior to claim the area for the Spanish colony, as well as establish another route to protect silver mines in Mexico. Pardo made a winter base at Joara, which he renamed Cuenca. The expedition built Fort San Juan and left 30 men, while Pardo traveled further, and built and staffed five other forts. He returned by a different route to Santa Elena on Parris Island, South Carolina, then a center of Spanish Florida. In the spring of 1568, natives killed all but one of the soldiers and burned the six forts in the interior, including the one at Fort San Juan. Although the Spanish never returned to the interior, this marked the first European attempt at colonization of the interior of what became the United States. A 16th-century journal by Pardo's scribe Bandera and archaeological findings since 1986 at Joara have confirmed the settlement.[18][19]

In 1584, Elizabeth I, granted a charter to Sir Walter Raleigh, for whom the state capital is named, for land in present-day North Carolina (then Virginia).[20] Raleigh established two colonies on the coast in the late 1580s, both ending in failure. It was the second American territory the English attempted to colonize. The demise of one, the "Lost Colony" of Roanoke Island, remains one of the mysteries of American history. Virginia Dare, the first English child to be born in North America, was born on Roanoke Island on August 18, 1587. Dare County is named for her.
As early as 1650, colonists from the Virginia colony moved into the area of Albemarle Sound. By 1663, King Charles II of England granted a charter to start a new colony on the North American continent which generally established its borders. He named it Carolina in honor of his father Charles I.[21] By 1665, a second charter was issued to attempt to resolve territorial questions. In 1710, due to disputes over governance, the Carolina colony began to split into North Carolina and South Carolina. The latter became a crown colony in 1729. A devastating series of smallpox epidemics swept the South.[22] According to Russell Thornton, "The 1738 epidemic was said to have killed one-half of the Cherokee, with other tribes of the area suffering equally."[23] It has been speculated that the Lumbee are the descendants of the lost colony.It has been said that the local Croatan Indians assimilated with the lost colony, that is why some of the Lumbee Tribe have fair skin and blue eyes.
Colonial period and Revolutionary War

The first permanent European settlers of North Carolina after the Spanish in the 16th century were English colonists who migrated south from Virginia, following a rapid growth of the colony and the subsequent shortage of available farmland. Nathaniel Batts was documented as one of the first of these Virginian migrants. He settled south of the Chowan River and east of the Great Dismal Swamp in 1655.[24] By 1663, this northeastern area of the Province of Carolina, known as the Albemarle Settlements, was undergoing full-scale British settlement.[25] During the same period, the English monarch Charles II gave the province to the Lords Proprietors, a group of noblemen who had helped restore Charles to the throne in 1660. The new province of "Carolina" was named in honor and memory of King Charles I (Latin: Carolus). In 1712, North Carolina became a separate colony. Except for the Earl Granville holdings, it became a royal colony seventeen years later.[26]
Differences in the settlement patterns of eastern and western North Carolina, or the low country and uplands, affected the political, economic, and social life of the state from the eighteenth until the 20th century. The Tidewater in eastern North Carolina was settled chiefly by immigrants from rural England and the Scottish Highlands. The upcountry of western North Carolina was settled chiefly by Scots-Irish, English and German Protestants, the so-called "cohee". Arriving during the mid-to-late 18th century, the Scots-Irish from Ireland were the largest immigrant group before the Revolution. During the American Revolutionary War, the English and Highland Scots of eastern North Carolina tended to remain loyal to the British Crown, because of longstanding business and personal connections with Great Britain. The English, Welsh, Scots-Irish and German settlers of western North Carolina tended to favor American independence from Britain.
Most of the English colonists arrived as indentured servants, hiring themselves out as laborers for a fixed period to pay for their passage. In the early years the line between indentured servants and African slaves or laborers was fluid. Some Africans were allowed to earn their freedom before slavery became a lifelong status. Most of the free colored families formed in North Carolina before the Revolution were descended from unions or marriages between free white women and enslaved or free African or African-American men. Because the mothers were free, their children were born free. Many had migrated or were descendants of migrants from colonial Virginia.[27] As the flow of indentured laborers to the colony decreased with improving economic conditions in Great Britain, more slaves were imported and the state's restrictions on slavery hardened. The economy's growth and prosperity was based on slave labor, devoted first to the production of tobacco.
On April 12, 1776, the colony became the first to instruct its delegates to the Continental Congress to vote for independence from the British crown, through the Halifax Resolves passed by the North Carolina Provincial Congress. The dates of both of these events are memorialized on the state flag and state seal.[28] Throughout the Revolutionary War, fierce guerrilla warfare erupted between bands of pro-independence and pro-British colonists. In some cases the war was also an excuse to settle private grudges and rivalries. A major American victory in the war took place at King's Mountain along the North Carolina–South Carolina border. On October 7, 1780 a force of 1000 mountain men from western North Carolina (including what is today the State of Tennessee) overwhelmed a force of some 1000 British troops led by Major Patrick Ferguson. Most of the British soldiers in this battle were Carolinians who had remained loyal to the British Crown (they were called "Tories"). The American victory at Kings Mountain gave the advantage to colonists who favored American independence, and it prevented the British Army from recruiting new soldiers from the Tories.

The road to Yorktown and America's independence from Great Britain led through North Carolina. As the British Army moved north from victories in Charleston and Camden, South Carolina, the Southern Division of the Continental Army and local militia prepared to meet them. Following General Daniel Morgan's victory over the British Cavalry Commander Banastre Tarleton at the Battle of Cowpens on January 17, 1781, southern commander Nathanael Greene led British Lord Charles Cornwallis across the heartland of North Carolina, and away from Cornwallis's base of supply in Charleston, South Carolina. This campaign is known as "The Race to the Dan" or "The Race for the River."[26]
Generals Greene and Cornwallis finally met at the Battle of Guilford Courthouse in present-day Greensboro on March 15, 1781. Although the British troops held the field at the end of the battle, their casualties at the hands of the numerically superior American Army were crippling. Following this "Pyrrhic victory", Cornwallis chose to move to the Virginia coastline to get reinforcements, and to allow the Royal Navy to protect his battered army. This decision would result in Cornwallis's eventual defeat at Yorktown, Virginia later in 1781. The Patriots' victory there guaranteed American independence.
Antebellum period
On November 21, 1789, North Carolina became the twelfth state to ratify the Constitution. In 1840, it completed the state capitol building in Raleigh, still standing today. Most of North Carolina's slave owners and large plantations were located in the eastern portion of the state. Although North Carolina's plantation system was smaller and less cohesive than those of Virginia, Georgia or South Carolina, there were significant numbers of planters concentrated in the counties around the port cities of Wilmington and Edenton, as well as suburban planters around the cities of Raleigh, Charlotte and Durham. Planters owning large estates wielded significant political and socio-economic power in antebellum North Carolina, placing their interests above those of the generally non-slave holding "yeoman" farmers of Western North Carolina. In mid-century, the state's rural and commercial areas were connected by the construction of a 129–mile (208 km) wooden plank road, known as a "farmer's railroad", from Fayetteville in the east to Bethania (northwest of Winston-Salem).[26]

Besides slaves, there were a number of free people of color in the state. Most were descended from free African Americans who had migrated along with neighbors from Virginia during the 18th century. After the Revolution, Quakers and Mennonites worked to persuade slaveholders to free their slaves. Some were inspired by their efforts and the language of men's rights, to arrange for manumission of their slaves. The number of free people of color rose markedly in the first couple of decades after the Revolution.[29]
On October 25, 1836 construction began on the Wilmington and Raleigh Railroad[30] to connect the port city of Wilmington with the state capital of Raleigh. In 1849 the North Carolina Railroad was created by act of the legislature to extend that railroad west to Greensboro, High Point, and Charlotte. During the Civil War the Wilmington-to-Raleigh stretch of the railroad would be vital to the Confederate war effort; supplies shipped into Wilmington would be moved by rail through Raleigh to the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia.
During the antebellum period, North Carolina was an overwhelmingly rural state, even by Southern standards. In 1860 only one North Carolina town, the port city of Wilmington, had a population of more than 10,000. Raleigh, the state capital, had barely more than 5,000 residents.
While slaveholding was slightly less concentrated than in some Southern states, according to the 1860 census, more than 330,000 people, or 33% of the population of 992,622 were enslaved African-Americans. They lived and worked chiefly on plantations in the eastern Tidewater. In addition, 30,463 free people of color lived in the state. They were also concentrated in the eastern coastal plain, especially at port cities such as Wilmington and New Bern where they had access to a variety of jobs. Free African Americans were allowed to vote until 1835, when the state revoked their right to vote.
American Civil War

In 1860, North Carolina was a slave state, in which about one-third of the population of 992,622 were enslaved African Americans. This was a smaller proportion than many Southern states. In addition, the state had just over 30,000 Free Negroes.[31] The state did not vote to join the Confederacy until President Abraham Lincoln called on it to invade its sister-state, South Carolina, becoming the last or second to last state to officially join the Confederacy. The title of "last to join the Confederacy" has been disputed because Tennessee informally seceded on May 7, 1861, making North Carolina the last to secede on May 20, 1861.[32][33] However, the Tennessee legislature did not formally vote to secede until June 8, 1861.[34]
North Carolina was the site of few battles, but it provided at least 125,000 troops to the Confederacy— far more than any other state. Approximately 40,000 of those troops never returned home, dying of disease, battlefield wounds, and starvation. North Carolina also supplied about 15,000 Union troops.[35] Elected in 1862, Governor Zebulon Baird Vance tried to maintain state autonomy against Confederate President Jefferson Davis in Richmond.
Even after secession, some North Carolinians refused to support the Confederacy. This was particularly true of non-slave-owning farmers in the state's mountains and western Piedmont region. Some of these farmers remained neutral during the war, while some covertly supported the Union cause during the conflict. Approximately 2,000 North Carolinians from western North Carolina enlisted in the Union Army and fought for the North in the war, and two additional Union Army regiments were raised in the coastal areas of the state that were occupied by Union forces in 1862 and 1863. Even so, Confederate troops from all parts of North Carolina served in virtually all the major battles of the Army of Northern Virginia, the Confederacy's most famous army. The largest battle fought in North Carolina was at Bentonville, which was a futile attempt by Confederate General Joseph Johnston to slow Union General William Tecumseh Sherman's advance through the Carolinas in the spring of 1865.[26] In April 1865, after losing the Battle of Morrisville, Johnston surrendered to Sherman at Bennett Place, in what is today Durham, North Carolina. This was the last major Confederate Army to surrender. North Carolina's port city of Wilmington was the last Confederate port to fall to the Union. It fell in the spring of 1865 after the nearby Second Battle of Fort Fisher.

The first Confederate soldier to be killed in the Civil War was Private Henry Wyatt, a North Carolinian. He was killed in the Battle of Big Bethel in June 1861. At the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863, the 26th North Carolina Regiment participated in Pickett/Pettigrew's Charge and advanced the farthest into the Northern lines of any Confederate regiment. During the Battle of Chickamauga the 58th North Carolina Regiment advanced farther than any other regiment on Snodgrass Hill to push back the remaining Union forces from the battlefield. At Appomattox Court House in Virginia in April 1865, the 75th North Carolina Regiment, a cavalry unit, fired the last shots of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the Civil War. For many years, North Carolinians proudly boasted that they had been "First at Bethel, Farthest at Gettysburg and Chickamauga, and Last at Appomattox."
Demographics
Demographics of North Carolina covers the varieties of ethinic groups that reside in North Carolia, along with the relevant trends.
Economy
In 2008 North Carolina's total gross state product was $400.2 billion. In 2011 the civilian labor force was at around 4.5 million with employment near 4.1 million. The working population is employed across the major employment sectors. The economy of North Carolina covers 15 metropolitan areas.[36]
Transportation
Transportation systems in North Carolina consists of air, water, road, rail, and public transportation.
Politics and government

North Carolina has a large number of statewide elected executive officials.
The government of North Carolina is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. These consist of the state govenor's office, a bicameral state legislature known as the general assembly, and a state court system. The state constitution delineates the structure and function of the state government. North Carolina has 13 seats in the U.S. House of Reperesenatives and two seats in the U.S. Senate. Changes have occured during the state's 400 year political history.
Education
Elementary and secondary education
Elementary and secondary public schools are overseen by the North Carolina Department of Public Instruction. The North Carolina Superintendent of Public Instruction is the secretary of the North Carolina State Board of Education, but the board, rather than the superintendent, holds most of the legal authority for making public education policy. In 2009, the board's chairman also became the "chief executive officer" for the state's school system.[37][38] North Carolina has 115 public school systems,[39] each of which is overseen by a local school board. A county may have one or more systems within it. The largest school systems in North Carolina are the Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools, Wake County Public School System, Guilford County Schools, Winston-Salem/Forsyth County Schools, and Cumberland County Schools. In total there are 2,338 public schools in the state, including 93 charter schools.[39]
Colleges and universities
In 1795, North Carolina opened the first public university in the United States—the University of North Carolina (currently named the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill). More than 200 years later, the University of North Carolina system encompasses 17 public universities including UNC-Chapel Hill, North Carolina State University, East Carolina University, Western Carolina University, UNC Asheville, UNC Charlotte, UNC Greensboro, UNC Pembroke, UNC Wilmington, UNC School of the Arts, and Appalachian State University. The system also supports several well-known historically African-American colleges and universities such as North Carolina A&T State University, North Carolina Central University, Winston-Salem State University, Elizabeth City State University, and Fayetteville State University. Along with its public universities, North Carolina has 58 public community colleges in its community college system.
North Carolina is also home to many well-known private colleges and universities including: Duke University, Wake Forest University, Elon University, Davidson College, Guilford College, the first coeducational institution of higher learning in the South, Salem College, the first school for young women in the South, Shaw University, the first historically black college or university in the South, John Wesley College (North Carolina), the oldest undergraduate theological education institution in North Carolina, and High Point University.
Sports
Athletes and sports teams from North Carolina compete at every level of competition in the United States including NASCAR the NBA, the NFL, and the NHL along with several colleges and universities in various conferences across an array of divisions. North Carolina is a state known for minor league sports. There are also a number of indoor football, indoor soccer, minor league basketball, and minor league ice hockey teams throughout the state.
Recreation

Due to geography, rich history, and growing industry, North Carolina provides a large range of recreational activities from swimming at the beach[40] to skiing in the mountains. North Carolina offers fall colors, freshwater and saltwater fishing, hunting, birdwatching, agritourism, ATV trails, ballooning, rock climbing, biking, hiking, skiing, boating and sailing, camping, canoeing, caving (spelunking), gardens, and arboretums. North Carolina has theme parks, aquariums, zoos, museums, historic sites, lighthouses, elegant theaters, concert halls, and fine dining.[41]
North Carolinians enjoy outdoor recreation utilizing numerous local bike paths, 34 state parks, and 14 national parks which are the Appalachian National Scenic Trail, the Blue Ridge Parkway, Cape Hatteras National Seashore, Cape Lookout National Seashore, Carl Sandburg Home National Historic Site at Flat Rock, Croatan National Forest in Eastern North Carolina, Fort Raleigh National Historic Site at Manteo, Great Smoky Mountains National Park, Guilford Courthouse National Military Park in Greensboro, Moores Creek National Battlefield near Currie, the Overmountain Victory National Historic Trail, Old Salem National Historic Site in Winston-Salem, the Trail of Tears National Historic Trail, Wright Brothers National Memorial in Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Uwharrie National Forest.
Culture
Music
North Carolina is known particularly for its tradition of old-time music, and many recordings were made in the early 20th century by folk song collector Bascom Lamar Lunsford. Musicians such as the North Carolina Ramblers helped solidify the sound of country music in the late 1920s, while the influential bluegrass musician Doc Watson also came from North Carolina. Both North and South Carolina are a hotbed for traditional rural blues, especially the style known as the Piedmont blues. Ben Folds Five originated in Winston-Salem, and Ben Folds still records and resides in Chapel Hill. Contemporary Jazz musician LeRoi Moore, now deceased, of the Dave Matthews Band was born in Durham, North Carolina.
MerleFest a musical tribute to Doc Watson takes place every April in Wilkesboro. The festival costs around $60.00 a person to get in through the four day time period. 12 and under are free. It brings in over $5 million every year and has over 90,000 in attendance.
The Triangle area has long been a well-known center for folk, rock, metal, and punk.[42] James Taylor grew up around Chapel Hill and his 1968 song "Carolina in My Mind" has been called an unofficial anthem for the state.[43][44][45] Other famous musicians from North Carolina include Chris Daughtry, Jimmy Herring, Michael Houser, Randy Travis, season 10 American Idol winner Scotty McCreery and The Avett Brothers.
Shopping
North Carolina has a variety of shopping choices. SouthPark Mall in Charlotte is currently the largest in the Carolinas and Tennessee with almost 2.0 million square feet. The mall also has many luxury and upscale stores like Burberry, Coach, Louis Vuitton, Nordstrom, Saks Fifth Avenue and many others. Other major malls throughout the state include Hanes Mall in Winston Salem, Crabtree Valley Mall and Triangle Town Center in Raleigh, Four Seasons Town Centre in Greensboro, Concord Mills in Concord, The Streets at Southpoint and Northgate Mall, in Durham. In High Point North Carolina, Oak Hollow Mall still exists to this day, but, with its recent sale to High Point University, the future of the establishment remains uncertain.
Food, drink and tobacco

A state culinary staple of North Carolina is pork barbecue. There are strong regional differences and rivalries over the sauces and method of preparation used in making the barbecue. The common trend across Western North Carolina is the use of Premium Grade Boston Butt, which is high in vitamins B1, B2, niacin (B3), B6, and selenium. Western North Carolina pork barbecue uses a tomato-based sauce, and only the pork shoulder (dark meat) is used. Western North Carolina barbecue is commonly referred to as Lexington barbecue after the Piedmont Triad town of Lexington, home of the Lexington Barbecue Festival which attracts over 100,000 visitors each October.[46][47] Eastern North Carolina pork barbecue uses a vinegar and red pepper based sauce and the "whole hog" is cooked, thus integrating both white and dark meat.
Krispy Kreme, an international chain of doughnut stores, was started in North Carolina; the company's headquarters are in Winston-Salem. Pepsi-Cola was first produced in 1898 in New Bern. A regional soft drink, Cheerwine, was created and is still based in the city of Salisbury. Despite its name, the hot sauce Texas Pete was created in North Carolina; its headquarters are also in Winston-Salem. The Hardees fast-food chain was started in Rocky Mount. Another fast-food chain, Bojangles', was started in Charlotte, and has its corporate headquarters there. A popular North Carolina restaurant chain is Golden Corral. Started in 1973, the chain was founded in Fayetteville, with headquarters located in Raleigh. Popular pickle brand Mount Olive Pickle Company was founded in Mount Olive in 1926. Cook Out, a popular fast food chain featuring burgers, hot dogs, and milkshakes in a wide variety of flavors, was founded in Greensboro in 1989 and has begun expanding outside of North Carolina.
Over the last decade, North Carolina has become a cultural epicenter and haven for internationally prized winning wine (Noni Bacca), internationally prized cheeses (Ashe County), "L'institut International aux Arts Gastronomiques: Conquerront Les Yanks les Truffes, 15/01/10" international hub for truffles (Garland Truffles), and beer making as tobacco land has been converted to grape orchards while state laws regulating alcohol content in beer allowed a jump in ABV from 6% to 15%. The Yadkin Valley in particular has become a strengthening market for grape production while the city of Asheville recently won the recognition of being named 'Beer City USA.' Asheville boasts the largest breweries per capita of any city in the United States. Recognized and marketed brands of beer in NC include Highland Brewing, Duck Rabbit Brewery, Mother Earth Brewery, Weeping Radish Brewery, Big Boss Brewing, Foothills Brewing and Carolina Brewing Company. As of March 27, 2010, Wilmington, North Carolina hosts Noni Bacca winery which earned 12 medals at the coveted Finger Lakes International Wine Competition.
Tobacco was one of the first major industries to develop after the Civil War. Many farmers grew some tobacco, and the invention of the cigarette made the product especially popular. Winston Salem is the birthplace of R. J. Reynolds Tobacco Company (RJR), founded by R. J. Reynolds in 1874 as one of 16 tobacco companies in the town. By 1914 it was selling 425 million packs of Camels a year. Today it is the second-largest tobacco company in the U.S. (behind Altria Group). RJR is an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Reynolds American Inc. which in turn is 42% owned by British American Tobacco.[48]
Ships named for the state
Several ships have been named for the state. Most famous is the USS North Carolina, a World War II battleship. The ship served in several battles against the forces of Imperial Japan in the Pacific theater during the war. Now decommissioned, it is part of the USS North Carolina Battleship Memorial in Wilmington. Another USS North Carolina, a nuclear attack submarine, was commissioned in Wilmington, North Carolina on May 3, 2008.[49]
State symbols
- State motto: Esse quam videri ("To be, rather than to seem") (1893)
- State song: "The Old North State" (1927)
- State flower: Dogwood (1941)
- State bird: Cardinal (1943)
- State colors: the red and blue of the N.C. and U.S. flags (1945)
- State toast: "The Tar Heel Toast" (1957)
- State tree: Longleaf Pine (1963)
- State shell: Scotch bonnet (1965)
- State mammal: Eastern Gray Squirrel (1969)
- State salt water fish: Red Drum (also known as the Channel bass) (1971)
- State insect: European honey bee (1973)
- State gemstone: Emerald (1973)
- State reptile: Eastern Box Turtle (1979)
- State rock: Granite (1979)
- State beverage: Milk (1987)
- State historical boat: Shad boat (1987)
- State language: English (1987)
- State dog: Plott Hound (1989)
- State military academy: Oak Ridge Military Academy (1991)
- State tartan: Carolina tartan (1991)[50]
- State vegetable: Sweet potato (1995)
- State red berry: Strawberry (2001)
- State blue berry: Blueberry (2001)
- State fruit: Scuppernong grape (2001)
- State wildflower: Carolina Lily (2003)
- State Christmas tree: Fraser Fir (2005)
- State carnivorous plant: Venus Flytrap (2005)
- State folk dance: Clogging (2005)
- State popular dance: Carolina shag (2005)
- State birthplace of traditional pottery: the Seagrove area (2005)
Armed forces installations
According to former Governor Mike Easley, North Carolina is the "most military friendly state in the nation."[51] Fort Bragg, near Fayetteville, is the largest and most comprehensive military base in the United States and is the headquarters of the XVIII Airborne Corps, 82nd Airborne Division, and the U.S. Army Special Operations Command. Serving as the airwing for Fort Bragg is Pope Field also located near Fayetteville.
Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune which, when combined with nearby bases Marine Corps Air Station (MCAS) Cherry Point, MCAS New River, Camp Geiger, Camp Johnson, Stone Bay and Courthouse Bay, makes up the largest concentration of Marines and sailors in the world. MCAS Cherry Point is home of the 2nd Marine Aircraft Wing. Located in Goldsboro, Seymour Johnson Air Force Base is home of the 4th Fighter Wing and 916th Air Refueling Wing. One of the busiest air stations in the United States Coast Guard is located at the Coast Guard Air Station in Elizabeth City. Also stationed in North Carolina is the Military Ocean Terminal Sunny Point in Southport.
See also
- Atlantic Ocean
- List of National Register of Historic Places in North Carolina
- List of people from North Carolina
- Outer Banks
- U.S. state
- Wildlife of North Carolina
References
- ^ "Apportionment Population and Number of Representatives, by State: 2010 Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-12-22.
- ^ a b Median Household Income, from U.S. Census Bureau (from 2007 American Community Survey, U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2009-04-09.
- ^ "North Carolina Climate and Geography". NC Kids Page. North Carolina Department of the Secretary of State. May 8, 2006. Retrieved 2006-11-07.
- ^ a b c "Elevations and Distances in the United States". U.S Geological Survey. April 29, 2005. Retrieved 2006-11-06.
- ^ "North Carolina Counties Map". Quickfacts.census.gov. 2009-01-07. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "The Industrial History of North Carolina: A Research Guide". Retrieved 2010-11-03.
- ^ "The Growth of Research Triangle Park" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-11-03.
- ^ "Mount Mitchell State Park " History". Retrieved 2010-11-07.
- ^ National and State Population Estimates – U.S. Census Bureau
- ^ "Watersheds". NC Office of Environmental Education. 2007-02-16.
- ^ John Hairr, The Great Hurricanes of North Carolina (2008) pp 139-150
- ^ "NOAA National Climatic Data Center". Retrieved 2006-10-24.
- ^ "NC residents band together after killer storms". News & Observer. April 21, 2011. Retrieved April 22, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ "Tornado outbreak is NC's most active on record". News & Observer. April 22, 2011. Retrieved April 22, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ "Average Weather for Fayetteville, NC - Temperature and Precipitation". Weather.com. Retrieved 2010-07-02.
- ^ Constance E. Richards, "Contact and Conflict", American Archaeologist, Spring 2008, p.14. Retrieved 26 June 2008.
- ^ Milton Ready, The Tar Heel State: A History of North Carolina (U. of South Carolina Press, 2005) pp 116, 120
- ^ Patrick Gibbs (March 2004). "David G. Moore, Robin A. Beck, Jr., and Christopher B. Rodning, "Joara and Fort San Juan: culture contact at the edge of the world", ''Antiquity'', Vol.78, No. 229,". Antiquity.ac.uk. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ Constance E. Richards, "Contact and Conflict" Warren Wilson College, American Archaeologist, Spring 2008. Retrieved 26 June 2008.
- ^ Randinelli, Tracey. Tanglewood Park. Orlando, Florida: Harcourt. p. 16. ISBN 0-15-333476-2.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "North Carolina State Library - North Carolina History". Statelibrary.dcr.state.nc.us. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "Cherokee Indians". Uncpress.unc.edu. 1919-11-16. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ Russell Thornton (1990) "American Indian holocaust and survival: a population history since 1492". University of Oklahoma Press. p.79. ISBN 080612220X
- ^ Fenn and Wood, Natives and Newcomers, pp. 24–25
- ^ Powell, North Carolina Through Four Centuries, p. 105
- ^ a b c d Lefler and Newsome, (1973)
- ^ "Paul Heinegg, ''Free African Americans in Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Maryland and Delaware''". Freeafricanamericans.com. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "The Great Seal of North Carolina". NETSTATE. Retrieved 2006-09-12. [dead link]
- ^ John Hope Franklin, Free Negroes of North Carolina, 1789–1860, Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1941, reprint, 1991
- ^ "NC Business History - Railroads". Historync.org. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ Historical Census Browser, 1860 US Census, University of Virginia[dead link]. Retrieved 21 March 2008.
- ^ "Center for Civic Education - Lincoln Bicentennial with Supplemental Lesson: Timeline". Civiced.org. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "Highlights: Secession". Docsouth.unc.edu. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "Today in History: June 8". Memory.loc.gov. 1959-04-09. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "Civil War Facts About North Carolina". Classbrain.com. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ Economy at a Glance. For North Carolina. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2011.
- ^ "North Carolina Public Schools". Ncpublicschools.org. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ News & Observer: Perdue's choice to lead state's school system takes office[dead link]
- ^ a b "NC Public School Facts". Ncpublicschools.org. Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ http://www.igovacation.com/search_rentals/stateinfo.asp?State=nc
- ^ "What To Do Across North Carolina". VisitNC.com. 2006. Archived from the original on 2006-12-01. Retrieved 2006-12-18.
- ^ Unterberger, Richie (1999). Music USA: The Rough Guide. The Rough Guides. ISBN 1-85828-421-X.
- ^ "Hey, James Taylor – You've got a ... bridge?". Rome News-Tribune. May 21, 2002. Retrieved June 28, 2009.
- ^ Hoppenjans, Lisa (October 2, 2006). "You must forgive him if he's ..." The News & Observer. Retrieved June 28, 2009. [dead link]
- ^ Waggoner, Martha (October 17, 2008). "James Taylor to play 5 free NC concerts for Obama". USA Today. Associated Press. Retrieved June 28, 2009.
- ^ Garner, Bob (2007). Bob Garner's Guide to North Carolina Barbecue. John F. Blair, Publisher. ISBN 9780895872548.
- ^ Craig, H. Kent (2006). "What is North Carolina-Style BBQ?". ncbbq.com. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
- ^ Nannie M. Tilley, The R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Company (2009)
- ^ "USS North Carolina 'brought to life' again". WRAL-TV. 2008-05-03. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
- ^ "Secretary of State of North Carolina". Retrieved 2011-07-24.
- ^ "Gov. easily vows to keep N.C. most military friendly state in the Nation" (Press release). State of North Carolina - Office of the Governor. 2006-05-13. Retrieved 2007-06-23.
Further reading
- Clay, James, and Douglas Orr, eds., North Carolina Atlas: Portrait of a Changing Southern State 1971
- Christensen, Rob. The Paradox of Tar Heel Politics (Chapel Hill, University of North Carolina Press, 2008).
- Cooper, Christopher A., and H. Gibbs Knotts, eds. The New Politics of North Carolina (Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2008)
- Crow; Jeffrey J. and Larry E. Tise; Writing North Carolina History (1979) online
- Fleer; Jack D. North Carolina Government & Politics (1994) online political science textbook
- Hawks; Francis L. History of North Carolina 2 vol 1857
- Kersey, Marianne M., and Ran Coble, eds., North Carolina Focus: An Anthology on State Government, Politics, and Policy, 2d ed., (Raleigh: North Carolina Center for Public Policy Research, 1989).
- Lefler; Hugh Talmage. A Guide to the Study and Reading of North Carolina History (1963) online
- Lefler, Hugh Talmage, and Albert Ray Newsome, North Carolina: The History of a Southern State (1954, 1963, 1973), standard textbook
- Link, William A. North Carolina: Change and Tradition in a Southern State (2009), 481pp history by leading scholar
- Luebke, Paul. Tar Heel Politics: Myths and Realities (1990).
- Powell William S. Dictionary of North Carolina Biography. Vol. 1, A-C; vol. 2, D-G; vol. 3, H-K. 1979-88.
- Powell, William S. North Carolina Fiction, 1734-1957: An Annotated Bibliography 1958
- Powell, William S. North Carolina through Four Centuries (1989), standard textbook
- Powell, William S. and Jay Mazzocchi, eds. Encyclopedia of North Carolina (2006) 1320pp; 2000 articles by 550 experts on all topics; ISBN 0-8078-3071-2. The best starting point for most research.
- Ready, Milton. The Tar Heel State: A History of North Carolina (2005) excerpt and text search
- WPA Federal Writers' Project. North Carolina: A Guide to the Old North State. 1939. famous WPA guide to every town
Primary sources
- Hugh Lefler, North Carolina History Told by Contemporaries (University of North Carolina Press, numerous editions since 1934)
- H. G. Jones, North Carolina Illustrated, 1524–1984 (University of North Carolina Press, 1984)
- North Carolina Manual, published biennially by the Department of the Secretary of State since 1941.
External links
![]() Geographic data related to North Carolina at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to North Carolina at OpenStreetMap
- General
- History
- University of North Carolina at Greensboro Libraries Digital Collections
- North Carolina State Guide, from the Library of Congress
- Government and education
- North Carolina state government
- North Carolina Department of Commerce
- North Carolina state library
- Energy & Environmental Data for North Carolina
- USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of North Carolina
- North Carolina facts from US Department of Agriculture ERS
- North Carolina Court System official site
- North Carolina facts from US Census Bureau
- North Carolina Travel and Tourism Website
- NC ECHO - North Carolina Exploring Cultural Heritage Online
- North Carolina Collection, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Green 'N' Growing: The History of Home Demonstration and 4-H Youth Development in North Carolina - hosted by NCSU Libraries Special Collections Research Center
- NC Office of Archives and History
- NC Museum of History
- NC Employment website
- North Carolina State Databases - Annotated list of searchable databases produced by North Carolina state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association.
- NCpedia - Information on North Carolina counties, communities, famous people, government, history and symbols.
- Other
- Template:Wikitravel
- Old Growth Forest Wilderness Areas in Western North Carolina
- Old Growth Forest Wilderness Areas in Eastern North Carolina
- The Appalachian Trail
- Updates of statewide trends since publication of The North Carolina Atlas in 2000
- Lost Colony Blog
- Sketches of North Carolina by William Henry Foote (1846) - Full-text history book
Related information
Template:North Carolina cities and mayors of 100,000 population
![]() United States
United States






