Pacific Northwest: Difference between revisions
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by 69.62.21.31 to version by Myasuda. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (557262) (Bot) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
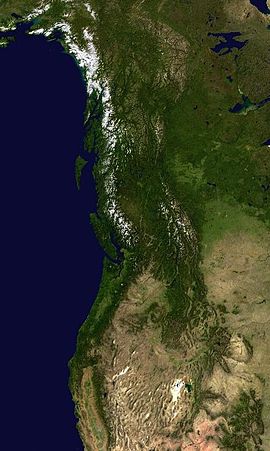
[[File:PacNW satellite.JPG|right|thumb|270px|The Pacific Northwest from [[space]]]] |
[[File:PacNW satellite.JPG|right|thumb|270px|The Pacific Northwest from [[space]]]] |
||
suck it loser |
|||
loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners.<ref name=schwantes>{{cite book|last=Schwantes|first=Carlos A.|title=The Pacific Northwest: an interpretive history|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=JImlIbueaXcC&pg=PA1|accessdate=14 December 2010|date=1 January 1996|publisher=University of Nebraska Press|isbn=9780803292284|pages=1–2}}</ref> A common concept of the Pacific Northwest includes the [[U.S. state]]s of [[Oregon]] and [[Washington (U.S. state)|Washington]], and the [[Provinces and territories of Canada|Canadian province]] of [[British Columbia]].<ref name="coates">{{cite book |last= Coates |first= Ken S. |editor1-last= Findlay |editor1-first= John M. |editor2-last= Coates |editor2-first= Ken S. |title= Parallel Destinies: Canadian-American Relations West of the Rockies |year= 2002 |publisher= University of Washington Press |isbn= 9780295982526 |pages= 3–5 |chapter= 1. Border Crossings |url= http://books.google.com/books?id=4leTYpWOE5UC&pg=PA3 |accessdate=14 December 2010}}</ref> This definition is often restricted further to include only the coastal areas west of the crest of the [[Cascade Mountains]] and [[Canadian Coast Mountains]]. Broader definitions may include the state of [[Alaska]] and the [[Yukon]] territory,<ref name="Hayes1999">{{cite book|last=Hayes|first=Derek|title=Historical atlas of the Pacific Northwest: maps of exploration and discovery : British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, Alaska, Yukon|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=sl57oHrVXGoC&pg=PA8|accessdate=14 December 2010|year=1999|publisher=Sasquatch Books|isbn=9781570612152|page=8}}</ref> and may reach east to the [[Rocky Mountains]].<ref name="coates"/> Definitions based on the historic [[Oregon Country]] reach east to the [[Continental Divide of the Americas|Continental Divide]], thus including nearly all of [[Idaho]] and parts of western [[Montana]] and western [[Wyoming]]. Sometimes the Pacific Northwest is defined as being the [[Northwestern United States]], wholly in the United States. Often these definitions are made by government agencies whose scope is limited to the United States.<ref>See, for example, this [http://www.nbii.gov/portal/server.pt/gateway/PTARGS_0_2_25589_1921_7072_43/http%3B/cbi-lap7.cbi.cr.usgs.gov%3B7097/publishedcontent/publish/geographic/southwest/pnwin_regional_ecosystems_intro/regionalecosystems_pnwin_l2_resized.jpg US [[United States Environmental Protection Agency|EPA]] map].</ref> Some definitions include, in addition to Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia, [[Southeast Alaska]], western Montana, the coast of northern [[California]] and a small part of northwestern [[Wyoming]].<ref name=sinclair>{{cite book|last1=Apostol|first1=Dean|last2=Sinclair|first2=Marcia|author3=Society for Ecological Restoration International|title=Restoring the Pacific Northwest: the art and science of ecological restoration in Cascadia|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=CsGyhzFBjyAC&pg=PR24|accessdate=14 December 2010|year=2006|publisher=Island Press|isbn=9781559630788|page=24}}</ref> The term "Pacific Northwest" should not be confused with the [[Northwest Territory]] (also known as the Great Northwest, a historic term in the United States) or the [[Northwest Territories]] of [[Canada]]. |
|||
The term '''Northwest Coast''' is often used when referring only to the coastal regions. The term '''Northwest Plateau''' has been used to describe the inland regions, although they are commonly referred to as "[[British Columbia Interior|the Interior]]" in British Columbia<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.interiorsavingscentre.com/index.shtml |title=Interior Savings Centre in Kamloops, British Columbia |publisher=Interiorsavingscentre.com |date= |accessdate=2010-08-18}}</ref> and the [[Inland Empire (Pacific Northwest)|Inland Empire]] in the United States. |
The term '''Northwest Coast''' is often used when referring only to the coastal regions. The term '''Northwest Plateau''' has been used to describe the inland regions, although they are commonly referred to as "[[British Columbia Interior|the Interior]]" in British Columbia<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.interiorsavingscentre.com/index.shtml |title=Interior Savings Centre in Kamloops, British Columbia |publisher=Interiorsavingscentre.com |date= |accessdate=2010-08-18}}</ref> and the [[Inland Empire (Pacific Northwest)|Inland Empire]] in the United States. |
||
Revision as of 15:12, 2 September 2011
suck it loser
loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners.[1] A common concept of the Pacific Northwest includes the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington, and the Canadian province of British Columbia.[2] This definition is often restricted further to include only the coastal areas west of the crest of the Cascade Mountains and Canadian Coast Mountains. Broader definitions may include the state of Alaska and the Yukon territory,[3] and may reach east to the Rocky Mountains.[2] Definitions based on the historic Oregon Country reach east to the Continental Divide, thus including nearly all of Idaho and parts of western Montana and western Wyoming. Sometimes the Pacific Northwest is defined as being the Northwestern United States, wholly in the United States. Often these definitions are made by government agencies whose scope is limited to the United States.[4] Some definitions include, in addition to Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia, Southeast Alaska, western Montana, the coast of northern California and a small part of northwestern Wyoming.[5] The term "Pacific Northwest" should not be confused with the Northwest Territory (also known as the Great Northwest, a historic term in the United States) or the Northwest Territories of Canada.
The term Northwest Coast is often used when referring only to the coastal regions. The term Northwest Plateau has been used to describe the inland regions, although they are commonly referred to as "the Interior" in British Columbia[6] and the Inland Empire in the United States.
The region's largest metropolitan areas are Seattle/Tacoma, Washington, with 3.3 million people;[7] Vancouver, British Columbia, with 2.3 million people;[8] and the Portland metropolitan area, with 2.2 million people.[9]
A key aspect of the Pacific Northwest is the US–Canada international border, which was established when the region was largely unsettled by non-indigenous peoples. The border along the 49th parallel and the Alaska Panhandle has had a powerful effect on the region. According to Canadian historian Ken Coates, the border has not merely influenced the Pacific Northwest—rather, "the region's history and character have been determined by the boundary".[2]
History
Indigenous peoples
The Pacific Northwest has been occupied by a diverse array of Indigenous American peoples for millennia, beginning with Paleo-Native Americans who explored and colonized the area roughly 15,000 years before Europeans arrived. The Pacific Coast is seen by a growing number of scholars as a major migration route for late Pleistocene peoples moving from northeast Asia into the Americas. Archaeological evidence for these earliest Native Americans is sketchy—in part because heavy glaciation, flooding, and post-glacial sea level rise have radically changed the landscape—but fluted Clovis-like points found in the region were probably left by Paleoindians at least 13,000 years ago. Even earlier evidence for human occupation dating back as much as 14,500 years ago is emerging from Paisley Caves in central Oregon.
With a history of human occupation spanning many millennia, and the incredible richness of Pacific Northwest fisheries (salmon, etc.), it is not surprising that the tribes who occupied the area historically were some of the most complex hunter-gatherer-fishers in history. They lived in large villages or towns, built plank houses and large canoes, and had sophisticated artistic and technological traditions. In British Columbia and Southeast Alaska, for instance, maritime tribes like the Tlingit and Haida erected the large and elaborately carved totem poles that are iconic of Pacific Northwest artistic traditions. Throughout the area, thousands of descendants of these proud Pacific Northwest tribes still live and many of their cultural traditions continue to be practiced.
Initial European exploration
In 1579 the British captain and erstwhile privateer Francis Drake sailed up the west coast of North America perhaps as far as Oregon or even British Columbia before returning south to land and make ship repairs. At this landing site, probably near present-day San Francisco, Drake claimed the region for England, naming it New Albion.[3][10] Juan de Fuca, a Greek captain in the employ of Spain, might have found the Strait of Juan de Fuca around 1592. The strait was named for him, but whether he discovered it or not has long been questioned.[11] During the early 1740s, Imperial Russia sent the Dane Vitus Bering to the region.[12] By the late 18th century and into the mid-19th century, Russian settlers had established several posts and communities on the northeast Pacific coast, eventually reaching as far south as Fort Ross, California. The Russian River was named after these settlements.
In 1774 the viceroy of New Spain sent Juan Pérez in the ship Santiago to the Pacific Northwest. Peréz made landfall on the Queen Charlotte Islands on July 18, 1774. The northernmost latitude he reached was 54°40′ N.[13] This was followed, in 1775, by another Spanish expedition, under the command of Bruno de Heceta and including Juan Peréz and Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra as officers. On July 14, 1775 they landed on the Olympic Peninsula near the mouth of the Quinault River. Due to an outbreak of scurvy, Heceta returned to Mexico. On August 17, 1775 he sighted the mouth of the Columbia River but could not tell if it was a river or a major strait. His attempt to sail in failed due to overly strong currents. He named it Bahia de la Asúnciõn. While Heceta sailed south, Quadra continued north in the expedition's second ship, the Sonora. He reached 59° N, before turning back.[14]
In 1778 English mariner Captain James Cook visited Nootka Sound on Vancouver Island and also voyaged as far as Prince William Sound. In 1779 a third Spanish expedition, under the command of Ignacio de Artega in the ship Princesa, and with Quadra as captain of the ship Favorite, sailed from Mexico to the coast of Alaska, reaching 61° N. Two further Spanish expeditions, in 1788 and 1789, both under Esteban Jose Martínez and Gonzalo López de Haro, sailed to the Pacific Northwest. During the second expedition they met the American captain Robert Gray near Nootka Sound. Upon entering Nootka Sound, they found William Douglas and his ship the Iphigenia. There followed the Nootka Crisis, which was resolved by agreements known as the Nootka Convention. In 1790 the Spanish sent three ships to Nootka Sound, under the command of Francisco de Eliza. After establishing a base at Nootka, Eliza sent out several exploration parties. Salvador Fidalgo was sent north to the Alaska coast. Manuel Quimper, with Gonzalo López de Haro as pilot, explored the Strait of Juan de Fuca, discovering the San Juan Islands and Admiralty Inlet in the process. Francisco de Eliza himself took the ship San Carlos into the Strait of Juan de Fuca. From a base at Port Discovery, his pilotos (masters) José María Narváez and Juan Carrasco explored the San Juan Islands, Haro Strait, Rosario Strait, and Bellingham Bay. In the process they discovered the Strait of Georgia and explored it as far north as Texada Island. The expedition returned to Nootka Sound by August 1791. Alessandro Malaspina, sailing for Spain, explored and mapped the coast from Yakutat Bay to Prince William Sound in 1791, then sailed to Nootka Sound. A scientific expedition in the manner of James Cook, Malaspina's scientists studied the Tlingit and Nuu-chah-nulth peoples before returning to Mexico. Another Spanish explorer, Jacinto Caamaño, sailed the ship Aranzazu to Nootka Sound in May 1792. There he met Quadra, who was in command of the Spanish settlement and Fort San Miguel. Quadra sent Caamaño north, to carefully explore the coast between Vancouver Island and Bucareli Bay, Alaska. Various Spanish maps, including Caamaño's, were given to George Vancouver in 1792, as the Spanish and British worked together to chart the complex coastline.[14]
From 1792 to 1794, George Vancouver charted the Pacific Northwest on behalf of Great Britain, including the Strait of Georgia, the bays and inlets of Puget Sound, and the Johnstone Strait–Queen Charlotte Strait and much of the rest of the British Columbia Coast and southeast Alaska shorelines.[13] For him the city of Vancouver and Vancouver Island are named, as well as Vancouver, Washington. From Mexico, Malaspina dispatched last Spanish exploration expedition in the Pacific Northwest, under Dionisio Alcalá Galiano and Cayentano Valdes aboard the schooners Sutil and Mexicana.[15] They met Vancouver in the Strait of Georgia on June 21, 1792. Vancouver had explored Puget Sound just previously. The Spanish explorers knew of Admiralty Inlet and the unexplored region to the south, but decided to sail north. They discovered and entered the Fraser River shortly before meeting Vancouver. After sharing maps and agreeing to cooperate, Galiano, Valdés, and Vancouver sailed north to Desolation Sound and the Discovery Islands, charting the coastline together. They passed through Johnstone Strait and returned to Nootka Sound. As a result, the Spanish explorers, who had set out from Nootka, became the first Europeans to circumnavigate Vancouver Island. Vancouver himself had entered the Strait of Juan de Fuca directly without going to Nootka first, so had not sailed completely around the island.[14]
In 1786 Jean-François de La Pérouse, representing France, sailed to the Queen Charlotte Islands after visiting Nootka Sound but any possible French claims to this region were lost when La Pérouse and his men and journals were lost in a shipwreck near Australia. Maritime fur trader Charles William Barkley also visited the area in the Imperial Eagle, a British ship falsely flying the flag of the Austrian Empire. American merchant sea-captain Robert Gray traded along the coast and discovered the mouth of the Columbia River.
Boundary disputes

Initial formal claims to the region were asserted by Spain, based on the Treaty of Tordesillas which, in the Spanish Empire's interpretation, endowed that empire with the Pacific Ocean as a "Spanish lake". Russian Maritime Fur Trade activity, through the Russian-America Company, extending from the farther side of the Pacific to 'Russian America' prompted Spain to send expeditions north to assert Spanish ownership, while at the same time British claims were made and advanced by Captain James Cook and subsequent expeditions by George Vancouver. Potential French, Austrian and Portuguese claims were never advanced. As of the Nootka Conventions, the last in 1794, Spain gave up its exclusive a priori claims and agreed to share the region with the other Powers, giving up its garrison at Nootka Sound in the process.
The United States later established a claim following the exploration of the region by the Lewis and Clark Expedition, partly through the negotiation of former Spanish claims north of the Oregon-California boundary. From the 1810s until the 1840s, modern-day Washington, Oregon, Idaho, and western Montana, along with most of British Columbia, were part of what the United States called the Oregon Country and Britain called the Columbia District. This region was jointly claimed by the United States and Great Britain after the Treaty of 1818, which established a condominium of interests in the region in lieu of a settlement. In 1840 American Charles Wilkes explored in the area. John McLoughlin, Chief Factor of the Hudson's Bay Company, headquartered at Fort Vancouver, was the de facto local political authority for most of this time.
This arrangement ended as U.S. settlement grew and President James K. Polk was elected on a platform of calling for annexation of the entire Oregon Country and of Texas. After his election, supporters coined the famous slogan "Fifty-four Forty or Fight", referring to 54°40' north latitude—the northward limit of the region.[16] After a war scare with the United Kingdom, the Oregon boundary dispute was settled in the 1846 Oregon Treaty, partitioning the region along the 49th parallel and resolving most but not all of the border disputes (see Pig War).
The mainland territory north of the 49th parallel remained unincorporated until 1858, when a mass influx of Americans and others during the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush forced the hand of Colony of Vancouver Island's Governor James Douglas, who declared the mainland a Crown Colony, although official ratification of his unilateral action was several months in coming. The two colonies were amalgamated in 1866 to cut costs, and joined the Dominion of Canada in 1871. The U.S. portion became the Oregon Territory in 1848; it was later subdivided into territories that were eventually admitted as states, the first of these being Oregon itself in 1859. See Washington Territory.
American expansionist pressure on British Columbia persisted after the colony became a province of Canada, even though Americans living in the province did not harbor annexationist inclinations. The Fenian Brotherhood openly organized and drilled in Washington, particularly in the 1870s and the 1880s, though no cross-border attacks were experienced. During the Alaska Boundary Dispute, U.S. President Teddy Roosevelt threatened to invade and annex British Columbia if Britain would not yield on the question of the Yukon ports. In more recent times, during the so-called "Salmon War" of the 1990s, Washington Senator Slade Gorton called for the U.S. Navy to "force" the Inside Passage, even though it is not an official international waterway. Disputes between British Columbia and Alaska over the Dixon Entrance of the Hecate Strait between Prince Rupert and the Queen Charlotte Islands have not been resolved.[17]
Geology
The Northwest is still highly geologically active, with both active volcanoes and geologic faults.[18]
Active volcanoes in the region include Mount Garibaldi, Mount Baker, Mount Rainier, Mount Saint Helens, which erupted in 1980, Mount Hood, Mount Jefferson, and Mount Shasta.
Geography
The Pacific Northwest is a diverse geographic region, dominated by several mountain ranges, including the Coast Mountains, the Cascade Range, the Olympic Mountains, the Columbia Mountains, and the Rocky Mountains. The highest peak in the Pacific Northwest is Mount Rainier, in the Washington Cascades, at 14,410 feet (4,392 m). Immediately inland from the Cascade Range there is a broad plateau, narrowing progressively northwards, only a few miles wide in Canada, and also getting higher. In the US this region, semi-arid and often completely arid, is known as the Columbia Plateau, while in British Columbia it is the Interior Plateau, also called the Fraser Plateau. The Columbia Plateau was the scene of massive ice-age floods, as a consequence there are many coulees, canyons, and plateaus. Much of the plateau, especially in eastern Washington, is irrigated farmland. The Columbia River cuts a deep and wide gorge around the rim of the Columbia Plateau, and through the Cascade Range on its way to the Pacific Ocean. After the Mississippi, more water flows through the Columbia than any other river in the lower 48 states.
Because many areas have plentiful rainfall, the Pacific Northwest has some of North America's most lush and extensive forests, and at one time, the largest trees in the world. Coastal forests in some areas are classified as temperate rain forest.
The major cities of Vancouver, Portland, Seattle, and Tacoma all began as seaports supporting the logging, mining, and farming industries of the region, but have developed into major technological and industrial centers (such as the Silicon Forest), which benefit from their location on the Pacific Rim.
If defined as Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia, the Pacific Northwest has four US National Parks: Crater Lake in Oregon, and Olympic, Mount Rainier, and North Cascades in Washington. The Redwood National and State Parks are in California, just south of the Oregon border. Glacier Bay National Park is located in southeast Alaska, as is Wrangell–St. Elias National Park. Other outstanding natural features include the Oregon Coast, the Columbia River Gorge, the Columbia River, Mount St. Helens, and Hells Canyon. There are several Canadian National Parks in the Pacific Northwest, including Pacific Rim National Park on the west coast of Vancouver Island, Mount Revelstoke National Park and Glacier National Park in the Selkirk Range alongside Rogers Pass, Kootenay National Park and Yoho National Park on the British Columbia flank of the Rockies, Gwaii Haanas National Park Reserve in the Queen Charlotte Islands, and the Gulf Islands National Park Reserve in the Strait of Georgia. Although unprotected by national parks and only a handful of provincial parks, the south-central Coast Mountains in British Columbia contain the five largest mid-latitude icefields in the world.
Climate
The Pacific Northwest experiences a wide variety of climates. An Oceanic climate ("marine west coast climate") occurs in most coastal areas, typically between the ocean and high mountain ranges. An Alpine climate dominates in the high mountains. Semi-arid and Arid climates are found east of the higher mountains, especially in rainshadow areas. The Harney Basin of Oregon is an example of arid climate in the Pacific Northwest. Humid continental climates occur inland on windward sides, in places such as Revelstoke, British Columbia. A Subarctic climate can be found farther north, especially in Yukon and Alaska.
Under the Köppen climate classification, a cool summer version of the dry-summer subtropical (Csb) designation, typically referred to as "Mediterranean", is assigned to many areas of the Pacific Northwest as far north as southern Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands, including cities such as Victoria, British Columbia, Seattle, and Portland.[20] These zones are not associated with a typical Mediterranean climate, and would be classified as Temperate Oceanic (Cfb), except dry-summer patterns typical to the Pacific Northwest meet Koeppen's minimum Cs thresholds. Other climate classification systems, such as Trewartha, place these areas firmly in the Oceanic zone (Do).[21]
Ecoregions
Much of the Pacific Northwest is forest. The Georgia Strait–Puget Sound basin is shared between British Columbia and Washington, and the Pacific temperate rain forests ecoregion, which is the largest of the world's temperate rain forest ecozones in the system created by the World Wildlife Fund, stretches along the coast from Alaska to California. The dryland area inland from the Cascade Range and Coast Mountains is very different from the terrain and climate of the Coast, and comprises the Columbia, Fraser and Thompson Plateaus and mountain ranges contained within them. The interior regions' climates are a northward extension of the Great Basin Desert which spans the Great Basin farther south, although by their northern reaches dryland and desert areas verge with boreal forest and various alpine flora regimes.
Population
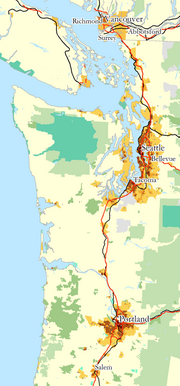
Most of the population of the Pacific Northwest is concentrated in the Vancouver–Seattle–Portland corridor. This area is sometimes seen as a megacity (also known as a conurbation, an agglomeration, or a megalopolis). This "megacity" stretches along Interstate 5 in the states of Oregon and Washington and Hwy 99 in the province of British Columbia. As of 2004, the combined populations of the Greater Vancouver/Lower Mainland area, the Seattle metropolitan area and the Portland metropolitan area totaled almost nine million people.
Largest cities by population in the Pacific Northwest
| City | State/Province | Population | Metropolitan Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seattle | Washington | 608,660 [22] | 3,439,809[23] |
| Portland | Oregon | 583,776[23] | 2,226,009[23] |
| Vancouver | British Columbia | 578,041[24] | 2,116,581[24] |
| Surrey | British Columbia | 394,976 [25] | [n 1] |
| Spokane | Washington | 208,916[22] | 471,221[26] |
| Boise | Idaho | 205,671[27] | 616,561[23] |
| Tacoma | Washington | 198,397[22] | [n 2] |
| Tri-Cities | Washington | 181,756[28][n 3] | 253,340[23] |
| Vancouver | Washington | 161,791[22] | [n 4] |
| Eugene | Oregon | 156,185[29] | 351,715[23] |
| Salem | Oregon | 154,637[29] | 390,738[23] |
| Abbotsford | British Columbia | 123,864[30] | 159,020[30] |
| Kelowna | British Columbia | 106,707[31] | 162,276[31] |
| Gresham | Oregon | 105,594[29] | [n 4] |
| Hillsboro | Oregon | 91,611[29] | [n 4] |
| Yakima | Washington | 91,067[28] | 243,231[28] |
| Beaverton | Oregon | 89,803[29] | [n 4] |
| Victoria | British Columbia | 78,057[32] | 330,088[32] |
| Olympia | Washington | 46,478[28] | 252,264[23] |
Politics
A major divide in political opinion separates the region's greatly more populated urban core and rural areas west of the mountains from its less populated rural areas to their east and (in B.C.) north.[33] The coastal areas—especially in the cities of Vancouver, Victoria, Bellingham, Seattle, Tacoma, Olympia, Portland, Corvallis, Eugene, and Ashland—are some of the most politically liberal parts of North America, consistently supporting left-wing political candidates and causes by significant majorities, while the Interior and North tend to be more conservative and consistently support right-wing candidates and causes. It should be noted that the religious right has far less influence throughout the region than elsewhere in the U.S., although it is very strong in the Fraser Valley, and also that certain areas of the BC Interior, particularly the West Kootenay and some areas of Vancouver Island and the BC Coast, have long histories of labour, environmental and social activism.
The urban core in addition to certain rural districts is known for supporting liberal political views, perceived as controversial in much of the rest of North America. Many jurisdictions have relatively liberal abortion laws, gender equality laws, legalized medical marijuana, and are supportive of LGBT rights, especially British Columbia, where gay marriage is legal, and Washington and Oregon, where same-sex civil unions are legal. Due to the urban core's size and voting impact, their counties and states as a whole have generally followed their leads (often to the disgruntlement of the more conservative rural areas). Oregon was the first U.S. state to legalize physician-assisted suicide, with the Death with Dignity Act of 1994. Washington State was the second when I-1000 passed in 2008. Colegio Cesar Chavez, the first fully accredited Hispanic college in the U.S., was founded in Mount Angel, Oregon in 1973. King County, Washington, of which Seattle is a part, rebranded itself in honor of Martin Luther King.
These areas, especially around Puget Sound, have a long history of political radicalism. The radical labor organizers called Wobblies were particularly strong there in the mines, lumber camps and shipyards. A number of anarchist communes sprung up there in the early 20th century (see Charles Pierce LeWarne's Utopias on Puget Sound, 1885-1915 for an excellent overview of this popular yet forgotten movement). Together with Winnipeg, Manitoba, Seattle is one of two major cities in North America in which the populace engaged in a general strike and was the first major American city to elect a woman mayor, Bertha Landes.[34] Socialist beliefs were once widespread (thanks in large part to the area's large numbers of Scandinavian immigrants) and the region has had a number of Socialist elected officials: so great was its influence that the U.S. Postmaster General, James Farley, jokingly toasted the "forty-seven states of the Union, and the Soviet of Washington", at a gala dinner in 1936.[35]
The region also has a long history of starting cooperative and communal businesses and organizations, including Group Health,[36] REI, Puget Consumer's Co-ops and numerous granges and mutual aid societies. It also has a long history of publicly owned power and utilities, with many of the region's cities owning their own public utilities. In part as a result, the region enjoys the lowest electrical power rates on the continent. In British Columbia, credit unions are common and popular cooperatively owned financial institutions.
Economy
- Agriculture (fruit, potatoes, Tillamook cheese, dairy, wine, vegetables, wheat, Cascade hops, barley, hazelnuts)
- Aerospace (Boeing Commercial Airplane unit, Air Canada, Alaska Air, CHC Helicopter, Esterline)
- Diversified (Jim Pattison Group, Finning, Washington Marine Group)
- Entertainment industry (film and television, Lions Gate Entertainment, Lionsgate Studios, Lionsgate Television, Vancouver Film Studios, Bridge Studios)
- Finance and Banking (RBC, HSBC Bank Canada, Russell Investments, Umpqua Holdings Corporation)
- Forestry (Weyerhaeuser, Canfor, Tolko, Boise Cascade)
- Fishing and canning (salmon, halibut, herring, geoducks and other clams, crab, sea-urchin)
- High Technology and E-commerce (Microsoft, Microsoft Canada, Intel, F5 Networks, Nintendo of America, Nintendo of Canada, Tektronix, Amazon.com, Expedia, Ballard Power Systems, MacDonald Dettwiler, EA Canada, Cymax Stores, Micron Technology)
- Higher Education
- British Columbia
- Washington
- Idaho
- Oregon
- Northern California
- Humboldt State University
- Montana
- Hydroelectric power (Grand Coulee Dam, Bonneville Dam, Bridge River Power Project)
- Mass Retail (London Drugs, Costco, Blenz, Starbucks, Tullys, Nordstrom, Zumiez, Albertsons)
- Microbrewing (BridgePort, Deschutes, MacTarnahan's, Nelson, Ninkasi, Pyramid, Widmer Brothers, Yukon)
- Mining (Goldcorp, Cominco)
- Outdoor Tourism (Alpine Skiing, Snowboarding, Hiking, Kayaking, Rafting, Fishing, Mountain Biking, Water sports)
- Shoes & Apparel (Nike, Adidas North America, Columbia, R.E.I., Lululemon)
- Real estate marketing & realty development/construction.
Aluminum smelting was once an important part of the region's economy due to the abundance of once-cheap hydroelectric power and despite any bauxite reserves in the region. Hydroelectric power generated by the hydroelectric dams on the Columbia River powered at least ten aluminum smelters during the mid-20th century. By the end of World War II these smelters were producing over a third of the United States' aluminum. Production rose during the 1950s and 1960s, then declined. By the first decade of the 21st century the aluminum industry in the Pacific Northwest was essentially defunct.[37] The Alcan smelter at Kitimat continues in operation and is fed by the diversion of the Nechako River (a tributary of the Fraser) to a powerhouse on the coast at Kemano, near Kitimat.
The region as a whole, but especially the Seattle eastern suburbs along with Vancouver, is a hot-bed of high-tech business. It is also a leading "creative class" economic driver, with a thriving cultural sector, many knowledge workers and numerous international advertising, media and design firms.
B.C., Washington and Oregon together generate more than $450 billion worth of goods and services annually. If the three were a separate country, their GDP would be in the top 30 economies of the world. [citation needed]
Culture
While the dominant culture in the Pacific Northwest today is Anglo-American and Anglo-Canadian, there is significant Mexican and Chinese influence. 23% of Vancouver, B.C. is Chinese, and 50% does not speak English as a first language.[38] Parts of Oregon and Washington are bilingual in both English and Spanish, and Native American culture is strong throughout the Pacific Northwest. The hippie movement also began in California and the Pacific Northwest. There have been proposals for certain parts of the Pacific Northwest becoming its own country because of the shared ecoregion and culture.[39][40] The most well known proposals are Ecotopia from the Nine Nations of North America and Cascadia. However, the region is strongly divided by the international border, and this division has grown more rather than less powerful over the 20th century.[41] In addition, although the metropolitan centers of Vancouver, Seattle, and Portland are bound into a kind of urbanized region, they originated and continue to thrive as east-west gateways, competing with each other, rather than north-south connectors.[41]
Environmentalism
Environmentalism is prominent throughout the region, especially west of the Cascades. Environmentally conscious services such as recycling and public transportation are widespread, most notably in the more populous areas. A recent statistical analysis ranked the 50 Greenest Cities in the United States, placing Portland, Oregon first, Eugene, Oregon fifth, and Seattle, Washington eighth.[42] The region as a whole is also known for its bicycle culture as an alternative form of transportation; Portland is considered the second most bicycle-friendly city in the world.[43] Portland is also the hub of American bicycle manufacturing; as a whole it generated over $68 million in revenue in 2007 alone.[43] Politically, the Pacific Northwest is actively involved in environmental efforts. The international organization Greenpeace was born in Vancouver in 1970 as part of a large public opposition movement in British Columbia to US nuclear weapons testing on Amchitka Island in the Aleutians. Liberal and Conservative Northwesterners, such as former U.S. Senator Slade Gorton (R-WA) and moderate Democrats like former Speaker of the House Tom Foley (D-WA), have been prominent in the development of conservative approaches to environmental protection. Seattle in particular is also home to a large number of publications and institutions concerned with the environment and sustainability, including both Worldchanging and Grist.org, the U.S.'s two largest online green magazines. The Pacific Northwest is also noted for a large number of gardening clubs, with Victoria having an annual flower count in February.
Music
The modern-era Pacific Northwest is known for indie music, especially grunge and alternative rock, as well as historically-strong folk music and world music traditions. Jimi Hendrix, The Kingsmen, Nirvana, Soundgarden, Presidents of The United States of America, Heart, Queensrÿche, Built to Spill, Death Cab for Cutie, DOA, Foo Fighters, Agalloch, Elliott Smith, The Decemberists, The Dandy Warhols, Sleater-Kinney, Modest Mouse, Cherry Poppin Daddies, Everclear, Swollen Members, Blue Scholars, Macklemore, Pedro the Lion, Alice in Chains, the Subhumans, Skinny Puppy, Front Line Assembly, Blitzen Trapper, Pink Martini, Postal Service, and Pearl Jam were local artists who became ground-breaking rock bands of their times. Many are associated with the famous independent label Sub Pop. KEXP.org is a popular and nationally-noted Seattle-based public indie music radio station. Among the area's largest music festivals are the Merritt Mountain Music Festival, the Vancouver Folk Music Festival, the Sasquatch! Music Festival in George, Washington, Seattle's Bumbershoot, and Portland's Musicfest NW. Other artists worthy of note who hail from the Pacific Northwest are Bryan Adams, Nelly Furtado, Neko Case, Sarah MacLachlan, Michael Bublé, Fleet Foxes, and Meredith Brooks.
Cuisine
Cuisine of the area include wild salmon, huckleberries, a wide variety of Asian cuisines, and locally-produced fruits, vegetables, and cheeses. Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Italian and Greek cuisines are prevalent throughout the Northwest (most especially in Vancouver), and reflect the historically strong presence of those communities in the restaurant industry there. Similarly eateries featuring Persian, Asian Fusion, and Indo-Canadian cuisines are common throughout in Greater Vancouver, as are ethnic specialty restaurants of all kinds. Ethnic staples ranging from frozen perogies to frozen dim sum are common in most supermarkets in these communities.
Locally-made craft beers and premium wines from various wine-growing area within the region are popular with drinkers and diners. Northern latitude and coastal breezes create a climate that attracts international recognition for its mostly family-owned and operated vineyards and wineries.
Portland is considered to be the microbrew capital of America,[44] and is home to the Widmer Brothers Brewery.
Cannabis use is relatively popular, especially around Vancouver BC, Bellingham, Seattle, Olympia, Spokane, Portland and Eugene. Several of these jurisdictions have made arrests for cannabis a low enforcement priority. Medical marijuana is legal in British Columbia,[45] Washington[46] and Oregon.[47]
Sports
Skiing, snowboarding, cycling, mountaineering, hiking, camping, hunting, fishing, boating, and water sports are popular outdoor activities. Vancouver, Seattle, Tacoma, and Portland are home to numerous professional sports teams, including the BC Lions, Vancouver Canucks, Vancouver Canadians, Vancouver Whitecaps FC, Seattle Mariners, Seattle Seahawks, Seattle Sounders FC, Seattle Storm, Washington Stealth, Everett Aquasox, Tacoma Rainiers, Portland Trail Blazers, and Portland Timbers. The Whitecaps, Sounders, and Timbers compete annually for the Cascadia Cup in Major League Soccer.
Sports fans in Oregon are particularly passionate; followers of the Portland Trail Blazers basketball team refer to themselves as the Sixth Man. In Seattle many fans are still upset over the move of the Seattle Sonics[citation needed] while supporters of the Seattle Seahawks football team are known officially as the 12th Man.[48] And the supporter groups, (namely the Emerald City Supporters, Timbers Army, and Southsiders) of the three MLS teams of the region are renowned for their passion and dedication to their teams.
Video games
Seattle is considered by Digital Trends magazine to be the top gaming city in America, a possible indicator of markedly higher rates of video game usage throughout the Pacific Northwest in general.[49] Major companies headquartered in the region include Microsoft (Seattle Metropolitan Area), Microsoft Canada (Vancouver), Nintendo of America (Seattle Metropolitan Area), Nintendo of Canada (Vancouver), and video games maker Electronic Arts (Vancouver), as well as VALVe (Seattle Metropolitan Area).
Demographics
In the US side of the region, Latinos make up a large portion of the agricultural labor force east of the Cascade Range, and are an increasing presence in the general labor force west of the Cascades. African Americans are less numerous in the Pacific Northwest, however the overall African American population has been growing in other smaller urban areas throughout the region, such as Spokane and Eugene.[50] African Americans tend to be concentrated in western urban areas such as Tacoma, south Seattle, and Portland. Nonetheless, blacks have a very large presence in Tacoma's Hilltop and South Tacoma neighborhoods, Seattle's Central District and Rainier Valley neighborhoods and in Portland's Northeast Quadrant. There are growing numbers of Africans in Vancouver BC as well as Jamaicans and blacks from the US. As of the first decade of the 21st century, many Asians were moving out and into middle class suburbs, though some would voice concern about preserving historical communities particularly in Vancouver. British Columbia has the largest Asian presence per-capita in North America, with 10% of the population being of Chinese ancestry and also large numbers of South Asians, Filipinos, and others. The Asian presence in the U.S. section of the Pacific Northwest is comparably smaller, with all Asian groups together comprising about 8% of Washington state's population, and smaller figures in Oregon and Idaho.
African-Americans have held the positions of Mayor in Seattle and Spokane; King County executive, while the state of Washington elected a Chinese American Governor during the 1990s, Gary Locke.
British Columbians of many ethnicities are prominent in all levels of politics and government, and the province has a number of "firsts" in Canadian political history, including the first non-white Premier, Ujjal Dosanjh (who is Indo-Canadian) and the first Asian Lieutenant-Governor, the Hon. David Lam. The current Lieutenant-Governor, Steven Point, is of aboriginal origin, being Stó:lō (the dominant type of Coast Salish in BC's Lower Mainland) from the Chilliwack area. The former leader of the opposition party, the NDP, is Carole James, who is of partial Métis origin. Colonial governor James Douglas was himself mulatto of Guyanese extraction and his wife was of Cree origin.
On LGBT representation in government, Oregon has been a national leader. At the time of his election to the office of Portland mayor in 2008, Sam Adams was the first openly gay individual to represent a city of Portland's size in the United States. In Silverton, Oregon, the same year, Stu Rasmussen was elected the first transgendered mayor in U.S. history. The first two LGBT state supreme court justices in the country both sit on the Oregon Supreme Court. Oregon Secretary of State Kate Brown, who is first in line to the governorship, is the highest-ranking openly bisexual politician in the U.S.
Language
The Pacific Northwest English accent is considered to be "very neutral" to most Americans. It does, however, possess the low back vowel merger, or the cot–caught merger. Pacific Northwest English is one of the closest living accents to conservative General American English. It lacks the Northern Cities Vowel Shift, and does not participate as strongly in the California Vowel Shift or the Canadian raising as do other regional accents. Because of its lack of any distinguishing vowel shift, the accent is very similar to and hard to distinguish from conservative speakers in other dialect regions especially the Northern Midlands, California, and the prairies.
Chinook Jargon was a pidgin or trade language established among the indigenous inhabitants of the region. After contact with Europeans, French, English and Cree words entered the language, and "eventually Chinook became the lingua franca for as many as 250,000 people along the Pacific Slope from Alaska to Oregon".[51] Chinook Jargon reached its height of usage in the 19th century though remained common in resource and wilderness areas, particularly but not exclusively by Native Americans and Canadian First Nations people, well into the 20th century. Today its influence is felt mostly in place names and a handful of localized slang terms, particularly the word skookum, which remains hallmark of people raised in the region.
Besides English and indigenous languages, Chinese has been common since the gold rushes of the mid-19th century, most particularly in British Columbia. Since the 1980s the Toishan, a Cantonese-based dialect which was predominant in the area, has been replaced by mainstream Cantonese and by Mandarin because of large-scale immigration from Asia. Punjabi is also common in Vancouver, which has very large Sikh communities.
Spirituality and religion
The Pacific Northwest has the lowest rate of church attendance in the United States and consistently reports the highest percentage of atheism;[52][53] this is most pronounced on the part of the region west of the Cascades.[54] A recent study indicates that one quarter of those in Washington and Oregon believe in no religion.[55]
Religion plays a smaller part in Pacific Northwest politics than in the rest of the United States. The religious right has considerably less political influence than in other regions. Political conservatives in the Pacific Northwest tend to identify more strongly with free-market libertarian values than they do with more religious social conservatives.[56]
That said, three of the four major international charities in the region are religious in nature: Northwest Medical Teams International, World Concern, World Vision International, and Mercy Corps. This is part of a long tradition of activist religion. The Skid Road group, a shelter offering soup and sermons to the unemployed and recovering alcoholics, was launched in Vancouver, with the Salvation Army having deep roots in the Gastown district, dating back to the era of the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway (1880s) and attained prominence in the same centers during the Klondike Gold Rush.
The region is also known as a magnet for a wide range of philosophical and spiritual belief systems. Eastern spiritual beliefs have been adopted by an unusually large number of people (by North American standards), and Tibetan Buddhism in particular has a strong local following.[57] The Northwest Tibetan Cultural Association, claimed to be the largest organization of its kind in the world, was founded in Portland in 1993.
The region is home to many unique Christian communities, ranging from the Doukhobors to the Mennonites. The Mennonite Central Committee Supportive Care Services is based in Abbotsford, BC.[58] Mennonite Central Committee and Mennonite Disaster Service enjoy a heavy rate of enlistment and donations from the strong Mennonite community in British Columbia's Fraser Valley. Also within the region there is a fairly strong representation of Orthodox churches (Greek, Russian, Serbian and others) as well as the Ukrainian Uniate Catholic church. Religious sees that are based in the Pacific Northwest include the Roman Catholic ecclesiastical provinces of Portland, Seattle, and Vancouver, Province 8 of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America, the Anglican Ecclesiastical Province of British Columbia and the Yukon, and the suffragan dioceses that make up those provinces.
Yogic teachings, Sufism, tribal and ancient beliefs and other philosophies are widely studied and appreciated in the region. The Lower Mainland of British Columbia has a very large Sikh community. There has been major growth in Chinese Buddhist temples since the increase in immigration from East Asia in the 1980s, especially in Vancouver.
Also in Vancouver, there is a small Hindu population, a number of Parsee (Zoroastrians), and an emerging Muslim population from South Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Balkans, Southeast Asia and elsewhere.
Some people in the area also embrace alternative religion, such as New Age spirituality and Neo-Paganism.[59]
- Before its closure in 2004, Mary Manin Morrissey's "megachurch" called Living Enrichment Center, located in Wilsonville, Oregon, was one of the biggest New Thought churches in the entire world, with a congregation estimated at between two thousand and five thousand members. Morrissey's "Life Keys" religious program was broadcast to several major networks around the U.S. West Coast.
- Neale Donald Walsch, author of Conversations with God, lives in Ashland, Oregon, where he runs a retreat center.
- Gangaji, an internationally recognized spiritual teacher and disciple of Poonjaji, lives in Ashland, Oregon.
- Established in more recent times, the training school of the immortal (according to the organization) being Ramtha is headquartered in Yelm, Washington.
- The followers of the Guru Rajneesh, the sannyasins, established a center for their beliefs and lifestyle near Antelope, Oregon, which included an ashram complex as well as, for a while, an attempted takeover of the local economy.
- The Emissaries of Divine Light are a notable presence in the region of 100 Mile House, British Columbia.
- More controversially, the commune run by Brother Twelve in the Gulf Islands of British Columbia early in the 20th century. Oregon's Willamette Valley has a large population of Russian Old Believers.[60]
See also
- Atlantic Northeast, another region shared between Canada and the US
- Cascadia (disambiguation)
- Climate change in Washington
- Megaregions of the United States
- Northwest Coast art
Notes and references
- Notes
- ^ Part of Vancouver metropolitan area.
- ^ Part of Seattle metropolitan area (Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA MSA).
- ^ Sum of the populations of the cities of Kennewick, Pasco, and Richland.
- ^ a b c d Part of Portland metropolitan area (Portland-Vancouver-Hillsboro, OR-WA MSA).
- References
- ^ Schwantes, Carlos A. (1 January 1996). The Pacific Northwest: an interpretive history. University of Nebraska Press. pp. 1–2. ISBN 9780803292284. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ a b c Coates, Ken S. (2002). "1. Border Crossings". In Findlay, John M.; Coates, Ken S. (eds.). Parallel Destinies: Canadian-American Relations West of the Rockies. University of Washington Press. pp. 3–5. ISBN 9780295982526. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ a b Hayes, Derek (1999). Historical atlas of the Pacific Northwest: maps of exploration and discovery : British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, Alaska, Yukon. Sasquatch Books. p. 8. ISBN 9781570612152. Retrieved 14 December 2010. Cite error: The named reference "Hayes1999" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ See, for example, this US EPA map.
- ^ Apostol, Dean; Sinclair, Marcia; Society for Ecological Restoration International (2006). Restoring the Pacific Northwest: the art and science of ecological restoration in Cascadia. Island Press. p. 24. ISBN 9781559630788. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ "Interior Savings Centre in Kamloops, British Columbia". Interiorsavingscentre.com. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "Best Places to Live in Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, Washington Metro Area (WA)". Bestplaces.net. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "Teachers/ Education". Metrovancouver.org. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "Doing Business In Portland, Oregon". Business.GOV.
- ^ Quanchi, Max; Robson, John (2005). Historical dictionary of the discovery and exploration of the Pacific islands. Scarecrow Press. pp. 84–85, 207. ISBN 9780810853959. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Hayes, Derek (1999). Historical atlas of the Pacific Northwest: maps of exploration and discovery : British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, Alaska, Yukon. Sasquatch Books. p. 16. ISBN 9781570612152. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Vitus Bering Biography Summary". BookRags.com. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ a b "Historical Timeline". Ubcic.bc.ca. 2007-09-13. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ a b c Hayes, Derek (1999). Historical Atlas of the Pacific Northwest: Maps of exploration and Discovery. Sasquatch Books. ISBN 1-57061-215-3.
- ^ "Captain Alexandro Malaspina". Malaspina University-College. Retrieved 2008-02-05.
- ^ "Fifty-Four Forty or Fight". Geography.about.com. 2010-06-14. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "The Alaska Boundary Dispute" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "Volcano Seismicity in the Pacific Northwest". Pnsn.org. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "Map of Cascadia". Sightline.org. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "HESS - Abstract - Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification". Hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net. 2010-07-04. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ "GLOBAL ECOLOGICAL ZONING FOR THE GLOBAL FOREST RESOURCES ASSESSMENT 2000". Fao.org. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ a b c d "U.S. Census Bureau Delivers Washington's 2010 Census Population Totals". United States Census Bureau. February 23, 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Population and Housing Occupancy Status: 2010 - United States -- Metropolitan Statistical Area; and for Puerto Rico". 2010 United States Census. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. April 14, 2011. Retrieved 12 July, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Census 2006 Community Profiles: Vancouver, City and CMA". Government of Canada. 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Census 2006 Community Profiles: Surrey, City and CMA". Government of Canada. 2006. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ^ "Washington population by county - Census 2010: Washington". The Spokesman-Review. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau Delivers Idaho's 2010 Census Population Totals". United States Census Bureau. February 23, 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Washington population by city - Census 2010: Washington". The Spokesman-Review. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "U.S. Census Bureau Delivers Oregon's 2010 Census Population Totals". United States Census Bureau. February 23, 2011. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ a b "Census 2006 Community Profiles: Abbotsford, City and CMA". Government of Canada. 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ a b "Census 2006 Community Profiles: Kelowna, City and CMA". Government of Canada. 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ a b "Census 2006 Community Profiles: Victoria, City and CMA". Government of Canada. 2006. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Font size Print E-mail Share (2000-10-25). "Northwest Passage". CBS News. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "Communism in Washington State - History and Memory Project". Depts.washington.edu. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "HistoryLink Essay: Group Health Cooperative - Part 1: Planting the Seeds, 1911-1945". Historylink.org. 2005-11-13. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ Aluminum, Columbia River History, Northwest Power & Conservation Council
- ^ Arthur Frommer (2008-12-08). "Vancouver's melting pot makes a terrific cultural stew". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ The Republic of Cascadia Retrieved on 2009-12-23
- ^ "Retrieved on 2009-12-23[http://www.worldchanging.com/archives/004331.html Retrieved on 2009-12-23". Cascadia-bioregion.tripod.com. 1924-05-03. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
{{cite web}}: External link in|title= - ^ a b Abbott, Carl (2002). "8. That Long Western Border". In Findlay, John M.; Coates, Ken S. (eds.). Parallel Destinies: Canadian-American Relations West of the Rockies. University of Washington Press. pp. 203–213–5. ISBN 9780295982526. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ Svoboda, Elizabeth (2010-08-07). "America's 50 Greenest Cities | Popular Science". Popsci.com. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ a b Bower, Craig S. (2008-06-19). "North America's most bike-friendly cities - Travel - Active Travel - msnbc.com". MSNBC. Retrieved 2010-08-18.
- ^ Gross, Matt (May 10, 2009). "Frugal Portland". The New York Times. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions - Medical Use of Marihuana, Health Canada
- ^ Washington Medical Marijuana Legality, Washington State RCW
- ^ "Oregon Medical Marijuana Legality". Oregon.gov. 2011-02-01. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "Spirit of 12". Seahawks.com. Retrieved 2010-08-18. [dead link]
- ^ "Seattle Top Gaming City?". Digital Trends. May 2, 2006.
- ^ "uwnews.washington.edu". uwnews.washington.edu. 1997-01-15. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "Can We Still Speak Chinook?". Thetyee.ca. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "Religion and Public Life in the Pacific Northwest". Religionatlas.org. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "Charting the unchurched in America". USA Today. March 7, 2002. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ "Religious identification in the U.S". Religioustolerance.org. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ "American Religious Identification Survey" (PDF). March 2009.
- ^ Vance, Chris (July 24, 2007). "Crosscut Seattle - Why Washington Republicans got creamed in 2006 and what they can do about it". Crosscut.com. Retrieved 2011-08-13.
- ^ Yardley, William (April 11, 2008). "Dalai Lama Arrives for a Five-Day Conference in Seattle, Very Much His Kind of Town". The New York Times. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ Mennonite Central Committee Supportive Care Services[dead link]
- ^ "ABC News: School Says Halloween Disrespectful to Witches". Abcnews.go.com. 2004-10-21. Retrieved 2011-02-19.
- ^ Oregon Historical Society article about Old Believers. Retrieved February 9, 2007.
Further reading
- Gastil, Raymond D., and Barnett Singer. The Pacific Northwest: Growth of a Regional Identity (McFarland, 2010) 221 pp. isbn 978-0-7864-4540-0
- Inglis, Robin. Historical Dictionary of the Discovery and Exploration of the Northwest Coast of America (Scarecrow, 2008) lxxvi+429 pp. isbn 978-0-8108-5551-9
- Schwantes, Carlos A. The Pacific Northwest: An Interpretive History (2nd ed. 2000)
External links
- Center for the Study of the Pacific Northwest at the University of Washington
- American Indians of the Pacific Northwest from the Library of Congress
- What is the Northwest? and a "Provocative description", articles from a commercial website
