Apronal
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.677 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
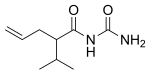
| Formula | C9H16N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 184.236 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Apronal (brand name Sedormid), or apronalide, also known as allylisopropylacetylurea or allylisopropylacetylcarbamide, is a hypnotic/sedative drug of the ureide (acylurea) group synthesized in 1926[1] by Hoffmann-La Roche that is no longer used except in Japan (See Japanese article). Though it is not a barbiturate, apronalide is similar in structure to the barbiturates (being an open-chain carbamide instead of having a heterocyclic ring).[2] In accordance, it is similar in action to the barbiturates, although considerably milder in comparison (formerly used as a daytime sedative at doses of 1 to 2 grams every 3 to 4 hours).[2] Upon the finding that it caused patients to develop thrombocytopenic purpura, apronalide was withdrawn from clinical use.[3]
See also
References
- ^ DE Patent 459903 - Verfahren zur Darstellung von Ureiden der Dialkylessigsaeuren
- ^ a b Roche Review ... Hoffman-La Roche, and Roche-organon. 1938. p. 164.
- ^ R. L. Vollum; D. G. Jamison; C. S. Cummins (20 May 2014). Fairbrother's Textbook of Bacteriology. Elsevier Science. pp. 152–. ISBN 978-1-4831-4178-7.
