Demographics of the United States: Difference between revisions
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by 198.46.101.146 to version by Futurist110. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (1568033) (Bot) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Census-2000-Data-Top-US-Ancestries-by-County.svg|thumb|400px|Largest ancestry groups by county, 2000.]] |
[[File:Census-2000-Data-Top-US-Ancestries-by-County.svg|thumb|400px|Largest ancestry groups by county, 2000.]] |
||
As of {{monthname|{{data United States|pst2|popbasemonth}}}} {{data United States|pst2|popbaseday}}, {{data United States|pst2|popbaseyear}}, the [[United States]] had a total resident population of {{formatnum:{{data United States | Poptoday }} }},<ref>According to [http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html U.S. Poplock U.S. Popclock]</ref> making it the [[List of countries by population|third most populous country]] in the world.<ref>[http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html U.S. & World Population Clocks]</ref> It is a very urbanized population, with 82% residing in cities and suburbs as of 2008 (the worldwide urban rate is 50.5%<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2212.html |title=CIA World Factbook |accessdate=2010-12-11 |month=December | year=2010 |publisher=[[CIA World Factbook]]}}{{dead link|date=February 2011|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2212.html}}</ref>). This leaves vast expanses of the country nearly uninhabited.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/us.html |title=CIA World Factbook |accessdate=2010-12-11 |2010 |publisher=[[CIA World Factbook]]}}</ref> [[California]] and [[Texas]] are the most populous states,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/2010/tables/10s0013.xls |title=Table 13. State Population - Rank, Percent Change, and Population Density |accessdate=2010-10-24 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |year=2008 |format=[[Microsoft Excel|Excel]]}}</ref> as the [[mean center of United States population]] has consistently shifted westward and southward.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cenpop/meanctr.pdf |title=Mean Center of Population for the United States: 1790 to 2000 |accessdate=2010-10-24 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |format=PDF}}</ref> [[New York City]] is the [[List of United States cities by population|most populous city in the United States]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/SUB-EST2009.html|title=Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places over 110,000, Ranked by July 1, 2009 Population: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2009 (SUB-EST2009-01)|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate=2011-05-19}}</ref> |
As of {{monthname|{{data United States|pst2|popbasemonth}}}} {{data United States|pst2|popbaseday}}, {{data United States|pst2|popbaseyear}}, the [[United States]] had a total resident population of {{formatnum:{{data United States | Poptoday }} }},<ref>According to [http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html U.S. Poplock U.S. Popclock]</ref> making it the [[List of countries by population|third most populous country]] in the world.<ref>[http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html U.S. & World Population Clocks]</ref> It is a very urbanized population, with 82% residing in cities and suburbs as of 2008 (the worldwide urban rate is 50.5%<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2212.html |title=CIA World Factbook |accessdate=2010-12-11 |month=December | year=2010 |publisher=[[CIA World Factbook]]}}{{dead link|date=February 2011|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2212.html}}</ref>). This leaves vast expanses of the country nearly uninhabited.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/us.html |title=CIA World Factbook |accessdate=2010-12-11 |2010 |publisher=[[CIA World Factbook]]}}</ref> [[California]] and [[Texas]] are the most populous states,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/2010/tables/10s0013.xls |title=Table 13. State Population - Rank, Percent Change, and Population Density |accessdate=2010-10-24 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |year=2008 |format=[[Microsoft Excel|Excel]]}}</ref> as the [[mean center of United States population]] has consistently shifted westward and southward.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cenpop/meanctr.pdf |title=Mean Center of Population for the United States: 1790 to 2000 |accessdate=2010-10-24 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |format=PDF}}</ref> [[New York City]] is the [[List of United States cities by population|most populous city in the United States]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/SUB-EST2009.html|title=Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places over 110,000, Ranked by July 1, 2009 Population: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2009 (SUB-EST2009-01)|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate=2011-05-19}}</ref> |
||
HELLLOOOOO :D |
|||
The [[total fertility rate]] in the United States estimated for 2011 is 1.89 children per woman, which is below the [[replacement fertility rate]] of approximately 2.1.{{#tag:Ref|In October 2012, the National Vital Statistics System reported that 2011 preliminary total fertility rate (TFR) in 2011 was 1,894.5 births per 100,000 women.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr59/nvsr59_03.pdf |title=Births: Preliminary Data for 2011 |volume=61 |issue=5 |date=October 3, 2012 |journal=National Vital Statistics reports |publisher=National Vital Statistics System}}</ref> The CIA Factbook estimates the U.S. Total Fertility Rate in 2010 as 2.06.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/docs/notesanddefs.html#2127 |title=CIA - The World Factbook - Notes and Definitions |accessdate=2010-02-01}}</ref>}} Compared to other Western countries, in 2011, U.S. fertility rate was lower than that of [[France]] (2.02) and the [[United Kingdom]] (1.97).<ref>[http://www.economist.com/node/21560266 Demography: Virility symbols]</ref> However, U.S. [[population growth]] is among the highest in industrialized countries,<ref name=ciapgr>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2002.html |title=CIA - The World Factbook -- Field Listing - Population growth rate |accessdate=2012-01-09 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]}}</ref> because the differences in fertility rates are less than the differences in immigration levels, which are higher in the U.S.<ref name=ciafertility>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2127rank.html |title=CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Total fertility rate |accessdate=2010-02-01 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2112rank.html |title=CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Net migration rate |accessdate=2009-02-23 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]}}</ref> The [[United States Census Bureau]] shows population increase of 0.75% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2012. Though high by industrialized country standards, this is below the world average annual rate of 1.09%.<ref name=ciapgr/> |
The [[total fertility rate]] in the United States estimated for 2011 is 1.89 children per woman, which is below the [[replacement fertility rate]] of approximately 2.1.{{#tag:Ref|In October 2012, the National Vital Statistics System reported that 2011 preliminary total fertility rate (TFR) in 2011 was 1,894.5 births per 100,000 women.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr59/nvsr59_03.pdf |title=Births: Preliminary Data for 2011 |volume=61 |issue=5 |date=October 3, 2012 |journal=National Vital Statistics reports |publisher=National Vital Statistics System}}</ref> The CIA Factbook estimates the U.S. Total Fertility Rate in 2010 as 2.06.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/docs/notesanddefs.html#2127 |title=CIA - The World Factbook - Notes and Definitions |accessdate=2010-02-01}}</ref>}} Compared to other Western countries, in 2011, U.S. fertility rate was lower than that of [[France]] (2.02) and the [[United Kingdom]] (1.97).<ref>[http://www.economist.com/node/21560266 Demography: Virility symbols]</ref> However, U.S. [[population growth]] is among the highest in industrialized countries,<ref name=ciapgr>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2002.html |title=CIA - The World Factbook -- Field Listing - Population growth rate |accessdate=2012-01-09 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]}}</ref> because the differences in fertility rates are less than the differences in immigration levels, which are higher in the U.S.<ref name=ciafertility>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2127rank.html |title=CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Total fertility rate |accessdate=2010-02-01 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2112rank.html |title=CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Net migration rate |accessdate=2009-02-23 |publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]}}</ref> The [[United States Census Bureau]] shows population increase of 0.75% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2012. Though high by industrialized country standards, this is below the world average annual rate of 1.09%.<ref name=ciapgr/> |
||
Revision as of 00:23, 26 March 2013

As of November 15, 2023, the United States had a total resident population of 336,656,000,[1] making it the third most populous country in the world.[2] It is a very urbanized population, with 82% residing in cities and suburbs as of 2008 (the worldwide urban rate is 50.5%[3]). This leaves vast expanses of the country nearly uninhabited.[4] California and Texas are the most populous states,[5] as the mean center of United States population has consistently shifted westward and southward.[6] New York City is the most populous city in the United States.[7] HELLLOOOOO :D The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2011 is 1.89 children per woman, which is below the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.1.[10] Compared to other Western countries, in 2011, U.S. fertility rate was lower than that of France (2.02) and the United Kingdom (1.97).[11] However, U.S. population growth is among the highest in industrialized countries,[12] because the differences in fertility rates are less than the differences in immigration levels, which are higher in the U.S.[13][14] The United States Census Bureau shows population increase of 0.75% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2012. Though high by industrialized country standards, this is below the world average annual rate of 1.09%.[12]
There were 155.6 million females in the United States in 2009. The number of males was 151.4 million. At age 85 and older, there were more than twice as many women as men. People under 20 years of age made up over a quarter of the U.S. population (27.3%), and people age 65 and over made up one-eighth (12.8%) in 2009.[15] The national median age was 36.8 years.[15] The United States Census Bureau defines White people as those "having origins in any of the original peoples of Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa. It includes people who reported “White” or wrote in entries such as Irish, German, Italian, Lebanese, Near Easterner, Arab, or Polish."[16] Whites constitute the majority of the U.S. population, with a total of 223,553,265 or 72.4% of the population in the 2010 United States Census. (72.4% = 63.7% "White + Not Hispanic or Latino" + 8.7% "White + Hispanic or Latino"). Despite major changes due to illegal and legal immigration since the 1960s and the higher birth-rates of nonwhites, the overall current majority of American citizens are still white, and American English-speaking though regional differences exist.
The American population more than tripled during the 20th century—at a growth rate of about 1.3% a year—from about 76 million in 1900 to 281 million in 2000. It reached the 200 million mark in 1967, and the 300 million mark on October 17, 2006.[17][18] Currently, population growth is fastest among minorities as a whole, and according to the Census Bureau's estimation for 2012, 50.4% of American children under the age of 1 belonged to minority groups.[19]
Hispanic and Latino Americans accounted for 69% of the national population growth of 2.9 million between July 1, 2005, and July 1, 2006.[20] Immigrants and their U.S.-born descendants are expected to provide most of the U.S. population gains in the decades ahead.[21]
The Census Bureau projects a U.S. population of 439 million in 2050, which is a 46% increase from 2007 (301.3 million).[22] However, the United Nations projects a U.S. population of 402 million in 2050, an increase of 32% from 2007 (the UN projects a gain of 38% for the world at large).[23] In either case, such growth is unlike most European countries, especially Germany, Russia, and Greece, or Asian countries such as Japan or South Korea, whose populations are slowly declining, and whose fertility rates are below replacement. Official census report, reported that 54.4% (2,150,926 out of 3,953,593) of births in 2010, were non Hispanic white. An increase of 0.34% compared to the previous year, which was 54.06%.[24]
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1790 | 3,929,214 | — | |
| 1800 | 5,236,631 | 33.3% | |
| 1810 | 7,239,881 | 38.3% | |
| 1820 | 9,638,453 | 33.1% | |
| 1830 | 12,866,020 | 33.5% | |
| 1840 | 17,069,453 | 32.7% | |
| 1850 | 23,191,876 | 35.9% | |
| 1860 | 31,443,321 | 35.6% | |
| 1870 | 38,558,371 | 22.6% | |
| 1880 | 49,371,340 | 28.0% | |
| 1890 | 62,979,766 | 27.6% | |
| 1900 | 76,212,168 | 21.0% | |
| 1910 | 92,228,531 | 21.0% | |
| 1920 | 106,021,568 | 15.0% | |
| 1930 | 123,202,660 | 16.2% | |
| 1940 | 132,165,129 | 7.3% | |
| 1950 | 151,325,798 | 14.5% | |
| 1960 | 179,323,175 | 18.5% | |
| 1970 | 203,211,926 | 13.3% | |
| 1980 | 226,545,805 | 11.5% | |
| 1990 | 248,709,873 | 9.8% | |
| 2000 | 281,421,906 | 13.2% | |
| 2010 | 308,745,538 | 9.7% | |
| 2012 (est.) | 313,914,040 | 1.7% | |
| Source: 1910–2010[25] | |||
History
In 1900, when the U.S. population was 76 million, there were 66.8 million Whites in the United States, representing 88% of the total population,[26] 8.8 million Blacks, with about 90% of them still living in Southern states,[27] and slightly more than 500,000 Hispanics.[28]
Under the current law, the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965,[29] the number of first-generation immigrants living in the United States has quadrupled,[30] from 9.6 million in 1970 to about 38 million in 2007.[31] During the 1950s, 250,000 legal immigrants entered the country annually; by the 1990s, the number was almost one million, and the vast majority of new immigrants have come from Latin America and Asia. In 2009, 37% of immigrants originated in Asia, 42% in the Americas, and 11% in Africa.[32] Almost 97% of residents of the 10 largest American cities in 1900 were non-Hispanic whites.[33] In 2006, non-Hispanic whites were the minority in thirty-five of the fifty largest cities.[34] The Census Bureau reported that minorities accounted for 50.4% of the children born in the U.S. between July 2010 and July 2011,[35] compared to 37% in 1990.[36]
In 2010 the state with the lowest fertility rate was Rhode Island, with 1,630.5 children per thousand women, while Utah had the greatest rate with 2,449.0 children per thousand women.[37] This correlates with the ages of the states' populations: Rhode Island has the ninth-oldest median age in the US — 39.2 — while Utah has the youngest — 29.0.[38]
Vital statistics
Source: National Vital statistics report based on 2010 US Census data[24]
The US total fertility rate as of 2010 is 1.931:
- 1.948 for White Americans (including white Hispanics)
- 1.791 for non-Hispanic Whites
- 1.958 for Black Americans (including black Hispanics)
- 1.972 for non-Hispanic Blacks
- 1.404 for Native Americans (including Hispanics)
- 1.689 for Asian Americans (including Hispanics)
- 2.350 for Hispanics(of all racial groups)
(Note that ~95% of Hispanics are included as "white Hispanics" by CDC, which does not recognize the Census' "Some other race" category and counts people in that category as white.)
The preliminary US total fertility rate for 2011 is 1.894: ![]() [39]
[39]
- 1.778 for non-Hispanic Whites

- 1.922 for non-Hispanic Blacks

- 1.377 for Native Americans (including Hispanics)

- 1.706 for Asian Americans (including Hispanics)

- 2.225 for Hispanics(of all racial groups)

| Average population (x 1,000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1935 | 2,377,000 | 1,392,752 | 984,248 | 46.08 | 2.19 | |||
| 1936 | 2,355,000 | 1,479,228 | 875,772 | 18.4 | 2.15 | |||
| 1937 | 2,413,000 | 1,450,427 | 962,573 | 18.7 | 2.17 | |||
| 1938 | 2,496,000 | 1,381,391 | 1,114,609 | 19.2 | 2.22 | |||
| 1939 | 2,466,000 | 1,387,897 | 1,141,731 | 18.8 | 2.17 | |||
| 1940 | 132,165 | 2,559,000 | 1,417,269 | 1,142,000 | 19.4 | 10.8 | 8.6 | 2.23 |
| 1941 | 133,002 | 2,703,000 | 1,397,642 | 1,305,358 | 20.3 | 10.5 | 9.8 | 2.33 |
| 1942 | 134,464 | 2,989,000 | 1,385,187 | 1,603,813 | 22.2 | 10.3 | 11.9 | 2.55 |
| 1943 | 136,003 | 3,104,000 | 1,459,544 | 1,644,306 | 22.8 | 10.7 | 12.1 | 2.64 |
| 1944 | 138,083 | 2,939,000 | 1,411,338 | 1,644,456 | 21.2 | 10.2 | 11.0 | 2.49 |
| 1945 | 139,994 | 2,858,000 | 1,401,719 | 1,456,281 | 20.4 | 10.0 | 10.4 | 2.42 |
| 1946 | 140,008 | 3,411,000 | 1,395,617 | 2,015,383 | 24.1 | 10.0 | 14.1 | 2.86 |
| 1947 | 145,023 | 3,817,000 | 1,445,370 | 2,371,630 | 26.6 | 10.0 | 16.6 | 3.18 |
| 1948 | 148,013 | 3,637,000 | 1,444,337 | 2,192,663 | 24.9 | 9.8 | 15.1 | 3.03 |
| 1949 | 149,336 | 3,649,000 | 1,443,607 | 2,205,393 | 24.5 | 9.7 | 14.8 | 3.04 |
| 1950 | 151,868 | 3,632,000 | 1,452,454 | 2,180,000 | 24.1 | 9.6 | 14.5 | 3.03 |
| 1951 | 154,056 | 3,823,000 | 1,482,099 | 2,340,901 | 24.8 | 9.6 | 15.2 | 3.20 |
| 1952 | 156,431 | 3,913,000 | 1,496,838 | 2,416,162 | 25.0 | 9.6 | 15.4 | 3.30 |
| 1953 | 159,047 | 3,965,000 | 1,447,459 | 2,142,000 | 25.2 | 9.1 | 16.1 | 3.36 |
| 1954 | 161,948 | 4,078,000 | 1,481,091 | 2,596,909 | 24.8 | 9.3 | 15.5 | 3.48 |
| 1955 | 163,476 | 4,097,000 | 1,528,717 | 2,568,283 | 25.0 | 9.3 | 14.3 | 3.52 |
| 1956 | 166,578 | 4,218,000 | 1,564,476 | 2,653,524 | 25.1 | 9.3 | 15.8 | 3.63 |
| 1957 | 169,637 | 4,308,000 | 1,633,128 | 2,666,872 | 25.3 | 9.5 | 15.8 | 3.71 |
| 1958 | 172,668 | 4,255,000 | 1,647,886 | 2,607,114 | 24.4 | 9.5 | 14.9 | 3.65 |
| 1959 | 175,642 | 4,244,796 | 1,656,814 | 2,587,982 | 24.0 | 9.4 | 14.7 | 3.66 |
| 1960 | 179,979 | 4,257,850 | 1,711,982 | 2,545,868 | 23.7 | 9.5 | 14.1 | 3.65 |
| 1961 | 182,992 | 4,268,326 | 1,701,522 | 2,566,804 | 23.3 | 9.3 | 14.0 | 3.62 |
| 1962 | 185,771 | 4,167,362 | 1,756,720 | 2,410,642 | 22.4 | 9.5 | 12.9 | 3.46 |
| 1963 | 188,483 | 4,098,020 | 1,813,549 | 2,284,471 | 21.7 | 9.6 | 12.1 | 3.32 |
| 1964 | 191,141 | 4,027,490 | 1,798,051 | 2,229,439 | 21.1 | 9.4 | 11.7 | 3.19 |
| 1965 | 193,526 | 3,760,358 | 1,828,136 | 1,932,222 | 19.4 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 2.91 |
| 1966 | 195,576 | 3,606,274 | 1,863,149 | 1,743,125 | 18.4 | 9.5 | 8.9 | 2.72 |
| 1967 | 197,457 | 3,520,959 | 1,851,323 | 1,669,636 | 17.8 | 9.4 | 8.4 | 2.56 |
| 1968 | 199,399 | 3,501,564 | 1,930,082 | 1,571,482 | 17.6 | 9.7 | 7.9 | 2.46 |
| 1969 | 201,385 | 3,600,206 | 1,921,990 | 1,678,216 | 17.9 | 9.5 | 8.4 | 2.46 |
| 1970 | 203,984 | 3,731,386 | 1,921,031 | 1,810,355 | 18.4 | 9.4 | 9.0 | 2.480 |
| 1971 | 206,827 | 3,555,970 | 1,927,542 | 1,628,428 | 17.2 | 9.3 | 7.9 | 2.266 |
| 1972 | 209,284 | 3,258,411 | 1,963,944 | 1,294,467 | 15.6 | 9.4 | 6.2 | 2.010 |
| 1973 | 211,357 | 3,136,965 | 1,973,003 | 1,163,962 | 14.8 | 9.5 | 5.3 | 1.879 |
| 1974 | 213,342 | 3,159,958 | 1,934,388 | 1,225,570 | 14.8 | 9.1 | 5.7 | 1.835 |
| 1975 | 215,465 | 3,144,198 | 1,892,879 | 1,251,319 | 14.6 | 8.8 | 5.8 | 1.774 |
| 1976 | 217,563 | 3,167,788 | 1,909,440 | 1,258,348 | 14.6 | 8.8 | 5.8 | 1.738 |
| 1977 | 219,760 | 3,326,632 | 1,899,597 | 1,427,035 | 15.1 | 8.6 | 6.5 | 1.789 |
| 1978 | 222,095 | 3,333,279 | 1,927,788 | 1,405,491 | 15.0 | 8.7 | 6.3 | 1.760 |
| 1979 | 224,567 | 3,494,398 | 1,913,841 | 1,580,557 | 15.6 | 8.5 | 7.1 | 1.808 |
| 1980 | 227,225 | 3,612,258 | 1,989,841 | 1,622,417 | 15.9 | 8.8 | 7.1 | 1.839 |
| 1981 | 229,466 | 3,629,238 | 1,977,981 | 1,651,257 | 15.8 | 8.6 | 7.2 | 1.812 |
| 1982 | 231,664 | 3,680,537 | 1,974,797 | 1,705,740 | 15.9 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 1.827 |
| 1983 | 233,792 | 3,638,933 | 2,019,201 | 1,619,732 | 15.6 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 1.799 |
| 1984 | 235,825 | 3,669,141 | 2,039,369 | 1,629,772 | 15.6 | 8.6 | 6.9 | 1.806 |
| 1985 | 237,924 | 3,760,561 | 2,086,440 | 1,674,121 | 15.8 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 1.844 |
| 1986 | 240,133 | 3,756,547 | 2,105,361 | 1,651,186 | 15.6 | 8.8 | 6.9 | 1.837 |
| 1987 | 242,289 | 3,809,394 | 2,123,323 | 1,686,071 | 15.7 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 1.872 |
| 1988 | 244,499 | 3,909,510 | 2,167,999 | 1,741,511 | 16.0 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 1.934 |
| 1989 | 246,819 | 4,040,958 | 2,150,466 | 1,890,492 | 16.4 | 8.7 | 7.7 | 2.014 |
| 1990 | 249,623 | 4,158,212 | 2,148,463 | 2,009,749 | 16.7 | 8.6 | 8.1 | 2.081 |
| 1991 | 252,981 | 4,110,907 | 2,169,518 | 1,941,389 | 16.2 | 8.6 | 7.7 | 2.062 |
| 1992 | 256,514 | 4,065,014 | 2,175,613 | 1,889,401 | 15.8 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 2.046 |
| 1993 | 259,919 | 4,000,240 | 2,268,553 | 1,731,687 | 15.4 | 8.7 | 6.7 | 2.019 |
| 1994 | 263,126 | 3,952,767 | 2,278,994 | 1,673,773 | 15.0 | 8.7 | 6.4 | 2.001 |
| 1995 | 266,278 | 3,899,589 | 2,312,132 | 1,587,457 | 14.6 | 8.7 | 6.0 | 1.978 |
| 1996 | 269,394 | 3,891,494 | 2,314,690 | 1,576,804 | 14.4 | 8.6 | 5.9 | 1.976 |
| 1997 | 272,647 | 3,880,894 | 2,314,245 | 1,566,649 | 14.2 | 8.5 | 5.7 | 1.971 |
| 1998 | 275,854 | 3,941,553 | 2,337,256 | 1,604,297 | 14.3 | 8.5 | 5.8 | 1,999 |
| 1999 | 279,040 | 3,959,417 | 2,391,399 | 1,568,018 | 14.2 | 8.6 | 5.6 | 2.007 |
| 2000 | 282,172 | 4,058,814 | 2,403,351 | 1,655,463 | 14.4 | 8.5 | 5.9 | 2.056 |
| 2001 | 285,082 | 4,025,933 | 2,416,425 | 1,609,508 | 14.1 | 8.5 | 5.6 | 2.030 |
| 2002 | 287,804 | 4,021,726 | 2,443,387 | 1,578,339 | 14.0 | 8.5 | 5.5 | 2.020 |
| 2003 | 290,326 | 4,089,950 | 2,448,288 | 1,641,662 | 14.1 | 8.4 | 5.5 | 2.047 |
| 2004 | 293,046 | 4,112,052 | 2,397,615 | 1,714,437 | 14.0 | 8.2 | 5.9 | 2.051 |
| 2005 | 295,753 | 4,138,349 | 2,448,017 | 1,690,332 | 14.0 | 8.3 | 5.7 | 2.057 |
| 2006 | 298,593 | 4,265,555 | 2,426,264 | 1,839,291 | 14.3 | 8.1 | 6.2 | 2.108 |
| 2007 | 301,580 | 4,316,233 | 2,423,712 | 1,892,521 | 14.3 | 8.0 | 6.3 | 2.120 |
| 2008 | 304,375 | 4,247,694 | 2,471,984 | 1,775,710 | 14.0 | 8.1 | 5.9 | 2.072 |
| 2009 | 307,007 | 4,130,665 | 2,437,163 | 1,693,502 | 13.5 | 7.9 | 5.6 | 2.002 |
| 2010 | 309,330 | 3,999,386 | 2,465,936 | 1,534,343 | 13.0 | 8.0 | 5.0 | 1.931 |
| 2011 | 3,953,593 | 2,513,171 | 1,440,422 | 12.7 | 8.1 | 4.6 | 1.89 |
Population density

The most densely populated state is New Jersey (1,121/mi2 or 433/km2). See List of U.S. states by population density for maps and complete statistics.
The United States Census Bureau publishes a popular "dot" or "nighttime" map showing population distribution at a resolution of 7,500 people,[40] as well as complete listings of population density by place name. [41]
Cities
The United States has dozens of major cities, including 9 of the 66 "global cities"[42] of all types, with 10 in the "alpha" group of global cities: New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, Washington, DC, Boston, San Francisco, Miami, Atlanta, Dallas, and Philadelphia.[43] As of 2011[update], the United States had 51 metropolitan areas with a population of over 1,000,000 people each. (See Table of United States Metropolitan Statistical Areas.)
As of 2011[update], about 250 million Americans live in or around urban areas. That means more than three-quarters of the U.S. population shares just about three percent of the U.S. land area.[44]
The following table shows the populations of the top ten metropolitan areas, as of the 2010 Census.
Largest metropolitan areas in the United States
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | ||
 New York  Los Angeles |
1 | New York | Northeast | 19,498,249 | 11 | Boston | Northeast | 4,919,179 |  Chicago  Dallas–Fort Worth |
| 2 | Los Angeles | West | 12,799,100 | 12 | Riverside–San Bernardino | West | 4,688,053 | ||
| 3 | Chicago | Midwest | 9,262,825 | 13 | San Francisco | West | 4,566,961 | ||
| 4 | Dallas–Fort Worth | South | 8,100,037 | 14 | Detroit | Midwest | 4,342,304 | ||
| 5 | Houston | South | 7,510,253 | 15 | Seattle | West | 4,044,837 | ||
| 6 | Atlanta | South | 6,307,261 | 16 | Minneapolis–Saint Paul | Midwest | 3,712,020 | ||
| 7 | Washington, D.C. | South | 6,304,975 | 17 | Tampa–St. Petersburg | South | 3,342,963 | ||
| 8 | Philadelphia | Northeast | 6,246,160 | 18 | San Diego | West | 3,269,973 | ||
| 9 | Miami | South | 6,183,199 | 19 | Denver | West | 3,005,131 | ||
| 10 | Phoenix | West | 5,070,110 | 20 | Baltimore | South | 2,834,316 | ||
Race and ethnicity
The U.S. population's distribution by race and ethnicity in 2010 was as follows- due to rounding, figures may not add up to the totals shown:[46]
Hispanic or Latino origin

Each of the racial categories includes people who identify their ethnicity as Hispanic or Latino.[47] U.S. federal law defines Hispanic or Latino as "those who classify themselves in one of the specific Hispanic or Latino categories listed on the Census 2000 or ACS questionnaire - "Mexican", "Puerto Rican", or "Cuban" - as well as those who indicate that they are "other Spanish, Hispanic, or Latino.""[48]
Persons whose ethnicity is identified as Hispanic or Latino may be of any race.
The total population of Hispanic and Latino Americans comprised 50.5 million or 16.3% of the national total in 2010.

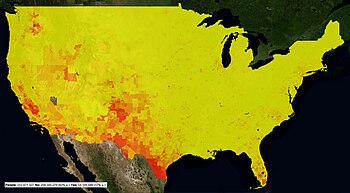
Breakdown by state
| State | Population | Non-Hispanic White | Hispanic/Latino | Black | AIAN1 | Asian | NHPI2 | Mixed Race |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 4,800,736 | 67.0 | 3.9 | 26.2 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0 | 1.5 |
| Alaska | 740,231 | 64.1 | 5.5 | 3.3 | 14.8 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 7.3 |
| Arizona | 6,694,017 | 57.8 | 29.6 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 3.4 |
| Arkansas | 2,937,979 | 74.5 | 6.4 | 15.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 2.0 |
| California | 38,053,956 | 40.1 | 37.6 | 6.2 | 1.0 | 13.0 | 0.4 | 4.9 |
| Colorado | 5,229,196 | 70.0 | 20.7 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 0.1 | 3.4 |
| Connecticut | 3,580,709 | 71.2 | 13.4 | 10.1 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 0 | 2.6 |
| Delaware | 947,934 | 65.3 | 8.2 | 21.4 | 0.5 | 3.2 | 0 | 2.7 |
| District of Columbia | 617,996 | |||||||
| Florida | 19,057,542 | 57.9 | 22.5 | 16.0 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| Georgia | 9,792,653 | 55.9 | 8.8 | 30.5 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 2.1 |
| Hawaii | 1,400,301 | 22.7 | 8.9 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 38.6 | 10.0 | 23.6 |
| Idaho | 1,607,582 | 84.0 | 11.2 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| Illinois | 12,869,257 | 63.7 | 15.8 | 14.5 | 0.3 | 4.6 | 0 | 2.3 |
| Indiana | 6,589,802 | 81.5 | 6.0 | 9.1 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0 | 2.0 |
| Iowa | 3,246,355 | 88.7 | 5.0 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 1.8 |
| Kansas | 2,963,118 | 78.2 | 10.5 | 5.9 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 3.0 |
| Kentucky | 4,369,356 | 86.3 | 3.1 | 7.8 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| Louisiana | 4,673,372 | 60.3 | 4.2 | 32.0 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 0 | 1.6 |
| Maine | 1,401,361 | 94.4 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0 | 1.6 |
| Maryland | 5,873,552 | 54.7 | 8.2 | 29.4 | 0.4 | 5.5 | 0.1 | 2.9 |
| Massachusetts | 6,601,629 | 76.1 | 9.6 | 6.6 | 0.3 | 5.3 | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| Michigan | 9,876,187 | 76.6 | 4.4 | 14.2 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 0 | 2.3 |
| Minnesota | 5,403,925 | 83.1 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 1.1 | 4.0 | 0 | 2.4 |
| Mississippi | 3,009,297 | 58.0 | 2.7 | 37.0 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0 | 1.1 |
| Missouri | 5,988,927 | 81.0 | 3.5 | 11.6 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 2.1 |
| Montana | 998,199 | 87.8 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 2.5 |
| Nebraska | 1,842,641 | 82.1 | 9.2 | 4.5 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 2.2 |
| Nevada | 2,723,322 | 54.1 | 26.5 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 7.2 | 0.2 | 4.7 |
| New Hampshire | 1,318,194 | 92.3 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 2.2 | 0 | 1.6 |
| New Jersey | 8,821,155 | 59.3 | 17.7 | 13.7 | 0.3 | 8.3 | 0 | 2.7 |
| New Mexico | 2,082,224 | 40.5 | 46.3 | 2.1 | 9.4 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 3.7 |
| New York | 19,465,197 | 58.3 | 17.6 | 15.9 | 0.6 | 7.3 | 0 | 3.0 |
| North Carolina | 9,656,401 | 65.3 | 8.4 | 21.5 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 0.1 | 2.2 |
| North Dakota | 682,591 | 88.9 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 0 | 1.8 |
| Ohio | 11,736,504 | 81.1 | 3.1 | 12.2 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0 | 2.1 |
| Oklahoma | 3,821,351 | 68.7 | 8.9 | 7.4 | 8.6 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 5.9 |
| Oregon | 3,851,074 | 78.5 | 11.7 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3.8 |
| Pennsylvania | 12,902,379 | 79.5 | 5.7 | 10.8 | 0.2 | 2.7 | 0 | 1.9 |
| Rhode Island | 1,060,567 | 76.4 | 12.4 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 3.3 |
| South Carolina | 4,825,364 | 64.1 | 5.1 | 27.9 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| South Dakota | 900,020 | 84.7 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 8.8 | 0.9 | 0 | 2.1 |
| Tennessee | 6,446,105 | 75.6 | 4.6 | 16.7 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| Texas | 25,901,361 | 45.3 | 37.6 | 11.8 | 0.7 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 2.7 |
| Utah | 2,863,885 | 80.4 | 13.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| Vermont | 685,741 | 94.3 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0 | 1.7 |
| Virginia | 8,101,024 | 64.8 | 7.9 | 19.4 | 0.4 | 5.5 | 0.1 | 2.9 |
| Washington | 6,830,038 | 72.5 | 11.2 | 3.6 | 1.5 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 4.7 |
| West Virginia | 1,882,994 | 93.2 | 1.2 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0 | 1.5 |
| Wisconsin | 5,726,986 | 83.3 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 1.0 | 2.3 | 0 | 1.8 |
| Wyoming | 600,626 | 85.9 | 8.9 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 2.2 |
- All Data from 2010 U.S. Census Bureau[49]
^1 American Indian or Alaskan Native
^2 Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
Vital statistics of Racial and Ethnic Groups
Source: National Center for Health Statistics[50]
Non-Hispanic white:
| Average population (x 1,000) | Live births1 | Deaths | Natural change1 | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19902 | 2,626,500 | 14.4 | 1.85 | |||||
| 19912 | 2,589,878 | 13.9 | 1.82 | |||||
| 19922 | 2,527,207 | 13.4 | 1.80 | |||||
| 1993 | 2,472,031 | 13.1 | 1.79 | |||||
| 1994 | 2,438,855 | 12.8 | 1.78 | |||||
| 1995 | 2,382,638 | 12.5 | 1.78 | |||||
| 1996 | 2,358,989 | 12.3 | 1.78 | |||||
| 1997 | 195,900 | 2,333,363 | 1,895,461 | 437,902 | 12.2 | 9.7 | 2.5 | 1.79 |
| 1998 | 196,600 | 2,361,462 | 1,912,802 | 448,660 | 12.2 | 9.7 | 2.5 | 1.82 |
| 1999 | 197,200 | 2,346,450 | 1,953,197 | 393,253 | 12.1 | 9.9 | 2.2 | 1.84 |
| 2000 | 197,300 | 2,362,968 | 1,959,919 | 403,049 | 12.2 | 9.9 | 2.3 | 1.87 |
| 2001 | 198,000 | 2,326,578 | 1,962,810 | 363,768 | 11.9 | 9.9 | 2.0 | 1.85 |
| 2002 | 198,700 | 2,298,156 | 1,981,973 | 316,183 | 11.7 | 10.0 | 1.7 | 1.84 |
| 2003 | 199,200 | 2,321,904 | 1,979,465 | 342,439 | 11.8 | 9.9 | 1.9 | 1.87 |
| 2004 | 199,800 | 2,296,683 | 1,933,382 | 363,301 | 11.7 | 9.7 | 2.0 | 1.87 |
| 2005 | 200,400 | 2,279,768 | 1,967,142 | 312,626 | 11.6 | 9.8 | 1.8 | 1.87 |
| 2006 | 200,800 | 2,308,640 | 1,944,617 | 364,023 | 11.7 | 9.7 | 2.0 | 1.90 |
| 2007 | 201,200 | 2,310,333 | 1,939,606 | 370,727 | 11.7 | 9.6 | 2.1 | 1.91 |
| 2008 | 201,700 | 2,267,817 | 1,981,198 | 286,619 | 11.5 | 9.8 | 1.7 | 1.87 |
| 2009 | 200,000 | 2,212,552 | 1,944,606 | 267,946 | 11.2 | 9.6 | 1.6 | 1.83 |
| 2010 | 200,127 | 2,162,406 | 1,967,619 | 194,050 | 10.9 | 9.8 | 1.1 | 1.79 |
| 2011 | 2,150,926 | 2,005,481 | 145,445 | 10.8 | 10.1 | 0.7 | 1.78 |
Non-Hispanic black:
| Average population (x 1,000) | Live births1 | Deaths | Natural change1 | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19902 | 28,800 | 661,701 | 23.0 | 2.55 | ||||
| 19912 | 29,800 | 666,758 | 22.4 | 2.53 | ||||
| 19922 | 30,400 | 657,450 | 21.6 | 2.48 | ||||
| 1993 | 31,000 | 641,273 | 20.7 | 2.41 | ||||
| 1994 | 31,700 | 619,198 | 19.5 | 2.31 | ||||
| 1995 | 32,300 | 587,781 | 18.2 | 2.19 | ||||
| 1996 | 32,800 | 578,099 | 17.6 | 2.14 | ||||
| 1997 | 33,400 | 581,431 | 273,381 | 308,050 | 17.4 | 7.4 | 10.0 | 2.14 |
| 1998 | 33,900 | 593,127 | 275,264 | 317,863 | 17.5 | 7.4 | 10.1 | 2.16 |
| 1999 | 34,400 | 588,981 | 281,979 | 307,002 | 17.1 | 7.6 | 9.5 | 2.13 |
| 2000 | 34,900 | 604,346 | 282,676 | 321,670 | 17.3 | 7.6 | 9.7 | 2.18 |
| 2001 | 35,400 | 589,917 | 284,343 | 305,574 | 16.6 | 7.5 | 9.1 | 2.11 |
| 2002 | 35,900 | 578,335 | 286,573 | 291,762 | 16.1 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 2.05 |
| 2003 | 36,200 | 576,033 | 287,968 | 288,065 | 15.9 | 7.4 | 8.5 | 2.04 |
| 2004 | 36,600 | 578,772 | 283,859 | 294,913 | 15.8 | 7.2 | 8.6 | 2.03 |
| 2005 | 36,900 | 583,759 | 289,163 | 294,596 | 15.8 | 7.3 | 8.5 | 2.03 |
| 2006 | 37,400 | 617,247 | 286,581 | 330,666 | 16.5 | 7.1 | 9.4 | 2.13 |
| 2007 | 37,800 | 627,191 | 286,366 | 340,825 | 16.6 | 7.0 | 9.6 | 2.14 |
| 2008 | 38,200 | 623,029 | 285,959 | 337,070 | 16.3 | 7.0 | 9.3 | 2.12 |
| 2009 | 38,700 | 609,584 | 282,982 | 326,602 | 15.7 | 7.2 | 8.5 | 2.05 |
| 2010 | 39,437 | 589,808 | 282,750 | 306,389 | 15.1 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 1.97 |
| 2011 | 583,079 | 287,482 | 295,597 | 14.7 | 7.2 | 7.5 | 1.92 |
Hispanics (of all racial groups):
| Average population (x 1,000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19902 | 22,300 | 595,073 | 26.7 | 2.96 | ||||
| 19912 | 23,500 | 623,085 | 26.5 | 2.96 | ||||
| 19922 | 24,600 | 643,271 | 26.1 | 2.96 | ||||
| 1993 | 25,800 | 654,418 | 25.4 | 2.89 | ||||
| 1994 | 26,900 | 665,026 | 24.7 | 2.84 | ||||
| 1995 | 28,200 | 679,768 | 24.1 | 2.80 | ||||
| 1996 | 29,500 | 701,339 | 23.8 | 2.77 | ||||
| 1997 | 30,900 | 709,767 | 95,460 | 614,307 | 23.0 | 3.1 | 19.9 | 2.68 |
| 1998 | 32,400 | 734,661 | 98,406 | 636,255 | 22.7 | 3.0 | 19.6 | 2.65 |
| 1999 | 34,000 | 764,339 | 103,740 | 660,599 | 22.5 | 3.1 | 19.4 | 2.65 |
| 2000 | 35,300 | 815,868 | 107,254 | 708,614 | 23.1 | 3.0 | 20.1 | 2.73 |
| 2001 | 37,200 | 851,851 | 113,413 | 738,438 | 22.9 | 3.1 | 19.9 | 2.73 |
| 2002 | 38,600 | 876,642 | 117,135 | 759,507 | 22.7 | 3.0 | 19.7 | 2.71 |
| 2003 | 40,000 | 912,329 | 122,026 | 790,303 | 22.8 | 3.1 | 19.8 | 2.74 |
| 2004 | 41,500 | 946,349 | 122,416 | 823,933 | 22.8 | 3.0 | 19.9 | 2.76 |
| 2005 | 43,000 | 985,505 | 131,161 | 854,344 | 22.9 | 3.1 | 19.9 | 2.79 |
| 2006 | 44,600 | 1,039,077 | 133,004 | 906,073 | 23.3 | 3.0 | 20.3 | 2.86 |
| 2007 | 46,200 | 1,062,779 | 135,519 | 927,260 | 23.0 | 3.0 | 20.1 | 2.84 |
| 2008 | 47,800 | 1,041,239 | 140,103 | 901,136 | 21.8 | 3.0 | 18.9 | 2.71 |
| 2009 | 49,200 | 999,548 | 141,576 | 857,972 | 20.3 | 2.9 | 17.4 | 2.53 |
| 2010 | 50,478 | 945,180 | 144,427 | 801,573 | 18.7 | 2.9 | 15.8 | 2.35 |
| 2011 | 912,290 | 149,234 | 763,056 | 17.5 | 2.9 | 14.6 | 2.23 |
Asian or Pacific Islander (including of Hispanic origin):
| Average population (x 1,000) | Live births1 | Deaths | Natural change1 | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 141,635 | 21,127 | 120,508 | 19.0 | 2.00 | |||
| 1991 | 145,372 | 22,173 | 123,199 | 18.3 | 1.93 | |||
| 1992 | 150,250 | 23,660 | 126,590 | 17.9 | 1.90 | |||
| 1993 | 152,800 | 25,386 | 127,414 | 17.3 | 1.84 | |||
| 1994 | 157,632 | 27,103 | 130,529 | 17.1 | 1.83 | |||
| 1995 | 160,287 | 28,297 | 131,990 | 16.7 | 1.80 | |||
| 1996 | 165,776 | 29,508 | 136,268 | 16.5 | 1.79 | |||
| 1997 | 169,769 | 30,756 | 139,013 | 16.2 | 1.76 | |||
| 1998 | 172,652 | 31,987 | 140,665 | 15.9 | 1.73 | |||
| 1999 | 180,776 | 33,675 | 147,101 | 15.9 | 1.75 | |||
| 2000 | 200,543 | 34,875 | 165,668 | 17.1 | 1.89 | |||
| 2001 | 200,279 | 37,048 | 163,231 | 16.1 | 1.79 | |||
| 2002 | 210,907 | 38,332 | 172,575 | 16.3 | 1.79 | |||
| 2003 | 221,203 | 40,127 | 181,076 | 16.4 | 1.82 | |||
| 2004 | 229,123 | 40,533 | 188,590 | 16.4 | 1.83 | |||
| 2005 | 231,108 | 43,194 | 187,914 | 15.9 | 1.78 | |||
| 2006 | 241,045 | 44,707 | 196,338 | 16.0 | 1.80 | |||
| 2007 | 254,488 | 45,609 | 208,879 | 16.4 | 1.85 | |||
| 2008 | 253,185 | 47,966 | 205,219 | 15.7 | 1.80 | |||
| 2009 | 251,089 | 49,225 | 201,864 | 15.1 | 1.74 | |||
| 2010 | 16,993 | 246,886 | 51,158 | 195,728 | 14.5 | 1.69 | ||
| 2011 | 253,864 | 53,298 | 200,566 | 14.5 | 1.71 |
American Indian or Alaskan Native (including of Hispanic origin):
| Average population (x 1,000) | Live births1 | Deaths | Natural change1 | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 39,051 | 8,316 | 30,735 | 18.9 | 2.19 | |||
| 1991 | 38,841 | 8,621 | 30,220 | 18.3 | 2.14 | |||
| 1992 | 39,453 | 8,953 | 30,500 | 17.9 | 2.14 | |||
| 1993 | 38,732 | 9,579 | 29,153 | 17.0 | 2.01 | |||
| 1994 | 37,740 | 9,637 | 28,103 | 16.0 | 1.95 | |||
| 1995 | 37,278 | 9,997 | 27,281 | 15.3 | 1.88 | |||
| 1996 | 37,880 | 10,127 | 27,753 | 14.9 | 1.86 | |||
| 1997 | 38,572 | 10,576 | 27,996 | 14.7 | 1.83 | |||
| 1998 | 40,272 | 10,845 | 29,427 | 14.8 | 1.85 | |||
| 1999 | 40,170 | 11,312 | 28,858 | 14.2 | 1.78 | |||
| 2000 | 41,668 | 11,363 | 30,305 | 14.0 | 1.77 | |||
| 2001 | 41,872 | 11,977 | 29,895 | 13.6 | 1.72 | |||
| 2002 | 42,368 | 12,415 | 29,953 | 13.3 | 1.68 | |||
| 2003 | 43,052 | 13,147 | 29,905 | 13.0 | 1.64 | |||
| 2004 | 43,927 | 13,124 | 30,803 | 12.8 | 1.61 | |||
| 2005 | 44,813 | 13,918 | 30,895 | 12.6 | 1.59 | |||
| 2006 | 47,721 | 14,037 | 33,684 | 13.0 | 1.63 | |||
| 2007 | 49,443 | 14,367 | 35,076 | 12.9 | 1.63 | |||
| 2008 | 49,537 | 14,785 | 34,752 | 12.5 | 1.57 | |||
| 2009 | 48,665 | 14,960 | 33,705 | 11.8 | 1.50 | |||
| 2010 | 4,263 | 46,760 | 15,520 | 31,240 | 11.0 | 1.40 | ||
| 2011 | 46,536 | 15,875 | 30,661 | 10.7 | 1.38 |
Notes:
1. The natural increase is slightly smaller than shown for non-Hispanic whites and slightly different for non-Hispanic blacks because the birth figures shown refer to mothers of that race, not the children. Most nonwhite babies of non-Hispanic white mothers are either Hispanic or black, and non-Hispanic black mothers occasionally have Hispanic children. On the other hand, all children born to Hispanic mothers, even if the mothers are white Hispanic, are counted as Hispanic.
2. New Hampshire did not start reporting Hispanic origin until 1993, and Oklahoma until 1991, so data from those states are excluded before then.
p Preliminary data.
Other groups
There were 22.1 million veterans in 2009.[51]
In 2010, the Washington Post estimated that there were 11 million illegal immigrants in the country.[52]
There were about 2 million people in prison in 2010.[53]
The 2000 U.S. Census counted same-sex couples in an oblique way; asking the sex and the relationship to the "main householder", whose sex was also asked. One organization specializing in analyzing gay demographic data reported, based on this count in the 2000 census and in the 2000 supplementary survey, that same-sex couples comprised between 0.99% and 1.13% of U.S. couples in 2000.[54] A 2006 report issued by The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation concluded that the number of same-sex couples in the U.S. grew from 2000 to 2005, from nearly 600,000 couples in 2000 to almost 777,000 in 2005. 4.1% of Americans aged 18–45 identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual[55]
A 2011 report by the Institute estimated that 4 million adults identify as gay or lesbian, representing 1.7% of the population over 18. A spokesperson said that, until recently, few studies have tried to eliminate people who had occasionally had behaved or had homosexual thoughts, from people who identified as lesbian or gay.[56] (Older estimates have varied depending on methodology and timing; see Demographics of sexual orientation for a list of studies.) The American Community Survey from the 2000 U.S. Census estimated 776,943 same-sex couple households in the country as a whole, representing about 0.5% of the population.[55]
Less than 1% of Americans currently serve in the Armed Forces.[57]
Projections
| 2010 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|
| Whites (including hispanics and Some other race) | 79.5% | 74.0% |
| Non-Hispanic Whites | 64.7% | 46.3% |
| African Americans (including hispanics) | 12.9% | 13.0% |
| Asian Americans (including hispanics) | 4.6% | 7.8% |
| Hispanics/Latinos (of any race) | 16.0% | 30.2% |
| Non-Hispanic/Latinos (of any race) | 84.0% | 69.8% |
A report by the U.S. Census Bureau projects a decrease in the ratio of Whites between 2010 and 2050, from 79.5% to 74.0%.[58] At the same time, Non-Hispanic Whites are projected to no longer make up the strong majority of the population by 2042, but will remain the largest single white ethnic group. In 2050 they will compose 46.3% of the population. Non-Hispanic whites made up 85% of the population in 1960.[59]
The report foresees the Hispanic or Latino population rising from 16% today to 30% by 2050, the African American percentage barely rising from 12.9% to 13.0%, and Asian Americans upping their 4.6% share to 7.8%. The U.S. has 310 million people as of October 2010, and is projected to reach 400 million by 2039 and 439 million in 2050.[22][60][61][62] It is further projected that 82% of the increase in population from 2005 to 2050 will be due to immigrants and their children.[63]
Of the nation's children in 2050, 62% are expected to be of a minority ethnicity, up from 44% today. Approximately 39% are projected to be Hispanic or Latino (up from 22% in 2008), and 38% are projected to be single-race, non-Hispanic Whites (down from 56% in 2008).[64]
In 2008, the US Census Bureau projected future censuses as follows:[22]
- 2010: 310,232,863
- 2020: 341,386,665
- 2030: 373,503,674
- 2040: 405,655,295
- 2050: 439,010,253
Religion
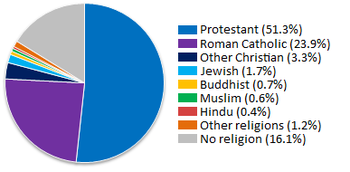
The table below is based mainly on selected data as reported to the United States Census Bureau. It only includes the voluntary self-reported membership of religious bodies with 750,000 or more. The definition of a member is determined by each religious body.[65] As of 2004[update], the US census bureau reported that about 13% of the population did not identify itself as a member of any religion.[66][clarification needed]
Religions of American adults
The United States government does not collect religious data in its census. The survey below, the American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS) 2008, was a random digit-dialed telephone survey of 54,461 American residential households in the contiguous United States. The 1990 sample size was 113,723; 2001 sample size was 50,281.
Adult respondents were asked the open-ended question, "What is your religion, if any?". Interviewers did not prompt or offer a suggested list of potential answers. The religion of the spouse or partner was also asked. If the initial answer was "Protestant" or "Christian" further questions were asked to probe which particular denomination. About one-third of the sample was asked more detailed demographic questions.
Religious Self-Identification of the U.S. Adult Population: 1990, 2001, 2008[69]
Figures are not adjusted for refusals to reply; investigators suspect refusals are possibly more representative of "no religion" than any other group.
| Group |
1990 adults x 1,000 |
2001 adults x 1,000 |
2008 adults x 1,000 |
Numerical Change 1990- 2008 as % of 1990 |
1990 % of adults |
2001 % of adults |
2008 % of adults |
change in % of total adults 1990- 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult population, total | 175,440 | 207,983 | 228,182 | 30.1% | ||||
| Adult population, Responded | 171,409 | 196,683 | 216,367 | 26.2% | 97.7% | 94.6% | 94.8% | -2.9% |
| Total Christian | 151,225 | 159,514 | 173,402 | 14.7% | 86.2% | 76.7% | 76.0% | -10.2% |
| Catholic | 46,004 | 50,873 | 57,199 | 24.3% | 26.2% | 24.5% | 25.1% | -1.2% |
| non-Catholic Christian | 105,221 | 108,641 | 116,203 | 10.4% | 60.0% | 52.2% | 50.9% | -9.0% |
| Baptist | 33,964 | 33,820 | 36,148 | 6.4% | 19.4% | 16.3% | 15.8% | -3.5% |
| Mainline Christian | 32,784 | 35,788 | 29,375 | -10.4% | 18.7% | 17.2% | 12.9% | -5.8% |
| Methodist | 14,174 | 14,039 | 11,366 | -19.8% | 8.1% | 6.8% | 5.0% | -3.1% |
| Lutheran | 9,110 | 9,580 | 8,674 | -4.8% | 5.2% | 4.6% | 3.8% | -1.4% |
| Presbyterian | 4,985 | 5,596 | 4,723 | -5.3% | 2.8% | 2.7% | 2.1% | -0.8% |
| Episcopalian/Anglican | 3,043 | 3,451 | 2,405 | -21.0% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.1% | -0.7% |
| United Church of Christ | 438 | 1,378 | 736 | 68.0% | 0.2% | 0.7% | 0.3% | 0.1% |
| Christian Generic | 25,980 | 22,546 | 32,441 | 24.9% | 14.8% | 10.8% | 14.2% | -0.6% |
| Jehovah's Witness | 1,381 | 1,331 | 1,914 | 38.6% | 0.8% | 0.6% | 0.8% | 0.1% |
| Christian Unspecified | 8,073 | 14,190 | 16,384 | 102.9% | 4.6% | 6.8% | 7.2% | 2.6% |
| Non-denominational Christian | 194 | 2,489 | 8,032 | 4040.2% | 0.1% | 1.2% | 3.5% | 3.4% |
| Protestant - Unspecified | 17,214 | 4,647 | 5,187 | -69.9% | 9.8% | 2.2% | 2.3% | -7.5% |
| Evangelical/Born Again | 546 | 1,088 | 2,154 | 294.5% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.9% | 0.6% |
| Pentecostal/Charismatic | 5,647 | 7,831 | 7,948 | 40.7% | 3.2% | 3.8% | 3.5% | 0.3% |
| Pentecostal - Unspecified | 3,116 | 4,407 | 5,416 | 73.8% | 1.8% | 2.1% | 2.4% | 0.6% |
| Assemblies of God | 617 | 1,105 | 810 | 31.3% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
| Church of God | 590 | 943 | 663 | 12.4% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.0% |
| Other Protestant Denomination | 4,630 | 5,949 | 7,131 | 54.0% | 2.6% | 2.9% | 3.1% | 0.5% |
| Seventh-Day Adventist | 668 | 724 | 938 | 40.4% | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
| Churches of Christ | 1,769 | 2,593 | 1,921 | 8.6% | 1.0% | 1.2% | 0.8% | -0.2% |
| Mormon/Latter-Day Saints | 2,487 | 2,697 | 3,158 | 27.0% | 1.4% | 1.3% | 1.4% | 0.0% |
| Total non-Christian religions | 5,853 | 7,740 | 8,796 | 50.3% | 3.3% | 3.7% | 3.9% | 0.5% |
| Jewish | 3,137 | 2,837 | 2,680 | -14.6% | 1.8% | 1.4% | 1.2% | -0.6% |
| Eastern Religions | 687 | 2,020 | 1,961 | 185.4% | 0.4% | 1.0% | 0.9% | 0.5% |
| Buddhist | 404 | 1,082 | 1,189 | 194.3% | 0.2% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.3% |
| Muslim | 527 | 1,104 | 1,349 | 156.0% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.3% |
| New Religious Movements & Others | 1,296 | 1,770 | 2,804 | 116.4% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.2% | 0.5% |
| None/ No religion, total | 14,331 | 29,481 | 34,169 | 138.4% | 8.2% | 14.2% | 15.0% | 6.8% |
| Agnostic+Atheist | 1,186 | 1,893 | 3,606 | 204.0% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.6% | 0.9% |
| Did Not Know/ Refused to reply | 4,031 | 11,300 | 11,815 | 193.1% | 2.3% | 5.4% | 5.2% | 2.9% |
Marriage
In 2010, the median age for marriage for men was 27; for women, 26.[70]
Income
In 2006, the median household income in the United States was around $46,000. Household and personal income depends on variables such as race, number of income earners, educational attainment and marital status.
| Type of household | Race and Hispanic origin | Region | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All households | Family households |
Nonfamily households |
Asian | Non-Hispanic White | Hispanic (of any race) |
Black | Northeast | Midwest | South | West |
| $70,784 | $91,162 | $41,797 | $101,418 | $77,999 | $57,981 | $48,297 | $77,422 | $71,129 | $63,368 | $79,430 |
| Age of Householder | Nativity of Householder | Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) Status | Educational Attainment of Householder* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under 65 years | 65 years and older | Native-born | Foreign-born | Inside MSA | Outside MSA | No high school diploma | High school, no college | Some college | Bachelor's degree or higher |
| $80,734 | $47,620 | $71,522 | $66,043 | $73,823 | $53,750 | $30,378 | $50,401 | $64,378 | $115,456 |
| *Householders aged 25 and older. In 2021, the median household income for this group was $72,046. | |||||||||
| Total workers | Full-Time, year-round workers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both sexes | Male | Female | Both sexes | Male | Female |
| $45,470 | $50,983 | $39,201 | $56,473 | $61,180 | $51,226 |
| Measure | Overall | Less than 9th grade | Some High School | High school graduate | Some college | Associate's degree | Bachelor's degree or higher | Bachelor's degree | Master's degree | Professional degree | Doctorate degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persons, age 25+ w/ earnings* | $46,985 | $25,162 | $26,092 | $34,540 | $39,362 | $42,391 | $66,423 | $60,705 | $71,851 | $102,741 | $101,526 |
| Male, age 25+ w/ earnings* | $52,298 | $30,089 | $31,097 | $40,852 | $47,706 | $52,450 | $80,192 | $71,666 | $91,141 | $126,584 | $121,956 |
| Female, age 25+ w/ earnings* | $40,392 | $18,588 | $19,504 | $27,320 | $31,837 | $36,298 | $57,355 | $51,154 | $62,522 | $92,780 | $85,551 |
| Persons, age 25+, employed full-time | $59,371 | $33,945 | $34,897 | $42,417 | $50,640 | $52,285 | $77,105 | $71,283 | $82,183 | $130,466 | $119,552 |
| Household | $69,228 | $29,609 | $29,520 | $47,405 | $60,392 | $68,769 | $106,936 | $100,128 | $114,900 | $151,560 | $142,493 |
| *Total work experience | |||||||||||
| 10th percentile | 20th percentile | 30th percentile | 40th percentile | 50th percentile | 60th percentile | 70th percentile | 80th percentile | 90th percentile | 95th percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ $15,700 | ≤ $28,000 | ≤ $40,500 | ≤ $55,000 | $70,800 | ≤ $89,700 | ≤ $113,200 | ≤ $149,100 | ≤ $212,100 | ≤ $286,300 |
| Source: US Census Bureau, 2021; income statistics for the year 2021 | |||||||||
Social class
Social classes in the United States lack distinct boundaries and may overlap. Even their existence (when distinguished from economic strata) is controversial. The following table provides a summary of some currently prominent academic theories on the stratification of American society:
| Dennis Gilbert, 2002 | William Thompson & Joseph Hickey, 2005 | Leonard Beeghley, 2004 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics |
| Capitalist class (1%) | Top-level executives, high-rung politicians, heirs. Ivy League education common. | Upper class (1%) | Top-level executives, celebrities, heirs; income of $500,000+ common. Ivy league education common. | The super-rich (0.9%) | Multi-millionaires whose incomes commonly exceed $3.5 million or more; includes celebrities and powerful executives/politicians. Ivy League education common. |
| Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly-educated (often with graduate degrees), most commonly salaried, professionals and middle management with large work autonomy. | Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly-educated (often with graduate degrees) professionals & managers with household incomes varying from the high 5-figure range to commonly above $100,000. | The rich (5%) | Households with net worth of $1 million or more; largely in the form of home equity. Generally have college degrees. |
| Middle class (plurality/ majority?; ca. 46%) |
College-educated workers with considerably higher-than-average incomes and compensation; a man making $57,000 and a woman making $40,000 may be typical. | ||||
| Lower middle class (30%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with a roughly average standard of living. Most have some college education and are white-collar. | Lower middle class (32%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with some work autonomy; household incomes commonly range from $35,000 to $75,000. Typically, some college education. | ||
| Working class (30%) | Clerical and most blue-collar workers whose work is highly routinized. Standard of living varies depending on number of income earners, but is commonly just adequate. High school education. | ||||
| Working class (32%) | Clerical, pink- and blue-collar workers with often low job security; common household incomes range from $16,000 to $30,000. High school education. | Working class (ca. 40–45%) |
Blue-collar workers and those whose jobs are highly routinized with low economic security; a man making $40,000 and a woman making $26,000 may be typical. High school education. | ||
| Working poor (13%) | Service, low-rung clerical and some blue-collar workers. High economic insecurity and risk of poverty. Some high school education. | ||||
| Lower class (ca. 14–20%) | Those who occupy poorly-paid positions or rely on government transfers. Some high school education. | ||||
| Underclass (12%) | Those with limited or no participation in the labor force. Reliant on government transfers. Some high school education. | The poor (ca. 12%) | Those living below the poverty line with limited to no participation in the labor force; a household income of $18,000 may be typical. Some high school education. | ||
| |||||
Health
In 2010, the average man weighed 194.7 pounds (88.3 kg); the average woman 164.7 pounds (74.7 kg).[74][dead link] The height of an American man was 5 feet 9 inches (1.75 m)[75] and woman 5 feet 3.8 inches (1.621 m)[76] The average BMI is 27.3 for males (overweight) and 28.5 for females (more overweight), with average female weight closer to the limit indicated for obesity (BMI about 30) than normal weight (BMI about 18.5–24.9).[77]
As of 2012, an estimated 26% of the population is obese,[78] 21% smoke,[79] and 11% have diabetes.[80]
A nationwide study in 2010 indicated that 19.5% of teens, aged 12–19, have developed "slight" hearing loss. "Slight" was defined as an inability to hear at 16 to 24 decibels.[81]
In 2011, an estimated 1.2 million people were living with HIV/AIDS in the United States.[82]
Cohorts in the United States
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2011) |
A study by William Strauss and Neil Howe, in their books Generations and Fourth Turning, looked at generational similarities and differences going back to the 15th century and concluded that over 80 year spans, generations proceed through 4 stages of about 20 years each. The first phase consists of times of relative crisis and the people born during this period were called "artists". The next phase was a "high" period and those born in this period were called "prophets". The next phase was an "awakening period" and people born in this period were called "nomads". The final stage was the "unraveling period" and people born in this period were called "heroes". The most recent "high period" occurred in the 1950s and 1960s (hence baby boomers are the most recent crop of "prophets").[citation needed]
The population of USA is about 678,300,000 definitive recent study of the US generational cohorts was done by Schuman and Scott (2012)in which a broad sample of adults of all ages were asked, "What world events are especially important to you?"[83] They found that 33 events were mentioned with great frequency. When the ages of the respondents were correlated with the expressed importance rankings, seven (some put 8 or 9) distinct cohorts became evident. Today the following descriptors are frequently used for these cohorts (currently mainly alive in 2000-10):
- Depression cohort, or GI (Fought and won World War II) (born from 1905/10 to 1919/21).
- Distinction: Currently, they represent the largest number of Nonagenarians and Centenarians alive in any time of US history.
- Memorable events: The Great Depression, high levels of unemployment, poverty, lack of creature comforts, financial uncertainty, peak of European immigration (though started from 1840 to ended by 1920), grew up during World War I, prohibitionism, radical politics, not too religious but mostly morally conservative, shorter life spans, and stressed Americanization or acculturation into a common mainstream U.S. culture.
- Key characteristics: strive for financial security, risk averse, waste-not-want-not attitude, strive for comfort, social cooperative, can be reactionary or hostile towards change, but are idealistic or progressive in improvements of quality of life.
- Pre 'World War II cohort', or Greatest (born from 1920/22 to 1927/30).
- Distinction: Established mainstream American culture in the mid-20th century.
- Memorable events: men left to go to war and some did not return, the personal experience of the war, women working in factories, focus on defeating a common enemy, unity of peoples in a country, sacrifice (i.e. food rations and donated material), devoted to the war effort, and placed white ethnics or those of Irish, Italian, Jewish and Southern or Central European descent in prominence.
- Key characteristics: the nobility of sacrifice for the common good, patriotism, socialism to a certain degree, team player, soldier, volunteerism, high work ethic, and some youthful experimentation in socially liberal practices but have generally been more socially conservative.
- World War II cohort, War Babies, or Silent (born from 1925/29 to 1942/45) - others subdivide them to Crash and New Deal cohorts.
- Distinction: Second smallest generation born in US history, the birth rate peaked low due to the Depression.
- Memorable events: sustained economic growth, social tranquility, The Cold War, McCarthyism, anti-communism, drug culture, conformity, the rise and peak of jazz music (1940s), early rock n' roll (1950s), fear of a nuclear war, and avoidance of discomfort with high emphasis on optimism.
- Key characteristics: conformity, social conservatism, patriotism, comparatively chaste or emphasized traditional values (i.e. manners or taboos) than younger cohorts (who disagreed with them), traditional family values, but had the nuclear family replaced the multi-generational kind, known as the "Silent" majority/generation, and had the appearance of sameness or "cookie cutter" type of sameness.
- Baby Boomer (born from 1943/46 to 1953/57).
- Distinction: One of two largest generations in size in US history.[citation needed]
- Memorable events: assassinations of JFK, Robert Kennedy, and Martin Luther King, Liberalism, political unrest, walk on the moon, Vietnam War, anti-war protests, social experimentation, sexual freedom, civil rights movement, environmental movement, women's movement, protests and riots, rise and peak of rock and roll, and experimentation with various intoxicating recreational substances.[citation needed]
- Key characteristics: idealistic, experimental, progressive, individualism, free spirited, social cause oriented, activism, social change, "Live and let live", "Do your own thing", Pacifism, Spiritualism, alternative lifestyles, deeply against racism as well sexism and ethnic prejudice, and first generation thought to demand an eradication of poverty by government programs (War on Poverty).
- Boomer cohort #2 - "Generation Jones," born 1954/56-1965/69.[citation needed]
- Distinction: The Peak years due to being children or teenagers when American power peaked in the global scene.
- Memorable events: Watergate, Nixon resigns, the cold war, the oil embargo, raging inflation, Disco, gasoline shortages, the American hostage crisis of Iran (1979–81), the U.S. Bicentennial celebrations in the 1970s, and cultural shift from McCarthyist conformity to hippie idealism to Yuppie fiscal conservative and/or social liberal phases.[citation needed]
- Key characteristics: less optimistic, fatalistic, principled, general cynicism, somewhat reactionary, easily bored, impatient, an urgent desire that things must change, born again Christian movement, yuppie social trends, challenged gender roles and racial stereotypes, and used drugs illegal since the early 20th century[84][85][86] thereby precipitating the modern War on Drugs in the 1970s and 1980s; yet often conservative & reactionary in later age.
- Generation X cohort (born from 1961/1967 to 1979/1985).
- In the U.S., some called Generation Xers the "baby bust" generation because of the drop in the birth rate following the baby boom.[87] The drop in fertility rates in America began in the late 1950s. But according to authors and demographers William Strauss and Neil Howe (who use 1961 to 1981 for Gen X birth years), there are approximately 88.5 million Gen Xers in the U.S. today.[88][89]
- Memorable events: Challenger explosion, Iran-Contra, Reaganomics, AIDS, Star Wars, MTV, home computers, video games, safe sex, divorce, single-parent families, end of Cold War-fall of Berlin Wall, Gulf War, 1992 L.A. Riots, 1995 Oklahoma City Bombing, the 1998 Bill Clinton-Monica Lewinsky sex scandal, and the arrival of the year 2000: new century (21st)/ new millennium (3rd).
- Key characteristics: pragmatic; independent, informal; entrepreneurial; somewhat pessimist; many grew up in single-parent households.[citation needed]
- Generation Y Cohort Millennials (born from 1977/1985 to 2000/2005).
- Distinction: Echo Boom they are second highest birth rate generation in US history.
- Memorable events: rise of the Internet, iPods, social network services, war on crime (reduced crime rates), cultural diversity, September 11 attacks, the Death of Osama Bin Laden, Afghanistan War and Iraq War, and affected by the 2008-09 global financial crisis or "Great Recession".
- Key characteristics: acceptance of change, technically savvy, environmental issues, globally minded, more socially liberal than previous generations, stricter laws on minors, high tech surveillance of public places, political correctness, no expectation of military service, and increased local volunteerism or community service.
- Generation Z also known as the Homeland Generation and "digital natives" are the generation who, at the earliest, were born after 2000 and are currently children. They may share some of Generation Y characteristics. They may be more tolerant and accepting of social groups (e.g. gay rights, including marriage) than recent previous generations.
U.S. Demographic birth cohorts

Subdivided groups are present when peak boom years or inverted peak bust years are present, and may be represented by a normal or inverted bell-shaped curve (rather than a straight curve). The boom subdivided cohorts may be considered as "pre-peak" (including peak year) and "post-peak". The year 1957 was the baby boom peak with 4.3 million births and 122.7 fertility rate. Although post-peak births (such as trailing edge boomers) are in decline, and sometimes referred to as a "bust", there are still a relative large number of births. The dearth-in-birth bust cohorts include those up to the valley birth year, and those including and beyond, leading up to the subsequent normal birth rate. The Baby boom began around 1943 to 1946.[citation needed]
From the decline in U.S. birth rates starting in 1958 and the introduction of the birth control pill in 1960, the Baby Boomer normal distribution curve is negatively skewed. The trend in birth rates from 1958 to 1961 show a tendency to end late in the decade at approximately 1969, thus returning to pre-WWII levels, with 12 years of rising and 12 years of declining birth rates. Pre-war birth rates were defined as anywhere between 1939 and 1941 by demographers such as the Taeuber's, Philip M. Hauser and William Fielding Ogburn.[90] From 1962 to 1964, trend analysis points to 1965 as being the first year to return to baseline birth rates, referring to this cohort as Generation X. Then came "Generation Y" also known as Millennials sometimes a second cohort of the Baby Bust era, and finally Generation Z who are mostly the children of Generation X.
Demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.[91]

Median age
- 36.8 years (male: 35.5 years, female: 38.1 years, 2010 est.)
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 20.2% (male 31,639,127/female 30,305,704)
- 15–64 years: 67% (male 102,665,043/female 103,129,321)
- 65 years and over: 12.8% (male 16,901,232/female 22,571,696) (2010 est.)
Population growth rate
- 0.963% (2011 est.)
Birth rate

- 13.5 births/1,000 population (2010 est.). This is the lowest in a century. There were 4,136,000 births in 2009.[92]
- 13.9 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2008)
- 14.3 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2007)[93]
In 2009, Time magazine reported that 40% of births were to unmarried women.[94] The following is a breakdown by race for unwed births: 17% Asian, 29% White, 53% Hispanics, 66% Native Americans, and 72% African American.[95]
The drop in the birth rate from 2007 to 2009 is believed to be associated with the Late-2000s recession[96]
Death rate
- 8.38 deaths/1,000 population (July 2010 est.)
Immigration
| Country | 2010 | Region | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mexico | 139,120 | Americas | 423,784 |
| China | 70,863 | Asia | 422,058 |
| India | 69,162 | Africa | 101,351 |
| Philippines | 58,173 | Europe | 88,730 |
| Dominican Rep. | 53,870 | All Immigrants | 1,042,625 |
- 13% of the population was foreign-born in 2009.[98]
Net migration rate
- 4.32 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2010 est.)
Sex ratios
- at birth: 1.048 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- total: 6.22 deaths/1,000 live births
- male: 6.9 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 5.51 deaths/1,000 live births (2010 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 78.11 years
- male: 75.65 years
- female: 80.69 years (2010 est.)

≤4.5% ≤5.5% ≤6.5% | ≤7.5% ≤8.5% ≤9.5% | ≤10.5% ≤11.5% >11.5% |
Total fertility rate
- 1.89 children born/woman (2011). Source: National Vital Statistics System.
Unemployment rate
As of September 2012[update], the U.S. unemployment rate was 7.9 percent (U3 Rate).[100]
As of July 2012[update], the U6 unemployment rate is 15 percent.[101] The U6 unemployment rate counts not only people without work seeking full-time employment (the more familiar U-3 rate), but also counts "marginally attached workers and those working part-time for economic reasons." Note that some of these part-time workers counted as employed by U-3 could be working as little as an hour a week. And the "marginally attached workers" include those who have gotten discouraged and stopped looking, but still want to work. The age considered for this calculation is 16 years and over.[102]
Nationality
- noun: American(s)
- adjective: American
See also
| This article is part of a series on |
| Income in the United States of America |
|---|
 |
|
|
- U.S. demographic birth cohorts
- Maps of American ancestries
- Languages of the United States
- Immigration to the United States
- Emigration from the United States
- Places in the United States with notable demographic characteristics
- Demographic history of the United States
- Race and ethnicity in the United States
- Urbanization in the United States
- Historical Statistics of the United States
Lists:
- Lists of U.S. cities with non-white majority populations
- List of metropolitan areas in the Americas
- List of U.S. states and territories by population
Income:
- Household income in the United States
- Personal income in the United States
- Affluence in the United States
- Highest-income places in the United States
- Lowest-income counties in the United States
Population:
- United States
- United States Census Bureau
- Demographics of the United States
- United States Office of Management and Budget
- United States Census Bureau
References
- ^ According to U.S. Poplock U.S. Popclock
- ^ U.S. & World Population Clocks
- ^ "CIA World Factbook". CIA World Factbook. 2010. Retrieved 2010-12-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)[dead link] - ^ "CIA World Factbook". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 2010-12-11.
{{cite web}}: Text "2010" ignored (help) - ^ "Table 13. State Population - Rank, Percent Change, and Population Density" (Excel). U.S. Census Bureau. 2008. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ^ "Mean Center of Population for the United States: 1790 to 2000" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places over 110,000, Ranked by July 1, 2009 Population: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2009 (SUB-EST2009-01)". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-05-19.
- ^ "Births: Preliminary Data for 2011" (PDF). National Vital Statistics reports. 61 (5). National Vital Statistics System. October 3, 2012.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook - Notes and Definitions". Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ In October 2012, the National Vital Statistics System reported that 2011 preliminary total fertility rate (TFR) in 2011 was 1,894.5 births per 100,000 women.[8] The CIA Factbook estimates the U.S. Total Fertility Rate in 2010 as 2.06.[9]
- ^ Demography: Virility symbols
- ^ a b "CIA - The World Factbook -- Field Listing - Population growth rate". CIA. Retrieved 2012-01-09.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Total fertility rate". CIA. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Net migration rate". CIA. Retrieved 2009-02-23.
- ^ a b "United States - Age and Sex". 2009 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ^ "The White Population: 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. August 2001. Retrieved 10 March 2011.
- ^ "Statistical Abstract of the United States" (PDF). United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "U.S. population hits 300 million mark". MSNBC (Associated Press). 2006-10-17. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
- ^ Morello, Carol and Mellnik, Ted. "Census: Minority Babies Are Now Majority in United States." Washington Post. May 17, 2012. Accessed 2012-05-17.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau: Minority Population Tops 100 Million". Archived from the original on 2008-04-20.
- ^ "U.S. Population Projections: 2005-2050 - Pew Hispanic Center". Pewhispanic.org. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ^ a b c "Projected Population by Single Year of Age, Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: July 1, 2000 to July 1, 2050". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ^ "World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision, Highlights, Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP.202; Table A.2" (PDF). United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2007). Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ^ a b http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_01.pdf
- ^ Resident Population Data. "Resident Population Data – 2010 Census". www.census.gov. Retrieved February 22, 2013.
- ^ "Demographics Trends in the 20th Century". U.S. Census Bureau.
- ^ "We the Americans: Blacks". Census.gov.
- ^ "Latinos and the Changing Face of America - Population Reference Bureau"
- ^ "Not Just Black and White: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives on Immigration, Race, and Ethnicity in the United States". Nancy Foner, George M. Fredrickson (2005). p.120. ISBN 0-87154-270-6
- ^ "Immigrants in the United States and the Current Economic Crisis", Demetrios G. Papademetriou and Aaron Terrazas, Migration Policy Institute, April 2009.
- ^ "Immigration Worldwide: Policies, Practices, and Trends". Uma A. Segal, Doreen Elliott, Nazneen S. Mayadas (2010). Oxford University Press US. p.32. ISBN 0-19-538813-5
- ^ "CBO: 748,000 Foreign Nationals Granted U.S. Permanent Residency Status in 2009 Because They Had Immediate Family Legally Living in America". CNSnews.com. January 11, 2011
- ^ ""The First Measured Century: An Illustrated Guide to Trends in America, 1900–2000"". Public Broadcasting Service (PBS).
- ^ "Changing Face of Western Cities". The Washington Post. August 21, 2006.
- ^ Exner, Rich (2012-07-03). "Americans under age 1 now mostly minorities, but not in Ohio: Statistical Snapshot". The Plain Dealer. Retrieved 2012-07-29.
- ^ "Non-white births outnumber white births for the first time in US". The Daily Telegraph. May 17, 2012.
- ^ ["http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_01.pdf" "Births: Final Data for 2010"]
- ^ ["http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=ACS_10_3YR_GCT0101.US01PR&prodType=table" "American FactFinder: Median age by state"]
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/nvsr.htm#vol61
- ^ Census 2010 Population Distribution in the United States and Puerto Rico. U.S. Census Bureau.
- ^ Density Using Land Area For States, Counties, Metropolitan Areas, and Places. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2007-12-14.
- ^
"The 2012 Global Cities Index". Retrieved 2013-01-05.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "The World According to GaWC - Classification of cities 2010". 2010. Retrieved 2013-01-05.
- ^ American cities on the rebound
- ^ "Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals: 2020–2023". United States Census Bureau. May 2023. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- ^ Overview of Race and Hispanic Origin: 2010
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau Guidance on the Presentation and Comparison of Race and Hispanic Origin Data". Retrieved 2007-04-05.
Race and Hispanic origin are two separate concepts in the federal statistical system. People who are Hispanic may be of any race. People in each race group may be either Hispanic or Not Hispanic. Each person has two attributes, their race (or races) and whether or not they are Hispanic.
{{cite web}}: line feed character in|quote=at position 86 (help) - ^ "American FactFinder Help: Hispanic or Latino origin". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau Data". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-07-13.
{{cite web}}: Text "2010" ignored (help) - ^ http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr60/nvsr60_01.pdf
- ^ Kanell, Michael E. (16 November 2009). "Number of veterans, October". Atlanta, Georgia: Atlanta Constitution-Journal. pp. A6. quoting the Bureau of Labor Statistics
- ^ Hsu, Spencer S. (2 May 2010). "Senate Democrats' plan highlights nation's shift to the right on immigration". Washington, DC: Washington Post. pp. A3.
- ^ Gerson, Michael (5 January 2010). "Column:More second chances". Melbourne, Florida: Florida Today. pp. 7A.
- ^ "2000 Census information on Gay and Lesbian Couples". gaydemographics.org.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ a b Gary J. Gates Template:PDFlink. The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation Law and Public Policy, UCLA School of Law October 2006. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ^ Press, Associated (March 1, 2011). "Research 4M adults in US identify as gay". Florida Today. Melbourne, Florida. pp. 1A.
- ^ Davenport, Christian (20 April 2010). "A disconnect at Magruder". Washington, DC: Washington Post. pp. B1.
- ^ a b "Table 4. Projections of the Population by Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: 2010 to 2050" (Excel). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2010-10-24.
- ^ U.S. Hispanic population to triple by 2050, USATODAY.com
- ^ White Americans no longer a majority by 2042[dead link]
- ^ U.S. to Grow Grayer, More Diverse
- ^ Pew Research Center: Immigration to Play Lead Role In Future U.S. Growth
- ^ Whites to become minority in U.S. by 2050, Reuters
- ^ An Older and More Diverse Nation by Midcentury, U.S. Census Press Releases, 14 August 2008 (archived from the original on 2008-08-22)
- ^ Table No. 68. Religious Bodies—Selected Data (p. 59), "Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004-2005 (tables 67-69)" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau.
- ^ "Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004-2005 (tables 67-69)" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau.
- ^ "Adherents.com". Adherents.com. Retrieved 2011-09 -1 9.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Section 1. Population" (PDF). Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004-2005. U.S. Census Bureau. p. 55. Retrieved 2008-06-29. (Table No. 67. Self-described religious identification of adult population: 1990 and 2001; data for 2001).
- ^ a b Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar (2009). "AMERICAN RELIGIOUS IDENTIFICATION SURVEY (ARIS) 2008" (PDF). Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Trinity College. Retrieved 2009-04-01.
- ^ Riley, Naomi Schaefer (6 June 2010). "Love conquers all. Except religion". Washington, DC: Washington Post. pp. B1, B4.
- ^ Semega, Jessica; Chen, Frances; Kollar, Melissa; Shrider, Emily A. "Income and Poverty in the United States: 2021" (PDF). US CENSUS BUREAU. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ "Personal Income: PINC-03". US CENSUS BUREAU. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ "Historical Income Tables: Households". US CENSUS BUREAU. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ Larry Copeland (2011-03-22). "Caution: Wide Load (and Just Getting Wider)". Florida Today.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|month=and|coauthors=(help) - ^ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/average-height-of-a-man.html
- ^ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/average-height-of-a-woman.html
- ^ http://nhlbisupport.com/bmi/bmi-m.htm
- ^ http://www.gallup.com/poll/158351/obesity-nearly-age-groups-2008.aspx
- ^ Saad, Lydia (August 22, 2012). "One in Five U.S. Adults Smoke, Tied for All-Time Low". Gallup. Retrieved 10 November 2012.
- ^ http://www.gallup.com/poll/151589/Diabetes-Rate-Levels-Off-2011.aspx
- ^ Caryn, Roni (2011-09-15). "Childhood - Hearing Loss Grows Among Teenagers". NYTimes.com. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ^ "HIV in the United States". Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 21 November 2011.
- ^ Schuman, H. and Scott, J. (1989), Generations and collective memories, American Sociological Review, vol. 54, 1989, pp. 359-81.
- ^ Illegal Drugs in America: A Modern History
- ^ The 1912 Hague International Opium Convention
- ^ History of Legislative Control Over Opium, Cocaine, and Their Derivatives
- ^ Encyclopedia of Identity By Ronald L. Jackson, II
- ^ William Strauss, Neil Howe (1991). Generations. New York, NY: Harper Perennial. p. 318. ISBN 0-688-11912-3.
- ^ The Gen X Files. "Latest Numbers for Generation X". Retrieved October 24, 2012.
- ^ Daddy's Gone to War: The Second ... - William M. Tuttle, Jr. - Google Books. Books.google.com. 1941-12-07. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook -- United States". CIA. Retrieved 2010-02-16.
- ^ Marchione, Marilynn (August 27, 2010). "Recession may have pushed U.S. birth rate to a new low". USA Today. Associated Press. Retrieved 2010-10-09.
- ^ Births, Marriages, Divorces, and Deaths: Provisional Data for 2009 National Vital Statistics Report Volume 58, Number 25, accessed August 28, 2010
- ^ Amy Sullivan (March 20, 2009). "Behind the Boom in Adult Single Motherhood". Time.
- ^ Press, Associated (7 November 2010). "Blacks rank highest in unwed births". Melbourne, Florida: Florida Today. pp. 9A.
- ^ "Birthrate Is Lowest in a Century" Associated Press article printed in The New York Times August 27, 2010, accessed August 28, 2010
- ^ "United States: Inflow of foreign-born population by country of birth, by year (table available by menu selection)". Migration Policy Institute. 2007.
- ^ Starr, Tena (28 April 2010). "Mexican farmworker's life like living in a "golden cage"". Barton, Vermont: the Chronicle. p. 12.
- ^ Current Unemployment Rates for States and Historical Highs/Lows, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- ^ "Employment Situation Summary". U.S. Dept. of Labor. 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2012-10-05.
- ^ "Table A-15. Alternative measures of labor underutilization". U.S. Bureau of Labor. Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- ^ "U6 Unemployment Rate". Portal Seven. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ^ "Metropolitan and NECTA Divisions published by CES". U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. January 28, 2011.
- ^ "May 2009 Metropolitan and Nonmetropolitan Area Definitions". U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. August 16, 2010.
External links
- United States Census Bureau
- New York Times: "Mapping the 2010 U.S. Census"
- 2000 Census of Population and Housing United States, U.S. Census Bureau
- U.S. Demographics and State Rankings
- Asian-Nation: Demographics of Asian American /2006-07-04-us-population_x.htm?csp=34 Countdown to 300 million
- Census Ancestry Map
- USA Today 2004 Election County by County Map
- BeliefNet State by State Religious Affiliation (archived from the original on 2008-04-21)
- Health by State
- U.S. Demographics and Maps
- America's Changing Demographics a Nightly Business Report special
- The Realignment of America - The Wall Street Journal
- Religion U.S. Census Bureau
- Google - public data "Population in the U.S.A."



