GL-II-73: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
templated cites |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
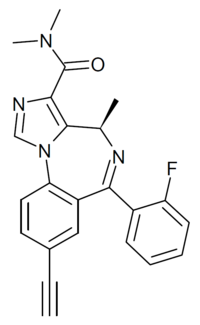
'''GL-II-73''' ('''GL-ii-073''') is a [[benzodiazepine]] derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as [[midazolam]] and [[adinazolam]]. It is described as an α<sub>5</sub> preferring [[positive allosteric modulator]] of the benzodiazepine site of [[GABAA receptor|GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor]]s, with weaker activity at α<sub>2</sub> and α<sub>3</sub> and no significant affinity for the α<sub>1</sub> subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with [[antidepressant]], [[anxiolytic]] and [[nootropic]] actions.<ref>{{cite patent | country = CA | number = 3016491 | inventor = Cook JM, Li G, Poe M, Savic M, Sibille E | assign1 = Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Faculty Of Pharmacy, University of Belgrade | assign2 = UWM Res Foundation Inc | title = Treatment of cognitive and mood symptoms in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders with alpha5-containing gabaa receptor agonists. | pubdate = 21 September 2017 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Prevot TD, Li G, Vidojevic A, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Santrac A, Knutson DE, Stephen MR, Kodali R, Zahn NM, Arnold LA | s2cid = 90987308 | display-authors = 6 | title = Potential combined pro-cognitive, anxiolytic and antidepressant properties of novel GABAA receptor positive modulators with preferential efficacy at the α5-subunit. | journal = bioRxiv | date = January 2018 | pages = 332908 | doi = 10.1101/332908 | url = https://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2018/05/29/332908.full.pdf }}</ref><ref name="pmid31192221">{{cite journal | vauthors = Prevot TD, Li G, Vidojevic A, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Santrac A, Knutson DE, Stephen MR, Kodali R, Zahn NM, Arnold LA, Scholze P, Fisher JL, Marković BD, Banasr M, Cook JM, Savic M, Sibille E | title = Novel Benzodiazepine-Like Ligands with Various Anxiolytic, Antidepressant, or Pro-Cognitive Profiles | journal = Molecular Neuropsychiatry | volume = 5 | issue = 2 | pages = 84–97 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 31192221 | pmc = 6528097 | doi = 10.1159/000496086 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.sibillelab.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/AAAS-Sibille.pdf | first = Etienne | last = Sibille | name-list-style = vanc | title = Brain Inhibitory GABAergic Function and Cognitive Deficits: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targeting. | work = Presentation for AAAS | date = February 2019 }}</ref><ref>Maramai S, Benchekroun M, Ward SE, Atack JR |
'''GL-II-73''' ('''GL-ii-073''') is a [[benzodiazepine]] derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as [[midazolam]] and [[adinazolam]]. It is described as an α<sub>5</sub> preferring [[positive allosteric modulator]] of the benzodiazepine site of [[GABAA receptor|GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor]]s, with weaker activity at α<sub>2</sub> and α<sub>3</sub> and no significant affinity for the α<sub>1</sub> subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with [[antidepressant]], [[anxiolytic]] and [[nootropic]] actions.<ref>{{cite patent | country = CA | number = 3016491 | inventor = Cook JM, Li G, Poe M, Savic M, Sibille E | assign1 = Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Faculty Of Pharmacy, University of Belgrade | assign2 = UWM Res Foundation Inc | title = Treatment of cognitive and mood symptoms in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders with alpha5-containing gabaa receptor agonists. | pubdate = 21 September 2017 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Prevot TD, Li G, Vidojevic A, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Santrac A, Knutson DE, Stephen MR, Kodali R, Zahn NM, Arnold LA | s2cid = 90987308 | display-authors = 6 | title = Potential combined pro-cognitive, anxiolytic and antidepressant properties of novel GABAA receptor positive modulators with preferential efficacy at the α5-subunit. | journal = bioRxiv | date = January 2018 | pages = 332908 | doi = 10.1101/332908 | url = https://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2018/05/29/332908.full.pdf }}</ref><ref name="pmid31192221">{{cite journal | vauthors = Prevot TD, Li G, Vidojevic A, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Santrac A, Knutson DE, Stephen MR, Kodali R, Zahn NM, Arnold LA, Scholze P, Fisher JL, Marković BD, Banasr M, Cook JM, Savic M, Sibille E | title = Novel Benzodiazepine-Like Ligands with Various Anxiolytic, Antidepressant, or Pro-Cognitive Profiles | journal = Molecular Neuropsychiatry | volume = 5 | issue = 2 | pages = 84–97 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 31192221 | pmc = 6528097 | doi = 10.1159/000496086 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.sibillelab.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/AAAS-Sibille.pdf | first = Etienne | last = Sibille | name-list-style = vanc | title = Brain Inhibitory GABAergic Function and Cognitive Deficits: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targeting. | work = Presentation for AAAS | date = February 2019 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Maramai S, Benchekroun M, Ward SE, Atack JR | title = Subtype Selective γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor (GABA<sub>A</sub>R) Modulators Acting at the Benzodiazepine Binding Site: An Update | journal = Journal of Medicinal Chemistry | volume = 63 | issue = 7 | pages = 3425–3446 | date = April 2020 | pmid = 31738537 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bernardo A, Lee P, Marcotte M, Mian MY, Rezvanian S, Sharmin D, Kovačević A, Savić MM, Cook JM, Sibille E, Prevot TD | display-authors = 6 | title = Symptomatic and neurotrophic effects of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulation in a mouse model of chronic stress | journal = Neuropsychopharmacology | volume = 47 | issue = 9 | pages = 1608–1619 | date = August 2022 | pmid = 35701547 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Perez SM, McCoy AM, Prevot TD, Mian MY, Carreno FR, Frazer A, Cook JM, Sibille E, Lodge DJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Hippocampal α5-GABA<sub>A</sub> Receptors Modulate Dopamine Neuron Activity in the Rat Ventral Tegmental Area | journal = Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science | volume = 3 | issue = 1 | pages = 78–86 | date = January 2023 | pmid = 36712569 }}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 05:01, 13 May 2023
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H19FN4O |
| Molar mass | 386.430 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
GL-II-73 (GL-ii-073) is a benzodiazepine derivative related in chemical structure to compounds such as midazolam and adinazolam. It is described as an α5 preferring positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with weaker activity at α2 and α3 and no significant affinity for the α1 subtype. In animal tests it was found to produce effects consistent with antidepressant, anxiolytic and nootropic actions.[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
See also
References
- ^ CA 3016491, Cook JM, Li G, Poe M, Savic M, Sibille E, "Treatment of cognitive and mood symptoms in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders with alpha5-containing gabaa receptor agonists.", published 21 September 2017, assigned to Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Faculty Of Pharmacy, University of Belgrade and UWM Res Foundation Inc
- ^ Prevot TD, Li G, Vidojevic A, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Santrac A, et al. (January 2018). "Potential combined pro-cognitive, anxiolytic and antidepressant properties of novel GABAA receptor positive modulators with preferential efficacy at the α5-subunit" (PDF). bioRxiv: 332908. doi:10.1101/332908. S2CID 90987308.
- ^ Prevot TD, Li G, Vidojevic A, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Santrac A, Knutson DE, Stephen MR, Kodali R, Zahn NM, Arnold LA, Scholze P, Fisher JL, Marković BD, Banasr M, Cook JM, Savic M, Sibille E (April 2019). "Novel Benzodiazepine-Like Ligands with Various Anxiolytic, Antidepressant, or Pro-Cognitive Profiles". Molecular Neuropsychiatry. 5 (2): 84–97. doi:10.1159/000496086. PMC 6528097. PMID 31192221.
- ^ Sibille E (February 2019). "Brain Inhibitory GABAergic Function and Cognitive Deficits: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targeting" (PDF). Presentation for AAAS.
- ^ Maramai S, Benchekroun M, Ward SE, Atack JR (April 2020). "Subtype Selective γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptor (GABAAR) Modulators Acting at the Benzodiazepine Binding Site: An Update". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 63 (7): 3425–3446. PMID 31738537.
- ^ Bernardo A, Lee P, Marcotte M, Mian MY, Rezvanian S, Sharmin D, et al. (August 2022). "Symptomatic and neurotrophic effects of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulation in a mouse model of chronic stress". Neuropsychopharmacology. 47 (9): 1608–1619. PMID 35701547.
- ^ Perez SM, McCoy AM, Prevot TD, Mian MY, Carreno FR, Frazer A, et al. (January 2023). "Hippocampal α5-GABAA Receptors Modulate Dopamine Neuron Activity in the Rat Ventral Tegmental Area". Biological Psychiatry Global Open Science. 3 (1): 78–86. PMID 36712569.
