Tokyo: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 199.227.112.41 (talk) to last version by SieBot |
|||
| Line 256: | Line 256: | ||
[[Image:Tokyo subway map.PNG|thumb|200px|Map of Tokyo Subway system, with transfer stations labeled.]] |
[[Image:Tokyo subway map.PNG|thumb|200px|Map of Tokyo Subway system, with transfer stations labeled.]] |
||
{{main|Transportation in Greater Tokyo}}<!-- Note to editors: Transportation in Greater Tokyo is a comprehensive article. The Transportation section of the article on Tokyo (this article) is a very brief introduction and includes very few specific details. Transportation in Tokyo contains a wealth of detail and can accommodate more so please contribute there! --> |
{{main|Transportation in Greater Tokyo}}<!-- Note to editors: Transportation in Greater Tokyo is a comprehensive article. The Transportation section of the article on Tokyo (this article) is a very brief introduction and includes very few specific details. Transportation in Tokyo contains a wealth of detail and can accommodate more so please contribute there! --> |
||
Tokyo is Japan's largest domestic and international hub for rail, ground, and air transportation. Public transportation within Tokyo is dominated by an extensive network of clean and efficient |
Tokyo is Japan's largest domestic and international hub for rail, ground, and air transportation. Public transportation within Tokyo is dominated by an extensive network of clean and efficient trains and subways run by a variety of operators, with buses, monorails and trams playing a secondary feeder role. Railway stations are not only transport, but the center of Tokyo and Japanese urban life, as everything is judged in relation to it, taking on the significance of highways in the United States and elsewhere. |
||
Within Tokyo, [[Tokyo International Airport]] ("Haneda") offers mainly domestic flights. Outside Tokyo, [[Narita International Airport]], in [[Narita]], [[Chiba Prefecture]], is the major gateway for international travelers. |
Within Tokyo, [[Tokyo International Airport]] ("Haneda") offers mainly domestic flights. Outside Tokyo, [[Narita International Airport]], in [[Narita]], [[Chiba Prefecture]], is the major gateway for international travelers. |
||
Revision as of 23:25, 10 August 2007
Tōkyō (東京, literally "Eastern capital") is a unique subnational administrative region of Japan with characteristics of both a prefecture and a city. It is the de facto capital of Japan,[1] the most populous subnational entity and city in the country, and the center of the most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 35 million people in the Greater Tokyo Area.[2] Tokyo is the seat of the Japanese government and the Imperial Palace, and the home of the Japanese Imperial Family. The twenty-three special wards of Tokyo, although each administratively a city in its own right, constitute the area informally considered as the "city of Tokyo" and are collectively one of the largest cities in the world with a total population of over 8 million people.[3] Tokyo has the largest metropolitan gross domestic product in the world for a city, and it held the title of the world's most expensive city for over a decade from 1992 through 2005.[4]
Prior to 1943, Tokyo was the name of both one of the 47 prefectures of Japan, Tokyo-fu, and the populous city of Tokyo in the eastern half of the prefecture. In 1943 the city and prefecture were merged into a unique prefecture-level government entity, known as Tōkyō-to 東京都 or "Tokyo Metropolis". This administrative region includes the twenty-three "special wards" of the former city, many suburban cities in the western half of the prefecture, and two chains of islands extending south into the Pacific Ocean. Over 12 million people, 10% of Japan's population, live within Tokyo Metropolis's prefecture boundaries.
Tokyo is considered one of the world's major global cities and a megacity. The word "Tokyo" may refer to Tokyo Metropolis as a whole, or only to the main urban mass under its jurisdiction (thus excluding west Tama and Izu / Ogasawara Islands), or even the whole of Greater Tokyo Area, which includes Tokyo, Kanagawa, Saitama, Chiba, Gunma, Tochigi, Ibaraki, and Yamanashi prefectures, depending on context. This article refers to Tokyo Metropolis unless otherwise stated.
History

Tokyo's rise to importance can be largely attributed to two men: Tokugawa Ieyasu and Emperor Meiji. Tokugawa Ieyasu made Edo (the forerunner of Tokyo) his base. When he became shogun in 1603, the town began to grow into the capital of his nationwide military government. It became one of the largest cities in the world with a population topping one million by the 18th century. It became the de facto capital of Japan even while the emperor lived in Kyoto, the imperial capital.
After about 263 years, the shogunate was overthrown under the banner of restoring imperial rule. In 1869, the 17-year-old Emperor Meiji moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" ("Eastern Capital") the year before. Tokyo was already the nation's political, economic, and cultural center, and the emperor's residence made it a de facto imperial capital as well with the former Edo Castle becoming the Imperial Palace. The city of Tokyo was established, and continued to be the capital until it was abolished as a municipality in 1943 and merged with the "Metropolitan Prefecture" of Tokyo.

Central Tokyo, like Osaka, has been designed since about the turn of the century (1900) to be centered around major train stations in a high density fashion, so suburban railways were built relatively cheaply at street level. This differs from other world cities such as Los Angeles that are low density automobile centric, and though expressways have been built, the basic design hasn't changed to this day.
Tokyo went on to suffer two major catastrophes and has recovered remarkably from both. One was the Great Kanto Earthquake in 1923, and the other was World War II. The firebombings in 1945, with 75,000 to 200,000 killed and half of the city destroyed, were almost as devastating as the atomic bombs of Hiroshima and Nagasaki combined.[5] After the war, Tokyo was completely rebuilt, and showcased to the world during the city's 1964 Summer Olympics. The 1970s brought new high-rise developments such as Sunshine 60, a new and controversial airport at Narita (well outside Tokyo), and a population increase to about 11 million (in the metropolitan area).
Tokyo's subway and commuter rail network became the busiest in the world as more and more people moved to the area. In the 1980s, real estate prices skyrocketed during an economic bubble. The bubble burst in the early 1990s and many companies, banks, and individuals were caught with real estate shrinking in value. A major recession followed, making the 1990s Japan's "lost decade" from which it is now slowly recovering.
Tokyo still sees new urban developments on large lots of less profitable land. Recent projects include Ebisu Garden Place, Tennozu Isle, Shiodome, Roppongi Hills, Shinagawa (now also a Shinkansen station), and Tokyo Station (Marunouchi side). Buildings of significance are demolished for more up-to-date shopping facilities such as Omotesando Hills. Land reclamation projects in Tokyo have also been going on for centuries. The most prominent is the Odaiba area, now a major shopping and entertainment center.
Tokyo was hit by powerful earthquakes in 1703, 1782, 1812, 1855 and 1923. The 1923 earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 8.3, killed 142,000 people.

There have been various plans proposed for transferring national government functions from Tokyo to secondary capitals in other regions of Japan, in order to slow down rapid development in Tokyo and revitalize economically lagging areas of the country. These plans have been controversial within Japan and have yet to be realized.
An older method of romanizing Japanese resulted in "Tokio" as an earlier spelling.
During the early Meiji period, the city was also called "Tōkei", an alternative pronunciation for the same Chinese characters representing "Tokyo". Some surviving official English documents use the spelling "Tokei".[6] This pronunciation is now obsolete.
Geography and administrative divisions
Tokyo Metropolis consists of three major parts: the twenty-three special wards (constituting the former Tokyo City); Tama area; and the islands.
The mainland portion of Tokyo lies northwest of Tokyo Bay and measures about 90 km east to west and 25 km north to south. It borders Chiba Prefecture to the east, Yamanashi Prefecture to the west, Kanagawa Prefecture to the south, and Saitama Prefecture to the north. Mainland Tokyo is further subdivided into the special wards (occupying the eastern half) and the Tama area (多摩地方) stretching westwards.

Also within the administrative boundaries of Tokyo Metropolis are two island chains in the Pacific Ocean directly south: the Izu Islands, which are almost parallel to the Izu Peninsula; and the Ogasawara Islands, which stretch more than 1,000 km away from mainland Japan.
Under Japanese law, Tokyo is designated as a to (都, often translated "metropolis"). Its administrative structure is similar to that of Japan's other prefectures. Within Tokyo lie dozens of smaller entities, most of them conventionally referred to as cities. It includes twenty-three special wards (特別区 -ku) which until 1943 comprised the city of Tokyo but are now separate, self-governing municipalities, each with a mayor and a council, and having the status of a city. In addition to these 23 municipalities, Tokyo also encompasses 26 more cities (市 -shi), five towns (町 -chō or machi), and eight villages (村 -son or -mura), each of which has a local government. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government is headed by a publicly-elected governor and metropolitan assembly. Its headquarters are in the ward of Shinjuku. They govern all of Tokyo, including lakes, rivers, dams, farms, remote islands, and national parks in addition to its famous neon jungle, skyscrapers and crowded subways.
The twenty-three special wards



The special wards (tokubetsu-ku) of Tokyo comprise the area formerly known as Tokyo City, usually simply known as "Tokyo". On July 1, 1943, Tokyo City was merged with Tokyo Prefecture (東京府, tokyo-fu) forming the current "metropolitan prefecture". As a result of this merger, unlike other city wards in Japan, these wards are not part of any city.
Each ward is a local municipality with its own elected mayor and assembly, differing from an ordinary city in that certain governmental functions are handled by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, and, for most, also differing in having no particular center and little cultural or similar distinctiveness from the immediate surroundings.
The term "central Tokyo" today may refer to the 23 special wards, the centres of Shinjuku, Minato, Chiyoda and Chūō connected and enclosed by the Yamanote Line, or to the three centrally-located wards of Chiyoda, Chūō and Minato. While the generally-accepted center of Tokyo is the Imperial Palace, as a rail-centric city, there are a number of major urban centers where business, shopping, and entertainment are concentrated around major train stations. These include:
- Shinjuku
- Location of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building. The area is best known for Tokyo's early skyscrapers, erected in the 1970s. Major department stores, electronics stores and hotels can also be found here. On the east side of Shinjuku Station, Kabuki-cho is notorious for its many bars and nightclubs. Shinjuku Station moves an estimated three million passengers a day, making it the busiest in the world.
- Marunouchi and Ōtemachi
- The main financial and business district of Tokyo has many headquarters of banks, trading companies and other major corporations. The area is seeing a major redevelopment with new buildings for shopping and entertainment constructed in front of Tokyo Station's Marunouchi side.
- Ginza and Yurakucho
- Major shopping and entertainment district with department stores, upscale shops selling brand-name goods, and movie theaters.
- Shinbashi
- An area revitalized by being the gateway to Odaiba and the new Shiodome Shiosite complex of high-rise buildings.
- Shinagawa
- In addition to the major hotels on the west side of Shinagawa Station, the former sleepy east side of the station has been redeveloped as a major center for business.
- Shibuya
- A long-time center of shopping, fashion and entertainment, especially for the younger set and includes the famous Harajuku. Shibuya is also home to some of Tokyo's largest and newest nightclubs.
- Ikebukuro
- The busiest interchange in north central Tokyo, featuring Sunshine City and various shopping destinations.
- Ueno
- Ueno Station serves areas north of Tokyo from where many people commute. Besides department stores and shops in Ameyoko, Ueno boasts Ueno Park, Ueno Zoo and major national museums. In spring, Ueno Park and adjacent Shinobazu Pond are prime places to view cherry blossoms.
- Odaiba
- A large, reclaimed, waterfront area that has become one of Tokyo's most popular shopping and entertainment districts.
- Nagatacho
- The political heart of Tokyo and the nation. It is the location of the Diet, government ministries, and party headquarters.
- Akasaka
- A district with a range of restaurants, clubs and hotels; many pedestrian alleys giving it a local neighbourhood feel. Next to Roppongi, Nagatacho, and Aoyama.
- Aoyama
- A neighborhood of Tokyo with parks, an enormous cemetery, expensive housing, trendy cafes and international restaurants. Includes the Omotesandō subway station.
Western Tokyo

To the west of the special wards, Tokyo Metropolis consists of cities, towns and villages that enjoy the same legal status as those elsewhere in Japan.
While serving a role as "bed towns" for those working in central Tokyo, some of these also have a local commercial and industrial base. Collectively, these are often known as Tama Area or Western Tokyo.
Cities
Twenty-six cities lie within the western part of Tokyo Prefecture:
The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has designated Hachioji, Tachikawa, Machida, Ome and Tama New Town as regional centres of the Tama area, as part of their plans to disperse urban functions away from central Tokyo.
Districts, towns and villages
The far west is occupied by the district (gun) of Nishitama. Much of this area is mountainous and unsuitable for urbanization. The highest mountain in Tokyo, Mount Kumotori, is 2,017 m high; other mountains in Tokyo include Mount Takasu (1737 m), Mount Odake (1266 m), and Mount Mitake (929 m). Lake Okutama, on the Tama River near Yamanashi Prefecture, is Tokyo's largest lake.
Islands
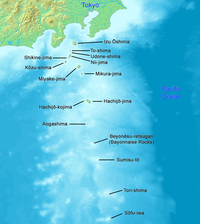
Tokyo's outlying islands extend as far as 1850 km from central Tokyo. Because of the islands' distance from the city, they are locally run by branches of the metropolitan government. The islands are organized into two towns and seven villages.
In Izu Islands, there are 2 towns and 6 villages. In Ogasawara Islands, there is only 1 village.
Izu Islands
The Izu Islands are a group of volcanic islands and form part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. The islands in order from closest to Tokyo are:
Izu Ōshima and Hachiojima are towns. The remaining islands are six villages, with Niijima and Skikinejima forming one village.
Ogasawara Islands
- Ogasawara—Ogasawara includes, from north to south, Chichi-jima, Nishinoshima, Haha-jima, Kita Iwo Jima, Iwo Jima, and Minami Iwo Jima. Ogasawara also administers two tiny outlying islands: Minami Torishima, the easternmost point in Japan and at 1,850 km the most distant island from central Tokyo, and Okino Torishima, the southernmost point in Japan. The last island is contested by the People's Republic of China as being only uninhabited rocks. The Iwo chain and the outlying islands are uninhabited, except of Japanese Self-Defense Forces personnel. Local populations are only found on Chichi-jima and Haha-jima. The islands form the Ogasawara village.
National Parks
There are four national parks in Tokyo Prefecture:
- Chichibu Tama Kai National Park, in Nishitama and spilling over into Yamanashi and Saitama Prefectures
- Meiji no Mori Takao Quasi-National Park, around Mount Takao to the south of Hachioji.
- Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, which includes all of the Izu Islands.
- Ogasawara National Park. As of 2006, efforts were being made to make Ogasawara National Park a UNESCO natural World Heritage Site.
Climate
Tokyo lies in the Humid subtropical climate zone, with hot humid summers and mild to cool winters. Its location on the coast of the Pacific Ocean affords Tokyo a milder climate than other cities worldwide at a similar latitude. Annual rainfall averages 138 cm (55 inches), with a wetter summer and a drier winter. Snowfall is sporadic, but does occur annually.
Economy
Tokyo has the largest metropolitan economy in the world. According to a study conducted by PricewaterhouseCoopers, the Tokyo urban area (35.2 million people) had a total GDP of US$1,191 billion in 2005 (at purchasing power parity), ranking again as the largest urban agglomeration GDP in the world.[7]
Tokyo is a major international finance center, is site of the headquarters of several of the world's largest investment banks and insurance companies, and serves as a hub for Japan's transportation, publishing, and broadcasting industries. During the centralized growth of Japan's economy following World War II, many large firms moved their headquarters from cities such as Osaka (the historical commercial capital) to Tokyo, in an attempt to take advantage of better access to the government. This trend has begun to slow due to ongoing population growth in Tokyo and the high cost of living there.
Tokyo was rated by the Economist Intelligence Unit as the most expensive (highest cost-of-living) city in the world for 14 years in a row ending in 2006.[8] Note that this is for living a Western corporate executive lifestyle, with items typically considered luxuries in large cities, like a detached house and several automobiles. Many Japanese get by fine on a budget in Tokyo, underpinning the high national savings rate.
The Tokyo Stock Exchange is the second largest in the world by market capitalization of listed shares, at $4.99 trillion.[1] Only the New York Stock Exchange is larger. However, its prominence has fallen significantly since early 1990s asset bubble peak, when it accounted for more than 60% of the entire world's stock market values.
Tokyo had 8,460 ha (20,900 acres) of agricultural land as of 2003[2], according to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, placing it last among the nation's prefectures. The farmland is concentrated in Western Tokyo. Perishables such as vegetables, fruits, and flowers can be conveniently shipped to the markets in the eastern part of the prefecture. Japanese leaf spinach and spinach are the most important vegetables; as of 2000, Tokyo supplied 32.5% of the Japanese leaf spinach sold at its central produce market.
With 36% of its area covered by forest, Tokyo has extensive growths of cryptomeria and Japanese cypress, especially in the mountainous western communities of Akiruno, Ōme, Okutama, Hachioji, Hinode, and Hinohara. Decreases in the price of lumber, increases in the cost of production, and advancing old age among the forestry population have resulted in a decline in Tokyo's output. In addition, pollen, especially from cryptomeria, is a major allergen for the nearby population centers.
Tokyo Bay was once a major source of fish. Presently, most of Tokyo's fish production comes from the outer islands, such as Izu Ōshima and Hachijōjima. Skipjack tuna, nori, and aji are among the ocean products.
Demographics
As one of the major cities of the world, Tokyo has over eight million people living within its 23 wards, and during the daytime, the population swells by over 2.5 million as workers and students commute from adjacent areas. This effect is even more pronounced in the three central wards of Chiyoda, Chūō, and Minato, whose collective population is less than 300,000 at night, but over two million during the day. The entire prefecture has 12,696,000 residents in March 2007, with an increase of over 3 million in the day.
| By area1 |
Tokyo Prefecture |
12.6 million |
|---|---|---|
| By age2 |
Juveniles (age 0-14) |
1.433 million (12%) |
| By hours3 |
Day |
14.667 million |
| By nationality |
Foreign residents |
353,8264 |
|
1 as of June 1, 2007. | ||
The five most common foreign nationalities found in Tokyo are Chinese (120,331), Korean (103,191), Filipino (31,505), American (18,043) and British (7,585).
Historic population
From its modest beginnings as a fishing village, it was chosen in 1603 to be the new Tokugawa headquarters, it grew from nearly nothing to over a million people and Japan's preeminent city by the mid-1700s, becoming one of the largest cities in the world at the time. Railways that began in the 1885 (Yamanote Line) facilitated rapid growth. The city continued to grow quickly; in 1920, a census upon joining the League of Nations accounted for 3,699,428 people; despite a series of fires, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions that have leveled the city countless times since its founding. Despite being hit by a major earthquake in 1923, by 1932 its population had swelled to seven million, second in the world to only New York City. In 1945 however, after the years of the Pacific War in World War II, the city's population was half of what it was before the war.
After World War II, the city was destroyed and rebuilt once again, and the 23 wards increased in population until the 1960s, when many Tokyo residents moved to the suburbs, as modern suburban rail networks facilitated commutes to Tokyo. Many of the newcomers were from other parts of Japan, and many companies relocated from the Kansai area. From the 1960s to around the year 2000, the 23 wards had been slowly losing population to suburbs, with Tokyo's 23 wards recording fewer than 8 million residents from a high of over 8.66 million.
More recently, as land prices had fallen drastically from their peak in 1991, a significant number of people have relocated to the 23 wards and the population is again rising, to 8.5 million today. Suburbs in Kanagawa and southern Saitama prefecture have experienced the most rapid growth in recent years (especially those bordering Tokyo 23 wards), while populations in other areas have stabilized or are falling slightly.
Years of major damage and deaths:
- 1657 Great Fire of Meireki, 100,000 die
- 1703 Earthquake
- 1707 Hōei eruption of Mount Fuji
- 1767 Earthquake
- 1772 Major fire 18000 die
- 1806 Major fire 10000 die
- 1855 Great Ansei Earthquake
- 1923 Great Kanto Earthquake 140,000 die
- 1942-1945 Bombing of Tokyo in World War II, about 250,000 die in U.S. Army Air Forces air raids
Other major disasters in Tokyo:
- 1833-1837 Tempo Famine
- 1853 Odawara earthquake
- 1868 Meiji restoration (revolution)
- 1872 Ginza fire
Nakamura-za and Ichimura-za, the most renowned Kabuki theaters of the time, were reduced to ashes 33 times between 1657 and 1841. The Nihonbashi district, the central part of Edo where merchants lived, was also afflicted with regular large blazes, being ravaged 10 times in the 200 years following the Meireki Fire.[9]
Transportation


Tokyo is Japan's largest domestic and international hub for rail, ground, and air transportation. Public transportation within Tokyo is dominated by an extensive network of clean and efficient trains and subways run by a variety of operators, with buses, monorails and trams playing a secondary feeder role. Railway stations are not only transport, but the center of Tokyo and Japanese urban life, as everything is judged in relation to it, taking on the significance of highways in the United States and elsewhere.
Within Tokyo, Tokyo International Airport ("Haneda") offers mainly domestic flights. Outside Tokyo, Narita International Airport, in Narita, Chiba Prefecture, is the major gateway for international travelers.
Rail is the primary mode of transportation in Tokyo, which has the most extensive urban railway network in the world and an equally extensive network of surface lines. JR East operates Tokyo's largest railway network, including the Yamanote Line loop that circles the center of downtown Tokyo. Tokyo Metro and Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation operate the subway network. The metropolitan government and private carriers operate bus routes. Local, regional, and national services are available, with major terminals at the giant railroad stations, including Tokyo and Shinjuku.
Expressways link the capital to other points in the Greater Tokyo area, the Kantō region, and the islands of Kyūshū and Shikoku.
Taxis operate in the special wards and the cities and towns. Long-distance ferries serve the islands of Tokyo and carry passengers and cargo to domestic and foreign ports.
Education
Being the nation's center of education, Tokyo has many universities, junior colleges, and vocational schools. Many of Japan's most prestigious universities are in Tokyo. The most prestigious is the University of Tokyo. Other schools include Keio University, Hitotsubashi University, and Waseda University.
Universities
Tokyo also has a few universities well-known for classes conducted in English. They include International Christian University, Sophia University, Waseda University and Temple University Japan. Tokyo has an array of Japanese universities. National universities include Tokyo Medical and Dental University, University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo Institute of Technology and University of Tokyo. There is only one public university, the Tokyo Metropolitan University, and Private Universities include, Keio University and Waseda University. These universities are the top private universities in Japan. For an extensive list of universities in Tokyo, see List of universities in Tokyo.
Primary and secondary schools
Publicly run kindergartens, elementary schools (years 1 through 6), and junior high schools (7 through 9) are operated by local wards or municipal offices. Public high schools in Tokyo are run by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Board of Education and are called "Metropolitan High Schools". Tokyo also has a great number of privately run schools from kindergarten through high school. For a list of high schools in Japan, see [3].
Culture

Tokyo is known for its many museums. Located in Ueno Park are the Tokyo National Museum, the country's largest museum and specializing in traditional Japanese art; the National Museum of Western Art; and the Tokyo Metropolitan Art Museum, which contains collections of Japanese modern art as well as over 10,000 Japanese and foreign films. Ueno Park also contains the National Museum of Science and the municipal zoo. Other museums include the Nezu Art Museum in Aoyama; the Edo-Tokyo Museum in the Sumida Ward across the Sumida River from the center of Tokyo; and the National Diet Library, National Archives, and the National Museum of Modern Art which are located near the Imperial Palace.
Tokyo is the national center of performing arts as well. There are many theatres in the city in which traditional forms of Japanese drama (like noh and kabuki) as well as modern dramas. Symphony orchestras and other musical organizations perform Western and traditional music. Tokyo also plays host to modern Japanese and Western pop and rock music.

Tokyo is home to many different festivals that occur throughout the city. Major festivals draw people from all over the city including the Sanno Festival at Hie Shrine, and the Sanja Festival at Asakusa Shrine. Many Japanese cities hold festivals called matsuri. The Kanda Matsuri in Tokyo is held every two years in May. The festival features a parade with elaborately decorated floats and thousands of people. Annually on the last Saturday of July, an enormous fireworks display is held over the Sumida River and it attracts over 1 million viewers. Once cherry blossoms,or sakura(桜), bloom in spring, many residents gather in parks such as Ueno Park, Inokashira Park, and the Shinjuku Gyöen National Gardens for picnics under the beautiful cherry trees.
Sports
The sports teams listed below are based in Tokyo.
Football (soccer)
- F.C. Tokyo
- Tokyo Verdy 1969
- Sagawa Express Tokyo S.C. (Tokyo)
- Yokogawa Musashino F.C. (Musashino city)
Baseball
Ice Hockey
Basketball
Volleyball
Rugby
Tennis
Tokyo hosts one of the ten prestigious Tier I tournaments on the women's tennis tour (WTA) and it takes place directly after the Australian Open, near the beginning of the tennis season. It attracts a vast number of top players each year, including Maria Sharapova, Martina Hingis, Ai Sugiyama, Elena Dementieva, Ana Ivanović and Lindsay Davenport. Tokyo also hosts another tennis event later in the year, after the US Open.
On the men's ATP tour Tokyo also hosts an tennis event, most recently won by world-number one and tennis superstar Roger Federer.
Tourism
Tokyo has many tourist sightseeing, cultural and sport attractions. These include famous temples, shrines, annual festivals and events, parks, scenic views, popular shopping and nightlife districts. Cultural highlights of Tokyo include museums, concert halls, and theaters.
Tokyo in popular media
As the largest city in Japan and the location of the country's largest broadcasters and studios, Tokyo is frequently the setting for many Japanese movies, television shows, animated series (anime), and comic books (manga). The best-known outside Japan may be the kaiju (monster movie) genre, in which landmarks of Tokyo are routinely destroyed by giant monsters such as Godzilla. Many comics and animated series are set in Tokyo, such as Digimon, Sailor Moon, Ranma ½, Azumanga Daioh, Beyblade, Yu-Gi-Oh! and even the western animation Hi Hi Puffy AmiYumi, have become popular across the world as well. Some futuristic anime and manga such as Akira often depict Tokyo as a sprawling metropolis in a post-apocalyptic setting; some often go so far as to have numbers designating different Tokyos.
Some Hollywood directors have turned to Tokyo as a filming location for movies set in Tokyo. Well-known examples from the postwar era include Tokyo Joe, My Geisha, and the James Bond film You Only Live Twice; well-known contemporary examples include Kill Bill, The Fast and the Furious: Tokyo Drift and Lost in Translation.
Sister relationships
Tokyo has sister relationships with eleven places worldwide[4]:
 Beijing, China
Beijing, China Berlin, Germany
Berlin, Germany Cairo, Egypt
Cairo, Egypt Jakarta, Indonesia
Jakarta, Indonesia Moscow, Russia
Moscow, Russia New South Wales, Australia
New South Wales, Australia
 New York City, United States
New York City, United States Paris, France
Paris, France Rome, Italy
Rome, Italy São Paulo, Brazil
São Paulo, Brazil Seoul, Republic of Korea
Seoul, Republic of Korea
In addition, Tokyo has a "partnership" agreement with the city of London [5] and many of the wards and cities within Tokyo maintain sister-city relationships with other foreign cities.
-
The Wako department store in Ginza
-
Skyline of Ginza
-
Skyline of Shibaura and Odaiba
-
Skyline of Shinjuku
-
National Diet Building, center of Japanese politics
-
Shinjuku Station, the world's busiest station
-
Tokyo Station, one of the main terminal stations in Japan
-
Tokyo Station from above
-
Shibuya Crossing
References
- ^ See capital of Japan for the debate on whether Tokyo is also the de jure capital.
- ^ "esa.un.org/unup/".
- ^ "www.nationsonline.org/oneworld/bigcities.htm".
- ^ "news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/in_depth/4669400.stm".
- ^ Tipton, Elise K. (2002). Modern Japan: A Social and Political History. Routledge. pp. p. 141.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ "www.soumu.metro.tokyo.jp/01soumu/archives/tokei_ibun.htm".
- ^ PriceWaterhouseCoopers, "UK Economic Outlook, March 2007", page 5. ""Table 1.2 – Top 30 urban agglomeration GDP rankings in 2005 and illustrative projections to 2020 (using UN definitions and population estimates)"" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-03-09.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Oslo is world's most expensive city: survey". Reuters. January 31, 2006. Retrieved February 1.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) (inactive). - ^ "www.jlpp.jp/english/list/works06/index02.html".
See also
External links
- Official Tokyo Metropolitan Government homepage
- Template:Wikitravel
- WikiSatellite view of Tokyo at WikiMapia
- Tokyo Japan Travel Guide and Photos












