Joseph Stalin
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. When this tag was added, its readable prose size was 17,000 words. (June 2023) |
Joseph Stalin | |
|---|---|
| |
 Stalin in 1943 | |
| General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union | |
| In office 3 April 1922 – 16 October 1952[a] | |
| Preceded by | Vyacheslav Molotov (as Responsible Secretary) |
| Succeeded by | Nikita Khrushchev (as First Secretary) |
| Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union[b] | |
| In office 6 May 1941 – 5 March 1953 | |
| First Deputy | Nikolai Voznesensky Vyacheslav Molotov Nikolai Bulganin |
| Preceded by | Vyacheslav Molotov |
| Succeeded by | Georgy Malenkov |
| Minister of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union[c] | |
| In office 19 July 1941 – 3 March 1947 | |
| Premier | Himself |
| Preceded by | Semyon Timoshenko |
| Succeeded by | Nikolai Bulganin |
| People's Commissar for Nationalities of the Russian SFSR | |
| In office 8 November 1917 – 7 July 1923 | |
| Premier | Vladimir Lenin |
| Preceded by | Office established |
| Succeeded by | Office abolished |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Iosif Vissarionovich Dzhugashvili 18 December [O.S. 6 December] 1878 Gori, Tiflis Governorate, Russian Empire |
| Died | 5 March 1953 (aged 74) Moscow, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union |
| Resting place |
|
| Political party | |
| Other political affiliations | |
| Spouses | |
| Children | |
| Parents | |
| Alma mater | Tiflis Theological Seminary |
| Awards | Full list |
| Signature |  |
| Nicknames |
|
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch | Red Army |
| Years of service | 1918–1920 |
| Rank | Generalissimus (from 1945) |
| Commands | Soviet Armed Forces (from 1941) |
| Battles/wars | |
Central institution membership Other offices held
| |
| Leader of the Soviet Union | |
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin[f] (born Dzhugashvili;[g] 18 December [O.S. 6 December] 1878 – 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who was the longest-serving leader of the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party from 1922 to 1952, and Chairman of the Council of Ministers (head of government) from 1941 until his death. Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, Stalin consolidated his power within the party and state to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically, he formalised his Leninist interpretation of Marxism as Marxism–Leninism, while the totalitarian political system which he established is known as Stalinism.
Born into a poor ethnic Georgian family in Gori in what was then the Russian Empire, Stalin attended the Tiflis Theological Seminary before joining the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. He raised funds for Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction via robberies, ransom kidnappings and protection rackets, and edited the party's newspaper, Pravda. He was repeatedly arrested and internally exiled to Siberia. After the Bolsheviks seized power in the October Revolution of 1917 and established a one-party state ruled by the Communist Party, Stalin joined its governing Politburo. Serving in the Russian Civil War before overseeing the Soviet Union's establishment in 1922, he rose to leader of the country following Lenin's death in 1924. Under Stalin, "socialism in one country" became a central tenet of the party's ideology, and under his Five-Year Plans from 1928, the country underwent forced agricultural collectivisation and rapid industrialisation, creating a centralised command economy. Stalin's policies exacerbated food shortages and contributed to a major famine in 1930–1933 in which five to seven million people died, largely in the Holodomor in Ukraine. To eradicate his remaining opposition and those he declared "enemies of the people", between 1936 and 1938 Stalin orchestrated the Great Purge, in which about 1.6 million were arrested and 700,000 executed. Under Stalin, an estimated 18 million people passed through the Gulag system of forced labour camps, of which at least 1.5 million died as a result, and mass deportations to remote regions affected more than six million, of which at least a million died. By 1937, he had absolute control over the party and government.
Stalin promoted Marxism–Leninism abroad through the Communist International and supported European anti-fascist movements during the 1930s, particularly in the Spanish Civil War. In 1939, his regime signed a non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany, enabling the Soviet invasion of Poland. Germany ended the pact by invading the Soviet Union in 1941, after which Stalin joined the Allies as one of the "Big Three". Despite huge losses, the Soviet Red Army repelled the German invasion and captured Berlin in 1945, ending World War II in Europe. The Soviet Union, which had annexed the Baltic states and territories from Finland and Romania amid the war, established Soviet-aligned governments in Central and Eastern Europe. The Soviet Union and the United States emerged as global superpowers and entered a period of tension known as the Cold War. Stalin presided over the country's post-war reconstruction and its first test of an atomic bomb in 1949. During these years, the country experienced another major famine and a state-sponsored antisemitic campaign which culminated in the "doctors' plot". After Stalin's death in 1953, he was eventually succeeded by Nikita Khrushchev, who in 1956 denounced his rule and initiated the "de-Stalinisation" of Soviet society.
Widely considered one of the 20th century's most significant figures, Stalin was the subject of a pervasive personality cult within the international Marxist–Leninist movement, which revered him as a champion of the working class and socialism. Since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Stalin has retained a degree of popularity in Russia and Georgia as an economic moderniser and wartime leader who cemented the Soviet Union's status as a leading world power. Conversely, his regime has been widely condemned for overseeing mass political repression and censorship, extensive detention and torture, systemic exploitation of forced labour, deportations of entire classes (in dekulakisation) and nationalities (characterised as ethnic cleansing or genocide), hundreds of thousands of executions, and man-made famines which killed millions.
Early life

Born Ioseb Jughashvili in Gori, Georgia, to a cobbler and a house cleaner, he grew up in the city and attended school there before moving to Tiflis (modern-day Tbilisi) to join the Tiflis Seminary. While a student at the seminary he embraced Marxism and became an avid follower of Vladimir Lenin, and left the seminary to become a revolutionary. After being marked by Russian secret police for his activities, he became a full-time revolutionary and was involved in a various criminal activities as a robber, gangster and arsonist.[1] He became one of the Bolsheviks' chief operatives in the Caucasus, organizing paramilitaries, spreading propaganda, raising money through bank robberies, and kidnappings and extortion. Stalin was captured and exiled to Siberia numerous times, but often escaped. He became one of Lenin's closest associates, which helped him rise to the heights of power after the Russian Revolution. In 1913 Stalin was exiled to Siberia for the final time, and remained in exile until the February Revolution of 1917, led to the overthrow of the Russian Empire. According to Oleg Khlevniuk, Stalin "filled an important role [in the October Revolution]"[2] and Stephen Kotkin similarly noted Stalin had been "in the thick of events" in the build-up.[3]
In Lenin's government
1917–1918: Consolidating power

On 26 October 1917, Lenin declared himself chairman of a new government, the Council of People's Commissars ("Sovnarkom").[4] Stalin backed Lenin's decision not to form a coalition with the Mensheviks and Socialist Revolutionary Party, although they did form a coalition government with the Left Socialist-Revolutionaries.[5] Stalin became part of an informal foursome leading the government, alongside Lenin, Trotsky, and Sverdlov.[6] Stalin's office was based near to Lenin's in the Smolny Institute,[7] and he and Trotsky were the only individuals allowed access to Lenin's study without an appointment.[8] Although not so publicly well known as Lenin or Trotsky,[9] Stalin's importance among the Bolsheviks grew.[10] He co-signed Lenin's decrees shutting down hostile newspapers,[11] and along with Sverdlov, he chaired the sessions of the committee drafting a constitution for the new Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic.[12] He strongly supported Lenin's formation of the Cheka security service and the subsequent Red Terror that it initiated; noting that state violence had proved an effective tool for capitalist powers, he believed that it would prove the same for the Soviet government.[13] Unlike senior Bolsheviks like Kamenev and Nikolai Bukharin, Stalin never expressed concern about the rapid growth and expansion of the Cheka and Red Terror.[13]

Having dropped his editorship of Pravda,[14] Stalin was appointed the People's Commissar for Nationalities.[15] He took Nadezhda Alliluyeva as his secretary[16] and at some point, married her, although the wedding date is unknown.[17] In November 1917, he signed the Decree on Nationality, according ethnic and national minorities living in Russia the right of secession and self-determination.[18] The decree's purpose was primarily strategic; the Bolsheviks wanted to gain favour among ethnic minorities but hoped that the latter would not actually desire independence.[19] That month, he travelled to Helsingfors to talk with the Finnish Social Democrats, granting Finland's request for independence in December.[19] His department allocated funds for establishment of presses and schools in the languages of various ethnic minorities.[20] Socialist revolutionaries accused Stalin's talk of federalism and national self-determination as a front for Sovnarkom's centralising and imperialist policies.[12]
Because of the ongoing First World War, in which Russia was fighting the Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary, Lenin's government relocated from Petrograd to Moscow in March 1918. Stalin, Trotsky, Sverdlov, and Lenin lived at the Kremlin.[21] Stalin supported Lenin's desire to sign an armistice with the Central Powers regardless of the cost in territory.[22] Stalin thought it necessary because — unlike Lenin — he was unconvinced that Europe was on the verge of proletarian revolution.[23] Lenin eventually convinced the other senior Bolsheviks of his viewpoint, resulting in the signing of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk in March 1918.[24] The treaty gave vast areas of land and resources to the Central Powers and angered many in Russia; the Left Socialist-Revolutionaries withdrew from the coalition government over the issue.[25] The governing RSDLP party was soon renamed, becoming the Russian Communist Party.[26]
1918–1921: Military command
After the Bolsheviks seized power, both right and left-wing armies rallied against them, generating the Russian Civil War.[27] In May 1918, amid a dwindling food supply, Sovnarkom sent Stalin to Tsaritsyn to take charge of food procurement in Southern Russia.[28] Eager to prove himself as a commander,[29] once there he took control of regional military operations.[30] He befriended two military figures, Kliment Voroshilov and Semyon Budyonny, who would form the nucleus of his military and political support base.[31] Believing that victory was assured by numerical superiority, he sent large numbers of Red Army troops into battle against the region's anti-Bolshevik White armies, resulting in heavy losses; Lenin was concerned by this costly tactic.[32] In Tsaritsyn, Stalin commanded the local Cheka branch to execute suspected counterrevolutionaries, sometimes without trial[33] and — in contravention of government orders — purged the military and food collection agencies of middle-class specialists, some of whom he also executed.[34] His use of state violence and terror was at a greater scale than most Bolshevik leaders approved of;[35] for instance, he ordered several villages to be torched to ensure compliance with his food procurement program.[36]
In December 1918, Stalin was sent to Perm to lead an inquiry into how Alexander Kolchak's White forces had been able to decimate Red troops based there.[37] He returned to Moscow between January and March 1919,[38] before being assigned to the Western Front at Petrograd.[39] When the Red Third Regiment defected, he ordered the public execution of captured defectors.[38] In September, he was returned to the Southern Front.[38] During the war, he proved his worth to the Central Committee, displaying decisiveness, determination, and willingness to take on responsibility in conflict situations.[29] At the same time, he disregarded orders and repeatedly threatened to resign when affronted.[40] He was reprimanded by Lenin at the 8th Party Congress for employing tactics which resulted in far too many deaths of Red Army soldiers.[41] In November 1919, the government nonetheless awarded him the Order of the Red Banner for his wartime service.[42]
The Bolsheviks won the Russian Civil War by the end of 1919.[43] By that time, Sovnarkom had turned its attention to spreading proletarian revolution abroad, to this end forming the Communist International in March 1919; Stalin attended its inaugural ceremony.[44] Although Stalin did not share Lenin's belief that Europe's proletariat were on the verge of revolution, he acknowledged that as long as it stood alone, Soviet Russia remained vulnerable.[45] In December 1918, he drew up decrees recognising Marxist-governed Soviet republics in Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia;[46] during the civil war these Marxist governments were overthrown and the Baltic countries became fully independent of Russia, an act Stalin regarded as illegitimate.[47] In February 1920, he was appointed to head the Workers' and Peasants' Inspectorate;[48] that same month he was also transferred to the Caucasian Front.[49]

Following earlier clashes between Polish and Russian troops, the Polish–Soviet War broke out in early 1920, with the Poles invading Ukraine and taking Kiev on 7 May.[50] On 26 May, Stalin was moved to Ukraine, on the Southwest Front.[51] The Red Army retook Kiev on 10 June and soon forced the Polish troops back into Poland.[52] On 16 July, the Central Committee decided to take the war into Polish territory.[53] Lenin believed that the Polish proletariat would rise up to support the Russians against Józef Piłsudski's Polish government.[53] Stalin had cautioned against this; he believed that nationalism would lead the Polish working-classes to support their government's war effort.[53] He also believed that the Red Army was ill-prepared to conduct an offensive war and that it would give White armies a chance to resurface in Crimea, potentially reigniting the civil war.[53] Stalin lost the argument, after which he accepted Lenin's decision and supported it.[49] Along the Southwest Front, he became determined to conquer Lvov; in focusing on this goal, he disobeyed orders in early August to transfer his troops to assist Mikhail Tukhachevsky's forces that were attacking Warsaw.[54]
In mid-August 1920, the Poles repulsed the Russian advance, and Stalin returned to Moscow to attend the Politburo meeting.[55] Tukhachevsky blamed Stalin for his defeat at the Battle of Warsaw.[56] In Moscow, Lenin and Trotsky also blamed him for his behaviour in the Polish–Soviet War.[57] Stalin felt humiliated and under-appreciated; on 17 August, he demanded demission from the military, which was granted on 1 September.[58] At the 9th Bolshevik Conference in late September, Trotsky accused Stalin of "strategic mistakes" in his handling of the war.[59] Trotsky claimed that Stalin sabotaged the campaign by disobeying troop transfer orders.[60] Lenin joined Trotsky in criticising him, and nobody spoke on his behalf at the conference.[61] Stalin felt disgraced and his antipathy toward Trotsky increased.[41] The Polish–Soviet War ended on 18 March 1921, when a peace treaty was signed in Riga.[62]
1921–1923: Lenin's final years

The Soviet government sought to bring neighbouring states under its domination; in February 1921 it invaded the Menshevik-governed Georgia,[63] while in April 1921, Stalin ordered the Red Army into Turkestan to reassert Russian state control.[64] As People's Commissar for Nationalities, Stalin believed that each national and ethnic group should have the right to self-expression,[65] facilitated through "autonomous republics" within the Russian state in which they could oversee various regional affairs.[66] In taking this view, some Marxists accused him of bending too much to bourgeois nationalism, while others accused him of remaining too Russocentric by seeking to retain these nations within the Russian state.[65]
Stalin's native Caucasus posed a particular problem because of its highly multi-ethnic mix.[67] Stalin opposed the idea of separate Georgian, Armenian, and Azeri autonomous republics, arguing that these would likely oppress ethnic minorities within their respective territories; instead, he called for a Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic.[68] The Georgian Communist Party opposed the idea, resulting in the Georgian affair.[69] In mid-1921, Stalin returned to the South Caucasus, there calling on Georgian communists to avoid the chauvinistic Georgian nationalism which marginalised the Abkhazian, Ossetian, and Adjarian minorities in Georgia.[70] On this trip, Stalin met with his son Yakov, and brought him back to Moscow;[71] Nadezhda had given birth to another of Stalin's sons, Vasily, in March 1921.[71]
After the civil war, workers' strikes and peasant uprisings broke out across Russia, largely in opposition to Sovnarkom's food requisitioning project; as an antidote, Lenin introduced market-oriented reforms: the New Economic Policy (NEP).[72] There was also internal turmoil in the Communist Party, as Trotsky led a faction calling for abolition of trade unions; Lenin opposed this, and Stalin helped rally opposition to Trotsky's position.[73] Stalin also agreed to supervise the Department of Agitation and Propaganda in the Central Committee Secretariat.[74] At the 11th Party Congress in 1922, Lenin nominated Stalin as the party's new General Secretary. Although concerns were expressed that adopting this new post on top of his others would overstretch his workload and give him too much power, Stalin was appointed to the position.[75] For Lenin, it was advantageous to have a key ally in this crucial post.[76]
Stalin is too crude, and this defect which is entirely acceptable in our milieu and in relationships among us as communists, becomes unacceptable in the position of General Secretary. I therefore propose to comrades that they should devise a means of removing him from this job and should appoint to this job someone else who is distinguished from comrade Stalin in all other respects only by the single superior aspect that he should be more tolerant, more polite and more attentive towards comrades, less capricious, etc.
— Lenin's Testament, 4 January 1923;[77] this was possibly composed by Krupskaya rather than Lenin himself.[78]
In May 1922, a massive stroke left Lenin partially paralysed.[79] Residing at his Gorki dacha, Lenin's main connection to Sovnarkom was through Stalin, who was a regular visitor.[80] Lenin twice asked Stalin to procure poison so that he could commit suicide, but Stalin never did so.[81] Despite this comradeship, Lenin disliked what he referred to as Stalin's "Asiatic" manner and told his sister Maria that Stalin was "not intelligent".[82] Lenin and Stalin argued on the issue of foreign trade; Lenin believed that the Soviet state should have a monopoly on foreign trade, but Stalin supported Grigori Sokolnikov's view that doing so was impractical at that stage.[83] Another disagreement came over the Georgian affair, with Lenin backing the Georgian Central Committee's desire for a Georgian Soviet Republic over Stalin's idea of a Transcaucasian one.[84]
They also disagreed on the nature of the Soviet state. Lenin called for establishment of a new federation named the "Union of Soviet Republics of Europe and Asia", reflecting his desire for expansion across the two continents and insisted that the Russian state should join this union on equal terms with the other Soviet states.[85] Stalin believed this would encourage independence sentiment among non-Russians, instead arguing that ethnic minorities would be content as "autonomous republics" within the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic.[86] Lenin accused Stalin of "Great Russian chauvinism"; Stalin accused Lenin of "national liberalism".[87] A compromise was reached, in which the federation would be renamed the "Union of Soviet Socialist Republics" (USSR).[85] The USSR's formation was ratified in December 1922; although officially a federal system, all major decisions were taken by the governing Politburo of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in Moscow.[88]
Their differences also became personal; Lenin was particularly angered when Stalin was rude to his wife Krupskaya during a telephone conversation.[89] In the final years of his life, Krupskaya provided governing figures with Lenin's Testament, a series of increasingly disparaging notes about Stalin. These criticised Stalin's rude manners and excessive power, suggesting that Stalin should be removed from the position of general secretary.[90] Some historians have questioned whether Lenin ever produced these, suggesting instead that they may have been written by Krupskaya, who had personal differences with Stalin;[78] Stalin, however, never publicly voiced concerns about their authenticity.[91] Most historians consider the document to be an accurate reflection of Lenin's views.[92] According to Stalin's secretary, Boris Bazhanov, Lenin "in general leaned towards a collegial leadership, with Trotsky in the first position".[93]
Consolidation of power
1924–1927: Succeeding Lenin

Lenin died in January 1924.[94] Stalin took charge of the funeral and was a pallbearer; against the wishes of Lenin's widow. The Politburo embalmed Lenin's corpse and placed it within a mausoleum in Red Square.[95] It was incorporated into a growing personality cult devoted to Lenin, with Petrograd being renamed "Leningrad" that year.[96] To bolster his image as a devoted Leninist, Stalin gave 9 lectures at Sverdlov University on the Foundations of Leninism.[97] During the 13th Party Congress in 1924, Lenin's Testament was read only to the leaders of the provincial delegations.[98] Embarrassed by its contents, Stalin offered his resignation as General Secretary; this act of humility saved him, and he was retained in the position.[99] According to Stalin's secretary, Boris Bazhanov, Stalin was jubilant over Lenin's death while "publicly putting on the mask of grief".[100]
As General Secretary, Stalin had a free hand in making appointments to his own staff, implanting his loyalists throughout the party and administration.[101] Favouring new party members from proletarian backgrounds to the "Old Bolsheviks" who tended to be middle class university graduates,[102] he ensured he had loyalists dispersed across the regions.[103] Stalin had much contact with young party functionaries,[104] and the desire for promotion led many provincial figures to seek to impress Stalin.[105] Stalin developed close relations with the trio at the heart of the secret police: Felix Dzerzhinsky, Genrikh Yagoda, and Vyacheslav Menzhinsky.[106] In his private life, he divided his time between his Kremlin apartment and a dacha at Zubalova;[107] his wife gave birth to a daughter, Svetlana, in February 1926.[108]
In the wake of Lenin's death, protagonists emerged in the struggle to become his successor: alongside Stalin was Trotsky, Zinoviev, Kamenev, Bukharin, Alexei Rykov, and Mikhail Tomsky.[109] Stalin saw Trotsky — whom he personally despised[110] — as the main obstacle to his dominance.[111] While Lenin had been ill Stalin with Kamenev and Zinoviev had formed an unofficial Triumvirate (known by its Russian name Troika), an alliance aimed at Trotsky.[112] Although Zinoviev was concerned about Stalin's growing authority, he rallied behind him at the 13th Congress as a counterweight to Trotsky, who now led a faction known as the Left Opposition.[113] The Left Opposition believed the NEP conceded too much to capitalism; Stalin was called a "rightist" for his support of the policy.[114] Stalin built up a retinue of supporters in the Central Committee,[115] while the Left Opposition were gradually removed from their positions of influence.[116] He was supported in this by Bukharin, who, like Stalin, believed that the Left Opposition's proposals would plunge the Soviet Union into instability.[117]

In late 1924, Stalin moved against Kamenev and Zinoviev, removing their supporters from key positions.[118] In 1925, the two moved into open opposition to Stalin and Bukharin.[119] At the 14th Party Congress in December, they launched an unsuccessful attack against Stalin's faction.[120] Stalin accused Kamenev and Zinoviev of reintroducing factionalism, and thus instability.[120] In mid-1926, Kamenev and Zinoviev joined with Trotsky's supporters to form the United Opposition against Stalin;[121] in October they agreed to stop factional activity under threat of expulsion, and later publicly recanted their views under Stalin's command.[122] The factionalist arguments continued, with Stalin threatening to resign in October and December 1926, and again in December 1927.[123] In October 1927, Zinoviev and Trotsky were removed from the Central Committee;[124] the latter was exiled to Kazakhstan and deported from the country in 1929.[125] Some United Opposition members who were repentant were later rehabilitated and returned to government.[126]
Stalin was now the party's supreme leader,[127] although he was not the head of government, a task he entrusted to ally Vyacheslav Molotov.[128] Other important supporters on the Politburo were Voroshilov, Lazar Kaganovich, and Sergo Ordzhonikidze,[129] with Stalin ensuring his allies ran state institutions.[130] At this point "Stalin was the leader of the oligarchs but he was far from a dictator".[131] His growing influence was reflected in naming of locations after him; in June 1924 the Ukrainian mining town of Yuzovka became Stalino,[132] and in April 1925, Tsaritsyn was renamed Stalingrad on the order of Mikhail Kalinin and Avel Enukidze.[133]
In 1926, Stalin published On Questions of Leninism.[134] Here, he argued for the concept of "socialism in one country", which he presented as an orthodox Leninist perspective. It nevertheless clashed with established Bolshevik views that socialism could not be established in one country, but could only be achieved globally through the process of world revolution.[134]
1927–1931: Dekulakisation, collectivisation, and industrialisation
Economic policy
We have fallen behind the advanced countries by fifty to a hundred years. We must close that gap in ten years. Either we do this or we'll be crushed.
This is what our obligations before the workers and peasants of the USSR dictate to us.
— Stalin, February 1931[135]
The Soviet Union lagged behind the industrial development of Western countries,[136] and there had been a shortfall of grain; 1927 produced only 70% of grain produced in 1926.[137] Stalin's government feared attack from Japan, France, the UK, Poland, and Romania.[138] Many communists, including in Komsomol, OGPU, and the Red Army, were eager to be rid of the NEP and its market-oriented approach;[139] they had concerns about those who profited from the policy: affluent peasants known as "kulaks" and small business owners or "NEPmen".[140] Stalin turned against the NEP, which put him on a course to the "left" even of Trotsky or Zinoviev.[141]
In early 1928, Stalin travelled to Novosibirsk, where he alleged that kulaks were hoarding grain and ordered them be arrested and their grain confiscated, with Stalin bringing much of the grain back to Moscow with him in February.[142] At his command, grain procurement squads surfaced across West Siberia and the Urals, with violence breaking out between these squads and the peasantry.[143] Stalin announced that both kulaks and the "middle peasants" must be coerced into releasing their harvest.[144] Bukharin and other Central Committee members were angry they had not been consulted about this measure, which they deemed rash.[145] In January 1930, the Politburo approved the liquidation of the kulak class; accused kulaks were rounded up and exiled to other parts of the country or concentration camps.[146] Large numbers died during the journey.[147] By July 1930, over 320,000 households had been affected by the de-kulakisation policy.[146] According to biographer Dmitri Volkogonov, de-kulakisation was "the first mass terror applied by Stalin in his own country."[148]

In 1929, the Politburo announced the mass collectivisation of agriculture,[150] establishing both kolkhozy collective farms and sovkhoz state farms.[151] Stalin barred kulaks from joining these collectives.[152] Although officially voluntary, many peasants joined the collectives out of fear they would face the fate of the kulaks; others joined amid intimidation and violence from party loyalists.[153] By 1932, about 62% of households involved in agriculture were part of collectives, and by 1936 this had risen to 90%.[154] Many collectivised peasants resented the loss of their private farmland,[155] and productivity slumped.[156] Famine broke out in many areas,[157] with the Politburo frequently ordering distribution of emergency food relief to these regions.[158]
Armed peasant uprisings against dekulakisation and collectivisation broke out in Ukraine, the North Caucasus, Southern Russia, and Central Asia, reaching their apex in March 1930; these were suppressed by army.[159] Stalin responded with an article insisting that collectivisation was voluntary and blaming violence and other excesses on local officials.[160] Although he and Stalin had been close for many years,[161] Bukharin expressed concerns about these policies; he regarded them as a return to Lenin's old "war communism" policy and believed that it would fail. By mid-1928 he was unable to rally sufficient support in the party to oppose the reforms.[162] In November 1929 Stalin removed him from the Politburo.[163]
Officially, the Soviet Union had replaced the "irrationality" and "wastefulness" of a market economy with a planned economy organised along a long-term, precise, and scientific framework; in reality, Soviet economics were based on ad hoc commandments issued from the centre, often to make short-term targets.[164] In 1928, the first five-year plan was launched, its main focus on boosting heavy industry;[165] it was finished a year ahead of schedule, in 1932.[166] The USSR underwent a massive economic transformation.[167] New mines were opened, new cities like Magnitogorsk constructed, and work on the White Sea–Baltic Canal began.[167] Millions of peasants moved to the cities, although urban house building could not keep up with the demand.[167] Large debts were accrued purchasing foreign-made machinery.[168]
Many of major construction projects, including the White Sea–Baltic Canal and the Moscow Metro, were constructed largely through forced labour.[169] The last elements of workers' control over industry were removed, with factory managers increasing their authority and receiving privileges and perks;[170] Stalin defended wage disparity by pointing to Marx's argument that it was necessary during the lower stages of socialism.[171] To promote intensification of labour, medals and awards as well as the Stakhanovite movement were introduced.[149] Stalin's message was that socialism was being established in the USSR while capitalism was crumbling amid the Wall Street crash.[172] His speeches and articles reflected his utopian vision of the Soviet Union rising to unparalleled heights of human development, creating a "new Soviet person".[173]
Cultural and foreign policy
In 1928, Stalin declared that class war between the proletariat and their enemies would intensify as socialism developed.[174] He warned of a "danger from the right", including in the Communist Party.[175] The first major show trial in the USSR was the Shakhty Trial of 1928, in which middle-class "industrial specialists" were convicted of sabotage.[176] From 1929 to 1930, show trials were held to intimidate opposition:[177] these included the Industrial Party Trial, Menshevik Trial, and Metro-Vickers Trial.[178] Aware that the ethnic Russian majority may have concerns about being ruled by a Georgian,[179] he promoted ethnic Russians throughout the state hierarchy and made Russian compulsory throughout schools and offices, albeit to be used in tandem with local languages in areas with non-Russian majorities.[180] Nationalist sentiment among ethnic minorities was suppressed.[181] Conservative social policies were promoted to enhance social discipline and boost population growth; this included a focus on strong family units and motherhood, re-criminalisation of homosexuality, restrictions on abortion and divorce, and abolition of the Zhenotdel women's department.[182]

Stalin desired a "cultural revolution",[183] entailing both creation of a culture for the "masses" and wider dissemination of previously elite culture.[184] He oversaw proliferation of schools, newspapers, and libraries, as well as advancement of literacy and numeracy.[185] Socialist realism was promoted throughout the arts,[186] while Stalin wooed prominent writers, namely Maxim Gorky, Mikhail Sholokhov, and Aleksey Nikolayevich Tolstoy.[187] He expressed patronage for scientists whose research fitted within his preconceived interpretation of Marxism; for instance, he endorsed research of an agrobiologist Trofim Lysenko despite the fact that it was rejected by the majority of Lysenko's scientific peers as pseudo-scientific.[188] The government's anti-religious campaign was re-intensified,[189] with increased funding given to the League of Militant Atheists.[181] Priests, imams, and Buddhist monks faced persecution.[177] Many religious buildings were demolished, most notably Moscow's Cathedral of Christ the Saviour, destroyed in 1931 to make way for the Palace of the Soviets.[190] Religion retained an influence over much of the population; in the 1937 census, 57% of respondents were willing to admit to being religious.[191]
Throughout the 1920s and beyond, Stalin placed a priority on foreign policy.[192] He personally met with a range of Western visitors, including George Bernard Shaw and H. G. Wells, both of whom were impressed with him.[193] Through the Communist International, Stalin's government exerted a strong influence over Marxist parties elsewhere;[194] initially, Stalin left the running of the organisation largely to Bukharin.[195] At its 6th Congress in July 1928, Stalin informed delegates that the main threat to socialism came not from the right but from non-Marxist socialists and social democrats, whom he called "social fascists";[196] Stalin recognised that in many countries, the social democrats were the Marxist-Leninists' main rivals for working-class support.[197] This preoccupation with opposing rival leftists concerned Bukharin, who regarded the growth of fascism and the far right across Europe as a far greater threat.[195] After Bukharin's departure, Stalin placed the Communist International under the administration of Dmitry Manuilsky and Osip Piatnitsky.[194]
Stalin faced problems in his family life. In 1929, his son Yakov unsuccessfully attempted suicide; his failure earned Stalin's contempt.[198] His relationship with Nadezhda was strained amid their arguments and her mental health problems.[199] In November 1932, after a group dinner in the Kremlin in which Stalin flirted with other women, Nadezhda shot herself.[200] Publicly, the cause of death was given as appendicitis; Stalin also concealed the real cause of death from his children.[201] Stalin's friends noted that he underwent a significant change following her suicide, becoming emotionally harder.[202]
1932–1939: Major crises
Famine
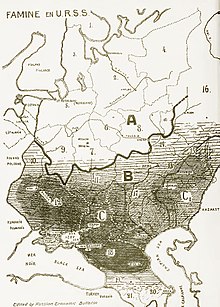
Within the Soviet Union, there was widespread civic disgruntlement against Stalin's government.[203] Social unrest, previously restricted largely to the countryside, was increasingly evident in urban areas, prompting Stalin to ease some of his economic policies in 1932.[204] In May 1932, he introduced a system of kolkhoz markets where peasants could trade their surplus produce.[205] Penal sanctions became more severe; at Stalin's instigation, in August 1932 a decree was introduced where the theft of even a handful of grain could be a capital offence.[206] The second five-year plan had its production quotas reduced from the first, with the main emphasis now on improving living conditions.[204] It therefore emphasised the expansion of housing space and production of consumer goods.[204] Like its predecessor, this plan was repeatedly amended to meet changing situations; there was for instance an increasing emphasis placed on armament production after Adolf Hitler became German chancellor in 1933.[207]
The Soviet Union experienced a major famine which peaked in the winter of 1932–33;[208] between five and seven million people died.[209] The worst affected areas were Ukraine and the North Caucasus, although the famine also affected Kazakhstan and several Russian provinces.[210] Historians have long debated whether Stalin's government had intended the famine to occur or not;[211] there are no known documents in which Stalin or his government explicitly called for starvation to be used against the population.[212] The 1931 and 1932 harvests had been poor because of weather conditions[213] and followed years in which lower productivity had resulted in a gradual decline in output.[209] Government policies—including the focus on rapid industrialisation, the socialisation of livestock, and emphasis on sown areas over crop rotation—exacerbated the problem;[214] the state had also failed to build reserve grain stocks.[215] Stalin blamed the famine on hostile elements and sabotage within the peasantry;[216] his government provided small amounts of food to famine-struck rural areas, although this was wholly insufficient.[217] The Soviet government believed that food supplies should be prioritised for the urban workforce;[218] for Stalin, the fate of Soviet industrialisation was far more important than the lives of the peasantry.[219] Grain exports, which were a major means of Soviet payment for machinery, declined heavily.[217] Stalin would not acknowledge that his policies had contributed to the famine,[206] the existence of which was kept secret from foreign observers.[220]
Ideological and foreign affairs
In 1935–36, Stalin oversaw a new constitution; its dramatic liberal features were designed as propaganda weapons.[221] He declared that "socialism, which is the first phase of communism, has basically been achieved in this country".[221] In 1938, The History of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Bolsheviks), colloquially known as the Short Course, was released;[222] biographer Robert Conquest later referred to it as the "central text of Stalinism".[223] Authorised Stalin biographies were also published,[224] although Stalin generally wanted to be portrayed as the embodiment of the Communist Party, rather than have his life story explored.[225] During the later 1930s, Stalin placed "a few limits on the worship of his own greatness".[225] By 1938, Stalin's inner circle had gained a degree of stability, containing the personalities who would remain there until his death.[226]

Seeking improved international relations, in 1934 the Soviet Union secured membership of the League of Nations, from which it had previously been excluded.[227] Stalin initiated confidential communications with Hitler in October 1933, shortly after the latter came to power.[228] Stalin admired Hitler, particularly his manoeuvres to remove rivals within the Nazi Party in the Night of the Long Knives.[229] Stalin nevertheless recognised the threat posed by fascism and sought to establish better links with the liberal democracies of Western Europe;[230] in May 1935, the Soviets signed a treaty of mutual assistance with France and Czechoslovakia.[231] At the Communist International's 7th Congress, held in July–August 1935, the Soviet government encouraged Marxist-Leninists to unite with other leftists as part of a popular front against fascism.[232]
When the Spanish Civil War broke out in July 1936, the Soviets sent 648 aircraft and 407 tanks to the left-wing Republican faction; these were accompanied by 3,000 Soviet troops and 42,000 members of the International Brigades set up by the Communist International.[233] Stalin took a personal involvement in the Spanish situation.[234] Germany and Italy backed the Nationalist faction, which was ultimately victorious in March 1939.[235] With the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in July 1937, the Soviet Union and China signed a non-aggression pact.[236] Stalin aided the Chinese Communist Party as they had suspended their civil war with the Kuomintang (KMT) nationalists and formed the desired United Front against Japanese aggression.[237]
The Great Terror

Stalin often gave conflicting signals regarding state repression.[238] In May 1933, he released many convicted of minor offences, ordering the security services not to enact further mass arrests and deportations.[239] In September 1934, he launched a commission to investigate false imprisonments; that same month he called for the execution of workers at the Stalin Metallurgical Factory accused of spying for Japan.[238] This mixed approach began to change in December 1934, after prominent party member Sergey Kirov was murdered.[240] Afterwards, Stalin became increasingly concerned by the threat of assassination, improved his personal security, and rarely went out in public.[241] State repression intensified after Kirov's death;[242] Stalin instigated this, reflecting his prioritisation of security.[243] Stalin issued a decree establishing NKVD troikas which could mete out rulings without involving the courts.[244] In 1935, he ordered the NKVD to expel suspected counterrevolutionaries from urban areas;[207] in early 1935, over 11,000 were expelled from Leningrad.[207] In 1936, Nikolai Yezhov became head of the NKVD.[245]
Stalin orchestrated the arrest of opponents in the Communist Party as well as sitting members of the Central Committee: denounced as Western-backed mercenaries, many were imprisoned or exiled internally.[246] The first Moscow Trial took place in August 1936; Kamenev and Zinoviev were among those accused of plotting assassinations, found guilty in a show trial, and executed.[247] The second Moscow Show Trial took place in January 1937,[248] and the third in March 1938, in which Bukharin and Rykov were accused of involvement in the alleged Trotskyite-Zinovievite terrorist plot and sentenced to death.[249] By late 1937, all remnants of collective leadership were gone from the Politburo, which was controlled entirely by Stalin.[250] There were mass expulsions from the party,[251] with Stalin commanding foreign communist parties to purge anti-Stalinist elements.[252]

Repressions further intensified in December 1936 and remained high until November 1938, a period known as the Great Purge.[243] In May 1937, this was followed by the arrest of most members of the military Supreme Command and mass arrests throughout the military, often on fabricated charges.[253] By the latter part of 1937, the purges had moved beyond the party and were affecting the wider population.[254] In July 1937, the Politburo ordered a purge of "anti-Soviet elements" in society, targeting anti-Stalin Bolsheviks, former Mensheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries, priests, ex-White Army soldiers, and common criminals.[255] That month, Stalin and Yezhov signed Order No. 00447, listing 268,950 people for arrest, of whom 75,950 were executed.[256] He initiated "national operations", the ethnic cleansing of non-Soviet ethnic groups—among them Poles, Germans, Latvians, Finns, Greeks, Koreans, and Chinese—through internal or external exile.[257] Approximately 1.6 million people were arrested, 700,000 were shot, and an unknown number died under NKVD torture.[258]

During the 1930s and 1940s, NKVD groups assassinated defectors and opponents abroad;[260] in August 1940, Trotsky was assassinated in Mexico, eliminating the last of Stalin's opponents among the former Party leadership.[261] These purges replaced most of the old guard, with younger officials who did not remember a time before Stalin's leadership and who were regarded as more loyal to him.[262] Party functionaries readily carried out their commands and sought to ingratiate themselves with Stalin, to avoid becoming victims.[263] Such functionaries often carried out more arrests and executions than their quotas set by government.[264]
Stalin initiated all key decisions during the Terror, personally directing many operations.[265] His motives in doing so have been much debated by historians.[258] His personal writings from the period were "unusually convoluted and incoherent", filled with claims about enemies encircling him.[266] He was particularly concerned at the success that right-wing forces had in overthrowing the leftist Spanish government,[267] fearing a domestic fifth column in the event of war with Japan and Germany.[268] The Great Terror ended when Yezhov was removed as the head of the NKVD, to be replaced by Lavrentiy Beria,[269] a man totally devoted to Stalin.[270] Yezhov was arrested in April 1939 and executed in 1940.[271] The Terror damaged the Soviet Union's reputation abroad, particularly among sympathetic leftists.[272] As it wound down, Stalin sought to deflect responsibility,[273] blaming its "excesses" and "violations of law" on Yezhov.[274] According to historian James Harris, research shows that the motivation behind the purges was not Stalin attempting to establish his own dictatorship; he was committed to building the socialist state envisioned by Lenin. The real motivation, according to Harris, was an excessive fear of counterrevolution.[275]
World War II
1939–1941: Pact with Nazi Germany
As a Marxist–Leninist, Stalin considered conflict between competing capitalist powers inevitable; after Nazi Germany annexed Austria and then part of Czechoslovakia in 1938, he recognised a war was looming.[276] He sought to maintain Soviet neutrality, hoping that a German war against France and Britain would lead to Soviet dominance in Europe.[277] Militarily, the Soviets also faced a threat from the east, with Soviet troops clashing with the expansionist Japanese in the latter part of the 1930s.[278] Stalin initiated a military build-up, with the Red Army more than doubling between January 1939 and June 1941, although in its haste to expand many of its officers were poorly trained.[279] Between 1940 and 1941 he also purged the military, leaving it with a severe shortage of trained officers when war broke out.[280]

As Britain and France seemed unwilling to commit to an alliance with the Soviet Union, Stalin saw a better deal with the Germans.[281] On 3 May 1939, Stalin replaced his western-oriented foreign minister Maxim Litvinov with Vyacheslav Molotov.[282] Germany began negotiations with the Soviets, proposing that Eastern Europe be divided between the two powers.[283] Stalin saw this as an opportunity both for territorial expansion and temporary peace with Germany.[284] In August 1939, the Soviet Union signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop pact with Germany, a non-aggression pact negotiated by Molotov and German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop.[285] A week later, Germany invaded Poland, sparking the UK and France to declare war on Germany.[286] On 17 September, the Red Army entered eastern Poland, officially to restore order amid the collapse of the Polish state.[287] On 28 September, Germany and the Soviet Union exchanged some of their newly conquered territories; Germany gained the linguistically Polish-dominated areas of Lublin Province and part of Warsaw Province while the Soviets gained Lithuania.[288] A German–Soviet Frontier Treaty was signed shortly after, in Stalin's presence.[289] The two states continued trading, undermining the British blockade of Germany.[290]
The Soviets further demanded parts of eastern Finland, but the Finnish government refused. The Soviets invaded Finland in November 1939, yet despite numerical inferiority, the Finns kept the Red Army at bay.[291] International opinion backed Finland, with the Soviets being expelled from the League of Nations.[292] Embarrassed by their inability to defeat the Finns, the Soviets signed an interim peace treaty, in which they received territorial concessions from Finland.[293] In June 1940, the Red Army occupied the Baltic states, which were forcibly merged into the Soviet Union in August;[294] they also invaded and annexed Bessarabia and northern Bukovina, parts of Romania.[295] The Soviets sought to forestall dissent in these new East European territories with mass repressions.[296] One of the most noted instances was the Katyn massacre of April and May 1940, in which around 22,000 members of the Polish armed forces, police, and intelligentsia were executed.[297]
The speed of the German victory over and occupation of France in mid-1940 took Stalin by surprise.[298] He increasingly focused on appeasement with the Germans to delay any conflict with them.[299] After the Tripartite Pact was signed by Axis Powers Germany, Japan, and Italy in October 1940, Stalin proposed that the USSR also join the Axis alliance.[300] To demonstrate peaceful intentions toward Germany, in April 1941 the Soviets signed a neutrality pact with Japan.[301] Although de facto head of government for a decade and a half, Stalin concluded that relations with Germany had deteriorated to such an extent that he needed to deal with the problem as de jure head of government as well: on 6 May, Stalin replaced Molotov as Premier of the Soviet Union.[302]
1941–1942: German invasion

In June 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union, initiating the war on the Eastern Front.[303] Despite intelligence agencies repeatedly warning him of Germany's intentions, Stalin was taken by surprise.[304] He formed a State Defense Committee, which he headed as Supreme Commander,[305] as well as a military Supreme Command (Stavka),[306] with Georgy Zhukov as its Chief of Staff.[307] The German tactic of blitzkrieg was initially highly effective; the Soviet air force in the western borderlands was destroyed within two days.[308] The German Wehrmacht pushed deep into Soviet territory;[309] soon, Ukraine, Byelorussia, and the Baltic states were under German occupation, and Leningrad was under siege;[310] and Soviet refugees were flooding into Moscow and surrounding cities.[311] By July, Germany's Luftwaffe was bombing Moscow,[310] and by October the Wehrmacht was amassing for a full assault on the capital. Plans were made for the Soviet government to evacuate to Kuibyshev, although Stalin decided to remain in Moscow, believing his flight would damage troop morale.[312] The German advance on Moscow was halted after two months of battle in increasingly harsh weather conditions.[313]
Going against the advice of Zhukov and other generals, Stalin emphasised attack over defence.[314] In June 1941, he ordered a scorched earth policy of destroying infrastructure and food supplies before the Germans could seize them,[315] also commanding the NKVD to kill around 100,000 political prisoners in areas the Wehrmacht approached.[316] He purged the military command; several high-ranking figures were demoted or reassigned and others were arrested and executed.[317] With Order No. 270, Stalin commanded soldiers risking capture to fight to the death describing the captured as traitors;[318] among those taken as a prisoner of war by the Germans was Stalin's son Yakov, who died in their custody.[319] Stalin issued Order No. 227 in July 1942, which directed that those retreating unauthorised would be placed in "penal battalions" used as cannon fodder on the front lines.[320] Amid the fighting, both the German and Soviet armies disregarded the law of war set forth in the Geneva Conventions;[321] the Soviets heavily publicised Nazi massacres of communists, Jews, and Romani.[322] Stalin exploited Nazi anti-Semitism, and in April 1942 he sponsored the Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee (JAC) to garner global Jewish support for the Soviet war effort.[323]

The Soviets allied with the United Kingdom and United States;[324] although the U.S. joined the war against Germany in 1941, little direct American assistance reached the Soviets until late 1942.[321] Responding to the invasion, the Soviets intensified their industrial enterprises in central Russia, focusing almost entirely on production for the military.[325] They achieved high levels of industrial productivity, outstripping that of Germany.[322] During the war, Stalin was more tolerant of the Russian Orthodox Church, allowing it to resume some of its activities and meeting with Patriarch Sergius in September 1943.[326] He also permitted a wider range of cultural expression, notably permitting formerly suppressed writers and artists like Anna Akhmatova and Dmitri Shostakovich to disperse their work more widely.[327] The Internationale was dropped as the country's national anthem, to be replaced with a more patriotic song.[328] The government increasingly promoted Pan-Slavist sentiment,[329] while encouraging increased criticism of cosmopolitanism, particularly the idea of "rootless cosmopolitanism", an approach with particular repercussions for Soviet Jews.[330] Comintern was dissolved in 1943,[331] and Stalin encouraged foreign Marxist–Leninist parties to emphasise nationalism over internationalism to broaden their domestic appeal.[329]
In April 1942, Stalin overrode Stavka by ordering the Soviets' first serious counter-attack, an attempt to seize German-held Kharkov in eastern Ukraine. This attack proved unsuccessful.[332] That year, Hitler shifted his primary goal from an overall victory on the Eastern Front to the goal of securing the oil fields in the southern Soviet Union crucial to a long-term German war effort.[333] While Red Army generals saw evidence that Hitler would shift efforts south, Stalin considered this to be a flanking move in a renewed effort to take Moscow.[334] In June 1942, the German Army began a major offensive in Southern Russia, threatening Stalingrad; Stalin ordered the Red Army to hold the city at all costs.[335] This resulted in the protracted Battle of Stalingrad.[336] In December 1942, he placed Konstantin Rokossovski in charge of holding the city.[337] In February 1943, the German troops attacking Stalingrad surrendered.[338] The Soviet victory there marked a major turning point in the war;[339] in commemoration, Stalin declared himself Marshal of the Soviet Union.[340]
1942–1945: Soviet counter-attack

By November 1942, the Soviets had begun to repulse the important German strategic southern campaign and, although there were 2.5 million Soviet casualties in that effort, it permitted the Soviets to take the offensive for most of the rest of the war on the Eastern Front.[341] Germany attempted an encirclement attack at Kursk, which was successfully repulsed by the Soviets.[342] By the end of 1943, the Soviets occupied half of the territory taken by the Germans from 1941 to 1942.[343] Soviet military industrial output also had increased substantially from late 1941 to early 1943 after Stalin had moved factories well to the east of the front, safe from German invasion and aerial assault.[344]
In Allied countries, Stalin was increasingly depicted in a positive light over the course of the war.[345] In 1941, the London Philharmonic Orchestra performed a concert to celebrate his birthday,[346] and in 1942, Time magazine named him "Man of the Year".[345] When Stalin learned that people in Western countries affectionately called him "Uncle Joe" he was initially offended, regarding it as undignified.[347] There remained mutual suspicions between Stalin, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, who were together known as the "Big Three".[348] Churchill flew to Moscow to visit Stalin in August 1942 and again in October 1944.[349] Stalin scarcely left Moscow throughout the war,[350] with Roosevelt and Churchill frustrated with his reluctance to travel to meet them.[351]
In November 1943, Stalin met with Churchill and Roosevelt in Tehran, a location of Stalin's choosing.[352] There, Stalin and Roosevelt got on well, with both desiring the post-war dismantling of the British Empire.[353] At Tehran, the trio agreed that to prevent Germany rising to military prowess yet again, the German state should be broken up.[354] Roosevelt and Churchill also agreed to Stalin's demand that the German city of Königsberg be declared Soviet territory.[354] Stalin was impatient for the UK and U.S. to open up a Western Front to take the pressure off of the East; they eventually did so in mid-1944.[355] Stalin insisted that, after the war, the Soviet Union should incorporate the portions of Poland it occupied pursuant to the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact with Germany, which Churchill opposed.[356] Discussing the fate of the Balkans, later in 1944 Churchill agreed to Stalin's suggestion that after the war, Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary, and Yugoslavia would come under the Soviet sphere of influence while Greece would come under that of the West.[357]

In 1944, the Soviet Union made significant advances across Eastern Europe toward Germany,[358] including Operation Bagration, a massive offensive in the Byelorussian SSR against the German Army Group Centre.[359] In 1944, the German armies were pushed out of the Baltic states (with the exception of the Ostland), which were then re-annexed into the Soviet Union.[360] As the Red Army reconquered the Caucasus and Crimea, various ethnic groups living in the region—the Kalmyks, Chechens, Ingushi, Karachai, Balkars, and Crimean Tatars—were accused of having collaborated with the Germans. Using the idea of collective responsibility as a basis, Stalin's government abolished their autonomous republics and between late 1943 and 1944 deported the majority of their populations to Central Asia and Siberia.[361] Over one million people were deported as a result of the policy.[362]
In February 1945, the three leaders met at the Yalta Conference.[363] Roosevelt and Churchill conceded to Stalin's demand that Germany pay the Soviet Union 20 billion dollars in reparations, and that his country be permitted to annex Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in exchange for entering the war against Japan.[364] An agreement was also made that a post-war Polish government should be a coalition consisting of both communist and conservative elements.[365] Privately, Stalin sought to ensure that Poland would come fully under Soviet influence.[366] The Red Army withheld assistance to Polish resistance fighters battling the Germans in the Warsaw Uprising, with Stalin believing that any victorious Polish militants could interfere with his aspirations to dominate Poland through a future Marxist government.[367] Although concealing his desires from the other Allied leaders, Stalin placed great emphasis on capturing Berlin first, believing that this would enable him to bring more of Europe under long-term Soviet control. Churchill was concerned that this was the case and unsuccessfully tried to convince the U.S. that the Western Allies should pursue the same goal.[368]
1945: Victory

In April 1945, the Red Army seized Berlin, Hitler killed himself, and Germany surrendered in May.[369] Stalin had wanted Hitler captured alive; he had his remains brought to Moscow to prevent them becoming a relic for Nazi sympathisers.[370] Many Soviet soldiers engaged in looting, pillaging, and rape, both in Germany and parts of Eastern Europe.[371] Stalin refused to punish the offenders.[368]
With Germany defeated, Stalin switched focus to the war with Japan, transferring half a million troops to the Far East.[372] Stalin was pressed by his allies to enter the war and wanted to cement the Soviet Union's strategic position in Asia.[373] On 8 August, in between the U.S. atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet army invaded Japanese-occupied Manchuria and defeated the Kwantung Army.[374] These events led to the Japanese surrender and the war's end.[375] Soviet forces continued to expand until they occupied all their territorial concessions, but the U.S. rebuffed Stalin's desire for the Red Army to take a role in the Allied occupation of Japan.[376]
At the Potsdam Conference in July–August 1945, Stalin repeated previous promises that he would refrain from a "Sovietization" of Eastern Europe.[377] Stalin pushed for reparations from Germany without regard to the base minimum supply for German citizens' survival, which worried Harry Truman and Churchill who thought that Germany would become a financial burden for Western powers.[378] He also pushed for "war booty", which would permit the Soviet Union to directly seize property from conquered nations without quantitative or qualitative limitation, and a clause was added permitting this to occur with some limitations.[378] Germany was divided into four zones: Soviet, U.S., British, and French, with Berlin itself—located within the Soviet area—also subdivided thusly.[379]
Post-war era
1945–1947: Post-war reconstruction and famine
After the war, Stalin was—according to Service—at the "apex of his career".[380] Within the Soviet Union he was widely regarded as the embodiment of victory and patriotism.[381] His armies controlled Central and Eastern Europe up to the River Elbe.[380] In June 1945, Stalin adopted the title of Generalissimus,[382] and stood atop Lenin's Mausoleum to watch a celebratory parade led by Zhukov through Red Square.[383] At a banquet held for army commanders, he described the Russian people as "the outstanding nation" and "leading force" within the Soviet Union, the first time that he had unequivocally endorsed the Russians over other Soviet nationalities.[384] In 1946, the state published Stalin's Collected Works.[385] In 1947, it brought out a second edition of his official biography, which eulogised him to a greater extent than its predecessor.[386] He was quoted in Pravda on a daily basis and pictures of him remained pervasive on the walls of workplaces and homes.[387]

Despite his strengthened international position, Stalin was cautious about internal dissent and desire for change among the population.[388] He was also concerned about his returning armies, who had been exposed to a wide range of consumer goods in Germany, much of which they had looted and brought back with them. In this he recalled the 1825 Decembrist Revolt by Russian soldiers returning from having defeated France in the Napoleonic Wars.[389] He ensured that returning Soviet prisoners of war went through "filtration" camps as they arrived in the Soviet Union, in which 2,775,700 were interrogated to determine if they were traitors. About half were then imprisoned in labour camps.[390] In the Baltic states, where there was much opposition to Soviet rule, de-kulakisation and de-clericalisation programs were initiated, resulting in 142,000 deportations between 1945 and 1949.[360] The Gulag system of forced labour camps was expanded further. By January 1953, three per cent of the Soviet population was imprisoned or in internal exile, with 2.8 million in "special settlements" in isolated areas and another 2.5 million in camps, penal colonies, and prisons.[391]
The NKVD were ordered to catalogue the scale of destruction during the war.[392] It was established that 1,710 Soviet towns and 70,000 villages had been destroyed.[393] The NKVD recorded that between 26 and 27 million Soviet citizens had been killed, with millions more being wounded, malnourished, or orphaned.[394] In the war's aftermath, some of Stalin's associates suggested modifications to government policy.[395] Post-war Soviet society was more tolerant than its pre-war phase in various respects. Stalin allowed the Russian Orthodox Church to retain the churches it had opened during the war.[396] Academia and the arts were also allowed greater freedom than they had prior to 1941.[397] Recognising the need for drastic steps to be taken to combat inflation and promote economic regeneration, in December 1947 Stalin's government devalued the rouble and abolished the ration-book system.[398] Capital punishment was abolished in 1947 but re-instituted in 1950.[399]
Stalin's health was deteriorating, and heart problems forced a two-month vacation in the latter part of 1945.[400] He grew increasingly concerned that senior political and military figures might try to oust him; he prevented any of them from becoming powerful enough to rival him and had their apartments bugged with listening devices.[401] He demoted Molotov,[402] and increasingly favoured Beria and Malenkov for key positions.[403] In 1949, he brought Nikita Khrushchev from Ukraine to Moscow, appointing him a Central Committee secretary and the head of the city's party branch.[404] In the Leningrad Affair, the city's leadership was purged amid accusations of treachery; executions of many of the accused took place in 1950.[405]
In the post-war period there were often food shortages in Soviet cities,[406] and the USSR experienced a major famine from 1946 to 1947.[407] Sparked by a drought and ensuing bad harvest in 1946, it was exacerbated by government policy towards food procurement, including the state's decision to build up stocks and export food internationally rather than distributing it to famine-hit areas.[408] Current estimates indicate that between one million and 1.5 million people died from malnutrition or disease as a result.[409] While agricultural production stagnated, Stalin focused on a series of major infrastructure projects, including the construction of hydroelectric plants, canals, and railway lines running to the polar north.[410] Much of this was constructed by prison labour.[410]
1947–1950: Cold War policy

In the aftermath of the Second World War, the British Empire declined, leaving the U.S. and USSR as the dominant world powers.[411] Tensions among these former Allies grew,[381] resulting in the Cold War.[412] Although Stalin publicly described the British and U.S. governments as aggressive, he thought it unlikely that a war with them would be imminent, believing that several decades of peace was likely.[413] He nevertheless secretly intensified Soviet research into nuclear weaponry, intent on creating an atom bomb.[380] Still, Stalin foresaw the undesirability of a nuclear conflict, saying in 1949 that "atomic weapons can hardly be used without spelling the end of the world."[414] He personally took a keen interest in the development of the weapon.[415] In August 1949, the bomb was successfully tested in the deserts outside Semipalatinsk in Kazakhstan.[416] Stalin also initiated a new military build-up; the Soviet army was expanded from 2.9 million soldiers, as it stood in 1949, to 5.8 million by 1953.[417]
The U.S. began pushing its interests on every continent, acquiring air force bases in Africa and Asia and ensuring pro-U.S. regimes took power across Latin America.[418] It launched the Marshall Plan in June 1947, with which it sought to undermine Soviet hegemony throughout Eastern Europe. The U.S. also offered financial assistance to countries as part of the Marshall Plan on the condition that they opened their markets to trade, aware that the Soviets would never agree.[419] The Allies demanded that Stalin withdraw the Red Army from northern Iran. He initially refused, leading to an international crisis in 1946, but one year later Stalin finally relented and moved the Soviet troops out.[420] Stalin also tried to maximise Soviet influence on the world stage, unsuccessfully pushing for Libya—recently liberated from Italian occupation—to become a Soviet protectorate.[421][422] He sent Molotov as his representative to San Francisco to take part in negotiations to form the United Nations, insisting that the Soviets have a place on the Security Council.[412] In April 1949, the Western powers established the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), an international military alliance of capitalist countries.[423] Within Western countries, Stalin was increasingly portrayed as the "most evil dictator alive" and compared to Hitler.[424] According to his daughter, Svetlana Alliluyeva she "remembered her father saying after [the war]: Together with the Germans we would have been invincible" [425]
In 1948, Stalin edited and rewrote sections of Falsifiers of History, published as a series of Pravda articles in February 1948 and then in book form. Written in response to public revelations of the 1939 Soviet alliance with Germany, it focused on blaming the Western powers for the war.[426] He also erroneously claimed that the initial German advance in the early part of the war, during Operation Barbarossa, was not a result of Soviet military weakness, but rather a deliberate Soviet strategic retreat.[427] In 1949, celebrations took place to mark Stalin's seventieth birthday (although he was 71 at the time,) at which Stalin attended an event in the Bolshoi Theatre alongside Marxist–Leninist leaders from across Europe and Asia.[428]
Eastern Bloc
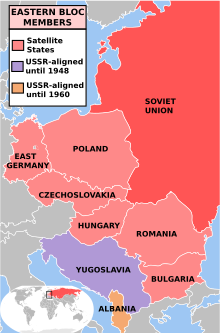
After the war, Stalin sought to retain Soviet dominance across Eastern Europe while expanding its influence in Asia.[360] Cautiously regarding the responses from the Western Allies, Stalin avoided immediately installing Communist Party governments across Eastern Europe, instead initially ensuring that Marxist-Leninists were placed in coalition ministries.[422] In contrast to his approach to the Baltic states, he rejected the proposal of merging the new communist states into the Soviet Union, rather recognising them as independent nation-states.[429] He was faced with the problem that there were few Marxists left in Eastern Europe, with most having been killed by the Nazis.[430] He demanded that war reparations be paid by Germany and its Axis allies Hungary, Romania, and the Slovak Republic.[381] Aware that these countries had been pushed toward socialism through invasion rather than by proletarian revolution, Stalin referred to them not as "dictatorships of the proletariat" but as "people's democracies", suggesting that in these countries there was a pro-socialist alliance combining the proletariat, peasantry, and lower middle-class.[431]
Churchill observed that an "Iron Curtain" had been drawn across Europe, separating the east from the west.[432] In September 1947, a meeting of East European communist leaders was held in Szklarska Poręba, Poland, from which was formed Cominform to co-ordinate the Communist Parties across Eastern Europe and also in France and Italy.[433] Stalin did not personally attend the meeting, sending Zhdanov in his place.[379] Various East European communists also visited Stalin in Moscow.[434] There, he offered advice on their ideas; for instance, he cautioned against the Yugoslav idea for a Balkan Federation incorporating Bulgaria and Albania.[434] Stalin had a particularly strained relationship with Yugoslav leader Josip Broz Tito due to the latter's continued calls for a Balkan federation and for Soviet aid for the communist forces in the ongoing Greek Civil War.[435] In March 1948, Stalin launched an anti-Tito campaign, accusing the Yugoslav communists of adventurism and deviating from Marxist–Leninist doctrine.[436] At the second Cominform conference, held in Bucharest in June 1948, East European communist leaders all denounced Tito's government, accusing them of being fascists and agents of Western capitalism.[437] Stalin ordered several assassination attempts on Tito's life and even contemplated an invasion of Yugoslavia itself.[438]
Stalin suggested that a unified, but demilitarised, German state be established, hoping that it would either come under Soviet influence or remain neutral.[439] When the U.S. and UK remained opposed to this, Stalin sought to force their hand by blockading Berlin in June 1948.[440] He gambled that the Western powers would not risk war, but they airlifted supplies into West Berlin until May 1949, when Stalin relented and ended the blockade.[423] In September 1949 the Western powers transformed Western Germany into an independent Federal Republic of Germany; in response the Soviets formed East Germany into the German Democratic Republic in October.[439] In accordance with their earlier agreements, the Western powers expected Poland to become an independent state with free democratic elections.[441] In Poland, the Soviets merged various socialist parties into the Polish United Workers' Party (PZPR), and vote rigging was used to ensure that the PZPR secured office.[436] The 1947 Hungarian elections were also rigged by Stalin, with the Hungarian Working People's Party taking control.[436] In Czechoslovakia, where the communists did have a level of popular support, they were elected the largest party in 1946.[442] Monarchy was abolished in Bulgaria and Romania.[443] Across Eastern Europe, the Soviet model was enforced, with a termination of political pluralism, agricultural collectivisation, and investment in heavy industry.[437] It was aimed at establishing economic autarky within the Eastern Bloc.[437]
Asia

In October 1949, Chinese communist leader Mao Zedong took power in China.[444] With this accomplished, Marxist governments now controlled a third of the world's land mass.[445] Privately, Stalin revealed that he had underestimated the Chinese Communists and their ability to win the civil war, instead encouraging them to make another peace with the KMT.[446] In December 1949, Mao visited Stalin. Initially Stalin refused to repeal the Sino-Soviet Treaty of 1945, which significantly benefited the Soviet Union over China, although in January 1950 he relented and agreed to sign a new treaty between the two countries.[447] Stalin was concerned that Mao might follow Tito's example by pursuing a course independent of Soviet influence, and made it known that if displeased he would withdraw assistance from China; the Chinese desperately needed said assistance after decades of civil war.[448]
At the end of the Second World War, the Soviet Union and the United States divided up the Korean Peninsula, formerly a Japanese colonial possession, along the 38th parallel, setting up a communist government in the north and a pro-Western, anti-communist government in the south.[449] North Korean leader Kim Il Sung visited Stalin in March 1949 and again in March 1950; he wanted to invade the south and although Stalin was initially reluctant to provide support, he eventually agreed by May 1950.[450] The North Korean Army launched the Korean War by invading South Korea in June 1950, making swift gains and capturing Seoul.[451] Both Stalin and Mao believed that a swift victory would ensue.[451] The U.S. went to the UN Security Council—which the Soviets were boycotting over its refusal to recognise Mao's government—and secured international military support for the South Koreans. U.S. led forces pushed the North Koreans back.[452] Stalin wanted to avoid direct Soviet conflict with the U.S., convincing the Chinese to aid the North.[453]
The Soviet Union was one of the first nations to extend diplomatic recognition to the newly created state of Israel in 1948, in hopes of obtaining an ally in the Middle East.[454] When the Israeli ambassador Golda Meir arrived in the USSR, Stalin was angered by the Jewish crowds who gathered to greet her.[455] He was further angered by Israel's growing alliance with the U.S.[456] After Stalin fell out with Israel, he launched an anti-Jewish campaign within the Soviet Union and the Eastern Bloc.[431] In November 1948, he abolished the JAC,[457] and show trials took place for some of its members.[458] The Soviet press engaged in vituperative attacks on Zionism, Jewish culture, and "rootless cosmopolitanism",[459] with growing levels of anti-Semitism being expressed across Soviet society.[460] Stalin's increasing tolerance of anti-Semitism may have stemmed from his increasing Russian nationalism or from the recognition that anti-Semitism had proved a useful mobilising tool for Hitler and that he could do the same;[461] he may have increasingly viewed the Jewish people as a "counter-revolutionary" nation whose members were loyal to the U.S.[462] There were rumours, although they have never been substantiated, that Stalin was planning on deporting all Soviet Jews to the Jewish Autonomous Region in Birobidzhan, eastern Siberia.[463]

1950–1953: Final years
In his later years, Stalin was in poor health.[464] He took increasingly long holidays; in 1950 and again in 1951 he spent almost five months on holiday at his Abkhazian dacha.[465] Stalin nevertheless mistrusted his doctors; in January 1952 he had one imprisoned after they suggested that he should retire to improve his health.[464] In September 1952, several Kremlin doctors were arrested for allegedly plotting to kill senior politicians in what came to be known as the doctors' plot; the majority of the accused were Jewish.[466] He instructed the arrested doctors to be tortured to ensure confession.[467] In November, the Slánský trial took place in Czechoslovakia as 13 senior Communist Party figures, 11 of them Jewish, were accused and convicted of being part of a vast Zionist-American conspiracy to subvert Eastern Bloc governments.[468] That same month, a much publicised trial of accused Jewish industrial wreckers took place in Ukraine.[469] In 1951, he initiated the Mingrelian affair, a purge of the Georgian branch of the Communist Party which resulted in over 11,000 deportations.[470]
From 1946 until his death, Stalin only gave three public speeches, two of which lasted only a few minutes.[471] The amount of written material that he produced also declined.[471] In 1950, Stalin issued the article "Marxism and Problems of Linguistics", which reflected his interest in questions of Russian nationhood.[472] In 1952, Stalin's last book, Economic Problems of Socialism in the USSR, was published. It sought to provide a guide to leading the country after his death.[473] In October 1952, Stalin gave an hour and a half speech at the Central Committee plenum.[474] There, he emphasised what he regarded as leadership qualities necessary in the future and highlighted the weaknesses of various potential successors, particularly Molotov and Mikoyan.[475] In 1952, he also eliminated the Politburo and replaced it with a larger version which he called the Presidium.[476]
Death, funeral and aftermath

On 1 March 1953, Stalin's staff found him semi-conscious on the bedroom floor of his Kuntsevo Dacha.[477] He had suffered a cerebral haemorrhage.[478] He was moved onto a couch and remained there for three days.[479] He was hand-fed using a spoon, given various medicines and injections, and leeches were applied to him.[478] Stalin died on 5 March 1953.[480] According to Svetlana, it had been "a difficult and terrible death".[481] An autopsy revealed that he had died of a cerebral haemorrhage and that his cerebral arteries were severely damaged by atherosclerosis.[482] It has been conjectured that Stalin was murdered;[483] Beria has been suspected of poisoning him, but no firm evidence has appeared.[478] According to a theory developed by historians Vladimir Naumov and Jonathan Brent, Stalin was poisoned with warfarin, most likely by Beria.[484]
Stalin's death was announced on 6 March.[485] His body was embalmed,[486] and then displayed in Moscow's House of Unions for three days.[487] The crowds of people coming to view the body were so large and disorganised that many people were killed in a crowd crush.[488] At the funeral on 9 March, Stalin's body was laid to rest in Lenin's Mausoleum in Red Square; hundreds of thousands attended.[489] That month featured a surge in arrests for "anti-Soviet agitation", as those celebrating Stalin's death came to police attention.[490] The Chinese government instituted a period of official mourning for Stalin's death.[491] A memorial service in his honour was also held at St George the Martyr, Holborn in London.[492]
Stalin left neither a designated successor nor a framework within which a peaceful transfer of power could take place.[493] The Central Committee met on the day of his death, after which Malenkov, Beria, and Khrushchev emerged as the party's dominant figures.[494] The system of collective leadership was restored, and measures introduced to prevent any one member from attaining autocratic domination.[495] The collective leadership included eight senior members of the Presidium of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, namely Georgy Malenkov, Lavrentiy Beria, Vyacheslav Molotov, Kliment Voroshilov, Nikita Khrushchev, Nikolai Bulganin, Lazar Kaganovich and Anastas Mikoyan.[496] Reforms to the Soviet system were immediately implemented.[497] Economic reform scaled back the mass construction projects, placed a new emphasis on house building, and eased the levels of taxation on the peasantry to stimulate production.[498] The new leaders sought rapprochement with Yugoslavia and a less hostile relationship with the U.S.,[499] and they pursued a negotiated end to the Korean War in July 1953.[500][501] The doctors who had been imprisoned were released and the anti-Semitic purges ceased.[502] A mass amnesty for certain categories of convicts was issued, halving the country's inmate population, while the state security and Gulag systems were reformed, with torture being banned in April 1953.[498]
Political ideology

Stalin claimed to have embraced Marxism at the age of fifteen,[503] and it served as the guiding philosophy throughout his adult life;[504] according to Kotkin, Stalin held "zealous Marxist convictions",[505] while Montefiore suggested that Marxism held a "quasi-religious" value for Stalin.[506] Although he never became a Georgian nationalist,[507] during his early life elements from Georgian nationalist thought blended with Marxism in his outlook.[508] The historian Alfred J. Rieber noted that he had been raised in "a society where rebellion was deeply rooted in folklore and popular rituals".[507] Stalin believed in the need to adapt Marxism to changing circumstances; in 1917, he declared that "there is dogmatic Marxism and there is creative Marxism. I stand on the ground of the latter".[509] Volkogonov believed that Stalin's Marxism was shaped by his "dogmatic turn of mind", suggesting that this had been instilled in the Soviet leader during his education in religious institutions.[510] According to scholar Robert Service, Stalin's "few innovations in ideology were crude, dubious developments of Marxism".[504] Some of these derived from political expediency rather than any sincere intellectual commitment;[504] Stalin would often turn to ideology post hoc to justify his decisions.[511] Stalin referred to himself as a praktik, meaning that he was more of a practical revolutionary than a theoretician.[512]
As a Marxist and an anti-capitalist, Stalin believed in an inevitable "class war" between the world's proletariat and bourgeoisie.[513] He believed that the working classes would prove successful in this struggle and would establish a dictatorship of the proletariat,[514] regarding the Soviet Union as an example of such a state.[515] He also believed that this proletarian state would need to introduce repressive measures against foreign and domestic "enemies" to ensure the full crushing of the propertied classes,[516] and thus the class war would intensify with the advance of socialism.[517] As a propaganda tool, the shaming of "enemies" explained all inadequate economic and political outcomes, the hardships endured by the populace, and military failures.[518] The new state would then be able to ensure that all citizens had access to work, food, shelter, healthcare, and education, with the wastefulness of capitalism eliminated by a new, standardised economic system.[519] According to Sandle, Stalin was "committed to the creation of a society that was industrialised, collectivised, centrally planned and technologically advanced."[520]
Stalin adhered to the Leninist variant of Marxism.[521] In his book, Foundations of Leninism, he stated that "Leninism is the Marxism of the epoch of imperialism and of the proletarian revolution".[522] He claimed to be a loyal Leninist,[523] although was—according to Service—"not a blindly obedient Leninist".[519] Stalin respected Lenin, but not uncritically,[524] and spoke out when he believed that Lenin was wrong.[519] During the period of his revolutionary activity, Stalin regarded some of Lenin's views and actions as being the self-indulgent activities of a spoiled émigré, deeming them counterproductive for those Bolshevik activists based within the Russian Empire itself.[525] After the October Revolution, they continued to have differences. Whereas Lenin believed that all countries across Europe and Asia would readily unite as a single state following proletariat revolution, Stalin argued that national pride would prevent this, and that different socialist states would have to be formed; in his view, a country like Germany would not readily submit to being part of a Russian-dominated federal state.[526] Khlevniuk nevertheless believed that the pair developed a "strong bond" over the years,[527] while Kotkin suggested that Stalin's friendship with Lenin was "the single most important relationship in Stalin's life".[528] After Lenin's death, Stalin relied heavily on Lenin's writings—far more so than those of Marx and Engels—to guide him in the affairs of state.[529] Stalin adopted the Leninist view on the need for a revolutionary vanguard who could lead the proletariat rather than being led by them.[514] Leading this vanguard, he believed that the Soviet peoples needed a strong, central figure—akin to a Tsar—whom they could rally around.[530] In his words, "the people need a Tsar, whom they can worship and for whom they can live and work".[531] He read about, and admired, two Tsars in particular: Ivan the Terrible and Peter the Great.[532] In the personality cult constructed around him, he was known as the vozhd, an equivalent to the Italian duce and German führer.[533]

Stalinism was a development of Leninism,[534] and while Stalin avoided using the term "Marxism-Leninism-Stalinism", he allowed others to do so.[535] Following Lenin's death, Stalin contributed to the theoretical debates within the Communist Party, namely by developing the idea of "Socialism in One Country". This concept was intricately linked to factional struggles within the party, particularly against Trotsky.[536] He first developed the idea in December 1924 and elaborated upon in his writings of 1925–26.[537] Stalin's doctrine held that socialism could be completed in Russia but that its final victory could not be guaranteed because of the threat from capitalist intervention. For this reason, he retained the Leninist view that world revolution was still a necessity to ensure the ultimate victory of socialism.[537] Although retaining the Marxist belief that the state would wither away as socialism transformed into pure communism, he believed that the Soviet state would remain until the final defeat of international capitalism.[538] This concept synthesised Marxist and Leninist ideas with nationalist ideals,[520] and served to discredit Trotsky—who promoted the idea of "permanent revolution"—by presenting the latter as a defeatist with little faith in Russian workers' abilities to construct socialism.[539]
Stalin viewed nations as contingent entities which were formed by capitalism and could merge into others.[540] Ultimately, he believed that all nations would merge into a single, global human community,[540] and regarded all nations as inherently equal.[541] In his work, he stated that "the right of secession" should be offered to the ethnic minorities of the Russian Empire, but that they should not be encouraged to take that option.[542] He was of the view that if they became fully autonomous, then they would end up being controlled by the most reactionary elements of their community; as an example, he cited the largely illiterate Tatars, whom he claimed would end up dominated by their mullahs.[542] Stalin argued that the Jews possessed a "national character" but were not a "nation" and were thus unassimilable. He argued that Jewish nationalism, particularly Zionism, was hostile to socialism.[543] According to Khlevniuk, Stalin reconciled Marxism with great-power imperialism and therefore expansion of the empire makes him a worthy to the Russian tsars.[518] Service argued that Stalin's Marxism was imbued with a great deal of Russian nationalism.[504] According to Montefiore, Stalin's embrace of the Russian nation was pragmatic, as the Russians were the core of the population of the USSR; it was not a rejection of his Georgian origins.[544] Stalin's push for Soviet westward expansion into eastern Europe resulted in accusations of Russian imperialism.[545]
Personal life and characteristics
Ethnically Georgian,[546] Stalin grew up speaking Georgian,[547] and did not begin learning Russian until eight or nine.[548] It has been argued his ancestry was Ossetian, because his genetic haplotype (G2a-Z6653) is considered typical of the Ossetians, but he never acknowledged an Ossetian identity.[549] He remained proud of his Georgian identity,[550] and throughout his life retained a heavy Georgian accent when speaking Russian.[551] Despite Stalin's affinity for Russia and Russians, he remained profoundly Georgian in lifestyle and personality.[552] Some colleagues described him as "Asiatic", and he supposedly once told a Japanese journalist that "I am not a European man, but an Asian, a Russified Georgian".[553] Service noted that Stalin "would never be Russian", could not credibly pass as one, and never tried to pretend he was.[554] Montefiore was of the view that "after 1917, [Stalin] became quadri-national: Georgian by nationality, Russian by loyalty, internationalist by ideology, Soviet by citizenship."[555] He used nicknames and pseudonyms, including "Koba", "Soselo", and "Ivanov",[556] adopting "Stalin" in 1912.
Stalin had a soft voice,[557] and when speaking Russian did so slowly, choosing his phrasing.[546] In private he often used coarse language and profanity, although avoided doing so in public.[558] Described as a poor orator,[559] Stalin's style was "simple and clear, without flights of fancy, catchy phrases or platform histrionics".[560] He rarely spoke before large audiences and preferred to express himself in writing.[561] His writing style was similar, being characterised by its simplicity, clarity, and conciseness.[562]

Stalin measured 1.70 m (5 feet 7 inches).[563][564] His mustached face was pock-marked from smallpox during childhood; this was airbrushed from published photographs.[565] He was born with a webbed left foot, and his left arm had been injured in childhood which left it shorter than his right and lacking in flexibility.[566]
During his youth, Stalin cultivated a scruffy appearance in rejection of middle-class aesthetic values.[567] By 1907, he grew his hair long and often wore a beard; for clothing, he often wore a traditional Georgian chokha or a red satin shirt with a grey coat and black fedora.[568] From mid-1918 he favoured military-style clothing, in particular long black boots, light-coloured collarless tunics, and a gun.[569] He was a lifelong smoker, who smoked both a pipe and cigarettes.[570] Publicly at least, Stalin had a minimalist lust and lived relatively plainly, with simple and inexpensive clothing and furniture;[571] his dominant interest was power.[572]
As leader of the Soviet Union, Stalin typically awoke around 11 am,[573] with lunch being served between 3-5 pm and dinner no earlier than 9 pm;[574] he then worked late.[575] He often dined with other Politburo members and their families.[576] As leader, he rarely left Moscow unless to go to a dacha for holiday;[577] he disliked travel,[578] and refused to by plane.[579] His choice of favoured holiday house changed,[580] although he holidayed in south USSR every year from 1925 to 1936 and 1945 to 1951.[581] He had a dacha at Zubalova, 35 km outside Moscow,[582] although ceased using it after Nadezhda's 1932 suicide.[583] After 1932, he favoured holidays in Abkhazia, being a friend of its leader, Nestor Lakoba.[584] In 1934, his new Kuntsevo Dacha was built; 9 km from the Kremlin, it became his primary residence.[585] In 1935, he began using a new dacha provided by Lakoba at Novy Afon;[586] in 1936, he had the Kholodnaya Rechka dacha built on the Abkhazian coast, designed by Miron Merzhanov.[587]
Personality

Trotsky and other Soviet figures promoted the idea that Stalin was a mediocrity.[588] This gained widespread acceptance outside the Soviet Union during his lifetime but was misleading.[589] According to Montefiore, "it is clear from hostile and friendly witnesses alike that Stalin was always exceptional, even from childhood".[589] Stalin had a complex mind,[590] self-control,[591] and an excellent memory.[592] He was a hard worker,[593] and displayed a keen desire to learn;[594] when in power, he scrutinised many details, from film scripts to architectural plans and military hardware.[595] According to Volkogonov, "Stalin's private life and working life were one and the same"; he did not take days off from political activities.[596] Although, Bazhanov described Stalin as having little education and making limited contributions to matters of state discussed at Politburo sessions.[597] Similarly, historian Robert William Davies viewed Stalin as being liable to fall under the sway of persuasive charlatans such as the pseudo-scientific, agronomist Trofim Lysenko due in part to his lack of education.[598] According to Lenin's sister, Maria Ilyinichna Ulyanova, Lenin stated that "Stalin is not intelligent at all",[599] but "valued Stalin as a practical type".[600]
Stalin could play different roles to different audiences,[601] and was adept at deception.[602] According to Bolshevik historian, Vladimir Nevsky, Stalin was appointed General Secretary because he used false rumours to convince Lenin the party faced a split. Nevsky claimed Lenin would deeply regret trusting Stalin and strove to correct with his "Testament".[603] Several historians have seen it appropriate to follow Lazar Kaganovich's description of there being "several Stalins" as a means of understanding him.[604] He was a good organiser,[605] with a strategic mind,[606] and judged others according to their inner strength, practicality, and cleverness.[607] He acknowledged he could be rude,[608] but rarely raised his voice;[609] as his health deteriorated he became unpredictable and bad-tempered.[610] Despite his tough-talking attitude, he could be charming;[611] when relaxed, he cracked jokes and mimicked others.[594] Montefiore suggested this charm was "the foundation of Stalin's power in the Party".[612] According to Service he was "decisive, competent, confident, and ambitious".[117]
Stalin was ruthless,[613] temperamentally cruel,[614] and had a propensity for violence high even among the Bolsheviks.[609] He lacked compassion,[615] something Volkogonov suggested might have been accentuated by years in prison and exile,[616] although he was capable of acts of kindness to strangers, even amid the Great Terror.[617] He was capable of self-righteous indignation,[618] and was resentful,[619] and vindictive,[620] holding on to grudges for many years.[621] By the 1920s, he was suspicious and conspiratorial, prone to believing people were plotting against him and that there were international conspiracies behind acts of dissent.[622] He never attended torture sessions or executions,[623] although Service thought Stalin "derived deep satisfaction" from degrading and humiliating people and enjoyed keeping even close associates in a state of "unrelieved fear".[545] Montefiore thought Stalin's brutality marked him out as a "natural extremist";[624] Service suggested he had tendencies toward a paranoid and sociopathic personality disorder.[590] According to Geoffrey Roberts, Stalin was not a psychopath.[625] He was instead an emotionally intelligent and feeling intellectual.[625] Other historians linked his brutality not to any personality trait, but unwavering commitment to the survival of the Soviet Union and the international Marxist–Leninist cause.[626] Conversely, E.A. Rees believed "it was psychopathy that bred tyranny". Rees cited a diagnosis performed by neuropathologist Vladimir Bekhterev on Stalin in 1927 and who described him as a "typical case of severe paranoia".[627]
Keenly interested in the arts,[628] Stalin admired artistic talent.[629] He protected several Soviet writers from arrest and prosecution, such as Mikhail Bulgakov, even when their work was labelled harmful to his regime.[630] He enjoyed listening to classical music,[631] owning around 2,700 records,[632] and frequently attending the Bolshoi Theatre during the 1930s and 40s.[633] His taste was conservative, favouring classical drama, opera, and ballet over what he dismissed as experimental "formalism".[548] He favoured classical forms in the visual arts, disliking avant-garde styles like cubism and futurism.[634] He was a voracious reader and kept a personal library of over 20,000 books.[635] Little was fiction,[636] although he could cite passages from Alexander Pushkin, Nikolay Nekrasov, and Walt Whitman by heart.[629] Stalin's favourite subject was history, closely followed by Marxist theory and then fiction.[625] Stalin knew Marxist theory well and according to Bullock was an "effective debater" who would quote Marx and Engels in his arguments.[637] He favoured historical studies, keeping up with debates in the study of Russian, Mesopotamian, ancient Roman, and Byzantine history.[471] He was interested in the reigns of Ivan the Terrible, Peter the Great and Catherine the Great.[625] An autodidact,[638] he claimed to read as many as 500 pages a day,[639] with Montefiore regarding him as an intellectual.[640] Lenin was his favourite author but he also read, and sometimes appreciated, a great deal of writing by Leon Trotsky and other archenemies.[625] Like all Bolshevik leaders, Stalin believed that reading could help transform not just people's ideas and consciousness, but human nature itself.[625] Stalin enjoyed watching films at night at cinemas installed in the Kremlin and his dachas.[641] He liked the Western genre,[642] although his favourite films were Volga Volga and Circus.[643]
Stalin was a keen and accomplished billiards player,[644] and collected watches.[645] He enjoyed practical jokes; for instance, he would place a tomato on the chairs of Politburo members and wait for them to sit on it.[646] When at social events, he encouraged singing,[647] as well as alcohol; he hoped others would drunkenly reveal their secrets to him.[648] As an infant, Stalin displayed a love of flowers,[649] and later became a keen gardener.[649] His Volynskoe suburb had a 20-hectare (50-acre) park, with Stalin devoting much attention to its agricultural activities.[650]
Stalin publicly condemned anti-Semitism,[651] although he was repeatedly accused of it.[652] People who knew him, such as Khrushchev, suggested he long harboured negative sentiments toward Jews,[653] and it has been argued that anti-Semitic trends in his policies were fuelled by Stalin's struggle against Trotsky.[654] After Stalin's death, Khrushchev claimed Stalin encouraged him to incite anti-Semitism in Ukraine, allegedly telling him that "the good workers at the factory should be given clubs so they can beat the hell out of those Jews."[655] In 1946, Stalin allegedly said privately that "every Jew is a potential spy".[656] Conquest stated that although Stalin had Jewish associates, he promoted anti-Semitism.[657] Service cautioned that there was "no irrefutable evidence" of anti-Semitism in Stalin's published work, although his private statements and public actions were "undeniably reminiscent of crude antagonism towards Jews";[658] he added that throughout Stalin's life, the Georgian "would be the friend, associate or leader of countless individual Jews".[659] According to Beria, Stalin had affairs with Jewish women.[660]
His ability to assume absolute power has remained a subject of debate.[661] Some historians have attributed his success to personal qualities.[662] Contrarily, political theorists, such as Trotsky, have emphasised the role of external conditions in facilitating the growth of a Soviet bureaucracy which served as a power base for Stalin.[663] Other historians have regarded premature deaths of prominent Bolsheviks such as Lenin and Yakov Sverdlov to have been key factors in Stalin's elevation. Sverdlov served as the original chairman of the party secretariat and considered a natural candidate for General Secretary.[664] Historian Peter Kenez believed Trotsky could have removed Stalin with the use of Lenin's testament, but acquiesced to the collective decision not to publish it.[665]
Relationships and family
Friendship was important to Stalin,[666] and he used it to gain and maintain power.[667] Kotkin observed that Stalin "generally gravitated to people like himself: parvenu intelligentsia of humble background".[668] He gave nicknames to his favourites.[669][670] Stalin's friendships "meandered between love, admiration, and venomous jealousy".[671] While Soviet leader he remained in contact with many old friends in Georgia, sending them letters and money.[672]
Stalin was not a womaniser.[673] According to Boris Bazhanov, Stalin's one-time secretary, "Women didn't interest him. His own woman [Alliluyeva] was enough for him, and he paid scant attention to her."[674] However, Montefiore noted that in his early life Stalin "rarely seems to have been without a girlfriend".[675] Montefiore described Stalin's favoured types as "young, malleable teenagers or buxom peasant women",[676] who would be supportive and unchallenging.[677] Stalin "regarded women as a resource for sexual gratification and domestic comfort".[678] Stalin married twice and had several children.[679]
Stalin married his first wife, Ekaterina Svanidze, in 1906. According to Montefiore, theirs was "a true love match";[680] Volkogonov suggested that she was "probably the one human being he had really loved".[681] When she died, Stalin allegedly said: "This creature softened my heart of stone."[682] However, Russian historian Anton Antonov-Ovseenko wrote that Stalin was physically abusive to her.[683] They had a son, Yakov, who often frustrated and annoyed Stalin.[684] Yakov had a daughter, Galina, before fighting for the Red Army in the Second World War. He was captured by the German Army and committed suicide.[685]

In 1914, Stalin, aged 35, had a relationship with Lidia Pereprygina, then 14, who became pregnant with Stalin's child.[686][687] Circa December 1914, Pereprygia gave birth to their child, although the infant died soon after.[688] In 1916, Lidia – now 15 – was pregnant again. She allegedly gave birth to their son, named Alexander Davydov, in around April 1917. Stalin, then absent, later came to know of the child's existence but showed no interest in him.[689]
Stalin's second wife was Nadezhda Alliluyeva; theirs was not an easy relationship, they often fought.[690] They had two biological children—a son, Vasily, and daughter, Svetlana, and adopted another son, Artyom Sergeev, in 1921.[691] It is unclear if Stalin ever had a mistress during or after this marriage.[692] She suspected he was unfaithful,[693] and committed suicide in 1932.[694] Stalin regarded Vasily as spoiled and often chastised his behaviour; as Stalin's son, Vasily was swiftly promoted through the Red Army and allowed a lavish lifestyle.[695] Conversely, Stalin had an affectionate relationship with Svetlana during her childhood,[696] and was very fond of Artyom.[691] He disapproved of Svetlana's suitors and husbands, putting a strain on their relationship.[697] After the Second World War, he made little time for his children and his family played a decreasingly important role in his life.[698] After Stalin's death, Svetlana changed her surname from Stalin to Alliluyeva,[499] and defected to the U.S.[699]
After Nadezhda's death, Stalin became increasingly close to his sister-in-law Zhenya Alliluyeva;[700] Montefiore believed they were lovers.[701] There are unproven rumours that from 1934 onward he had a relationship with his housekeeper Valentina Istomina.[702] Montefiore claimed Stalin had at least two illegitimate children,[703] although he never recognised them as being his.[704] One of them, Konstantin Kuzakov, taught philosophy at the Leningrad Military Mechanical Institute, but never met Stalin.[705] The other, Alexander, was the son of Lidia Pereprygina; he was raised as the son of a peasant fisherman and the Soviet authorities made him swear never to reveal Stalin was his biological father.[706] Stalin was complicit with the persecution of relatives of his former wives such as Maria and Alexander Svanidze who were arrested and eliminated during the Great Purge.[707]
Legacy

The historian Robert Conquest stated that Stalin perhaps "determined the course of the twentieth century" more than any other individual.[708] Biographers like Service and Volkogonov have considered him an outstanding and exceptional politician;[709] Montefiore labelled Stalin as "that rare combination: both 'intellectual' and killer", a man who was "the ultimate politician" and "the most elusive and fascinating of the twentieth-century titans".[710] According to historian Kevin McDermott, interpretations of Stalin range from "the sycophantic and adulatory to the vitriolic and condemnatory."[711] For most Westerners and anti-communist Russians, he is viewed overwhelmingly negatively as a mass murderer;[711] for significant numbers of Russians and Georgians, he is regarded as a great statesman and state-builder.[711]
According to Service, Stalin strengthened and stabilised the Soviet Union.[712] Service suggested that the country might have collapsed long before 1991 without Stalin.[712] In under three decades, Stalin transformed the Soviet Union into a major industrial world power,[713] one which could "claim impressive achievements" in terms of urbanisation, military strength, education and Soviet pride.[714] Under his rule, the average Soviet life expectancy grew due to improved living conditions, nutrition and medical care[715] as mortality rates also declined.[716] Although millions of Soviet citizens despised him, support for Stalin was nevertheless widespread throughout Soviet society.[714] Conversely, the historian Vadim Rogovin argued that the Great Terror which had gained traction in 1937 "caused losses to the communist movement both in the USSR and throughout the world from which the movement has not recovered to this very day".[717] Similarly, Khrushchev believed his widespread purges of the "most advanced nucleus of people" among the Old Bolsheviks and leading figures in the military and scientific fields had "undoubtedly" weakened the nation.[718]

Stalin's necessity for the Soviet Union's economic development has been questioned, and it has been argued that Stalin's policies from 1928 onwards may have only been a limiting factor.[719] Stalin's Soviet Union has been characterised as a totalitarian state,[720] with Stalin its authoritarian leader.[721] Various biographers have described him as a dictator,[722] an autocrat,[723] or accused him of practising Caesarism.[724] Montefiore argued that while Stalin initially ruled as part of a Communist Party oligarchy, the Soviet government transformed from this oligarchy into a personal dictatorship in 1934,[725] with Stalin only becoming "absolute dictator" between March and June 1937, when senior military and NKVD figures were eliminated.[726] According to Kotkin, Stalin "built a personal dictatorship within the Bolshevik dictatorship."[727] In both the Soviet Union and elsewhere he came to be portrayed as an "Oriental despot".[728] Dmitri Volkogonov characterised him as "one of the most powerful figures in human history."[729] McDermott stated that Stalin had "concentrated unprecedented political authority in his hands."[730] Service stated that Stalin "had come closer to personal despotism than almost any monarch in history" by the late 1930s.[731]

McDermott nevertheless cautioned against "over-simplistic stereotypes"—promoted in the fiction of writers like Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn, Vasily Grossman, and Anatoly Rybakov—that portrayed Stalin as an omnipotent and omnipresent tyrant who controlled every aspect of Soviet life through repression and totalitarianism.[732] Service similarly warned of the portrayal of Stalin as an "unimpeded despot", noting that "powerful though he was, his powers were not limitless", and his rule depended on his willingness to conserve the Soviet structure he had inherited.[733] Kotkin observed that Stalin's ability to remain in power relied on him having a majority in the Politburo at all times.[734] Khlevniuk noted that at various points, particularly when Stalin was old and frail, there were "periodic manifestations" in which the party oligarchy threatened his autocratic control.[610] Stalin denied to foreign visitors that he was a dictator, stating that those who labelled him such did not understand the Soviet governance structure.[735]
A vast literature devoted to Stalin has been produced.[736] During Stalin's lifetime, his approved biographies were largely hagiographic in content.[737] Stalin ensured that these works gave very little attention to his early life, particularly because he did not wish to emphasise his Georgian origins in a state numerically dominated by Russians.[738] Since his death many more biographies have been written,[739] although until the 1980s these relied largely on the same sources of information.[739] Under Mikhail Gorbachev's Soviet administration various previously classified files on Stalin's life were made available to historians,[739] at which point Stalin became "one of the most urgent and vital issues on the public agenda" in the Soviet Union.[740] After the dissolution of the Union in 1991, the rest of the archives were opened to historians, resulting in much new information about Stalin coming to light,[741] and producing a flood of new research.[736]
Leninists remain divided in their views on Stalin; some view him as Lenin's authentic successor, while others believe he betrayed Lenin's ideas by deviating from them.[545] The socio-economic nature of Stalin's Soviet Union has also been much debated, varyingly being labelled a form of state socialism, state capitalism, bureaucratic collectivism, or a totally unique mode of production.[742] Socialist writers like Volkogonov have acknowledged that Stalin's actions damaged "the enormous appeal of socialism generated by the October Revolution".[743]
Death toll
With a high number of excess deaths occurring under his rule, Stalin has been labelled "one of the most notorious figures in history".[712] These deaths occurred as a result of collectivisation, famine, terror campaigns, disease, war and mortality rates in the Gulag. As the majority of excess deaths under Stalin were not direct killings, the exact number of victims of Stalinism is difficult to calculate due to lack of consensus among scholars on which deaths can be attributed to the regime.[744] Stalin has also been accused of genocide in the cases of forced population transfer of ethnic minorities in the Soviet Union and the famine in Ukraine.[745] Under Stalin, the death penalty was extended to adolescents as young as 12 years old in 1935.[746]

Official records reveal 799,455 documented executions in the Soviet Union between 1921 and 1953; 681,692 of these were carried out between 1937 and 1938, the years of the Great Purge.[747] According to historian Michael Ellman, the best modern estimate for the number of repression deaths during the purge is 950,000 to 1.2 million, which includes executions and deaths in detention or soon after release.[748] Archival data shows that 1,053,829 perished in the Gulag system from 1934 to 1953,[749] though current historical consensus is that of the 18 million people who passed through the Gulag camps from 1930 to 1953, between 1.5 and 1.7 million died as a result of their incarceration.[750] Furthermore, about 6.3 million people were affected by mass deportations of kulaks and ethnic minorities between 1930 and 1952, of which an estimated 1 to 1.5 million died as a result.[751] Historian and archival researcher Stephen G. Wheatcroft and Ellman attribute roughly 3 to 3.5 million deaths to Stalin's regime, including executions and deaths from criminal negligence.[752] Wheatcroft and historian R. W. Davies estimate famine deaths at 5.5–6.5 million[753] while scholar Steven Rosefielde gives a number of 8.7 million.[754]
In 2011, historian Timothy D. Snyder summarised modern data made after the opening of the Soviet archives in the 1990s and states that Stalin's regime was responsible for 9 million deaths, with 6 million of these being deliberate killings. He further states that estimates of 20 million or above, which were made before access to the archives, are not credible.[755] According to Rogovin, 80–90% of the members of the Central Committee elected at the Sixth through to the Seventeenth Congresses were physically annihilated.[756]
In the Soviet Union and post-Soviet states
Shortly after his death, the Soviet Union went through a period of de-Stalinization. Malenkov denounced the Stalin personality cult,[757] which was subsequently criticised in Pravda.[758] In 1956, Khrushchev gave his "Secret Speech", titled "On the Cult of Personality and Its Consequences", to a closed session of the Party's 20th Congress. There, Khrushchev denounced Stalin for both his mass repression and his personality cult.[759] He repeated these denunciations at the 22nd Party Congress in October 1962.[760] In October 1961, Stalin's body was removed from the mausoleum and buried in the Kremlin Wall Necropolis, the location marked by a bust.[761] Stalingrad was renamed Volgograd.[762]
Khrushchev's de-Stalinisation process in Soviet society ended when he was replaced as leader by Leonid Brezhnev in 1964; the latter introduced a level of re-Stalinisation within the Soviet Union.[763] In 1969 and again in 1979, plans were proposed for a full rehabilitation of Stalin's legacy but on both occasions were halted due to fears of damaging the USSR's public image.[764] Gorbachev saw the total denunciation of Stalin as necessary for the regeneration of Soviet society.[765] After the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991, the first president of the new Russian Federation, Boris Yeltsin, continued Gorbachev's denunciation of Stalin but added to it a denunciation of Lenin.[765] His successor Vladimir Putin did not seek to rehabilitate Stalin but emphasised the celebration of Soviet achievements under Stalin's leadership rather than the Stalinist repressions.[766] In October 2017, Putin opened the Wall of Grief memorial in Moscow, noting that the "terrible past" would neither be "justified by anything" nor "erased from the national memory".[767] In a 2017 interview, Putin added that while "we should not forget the horrors of Stalinism", the excessive demonisation of Stalin "is a means to attack [the] Soviet Union and Russia".[768] In recent years, the government and general public of Russia has been accused of rehabilitating Stalin.[769]

Amid the social and economic turmoil of the post-Soviet period, many Russians viewed Stalin as having overseen an era of order, predictability, and pride.[770] He remains a revered figure among many Russian nationalists, who feel nostalgic about the Soviet victory over Nazi Germany in World War II,[771] and he is regularly invoked approvingly within both Russia's far-left and far-right.[772]
Polling by the Levada Center suggest Stalin's popularity has grown since 2015, with 46% of Russians expressing a favourable view of him in 2017 and 51% in 2019.[773] In a 2021 poll, a record 70% of Russians indicated they had a mostly/very favourable view of Stalin.[774] The same year, a survey by the Center showed that Joseph Stalin was named by 39% of Russians as the "most outstanding national figure of all time" and, while nobody received an absolute majority, Stalin was very clearly in first place, followed by another Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin with 30% and Russian poet Alexander Pushkin with 23%.[775][776] At the same time, there was a growth in pro-Stalinist literature in Russia, much relying upon the misrepresentation or fabrication of source material.[777] In this literature, Stalin's repressions are regarded either as a necessary measure to defeat "enemies of the people" or the result of lower-level officials acting without Stalin's knowledge.[777]
The only other part of the former Soviet Union other than Russia where admiration for Stalin has remained consistently widespread is Georgia, although Georgian attitudes have been very divided.[778] A number of Georgians resent criticism of Stalin, the most famous figure from their nation's modern history.[771] A 2013 survey by Tbilisi State University found 45% of Georgians expressing "a positive attitude" to him.[779] A 2017 Pew Research survey had 57% of Georgians saying he played a positive role in history, compared to 18% of those expressing the same for Mikhail Gorbachev.[780]
Some positive sentiment can also be found elsewhere in the former Soviet Union. A 2012 survey commissioned by the Carnegie Endowment found 38% of Armenians concurring that their country "will always have need of a leader like Stalin".[781][782] In early 2010, a new monument to Stalin was erected in Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine.[783] In December 2010, unknown persons decapitated it and it was destroyed in a bomb attack in 2011.[784] In a 2016 Kyiv International Institute of Sociology poll, 38% of respondents had a negative attitude to Stalin, 26% a neutral one and 17% a positive, with 19% refusing to answer.[785]
See also
- European interwar dictatorships
- List of places named after Joseph Stalin
- List of statues of Joseph Stalin
Explanatory notes
- ^ The office of General Secretary was abolished in 1952, but Stalin continued to exercise its powers as the highest-ranking member of the party Secretariat.
- ^ Before 1946, the title of the office was Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars.
- ^ Before 1946, the title of the office was People's Commissar for Defense, and briefly People's Commissar for the Armed Forces.
- ^ Founded as the RSDLP(b) in 1912; renamed the RCP(b) in 1918, AUCP(b) in 1925, and CPSU in 1952.
- ^ While forced to give up control of the Secretariat almost immediately after succeeding Stalin as the body's de facto head, Malenkov was still recognised as "first among equals" within the regime for over a year. As late as March 1954, he remained listed as first in the Soviet leadership and continued to chair meetings of the Politburo.
- ^ English: /ˈstɑːlɪn/; Russian: Иосиф Виссарионович Сталин, romanized: Iosif Vissarionovich Stalin, IPA: [ɪˈosʲɪf vʲɪssərʲɪˈonəvʲɪtɕ ˈstalʲɪn] ; Georgian: იოსებ ბესარიონის ძე სტალინი, romanized: Ioseb Besarionis dze Stalini
- ^ Stalin's Georgian birth name was Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili (Georgian: იოსებ ბესარიონის ძე ჯუღაშვილი), the Russified equivalent of which was Iosif Vissarionovich Dzhugashvili (Russian: Иосиф Виссарионович Джугашвили; pre-1918: Іосифъ Виссаріоновичъ Джугашвили). He adopted the alias "Stalin" during his years as a revolutionary, and made it his legal name after the October Revolution.
References
Citations
- ^ Montefiore, Simon Sebag (27 May 2010). Young Stalin. Orion. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-2978-6384-7.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 53.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 177.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 147–148; Kotkin 2014, pp. 227–228, 229; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 52.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, pp. 28–29; Service 2004, p. 148.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 71; Kotkin 2014, p. 228.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 71; Kotkin 2014, p. 229.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 27; Kotkin 2014, p. 226.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 150.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 157.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 149.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 155.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 158.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 148.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 70; Volkogonov 1991, p. 30; Service 2004, p. 148; Kotkin 2014, p. 228; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 52.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 72; Service 2004, p. 151.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 72; Service 2004, p. 167; Kotkin 2014, p. 264; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 49.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 71.
- ^ a b Conquest 1991, p. 71; Service 2004, p. 152.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 153.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 72; Service 2004, pp. 150–151; Kotkin 2014, pp. 259–264.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 75; Service 2004, pp. 158–161; Kotkin 2014, p. 250.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 159–160; Kotkin 2014, p. 250.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 75; Service 2004, p. 161; Kotkin 2014, pp. 257–258.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 161; Kotkin 2014, pp. 258–259, 265.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 259.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 165; Kotkin 2014, pp. 268–270.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 77; Volkogonov 1991, p. 39; Montefiore 2003, p. 27; Service 2004, p. 163; Kotkin 2014, pp. 300–301; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 54.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 173.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 164; Kotkin 2014, pp. 302–303.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 78, 82; Montefiore 2007, p. 28; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 55.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 81; Service 2004, p. 170.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 46; Montefiore 2007, p. 27; Kotkin 2014, pp. 305, 307; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 56–57.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 78–79; Volkogonov 1991, p. 40; Service 2004, p. 166; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 55.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 171.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 169.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 83–84; Service 2004, p. 172; Kotkin 2014, p. 314.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 172.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 85; Service 2004, p. 172.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 173, 174.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 185.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 86; Volkogonov 1991, p. 45; Kotkin 2014, p. 331.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 175.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 91; Service 2004, p. 175.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 176.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 199.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 203, 190.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 174.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 178.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 176; Kotkin 2014, pp. 352–354.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 178; Kotkin 2014, p. 357; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 59.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 176–177.
- ^ a b c d Service 2004, p. 177.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 87; Service 2004, p. 179; Kotkin 2014, p. 362; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 60.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 180, 182; Kotkin 2014, p. 364.
- ^ Brackman 2004, p. 135.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 182.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 182; Kotkin 2014, pp. 364–365.
- ^ Davies 2003, p. 211; Service 2004, pp. 183–185; Kotkin 2014, pp. 376–377.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 377.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 184–185; Kotkin 2014, p. 377.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 392.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, pp. 396–397.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 388.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 202.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 199–200; Kotkin 2014, p. 371.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 200.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 194–196; Kotkin 2014, p. 400.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 194–195; Kotkin 2014, pp. 479–481.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 203–205; Kotkin 2014, p. 400.
- ^ a b Conquest 1991, p. 127; Service 2004, p. 232.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 89; Service 2004, p. 187; Kotkin 2014, p. 344; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 64.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 186.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 188.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 96; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 78–70; Service 2004, pp. 189–190; Kotkin 2014, p. 411.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 190.
- ^ Service 2000, p. 369; Service 2004, p. 209; Kotkin 2014, p. 504.
- ^ a b Kotkin 2014, p. 501.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 97; Volkogonov 1991, p. 53; Service 2004, p. 191.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 191–192; Kotkin 2014, p. 413.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 192; Kotkin 2014, p. 414; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 68.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 102; Service 2004, pp. 191–192; Kotkin 2014, p. 528.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 98; Service 2004, p. 193; Kotkin 2014, p. 483; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 69–70.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 95; Service 2004, p. 195; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 71–72.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 195.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 71; Service 2004, p. 194; Kotkin 2014, pp. 475–476; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 68–69.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 98–99; Service 2004, p. 195; Kotkin 2014, pp. 477, 478; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 69.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 74; Service 2004, p. 206; Kotkin 2014, p. 485.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 99–100, 103; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 72–74; Service 2004, pp. 210–211; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 70–71.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 100–101; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 53, 79–82; Service 2004, pp. 208–209; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 71.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 528.
- ^ Suny 2020b, p. 59.
- ^ Bazhanov & Doyle 1990, p. 62.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 104; Montefiore 2003, p. 30; Service 2004, p. 219; Kotkin 2014, p. 534; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 79.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 110; Montefiore 2003, p. 30; Service 2004, p. 219; Kotkin 2014, pp. 542–543.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 130; Montefiore 2003, p. 30; Service 2004, p. 221; Kotkin 2014, p. 540.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 111–112; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 117–118; Service 2004, p. 221; Kotkin 2014, p. 544.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 222–224; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 79.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 111; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 93–94; Service 2004, pp. 222–224; Kotkin 2014, pp. 546–548; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 79.
- ^ Kuromiya, Hiroaki (16 August 2013). Stalin. Routledge. p. 60. ISBN 978-1-3178-6780-7. Archived from the original on 19 July 2023. Retrieved 10 July 2023.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 426.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 453.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 455.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 469.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 432.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, pp. 495–496.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 127; Service 2004, p. 235.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 127; Service 2004, p. 238.
- ^ Fainsod & Hough 1979, p. 111.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 136.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 27.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 98; Kotkin 2014, p. 474; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 52.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 214–215, 217.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 87.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 225.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 227.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 228.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 228; Kotkin 2014, p. 563.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 240.
- ^ a b Service 2004, pp. 240–243; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 82–83.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 126; Conquest 2008, p. 11; Kotkin 2014, p. 614; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 83.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 137, 138; Kotkin 2014, p. 614.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 247; Kotkin 2014, pp. 614, 618; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 91.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 85.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 139, 151; Service 2004, pp. 282–283; Conquest 2008, pp. 11–12; Kotkin 2014, pp. 676–677; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 85.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 164; Service 2004, p. 282.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 276.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 277–278.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 277, 280; Conquest 2008, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 278.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 39.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 130.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 130; Volkogonov 1991, p. 160; Kotkin 2014, p. 689.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 244.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 273.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 256.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 254.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 172–173; Service 2004, p. 256; Kotkin 2014, pp. 638–639.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 144, 146; Service 2004, p. 258.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 256; Kotkin 2014, p. 571.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 253; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 101.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 147–148; Service 2004, pp. 257–258; Kotkin 2014, pp. 661, 668–669, 679–684; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 102–103.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 258; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 103.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 258.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 258; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 105.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 267.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 160; Volkogonov 1991, p. 166.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 167.
- ^ a b Sandle 1999, p. 231.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 265–266; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 110–111.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 234.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 266; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 112.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 113.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 271.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 270.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 270; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 116.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 272; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 116.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 272.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 270; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 113–114.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 160; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 114.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 174.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 172; Service 2004, p. 260; Kotkin 2014, p. 708.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 158; Service 2004, p. 266; Conquest 2008, p. 18.
- ^ Sandle 1999, pp. 227, 229.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 259.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 274.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 265.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 118.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 186, 190.
- ^ Sandle 1999, pp. 231–233.
- ^ Sandle 1999, pp. 241–242.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 269.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 300.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 152–153; Sandle 1999, p. 214; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 107–108.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 108.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 152–155; Service 2004, p. 259; Kotkin 2014, pp. 687, 702–704, 709; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 107.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 268.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 155.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 324.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 326.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 301.
- ^ Sandle 1999, pp. 244, 246.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 299.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 304.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, pp. 111, 127; Service 2004, p. 308.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 246; Montefiore 2003, p. 85.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 302–303.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 211, 276–277; Service 2004, p. 307.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 157.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 191.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 325.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 379.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 183–184.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 282.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 261.
- ^ McDermott 1995, pp. 410–411; Conquest 1991, p. 176; Service 2004, pp. 261, 383; Kotkin 2014, p. 720.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 173.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 289; Kotkin 2014, p. 595.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 289.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 169; Montefiore 2003, p. 90; Service 2004, pp. 291–292.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 94, 95; Service 2004, pp. 292, 294.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 297.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 316.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 310.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 310; Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, p. 627.
- ^ a b Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, p. 628.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 318.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 312; Conquest 2008, pp. 19–20; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 117.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 117.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 119.
- ^ Ellman 2005, p. 823.
- ^ Ellman 2005, p. 824; Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, pp. 628, 631.
- ^ Ellman 2005, pp. 823–824; Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, p. 626; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 117.
- ^ Ellman 2005, p. 834.
- ^ Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, p. 626.
- ^ Ellman 2005, p. 824; Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, pp. 627–628; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 120.
- ^ a b Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, p. 627.
- ^ Ellman 2005, p. 833; Kuromiya 2008, p. 665.
- ^ Davies & Wheatcroft 2006, p. 628; Ellman 2007, p. 664.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 164; Kotkin 2014, p. 724.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 319.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 212; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 552–443; Service 2004, p. 361.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 212.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 361.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 362.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 216.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 386.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 217.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 176; Montefiore 2003, p. 116; Service 2004, p. 340.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 218; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 123, 135.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 135.
- ^ Haslam 1979, pp. 682–683; Conquest 1991, p. 218; Service 2004, p. 385; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 135.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 219; Service 2004, p. 387.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 154.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 387, 389.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 156.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 392.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 126.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 125.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 179; Montefiore 2003, pp. 126–127; Service 2004, p. 314; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 128–129.
- ^ Overy 2004, p. 327.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 128, 137.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 347.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 315.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 139.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 314–317.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 139, 154–155, 164–172, 175–176; Service 2004, p. 320; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 139.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 139–140.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 192–193; Service 2004, p. 346; Conquest 2008, p. 24; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 140.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 176–177.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 349.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 391.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 201; Service 2004, p. 349; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 140.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 141, 150.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 350; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 150–151.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 203–204; Service 2004, pp. 350–351; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 150.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 204; Service 2004, pp. 351, 390; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 151.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 151.
- ^ Hockstader, Lee (10 March 1995). "From a ruler's embrace to a life in disgrace". Washington Post (Arq. in WikiWix Archive).
- ^ Service 2004, p. 394.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 230; Service 2004, p. 394; Overy 2004, p. 338; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 174.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 137–138, 147.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 140.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 204.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 151, 159.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 152.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 347–248; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 125, 156–157.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 153, 156–157.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 367.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 245.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 209; Service 2004, p. 369; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 160.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 162.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 157.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 159.
- ^ Harris 2017, pp. 1–5, 16.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 308.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 220–221; Service 2004, pp. 380–381.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 392–393; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 163, 168–169.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 185–186.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 232–233, 236.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 399–400.
- ^ Nekrich 1997, p. 109.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 220; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 166.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 220; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 168, 169.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 221; Roberts 1992, pp. 57–78; Service 2004, p. 399; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 166.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 222; Roberts 1992, pp. 57–78; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 169.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 222; Roberts 2006, p. 43.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 223; Service 2004, pp. 402–403; Wettig 2008, p. 20.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 224.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 224; Service 2004, p. 405.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 228; Service 2004, p. 403; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 172–173.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 279; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 173.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 403; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 173.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 227; Service 2004, pp. 404–405; Wettig 2008, pp. 20–21; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 173.
- ^ Brackman 2001, p. 341; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 173.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 170.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 229; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 170.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 229; Service 2004, p. 405.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 229; Service 2004, p. 406.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 231; Brackman 2001, pp. 341, 343; Roberts 2006, p. 58.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 233; Roberts 2006, p. 63.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 234; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 180.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 410–411; Roberts 2006, p. 82; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 198.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 408–409, 411–412; Roberts 2006, p. 67; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 199–200, 202.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 414–415; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 206–207.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 413.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 420.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 417; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 201–202.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 235; Service 2004, p. 416.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 418.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 417.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 248–249; Service 2004, p. 420; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 214–215.
- ^ Glantz 2001, p. 26.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 421, 424; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 220.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 482; Roberts 2006, p. 90.
- ^ Gellately 2007, p. 391.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 239–240; Roberts 2006, p. 98; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 209.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 241; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 210.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 241–242; Service 2004, p. 521.
- ^ Roberts 2006, p. 132; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 223.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 423.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 422.
- ^ Overy 2004, p. 568.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 211.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 421.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 442–443; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 242–243.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 441.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 442.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 446.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 446–447.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 260; Service 2004, p. 444.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 254; Service 2004, p. 424; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 221–222.
- ^ Roberts 2006, pp. 117–118.
- ^ Roberts 2006, p. 124.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 425.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 426.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 427.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 428; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 225.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 225.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 429; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 226; Journal of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR, 13 March 1943.
- ^ Roberts 2006, p. 155.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 255; Roberts 2006, p. 156; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 227.
- ^ Roberts 2006, p. 159.
- ^ Roberts 2006, p. 163.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 452.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 466.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 317; Service 2004, p. 466.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 458.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 252; Service 2004, p. 460; Khlevniuk 2015.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 456.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 460.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 262; Service 2004, p. 460; Roberts 2006, p. 180; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 229–230.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 462.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 463.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 244, 251; Service 2004, pp. 461, 469; Roberts 2006, p. 185; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 223, 229.
- ^ Roberts 2006, pp. 186–187.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 464–465; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 244.
- ^ Roberts 2006, pp. 194–195.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 469; Roberts 2006, pp. 199–201.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 492.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 258; Service 2004, p. 492; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 232–233.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 233.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 264; Service 2004, p. 465; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 244.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 465–466.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 465–466; Roberts 2006, pp. 241–244.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 471; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 245.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 471–472; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 244.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 473.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 474; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 247.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 479–480.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 265; Service 2004, p. 473; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 234.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 474.
- ^ Glantz 1983.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 476; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 248–249.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 268; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 248.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 267; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 249.
- ^ Roberts 2006, pp. 274–275.
- ^ a b Wettig 2008, pp. 90–91.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 506.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 481.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 484.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 493; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 247.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 480–481.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 479.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 541.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 543–544.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 548.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 485; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 262.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 485.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 493; Roberts 2006, p. 202.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 268.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 482.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 482–483.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 482; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 261.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 500.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 496.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 497.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 497; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 274–278.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 289.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 269; Service 2004, p. 491.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 526; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 268.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 531–532; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 272–273.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 534.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 303.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 534–535; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 282.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 300–301.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 498; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 261.
- ^ Ellman 2000, pp. 611, 618–620.
- ^ Ellman 2000, p. 622; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 261.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 299.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 502–503.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 503.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 487.
- ^ Gaddis 2005, p. 57.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 508.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 508; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 293.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 297.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 502.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 504; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 267.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 504.
- ^ Mazov, Sergei (9 August 2006). "The USSR and the Former Italian Colonies, 1945–50". Cold War History. 3 (3): 49–78. doi:10.1080/14682740312331391618. S2CID 153413935. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 494.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 507; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 281.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 551.
- ^ Lukacs, John (2006). June 1941: Hitler and Stalin. Yale University Press. p. 160. ISBN 0-3001-2364-7.
- ^ Roberts 2002, pp. 96–98.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 264.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 296; Service 2004, pp. 548–549; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 290.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 517.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 483.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 518.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 279; Service 2004, p. 503.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 286; Service 2004, p. 506; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 267.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 511.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 286–287; Service 2004, p. 515.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 515.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 516.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 287.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 507.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 280; Service 2004, p. 507; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 281.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 476.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 512, 513.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 513.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 301; Service 2004, p. 509; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 286.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 509.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 553.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 509; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 287–291.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 552; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 287.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 552; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 294.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 302; Service 2004, p. 553; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 294–295.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 554.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 554; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 295–296.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 555–556; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 296.
- ^ Yegorov, 15 December 2017.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 291.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 285.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 291; Service 2004, p. 577; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 284.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 567; Brackman 2001, pp. 384–385.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 291; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 308–309.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 576–577.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 290.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 286.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 577; Overy 2004, p. 565; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 309.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 571.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 572; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 195.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 309; Etinger 1995, p. 104; Service 2004, p. 576; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 307.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 309; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 307–308.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 308; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 307.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 308.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 304–305.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 560.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 564–565.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 307; Service 2004, pp. 566–567.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 578.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 579; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 306.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 305–306.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 311; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 571–572; Service 2004, pp. 582–584; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 142, 191.
- ^ a b c Conquest 1991, p. 312.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 311–312; Volkogonov 1991, p. 572; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 142.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 313; Volkogonov 1991, p. 574; Service 2004, p. 586; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 313.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 313; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 313–314.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 189.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 587.
- ^ Wines, Michael (5 March 2003). "New Study Supports Idea Stalin Was Poisoned". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 10 May 2022. Retrieved 24 September 2022.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 588.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 588; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 314.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 317.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 588; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 317.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 576; Service 2004, p. 589; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 318.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 319.
- ^ Li 2009, p. 75.
- ^ Evans 1953.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 310.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 586–587.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 312.
- ^ Ra'anan 2006, p. 20.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 591.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 315.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 593.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 316.
- ^ Cohen, Warren I. (2013). "The Korean War and Its Consequences". The New Cambridge History of American Foreign Relations. Vol. 4: Challenges to American Primacy, 1945 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. pp. 58–78. doi:10.1017/CHO9781139032513.006. ISBN 978-1-1390-3251-3.
- ^ Etinger 1995, pp. 120–121; Conquest 1991, p. 314; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 314.
- ^ Rieber 2005, p. 32.
- ^ a b c d Service 2004, p. 9.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. xi.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 336.
- ^ a b Rieber 2005, p. 43.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 67.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 136; Kotkin 2014, p. 205; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 47.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 7.
- ^ McDermott 2006, p. 7.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 92; Kotkin 2014, p. 462.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 93; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 7.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 93.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 216.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 93–94.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 214; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 8.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 8.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 94.
- ^ a b Sandle 1999, p. 211.
- ^ Deutscher 1966, p. 86; Kotkin 2014, pp. 10, 699.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 545.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 92.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 211.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 95; Montefiore 2007, p. 211.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 179–180.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 67.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 531.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 93–94.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 333; Kotkin 2014, p. 586.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 158.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 256; Service 2004, p. 333; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 94.
- ^ Kotkin 2017, p. 7.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 352.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 357.
- ^ Sandle 1999, pp. 208–209.
- ^ a b Sandle 1999, p. 209.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 261.
- ^ Sandle 1999, p. 210.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 98.
- ^ Overy 2004, p. 552.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 99.
- ^ Overy 2004, p. 565.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 310, 579.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 5.
- ^ a b Conquest 1991, p. 1.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 1; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 97.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 97.
- ^ Foltz 2021, pp. 94–97.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, pp. 66–67.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 1; Montefiore 2003, p. 2; Montefiore 2007, p. 42; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 97.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 579.
- ^ Rieber 2005, p. 18.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 85.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 268.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 395.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 183; Volkogonov 1991, p. 5; Kotkin 2017, p. 5.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 37.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 149; Volkogonov 1991, p. 49; Service 2004, p. 334; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 52.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, pp. xx–xxi.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 329.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 21; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 97.
- ^ Kotkin 2017, p. 40. "He stood five feet seven inches, or about 1.7 meters, roughly the same as Napoleon and one inch [2.5 cm] shorter than Hitler, who was 1.73 meters."
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 65.
- ^ Kotkin 2017, p. 4.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 25; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 13–14.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 44.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, pp. 9–10.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 167; Kotkin 2017, p. 1.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 282; Volkogonov 1991, p. 146; Service 2004, pp. 435, 438, 574; Kotkin 2017, p. 1.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 311; Volkogonov 1991, p. 102; Montefiore 2003, pp. 36–37; Service 2004, pp. 497–498.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 102; Service 2004, p. 498.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 60.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 60; Service 2004, p. 525.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 525.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 35, 60.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 331.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 102, 227.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 195; Kotkin 2017, p. 3.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 64.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 191.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 57–58; Kotkin 2014, p. 594.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 102.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 66–67; Service 2004, p. 296.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 215; Montefiore 2003, p. 103; Service 2004, p. 295.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 178.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 572.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. xvi; Volkogonov 1991, p. xxiii; Service 2004, p. 4; Montefiore 2007, p. xxiv.
- ^ a b Montefiore 2007, p. xxiv.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 343.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 8; Service 2004, p. 337.
- ^ Conquest 1991, pp. 193, 274; Volkogonov 1991, p. 63; Service 2004, p. 115; Kotkin 2014, p. 425; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 148.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 42; Montefiore 2007, p. 353; Kotkin 2014, pp. 424, 465, 597.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 115.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 4–5.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 145.
- ^ Bazhanov & Doyle 1990, p. 181.
- ^ Davies, Robert William (1989). Soviet History in the Gorbachev Revolution. Indiana University Press. p. 70. ISBN 978-0-2533-1604-2. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 191.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, pp. 528–600.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 317; Volkogonov 1991, p. xxvi; McDermott 2006, p. 13.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. xvi; Service 2004, p. 18; McDermott 2006, p. 13.
- ^ Rogovin, Vadim Zakharovich (2021). Was There an Alternative? Trotskyism: a Look Back Through the Years. Mehring Books. p. 47. ISBN 978-1-8936-3897-6.
- ^ McDermott 2006, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 42; Kotkin 2014, p. 424.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 424.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 342.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 120; Kotkin 2014, p. 648.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 337.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. 145.
- ^ McCauley 2003, p. 92; Montefiore 2003, pp. 49–50; Kotkin 2014, pp. 117, 465; Kotkin 2017, p. 5.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 41.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 338; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 53.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 318; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 7.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 4; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 7.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 8.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 334.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 258; Montefiore 2007, p. 285.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 4, 344.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 597; Kotkin 2017, p. 6.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 10, 344; Kotkin 2017, p. 5.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 336; Kotkin 2014, p. 736.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 175.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 42.
- ^ a b c d e f Roberts 2022, p. 2.
- ^ McDermott 2006, p. 12.
- ^ Rees, E. A. (15 October 2013). Iron Lazar: A Political Biography of Lazar Kaganovich. Anthem Press. p. 219. ISBN 978-1-7830-8057-1. Archived from the original on 30 June 2023. Retrieved 23 June 2023.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 620.
- ^ a b Montefiore 2007, p. 60.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 96.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 73; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 6.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 6.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, pp. 127, 148.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 131.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 86; Service 2004, p. 9; McDermott 2006, p. 19; Kotkin 2017, pp. 1–2, 5.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 93.
- ^ Bullock 1992, p. 33.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 86; Kotkin 2014, pp. 117, 676.
- ^ McCauley 2003, p. 93; Montefiore 2003, p. 86; Service 2004, p. 560; McDermott 2006, p. 19.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 86.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 127; Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 2–3.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 282; McCauley 2003, p. 90.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 145.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 58, 507; Kotkin 2017, p. 1.
- ^ Kotkin 2017, p. 1.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 283; Service 2004, p. 437.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 522.
- ^ McCauley 2003, p. 90; Service 2004, pp. 437, 522–523; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 5.
- ^ a b Montefiore 2007, p. 24.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 3–4.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, pp. 319, 637.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 55.
- ^ Etinger 1995, p. 103; Montefiore 2007, p. 165.
- ^ Etinger 1995, p. 103; Rappaport 1999, p. 297.
- ^ Pinkus 1984, pp. 107–108; Brackman 2001, p. 390.
- ^ Brent & Naumov 2004, p. 184.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 8.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 567–568.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 77.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 237.
- ^ Pipes, Richard (1998). Three "whys" of the Russian Revolution. Pimlico. pp. 63–65. ISBN 978-0-7126-7362-4. Archived from the original on 13 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ Holmes, Leslie (27 August 2009). Communism: A Very Short Introduction. OUP Oxford. pp. 10–15. ISBN 978-0-1995-5154-5. Archived from the original on 13 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ Trotsky, Leon (1991). The Revolution Betrayed: What is the Soviet Union and where is it Going?. Mehring Books. pp. 85–98. ISBN 978-0-9290-8748-1. Archived from the original on 13 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ Mccauley, Martin (13 September 2013). Stalin and Stalinism: Revised 3rd Edition. Routledge. p. 35. ISBN 978-1-3178-6369-4. Archived from the original on 13 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ Kenez, Peter (13 March 1999). A History of the Soviet Union from the Beginning to the End. Cambridge University Press. p. 77. ISBN 978-0-5213-1198-4. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 49; Fitzpatrick 2015, p. 65.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 49.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 9.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 151.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 112.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 135.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 522; Montefiore 2003, p. 135; Montefiore 2007, p. 368.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 13.
- ^ Bazhanov & Doyle 1990, p. 106.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 73.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 209.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 80; Montefiore 2007, p. 209.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 80.
- ^ McCauley 2003, p. 90.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 5.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 4.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 202.
- ^ Antonov-Ovseenko, Anton (1983). The Time of Stalin: Portrait of a Tyranny. Harper & Row. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-0603-9027-3. Archived from the original on 28 August 2023. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 149; Service 2004, p. 64; Montefiore 2007, p. 167; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 25.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, pp. 150–151; Montefiore 2007, p. 364.
- ^ Suny 2020, p. 559; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 30.
- ^ Гамов, Александр (8 November 2018). "Stalin promised the gendarmes that he would marry his 14-year-old mistress as soon as she became an adult". Kp.ru -. Archived from the original on 13 July 2023. Retrieved 21 May 2023.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, pp. 292–293.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, pp. 298, 300.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 8.
- ^ a b Montefiore 2003, p. 9.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 13; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 255; Kotkin 2017, p. [page needed].
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 12.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 154; Montefiore 2003, p. 16; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 255.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 257, 259–260.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 215; Volkogonov 1991, p. 153; Montefiore 2003, pp. 9, 227; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 256.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 260; Service 2004, p. 521.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, pp. 250, 259.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 260.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, pp. 142–144.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 144.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 521.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 365.
- ^ Khlevniuk 2015, p. 252.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, pp. 365–366.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. 366.
- ^ Greensmith, James (6 April 2023). In the Mind of Stalin. Pen and Sword History. p. 71. ISBN 978-1-3990-6361-6. Archived from the original on 19 July 2023. Retrieved 8 July 2023.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. xi.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 108; Service 2004, p. 5.
- ^ Montefiore 2007, p. xxii.
- ^ a b c McDermott 2006, p. 1.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 3.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 546; Service 2004, p. 3.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 602.
- ^ Wheatcroft 1999.
- ^ Ellman 2002, p. 1164.
- ^ Rogovin, Vadim Zakharovich (1998). 1937: Stalin's Year of Terror. Mehring Books. p. xxviii. ISBN 978-0-9290-8777-1.
- ^ Khrushchev, Nikita Sergeevich; Khrushchev, Serge (2004). Memoirs of Nikita Khrushchev. Penn State Press. p. 156. ISBN 978-0-2710-2861-3. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Cheremukhin et al. 2013; Dower & Markevich 2018, p. 246.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 602; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 190.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 732.
- ^ McCauley 2003, p. 8; Service 2004, p. 52; Montefiore 2007, p. 9; Kotkin 2014, p. xii; Khlevniuk 2015, p. 12.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 194; Volkogonov 1991, p. 31; Service 2004, p. 370.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 77.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 124.
- ^ Montefiore 2003, p. 215.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 4.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. xvii; McDermott 2006, p. 5.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. xviii.
- ^ McDermott 2006, p. 2.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 370.
- ^ McDermott 2006, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 8, 9.
- ^ Kotkin 2014, p. 596.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 182.
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. ix.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 4.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 13.
- ^ a b c Service 2004, p. 6.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. xiii.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 6; Montefiore 2007, p. xxi.
- ^ Sandle 1999, pp. 265–266.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 173.
- ^ Ellman 2002, pp. 1163–1164.
- ^ Chang 2019; Moore 2012.
- ^ Mccauley, Martin (13 September 2013). Stalin and Stalinism: Revised 3rd Edition. Routledge. p. 49. ISBN 978-1-3178-6369-4.
- ^ Getty, Rittersporn & Zemskov 1993, p. 1022.
- ^ Ellman 2002, pp. 1162–1163.
- ^ Getty, Rittersporn & Zemskov 1993, p. 1024.
- ^ Healey 2018, p. 1049: "New studies using declassified Gulag archives have provisionally established a consensus on mortality and 'inhumanity.' The tentative consensus says that once secret records of the Gulag administration in Moscow show a lower death toll than expected from memoir sources, generally between 1.5 and 1.7 million (out of 18 million who passed through) for the years from 1930 to 1953."
- ^ Ellman 2002, pp. 1159–1160.
- ^ Wheatcroft 1996, pp. 1334, 1348; Ellman 2002, p. 1172.
- ^ Davies & Wheatcroft 2004, p. 401.
- ^ Rosefielde 1996.
- ^ Snyder 2010, p. 384; Snyder, 27 January 2011.
- ^ Rogovin, Vadim Z (2021). Was There an Alternative? 1923–1927: Trotskyism: a Look Back Through the Years. Mehring Books. p. 495. ISBN 978-1-8936-3896-9.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 314.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 592.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 314; Volkogonov 1991, pp. 577–579; Service 2004, p. 594.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 594.
- ^ Volkogonov 1991, p. 576; Service 2004, p. 594.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 595.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 315; Service 2004, p. 595.
- ^ Conquest 1991, p. 315.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 596.
- ^ Service 2004, pp. 596–597.
- ^ BBC, 5 June 2018.
- ^ Rutland, 13 June 2019.
- ^ Nemtsova, 17 May 2021; Lentine, 25 June 2022.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 598.
- ^ a b Service 2004, p. 7.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 599.
- ^ Taylor, 15 February 2017; Luhn, 16 April 2019; BBC, 18 April 2019.
- ^ Arkhipov, Ilya (16 April 2019). "Russian Support for Stalin Surges to Record High, Poll Says". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 3 October 2020. Retrieved 8 October 2020.
- ^ "САМЫЕ ВЫДАЮЩИЕСЯ ЛИЧНОСТИ В ИСТОРИИ". levada.ru. 21 June 2021. Archived from the original on 30 June 2021. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- ^ Coynash, 22 June 2021. "The renowned Levada Centre has carried out a survey to find out whom Russians would name as the "ten most outstanding national figures of all time". While nobody received an absolute majority, Soviet dictator Joseph Stalin was very clearly ahead, being named by 39% of the respondents."
- ^ a b Khlevniuk 2015, p. x.
- ^ Service 2004, p. 597.
- ^ Bell, 5 March 2013.
- ^ Masci, 29 June 2017.
- ^ Bakradze et al. 2013.
- ^ The Moscow Times, 2 March 2013.
- ^ Snyder, 26 May 2010.
- ^ "У Запоріжжі підірвали пам'ятник Сталіну" [Stalin Monument Blown Up in Zaporizhzhia] (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 14 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ Ukrayinska Pravda, 4 March 2015.
Bibliography
Academic books and journals
- Bazhanov, Boris; Doyle, David W. (1990). Bazhanov and the Damnation of Stalin. Ohio University Press. ISBN 978-0-5850-7670-6.
- Brackman, Roman (2001). The Secret File of Joseph Stalin: A Hidden Life. Frank Cass Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7146-5050-0.
- Brackman, Roman (2004). The Secret File of Joseph Stalin: A Hidden Life. Frank Cass Publishers.
- Brent, Jonathan; Naumov, Vladimir (2004). Stalin's Last Crime: The Plot Against the Jewish Doctors, 1948–1953. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-0620-1367-5.
- Bullock, Alan (1992). Hitler and Stalin: Parallel Lives. Alfred A. Knopf.
- Chang, Jon K. (8 April 2019). "Ethnic Cleansing and Revisionist Russian and Soviet History". Academic Questions. 32 (2): 270. doi:10.1007/s12129-019-09791-8 (inactive 31 January 2024). S2CID 150711796.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2024 (link) - Conquest, Robert (1991). Stalin: Breaker of Nations. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-1401-6953-9.
- Conquest, Robert (2008). The Great Terror: A Reassessment (fortieth anniversary ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1953-1699-5.
- Davies, Norman (2003) [1972]. White Eagle, Red Star: The Polish-Soviet War 1919–20 and 'the Miracle on the Vistula'. Pimlico. ISBN 978-0-7126-0694-3.
- Davies, Robert; Wheatcroft, Stephen (2004). The Industrialisation of Soviet Russia Volume 5: The Years of Hunger: Soviet Agriculture 1931–1933. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-2302-3855-8.
- Davies, Robert; Wheatcroft, Stephen (2006). "Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33: A Reply to Ellman" (PDF). Europe-Asia Studies. 58 (4): 625–633. doi:10.1080/09668130600652217. JSTOR 20451229. S2CID 145729808. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 June 2019. Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- Deutscher, Isaac (1966). Stalin (revised ed.). Penguin.
- Dović, Marijan; Helgason, Jón Karl, eds. (2019). Great Immortality: Studies on European Cultural Sainthood. National Cultivation of Culture. Vol. 18. ISBN 978-9-0043-9513-8. Archived from the original on 21 November 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- Dower, Paul Castañeda; Markevich, Andrei (May 2018). "Labor Misallocation and Mass Mobilization: Russian Agriculture during the Great War" (PDF). The Review of Economics and Statistics. 100 (2): 245–259. doi:10.1162/REST_a_00726. S2CID 55486912. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 June 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2020.
- Ellman, Michael (2000). "The 1947 Soviet Famine and the Entitlement Approach to Famines". Cambridge Journal of Economics. 24 (5): 603–630. doi:10.1093/cje/24.5.603.
- Ellman, Michael (2002). "Soviet Repression Statistics: Some Comments" (PDF). Europe-Asia Studies. 54 (7): 1151–1172. doi:10.1080/0966813022000017177. S2CID 43510161. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 May 2019. Retrieved 22 September 2018.
- Ellman, Michael (2005). "The Role of Leadership Perceptions and of Intent in the Soviet Famine of 1931–1934" (PDF). Europe-Asia Studies. 57 (6): 823–841. doi:10.1080/09668130500199392. S2CID 13880089. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 February 2009. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
- Ellman, Michael (2007). "Stalin and the Soviet Famine of 1932–33 Revisited". Europe-Asia Studies. 59 (4): 663–693. doi:10.1080/09668130701291899. S2CID 53655536.
- Etinger, Iakov (1995). "The Doctors' Plot: Stalin's Solution to the Jewish Question". In Ro'i, Yaacov (ed.). Jews and Jewish Life in Russia and the Soviet Union. The Cummings Center Series. Frank Cass. pp. 103–124. ISBN 0-7146-4619-9.
- Fainsod, Jerry F.; Hough, Merle (1979). How the Soviet Union is Governed. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-6744-1030-5.
- Foltz, Richard (2021). The Ossetes: Modern-Day Scythians of the Caucasus. Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-0-7556-1845-3. Archived from the original on 18 February 2023. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- Gaddis, John L. (2005). The Cold War: A New History. Penguin Press. ISBN 978-0-1430-3827-6.
- Gellately, Robert (2007). Lenin, Stalin, and Hitler: The Age of Social Catastrophe. Jonathan Cape. ISBN 978-0-2240-6283-1.
- Getty, J. Arch; Rittersporn, Gábor; Zemskov, Viktor (1993). "Victims of the Soviet penal system in the pre-war years: a first approach on the basis of archival evidence" (PDF). American Historical Review. 98 (4): 1017–1049. doi:10.2307/2166597. JSTOR 2166597. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 December 2019. Retrieved 21 September 2018.
- Glantz, David (1983). "August Storm: The Soviet 1945 Strategic Offensive in Manchuria" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 September 2017. Retrieved 1 December 2018.
- Glantz, David (2001). "The Soviet-German War 1941–45 Myths and Realities: A Survey Essay" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 July 2011.
- Cheremukhin, Anton; Golosov, Mikhail; Guriev, Sergei; Tsyvinski, Aleh (2013). Was Stalin Necessary for Russia's Economic Development? (PDF). w19425. National Bureau of Economic Research. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 August 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- Fitzpatrick, Sheila (2015). On Stalin's Team: The Years of Living Dangerously in Soviet Politics. Melbourne University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-7421-7.
- Harris, James (2017). The Great Fear: Stalin's Terror of the 1930s. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1987-9786-9.
- Haslam, Jonathan (1979). "The Comintern and the Origins of the Popular Front 1934–1935". The Historical Journal. 22 (3): 673–691. doi:10.1017/s0018246x00017039. S2CID 159573290.
- Healey, Dan (1 June 2018). "GOLFO ALEXOPOULOS. Illness and Inhumanity in Stalin's Gulag". The American Historical Review. 123 (3): 1049–1051. doi:10.1093/ahr/123.3.1049. Archived from the original on 8 July 2018. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- Himmer, Robert (1986). "On the Origin and Significance of the Name "Stalin"". The Russian Review. 45 (3): 269–286. doi:10.2307/130111. JSTOR 130111.
- Khlevniuk, Oleg V. (2015). Stalin: New Biography of a Dictator. Translated by Nora Seligman Favorov. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-3001-6388-9.
- Kotkin, Stephen (2014). Stalin: Paradoxes of Power, 1878–1928. Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-7139-9944-0.
- Kotkin, Stephen (2017). Stalin: Waiting for Hitler, 1929–1941. Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-7139-9945-7.
- Kuromiya, Hiroaki (2008). "The Soviet Famine of 1932–1933 Reconsidered". Europe-Asia Studies. 60 (4): 663–675. doi:10.1080/09668130801999912. JSTOR 20451530. S2CID 143876370.
- Li, Hua-yu (2009). "Reactions of Chinese Citizens to the Death of Stalin: Internal Communist Party Reports". Journal of Cold War Studies. 11 (2): 70–88. doi:10.1162/jcws.2009.11.2.70. S2CID 57561115. Archived from the original on 24 June 2016. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- McCauley, Martin (2003). Stalin and Stalinism (third ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0-5825-0587-2.
- McDermott, Kevin (1995). "Stalin and the Comintern during the 'Third Period', 1928–33". European History Quarterly. 25 (3): 409–429. doi:10.1177/026569149502500304. S2CID 144922280.
- McDermott, Kevin (2006). Stalin: Revolutionary in an Era of War. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-3337-1122-4.
- Montefiore, Simon Sebag (2003). Stalin: The Court of the Red Tsar. Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-1-8421-2726-1.
- Montefiore, Simon Sebag (2007). Young Stalin. Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-2978-5068-7.
- Moore, Rebekah (2012). "'A Crime Against Humanity Arguably Without Parallel in European History': Genocide and the "Politics" of Victimhood in Western Narratives of the Ukrainian Holodomor". Australian Journal of Politics & History. 58 (3): 367–379. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8497.2012.01641.x.
- Nekrich, Alexander (1997). Pariahs, Partners, Predators: German-Soviet Relations, 1922–1941. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-2311-0676-9.
- Ra'anan, Uri, ed. (2006). Flawed Succession: Russia's Power Transfer Crises. Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0-7391-1403-2. Archived from the original on 1 January 2021. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- Overy, Richard J. (2004). The Dictators: Hitler's Germany and Stalin's Russia. Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-3930-2030-4.
- Pinkus, Benjamin (1984). The Soviet Government and the Jews 1948–1967: A Documented Study. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5212-4713-9.
- Rappaport, Helen (1999). Joseph Stalin: A Biographical Companion. ABC-Clio. ISBN 978-1-5760-7084-0.
- Rieber, Alfred J. (2005). "Stalin as Georgian: The Formative Years". In Davies, Sarah; James Harris (eds.). Stalin: A New History. Cambridge University Press. pp. 18–44. ISBN 978-1-1394-4663-1.
- Roberts, Geoffrey (1992). "The Soviet Decision for a Pact with Nazi Germany". Soviet Studies. 55 (2): 57–78. doi:10.1080/09668139208411994. JSTOR 152247.
- Roberts, Geoffrey (2002). "Stalin, the Pact with Nazi Germany, and the Origins of Postwar Soviet Diplomatic Historiography". Journal of Cold War Studies. 4 (4): 93–103. doi:10.1162/15203970260209527. S2CID 57563511.
- Roberts, Geoffrey (2006). Stalin's Wars: From World War to Cold War, 1939–1953. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-3001-5040-7.
- Roberts, Geoffrey (2022). Stalin's Library: A Dictator and His Books. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-3001-7904-0. Archived from the original on 3 February 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2022.
- Rosefielde, Steven (September 1996). "Stalinism in Post-Communist Perspective: New Evidence on Killings, Forced Labour and Economic Growth in the 1930s". Europe-Asia Studies. 48 (6): 959–987. doi:10.1080/09668139608412393.
- Sandle, Mark (1999). A Short History of Soviet Socialism. UCL Press. doi:10.4324/9780203500279. ISBN 978-1-8572-8355-6.
- Semeraro, David A. S. (2017). Joseph Stalin. Pen & Sword Books. ISBN 978-1-5267-0205-0. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- Service, Robert (2000). Lenin: A Biography. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-3337-2625-9.
- Service, Robert (2004). Stalin: A Biography. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-3337-2627-3.
- Snyder, Timothy (2010). Bloodlands: Europe between Hitler and Stalin. Vintage Books. ISBN 978-1-4070-7550-1.
- Suny, Ronald (2020b). Red Flag Wounded. Verso Books. p. 59. ISBN 978-1-7887-3074-7. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- Suny, R. G. (2020). Stalin: Passage to Revolution. Princeton University Press. excerpt Archived 19 November 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Volkogonov, Dimitri (1991). Stalin: Triumph and Tragedy. Translated by Shukman, Harold. Weidenfeld and Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-2978-1080-3.
- Wettig, Gerhard (2008). Stalin and the Cold War in Europe. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-7425-5542-6.
- Wheatcroft, Stephen (1996). "The Scale and Nature of German and Soviet Repression and Mass Killings, 1930–45" (PDF). Europe-Asia Studies. 48 (8): 1319–1353. doi:10.1080/09668139608412415. JSTOR 152781. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 12 June 2006.
- Wheatcroft, Stephen (1999). "The Great Leap Upwards: Anthropometric Data and Indicators of Crises and Secular Change in Soviet Welfare Levels, 1880–1960". Slavic Review. 58 (1): 27–60. doi:10.2307/2672986. JSTOR 2672986. PMID 22368819. S2CID 43228133.
Magazines, newspapers and websites
- "Joseph Stalin: An Address Given by the Rev. Stanley Evans, M.A., at a Memorial Service for Joseph Stalin at the Church of St. George, Queen Square, London, on March 13th, 1953".
• "[online]". Society of Socialist Clergy and Ministers. 1953. Archived from the original on 11 August 2022. Retrieved 7 June 2022 – via anglicanhistory.org, transcribed by Richard Mammana 2019.
• "[online]". Archived from the original on 21 November 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2022. - Bakradze, Lasha; Gudjov, Lev; Lipman, Maria; Wall, Thomas (1 March 2013). "The Stalin Puzzle: Deciphering Post-Soviet Public Opinion". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Archived from the original on 2 April 2017. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- Bell, Bethany (5 March 2013). "Georgia Divided Over Stalin 'Local Hero' Status in Gori". BBC. Archived from the original on 19 July 2018. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- Coynash, Halya (22 June 2021). "Russians name Stalin as the most 'outstanding' figure of all times". Kharkiv Human Rights Protection Group. Archived from the original on 21 June 2021.
- Lentine, Gina (15 January 2022). "Moscow's Memory Wars: Putin seeks to whitewash Russia's Stalinist past". Atlantic Council. Archived from the original on 25 June 2022. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- Luhn, Alec (16 April 2019). "Record 70 Percent of Russians Say Stalin Played a Positive Role in Their Country's History". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- Masci, David (29 June 2017). "In Russia, Nostalgia for USSR and Positive Feelings about Stalin". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on 29 November 2020. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- Montefiore, Simon Sebag (6 September 2007). "Stalin, his father and the Rabbit". The New Statesman. Archived from the original on 8 August 2022. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- Nemtsova, Anna (17 May 2021). "'The best master': Russia's new Stalin Center evokes pride, revulsion". NBC News. Archived from the original on 25 June 2022. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- "Poll Finds Stalin's Popularity High". The Moscow Times. 2 March 2013. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 20 March 2017.
- Rutland, Peter (13 June 2019). "Perspective – Putin's dangerous campaign to rehabilitate Stalin". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 4 October 2021. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- Snyder, Timothy D. (26 May 2010). "Springtime for Stalin". The New York Review of Books. Archived from the original on 24 October 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- Snyder, Timothy D. (27 January 2011). "Hitler vs. Stalin: Who Was Worse?". The New York Review of Books. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- Taylor, Adam (15 February 2017). "Positive Views of Stalin among Russian Reach 16-year High, Poll Shows". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- "Wall of Grief: Putin Opens First Soviet Victims Memorial". BBC. 5 June 2018. Archived from the original on 5 June 2018. Retrieved 30 October 2017.
- "Why So Many Russian like Dictator Stalin". BBC News. 18 April 2019. Archived from the original on 19 July 2019. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- Yegorov, Oleg (15 December 2017). "Why did the USSR help to create Israel, but then became its foe". Russia Beyond. Archived from the original on 4 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- "Do Stalina pozytyvno stavlyatʹsya menshe 1/5 ukrayintsiv" До Сталіна позитивно ставляться менше 1/5 українців [Less Than 1/5 of Ukrainians Have a Positive Attitude Towards Stalin]. Ukrayinska Pravda (in Ukrainian). 4 March 2015. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- "О присвоении Верховному Главнокомандующему вооруженными силами СССР Сталину И. В. военного звания Маршала Советского Союза" [On the assignment of the military rank of Marshal of the Soviet Union to the Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces of the USSR Stalin I.V.] (PDF). Ведомости Верховного Совета СССР [Journal of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR] (in Russian). 13 March 1943. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 November 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
External links
- Stalin Library (with all 13 volumes of Stalin's works and "volume 14")
- Library of Congress: Revelations from the Russian Archives
- Electronic archive of Stalin's letters and presentations
- Stalin digital archive
- Joseph Stalin Newsreels // Net-Film Newsreels and Documentary Films Archive
- Stalin Biography from Spartacus Educational
- A List of Key Documentary Material on Stalin
- Stalinka: The Digital Library of Staliniana
- Newspaper clippings about Joseph Stalin in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
- CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2024
- Russification
- Joseph Stalin
- Stalinism
- 1878 births
- 1953 deaths
- 20th-century atheists
- Age controversies
- Anti-fascists
- Anti-Asian sentiment
- Anti-Korean sentiment
- Anti-Polish sentiment
- Anti-religious campaign in the Soviet Union
- Anti-revisionists
- Anti-Romanian sentiment
- Anti-Ukrainian sentiment
- Anti-Zionism in the Soviet Union
- Atheists from Georgia (country)
- Bolsheviks
- Burials at the Kremlin Wall Necropolis
- Central Committee of the Communist Party of Ukraine (Soviet Union) members
- Collars of the Order of the White Lion
- Comintern people
- Communism in Russia
- Communists from Georgia (country)
- First convocation members of the Verkhovna Rada of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
- Former Georgian Orthodox Christians
- Generalissimos
- Genocide perpetrators
- Great Purge perpetrators
- Heads of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
- Heads of government of the Soviet Union
- Heroes of Socialist Labour
- Heroes of the Soviet Union
- Holodomor
- Honorary Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences
- Male poets from Georgia (country)
- Marshals of the Soviet Union
- Marxism–Leninism
- Old Bolsheviks
- People from Gori, Georgia
- People from Tiflis Governorate
- People of the Cold War
- People of the Polish–Soviet War
- People of the Russian Civil War
- People of the Russian Revolution
- People of World War II from Georgia (country)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 8th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 9th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 10th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 11th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 12th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 13th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 14th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 15th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 16th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 17th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Orgburo of the 18th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 11th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 12th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 13th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 14th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 15th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 16th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 17th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 18th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Secretariat of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
- Members of the Bureau of the 7th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 8th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 9th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 10th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 11th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 12th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 13th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 14th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 15th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 16th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 17th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Politburo of the 18th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Presidium of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
- Members of the Central Committee of the 6th Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 7th Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 6th Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 7th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 8th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 9th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 10th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 11th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 12th Congress of the Russian Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 13th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 14th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 15th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 16th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 17th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 18th Congress of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks)
- Members of the Central Committee of the 19th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union
- Ministers of defence of the Soviet Union
- Politicians from Georgia (country)
- Politicide perpetrators
- Perpetrators of the Red Terror (Russia)
- Recipients of the Czechoslovak War Cross
- Recipients of the Order of Lenin
- Recipients of the Order of Suvorov, 1st class
- Recipients of the Order of the Red Banner
- Recipients of the Order of Victory
- Revolutionaries from Georgia (country)
- Russian atheism activists
- Russian communist poets
- Russian communist writers
- Russian communists
- Russian exiles
- Russian political writers
- Russian revolutionaries
- Russian Social Democratic Labour Party members
- Signatories of the Treaty on the Creation of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
- Soviet Georgian generals
- Soviet people of World War II
- Time Person of the Year
- Unsolved deaths in Russia
- World War II political leaders
