Classic Mac OS
 | |
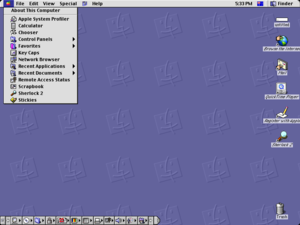 Screenshot of Mac OS 9 | |
| Developer | Apple Computer |
|---|---|
| OS family | Macintosh |
| Working state | Historic, not supported |
| Source model | Closed source |
| Initial release | January 24, 1984[1][2] |
| Final release | 9.2.2 / December 5, 2001[3] |
| Marketing target | Personal computing |
| Platforms | |
| Kernel type | Monolithic for 68k, nanokernel for PowerPC |
| Default user interface | Graphical |
| License | Commercial software, proprietary software |
| Succeeded by | Mac OS X |
| Support status | |
| Historical, unsupported as of February 1, 2002 | |
| Part of a series on |
| Classic Mac OS |
|---|
 |
| Part of a series on |
| macOS |
|---|
Mac OS (originally System Software; retronym: Classic Mac OS[a]) is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept.[4] It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.
Apple released the original Macintosh on January 24, 1984. The first version of the system software, which had no official name, was partially based on the Lisa OS, which Apple previously released for the Lisa computer in 1983. As part of an agreement allowing Xerox to buy shares in Apple at a favorable price, it also used concepts from the Xerox PARC Alto computer, which former Apple CEO Steve Jobs and other Lisa team members had previewed.[1] This operating system consisted of the Macintosh Toolbox ROM and the "System Folder", a set of files that were loaded from disk. The name Macintosh System Software came into use in 1987 with System 5. Apple rebranded the system as Mac OS in 1996, starting officially with version 7.6, due in part to its Macintosh clone program.[5] That program ended after the release of Mac OS 8 in 1997.[6] The last major release of the system was Mac OS 9 in 1999.[7]
Initial versions of the System Software ran one application at a time. With the Macintosh 512K, a system extension called the Switcher was developed to use this additional memory to allow multiple programs to remain loaded. The software of each loaded program used the memory exclusively; only when activated by the Switcher did the program appear, even the Finder's desktop. With the Switcher, the now familiar Clipboard feature allowed copy and paste between the loaded programs across switches including the desktop.
With the introduction of System 5, a cooperative multitasking extension called MultiFinder was added, which allowed content in windows of each program to remain in a layered view over the desktop, and was later integrated into System 7 as part of the operating system along with support for virtual memory. By the mid-1990s, however, contemporary operating systems such as Windows NT, OS/2, NeXTSTEP, BSD, and Linux had all brought pre-emptive multitasking, protected memory, access controls, and multi-user capabilities to desktop computers. The Macintosh's limited memory management and susceptibility to conflicts among extensions that provide additional functionality, such as networking or support for a particular device,[8] led to significant criticism of the operating system, and was a factor in Apple's declining market share at the time.
After two aborted attempts at creating a successor to the Macintosh System Software called Taligent and Copland, and a four-year development effort spearheaded by Steve Jobs's return to Apple in 1997, Apple replaced Mac OS with a new operating system in 2001 named Mac OS X. It retained most of the user interface design elements of the Classic Mac OS, and there was some overlap of application frameworks for compatibility, but the two operating systems otherwise have completely different origins and architectures.[citation needed]
The final updates to Mac OS 9 released in 2001 provided interoperability with Mac OS X. The name "Classic" that now signifies the historical Mac OS as a whole is a reference to the Classic Environment, a compatibility layer that helped ease the transition to Mac OS X (now macOS).[9]
Initial concept
The Macintosh project started in late 1978 with Jef Raskin, who envisioned an easy-to-use, low-cost computer for the average consumer. In September 1979, Raskin began looking for an engineer who could put together a prototype. Bill Atkinson, a member of the Apple Lisa team, introduced Raskin to Burrell Smith, a service technician who had been hired earlier that year.
Apple's concept for the Macintosh deliberately sought to minimize the user's awareness of the operating system. Many basic tasks that required more operating system knowledge on other systems could be accomplished by mouse gestures and graphic controls on a Macintosh. This would differentiate it from its contemporaries such as MS-DOS, which use a command-line interface consisting of terse, abbreviated textual commands.
In January 1981, Steve Jobs completely took over the Macintosh project. Jobs and a number of Apple engineers visited Xerox PARC in December 1979, three months after the Lisa and Macintosh projects had begun. After hearing about the pioneering GUI technology being developed at Xerox PARC from former Xerox employees like Raskin, Jobs negotiated a visit to see the Xerox Alto computer and Smalltalk development tools in exchange for Apple stock options.[10] The final Lisa and Macintosh operating systems use concepts from the Xerox Alto, but many elements of the graphical user interface were created by Apple including the menu bar, pull-down menus, and the concepts of drag and drop and direct manipulation.[11]
Unlike the IBM PC, which uses 8 kB of system ROM for power-on self-test (POST) and basic input/output system (BIOS), the Mac ROM is significantly larger (64 kB) and holds key OS code. Much of the original Mac ROM code was written by Andy Hertzfeld, a member of the original Macintosh team. He was able to conserve precious ROM space by writing routines in assembly language code optimized with "hacks", or clever programming tricks.[12] In addition to the ROM, he also coded the kernel, the Macintosh Toolbox, and some of the desktop accessories (DAs). The icons of the operating system, which represent folders and application software, were designed by Susan Kare, who later designed the icons for Microsoft Windows 3.0. Bruce Horn and Steve Capps wrote the Macintosh Finder, as well as a number of Macintosh system utilities.
Apple aggressively advertised their new machine. After its release, the company bought all 39 pages of advertisement space in the 1984 November/December edition of Newsweek magazine. The Macintosh quickly outsold its more sophisticated but much more expensive predecessor, the Lisa. Apple quickly developed MacWorks, a product that allowed the Lisa to emulate Macintosh system software through System 3, by which time it had been discontinued as the rebranded Macintosh XL. Many of the Lisa's operating system advances would not appear in the Macintosh operating system until System 7 or later.
Architecture
Compatibility
Early versions of Mac OS are compatible only with Motorola 68000-family Macintoshes. As Apple introduced computers with PowerPC hardware, the OS was ported to support this architecture. Mac OS 8.1 is the last version that could run on a 68k processor (the 68040).
In systems prior to PowerPC G3-based systems, significant parts of the system are stored in physical ROM on the motherboard. The initial purpose of this is to avoid having the OS use up most of the 128KiB RAM of the initial Macintosh—the initial ROMs were 64KiB. This architecture also allows for a completely graphical OS interface at the lowest level without the need for a text-only console or command-line mode: boot time errors, such as finding no functioning disk drives, are communicated to the user graphically, usually with an icon or the distinctive Chicago bitmap font and a Chime of Death or a series of beeps. This is in contrast to MS-DOS and CP/M computers of the time, which display such messages in a mono-spaced font on a black background, and require the use of the keyboard rather than a mouse, for input. To provide such niceties at a low level, early Mac OS depends on core system software in ROM on the motherboard, which also ensured that only Apple computers or licensed clones (with the copyright-protected ROMs from Apple) can run Mac OS.
Mac clones
Several computer manufacturers over the years made Macintosh clones that were capable of running Mac OS. From 1995 to 1997, Apple licensed Macintosh ROMs to several companies, notably Power Computing, UMAX and Motorola. These machines normally ran various versions of Classic Mac OS. Steve Jobs ended the clone-licensing program after returning to Apple in 1997.
Support for Macintosh clones was first exhibited in System 7.5.1, which was the first version to include the "Mac OS" logo (a variation on the original Happy Mac startup icon), and Mac OS 7.6 was the first to be named "Mac OS" instead of "System". These changes were made to disassociate the operating system from Apple's own Macintosh models.[13]
File systems
The Macintosh originally used the Macintosh File System (MFS), a flat file system with only one level of folders. This was quickly replaced in 1985 by the Hierarchical File System (HFS), which had a true directory tree. Both file systems are otherwise compatible. An improved file system named HFS Plus ("HFS+" or "Mac OS Extended") was announced in 1997 and implemented in 1998.[14]
Files in most file systems used with DOS, Windows, Unix, or other operating systems have only one "fork". By contrast, MFS and HFS give files two different "forks". The data fork contains the same sort of information as a file in other file systems, such as the text of a document or the bitmaps of an image file. The resource fork contains other structured data such as menu definitions, graphics, sounds, or code segments that would be incorporated into a program's file format on other systems. An executable file might consist only of resources (including code segments) with an empty data fork, while a data file might have only a data fork with no resource fork. A word processor file could contain its text in the data fork and styling information in the resource fork so that an application that does not recognize the styling information can still read the raw text.
On the other hand, these forks would challenge interoperability with different operating systems. In copying or transferring a Mac OS file to a non-Mac system, the default implementations would strip the file of its resource fork. Most data files contained only nonessential information in their resource fork, such as window size and location, but program files would be inoperative without their resources. This necessitated such encoding schemes as BinHex and MacBinary, which allowed a user to encode a dual-forked file into a single stream, or inversely take a single stream so-encoded and reconstitute it into a dual-forked file usable by Mac OS.
Release history
System 1, 2, 3, and 4
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2019) |
As part of Apple's goal of creating a computer with appliance-like simplicity, there is no explicit distinction made between the operating system software and the hardware it runs on. Because of this, early versions of the operating system do not have a distinct name. The software consists of two user-visible files: the System file, and the Finder, an application used for file management that also displays the Desktop. The two files are contained in a folder directory labeled "System Folder", which contains other resource files, like a printer driver, needed to interact with the System.[5] Version numbers of the operating system are based on the version numbers of these two files.
- System 1.0, 1.1, and 2.0 use a flat file system named Macintosh File System (MFS). The Finder provides virtual folders that could be used to organize files, but these folders are not visible from any other application and do not exist on the disk.
- System 2.0 added support for AppleTalk and the newly introduced LaserWriter to use it.
- System 2.1 (Finder 5.0) introduced the Hierarchical File System (HFS) which has real directories. This version was specifically to support the Hard Disk 20 and only implements HFS in RAM; startup and most floppy disks remain MFS 400 K volumes.
- System 3.0 (Finder 5.1) was introduced with the Macintosh Plus, officially implementing HFS, 800K startup drives, support for several new technologies including SCSI and AppleShare, and Trash "bulging" (i.e., when the Trash contains files, it gains a bulged appearance).
- System 4.0 was released with the Macintosh SE and System 4.1 first shipped with the Macintosh II—these new machines required additional support for the first expansion slots, the Apple Desktop Bus (ADB), internal hard drives and, on the Macintosh II, external color displays and the first Motorola 68020 processor. System 4.0 was the first release to support color graphics; previous releases did not support color.[15]
These releases can only run one application at a time, except for desk accessories, though special application shells such as Multi-Mac[16] or Switcher (discussed under MultiFinder) could work around this. Visible changes are best reflected in the version number of the Finder, where major leaps are found between 1.x, 4.x, 5.x, and 6.x.
In the late 1990s, Apple retroactively gave these older releases a single name.
| System Software Release[5] | System Version[5] | Release Date[5] | Finder Version[5] | LaserWriter Version[5] | Release Information[5] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macintosh System Software | 1.0 (.97)[17] | January 24, 1984[1][2] | 1.0 | Initial Release | |
| Macintosh System Software (0.1) | 1.1 | May 1984[1] | 1.1g | Maintenance Release, Added Mountain scene, About box, Clean Up Command | |
| Macintosh System Software (0.3 & 0.5) | 2.0 | April 1985[18] | 4.1 | Finder Update: Introduced "New Folder" and "Shut Down" commands, and installation of a "MiniFinder" application for quickly launching any of the chosen applications
System: Introduced screenshots using ⌘ Command+⇧ Shift+3 | |
| Macintosh System Software[17][19] | 2.1[17] | September 1985[17] | 5.0[19] | Release for Hard Disk 20 support[17][19] | |
| Macintosh System Software (0.7) | 3.0 | January 1986[1] | 5.1 | 1.1[citation needed] | Introduced with Macintosh Plus[1] |
| System Software 1.0 | 3.1 | February 1986[1] | 5.2 | 1.1 | |
| System Software 1.1 | 3.2 | June 1986[20] | 5.3 | 3.1 | Fixed problems with data loss, system crashes; updated Chooser and Calculator.[20] |
| AppleShare 1.0 | 3.3 | January 1987 | 5.4 | AppleShare 1.0 Work Station Installer disk (for the Macintosh 512K) | |
| AppleShare 1.1[21] | 3.3[21] | 1987 | 5.5[21] | AppleShare 1.1 Work Station Installer disk (for the Macintosh 512K)[21] | |
| AppleShare 2.0[21] | 3.4[21] | 1988 | 6.1[21] | AppleShare 2.0 Macintosh 512Ke Work Station Installer disk[21] | |
| System Software 2.0 | 4.0 | January 1987[1] | 5.4 | 3.3 | Release for Macintosh SE. Introduced AppleShare[citation needed] |
| System Software 2.0.1 | 4.1 | March 2, 1987 | 5.5 | 4.0 | Release for Macintosh II. Updated LaserWriter Driver |
System Software 5
Towards the end of 1987, Apple introduced a package titled "Apple Macintosh System Software Update 5.0".[22] For the first time, the Macintosh operating system was offered as a distinct retail product that included four 800K disks and three manuals, at a cost of US$49. The software itself was still freely available through user groups and bulletin board services. While the product box presented this update to the operating system as "version 5.0", this number does not appear in the software itself. Three of the four disks (System Tools 1, System Tools 2 and Utilities 1) are all bootable, and the user can boot off whichever floppy contains the tools the user needs. For instance, System Tools 2 is the only disk with printer drivers, and Utilities 1 is the only disk with Disk First Aid and Apple HD SC Setup. Because the disks are named System Tools, users and the press commonly referred to this version as "System Tools 5.0".
The primary new feature of System 5 is MultiFinder, an extension that lets the system run several programs at once. The system uses a cooperative multitasking model, meaning that time is given to the background applications only when the foreground application yields control. A change in system functions that applications were already calling to handle events make many existing applications share time automatically, as well as being allowed to perform tasks in the background.[22] Users can also choose not to use MultiFinder, thereby using a single application at a time. In 1990 InfoWorld tested four multitasking options for PC and Mac, viewing MultiFinder positively overall, but noting that its presence halved the speed of file transfer and printing compared to the single-tasking System 6 without MultiFinder.[23]
| System Software Release[5] |
Release Date[5] |
System Version[5] |
Software Version[5] | Release Information[5] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finder | MultiFinder | LaserWriter | ||||
| 5.0 | October 1987[24] | 4.2 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | Initial Release |
| 5.1 | November 1987 | 4.3 | 5.1 | Updated LaserWriter Driver and new version of Apple HD SC Setup | ||
System Software 6
System Software 6 (also referred to as "System 6") is a consolidation release of the Macintosh system software, producing a complete, stable, and long-lasting operating system. Two major hardware introductions requiring additional support under System 6 are the 68030 processor and 1.44 MB SuperDrive debuting with the Macintosh IIx and Macintosh SE/30. Later updates include support for the first specialized laptop features with the introduction of the Macintosh Portable. From System 6 forward, the Finder has a unified version number closely matching that of the System, alleviating much of the confusion caused by the often considerable differences between earlier Systems.[25]
| System Version[5] |
Release Date[5] |
Software Version[5] | Release Information[5] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finder | MultiFinder | LaserWriter | |||
| 6.0 | April 1988 | 6.1 | 6.0 | 5.2 | Initial Release |
| 6.0.1 | September 19, 1988 | 6.1.1 | 6.0.1 | Release for Macintosh IIx (1988) | |
| 6.0.2 | Late 1988 | 6.1 | Maintenance Release | ||
| 6.0.3 | March 7, 1989 | 6.0.3 | Release for Macintosh IIcx (1989) | ||
| 6.0.4 | September 20, 1989 | 6.1.4 | 6.0.4 | Release for Macintosh Portable and IIci (1989) | |
| 6.0.5 | March 19, 1990[26] | 6.1.5 | 6.0.5 | Release for Macintosh IIfx (1990) | |
| 6.0.6 | October 15, 1990 | 6.1.6 | 6.0.6 | Not released because of AppleTalk bug[27] | |
| 6.0.7 | October 16, 1990 | 6.1.7 | 6.0.7 | Official release for Macintosh LC, IIsi and Classic (1990) | |
| 6.0.8 | May 13, 1991 | 6.1.8 | 6.0.8 | 7.0 | Updated printing software to match software of System 7.0 |
| 6.0.8L | March 23, 1992 | Limited maintenance release for Pacific customers | |||
System 7/Mac OS 7
On May 13, 1991, System 7 was released. It was a major upgrade over System 6, adding a significant user interface overhaul, new applications, stability improvements and many new features. Its introduction coincides with the release of and provided support for the 68040 Macintosh line. The System 7 era saw numerous changes in the Macintosh platform including a proliferation of Macintosh models, the 68k to Power Macintosh transition as well as the rise of Microsoft Windows, increasing use of computer networking and the explosion in the popularity of the Internet.
One of the most significant features of System 7 is virtual memory support, an essential subsystem anticipated for years, which only exists for previous Systems in a third party extension named Virtual from Connectix.[23] Accompanying this was a move to 32-bit memory addressing, necessary for the ever-increasing amounts of RAM available to the Motorola 68030 CPU, and 68020 CPUs with a 68851 PMMU. This process involves making all of the routines in OS code use the full 32-bits of a pointer as an address—prior systems used the upper 8 bits as flags. This change is known as being "32-bit clean". While System 7 itself is 32-bit clean, many existing machines and thousands of applications were not, so it was some time before the process was completed. To ease the transition, the "Memory" control panel contains a switch to disable this feature, allowing for compatibility with older applications.
Another notable System 7 feature is built-in cooperative multitasking. In System Software 6, this function was optional through the MultiFinder. System 7 also introduced aliases, similar to symbolic links on Unix, shortcuts that were introduced in later versions of Microsoft Windows, and shadows in IBM OS/2. System extensions were enhanced by being moved to their own subfolder; a subfolder in the System Folder was also created for the control panels. In System 7.5, Apple includes the Extensions Manager, a previously third-party program which simplified the process of enabling and disabling extensions.
The Apple menu, home only to desk accessories in System 6, was made more general-purpose: the user could now make often-used folders and applications—or anything else they desired—appear in the menu by placing aliases to them in an "Apple Menu Items" subfolder of the System Folder. System 7 also introduced the following: AppleScript, a scripting language for automating tasks; 32-bit QuickDraw, supporting so-called "true color" imaging, previously available as a system extension; and TrueType, an outline font standard.
The Trash, under System 6 and earlier, empties itself automatically when shutting down the computer—or, if MultiFinder is not running, when launching an application. System 7 reimplements the Trash as a special hidden folder, allowing files to remain in it across reboots until the user deliberately chose the "Empty Trash" command.
System 7.1
System 7.1 is mainly a bugfix release, with a few minor features added. One of the major new features of System 7.1 was moving fonts out of the System file into the Fonts folder in the System Folder. Previously a resource-copying utility such as ResEdit or Font D/A Mover was required for installing fonts. System 7.1 is not only the first Macintosh operating system to cost money (all previous versions were free or sold at the cost of the floppies), but also received a "Pro" sibling (version 7.1.1) with extra features. System 7.1.2 was the first version to support PowerPC-based Macs. System 7.1 also introduces the System Enablers as a method to support new models without updating the actual System file. This leads to extra files inside the system folder (one per new model supported).
System 7.5
System 7.5 introduces a large number of new features, many of which are based on shareware applications that Apple bought and included into the new system.[28] On the newer PowerPC machines, System 7.5 may have stability problems partly due to a new memory manager (which can be turned off),[citation needed] and issues with the handling of errors in the PowerPC code (all PowerPC exceptions map to Type 11). These issues do not affect 68k-architecture machines. System 7.5 is contemporary with Apple's failed Copland effort as well as the release of Windows 95.
Mac OS 7.6
Stability improved in PowerPC-based Macs with Mac OS 7.6, which dropped the "System" moniker as a more trademarkable name was needed in order to license the OS to the growing market of third-party Macintosh clone manufacturers. Mac OS 7.6 required 32-bit-clean ROMs, and so it dropped support for every Mac with a 68000 processor, as well as the Mac II, Mac IIx, Mac IIcx, and Mac SE/30.
| System Version[5] | Release Information[5] |
|---|---|
| System 7.0 | integrated MultiFinder always enabled |
| System 7.0.1 | introduced with LC II and Quadra series |
| System 7.0.1P | |
| System 7 Tuner | update for both 7.0 and 7.0.1 |
| System 7.1 | introduced the Fonts folder |
| System 7.1P | |
| System 7.1P1 | |
| System 7.1P2 | |
| System 7.1P3 | last "P" release with new features |
| System 7.1P4 | |
| System 7.1P5 | |
| System 7.1P6 | |
| System 7.1 Pro | version 7.1.1, combined with PowerTalk, Speech Manager, MacInTalk, Thread Manager |
| System 7.1.2 | Macs equipped with a PowerPC processor |
| System 7.1.2P | only for Performa/LC/Quadra 630 series, very quickly replaced by 7.5 |
| System 7.5 | |
| System 7.5.1 | System 7.5 Update 1.0—the first Macintosh operating system to call itself "Mac OS" |
| System 7.5.2 | Power Macs that use PCI, usable only on these Power Macs and PowerBooks 5300, 190, and Duo 2300 |
| System 7.5.3 | System 7.5 Update 2.0 |
| System 7.5.3L | only for Macintosh clones |
| System 7.5.3 Revision 2 | |
| System 7.5.3 Revision 2.1 | only for Performa 6400/180 and 6400/200 |
| System 7.5.4 | withdrawn within hours of release and replaced by 7.5.5 |
| System 7.5.5 | last to support non-32-bit-clean Macs, including all with less than a 68030 CPU except the Macintosh LC |
| Mac OS 7.6 | name formally changed because of the experimental clone program, although System 7.5.1 and later used the "Mac OS" name on the splash screen |
| Mac OS 7.6.1 | proper PowerPC error handling introduced |
Mac OS 8

Mac OS 8 was released on July 26, 1997, the same month Steve Jobs became the de facto CEO of Apple. It was mainly released to keep the Mac OS moving forward during a difficult time for Apple. Initially planned as Mac OS 7.7, it was renumbered "8" to exploit a legal loophole and accomplish Jobs's goal of terminating third-party manufacturers' licenses to System 7 and shutting down the Macintosh clone market.[29]
Mac OS 8 added a number of features from the abandoned Copland project, while leaving the underlying operating system unchanged. A multi-threaded Finder was included; files could now be copied in the background. The GUI was changed in appearance to a new shaded greyscale look named Platinum, and the ability to change the appearance themes (also known as skins) was added with a new control panel (though Platinum was the only one shipped). This capability was provided by a new "appearance" API layer within the OS, one of the few significant changes.
Apple sold 1.2 million copies of Mac OS 8 in its first two weeks of availability and 3 million within six months. In light of Apple's financial difficulties at the time, there was a large grassroots movement among Mac users to upgrade and "help save Apple". Even some pirate groups refused to redistribute the OS.[30]
Mac OS 8.1
Mac OS 8.1 introduced an updated version of the Hierarchical File System named HFS+, which fixed many of the limitations of the earlier system and continued to be used in macOS up until macOS High Sierra, when it was replaced with the Apple File System. There are some other interface changes such as separating network features from printing, and some improvements to application switching. However, in underlying technical respects, Mac OS 8 is not very different from System 7.
Mac OS 8.5
Mac OS 8.5 focuses on speed and stability, with most 68k code replaced by modern code native to the PowerPC. It also improved the appearance of the user interface, although the theming feature was cut late in development.
| System Version[5] | Release Information[5] |
|---|---|
| Mac OS 8.0 | first version to require a 68040 processor, dropping support for the remainder of the Macintosh II series and other 68030 Macs. It also added support for the PowerPC G3 processor |
| Mac OS 8.1 | last Mac OS release to run on a 68k processor, and it added support for USB on the iMac and added support for the HFS+ filesystem, also called Mac OS Extended |
| Mac OS 8.5 | first version to run solely on a PowerPC processor, and it added built-in support for FireWire. It also added Sherlock and added support for the Power Macintosh G3 |
| Mac OS 8.5.1 | added bug fixes to lessen system crashes |
| Mac OS 8.6 | included a new nanokernel for improved performance and Multiprocessing Services 2.0 support, improved PowerBook battery life, and added support for the PowerPC G4 processor |
Mac OS 9
Mac OS 9, the last major revision of the Classic Mac OS, was released on October 23, 1999.[7] It is generally a steady evolution from Mac OS 8. Early development releases of Mac OS 9 were numbered 8.7.
Mac OS 9 added improved support for AirPort wireless networking. It introduced an early implementation of multi-user support. Though not a true multi-user operating system, Mac OS 9 does allow multiple desktop users to have their own data and system settings. An improved Sherlock search engine added several new search plug-ins. Mac OS 9 also provides a much improved memory implementation and management. AppleScript was improved to allow TCP/IP and networking control. Mac OS 9 also makes the first use of the centralized Apple Software Update to find and install OS and hardware updates.
Other new features included its on-the-fly file encryption software with code signing and Keychain technologies, Remote Networking and File Server packages, and much improved list of USB drivers.
Mac OS 9 also added some transitional technologies to help application developers adopt some Mac OS X features before the introduction of the new OS to the public, to help ease the transition. These included new APIs for the file system and the bundling of the Carbon library that apps could link against instead of the traditional API libraries—apps that were adapted to do this could be run natively on Mac OS X as well. Other changes were made beginning with the Mac OS 9.1 update to allow it to be launched in the Classic Environment within Mac OS X.
The final update to the Classic Mac OS was version 9.2.2, released on December 5, 2001.[31]
| System Version[5] | Release Information[5] |
|---|---|
| Mac OS 9.0 | initial retail version of Mac OS 9 |
| Mac OS 9.0.2 | |
| Mac OS 9.0.3 | |
| Mac OS 9.0.4 | |
| Mac OS 9.1 | included with Mac OS X 10.0 |
| Mac OS 9.2 | update for improved Mac OS X compatibility |
| Mac OS 9.2.1 | |
| Mac OS 9.2.2 | final release of Classic Mac OS |
Transition to Mac OS X

macOS (originally "Mac OS X" and then "OS X")[32] is Apple's current Mac operating system that officially succeeded the Classic Mac OS in 2001. Although it was originally marketed as simply "version 10" of Mac OS, it has a history that is largely independent of the earlier Mac OS releases.
The macOS architectural legacy is the successor to Mac OS 9 and the Classic Mac OS legacy. However, unlike the Classic Mac OS, it is a Unix-based operating system[33] built on NeXTSTEP and technology developed at NeXT from the late 1980s until early 1997, when Apple purchased the company, and its CEO Steve Jobs returned to Apple.[34] macOS also makes use of the BSD codebase and the XNU kernel,[35] and its core set of components is based upon Apple's open source Darwin operating system.
An early version of the operating system, Mac OS X Server 1.0, was released in 1999. It retains the "Platinum" appearance from the Classic Mac OS and even resembles OPENSTEP in places, with the first version to arrive with the new Aqua user interface. The first consumer version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released on March 24, 2001, supporting the new Aqua user interface. Mac OS X was renamed "OS X" in 2011 and "macOS" in 2016.
Users of the Classic Mac OS generally upgraded to Mac OS X, but it was criticized in its early years as more difficult and less user-friendly than the original Mac OS, for the lack of certain features that had not yet been reimplemented in the new OS, for being slower on the same hardware (especially older hardware), and for incompatibilities with the older OS.[36] Because drivers (for printers, scanners, tablets, etc.) written for the older Mac OS were not compatible with Mac OS X, inconsistent program support with the Classic Environment program used to run the older operating system's programs on Mac OS X, and the lack of Mac OS X support for older Apple computers before late 1997; some Macintosh users continued using the older Classic Mac OS for a few years after the original release of Mac OS X. Steve Jobs encouraged people to upgrade to Mac OS X by staging a mock funeral for Mac OS 9 at WWDC 2002.[37]
Classic
PowerPC versions of Mac OS X up to and including Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger include a compatibility layer for running older Mac applications, the Classic Environment. Originally codenamed the "blue box", the environment runs a nearly complete Mac OS 9 operating system, version 9.1 or later, as a Mac OS X application. This allows applications that have not been ported to the Carbon API to run on Mac OS X. This is reasonably seamless, though "classic" applications retain their original Mac OS 9 appearance and do not gain the Mac OS X "Aqua" appearance.
Early New World ROM PowerPC-based Macs shipped with Mac OS 9.2 as well as Mac OS X. Mac OS 9.2 had to be installed by the user—it was not installed by default on hardware revisions released after Mac OS X 10.4. Most well-written "classic" Mac OS applications function properly under this environment, but compatibility is assured only if the software was written to be unaware of the actual hardware and to interact solely with the operating system. The Classic Environment is not available on Intel-based Mac systems or the latest Apple silicon Macs due to the incompatibility of Mac OS 9 with both the x86 and ARM hardware.
Emulation
68k emulators
Third-party Macintosh emulators, such as vMac, Basilisk II, and Executor, eventually made it possible to run the Classic Mac OS on Intel-based PCs. These emulators were restricted to emulating the 68k series of processors, and as such most could not run versions of the Mac OS that succeeded 8.1, which required PowerPC processors. Most also required a Mac ROM image or a hardware interface supporting a real Mac ROM chip; those requiring an image are of dubious legal standing as the ROM image may infringe on Apple's intellectual property.
A notable exception was the Executor commercial software product from Abacus Research & Development, the only product that used 100% reverse-engineered code without the use of Apple technology. It ran extremely quickly but never achieved more than a minor subset of functionality. Few programs were completely compatible and many were extremely crash-prone if they ran at all. Executor filled a niche market for porting 68k Mac applications to x86 platforms; development ceased in 2002 and the source code was released by the author in late 2008.[38] Emulators using Mac ROM images offered near complete Mac OS compatibility, and later versions offered excellent performance as modern x86 processor performance increased exponentially.
Apple included its own Mac 68k emulator that ran seamlessly on all PowerPC-based versions of the Classic Mac OS.[39] Apple also sold a Mac 68k emulator for SPARC-based (Solaris) and PA-RISC based (HP-UX) systems called Macintosh Application Environment (MAE), which could run variants of System 7.x inside an X11 window.
PowerPC emulators
As of 2021 the most capable PowerPC emulator is QEMU[40] In comparison with 68k-emulator development, PowerPC emulation is more complex and requires more CPU power. The emulator is capable of running Classic Mac OS and OS X at full speed with networking and sound in most cases.[41] QEMU has official support for Classic Mac OS version 9.0 through 9.2 and Mac OS X 10.0 up to and including 10.5.[42] QEMU has several advantages over other PowerPC emulators namely supporting a wide range of platforms from Linux to Mac and Windows on current CPU architectures.[42]
Another PowerPC emulator is SheepShaver, which has been around since 1998 for BeOS on the PowerPC platform, but in 2002 was open-sourced, and efforts began to port it to other platforms. Originally it was not designed for use on x86 platforms and required an actual PowerPC processor present in the machine it was running on similar to a hypervisor. Although it provides PowerPC processor support, it can run only up to Mac OS 9.0.4 because it does not emulate a memory management unit.
Other examples include ShapeShifter (by the same developer that created SheepShaver), Fusion, PearPC and iFusion. The latter ran Classic Mac OS with a PowerPC "coprocessor" accelerator card. Using this method has been said to equal or better the speed of a Macintosh with the same processor, especially with respect to the 68k series due to real Macs running in MMU trap mode, hampering performance.[citation needed]
Apple's initial version of Rosetta is a PowerPC emulator allowing Intel-based Macs to run PowerPC Mac OS X applications, but is unable to run non-Carbon Classic Mac OS (9.2.2 or earlier) applications.[43] Rosetta was available for all Intel releases of OS X until version 10.7 Lion.
Timeline
| Timeline of Mac operating systems |
|---|
 |
See also
- List of Apple operating systems
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of the graphical user interface
- Inside Macintosh
- Apple Computer, Inc. v. Microsoft Corp.
- List of old Macintosh software
Notes
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Linzmayer, Owen W. (2004). Apple Confidential 2.0. No Starch Press. Archived from the original on November 13, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ a b "The Macintosh Product Introduction Plan". Stanford University Libraries & Academic Information Resources. Archived from the original on July 21, 2010.
- ^ "Mac OS 9.2.2 Document and Software". Apple Computer. December 5, 2001. Archived from the original on April 21, 2006. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
- ^ Morgenstern, David. "Useful command line tips for programmers and Mac managers". ZDNet. Archived from the original on July 28, 2020. Retrieved October 13, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w "Macintosh: System Software Version History". Apple Computer. August 7, 2001. Archived from the original on March 10, 2014. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
- ^ Gruman, Galen (November 1997). "Why Apple Pulled the Plug". Macworld. Vol. 14, no. 11. pp. 31–36.
- ^ a b "October 23, 1999: Mac OS 9 Released". AppleMatters.com. Archived from the original on October 28, 2009. Retrieved November 28, 2009.
- ^ Hertzfeld, Andy, folklore.org: The Original Macintosh: Mea Culpa, archived from the original on June 19, 2010, retrieved May 10, 2010
- ^ "A Brief History of the Classic Mac OS – Low End Mac". 2012-07-26. Archived from the original on October 5, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ Mike Tuck (2001-08-12). "The Real History of the GUI". Archived from the original on 2022-01-03. Retrieved July 23, 2020.
- ^ Bruce Horn. "On Xerox, Apple and Progress". Archived from the original on August 26, 2009. Retrieved September 1, 2009.
- ^ "Folklore.org: We're Not Hackers!". www.folklore.org. Archived from the original on September 27, 2016. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ^ "System 7.5 and Mac OS 7.6: The Beginning and End of an Era". 2014-06-27. Archived from the original on September 24, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
Mac OS 7.6 deserves some special mention. The most obvious difference is the name change; this was for the Mac clone manufacturers, who weren't making Macintoshes but "Mac OS Computers".
- ^ "New Mac OS Extended Format (HFS+) Available". Apple Developer News. 1997. Archived from the original on May 12, 2008. Retrieved March 28, 2007.
- ^ Goodin, Sue; Wilson, Dave. "Programming the New Macs". MacTech. 3 (5). Archived from the original on 24 June 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2022.
- ^ Josh Burker (2002). "Multi-Mac". Archived from the original on August 22, 2016. Retrieved December 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Kottwitz, Randal L. (January 1, 1986). The Power User's Manual. New York: MacUser Publications, Inc. p. 11. ISBN 978-0961746209.
- ^ "Mac GUI". Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ a b c "Hard Disk 20: Boot From HD20 Locks Up HD20 and Macintosh". Apple Inc. November 10, 1988. Archived from the original on January 22, 2022. Retrieved January 21, 2022.; Denny, Bob (November 1985). "Programming for HFS Compatibility". MacTech Magazine. 2 (1). Westlake Village, CA: 8. Archived from the original on May 12, 2008. Retrieved May 2, 2008.
- ^ a b "Mac GUI". Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "System Software: Configs for Mac 128K, XL, 512, & 512KE (7/94)". Apple Inc. August 3, 1994. Archived from the original on February 24, 2008. Retrieved May 2, 2008.
- ^ a b Wiggins, Robert (March 1998). "All Systems Go - System Update 5.0". MacUser. Martin Mazner. pp. 126–138.
- ^ a b "Orchestrating applications". InfoWorld. September 24, 1990. p. 83. Archived from the original on March 25, 2021. Retrieved March 8, 2019.
- ^ "The Early Mac OS". Applemuseum.bott.org. Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- ^ "Apple Macintosh before System 7". Archived from the original on November 21, 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ "Mac GUI". Archived from the original on July 14, 2011. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ^ "System 6.0.7 Fixed Two System 6.0.6 Problems". Support.apple.com. February 18, 2012. Archived from the original on August 10, 2014. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- ^ Ean Houts (1994-09-05). "QuickDraw GX is the big draw for System 7.5". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on 2021-10-20. Retrieved 2016-10-27.
Apple has added a few features to spruce up the interface in System 7.5, although these have previously been available as utilities or shareware for quite some time.
; Wood, Steve (June 18, 1999). "Busman's Holiday: Disappearing Software". Archived from the original on March 27, 2012. - ^ Beale, Steven (October 1997). "Mac OS 8 Ships with No License Deal". Macworld. Vol. 14, no. 10. pp. 34–36.
- ^ Jeff Walsh (1997-07-28). "Latest Mac OS pleases end-users". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on 2022-01-21. Retrieved 2020-10-30.; "Where do you want to pirate today?". Forbes. August 8, 1997. Archived from the original on August 27, 2017. Retrieved August 25, 2017.
the latest word out in the Macwarez scene is that pirates shouldn't copy Apple's OS8—Mac's latest operating system—they should buy it, since Apple so desperately needs the money.
- ^ "Mac OS 9.2.2 Document and Software". Apple Inc. December 5, 2001. Archived from the original on April 21, 2006. Retrieved February 23, 2017.
- ^ "What is an operating system (OS)?". Apple, Inc. July 15, 2004. Archived from the original on July 22, 2010. Retrieved September 6, 2014.
- ^ "Mac OS X and Unix – Apple" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 30, 2009. Retrieved February 5, 2016.
- ^ Apple Computer (December 20, 1996). "Apple Computer, Inc. Agrees to Acquire NeXT Software Inc". Archived from the original on January 16, 1999. Retrieved February 23, 2017.
- ^ "Mac OS X: What is BSD?". Archived from the original on February 19, 2013. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "OS X 10.1". 2001-10-15. Archived from the original on January 19, 2012. Retrieved June 14, 2017.
- ^ "Jobs: OS 9 is Dead, Long Live OS X – Macworld". May 2002. Archived from the original on September 24, 2016. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "Executor source code". GitHub. 2018-12-08. Archived from the original on January 2, 2018. Retrieved September 23, 2016.
- ^ "The 68LC040 Emulator (IM: PS)". Apple Developer. 1996-07-03. Archived from the original on 2022-01-21. Retrieved 2021-12-26.
- ^ "Why emulation of PowerPC Macs was underwhelming". Reddit.com. Reddit. September 4, 2018. Archived from the original on November 14, 2021. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- ^ "Running Qemu-system-ppc with Mac OS/OSX guests in macOS". emaculation.com. emaculation. January 10, 2021. Archived from the original on December 30, 2021. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- ^ a b "Documentation/Platforms/PowerPC". wiki.qemu.org. February 27, 2021. Archived from the original on December 20, 2021. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- ^ "What Can Be Translated?" (PDF). Universal Binary Programming Guidelines, Second Edition. Apple. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 3, 2012. Retrieved September 5, 2011.
External links
- Apple Discussions: Classic Mac OS – Apple's official forum for Classic Mac OS
- The Real History of the GUI – An article about the history of GUIs
- Apple Macintosh before System 7 Archived 2021-11-18 at the Wayback Machine – A comprehensive guide to Mac OS releases prior to System 7
- Folklore.org – A site of anecdotes shared by the creators of the first Macintosh
- The Vintage Mac Museum – Information on Macintosh systems from System 1 to System 7
- Macintosh System 1 in your browser – A web-based simulator
- Macintosh System 7 in your browser – A web-based simulator
- BYTE Magazine September 1986 – A feature on Amiga vs. Macintosh
