Mibolerone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cheque Drops, Matenon |
| Other names | U-10997; CDB-904; Dimethylnandrolone; Dimethylnortestosterone;[1] DMNT; 7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nortestosterone; 7α,17α-Dimethylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Progestogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.951 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.458 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
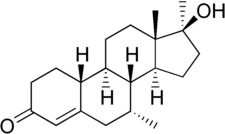
Mibolerone, also known as dimethylnortestosterone (DMNT) and sold under the brand names Cheque Drops and Matenon, is a synthetic, orally active, and extremely potent anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) derivative which was marketed by Upjohn for use as a veterinary drug.[3][4][5] It was indicated specifically as an oral treatment for prevention of estrus (heat) in adult female dogs.[3]
Side effects
[edit]Pharmacology
[edit]Pharmacodynamics
[edit]Mibolerone has both higher affinity and greater selectivity for the androgen receptor (AR) than does the related potent AAS metribolone (17α-methyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone),[6][7] although potent and significant progestogenic activity remains present.[8] However, another study found that mibolerone and metribolone had similar affinity for the progesterone receptor (PR) but that mibolerone only had around half the affinity of metribolone for the AR.[9]
| Compound | Chemical name | PR | AR | ER | GR | MR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | T | 1.0 | 100 | <0.1 | 0.17 | 0.9 | ||
| Nandrolone | 19-NT | 20 | 154 | <0.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 | ||
| Trenbolone | ∆9,11-19-NT | 74 | 197 | <0.1 | 2.9 | 1.33 | ||
| Trestolone | 7α-Me-19-NT | 50–75 | 100–125 | ? | <1 | ? | ||
| Normethandrone | 17α-Me-19-NT | 100 | 146 | <0.1 | 1.5 | 0.6 | ||
| Metribolone | ∆9,11-17α-Me-19-NT | 208 | 204 | <0.1 | 26 | 18 | ||
| Mibolerone | 7α,17α-DiMe-19-NT | 214 | 108 | <0.1 | 1.4 | 2.1 | ||
| Dimethyltrienolone | ∆9,11-7α,17α-DiMe-19-NT | 306 | 180 | 0.1 | 22 | 52 | ||
| Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were progesterone for the PR, testosterone for the AR, estradiol for the ER, DEXA for the GR, and aldosterone for the MR. | ||||||||
Chemistry
[edit]Mibolerone, also known as 7α,17α-dimethyl-19-nortestosterone (DMNT) or as 7α,17α-dimethylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one,[8] is a synthetic estrane steroid and a 17α-alkylated derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). It is the 17α-methyl derivative of trestolone (7α-methyl-19-nortestosterone; MENT).[8] Other related AAS include metribolone (17α-methyl-δ9,11-19-nortestosterone) and dimethyltrienolone (7α,17α-dimethyl-δ9,11-19-nortestosterone).
Synthesis
[edit]Nandrolone (1) appears to be used to make mibolerone. For comparison, also see bolasterone and calusterone. The first step involves extending the conjugation of the enone function by an additional double bond. Chloranil (tetrachloroquinone) is the forerunner of dichlorodicyanoquinone (DDQ), a reagent used extensively for introducing additional unsaturation in the progestin and corticoid series.

In the case at hand, heating acetate (1) with chloranil gives the conjugated dienone (2), and reaction of that compound with methylmagnesium bromide in the presence of cuprous chloride leads to addition of the methyl group to position 7 at the end of the conjugated system (3). The stereochemistry of the product again illustrates the preference for additions from the backside. The alcohol at C17 is then oxidized to a ketone (4). Enamines are commonly used to activate adjacent functions; they are also not infrequently used, as in this case, as protecting groups. Thus, reaction of the intermediate with pyrrolidine gives dienamine (5). This transformation emphasizes the clear difference in reactivity between ketones at C7 and C17. A second methyl Grignard addition gives the corresponding 17α-methyl derivative. Hydrolysis of the enamine function then affords mibolerone (6).
The same structure of 3 and 4 also containing an 11β-fluoro group has also been described in the patent literature.[12]
History
[edit]Mibolerone was first synthesized in 1963.[13][5]
Society and culture
[edit]Generic names
[edit]Mibolerone is the generic name of the drug and its INN, USAN, and BAN.[3][4] It is also known as dimethylnortestosterone (DMNT) and by its former developmental code name U-10997.[3][4]
Brand names
[edit]Mibolerone has been marketed under the brand names Cheque Drops and Matenon.[4][3][5]
References
[edit]- ^ Morton IK, Hall JM (31 October 1999). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 181–. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-15.
- ^ a b c d e Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 822–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b c d Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 689–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b c William Llewellyn (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 395–. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ^ Murthy LR, Johnson MP, Rowley DR, Young CY, Scardino PT, Tindall DJ (1986). "Characterization of steroid receptors in human prostate using mibolerone". Prostate. 8 (3): 241–53. doi:10.1002/pros.2990080305. PMID 2422638. S2CID 43768386.
- ^ Schilling K, Liao S (1984). "The use of radioactive 7 alpha, 17 alpha-dimethyl-19-nortestosterone (mibolerone) in the assay of androgen receptors". Prostate. 5 (6): 581–8. doi:10.1002/pros.2990050603. PMID 6333679. S2CID 86370224.
- ^ a b c Markiewicz L, Gurpide E (1997). "Estrogenic and progestagenic activities of physiologic and synthetic androgens, as measured by in vitro bioassays". Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 19 (4): 215–22. PMID 9228646.
- ^ Loughney DA, Schwender CF (1992). "A comparison of progestin and androgen receptor binding using the CoMFA technique". J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 6 (6): 569–81. Bibcode:1992JCAMD...6..569L. doi:10.1007/bf00126215. PMID 1291626. S2CID 22004130.
- ^ Delettré J, Mornon JP, Lepicard G, Ojasoo T, Raynaud JP (January 1980). "Steroid flexibility and receptor specificity". J. Steroid Biochem. 13 (1): 45–59. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(80)90112-0. PMID 7382482.
- ^ Ojasoo T, Delettré J, Mornon JP, Turpin-VanDycke C, Raynaud JP (1987). "Towards the mapping of the progesterone and androgen receptors". J. Steroid Biochem. 27 (1–3): 255–69. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(87)90317-7. PMID 3695484.
- ^ U.S. patent 7,361,645 (2008 to Bayer Schering Pharma Ag).
- ^ Schänzer W (1996). "Metabolism of anabolic androgenic steroids". Clin. Chem. 42 (7): 1001–20. doi:10.1093/clinchem/42.7.1001. PMID 8674183.
External links
[edit]- Cheque Drops (mibolerone) - William Llewellyn's Anabolic.org Archived 2016-07-26 at the Wayback Machine
