Ethinamate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.355 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 167.205 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ethinamate (Valamin, Valmid) is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependency.
Ethinamate has been replaced by other medicines (particularly benzodiazepines), and it is not available in the Netherlands, the United States or Canada.
Chemistry
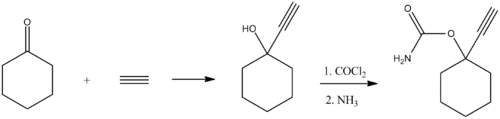
Ethinamate (1-ethynylcyclohexanone carbamate) is synthesized by combining acetylene with cyclohexanone and then transforming the resulting carbinol into a carbamate by the subsequent reaction with phosgene, and later with ammonia. Some lithium metal or similar is used to make the acetylene react with the cyclohexanone in the first step.[1][2]
References
- ^ H. Pfeiffer, K. Junkman, U.S. patent 2,816,910 (1957)
- ^ H. Emde, W. Grimme, DE 1021843 (1953)