Political colour
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|

Political colours are colours used to represent a political party, either officially or unofficially. Parties in different countries with similar ideologies sometimes use similar colours. For example, the colour red symbolises left-wing ideologies in many countries (cf. Red Flag, Red Army, Red Scare). However, the political associations of a given colour vary from country to country; for example, red is also the colour associated with the conservative Republican Party in the United States. Politicians making public appearances will often identify themselves by wearing rosettes, flowers or ties in the colour of their political party.
Black
- Black is primarily associated with anarchism (see anarchist symbolism), fascism (see blackshirts), and jihadism (see Black Standard).
- Anti-clerical parties in the late 19th and early 20th centuries sometimes used the colour black in reference to the officials of the Catholic Church, because the cassock is usually black.
- In Germany and Austria, black is the colour historically associated with Christian-democratic parties, such as the CDU and Austrian People's Party.
- In Greece, black is the colour of the Golden Dawn, a far-right political party.
- In Italy, black is the colour of fascism, because it was the official colour of the National Fascist Party. As a result, modern Italian parties would not use black as their political colour.
- In the Islamic world, black flags (often with a white shahadah) are sometimes used by jihadist groups. Black was the colour of the Abbasid caliphate. It is also commonly used by Shia Muslims, as it is also associated with mourning the death of Hussein ibn Ali. It is now known as the flag colour of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant.
- In Russia, black represented monarchism and nationalist movements such as the Black Hundreds before their defeat at the hands of the communists.
Blue
Blue is usually associated with conservative parties, originating from its use by the Tory party (the predecessor of the Conservative Party) in the United Kingdom.
- The field of the flag of the United Nations is light blue, chosen to represent peace and hope. It has given rise to the term bluewashing.
- In Austria, blue is the colour of the right-wing populist Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ).
- In Australia, blue is the colour of the Liberal Party-led Coalition, which is generally socially conservative but economically liberal in its policies and politics.
- In Belize, blue is the color of social-democratic People's United Party.
- In Belgium, blue is associated with liberalism, used both by the Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats as the Reformist Movement.
- In Bolivia is the color of the left-wing Movement for Socialism.
- In Canada, in federal-level politics, the official colour for the Conservative Party of Canada is blue, while in the province of Québec, light blue is associated with nationalist and secessionist movements (in reference to the province's prominently blue flag).
- In Costa Rica is the color normally associated with the Social Christian Unity Party, alongside red.
- In Ethiopia, blue is the colour of Semayawi Party Ethiopia. It represents Hope Unity and Peace. Semayawi is an Amharic word meaning blue.
- In Germany, blue is the colour of CSU. The right-wing populist party AfD also uses the colour blue.
- In India, blue is associated with the Dalit movement.[1]
- In Ireland, blue is associated with the conservative Fine Gael party, known colloquially as "The Blueshirts" in reference to their roots in the right wing National Guard of the 1930s.
- Two parties in Japan use blue; democratic socialist Social Democratic Party and social-liberal Democratic Party.
- The colour blue, normally of a lighter shade, is of prime significance in Judaism. The Flag of Israel features two blue horizontal stripes and a blue Star of David. See also tekhelet and Zionism. The colour is also strongly identified with the right wing Likud party.
- In Lebanon, blue is the colour for the Future Movement.
- In Malta, blue is colour of the Nationalist Party.
- In Paraguay, blue is the color of the Radical Liberal Party, one of the country's historical parties.
- In Romania, blue is generally associated with center-right or right-wing parties and a number of such parties use the color officially, such the National Liberal Party, the People's Movement Party, the Alliance of Liberals and Democrats, the National Democratic Party, the New Republic, M10, as well as the now-defunct Conservative Party.
- In South Africa, blue is usually associated with liberal political parties, the most popular being the Democratic Alliance, the largest opposition party. The colour blue was also used by the United Party, from which the Progressive Party (the most senior ancestor of the Democratic Alliance) split in 1959.
- In South Korea, blue now represents the center-left liberal Democratic parties since 2014. Before 2012 blue represented the conservative parties.
- Turquoise, is used to represent Turkic peoples and Turkic heritage. It is also the colour of neo-Ottomanism represented by the AKP as a contrast to the republican Red represented by Kemalists.[citation needed]
- In Taiwan, blue represents Kuomintang (KMT), the largest conservative party. Blue refers to KMT and their allies Pan-blue coalition.
- In the United States, since 2000, the mass media have associated blue with the Democratic Party. In 2010, the party unveiled a blue official logo.[2] (See Red states and blue states.) In the United States, blue is also often associated with organized labor, since it represents "blue collar" workers (see, for instance, the Blue-green alliance).
- Opposite in Puerto Rico, the conservative New Progressive Party uses blue.
- Also use in Venezuela to represent the Democratic Unity Roundtable, the large multi-ideological coalition of parties in opposition, probably as a counterpart to PSUV's red.
Brown
- The Marijuana Party of Canada uses the colour brown.
- Brown has been associated with Nazism, because the Sturmabteilung (SA) were called "brownshirts." In Europe and elsewhere, the colour brown is sometimes used to refer to fascists in general.[citation needed]
- Brown is sometimes used to describe the opposite of green parties, that is, to describe parties that care little about pollution.[3]
Buff
Buff was the colour of the Whig faction in British politics from the early 18th century until the middle of the 19th century. As such it is sometimes used to represent the current political left (in opposition to blue, which represented the Tories and then the Conservatives and political right.)
Grey
- Grey is sometimes used by parties that represent the interests of pensioners and senior citizens, such as "The Greys" in Germany.
- Grey can also be used to refer to reactionary independence or secessionist movements, due to its association with the Confederate States of America.
- Grey is often used to represent Independent politicians.
- Grey was the Colour of völkisch Groups in Weimar Germany.
- Grey is the color of the Anti-Corruption Party in Honduras.
Green
Green is notably the colour for both environmentalist and Islamic political parties and movements.
- Fern Green is occasionally used by political organizations and groups who advocate the legalization of Medicinal use of Marijuana.
- Sea green was used as a symbol by members of the Levellers in 17th century Britain; for this reason, it is occasionally used to represent radical liberalism.
- Green has sometimes also been linked to agrarian movements, such as the Populist Party in the US in the 1890s, and the current-day Nordic Agrarian parties, as well as the National Party of Australia, a conservative party traditionally representing regional and agricultural interests.
- In Britain of the 1930s, the National Labour Organisation used green.
- In Costa Rica, green is the color of the social democratic National Liberation Party.
- In Ecuador is associated with the socialist coalition PAIS Alliance.
- In Europe, green represents European Federalism, particularly in the Federalist Flag which shows an elongated green letter 'E'.
- In Greece, green is the colour of the Panhellenic Socialist Movement, a social democratic party. Likewise it is used by the Greek Cypriot social democrats, EDEK.
- In Honduras is the color of the Christian Democratic Party.
- In Iran, green has been used by the Iranian Green Movement, a political movement that arose after the 2009 Iranian presidential election, in which protesters demanded the removal of Mahmoud Ahmadinejad from office.
- Irish Nationalist and Irish Republican movements have used the colour green.
- Green, considered the holy colour of Islam, is also used by some Islamists, such as Hamas.
- In Japan the liberal-conservative Liberal Democratic Party uses green.
- In Morocco see Green March
- The color of Peru's Christian People's Party, Christian democratic party.
- Puerto Rico's Puerto Rican Independence Party, a social democratic party, uses green.
- In Romania, green is historically associated with the extremist Iron Guard of the interwar era. Presently, it is used by the Democratic Union of Hungarians in Romania as a primary color, and also by various green parties such as the Ecologist Party of Romania and The Greens.
- In South Africa green represents the Africa Muslim Party
- In South Africa, green often represents the national liberation movement against the apartheid government. It is used by several South African political parties including the African National Congress, United Christian Democratic Party, African People's Convention, Pan Africanist Congress of Azania and Economic Freedom Fighters.
- In South Korea, green represents the liberal People's Party and the Green Party Korea.
- In Taiwan, green often represents Democratic Progressive Party, the party and Taiwan independence movements have used the colour green.
- In Tanzania, green represents the Chama Cha Mapinduzi.
- In Italy, green is the colour of Lega Nord, a regionalist political party.
- In Venezuela, green has been the traditional colour of the Copei party, one of the two parties that dominated the country's politics in the late 20th century (alongside Democratic Action) and one of the parties currently in opposition to the PSUV.
Orange
Orange is the traditional colour of the Christian democrats, and it can also represent various kinds of populist parties. Such is the case in Austria, Germany, France, Portugal, Switzerland, Finland, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic and Turkey.
- Orange is often used to represent the mutualist current in anarchist politics, as a middle ground between pro-market currents such as anarcho-capitalism (associated with the colour yellow of liberalism) and anti-market currents such as anarcho-syndicalism and anarcho-communism (associated with the colour red of communism and socialism).
- Humanism also uses orange and is the color of the Humanist International, it is the color of the humanist parties in Argentina, Brazil, Costa Rica and Chile, to name a few.
- In Canada, orange is the colour of the New Democratic Party (NDP), a social-democratic party. Most social-democratic parties around the world use red or pink, but in Canada the colour red was already long associated with the Liberals when the NDP was founded.
- In Colombia orange is unofficially associated with Social Party of National Unity, a Third Way party.[4] Orange is the official color of Libertarian Party.
- In Costa Rica it was the color used for the socialist Democratic Force party, main alternative to the two major parties during the 90s.
- In Czech Republic, the Czech Social Democratic Party (ČSSD) changed its official colour in 2006 from red to orange.
- In Ecuador was the color of the social democratic Democratic Left party.
- The German Pirate Party uses the colour orange.
- In Hungary, orange is the official color of, and prominently associated with, the national conservative Fidesz party. Fidesz has run on a joint list with the Christian-Democratic KDNP since 2010.
- In Israel, orange is linked to anti-disengagement rallies and other right wing and pro-settlement activity.
- In New Zealand the Electoral Commission rejected a proposed orange logo[5] for being likely to confuse or mislead voters by being too similar to the colour used by the country's electoral agencies.[6]
- In the Netherlands orange is in use as the secondary colour of the Dutch People's Party for Freedom and Democracy. The colour orange is more widely associated with the House of Orange-Nassau and Orangism.
- In Northern Ireland, orange is associated with Unionism and the Orange Order.
- In Romania, the center-right Democratic Liberal Party used orange as its official color.
- In South Africa, orange is often associated with conservative Afrikaner political movements. Orange was the official colour of the National Party which was the country's governing party from 1948 to 1994; additionally its successor, the New National Party used the colour orange. It is the used by the Christian democratic and Afrikaner nationalist party Freedom Front Plus. Orange red is the official colour of the Independent Democrats, a Social democratic political party in the Northern and Western Cape Provinces.
- In Spain is the color of the right-wing liberal party Citizens.
- In the United Kingdom, orange was the colour of the historical Liberal Party. The contemporary successors to the Liberals - the Liberal Democrats - use orange.
- In Puerto Rico is the color of Puerto Ricans for Puerto Rico
- In Ukraine, orange was the colour of liberal groups that participated in the "Orange Revolution". This gave the colour orange a certain association with radical anti-authoritarian politics in some countries, and it has been used as such by groups and organizations in the Middle East – for example in Lebanon, the Palestinian Authority, Egypt, Bahrain and Israel.
Pink
- Pink is sometimes used by social-democratic parties, such as in France and Portugal. The more traditional colour of social democracy is red (because social democracy is descended from the democratic socialist movement), but some countries have large social-democratic parties alongside large socialist or communist parties, so that it would be confusing for them all to use red. In such cases, social democrats are usually the ones who give up red in favor of a different colour. Pink is often chosen because it is seen as a softer, less aggressive version of red, in the same way that social democracy is more centrist and less militant than socialism.
- Some European liberal parties use pink or magenta as their party colour. Examples include the Danish Social Liberal Party and NEOS – The New Austria.
- In some European nations and the United States, pink is associated with homosexuality and the pink flag is used as a symbol in support of civil rights for LGBT people. This goes back to the Nazi German policy of appending pink triangles to the clothing of homosexual prisoners.
- Pink is the colour of the feminist party Feminist Initiative in Sweden.
Purple
Although purple has some older associations with monarchism, it is the most prominent colour that is not traditionally connected to any major contemporary ideology. As such, it is sometimes used to represent a mix of different ideologies, or new protest movements that are critical of all previously-existing parties.
- Purple is often associated with feminism and, when combined with black, is often used to represent anarcha-feminism.
- In Europe, purple has been used to represent the 'Purple governments' of Belgium and the Netherlands, formed by an alliance of 'red' social-democratic and 'blue' liberal parties.
- In Italy, purple has been adopted by anti-Silvio Berlusconi protesters (see Purple people) as an alternative from other colours and political parties.
- In Ireland, purple is the colour of the Social Democrats which supports a Nordic model of social democracy.
- In Mexico is the color of the Humanist Party.
- In Poland, purple is the colour of Partia Razem a new left-wing social-democratic political party formed in 2015
- In Romania, purple was used by the populist and eurosceptic People's Party – Dan Diaconescu, active between 2011–2015.
- In Spain, purple is the colour of Podemos a new left-wing party that emerged from the 15-M Movement protests.
- Purple is the colour of the Swedish Pirate Party and Icelandic Pirate Party, and several international Pirate parties share the colour along with black.
- In the United Kingdom purple is associated with Euroscepticism, being the official colours of the UK Independence Party (along with yellow).
- In the United States purple is the official colour of the Veterans Party of America which is a centrist constitutional based party with a mix of the dominate two parties colours. Also based on the colour of the Purple Heart Medal.
- Also the color of social democratic Vermont Progressive Party.
- Purple is also unofficially used in the United States to denote a "swing state" (i.e., one contested frequently between the Republican Party, whose unofficial colour is red, and the Democratic Party, whose unofficial colour is blue.) Purple is also used by centrists to represent a combination of beliefs belonging to the Republicans (red) and the Democrats (blue) (see above). It has also been used to reference Purple America, a term used in contrast to "blue" or "red", noting the electoral differences nationwide are observed more on discrepancies instead of unity. (See Red states and blue states.)
- In Uruguay is the color of the social democratic Independent Party.
- In Venezuela is use by socialist People's Electoral Movement.
Red
Red is traditionally associated with socialism and communism. The oldest symbol of socialism (and, by extension, communism) is the Red Flag, which dates back to the French Revolution in the 18th century and the revolutions of 1848. Before this nascence, the color red was generally associated with monarchy or the Church due to the symbolism and association of Christ's blood. The colour red was chosen to represent the blood of the workers who died in the struggle against capitalism. All major socialist and communist alliances and organisations – including the First, Second, and Third Internationals – used red as their official colour. The association between the colour red and communism is particularly strong. Communists use red much more often and more extensively than other ideologies use their respective traditional colours.
- In Europe and Latin America, red is also associated with parties of social democracy, and often their allies within the labor movement. Sometimes these parties use pink instead, as a "moderate" colour instead of the more "radical" red, or "pink" used to describe the more moderate faction or membership within a left-wing party.
- Red is also the traditional colour of liberal parties in Latin America, and was the colour use, for example, in Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Honduras, Mexico and Uruguay for liberal parties. However these parties follow progressive liberalism more than classic liberalism, thus seating in the centre-left.
- In the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand and Ireland, red is also the colour of the labour movement and the Labour (spelled 'Labor' in Australia) Parties in those countries. The use of red as a symbol is referenced in the UK Labour Party's anthem, The Red Flag.[7]
- Belize's main conservative party United Democratic Party it's represented by the red color.
- In Canada, red has always been associated with the Liberal Party of Canada, because one of its predecessors was the Parti rouge (French for "Red Party").
- Japan's buddhist party Komeito has a red sun as flag.
- The Colorado Party of Paraguay, a right-wing conservative party, uses red as the name suggests, its main rival the liberal Partido Liberal Radical uses blue, contrary to the rest of Latin America.
- The Liberty Korea Party, which is the dominant conservative party in South Korea, uses red as their official color. Before 2012, the conservative parties used blue as their official color.
- In Thailand the Red Shirt movement derives its populist base from amongst the working class and rural communities, which oppose the established power elite in Bangkok.
- A key exception to the international convention of red to mean socialism is the United States. Since about the year 2000, the mass media have associated red with the Republican Party, despite the fact that the Republican Party is a conservative party. (See Red states and blue states.) The use is probably entrenched, as many political organisations (for example the website RedState) now use the term.
- The opposite in the case of Puerto Rico, as the liberal Popular Democratic Party uses red.
Saffron
In India, saffron is traditionally associated with Hinduism, Hindutva and the Hindu nationalist movement.[8] Saffron was chosen because in Hindu Sanatana Dharma, the deep saffron colour is associated with sacrifice, religious abstinence, quest for light and salvation. Saffron or "Bhagwa" is the most sacred colour for the Hindus and is often worn by Sanyasis who have left their home in search of the ultimate truth.
White
White is today mainly linked to pacifism (as in the surrender flag) and in politics of the United Kingdom to independent politicians such as Martin Bell.
- Historically, it was associated with support for absolute monarchy, starting with the supporters of the Bourbon dynasty of France, because it was the dynasty's colour. Later it was used by the Czarist Whites who fought against the communist "Reds" in the Russian Civil War, because the Russian "Whites" had similar goals to the French "Whites" of a century earlier.
- Because of its use by anti-communist forces in Russia, the colour white came to be associated in the 20th century with many different anti-communist and counter-revolutionary groups, even those that did not support absolute monarchy (for example, the Finnish "Whites" who fought against the socialist "Reds" in the civil war following the independence of Finland). In some revolutions, red is used to represent the revolutionaries and white is used to represent the supporters of the old order, regardless of the ideologies or goals of the two sides.
- In Italy a red cross on a white shield (scudo crociato) is the emblem of Catholic parties, from the historical Christian Democracy party.
- In Afghanistan, the Taliban reversed the Islamist schema, using black shahada on a white background (symbol of purity).
- In Singapore, white is the colour associated with the People's Action Party, the party that has been in power, and dominating the Parliament, since the country's independence.
- In Uruguay the conservative National Party it's also known as "White Party", counterpart of the liberal "Red Party" during the two-party era.
- In Venezuela, white has been the traditional colour of the Democratic Action party, one of the two parties that dominated the country's politics in the late XX century (alongside Copei) and one of the parties currently in opposition to the PSUV.
Yellow
Yellow is the colour most commonly associated with liberalism. It is the official colour of the Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe (ALDE), as well as being the colour of liberal parties in Germany, Romania, Estonia and the United Kingdom (the Liberal Democrats). Yellow or gold, usually together with blue or purple, is also often used to represent libertarianism.
- In Latin America it is not unusual for left-wing parties to use yellow, as red was the traditional color of liberals.
- Yellow is also associated with Judaism and the Jewish people, although this may be seen negatively (see also Yellow badge) and since 1945, the blue Star of David is preferred.
- In East and Southeast Asia, yellow used to represent monarchies. For instance, in Thailand, yellow represents King Bhumibol. It was also the colour of the pro-monarchy Panchayat system in the Kingdom of Nepal.
- It is also a common color to represent Buddhism, monks in Burma used it in the anti-government protests.
- In Argentina is the color for liberal right-wing party Republican Proposal, led by Mauricio Macri.
- In Colombia is the color of left-wing party Alternative Democratic Pole.
- In Costa Rica is the color associated with social democratic and progressive Citizens' Action Party (generally under a darker gold tone) and left-wing Broad Front (which uses a more lighter tone), it is also the color of several unions.
- In Honduras is the color of far-left party Democratic Unification Party.
- In Hong Kong, yellow refers to democracy because of the yellow umbrellas that were raised during the Umbrella Revolution in 2014.
- In the Philippines, yellow mostly refers to the People Power Revolution, Liberal Party, and the Aquino family.
- In the United States, the Libertarian Party uses the color yellow in reference to the Gadsden Flag, a yellow banner featuring a snake and the phrase, "DON'T TREAD ON ME."
- Humanist and progressive party Primero Justicia in Venezuela uses yellow.
By country
Notable national political colour schemes include:
- In Argentina, the peronist Justicialist Party (PJ) uses blue, the centrist Radical Civic Union (UCR) uses red, the centre-right Republican Proposal (Pro) uses yellow, the centre-right peronist Renewal Front uses black, the centre-left Progressives use orange, and the leftist Workers' Left Front uses dark red.
- In Austria, the Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ) uses red, the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) uses black, the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) uses blue, NEOS uses magenta, and The Greens use green.
- In Brazil, left-wing Worker's Party (PT) uses red and centre-right Brazilian Social Democracy Party (PSDB) uses blue.
- In Belize there's an inversion of the traditional colors, as conservative UDP uses red and democratic socialist PUP uses blue.
- In Belgium, the liberal parties (Open VLD and MR) use blue, the Christian Democrats (CD&V and cdH) use orange and the social-democratic parties (Sp.a and PS) use red. The colour of the Flemish nationalist party New-Flemish Alliance (N-VA) is yellow.
- In Bolivia, left-wing Movement for Socialism uses blue and white, Christian Democratic Party (Bolivia) uses red, white and green and conservative National Unity Front uses yellow and blue.
- In Canada, in federal-level politics, the official colour for the centre-right Conservative Party of Canada is blue, the centrist Liberal Party of Canada uses red, and the social-democratic New Democratic Party (NDP) uses orange. The separatist Bloc Québécois uses a lighter blue, while the Green Party of Canada uses green.
- In Costa Rica it's common for parties to use flags generally with two colors, the social democratic National Liberation uses green and white, progressive Citizens' Action uses yellow and red, socialist Broad Front uses yellow and black, classical liberal Libertarian Movement uses red and white, Christian democrat Social Christian Unity uses blue and red. This causes the party members to be often call by the combination of both colors; for example verdiblancos (green and whites) for PLN's supporters, rojiamarillos (red and yellows) for PAC's supporters, etc.
- In Denmark, the centre-left Social Democrats and allied parties are known as the red bloc, and the centre-right Liberal Party and allies are the blue bloc.
- In France, the centre-left Socialist Party uses pink, while the left-wing Left Front, including the Communist Party, uses red. Minor far-left parties are usually represented by dark red. The Greens, of course, use green. The centrist Democratic Movement (MoDem) uses orange. The main party of the centre-right, The Republicans (LR) uses blue, while its ally the Union of Democrats and Independents uses a lighter blue. The far-right National Front uses navy blue (bleu marine), a play on the name of the party's leader, Marine Le Pen.
- In Germany, the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) uses orange (officially) and its Bavarian counterpart, the Christian Social Union, uses light blue. When represented together, the CDU/CSU is often depicted using black. The Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) uses red, Alliance '90/The Greens uses green, The Left is indicated with dark red or purple. The liberal Free Democratic Party (FDP) uses yellow and the far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) uses blue.
- In Honduras political parties use flags. The Liberal Party uses a red and white flag, the conservative National Party uses a blue flag with a white star, the Zelayista Liberty and Refoundation party uses a red flag with black letter and a white star, the left-wign Democratic Unification party uses a yellow flag with red letters and the Christian Democratic Party uses a green flag with white letters.
- In Hungary orange is used to denote the national conservative Fidesz, red the socialist MSzP, black or gray the right-wing nationalist Jobbik, green the green-liberal Politics Can Be Different (LMP), and blue the (now extra-parliamentary) Free Democrats. These colors are sometimes not officially used by the parties themselves, as many political groups exclusively use the Hungarian tricolor's colors (red, white, and green) in their own licensed literature and logos.
- In Ireland, Fine Gael uses blue, Fianna Fáil uses green, the Labour Party uses red, Sinn Féin uses dark green, the AAA-PBP is indicated by orange, the Social Democrats use purple, and the Green Party are indicated by lime green. Independent politicians, a major force in Ireland, are indicated by white or grey.
- In Italy, the centre-left Democratic Party (PD) is indicated by red or orange, the centre-right Forza Italia by azure, and the populist Five Star Movement (M5S) by yellow.
- In Mexico, the left-wing Party of the Democratic Revolution (PRD) uses yellow and black. The right-wing National Action Party (PAN) uses blue and white, the colours of the Virgin of Guadalupe, symbol of Mexican Catholicism. The Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) is indicated by the Mexican tricolour.
- In Moldova, the conservative Liberal Democratic Party (PLDM) uses green, the social-democratic Democratic Party of Moldova (PDM) uses dark blue, and the Liberal Party (PL) uses pale blue.
- In the Netherlands, four parties use green: the social-liberal Democrats 66 (D66) use light green and both the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) and animal-rights party Party for the Animals (PvdD) use a darker green. GreenLeft uses a combination of green and red, although green is used more often. Blue is used by the conservative-liberal People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD). The Labour Party and Socialist Party are both associated with red.
- In Nicaragua the parties use flags as it's common in Central America, the Sandinista National Liberation Front uses a red and black flag and the liberals use a red and white flag.
- In the Philippines, the centrist Liberal Party uses yellow, the conservative Kilusang Bagong Lipunan (KBL) uses red, and the populist United Nationalist Alliance (UNA) uses orange. Aside from these "party colors", individual candidates may use a different colour; the colours of the three parties mentioned were derived from the preferred colours of Benigno Aquino, Jr., Ferdinand Marcos and Joseph Estrada, respectively. The Christian democrats Lakas–CMD uses blue and gold, and the Nacionalista Party, while using the colours of the flag of the Philippines, had used green, and lately orange, the preferred colour of 2010 presidential nominee Manny Villar. The left, while popularly known as "reds", had not used that colour in elections, using instead purple or dark blue. Other parties use party colours sparingly.
- In Portugal, the centre-left Socialist Party (PS) use pink, on the centre-right Social Democratic Party (PSD) uses orange, and the People's Party (CDS–PP) uses blue.
- In South Korea, the ruling conservative party Liberty Korea Party (former Saenuri Party) uses red as its colour, even though red is considered a leftist colour in Korea. In this case it is a kind of political strategy, to emphasize change and evolution.
- In Sweden, blue is used for the Moderate Party while red is used for the Social Democratic Party. Green is used by the Centre Party and the Green Party.
- In Taiwan, the leading groups of parties are the Pan-Blue Coalition, which leans more towards Chinese nationalism, and the Pan-Green Coalition, which leans more towards Taiwanese independence. The New Party uses yellow as its party colour even though its policies are conservative; the Democratic Progressive Party uses green even though its international alignment is with the Liberal International and not the Green parties.
- In the United Kingdom (excluding Northern Ireland), the Conservative Party uses blue, the Labour Party uses red, and the Liberal Democrats use gold and orange. The right-wing populist UK Independence Party has chosen to use the non-aligned colour purple. The British National Party (BNP) use the colours of the Union Jack, The centrist Social Democratic Party (SDP) used red and blue. The Scottish National Party (SNP) uses yellow and black, and Plaid Cymru (PC) uses gold and green.
- In Northern Ireland, the Unionist parties in the Northern Ireland Assembly are called the "orange block" and the Nationalist parties are the "green block".
- Some of the established political parties use or have used different colour variations in certain localities. This was common in British politics up to the 1970s. The traditional colour of the Penrith and the Border Conservatives was yellow, rather than dark blue - even in the 2010 election Conservative candidates in Penrith and the neighbouring constituency of Westmorland and Lonsdale wore blue and yellow rosettes. In North East England, the Conservatives traditionally used red, Labour green, and the Liberals blue and orange. In parts of East Anglia the Conservatives used pink and blue, whilst in Norwich their colours were orange and purple. The Liberals and Conservatives used blue and red respectively in West Wales, while in parts of Cheshire the Liberals were red and Labour yellow. During the 18th and 19th centuries the Tories used orange in Birmingham, pink in Whitby and red in East Worcestershire, whilst the Whigs were blue in Kendal, purple in Marlborough and orange in Wakefield.[9] The traditional colour of the Warwickshire Liberals was green, rather than orange.
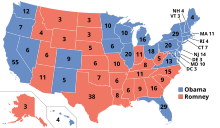
- In the United States the two major political parties use the national colors – red, white, and blue. Historically, the only common situation in which it has been necessary to assign a single colour to a party has been in the production of political maps in graphical displays of election results. In such cases, there had been no consistent association of particular parties with particular colours. In the weeks following the 2000 election, however, there arose the terminology of red states and blue states, in which the conservative Republican Party was associated with red and the liberal Democratic Party with blue. Political observers latched on to this association, which resulted from the use of red for Republican victories and blue for Democratic victories on the display map of a television network. In 2004, the association was mostly kept. As of November 2012, maps for presidential elections produced by the U.S. government also use blue for Democrats and red for Republicans.[10] In September 2010, the Democratic Party officially adopted an all-blue logo.[2] Around the same time, the official Republican website began using a red logo.
- This association has potential to confuse foreign observers in that, as described above, red is traditionally a left-wing colour, while blue is typically associated with right-wing politics.
- There is some historical use of blue for Democrats and red for Republicans: in the late 19th century and early 20th century, Texas county election boards used colour-coding to help Spanish speakers and illiterates identify the parties,[11] however, this system was not applied consistently in Texas and was not picked up on a national level; for instance, in 1888, Grover Cleveland and Benjamin Harrison used maps that coded blue for the Republicans, the colour Harrison perceived to represent the Union and "Lincoln's Party" and red for the Democrats.[12]
- In Puerto Rico the three main parties are; Partido Nuevo Progresista (blue), Partido Popular Democrático (red) and Partido Independentista Puertorriqueño (green).
See also
- Political uniform
- List of political party symbols
- NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems#Affiliation
References
- ^ Blue is the colour of peace
- ^ a b "Change That Matters". Democrats.org. 14 September 2010. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Millner, Antony; Ollivier, Hélène; Simon, Leo (2016). "Policy experimentation, political competition, and heterogeneous beliefs". Journal of Public Economics. 120: 84–96. doi:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2014.08.008.
- ^ . 16 September 2013 http://www.eluniversal.com.co/politica/presidente-santos-reafirmo-que-pertenece-al-partido-de-la-u-134959. Retrieved 15 March 2016.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Electoral Commission (27 November 2007). "The Family Party - Applications to register party name and logo". Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ Electoral Commission (17 December 2007). "The Family Party registered, logo declined". Retrieved 20 June 2014.
- ^ Peter Hitchens (26 March 2010). The Cameron Delusion. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-4411-2390-9.
- ^ Véronique Bénéï (2005). Manufacturing Citizenship: education and nationalism in Europe, South Asia and China. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-36488-4.
- ^ Kelly, Jon (4 May 2015). "The seats where Tories weren't blue and Labour wasn't red". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 4 May 2015.
- ^ "Historic Election Results". The U.S. National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ "Handbook of Texas Online – REDS AND BLUES". Tshaonline.org. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Rowe, Tara A. (13 January 2005). "The Political Game: The Red and Blue State Phenomenon". Politicalgame.blogspot.com. Retrieved 17 October 2011.