Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 42nd President of the United States | |
| In office January 20, 1993 – January 20, 2001 | |
| Vice President | Al Gore |
| Preceded by | George H. W. Bush |
| Succeeded by | George W. Bush |
| 40th and 42nd Governor of Arkansas | |
| In office January 11, 1983 – December 12, 1992 | |
| Lieutenant | |
| Preceded by | Frank D. White |
| Succeeded by | Jim Guy Tucker |
| In office January 9, 1979 – January 19, 1981 | |
| Lieutenant | Joe Purcell |
| Preceded by | Joe Purcell (Acting) |
| Succeeded by | Frank D. White |
| 50th Attorney General of Arkansas | |
| In office January 3, 1977 – January 9, 1979 | |
| Governor |
|
| Preceded by | Jim Guy Tucker |
| Succeeded by | Steve Clark |
| Personal details | |
| Born | William Jefferson Blythe III August 19, 1946 Hope, Arkansas, U.S. |
| Political party | Democratic |
| Spouse | |
| Children | Chelsea |
| Parents | |
| Alma mater | |
| Awards | Presidential Medal of Freedom See more |
| Signature | |
| ||
|---|---|---|
|
Personal 40th and 42nd Governor of Arkansas 42nd President of the United States Tenure Appointments Presidential campaigns
|
||
| Part of a series on |
| New Democrats |
|---|
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton (born William Jefferson Blythe III; August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Clinton was Governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and 1983 to 1992, and Arkansas Attorney General from 1977 to 1979. A member of the Democratic Party, ideologically Clinton was a New Democrat, and many of his policies reflected a centrist "Third Way" political philosophy.
Clinton was born and raised in Arkansas, and is an alumnus of Georgetown University, where he was a member of Kappa Kappa Psi and the Phi Beta Kappa Society and earned a Rhodes Scholarship to attend the University of Oxford. Clinton is married to Hillary Clinton, who served as United States Secretary of State from 2009 to 2013, who was a Senator from New York from 2001 to 2009, and who is the Democratic nominee for President of the United States in 2016. Both Clintons earned law degrees from Yale Law School, where they met and began dating. As Governor of Arkansas, Clinton overhauled the state's education system, and served as chairman of the National Governors Association.
Clinton was elected President in 1992, defeating incumbent George H. W. Bush. At age 46, Clinton was the third-youngest president, and the first from the Baby Boomer generation. Clinton presided over the longest period of peacetime economic expansion in American history, and signed into law the North American Free Trade Agreement. After failing to pass national health care reform, the Democratic House was ousted when the Republican Party won control of the Congress in 1994, for the first time in 40 years. Two years later, in 1996, Clinton became the first Democrat since Franklin D. Roosevelt to be elected to a second term. Clinton passed welfare reform and the State Children's Health Insurance Program, providing health coverage for millions of children.
In 1998, Clinton was impeached by the House of Representatives for perjury before a grand jury and obstruction of justice during a lawsuit against him, both related to a scandal involving White House (and later Department of Defense) employee Monica Lewinsky. Clinton was acquitted by the U.S. Senate in 1999, and served his complete term of office. The Congressional Budget Office reported a budget surplus between the years 1998 and 2000, the last three years of Clinton's presidency. In foreign policy, Clinton ordered U.S. military intervention in the Bosnia and Kosovo wars, signed the Iraq Liberation Act in opposition to Saddam Hussein, and participated in the 2000 Camp David Summit to advance the Israeli–Palestinian peace process.
Clinton left office with the highest end-of-office approval rating of any U.S. President since World War II. Since then, Clinton has been involved in public speaking and humanitarian work. Clinton created the William J. Clinton Foundation to address international causes, such as the prevention of AIDS and global warming. In 2004, Clinton published his autobiography My Life. Clinton has remained active in politics by campaigning for Democratic candidates, including his wife's campaigns for the Democratic presidential nomination in 2008 and 2016, and Barack Obama's presidential campaigns in 2008 and 2012.
In 2009, Clinton was named the United Nations Special Envoy to Haiti, and after the 2010 Haiti earthquake, Clinton teamed with George W. Bush to form the Clinton Bush Haiti Fund. Since leaving office, Clinton has been rated highly in public opinion polls of U.S. Presidents.
Early life and career

Clinton was born on August 19, 1946, at Julia Chester Hospital in Hope, Arkansas, and named William Jefferson Blythe III.[2][3] He was the son of William Jefferson Blythe Jr. (1910–1946), a traveling salesman who had died in an automobile accident three months before his birth, and Virginia Dell Cassidy (1923–1994).[4] His parents had been married on 4 September 1943, but this later proved to be bigamous, as Blythe was still married to a previous wife.[5] Soon after their son was born, his mother traveled to New Orleans to study nursing, leaving her son in Hope with her parents Eldridge and Edith Cassidy, who owned and ran a small grocery store.[3] At a time when the Southern United States was segregated racially, Clinton's grandparents sold goods on credit to people of all races.[3] In 1950, Bill's mother returned from nursing school and married Roger Clinton Sr., who owned an automobile dealership in Hot Springs, Arkansas, with his brother and Earl T. Ricks.[3] The family moved to Hot Springs in 1950.
Although he immediately assumed use of his stepfather's surname, it was not until Clinton turned fifteen[6] that he formally adopted the surname Clinton as a gesture toward his stepfather.[3] Clinton says he remembers his stepfather as a gambler and an alcoholic who regularly abused his mother and half-brother, Roger Clinton Jr., to the point where he intervened multiple times with the threat of violence to protect them.[3][7]
In Hot Springs, Clinton attended St. John's Catholic Elementary School, Ramble Elementary School, and Hot Springs High School—where he was an active student leader, avid reader, and musician.[3] Clinton was in the chorus and played the tenor saxophone, winning first chair in the state band's saxophone section. He briefly considered dedicating his life to music, but as he noted in his autobiography My Life
Sometime in my sixteenth year, I decided I wanted to be in public life as an elected official. I loved music and thought I could be very good, but I knew I would never be John Coltrane or Stan Getz. I was interested in medicine and thought I could be a fine doctor, but I knew I would never be Michael DeBakey. But I knew I could be great in public service.[3]
Clinton's interest in law also began in Hot Springs High, when in his Latin class he took up the challenge to argue the defense of the ancient Roman Senator Catiline in a mock trial.[8] After a vigorous defense that made use of his "budding rhetorical and political skills", he told the Latin teacher Elizabeth Buck that it "made him realize that someday he would study law".[9]
Clinton has named two influential moments in his life that contributed to his decision to become a public figure, both occurring in 1963. One was his visit as a Boys Nation senator to the White House to meet President John F. Kennedy.[3][7] The other was watching Martin Luther King, Jr.'s 1963 I Have a Dream speech on TV, which impressed him enough that he later memorized it.[10]
College and law school years
Georgetown University

With the aid of scholarships, Clinton attended the Edmund A. Walsh School of Foreign Service at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C., receiving a Bachelor of Science in Foreign Service (B.S.) degree in 1968.
In 1964 and 1965, Clinton won elections for class president.[11] From 1964 to 1967, he was an intern and then a clerk in the office of Arkansas Senator J. William Fulbright.[3] While in college, he became a brother of co-ed service fraternity Alpha Phi Omega[12] and was elected to Phi Beta Kappa. Clinton was also a member of the Order of DeMolay,[13] a youth group affiliated with Freemasonry, but he never became a Freemason. He is a member of Kappa Kappa Psi honorary band fraternity.[14]
Rhodes Scholar
Upon graduation, he won a Rhodes Scholarship to University College, Oxford where he studied Philosophy, Politics and Economics, though because he had switched programs and had left early for Yale University, he did not receive a degree there.[7][15][16] He developed an interest in rugby union, playing at Oxford[17] and later for the Little Rock Rugby club in Arkansas.[citation needed]
Vietnam War opposition and draft controversy
While at Oxford he also participated in Vietnam War protests and organized an October 1969 Moratorium to End the War in Vietnam event.[3]
Clinton received Vietnam War draft deferments during 1968 and 1969 while he was in England.[18] Planning to attend law school in the U.S, and aware that he might lose his draft deferment, he tried unsuccessfully to obtain positions in the National Guard or Air Force, and then made arrangements to join the Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC) program at the University of Arkansas.[19]
He subsequently decided not to join the ROTC, saying in a letter to the officer in charge of the program he had planned to join that he opposed the war, but did not think it was honorable to use ROTC, National Guard, or Reserve service to avoid serving in Vietnam. He further stated that because he opposed the war, he would not volunteer to serve in uniform, but would subject himself to the draft, and would serve if selected only as a way "to maintain my political viability within the system".[20] Clinton registered for the draft and received a high number (311), meaning that those whose birthdays had been drawn as numbers 1 to 310 would have to be drafted before him, making it unlikely that he would be drafted. (In fact, the highest number drafted was 195.)[21]
Colonel Eugene Holmes, the Army officer who had been involved with Clinton's ROTC application, suspected that Clinton attempted to manipulate the situation to avoid the draft and avoid serving in uniform. He issued a notarized statement during the 1992 presidential campaign:
I was informed by the draft board that it was of interest to Senator Fulbright's office that Bill Clinton, a Rhodes Scholar, should be admitted to the ROTC program ... I believe that he purposely deceived me, using the possibility of joining the ROTC as a ploy to work with the draft board to delay his induction and get a new draft classification.[22]
During the 1992 campaign it was revealed that Clinton's uncle had attempted to secure him a position in the Navy Reserve, which would have kept him from going to Vietnam. This effort was unsuccessful and Clinton said in 1992 that he had been unaware of it until then.[23] Although legal, Clinton's actions with respect to the draft and deciding whether to serve in the military were criticized by conservatives and some Vietnam veterans during his first presidential campaign, some of whom charged that he had used Fulbright's influence to avoid military service.[24][25] Clinton's 1992 campaign manager, James Carville, successfully argued that Clinton's letter in which he declined to join the ROTC should be made public, insisting that voters, many of whom had also opposed the Vietnam War, would understand and appreciate his position.[26]
Law school
After Oxford, Clinton attended Yale Law School and earned a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree in 1973.[3][7] In the Yale Law Library in 1971 he met fellow law student Hillary Rodham, who was a year ahead of him.[3][27] They began dating and soon were inseparable. After only about a month, Clinton postponed his plans to be a coordinator for the George McGovern campaign for the 1972 United States presidential election in order to move in with her in California.[28] They married on October 11, 1975, and their only child, Chelsea, was born on February 27, 1980.[27]
Clinton did eventually move to Texas with Rodham to take a job leading George McGovern's effort there in 1972. He spent considerable time in Dallas, at the campaign's local headquarters on Lemmon Avenue, where he had an office. Clinton worked with future two-term mayor of Dallas, Ron Kirk, future governor of Texas, Ann Richards, and then unknown television director (and future filmmaker) Steven Spielberg.[citation needed]
Early political career
Governor of Arkansas (1979–81 and 1983–92)
After graduating from Yale Law School, Clinton returned to Arkansas and became a law professor at the University of Arkansas. In 1974 he ran for the House of Representatives. Running in a conservative district against incumbent Republican John Paul Hammerschmidt, Clinton's campaign was bolstered by the anti-Republican and anti-incumbent mood resulting from the Watergate scandal. Hammerschmidt, who had received 77 percent of the vote in 1972, defeated Clinton by only a 52 percent to 48 percent margin. In 1976 Clinton ran for Arkansas Attorney General. With only minor opposition in the primary and no opposition at all in the general election,[29] Clinton was elected.[7]

Clinton was elected Governor of Arkansas in 1978, having defeated the Republican candidate Lynn Lowe, a farmer from Texarkana. He became the youngest governor in the country at 32. Due to his youthful appearance, Clinton was often called the "Boy Governor".[30][31][32] He worked on educational reform and Arkansas's roads, with wife Hillary leading a successful committee on urban health care reform. However, his term included an unpopular motor vehicle tax and citizens' anger over the escape of Cuban refugees (from the Mariel boatlift) detained in Fort Chaffee in 1980. Monroe Schwarzlose of Kingsland in Cleveland County, polled 31 percent of the vote against Clinton in the Democratic gubernatorial primary of 1980. Some suggested Schwarzlose's unexpected voter turnout foreshadowed Clinton's defeat in the general election that year by Republican challenger Frank D. White. As Clinton once joked, he was the youngest ex-governor in the nation's history.[7]
Clinton joined friend Bruce Lindsey's Little Rock law firm of Wright, Lindsey and Jennings.[33] In 1982, he was again elected governor and kept the office for ten years; beginning with the 1986 election, Arkansas had changed its gubernatorial term of office from two to four years. During his term he helped transform Arkansas's economy and improved the state's educational system.[34] For senior citizens, he removed the sales tax from medications and increased the home property-tax exemption.[35] He became a leading figure among the New Democrats, a group of Democrats who advocated welfare reform, smaller government, and other policies not supported by liberals. Formally organized as the Democratic Leadership Council (DLC), the New Democrats argued that in light of President Ronald Reagan's landslide victory in 1984, the Democratic Party needed to adopt a more centrist political stance in order to succeed at the national level.[35][36] Clinton delivered the Democratic response to President Reagan's 1985 State of the Union Address and served as Chair of the National Governors Association from 1986 to 1987, bringing him to an audience beyond Arkansas.[7]
In the early 1980s, Clinton made reform of the Arkansas education system a top priority. Chaired by Clinton's wife Hillary Rodham Clinton, also an attorney and chair of the Legal Services Corporation, the Arkansas Education Standards Committee transformed Arkansas's education system from the worst in the United States to one of the best. Proposed reforms included more spending for schools (supported by a sales-tax increase), better opportunities for gifted children, vocational education, higher teachers' salaries, more course variety, and compulsory teacher competency exams. The reforms passed in September 1983 after Clinton called a special legislative session—the longest in Arkansas history.[34] Many have considered this the greatest achievement of the Clinton governorship.[7][35] He defeated four Republican candidates for governor: Lowe (1978), White (1982 and 1986), Jonesboro businessmen Woody Freeman (1984), and Sheffield Nelson of Little Rock (1990).[29]

The Clintons' personal and business affairs in the 1980s included transactions that became the basis of the Whitewater controversy investigation that later dogged his presidential administration.[37] After extensive investigation over several years, no indictments were made against the Clintons related to the years in Arkansas.[7][38]
According to some sources, Clinton was in his early years a death penalty opponent who switched positions.[39][40] During Clinton's term, Arkansas performed its first executions since 1964 (the death penalty had been re-enacted on March 23, 1973).[41] As Governor, he oversaw four executions: one by electric chair and three by lethal injection. Later, as president, Clinton was the first President to pardon a death-row inmate since the federal death penalty was reintroduced in 1988.[42]
1988 Democratic presidential primaries
In 1987, there was media speculation Clinton would enter the race after then-New York Governor Mario Cuomo declined to run and Democratic front-runner Gary Hart withdrew owing to revelations of marital infidelity. Clinton decided to remain as Arkansas governor (following consideration for the potential candidacy of Hillary Rodham Clinton for governor, initially favored—but ultimately vetoed—by the First Lady).[43] For the nomination, Clinton endorsed Massachusetts Governor Michael Dukakis. He gave the nationally televised opening night address at the 1988 Democratic National Convention, but his speech, which was 33 minutes long and twice as long as it was expected to be, was criticized for being too long[44] and poorly delivered.[45] Presenting himself as a moderate and a member of the New Democrat wing of the Democratic Party, he headed the moderate Democratic Leadership Council in 1990 and 1991.[35][46]
Presidency (1993–2001)
During his presidency, Clinton advocated for a wide variety of legislation and programs, much of which was enacted into law or was implemented by the executive branch. His policies, particularly the North American Free Trade Agreement and welfare reform, have been attributed to a centrist Third Way philosophy of governance.[47][48] On budgetary matters his policy of fiscal conservatism helped to reduce deficits.[49][50] Clinton presided over the longest period of peacetime economic expansion in American history.[51][52][53] The Congressional Budget Office reported budget surpluses of $69 billion in 1998, $126 billion in 1999, and $236 billion in 2000,[54] during the last three years of Clinton's presidency.[55] The U.S. treasury reported a debt of $5.413 trillion in 1997, and a debt of $5.656 trillion in 1999.[clarification needed][56] At the end of his presidency, Clinton moved to New York and helped his wife win election to the U.S. Senate there.
1992 presidential campaign
In the first primary contest, the Iowa Caucus, Clinton finished a distant third to Iowa Senator Tom Harkin. During the campaign for the New Hampshire primary, reports of an extramarital affair with Gennifer Flowers surfaced. As Clinton fell far behind former Massachusetts Senator Paul Tsongas in the New Hampshire polls,[7] following Super Bowl XXVI, Clinton and his wife Hillary went on 60 Minutes to rebuff the charges. Their television appearance was a calculated risk, but Clinton regained several delegates. He finished second to Tsongas in the New Hampshire primary, but after trailing badly in the polls and coming within single digits of winning, the media viewed it as a victory. News outlets labeled him "The Comeback Kid" for earning a firm second-place finish.[57]
Winning the big prizes of Florida and Texas and many of the Southern primaries on Super Tuesday gave Clinton a sizable delegate lead. However, former California Governor Jerry Brown was scoring victories and Clinton had yet to win a significant contest outside his native South.[7][46] With no major Southern state remaining, Clinton targeted New York, which had many delegates. He scored a resounding victory in New York City, shedding his image as a regional candidate.[46] Having been transformed into the consensus candidate, he secured the Democratic Party nomination, finishing with a victory in Jerry Brown's home state of California.[7]

During the campaign, questions of conflict of interest regarding state business and the politically powerful Rose Law Firm, at which Hillary Rodham Clinton was a partner, arose. Clinton argued the questions were moot because all transactions with the state had been deducted before determining Hillary's firm pay.[3][58] Further concern arose when Bill Clinton announced that, with Hillary, voters would be getting two presidents "for the price of one".[59]
While campaigning for U.S. President, the then-Governor Clinton returned to Arkansas to see that Ricky Ray Rector would be executed. After killing a police officer and a civilian, Rector shot himself in the head, leading to what his lawyers said was a state where he could still talk but did not understand the idea of death. According to Arkansas state and Federal law, a seriously mentally impaired inmate cannot be executed. The courts disagreed with the allegation of grave mental impairment and allowed the execution. Clinton's return to Arkansas for the execution was framed in a The New York Times article as a possible political move to counter "soft on crime" accusations.[39][60]
Because Bush's approval ratings were around 80 percent during the Gulf War, he was described as unbeatable. However, when Bush compromised with Democrats to try to lower Federal deficits, he reneged on his promise not to raise taxes, hurting his approval rating. Clinton repeatedly condemned Bush for making a promise he failed to keep.[46] By election time, the economy was souring and Bush saw his approval rating plummet to just slightly over 40 percent.[46][61] Finally, conservatives were previously united by anti-communism, but with the end of the Cold War, the party lacked a uniting issue. When Pat Buchanan and Pat Robertson addressed Christian themes at the Republican National Convention—with Bush criticizing Democrats for omitting God from their platform—many moderates were alienated.[62] Clinton then pointed to his moderate, "New Democrat" record as governor of Arkansas, though some on the more liberal side of the party remained suspicious.[63] Many Democrats who had supported Ronald Reagan and Bush in previous elections switched their support to Clinton.[64] Clinton and his running mate, Al Gore, toured the country during the final weeks of the campaign, shoring up support and pledging a "new beginning".[64]
Clinton won the 1992 presidential election (43.0 percent of the vote) against Republican incumbent George H. W. Bush (37.4 percent of the vote) and billionaire populist Ross Perot, who ran as an independent (18.9 percent of the vote) on a platform focusing on domestic issues; a significant part of Clinton's success was Bush's steep decline in public approval.[64] Clinton's election ended twelve years of Republican rule of the White House and twenty of the previous twenty-four years. The election gave Democrats full control of the United States Congress,[4] the first time one party controlled both the executive and legislative branches since Democrats held the 96th United States Congress during the presidency of Jimmy Carter.[65][66]
First term
"Our democracy must be not only the envy of the world but the engine of our own renewal. There is nothing wrong with America that cannot be cured by what is right with America."
Inaugural address, January 20, 1993.[67]
Clinton was inaugurated as the 42nd President of the United States on January 20, 1993. Shortly after taking office, Clinton signed the Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993 on February 5, which required large employers to allow employees to take unpaid leave for pregnancy or a serious medical condition. This action had bipartisan support,[68] and proved quite popular with the public.[69]
Two days after taking office, on January 22, 1993—the 20th anniversary of the U.S. Supreme Court decision in Roe v. Wade, Clinton reversed restrictions on domestic and international family planning programs that had been imposed by Reagan and Bush.[70] Clinton said that abortion should be kept "safe, legal, and rare"—a slogan that had been suggested by University of California, San Diego political scientist Samuel L. Popkin and first used by Clinton in December 1991, while campaigning.[71] During the eight years of the Clinton administration, the U.S. abortion rate declined by about 18.4 percent.[72]
On February 15, 1993, Clinton made his first address to the nation, announcing his plan to raise taxes to cap the budget deficit.[73] Two days later, in a nationally televised address to a joint session of Congress, Clinton unveiled his economic plan. The plan focused on reducing the deficit rather than on cutting taxes for the middle class, which had been high on his campaign agenda.[74] Clinton's advisers pressured him to raise taxes on the theory that a smaller federal budget deficit would reduce bond interest rates.[75]
On May 19, 1993, Clinton fired seven employees of the White House Travel Office, causing the White House travel office controversy even though the Travel Office staff served at the pleasure of the president and could be dismissed without cause. The White House responded to the controversy by claiming the firings were done because of financial improprieties that had been revealed by a brief FBI investigation.[76] Critics contended the firings had been done to allow friends of the Clintons to take over the travel business and that the involvement of the FBI was unwarranted.[77]

Clinton signed the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993 in August of that year, which passed Congress without a Republican vote. It cut taxes for fifteen million low-income families, made tax cuts available to 90 percent of small businesses,[78] and raised taxes on the wealthiest 1.2 percent of taxpayers. Additionally, through the implementation of spending restraints, it mandated the budget be balanced over a number of years.[79]
Clinton made a major speech to Congress regarding a health care reform plan on September 22, 1993, aimed at achieving universal coverage through a national health care plan. This was one of the most prominent items on Clinton's legislative agenda, and resulted from a task force headed by Hillary Clinton. Though at first well received in political circles, it was eventually doomed by well-organized opposition from conservatives, the American Medical Association, and the health insurance industry. However, John F. Harris, a biographer of Clinton's, states the program failed because of a lack of coordination within the White House.[38] Despite the Democratic majority in Congress, the effort to create a national health care system ultimately died when compromise legislation by George J. Mitchell failed to gain a majority of support in August 1994. It was the first major legislative defeat of Clinton's administration.[35][38]
In November 1993, David Hale, the source of criminal allegations against Bill Clinton in the Whitewater controversy, alleged that Clinton, while governor of Arkansas, pressured him to provide an illegal $300,000 loan to Susan McDougal, the partner of the Clintons in the Whitewater land deal.[80] A U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission investigation did result in convictions against the McDougals for their role in the Whitewater project, but the Clintons themselves were never charged, and Clinton maintains innocence in the affair.
Clinton signed the Brady Bill into law on November 30, 1993, which mandated federal background checks on firearm purchasers in the United States, and imposed a five-day waiting period on purchases, until the NICS system was implemented in 1998. He also expanded the Earned Income Tax Credit, a subsidy for low-income workers.[38]
In December that year, allegations by Arkansas state troopers Larry Patterson and Roger Perry were first reported by David Brock in the American Spectator. Later known as Troopergate, the allegations by these men were that they arranged sexual liaisons for Bill Clinton back when he was governor of Arkansas. The story mentioned a woman named Paula, a reference to Paula Jones. Brock later apologized to Clinton, saying the article was politically motivated "bad journalism" and that "the troopers were greedy and had slimy motives".[81]


That month, Clinton implemented a Department of Defense directive known as "Don't Ask, Don't Tell", which allowed gay men and women to serve in the armed services provided they kept their sexuality a secret, and forbade the military from inquiring about an individual's sexual orientation.[82] The policy was developed as a compromise after Clinton's proposal to allow gays to serve openly in the military met staunch opposition from prominent Congressional Republicans and Democrats, including Senators John McCain (R-AZ) and Sam Nunn (D-GA). According to David Mixner, Clinton's support for the compromise led to a heated dispute with Vice President Al Gore, who felt that "the President should lift the ban ... even though [his executive order] was sure to be overridden by the Congress".[83] Some gay-rights advocates criticized Clinton for not going far enough and accused him of making his campaign promise to get votes and contributions.[84] Their position was that Clinton should have integrated the military by executive order, noting that President Harry S. Truman used executive order to racially desegregate the armed forces. Clinton's defenders argue that an executive order might have prompted the Senate to write the exclusion of gays into law, potentially making it harder to integrate the military in the future.[35] Later in his presidency, in 1999, Clinton criticized the way the policy was implemented, saying he did not think any serious person could say it was not "out of whack".[85] The policy remained controversial, and was finally repealed in 2011, removing open sexual preference as a reason for dismissal from the armed forces.[86]
On January 1, 1994, Clinton signed the North American Free Trade Agreement into law.[87] Throughout his first year in office, Clinton consistently supported ratification of the treaty by the U.S. Senate. Clinton and most of his allies in the Democratic Leadership Committee strongly supported free trade measures; there remained, however, strong disagreement within the party. Opposition came chiefly from anti-trade Republicans, protectionist Democrats and supporters of Ross Perot. The bill passed the house with 234 votes against 200 opposed (132 Republicans and 102 Democrats voting in favor; 156 Democrats, 43 Republicans, and 1 independent against). The treaty was then ratified by the Senate and signed into law by the President.[87]
The Omnibus Crime Bill, which Clinton signed into law in September 1994,[88] made many changes to U.S. crime and law enforcement legislation including the expansion of the death penalty to include crimes not resulting in death, such as running a large-scale drug enterprise. During Clinton's re-election campaign he said, "My 1994 crime bill expanded the death penalty for drug kingpins, murderers of federal law enforcement officers, and nearly 60 additional categories of violent felons."[89] It also included a subsection of assault weapons ban for a ten-year period.
The Clinton administration also launched the first official White House website, whitehouse.gov, on October 21, 1994.[90][91] It was followed by three more versions, resulting in the final edition launched in 2000.[92][93] The White House website was part of a wider movement of the Clinton administration toward web-based communication. According to Robert Longley, "Clinton and Gore were responsible for pressing almost all federal agencies, the U.S. court system and the U.S. military onto the Internet, thus opening up America's government to more of America's citizens than ever before. On July 17, 1996, Clinton issued Executive Order 13011 – Federal Information Technology, ordering the heads of all federal agencies to utilize information technology fully to make the information of the agency easily accessible to the public."[94]
After two years of Democratic Party control, the Democrats lost control of Congress in the mid-term elections in 1994, for the first time in forty years.[95]


The White House FBI files controversy of June 1996 arose concerning improper access by the White House to FBI security-clearance documents. Craig Livingstone, head of the White House Office of Personnel Security, improperly requested, and received from the FBI, background report files without asking permission of the subject individuals; many of these were employees of former Republican administrations.[96] In March 2000, Independent Counsel Robert Ray determined that there was no credible evidence of any crime. Ray's report further stated, "there was no substantial and credible evidence that any senior White House official was involved" in seeking the files.[97]
On September 21, 1996, Clinton signed into law the Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA), which defines marriage for federal purposes as the legal union of one man and one woman, allowing individual states to refuse to recognize gay marriages performed in other states.[98] Paul Yandura, speaking for the White House gay and lesbian liaison office, said that Clinton's signing of DOMA "was a political decision that they made at the time of a re-election". In defense of his actions, Clinton has said that DOMA was an attempt to "head off an attempt to send a constitutional amendment banning gay marriage to the states", a possibility he described as highly likely in the context of a "very reactionary Congress".[99] Administration spokesman Richard Socarides said, "the alternatives we knew were going to be far worse, and it was time to move on and get the president re-elected."[100] Clinton himself stated that DOMA was something "which the Republicans put on the ballot to try to get the base vote for President Bush up, I think it's obvious that something had to be done to try to keep the Republican Congress from presenting that".[101] Others were more critical. The veteran gay rights and gay marriage activist Evan Wolfson has called these claims "historic revisionism".[100] In a July 2, 2011, editorial The New York Times opined, "The Defense of Marriage Act was enacted in 1996 as an election-year wedge issue, signed by President Bill Clinton in one of his worst policy moments."[102] Ultimately, in United States v. Windsor, the U.S. Supreme Court struck down DOMA in June 2013.[103]
Despite DOMA, Clinton was the first President to select openly gay persons for Administration positions,[104] and is generally credited as the first President to publicly champion gay rights.[105] During his Presidency, Clinton controversially issued two substantial executive orders on behalf of gay rights, the first lifting the ban on security clearances for LGBT federal employees[106] and the second outlawing discrimination based on sexual orientation in the federal civilian workforce.[107] Under President Clinton's leadership, federal funding for HIV/AIDS research, prevention and treatment more than doubled.[108] And Clinton also pushed for passing hate crimes laws for gays and for the private sector Employment Non-Discrimination Act, which, buoyed by his lobbying, failed to pass the Senate by a single vote in 1996.[109] Advocacy for these issues, paired with the politically unpopular nature of the gay rights movement at the time, led to enthusiastic support for Clinton's election and reelection by the Human Rights Campaign.[105] Clinton came out for gay marriage in July 2009[110] and urged the Supreme Court to overturn DOMA in 2013.[111] He was later honored by GLAAD for his prior pro-gay stances and his reversal on DOMA.[112]
"When I took office, only high energy physicists had ever heard of what is called the Worldwide Web ... Now even my cat has its own page."
Bill Clinton's announcement of Next Generation Internet initiative, October 1996.[113]
The 1996 United States campaign finance controversy was an alleged effort by the People's Republic of China (PRC) to influence the domestic policies of the United States, before and during the Clinton administration, and involved the fundraising practices of the administration itself. The Chinese government denied all accusations.[114]
As part of a 1996 initiative to curb illegal immigration, Clinton signed the Illegal Immigration Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act (IIRIRA) on September 30, 1996. Appointed by Clinton,[115] the U.S. Commission on Immigration Reform recommended reducing legal immigration from about 800,000 people a year to about 550,000.[116][117]
Ken Gormley, author of The Death of American Virtue: Clinton vs. Starr, reveals in his book that President Clinton narrowly escaped possible assassination in the Philippines in November 1996. During his visit to the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum in Manila, while he was on his way to meet with a senior member of the Philippine government, Clinton was saved from danger minutes before his motorcade was scheduled to drive over a bridge charged with a timed improvised explosive device (IED).[118] According to officials, the IED was large enough to "blow up the entire presidential motorcade".[119] Details of the plot were revealed to Gormley by Lewis C. Merletti, former member of the Presidential Protection Detail and Director of the Secret Service. Intelligence officers intercepted a radio transmission indicating that there was a wedding cake under a bridge.[118] This alerted Merletti and others as Clinton's motorcade was scheduled to drive over a major bridge in downtown Manila.[119] Once more, the word "wedding" was the code name used by a terrorist group for a past assassination attempt.[119] Merletti wanted to reroute the motorcade, but the alternate route would add forty-five minutes to the drive time. Clinton was very angry, as he was already late for the meeting, but following the advice of the secret service possibly saved his life. Two other bombs had been discovered in Manila earlier in the week so the threat level that day was high.[120] Security personnel at the Manila International Airport uncovered several grenades and a timing device in a travel bag.[121] Officials also discovered a bomb near a major U.S. naval base.[121] The President was scheduled to visit both of these locations later in the week. An intense investigation took place into the events in Manila and it was discovered that the group behind the bridge bomb was a Saudi terrorist group in Afghanistan known as al-Qaeda and the plot was masterminded by Osama bin Laden.[119] Until recently, this thwarted assassination attempt was never made public and remained top secret. Only top members of the U.S. intelligence community were aware of these events.[119]
1996 presidential election

In the 1996 presidential election, Clinton was re-elected, receiving 49.2 percent of the popular vote over Republican Bob Dole (40.7 percent of the popular vote) and Reform candidate Ross Perot (8.4 percent of the popular vote), becoming the first Democratic incumbent since Lyndon Johnson to be elected to a second term and the first Democrat since Franklin D. Roosevelt to be elected President more than once.[122] The Republicans lost three seats in the House and gained two in the Senate, but retained control of both houses of the 105th United States Congress. Clinton received 379, or over 70 percent of the Electoral College votes, with Dole receiving 159 electoral votes.
Second term

In the January 1997 State of the Union address, Clinton proposed a new initiative to provide health coverage to up to five million children. Senators Ted Kennedy—a Democrat—and Orrin Hatch—a Republican—teamed up with Hillary Rodham Clinton and her staff in 1997, and succeeded in passing legislation forming the State Children's Health Insurance Program (SCHIP), the largest (successful) health care reform in the years of the Clinton Presidency. That year, Hillary Clinton shepherded through Congress the Adoption and Safe Families Act and two years later she succeeded in helping pass the Foster Care Independence Act. He negotiated the passage of the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 by the Republican Congress. In October 1997, he announced he was getting hearing aids, due to hearing loss attributed to his age, and his time spent as a musician in his youth.[123] In 1999 Clinton signed into law the Financial Services Modernization Act also known as the Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act, which repealed the part of the Glass–Steagall Act that had prohibited a bank from offering a full range of investment, commercial banking, and insurance services since its enactment in 1933.[124]
Impeachment and acquittal

After the 1998 elections, the House impeached Clinton, alleging perjury and obstruction of justice related to the Lewinsky scandal.[38] Clinton was only the second U.S. President to be impeached, after Andrew Johnson. Impeachment proceedings were based on allegations that Clinton had illegally lied about and covered up his relationship with 22-year-old White House (and later Department of Defense) employee Monica Lewinsky.[125] After the Starr Report was submitted to the House providing what it termed "substantial and credible information that President Clinton Committed Acts that May Constitute Grounds for an Impeachment",[126] the House began impeachment hearings against Clinton before the mid-term elections. To hold impeachment proceedings, the Republican leadership called a lame-duck session in December 1998.
While the House Judiciary Committee hearings ended in a straight party-line vote, there was lively debate on the House floor. The two charges passed in the House (largely with Republican support, but with a handful of Democratic votes as well) were for perjury and obstruction of justice. The perjury charge arose from Clinton's testimony before a grand jury that had been convened to investigate perjury he may have committed in his sworn deposition during Paula Jones's sexual harassment lawsuit.[127] The obstruction charge was based on his actions to conceal his relationship with Lewinsky before and after that deposition.
The Senate later acquitted Clinton on both charges.[128] The Senate refused to meet to hold an impeachment trial before the end of the old term, so the trial was held over until the next Congress. Clinton was represented by Washington law firm Williams & Connolly.[129] The Senate finished a twenty-one-day trial on February 12, 1999, with the vote of 55 Not Guilty/45 Guilty on the perjury charge[128] and 50 Not Guilty/50 Guilty on the obstruction of justice charge.[130] Both votes fell short of the Constitutional two-thirds majority requirement to convict and remove an officeholder. The final vote was generally along party lines, with no Democrats voting guilty, and only a handful of Republicans voting not guilty.[128]
On January 19, 2001, Clinton's law license was suspended for five years after he acknowledged to an Arkansas circuit court that he had engaged in conduct prejudicial to the administration of justice in the Jones case.[131][132]
Pardons and commutations
Clinton controversially issued 141 pardons and 36 commutations on his last day in office on January 20, 2001.[38][133] Most of the controversy surrounded Marc Rich and allegations that Hillary Clinton's brother, Hugh Rodham, accepted payments in return for influencing the president's decision-making regarding the pardons.[134] Federal prosecutor Mary Jo White was appointed to investigate the pardon of Rich. She was later replaced by then-Republican James Comey, who found no wrongdoing on Clinton's part. Some of Clinton's pardons remain a point of controversy.[135]
Military and foreign events


Many military events occurred during Clinton's presidency. The Battle of Mogadishu occurred in Somalia in 1993. During the operation, two U.S. helicopters were shot down by rocket-propelled grenade attacks to their tail rotors, trapping soldiers behind enemy lines. This resulted in an urban battle that killed 18 American soldiers, wounded 73 others, and one was taken prisoner. There were many more Somali casualties. Some of the American bodies were dragged through the streets—a spectacle broadcast on television news programs. In response, U.S. forces were withdrawn from Somalia and later conflicts were approached with fewer soldiers on the ground. In 1995, U.S. and NATO aircraft attacked Bosnian Serb targets to halt attacks on U.N. safe zones and to pressure them into a peace accord. Clinton deployed U.S. peacekeepers to Bosnia in late 1995, to uphold the subsequent Dayton Agreement.

In February 1996, the Clinton administration agreed to pay Iran US$131.8 million in settlement to discontinue a case brought by Iran in 1989 against the U.S. in the International Court of Justice after the shooting down of Iran Air Flight 655 by the U.S. Navy guided missile cruiser.[136]
Capturing Osama bin Laden had been an objective of the U.S. government during the presidency of Bill Clinton (and continued to be until bin Laden's death in 2011).[137] Despite claims by Mansoor Ijaz and Sudanese officials that the Sudanese government had offered to arrest and extradite bin Laden and that U.S. authorities rejected each offer[138] the 9/11 Commission Report stated that "we have not found any reliable evidence to support the Sudanese claim".[139]
In response to a 1996 State Department warning about bin Laden and the 1998 bombings of U.S. embassies in East Africa by al-Qaeda (which killed 224 people, including 12 Americans), Clinton ordered several military missions to capture or kill bin Laden, both of which were unsuccessful.[140] In August 1998, Clinton ordered cruise missile strikes on terrorist targets in Afghanistan and Sudan, targeting the Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory in Sudan, which was suspected of assisting bin Laden in making chemical weapons, and bin Laden's terrorist training camps in Afghanistan.[141]

To stop the ethnic cleansing and genocide[142][143] of Albanians by anti-guerilla military units in the former Federal Republic of Yugoslavia's province of Kosovo, Clinton authorized the use of U.S. Armed Forces in a NATO bombing campaign against Yugoslavia in 1999, named Operation Allied Force. General Wesley Clark was Supreme Allied Commander of NATO and oversaw the mission. With United Nations Security Council Resolution 1244, the bombing campaign ended on June 10, 1999. The resolution placed Kosovo under UN administration and authorized a peacekeeping force to be deployed to the region.[144] NATO announced that its forces had suffered zero combat deaths,[145] and two deaths from an Apache helicopter crash.[146] Opinions in the popular press criticized pre-war genocide statements by the Clinton administration as greatly exaggerated.[147][148] In 2001, the U.N.-supervised Supreme Court of Kosovo ruled that genocide did not take place, but recognized "a systematic campaign of terror, including murders, rapes, arsons and severe maltreatments".[149] The term "ethnic cleansing" was used as an alternative to "genocide" to denote not just ethnically motivated murder but also displacement, though critics charge there is no difference.[150] Slobodan Milošević, the president of Yugoslavia at the time of the atrocities, was eventually brought to trial before the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia in the Hague on charges of crimes against humanity, genocide, and war crimes.[151] Milošević died in 2006, before the completion of the trial.[151][152]
In Clinton's 1998 State of the Union Address, he warned Congress that Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein was building an arsenal of chemical, biological and nuclear weapons:
Saddam Hussein has spent the better part of this decade, and much of his nation's wealth, not on providing for the Iraqi people, but on developing nuclear, chemical and biological weapons and the missiles to deliver them. The United Nations weapons inspectors have done a truly remarkable job, finding and destroying more of Iraq's arsenal than was destroyed during the entire gulf war. Now, Saddam Hussein wants to stop them from completing their mission. I know I speak for everyone in this chamber, Republicans and Democrats, when I say to Saddam Hussein, "You cannot defy the will of the world", and when I say to him, "You have used weapons of mass destruction before; we are determined to deny you the capacity to use them again.[153]
Seeking to weaken Hussein's grip on power, Clinton signed the Iraq Liberation Act of 1998 into law on October 31, 1998, which instituted a policy of "regime change" against Iraq, though it explicitly stated it did not provide for direct intervention on the part of American military forces.[154][155] The administration then launched a four-day bombing campaign named Operation Desert Fox, lasting from December 16 to 19, 1998. At the end of this operation Clinton announced that "So long as Saddam remains in power, he will remain a threat to his people, his region, and the world. With our allies, we must pursue a strategy to contain him and to constrain his weapons of mass destruction program, while working toward the day Iraq has a government willing to live at peace with its people and with its neighbors."[156] American and British aircraft in the Iraq no-fly zones attacked hostile Iraqi air defenses 166 times in 1999 and 78 times in 2000.[157][158]
Clinton's November 2000 visit to Vietnam was the first by a U.S. president since the end of the Vietnam War.[159] On October 10, 2000, Clinton signed into law the U.S.–China Relations Act of 2000, which granted permanent normal trade relations (PNTR) trade status to People's Republic of China.[160] The president asserted that free trade would gradually open China to democratic reform.[161] Clinton also oversaw a boom of the U.S. economy. Under Clinton, the United States had a projected federal budget surplus for the first time since 1969.[162]
After initial successes such as the Oslo Accords of the early 1990s, which also led to the Israel–Jordan peace treaty in 1994 and the Wye River Memorandum in October 1998, Clinton attempted an effort to end the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. He brought Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Barak and Palestinian Authority chairman Yasser Arafat together at Camp David for the Camp David Summit in July 2000, which lasted 14 days.[38] Following the failures of the peace talks, Clinton stated Arafat "missed the opportunity" to facilitate a "just and lasting peace". In his autobiography, Clinton blames Arafat for the collapse of the summit.[3][163] Following another attempt in December 2000 at Bolling Air Force Base, in which the President offered the Clinton Parameters, the situation broke down completely after the end of the Taba Summit and with the start of the Second Intifada.[38]
Judicial appointments

Clinton appointed two justices to the Supreme Court: Ruth Bader Ginsburg in 1993[164] and Stephen Breyer in 1994.[165]
Along with his two Supreme Court appointments, Clinton appointed 66 judges to the United States courts of appeals and 305 judges to the United States district courts. His 373 judicial appointments are the second most in American history behind those of Ronald Reagan. Clinton also experienced a number of judicial appointment controversies, as 69 nominees to federal judgeships did not receive a vote in the Republican-controlled Senate Judiciary Committee. In all, 84 percent of his nominees were confirmed.[166]
Among the judges appointed by Clinton to the courts of appeals was Sonia Sotomayor, who was nominated by Clinton in 1997 to the Second Circuit and confirmed in 1998, following a delay of more than a year caused by Republican opposition.[167][168]
Clinton was the first president in history to appoint more women and minority judges than white male judges to the federal courts.[169] In his eight years in office, 11.6% of Clinton's court of appeals nominees and 17.4% of his district court nominees were black; 32.8% of his court of appeals nominees and 28.5% of his district court nominees were women.[170] Clinton appointed the first African American judges to the Fourth Circuit (Roger Gregory) and the Seventh Circuit (Ann Claire Williams).[170] Clinton also appointed the nation's first openly gay or lesbian federal judge when he named Deborah Batts to the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. Batts was confirmed by the Senate in a voice vote in 1994.[171]
Public opinion
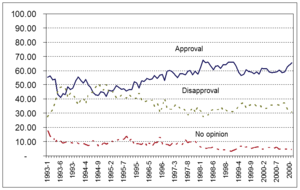
Clinton's job approval rating fluctuated in the 40s and 50s throughout his first term. In his second term, his rating consistently ranged from the high-50s to the high-60s.[172] After his impeachment proceedings in 1998 and 1999, Clinton's rating reached its highest point.[173] According to a CBS News/New York Times poll, Clinton left office with an approval rating of 68 percent, which matched those of Ronald Reagan and Franklin D. Roosevelt as the highest ratings for departing presidents in the modern era.[174] Clinton's average Gallup poll approval rating for his last quarter in office was 61%, the highest final quarter rating any president has received for fifty years.[175] Forty-seven percent of the respondents identified themselves as being Clinton supporters.[175]
As he was leaving office, a CNN/USA Today/Gallup poll revealed that 45 percent of Americans said they would miss him; 55 percent thought he "would have something worthwhile to contribute and should remain active in public life"; 68 percent thought he would be remembered more for his "involvement in personal scandal" than for "his accomplishments"; and 58 percent answered "No" to the question "Do you generally think Bill Clinton is honest and trustworthy?"[175] The same percentage said he would be remembered as either "outstanding" or "above average" as a president, while 22 percent said he would be remembered as "below average" or "poor".[175] ABC News characterized public consensus on Clinton as, "You can't trust him, he's got weak morals and ethics – and he's done a heck of a good job."[176]
In May 2006, a CNN poll comparing Clinton's job performance with that of his successor, George W. Bush, found that a strong majority of respondents said Clinton outperformed Bush in six different areas questioned.[177] Gallup polls in 2007 and 2011 showed that Clinton was regarded by 13% of Americans as the greatest president in U.S. history.[178][179]
In 2014, 18% of respondents in a Quinnipiac University Polling Institute poll of American voters regarded Clinton as the best president since World War II, making him the third most popular among postwar presidents, behind John F. Kennedy and Ronald Reagan.[180] The same poll showed that just 3% of American voters regarded Clinton as the worst president since World War II.[180]
A 2015 poll by The Washington Post asked 162 scholars of the American Political Science Association to rank all the U.S. presidents in order of greatness. According to their findings, Clinton ranked eighth overall, with a rating of 70 percent.[181]
Public image

As the first baby boomer president, Clinton was the first president in more than half a century not to have been alive during World War II.[182] Authors Martin Walker and Bob Woodward state Clinton's innovative use of sound bite-ready dialogue, personal charisma, and public perception-oriented campaigning was a major factor in his high public approval ratings.[183][184] When Clinton played the saxophone on The Arsenio Hall Show, he was described by some religious conservatives as "the MTV president".[185] Opponents sometimes referred to him as "Slick Willie", a nickname which was first applied to him in 1980 by Pine Bluff Commercial journalist Paul Greenberg;[186] Greenberg believed that Clinton was abandoning the progressive policies of previous Arkansas Governors such as Winthrop Rockefeller, Dale Bumpers and David Pryor.[186] The claim "Slick Willie" would last throughout his presidency.[187] Standing at a height of 6 ft 2 in (1.88 m), Clinton is tied with five others as the fourth-tallest president in the nation's history.[188][189] His folksy manner led him to be nicknamed Bubba, especially in the South.[190] Since 2000, he has frequently been referred to as "The Big Dog" or "Big Dog".[191][192] His prominent role in campaigning for President Obama during the 2012 presidential election and his widely publicized speech at the 2012 Democratic National Convention, where he officially nominated Obama and criticized Republican nominee Mitt Romney and Republican policies in detail, earned him the nickname "Explainer-in-Chief".[193][194]
Clinton drew strong support from the African American community and made improving race relations a major theme of his presidency.[195] In 1998, Nobel laureate Toni Morrison called Clinton "the first Black president", saying, "Clinton displays almost every trope of blackness: single-parent household, born poor, working-class, saxophone-playing, McDonald's-and-junk-food-loving boy from Arkansas".[196] Noting that Clinton's sex life was scrutinized more than his career accomplishments, Morrison compared this to the stereotyping and double standards that blacks typically endure.[196]
Shortly after he took office, conservative newspaper owner Richard Mellon Scaife organized a fundraising campaign to smear Clinton's image in the media.[197] Leading the Arkansas Project, Scaife and other associates sought to find sources in Clinton's home state of Arkansas who would be willing to dish out negative allegations against the President.[197]

In 1994, Paula Jones brought a sexual harassment lawsuit against Clinton, claiming he made unwanted advances in 1991, which he denied. In April 1998, the case was initially dismissed by Judge Susan Webber Wright as lacking legal merit.[198] But Jones appealed Webber Wright's ruling, and her suit gained traction following Clinton's admission to having an affair with Monica Lewinsky in August 1998.[199] In 1998, lawyers for Paula Jones released court documents contending a pattern of sexual harassment by Clinton when he was governor of Arkansas. Robert S. Bennett, Clinton's main lawyer for the case, called the filing "a pack of lies" and "an organized campaign to smear the President of the United States" funded by Clinton's political enemies.[200] Clinton later agreed to an out-of-court settlement, paying $850,000.[201] Bennett said that the President made the settlement only so he could end the lawsuit for good and move on with his life.[202] During the deposition for the Jones lawsuit, which was held at the White House,[203] Clinton denied having sexual relations with Monica Lewinsky – a denial that became the basis for an impeachment charge of perjury.[204]
In 1992, Gennifer Flowers stated that she had a relationship with Clinton that began in 1980.[205] Flowers at first denied that she had an affair with Clinton, but later changed her story.[206][207] After Clinton at first denied having a relationship with Flowers on 60 Minutes, he later admitted that he had a sexual encounter with Flowers.[208]

In 1998, Kathleen Willey alleged that Clinton groped her in a hallway in 1993. An independent counsel determined Willey gave "false information" to the FBI, inconsistent with sworn testimony related to the Jones allegation.[209] On March 19, 1998, Julie Hiatt Steele, a friend of Willey, released an affidavit, accusing the former White House aide of asking her to lie to corroborate Ms. Willey's account of being sexually groped by President Clinton in the Oval Office.[210] An attempt by Kenneth Starr to prosecute Steele for making false statements and obstructing justice ended in a mistrial and Starr declined to seek a retrial after Steele sought an investigation against the former Independent Counsel for prosecutorial misconduct.[211] Linda Tripp's grand jury testimony also differed from Willey's claims regarding inappropriate sexual advances.[212]
Also in 1998, Juanita Broaddrick alleged that Clinton had raped her in the spring of 1978, although she stated she did not remember the exact date.[213] In another 1998 event, Elizabeth Gracen recanted a six-year-old denial and stated she had a one-night stand with Clinton in 1982.[214] Gracen later apologized to Hillary Clinton.[215] Throughout the year, however, Gracen eluded a subpoena from Kenneth Starr to testify her claim in court.[216]
Post-presidency (since 2001)
Bill Clinton continues to be active in public life, giving speeches, fundraising, and founding charitable organizations.[217] Clinton has spoken in prime time at every Democratic National Convention since 1988.[218] Robert Reich has suggested that Clinton is in a state of "permanent election", due to the impeachment proceedings during his presidency and his continuing support in the campaigns of his wife Hillary Clinton.[219]
Activities until 2008 campaign
In 2002, Clinton warned that pre-emptive military action against Iraq would have unwelcome consequences,[220][221] and later claimed to have opposed the Iraq War from the start (though some dispute this).[222] In 2005, Clinton criticized the Bush administration for its handling of emissions control, while speaking at the United Nations Climate Change conference in Montreal.[223]
The William J. Clinton Presidential Center and Park in Little Rock, Arkansas was dedicated in 2004.[224] Clinton released a best-selling autobiography, My Life in 2004.[225] In 2007, he released Giving: How Each of Us Can Change the World, which also became a The New York Times Best Seller and garnered positive reviews.[226]

In the aftermath of the 2004 Asian tsunami, U.N. Secretary-General Kofi Annan appointed Clinton to head a relief effort.[227] After Hurricane Katrina, Clinton joined with fellow former President George H. W. Bush to establish the Bush-Clinton Tsunami Fund in January 2005, and the Bush-Clinton Katrina Fund in October of that year.[228] As part of the tsunami effort, these two ex-presidents appeared in a Super Bowl XXXIX pre-game show,[229] and traveled to the affected areas.[230] They also spoke together at the funeral of Boris Yeltsin in 2007.[231]

Based on his philanthropic worldview,[232] Clinton created the William J. Clinton Foundation to address issues of global importance. This foundation includes the Clinton Foundation HIV and AIDS Initiative (CHAI), which strives to combat that disease, and has worked with the Australian government toward that end. The Clinton Global Initiative (CGI), begun by the Clinton Foundation in 2005, attempts to address world problems such as global public health, poverty alleviation and religious and ethnic conflict.[233] In 2005, Clinton announced through his foundation an agreement with manufacturers to stop selling sugared drinks in schools.[234] Clinton's foundation joined with the Large Cities Climate Leadership Group in 2006 to improve cooperation among those cities, and he met with foreign leaders to promote this initiative.[235] The foundation has received donations from a number of governments all over the world, including Asia and the Middle East.[236] In 2008, Foundation director Inder Singh announced deals to reduce the price of anti-malaria drugs by 30 percent in developing nations.[237] Clinton also spoke in favor of California Proposition 87 on alternative energy, which was voted down.[238]
2008 presidential election
During the 2008 Democratic presidential primary campaign, Clinton vigorously advocated on behalf of his wife, Hillary Clinton. Through speaking engagements and fundraisers, he was able to raise $10 million toward her campaign.[239] Some worried that as an ex-president, he was too active on the trail, too negative to Clinton rival Barack Obama, and alienating his supporters at home and abroad.[240] Many were especially critical of him following his remarks in the South Carolina primary, which Obama won. Later in the 2008 primaries, there was some infighting between Bill and Hillary's staffs, especially in Pennsylvania.[241] Considering Bill's remarks, many thought that he could not rally Hillary supporters behind Obama after Obama won the primary.[242] Such remarks lead to apprehension that the party would be split to the detriment of Obama's election. Fears were allayed August 27, 2008, when Clinton enthusiastically endorsed Obama at the 2008 Democratic National Convention, saying that all his experience as president assures him that Obama is "ready to lead".[243] After Hillary Clinton's presidential campaign was over, Bill Clinton continued to raise funds to help pay off her campaign debt.[244][245]
After the 2008 election

In 2009, Clinton travelled to North Korea on behalf of two American journalists imprisoned in North Korea. Euna Lee and Laura Ling had been imprisoned for illegally entering the country from China.[246] Jimmy Carter had made a similar visit in 1994.[246] After Clinton met with North Korean leader Kim Jong-il, Kim issued a pardon.[247][248]
Since then, Clinton has been assigned a number of other diplomatic missions. He was named United Nations Special Envoy to Haiti in 2009.[249] In response to the 2010 Haiti earthquake, U.S. President Barack Obama announced that Clinton and George W. Bush would coordinate efforts to raise funds for Haiti's recovery.[250] Clinton continues to visit Haiti to witness the inauguration of refugee villages, and to raise funds for victims of the earthquake.[251] In 2010, Clinton announced support of, and delivered the keynote address for, the inauguration of NTR, Ireland's first environmental foundation.[252][253] At the 2012 Democratic National Convention, Clinton gave a widely praised speech nominating Barack Obama.[254]
Post-presidential health concerns
In September 2004, Clinton received a quadruple bypass surgery.[255] In March 2005, he underwent surgery for a partially collapsed lung.[256] On February 11, 2010, he was rushed to NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital in New York City after complaining of chest pains, and had two coronary stents implanted in his heart.[255][257] After this experience, Clinton adopted the plant-based whole foods (vegan) diet recommended by doctors Dean Ornish and Caldwell Esselstyn.[258]
Wealth

The Clintons accrued several million dollars in legal bills during his presidency; they were paid off four years after he left office.[259] Both Bill and Hillary Clinton have received millions of dollars in book authorship fees.[260] In February 2016, CNN reported that documents show the Clintons combined to receive more than $153 million in paid speeches from 2001 until spring 2015.[261] In May 2015, The Hill reported that Bill and Hillary Clinton have made more than $25 million in speaking fees since the start of 2014, and that Hillary Clinton also made $5 million or more from her book, Hard Choices, during the same time period.[262] In July 2014, The Wall Street Journal reported that at the end of 2012, the Clintons were worth between $5 million and $25.5 million, and that in 2012 (the last year they were required to disclose the information) the Clintons made between $16 and $17 million, mostly from speaking fees earned by the former president.[263] Clinton earned more than $104 million from paid speeches between 2001 and 2012.[264] In June 2014, ABC News and The Washington Post reported that Bill Clinton has made more than $100 million giving paid speeches since leaving public office, and in 2008, the New York Times reported that the Clintons' income tax returns[265] show they have made $109 million in the 8 years from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2007, including almost $92 million from his speaking and book-writing.[260][266][267][268]
Bill Clinton has given dozens of paid speeches each year, mostly to corporations and philanthropic groups in North America and Europe, often earning $100,000 to $300,000 per speech.[261][269][270][271] Hillary Clinton said that she and Bill came out of the White House financially "broke" and in debt, especially due to large legal fees incurred during their years in the White House. "We had no money when we got there, and we struggled to, you know, piece together the resources for mortgages, for houses, for Chelsea's education." She added, "Bill has worked really hard ... we had to pay off all our debts ... he had to make double the money because of, obviously, taxes; and then pay off the debts, and get us houses, and take care of family members."[267]
Honors and recognition


Various colleges and universities have awarded Clinton honorary degrees, including Doctorate of Law degrees[272][273] and Doctor of Humane Letters degrees.[274] He is an Honorary Fellow of University College, Oxford, which he attended as a Rhodes Scholar.[275] Schools have been named for Clinton,[276][277][278] and statues have been built to pay him homage.[279][280] U.S. states where he has been honored include Missouri,[281] Arkansas,[282] Kentucky,[283] and New York.[284] He was presented with the Medal for Distinguished Public Service by Secretary of Defense William Cohen in 2001.[285] The Clinton Presidential Center was opened in Little Rock, Arkansas in his honor on December 5, 2001.[286]
He has been honored in various other ways, in countries that include the Czech Republic,[287] Papua New Guinea,[288] Germany,[289] and Kosovo.[279] The Republic of Kosovo, in gratitude for his help during the Kosovo War, renamed a major street in the capital city of Pristina as Bill Clinton Boulevard and added a monumental Clinton statue.[290][291][292]
Clinton was selected as Time's "Man of the Year" in 1992,[293] and again in 1998, along with Ken Starr.[294] From a poll conducted of the American people in December 1999, Clinton was among eighteen included in Gallup's List of Widely Admired People of the 20th century.[295] He was honored with a Grammy Award for Best Spoken Word Album for Children, a J. William Fulbright Prize for International Understanding,[296] a TED Prize (named for the confluence of technology, entertainment and design),[297] and was named as an Honorary GLAAD Media Award recipient for his work as an advocate for the LGBT community.[298]
In 2011, President Michel Martelly of Haiti awarded Clinton with the National Order of Honour and Merit to the rank of Grand Cross "for his various initiatives in Haiti and especially his high contribution to the reconstruction of the country after the earthquake of January 12, 2010". Clinton declared at the ceremony that "in the United States of America, I really don't believe former American presidents need awards anymore, but I am very honored by this one, I love Haiti, and I believe in its promise".[299]
U.S. President Barack Obama awarded Clinton the Presidential Medal of Freedom on November 20, 2013.[300]
Authored books
- Between Hope and History. New York: Times Books. 1996. ISBN 978-0-8129-2913-3.
- My Life (1st ed.). New York: Vintage Books. 2004. ISBN 978-1-4000-3003-3.
- Giving: How Each of Us Can Change the World (1st ed.). New York: Knopf. 2007. ISBN 0-307-26674-5.
- Back to Work: Why We Need Smart Government for a Strong Economy. Knopf. 2011. ISBN 978-0-307-95975-1.
Recordings
Bill Clinton is one of the narrators on a 2003 recording of Sergei Prokofiev's Peter and the Wolf, on Pentatone, together with Mikhail Gorbachev and Sophia Loren.
See also
- Clinton family
- Clinton School of Public Service
- Gun control policy of the Clinton Administration
- Historical rankings of Presidents of the United States
- List of Governors of Arkansas
- List of Presidents of the United States
- List of Presidents of the United States by previous experience
References
- ^ He was raised a Southern Baptist. (i.e., a member of the Southern Baptist Convention SBC). Clinton left the SBC due to disagreement with its conservative positions (detail: here); see also: New Baptist Covenant.
- ^ "Directory of Irish Genealogy: American Presidents with Irish Ancestors". Homepage.eircom.net. March 23, 2004. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Clinton, Bill (2004). My Life. Random House. ISBN 1-4000-3003-X.
- ^ a b "Biography of William J. Clinton". The White House. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Andrews, Edmund (June 21, 1993). "Clinton Reported to Have A Brother He Never Met". New York Times.
- ^ "Oprah Talks to Bill Clinton". O, The Oprah Magazine. August 2004. Retrieved December 18, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Maraniss, David (1996). First In His Class: A Biography Of Bill Clinton. Touchstone. ISBN 0-684-81890-6.
- ^ Soni, Jimmy (June 25, 2013). "10 Things You Definitely Didn't Know About Bill Clinton". The Huffington Post.
- ^ David Maraniss (1996). First In His Class: A Biography of Bill Clinton. Touchstone. p. 43.
- ^ "It All Began in a Place Called Hope (Archived whitehouse.gov Article)". The White House. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Robert E. Levin, Bill Clinton: The Inside Story, 1992, pages xxiv–xxv
- ^ "About Leadership". APO.org. Retrieved April 7, 2013.
- ^ DeMolay - Hall Of Fame » William Clinton, quote: "Clinton was initiated into Hot Springs Chapter in Hot Springs, Arkansas, in 1961, where he served as Master Councilor. He received the Chevalier in 1964, and the Legion of Honor in 1979. Clinton was inducted into the DeMolay Hall of Fame on May 1, 1988."
- ^ "Prominent Members". Kappa Kappa Psi. Retrieved August 30, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ Dowd, Maureen (June 9, 1994). "Oxford Journal; Whereas, He Is an Old Boy, If a Young Chief, Honor Him". The New York Times. Retrieved July 17, 2009.
- ^ Christopher Hitchens. "Chris or Christopher?". Hitch-22: A Memoir. London, England: Atlantic books. pp. 106–107. ISBN 978-1-84354-922-2.
- ^ Cain, Nick; Growden, Greg. "21: Ten Peculiar Facts about Rugby". Rugby Union for Dummies (2 ed.). Chichester, England: John Wiley and Sons. p. 297. ISBN 978-0-470-03537-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Neil Hamilton, Presidents: A Biographical Dictionary, 2005, page 367
- ^ Steven Gillon, The Pact: Bill Clinton, Newt Gingrich, and the Rivalry that Defined a Generation, 2008, page 21
- ^ New York Times, The 1992 Campaign; A Letter by Clinton on His Draft Deferment: 'A War I Opposed and Despised', February 13, 1992
- ^ Lauter, David (February 13, 1992). "Clinton Releases '69 Letter on ROTC and Draft Status". Los Angeles Times. Los Angeles, CA.
- ^ Morris, Roger (April 25, 1999). Partners in Power: The Clintons and Their America. Regnery Publishing. p. 100. ISBN 978-0-89526-302-5. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ CNN, All Politics (1997). "Clinton's Draft Deferrment". CNN. Retrieved June 19, 2014.
{{cite news}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Bill Clinton's Draft Letter". Frontline. PBS. November 23, 1991. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Frammolino, Ralph (April 6, 1992). "ROTC Officer Unaware of Draft Notice: Clinton: The man whose action kept the future governor in school says he was not told of 1969 induction letter. Draft board insists none was sent". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved January 6, 2013.
- ^ Public Broadcasting System, Frontline: Interview with James Carville, 2000
- ^ a b "Hillary Rodham Clinton". The White House. Archived from the original on July 24, 2011. Retrieved August 26, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Gerstein, Josh (November 26, 2007). "The Clintons' Berkeley Summer of Love". The New York Sun. Retrieved May 9, 2009.
- ^ a b "Bill Clinton Political Career". CNN. 1997. Archived from the original on September 20, 2002. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Adam Cohen (December 12, 2007). "Bill and Hillary Clinton's Pitch in Iowa: 'I Love the '90s'". The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ R. Emmett Tyrrell, Jr. (1996). Boy Clinton: The Political Biography. Eagle Publishing. ISBN 978-0-89526-439-8.
- ^ Michael Kelly (November 27, 1992). "Little Rock Hopes Clinton Presidency Will Put Its Dogpatch Image to Rest". The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Jonathan W. Nicholsen. "Bill Clinton Timeline". Timeline Help. Retrieved August 30, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ a b Pendleton, Scott (July 21, 1992). "Governor Gets High Marks for Public Education Reforms". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ a b c d e f Klein, Joe (2002). The Natural: The Misunderstood Presidency of Bill Clinton. Doubleday. ISBN 0-7679-1412-0.
- ^ "Bill Clinton, New Democrat". DLC. July 25, 2004. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
- ^ Blumenthal, Sidney (2003). The Clinton Wars (1st ed.). Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 0-374-12502-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Harris, John F. (2006). The Survivor: Bill Clinton in the White House (1st ed.). Random House Trade Paperbacks. ISBN 0-375-76084-9.
- ^ a b George Stephanopoulos, All Too Human: A Political Education, 1999, ISBN 978-0-316-92919-6
- ^ Nguyen, Alexander (July 14, 2000). "Bill Clinton's Death Penalty Waffle—and Why It's Good News for Execution's Foes". The American Prospect. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
In his early days, Clinton opposed the death penalty. And while he and his wife Hillary Rodham Clinton were both teaching at the University of Arkansas Law School, she wrote an appellate brief that helped save a mentally retarded man from execution. "Clinton was against the death penalty," says Arkansas attorney Jeff Rosenzweig, who, like Clinton, grew up in Hot Springs, Arkansas. "He told me so."
- ^ "Arkansas". Death Penalty Information Center. Archived from the original on February 27, 2010. Retrieved February 24, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Clemency". Death Penalty Information Center. Archived from the original on February 21, 2010. Retrieved February 24, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ David Maraniss, First in His Class: A Biography of Bill Clinton (New York: Random House, 1996; ISBN 978-0-684-81890-0).
- ^ Church, George J. (January 27, 1992). "Cover: Is Bill Clinton For Real?". Time. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Kornacki, Steve (July 30, 2012). "When Bill Clinton died onstage". Salon. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e Woodward, Bob (2005). The Choice: How Bill Clinton Won. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-8514-X.
- ^ Safire, William (December 6, 1993). "Essay; Looking Beyond Peace". The New York Times. Retrieved October 29, 2008.
- ^ Duffy, Michael; Barrett, Laurence I.; Blackman, Ann; Carney, James (November 29, 1993). "Secrets Of Success". Time. Retrieved October 29, 2008.
- ^ Bob Woodward (September 15, 2007). "Greenspan Is Critical Of Bush in Memoir". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 9, 2014.
- ^ Steve Schifferes (January 15, 2001). "Bill Clinton's economic legacy". BBC News. Retrieved January 9, 2014.
- ^ Baker, Peter (February 3, 2008). "Bill Clinton's Legacy". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 13, 2010.
- ^ "Bill Clinton". History.com. Retrieved July 13, 2010.
- ^ Stevenson, Richard (February 8, 2000). "The Battle of the Decades; Reaganomics vs. Clintonomics Is a Central Issue in 2000". The New York Times. Retrieved March 15, 2011.
- ^ "Revenues, Outlays, Deficits, Surpluses, and Debt Held by the Public, 1968 to 2007, in Billions of Dollars". Congressional Budget Office. September 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 8, 2013. Retrieved July 13, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Budget and Deficit Under Clinton". FactCheck.org. Archived from the original on July 28, 2011. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Historical Debt Outstanding – Annual 1950–1999". Treasury Direct.
- ^ Herste, Amy (January 11, 2001). "Clinton thanks New Hampshire for making him the 'Comeback Kid'". CNN. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Ifill, Gwen (March 17, 1992). "Hillary Clinton Defends Her Conduct in Law Firm". The New York Times. Retrieved March 28, 2008.
- ^ MacGillis, Alec; Kornblut, Anne E. (December 21, 2007). "Hillary Clinton Embraces Her Husband's Legacy". The Washington Post. p. A1. Retrieved March 28, 2008.
- ^ Applebome, Peter (January 25, 1992). "Arkansas Execution Raises Questions on Governor's Politics". The New York Times. Retrieved March 28, 2008.
- ^ "How the Presidents Stack Up: A look at U.S. presidents' job-approval ratings". The Wall Street Journal. 2006. Archived from the original on October 25, 2008. Retrieved October 30, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Le Beau, Bryan. "The Political Mobilization of the New Christian Right". Creighton University. Archived from the original on December 6, 2006. Retrieved December 1, 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Walker, Martin (January 6, 1992). "Tough love child of Kennedy". The Guardian. London. Retrieved October 12, 2007.
- ^ a b c "On this day (November 4) in 1992: Clinton beats Bush to the White House". BBC News. November 4, 1992. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved October 31, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Party Division in the Senate, 1789–present". United States Senate. Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "House History". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Clinton, Bill (January 20, 1993). "First Inaugural Address of William J. Clinton; January 20, 1993". Yale Law School. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "U.S. Senate Roll Call Votes 103rd Congress – 1st Session". United States Senate. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "New Nationwide Poll Shows Strong Support for Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)" (PDF). Protect Family Leave. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Sharon L. Camp, The Politics of U.S. Population Assistance, in Beyond the Numbers: A Reader on Population, Consumption and the Environment (ed. Laurie Ann Mazur), p. 130.
- ^ Amy Sullivan, The Party Faithful: How and Why Democrats Are Closing the God Gap (Simon & Schuster: 2008), pp. 91–92.
- ^ Sullivan, The Party Faithful, pp. 236–37.
- ^ Richard L. Burke (February 15, 1993). "White House Hones All-Out Campaign to Sell Sacrifice". The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "The Clinton Years: Chronology". Frontline: PBS. Archived from the original on May 2, 2010. Retrieved June 13, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Woodward, Bob (2000). Maestro. New York: Simon & Schuster. p. 116.
- ^ Hillary Clinton (2003). Living History. Simon & Schuster. p. 172. ISBN 0-7432-2224-5.
- ^ Ken Gormley (2010). The Death of American Virtue: Clinton vs. Starr. New York: Crown Publishers. pp. 70–71. ISBN 978-0-307-40944-7.
- ^ Clinton, Bill (August 3, 1993). "Presidential Press Conference in Nevada". Archived from the original on September 27, 2007.
- ^ Clinton, Bill (January 25, 1994). "William J. Clinton: Address Before a Joint Session of the Congress on the State of the Union". Presidency.ucsb.edu. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ Jonathan Broder; Murray Waas (March 17, 1998). "The Road To Hale". Salon. Archived from the original on June 16, 2006. Retrieved August 25, 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Karl, Jonathan (March 10, 1998). "Reporter Apologizes For Clinton Sex Article". CNN. Archived from the original on June 14, 2008.
- ^ Feder, Jody (2010). "Don't Ask, Don't Tell": A Legal Analysis. DIANE Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4379-2208-0.
- ^ Mixner, David (November 25, 2009). Stranger Among Friends. Random House Publishing Group. pp. 495–497. ISBN 978-0-307-42958-2. Retrieved September 12, 2014.
- ^ John Cloud (November 1996). "Stranger Among Friends. – book reviews". Washington Monthly. Retrieved August 30, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ "President seeks better implementation of 'don't ask, don't tell'". CNN. December 11, 1999. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Obama certifies end of military's gay ban". NBC News. Reuters. July 22, 2011. Archived from the original on July 29, 2011. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Don C. Livingston; Kenneth A. Wink (1997). "The Passage of the North American Free Trade Agreement in the U.S. House of Representatives: Presidential Leadership or Presidential Luck?". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 27.
- ^ "HR 3355 – Omnibus Crime Bill". votesmart.org. Retrieved September 12, 2015.
- ^ "Bill Clinton". 4to40.com. Retrieved November 4, 2010.
- ^ "Welcome to the White House". Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "The Clinton White House Web Site". Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Welcome to the White House". Archived from the original on July 23, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Longley, Robert. "The Clinton White House Web Site: Part 2: Preserving the Clinton White House Web Site". Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Longley, Robert. "The Clinton White House Web Site: Part 1: Perhaps the most important Web site in American history". About.com. Retrieved June 6, 2007.
- ^ Hulsey, Byron. "The Altered Terrain of American Politics (Review of Do Elections Matter?)". Retrieved October 29, 2008.
- ^ Robert Ray (March 16, 2000). "Final Report of the Independent Counsel ... of the Investigation In Re: Anthony Marceca" (PDF). United States Government Printing Office. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Independent counsel: No evidence to warrant prosecution against first lady in 'filegate'". CNN. July 28, 2000. Archived from the original on May 29, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "PUBLIC LAW 104 – 199 – DEFENSE OF MARRIAGE ACT". U.S. Government Printing Office.
- ^ Frank Rich (February 26, 2012). "Bill Clinton's shifting justifications for signing the Defense of Marriage Act". New York.
- ^ a b Chris Geidner (September 29, 2011). "Becoming Law". MetroWeekly.
- ^ "Bill Clinton's Justifications for Signing DOMA – New York Magazine". New York. Retrieved March 28, 2015.
- ^ "Unfinished Business: The Defense of Marriage Act". The New York Times. July 2, 2011.
- ^ Richard Socarides (June 26, 2013). "How The Court Ruled on DOMA and Prop. 8". The New Yorker. Retrieved March 28, 2015.
- ^ "ClintonGore Accomplishments: Gay and Lesbian Americans". Clinton2.nara.gov. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ a b Socarides, Richard. "Why Bill Clinton Signed the Defense of Marriage Act". The New Yorker. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ Volsky, Igor. (August 5, 1995) Clinton Issued Order Letting Gays Get Security Clearances 16 Years Ago Today
- ^ "Clinton Grants Gay Workers Job Protection". The New York Times. May 29, 1998. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ "2000.12.01: (Fact Sheet) Clinton Administration Record on HIV/AIDS". Archive.hhs.gov. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ "S. 2056 (104th): Employment Nondiscrimination Act of 1996 (On Passage of the Bill)". Govtrack.us. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ "Bill Clinton Backs Same-Sex Marriage". The Nation. July 14, 2009. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ Clinton, Bill (March 7, 2013). "It's time to overturn DOMA". The Washington Post. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ "GLAAD honours Bill Clinton". 3 News NZ. April 22, 2013.
- ^ Gregory Gromov. "History of the Internet and World Wide Web". Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Bob Woodward; Brian Duffy (February 13, 1997). "Chinese Embassy Role In Contributions Probed". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Louis Freedberg (June 2, 1995). "New Limits In Works on Immigration / Powerful commission focusing on families of legal entrants". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Plummer Alston Jones (2004). Still struggling for equality: American public library services with minorities. Libraries Unlimited. p. 154. ISBN 1-59158-243-1.
- ^ Robert Pear (June 8, 1995). "Clinton Embraces a Proposal To Cut Immigration by a Third". The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ a b Discovery TV. "Clinton Assassination Attempt – Secret Service Secrets". YouTube. Retrieved March 29, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Gormley, Ken (February 1, 2011). The Death of American Virtue: Clinton vs. Starr. Crown Publishing Group. p. 800. ISBN 0-307-40945-7.
- ^ N.A. "Bombs Found As Manila Readies For APEC Summit". The Seattle Times.
{{cite news}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b N.A. "Explosives Found Near Summit Site". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press.
{{cite news}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Jones, Charles O. (2005). The Presidency in a Separated System. The Brookings Institution. p. 318.
- ^ Shogren, Elizabeth (October 4, 1997). "Clinton to Get Hearing Aids for Both Ears". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
- ^ "Financial Services Modernization Act of 1999". Federal Reserve History. Retrieved September 12, 2015.
- ^ "Time Line". The Washington Post. September 13, 1998. p. A32. Retrieved January 20, 2007.
- ^ The Starr Report: The Findings of Independent Counsel Kenneth Starr on President Clinton and the Lewinsky Affair. 1998. ISBN 1-891620-24-X.
- ^ Dan Froomkin (August 26, 1999). "Case Closed". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ a b c Senate LIS (February 12, 1999). "U.S. Senate Roll Call Votes 106th Congress – 1st Session: vote number 17 – Guilty or Not Guilty (Art I, Articles of Impeachment v. President W. J. Clinton)". United States Senate. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Clinton impeached". BBC News. December 19, 1998. Archived from the original on December 11, 2008. Retrieved October 29, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Senate Acquits President Clinton". The Washington Post. February 13, 1999. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- ^ Neal v. Clinton, Civ. No. 2000-5677, Agreed Order of Discipline (Ark. Cir. Ct. 2001) ("Mr. Clinton admits and acknowledges ... that his discovery responses interfered with the conduct of the Jones case by causing the court and counsel for the parties to expend unnecessary time, effort, and resources").
- ^ "Bill cops a plea". The Wall Street Journal. January 22, 2001.
- ^ "Clinton Pardon's List". The Washington Post. Associated Press. January 20, 2001. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Clinton pardons: Cast of characters". BBC News. February 22, 2001. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Curl, Joseph (August 30, 2011). "Clintons hit over Libby criticism". The Washington Times.
- ^ "America's Flight 17". Slate. July 23, 2014.
- ^ "Bill Clinton: I got closer to killing bin Laden". CNN. September 24, 2006. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Ijaz, Mansoor (December 5, 2001). "Clinton Let Bin Laden Slip Away and Metastisize". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved June 13, 2010.
- ^ "Staff Statement No. 5" (PDF). 9/11 Commission. Retrieved August 6, 2009.
- ^ Lichtblau, Eric (August 17, 2005). "State Dept. Says It Warned About bin Laden in 1996". The New York Times. Retrieved November 4, 2010.
- ^ John Pike. "BGM-109 Tomahawk – Smart Weapons". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ Cohen, William (April 7, 1999). "Secretary Cohen's Press Conference at NATO Headquarters". Archived from the original on May 29, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Clinton, Bill (August 30, 2011). "Press Conference by the President".
- ^ "Resolution 1244 (1999)". NATO. June 10, 1999. Archived from the original on June 29, 2011. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Adam Roberts (April 10, 2003). "The Impact of the Laws of War in Contemporary Conflicts (PDF)" (PDF). Princeton University. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ "Two die in Apache crash". BBC News. May 5, 1999. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ Pilger, John (September 4, 2000). "US and British officials told us that at least 100,000 were murdered in Kosovo. A year later, fewer than 3,000 bodies have been found". New Statesman.
- ^ Daniel Pearl; Robert Block (December 31, 1999). "War in Kosovo Was Cruel, Bitter, Savage; Genocide It Wasn't". The Wall Street Journal. p. A1.
- ^ "Kosovo assault 'was not genocide'". BBC News. September 7, 2001. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ George J. Andreopoulos. "Ethnic Cleansing". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ a b "The charges against Milosevic". BBC News. March 11, 2006. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ Milosevic's war crimes trial a 4-year marathon, CNN (March 11, 2006).
- ^ Clinton, Bill (January 27, 1998). "Text of President Clinton's 1998 State of the Union Address". The Washington Post (Press release). Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Iraq Liberation Act of 1998, H.R.4655, One Hundred Fifth Congress of United States of America at Second Session". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on February 18, 2007. Retrieved February 18, 2007.
- ^ "H.R.4655 – Iraq Liberation Act of 1998".
- ^ "Address to the Nation on Completion of Military Strikes in Iraq". Presidency.ucsb.edu. December 19, 1998. Retrieved July 22, 2013.
- ^ John Pike. "Operation Southern Watch". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved July 22, 2013.
- ^ John Pike. "Operation Northern Watch". Web.archive.org. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved July 22, 2013.
- ^ "Clinton's Vietnam visit". BBC News. November 16, 2000. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Smith, Matt (October 10, 2000). "Clinton signs China trade bill". CNN. Retrieved July 3, 2014.
- ^ Peter B. Levy (2002). Encyclopedia of the Clinton Presidency. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 57. ISBN 0-313-31294-X.
- ^ "Historical Budget Data" (PDF). Congressional Budget Office. January 26, 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 1, 2007. Retrieved January 20, 2007.
- ^ Shyovitz, David. "Camp David 2000". Jewish Virtual Library. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Biographies of Current Justices of the Supreme Court". Supremecourt.gov. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Appointment and swearing in of Justice Breyer, 1994". Law.onecle.com. September 30, 1994. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Biographical Directory of Federal Judges". Federal Judicial Center. Retrieved August 29, 2011.
- ^ Meg Greene, Sonia Sotomayor: A Biography (ABC-CLIO, 2012), pp. 121–29.
- ^ Sonia Sotomayor Fast Facts, CNN Library (June 22, 2015).
- ^ Nancy Scherer, Scoring Points: Politicians, Activists, and the Lower Federal Court Appointment Process (Stanford University Press, 2005), p. 85.
- ^ a b Scherer, p. 85.
- ^ Henry J. Reske, Appointment Breaks Barrier: First Openly Gay Federal Judge Assumes Duties, ABA Journal (December 1994), p. 27.
- ^ "Bill Clinton: Job Ratings". Pollingreport.com. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
- ^ "Clinton's approval rating up in wake of impeachment". CNN. December 20, 1998. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Bootie Cosgrove-Mather (June 7, 2004). "A Look Back at the Polls". CBS News. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ a b c d David W. Moore, Clinton Leaves Office With Mixed Public Reaction, Gallup Organization (January 12, 2001).
- ^ Gary Langer (January 17, 2001). "Poll: Clinton Legacy Mixed". ABC News. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- ^ "Poll: Clinton outperformed Bush". CNN. May 15, 2006. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Lydia Saad, Lincoln Resumes Position as Americans' Top-Rated President: Reagan and Clinton lead among members of their respective parties, Gallup (February 19, 2007).
- ^ Frank Newport, [Americans Say Reagan Is the Greatest U.S. President: Lincoln and Clinton next on the list; Washington fifth], Gallup (February 18, 2011).
- ^ a b Obama Is First As Worst President Since WWII, Quinnipiac University National Poll Finds; More Voters Say Romney Would Have Been Better, Quinnipiac University (July 2, 2014).
- ^ New ranking of U.S. presidents puts Lincoln at No. 1, Obama at 18; Kennedy judged most overrated – The Washington Post.. Retrieved March 24, 2015
- ^ Sandalow, Marc (January 14, 2001). "Clinton Era Marked by Scandal, Prosperity: 1st Baby Boomer in White House Changed Notions of Presidency". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on June 11, 2008. Retrieved October 29, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Martin Walker, Clinton: the President they deserve, Fourth Estate 1999
- ^ Bob Woodward, The choice: how Clinton won, Touchstone 1996, ISBN 0-684-81308-4
- ^ Bresler, Robert J. (January 2001). "The Muddled Meaning of the 2000 Election". USA Today (Society for the Advancement of Education). Retrieved January 2, 2007.[dead link]
- ^ a b American Frontline:Stories of Bill. Retrieved May 4, 2015
- ^ Mérida, Kevin (December 20, 1998). "It's Come To This: A Nickname That's Proven Hard to Slip". The Washington Post.
- ^ Baker, Peter (October 11, 2007). "Head and Shoulders Above the Rest". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on July 28, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Carnahan, Ira (May 19, 2004). "Presidential Timber Tends To Be Tall". Forbes. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Hurt, Charles; Campanile, Carl (June 27, 2007). "Rudy Bops Bubba". New York Post. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
- ^ Dowd, Maureen (October 22, 2000). "Liberties; Dare Speak His Name". The New York Times. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
They're going to have to let the big dog run.
- ^ Rutenberg, Jim; Zernike, Kate (September 20, 2010). "Bill Clinton Stumps for Obama". The New York Times. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
The Big Dog, as he is known among those in the tight world of Clinton associates ...
- ^ McDuffee, Allen (September 6, 2012). "Bill Clinton's DNC speech as 'explainer in chief,' 'it takes some brass,' and more [AM Briefing]". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 25, 2013.
- ^ Poniewozik, James (September 6, 2012). "The Morning After: Obama Turns to Bill Clinton, Explainer-in-Chief". Time. Retrieved January 25, 2013.
- ^ "A Conversation With President Bill Clinton on Race in America Today". Center for American Progress. July 16, 2004. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ a b Morrison, Toni (October 1998). "Clinton as the first black president". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on October 21, 2006. Retrieved December 1, 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Robert G. Kaiser; Ira Chinoy (May 2, 1999). "Scaife: Funding Father of the Right". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 19, 2013.
- ^ "Clinton Welcomes Jones Decision; Appeal Likely". CNN. April 2, 1998. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ "Text of Jones's Appeal". The Washington Post. July 31, 1998. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ^ Clines, Francis X. (March 14, 1998). "Testing of a President: The Accuser; Jones Lawyers Issue Files Alleging Clinton Pattern of Harassment of Women". The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Appeals court ponders Paula Jones settlement". CNN. November 18, 1998. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Baker, Peter (November 14, 1998). "Clinton Settles Paula Jones Lawsuit for $850,000". The Washington Post. Retrieved October 27, 2011.
- ^ "Deposition of William Jefferson Clinton, January 17, 1998". CNN. March 13, 1998. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ "Lewinsky scandal". The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. Columbia University Press. 2008. Archived from the original on June 18, 2009. Retrieved February 9, 2010.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Declaration of Gennifer Flowers". The Washington Post. March 13, 1998. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
- ^ "Gennifer Flowers may proceed with defamation suit". Reporters Committee for Freedom of the Press. November 19, 2002. Archived from the original on December 9, 2007. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
At the press conference, Flowers – who initially denied allegations that she had an affair with then Arkansas governor Bill Clinton but then changed her story – played tapes of conversations she had secretly recorded between herself and Clinton
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Archived copy". Retrieved May 27, 2012.[dead link]
- ^ Clines, Francis X. (March 14, 1998). "Testing Of A President: The Accuser; Jones Lawyers Issue Files Alleging Clinton Pattern Of Harassment Of Women". The New York Times. Retrieved March 20, 2008.
In his January deposition, the President, though finally confirming a sexual encounter with Ms. Flowers, was precise in denying Ms. Willey's report that he had sought to kiss her and feel her breasts in an encounter in his private dining room off the Oval Office.
- ^ "The Lives Of Kathleen Willey". CNN. March 30, 1998. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ John M. Broder (March 19, 1998). "Friend Accuses Willey for Plea to her to Lie". The New York Times. Retrieved February 15, 2014.
- ^ Peter Levy (November 30, 2001). Encyclopedia of the Clinton Presidency. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 328–329. ISBN 978-0-313-31294-6. Retrieved February 15, 2014.
- ^ "Stalking the president". Salon. January 1999. Archived from the original on January 29, 2011. Retrieved February 15, 2014.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Full Transcript of NBC Dateline report on Juanita Broaddrick". February 1999. Archived from the original on February 16, 2006.
- ^ "All the President's Women – Elizabeth Ward Gracen". Comedy on Tap.
- ^ "Former Miss America Apologizes To First Lady". CNN. April 25, 1998. Archived from the original on June 14, 2008. Retrieved November 9, 2008.
- ^ "Big Year for the Bad News Bearers". The Washington Post. December 24, 1998.
- ^ Josh Gerstein (January 17, 2006). "Clinton Eligible, Once Again, To Practice Law". New York Sun. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Bill Clinton's Democratic Convention Speeches, The New York Times (September 5, 2012).
- ^ The Permanent Election. (August 27, 2003) The American Prospect. Retrieved February 3, 2016.
- ^ "House Passes Resolution Authorizing Use of Force in Iraq; New Jerssy Supreme Court Hears Argument For, Against New Democrat on Ballot". CNN. October 2, 2002. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
- ^ Andrew Grice (October 3, 2002). "Clinton urges caution over Iraq as Bush is granted war powers". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on August 21, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
As a preemptive action today, however well-justified, may come back with unwelcome consequences in the future. And because I don't care – and I've done this. I've ordered these kinds of actions. I don't care how precise your bombs and your weapons are, when you set them off, innocent people will die.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Bill Clinton Says He Opposed Iraq War from Start (UPDATED)". Outsidethebeltway.com. November 28, 2007. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ "Last-minute climate deals reached". BBC News. December 10, 2005. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Clinton Library open for business". BBC News. November 18, 2004. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ Glaister, Dan (May 22, 2006). "Oprah Winfrey book deal tops Clinton's $12 m". The Guardian. London. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Best Sellers". The New York Times. September 23, 2007. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013. Retrieved September 18, 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Clinton to be U.N.'s envoy on tsunami relief". MSNBC. Associated Press. February 1, 2005. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "2006 Philadelphia Liberty Medal Award". Constitutioncenter.org. Retrieved August 26, 2011.
- ^ Maske, Mark (January 27, 2005). "Senior Bush, Clinton to Appear at Super Bowl". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ^ "Bush, Clinton end tsunami visit". BBC News. February 21, 2005. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ "Former Presidents Bush, Clinton Represent U.S. at Boris Yeltsin's Funeral". Fox News Channel. April 24, 2007.
- ^ Jon Meacham (December 20, 2009). "Planetary Problem Solver". Newsweek. Archived from the original on August 16, 2011. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Clinton Global Initiative". Clinton Global Initiative. June 19, 2011. Archived from the original on August 7, 2011. Retrieved August 17, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "William J. Clinton Foundation announces agreement to reduce junk food in schools". Comcast.net. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ^ "Clinton Foundation and Climate Partnership, Press Release". August 1, 2006. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007.
- ^ Baker, Peter; Davies, Anne (November 18, 2008). "Obama team turns scrutiny on Bill Clinton". The Age. Melbourne. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Pohla Smith (August 20, 2008). "Young man combines expertise in economics and social issues at Clinton Foundation". Pittsburg Post-Gazette. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Indravudh, Peach (October 15, 2006). "Clinton backs Prop. 87". Daily Bruin. UCLA. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Robert Yoon (July 30, 2008). "Bill Clinton 2007 speech haul tops $10 million". CNN. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Vaughn Ververs (January 26, 2008). "Analysis: Bill Clinton's Lost Legacy". CBS News. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Peter Baker And Jim Rutenberg (June 8, 2008). "The Long Road to a Clinton Exit". The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ Jonathan Alter (August 6, 2008). "A Catharsis in Denver?". Newsweek. Archived from the original on November 10, 2011. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Lynn Sweet (August 28, 2008). "Bill Clinton vouches for Obama: now 'ready to lead'". Chicago Sun-Times. Archived from the original on October 17, 2011. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Clinton Turns to Husband's Charity to Retire Campaign Debt". Fox News Channel. December 24, 2008. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Stephanie Condon (May 13, 2010). "Bill Clinton Raffles Himself to Pay Hillary's Campaign Debt". CBS News. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ a b "Bill Clinton meets N Korea leader". BBC News. August 4, 2009. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "North Korea pardons US reporters". BBC News. August 4, 2009. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Landler, Mark; Baker, Peter (August 5, 2009). "Bill Clinton and Journalists in Emotional Return to U.S." The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2011.
- ^ "Bill Clinton to be UN Haiti envoy". BBC News. May 19, 2009. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ "Presidents Clinton, Bush lead effort to raise funds for Haiti". CNN. January 16, 2010. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Jacob Kushner (August 17, 2011). "Clinton launches business loan program in Haiti". ABC News. Associated Press. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ Emmet Oliver (March 5, 2010). "Clinton backs NTR's environment foundation". The Irish Independent. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "President Bill Clinton Delivers Keynote Address". NTR Foundation. March 4, 2010. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "Bill Clinton brings it for Obama". CNN. September 6, 2012.
- ^ a b "Bill Clinton 'in good spirits' after heart procedure". BBC News. February 12, 2010. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "Clinton surgery called successful". MSNBC. Associated Press. March 10, 2005. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Mark Egan (February 11, 2010). "Bill Clinton in good spirits after heart procedure". Reuters. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ David S. Martin (August 18, 2011). "From omnivore to vegan: The dietary education of Bill Clinton". CNN. Retrieved September 17, 2012.
- ^ "Clintons Pay Off Legal Bills". June 14, 2005. Retrieved March 28, 2015.
- ^ a b McIntire, Mike (April 5, 2008). "Clintons made $109 Million in Last 8 Years". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Robert Yoon (February 6, 2016). "$153 million in Bill and Hillary Clinton speaking fees, documented". CNN. Retrieved February 7, 2016.
- ^ Ben Kamisar, Clintons earned more than $25 million for speeches since 2014 (May 15, 2015), The Hill
- ^ The Bill and Hillary Clinton Money Machine Taps Corporate Cash, BRODY MULLINS, PETER NICHOLAS and REBECCA BALLHAUS, The Wall Street Journal, July 1, 2014
- ^ Epstein, Jennifer. "Clinton Family Speeches Netted as Much as $26 Million for Foundation". Bloomberg. Retrieved May 23, 2015.
- ^ (linked in the NYT article)
- ^ How the Clintons went from 'dead broke' to rich: Bill earned $104.9 million for speeches (June 26, 2014), The Washington Post
- ^ a b Hillary Clinton Defends High-Dollar Speaking Fees (June 9, 2014), ABC News and Good Morning America
- ^ Bill's $500,000 Kuwait Lecture (November 17, 2008), The Daily Beast
- ^ Josh Gerstein, Clinton Eligible, Once Again, To Practice Law, New York Sun, January 17, 2006, downloaded from N.Y. Sun article.
- ^ Healy, Patrick (May 10, 2007). "Bill Clinton Ponders a role as 'First Gentlemen', NY Times, 2007". The New York Times. Retrieved May 22, 2010.
- ^ Bentley, Daniel (February 24, 2007). "Forty Million Dollar Bill, Independent, 2007". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on October 15, 2007. Retrieved May 22, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Honorary Degrees". UNC-Chapel Hill Office of Faculty Governance. 1993. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "President Bill Clinton with an honorary doctorate of law". Tulane University. May 19, 2006. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "Clinton to address graduates, Honorary doctorate will be bestowed". RIT News, Rochester Institute of Technology. May 18, 2007. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "www.univ.ox.ac.uk". University of Oxford.
- ^ "Clinton Elementary". Compton Unified School District. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved August 31, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "William Jefferson Clinton Middle School". Los Angeles Unified School District. Retrieved August 31, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ "Clinton School of Public service". University of Arkansas. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Kosovo unveils Clinton's statue". BBC News. November 1, 2009. Archived from the original on November 2, 2009. Retrieved November 2, 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Kosovo to honor Bill Clinton with statue". Reuters. May 23, 2007. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- ^ DeMolay International. "DeMolay Hall of Fame". Demolay.org. Archived from the original on September 5, 2010. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Purdum, Todd S. (October 17, 2002). "Campaign Season; Another First for Clinton". The New York Times. Retrieved August 6, 2009.
- ^ Kentucky Colonels, Honorable Order of. "Colonels website". Honorable Order of Kentucky Colonels. Archived from the original on June 25, 2009. Retrieved December 21, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Dunlap, David (November 23, 2004). "Pataki Offers Peek at 9/11 Memorial Progress". The New York Times. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "Secretary of Defense William S. Cohen presents the Department of Defense Medal for Distinguished Public Service to President Bill Clinton in a ceremonial farewell at Fort Myer, Va., on Jan. 5, 2001". U.S. Department of Defense. Retrieved September 1, 2011.
- ^ Van Natta, Don, Jr. (June 28, 1999). "Dinner for a Presidential Library, Contributions Welcome". The New York Times. Retrieved December 17, 2009.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "List of Individuals Awarded the Order of the White Lion". Old.hrad.cz. October 13, 2005. Retrieved August 6, 2009.
- ^ "It's now 'Chief Bill Clinton". United Press International. December 3, 2006. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "International Prize of the city of Aachen (German)". Archived from the original on February 6, 2008.
- ^ Mike Nizza (May 23, 2007). "Statue Watch: Bill Clinton Edition". The New York Times. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ Dan Bilefsky (December 17, 2007). "Kosovo Struggles to Forge an Identity". The New York Times. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ Dan Bilefsky (December 9, 2007). "Kosovo: Forging an identity on eve of new era". The New York Times. Retrieved October 8, 2012.
- ^ Elizabeth P. Valk (January 4, 1993). "Bill Clinton, Man of the Year". Time. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ Nancy Gibbs (December 28, 1998). "Kenneth Starr & Bill Clinton, Men of the Year". Time. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ The Gallup Poll 1999. Wilmington, DE: Scholarly Resources Inc. 1999. pp. 248–249.
- ^ AmericaLive (October 22, 2010). "President Bill Clinton Biography". CNN.
- ^ "2007 TED Prize winner Bill Clinton on TEDTalks". TED Blog. April 4, 2007. Archived from the original on July 28, 2011. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "24th Annual GLAAD Media Awards – Los Angeles". GLAAD. Retrieved April 7, 2013.
- ^ Press, ed. (July 22, 2011). "Haiti – Social: Bill Clinton receives the National Order of Honor and Merit to the rank Grand Cross gold plated". Haiti Libre. Retrieved March 14, 2016.
- ^ Jackson, David (November 20, 2013). "Obama awards Medal of Freedom to Clinton, Oprah, others". USA Today. Retrieved November 20, 2013.
Further reading
Primary sources
- Clinton, Bill. (with Al Gore). Science in the National Interest. Washington, D.C.: The White House, August 1994.
- --- (with Al Gore). The Climate Change Action Plan. Washington, D.C.: The White House, October 1993.
- Taylor Branch The Clinton Tapes: Wrestling History with the President. (2009) Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4165-4333-6
- Official Congressional Record Impeachment Set: ... Containing the Procedures for Implementing the Articles of Impeachment and the Proceedings of the Impeachment Trial of President William Jefferson Clinton. Washington, D.C.: U.S. G.P.O., 1999.
- Public Papers of the Presidents of the United States, William J. Clinton. Washington, D.C.: Office of the Federal Register, National Archives and Records Administration: For sale by the Supt. of Docs., U.S. G.P.O., 1994–2002.
- S. Daniel Abraham Peace Is Possible, foreword by Bill Clinton
Popular books
- Peter Baker The Breach: Inside the Impeachment and Trial of William Jefferson Clinton (2000) ISBN 0-684-86813-X
- James Bovard Feeling Your Pain: The Explosion and Abuse of Government Power in the Clinton-Gore Years (2000) ISBN 0-312-23082-6
- Joe Conason and Gene Lyons The Hunting of the President: The Ten-Year Campaign to Destroy Bill and Hillary Clinton (2003) ISBN 0-312-27319-3
- Elizabeth Drew On the Edge: The Clinton Presidency (1994) ISBN 0-671-87147-1
- David Gergen Eyewitness to Power: The Essence of Leadership. (2000) ISBN 0-684-82663-1
- Nigel Hamilton Bill Clinton: An American Journey (2003) ISBN 0-375-50610-1
- Christopher Hitchens No One Left to Lie to: The Triangulations of William Jefferson Clinton (1999) ISBN 1-85984-736-6
- Michael Isikoff Uncovering Clinton: A Reporter's Story (1999) ISBN 0-609-60393-0
- Mark Katz Clinton and Me: A Real-Life Political Comedy (2004) ISBN 978-0-7868-6949-7
- David Maraniss The Clinton Enigma: A Four and a Half Minute Speech Reveals This President's Entire Life (1998) ISBN 0-684-86296-4
- Dick Morris with Eileen McGann Because He Could (2004) ISBN 0-06-078415-6
- Richard A. Posner An Affair of State: The Investigation, Impeachment, and Trial of President Clinton (1999) ISBN 0-674-00080-3
- Mark J. Rozell The Clinton Scandal and the Future of American Government (2000) ISBN 0-87840-777-4
- Timperlake, Edward, and William C. Triplett II Year of the Rat: How Bill Clinton Compromised U.S. Security for Chinese Cash. Washington, D.C.: Regnery Publishing, 1998. ISBN 0-89526-333-5
- Michael Waldman POTUS Speaks: Finding the Words That Defined the Clinton Presidency (2000) ISBN 0-7432-0020-9
- Ivory Tower Publishing Company. Achievements of the Clinton Administration: the Complete Legislative and Executive. (1995) ISBN 0-88032-748-0
Scholarly studies
- Campbell, Colin, and Bert A. Rockman, eds. The Clinton Legacy (Chatham House Pub, 2000)
- Cohen; Jeffrey E. "The Polls: Change and Stability in Public Assessments of Personal Traits, Bill Clinton, 1993–99" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 31, 2001
- Cronin, Thomas E. and Michael A. Genovese; "President Clinton and Character Questions" Presidential Studies Quarterly Vol. 28, 1998
- Davis; John. "The Evolution of American Grand Strategy and the War on Terrorism: Clinton and Bush Perspectives" White House Studies, Vol. 3, 2003
- Dumbrell, John. "Was there a Clinton doctrine? President Clinton's foreign policy reconsidered". Diplomacy and Statecraft 13.2 (2002): 43–56.
- Edwards; George C. "Bill Clinton and His Crisis of Governance" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 28, 1998
- Fisher; Patrick. "Clinton's Greatest Legislative Achievement? the Success of the 1993 Budget Reconciliation Bill" White House Studies, Vol. 1, 2001
- Glad; Betty. "Evaluating Presidential Character" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 28, 1998
- Harris, John F. The Survivor: Bill Clinton in the White House (2006).
- Head, Simon. The Clinton System (January 30, 2016), The New York Review of Books
- Hyland, William G. . Clinton's World: Remaking American Foreign Policy (1999) ISBN 0-275-96396-9
- Jewett, Aubrey W. and Marc D. Turetzky; "Stability and Change in President Clinton's Foreign Policy Beliefs, 1993–96" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 28, 1998
- Kim, Claire Jean. "Managing the Racial Breach: Clinton, Black‐White Polarization, and the Race Initiative". Political Science Quarterly 117.1 (2002): 55–79. online
- Laham, Nicholas, A Lost Cause: Bill Clinton's Campaign for National Health Insurance (1996)
- Lanoue, David J. and Craig F. Emmert; "Voting in the Glare of the Spotlight: Representatives' Votes on the Impeachment of President Clinton" Polity, Vol. 32, 1999
- Levy, Peter B. Encyclopedia of the Clinton presidency (Greenwood, 2002)
- Maurer; Paul J. "Media Feeding Frenzies: Press Behavior during Two Clinton Scandals" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 29, 1999
- Nie; Martin A. "'It's the Environment, Stupid!': Clinton and the Environment" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 27, 1997 in JSTOR
- O'Connor; Brendon. "Policies, Principles, and Polls: Bill Clinton's Third Way Welfare Politics 1992–1996" The Australian Journal of Politics and History, Vol. 48, 2002
- Poveda; Tony G. "Clinton, Crime, and the Justice Department" Social Justice, Vol. 21, 1994
- Renshon; Stanley A. The Clinton Presidency: Campaigning, Governing, and the Psychology of Leadership Westview Press, 1995
- Romano, Flavio. Clinton and Blair: the political economy of the third way (Routledge, 2007)
- Renshon; Stanley A. "The Polls: The Public's Response to the Clinton Scandals, Part 1: Inconsistent Theories, Contradictory Evidence" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 32, 2002
- Rushefsky, Mark E. and Kant Patel. Politics, Power & Policy Making: The Case of Health Care Reform in the 1990s (1998) ISBN 1-56324-956-1
- Schantz, Harvey L. Politics in an Era of Divided Government: Elections and Governance in the Second Clinton Administration (2001) ISBN 0-8153-3583-0
- Troy, Gill. The Age of Clinton: America in the 1990s (2015)
- Warshaw, Shirley Anne. The Clinton Years (Infobase Publishing, 2009)
- Wattenberg; Martin P. "The Democrats' Decline in the House during the Clinton Presidency: An Analysis of Partisan Swings" Presidential Studies Quarterly, Vol. 29, 1999
- Wattier; Mark J. "The Clinton Factor: The Effects of Clinton's Personal Image in 2000 Presidential Primaries and in the General Election" White House Studies, Vol. 4, 2004
External links
Official
Organizations
Interviews, speeches, and statements
- Appearances on C-SPAN
- Bill Clinton at TED
- Full audio of a number of Clinton speeches Miller Center of Public Affairs
- Oral History Interview with Bill Clinton from Oral Histories of the American South, June 1974
- "The Wanderer", a profile from The New Yorker, September 2006
Media coverage
- Bill Clinton collected news and commentary at The Guardian
- Bill Clinton collected news and commentary at The New York Times
- Template:WSJ topic
Other
- Template:Dmoz
- Extensive essays on Bill Clinton and shorter essays on each member of his cabinet and First Lady from the Miller Center of Public Affairs
- "Life Portrait of Bill Clinton", from C-SPAN's American Presidents: Life Portraits, December 20, 1999
- Clinton an American Experience documentary
- Bill Clinton
- 1946 births
- Living people
- 20th-century American writers
- 21st-century American writers
- 20th-century Baptists
- 21st-century Baptists
- 20th-century American politicians
- 21st-century American politicians
- Alumni of University College, Oxford
- Ambassadors of the United States to Haiti
- American autobiographers
- American gun control advocates
- American health activists
- American humanitarians
- American memoirists
- American political writers
- American male writers
- American Rhodes Scholars
- Arkansas Attorneys General
- Arkansas Democrats
- Arkansas lawyers
- American saxophonists
- American people of Scotch-Irish descent
- American people of Irish descent
- American people of English descent
- American people of Scottish descent
- Baptists from the United States
- Candidates in United States elections, 1980
- Family of Bill and Hillary Clinton
- Collars of the Order of the White Lion
- Democratic Party Presidents of the United States
- Democratic Party state governors of the United States
- Democratic Party (United States) presidential nominees
- Edmund A. Walsh School of Foreign Service alumni
- Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
- Fellows of University College, Oxford
- Governors of Arkansas
- Grammy Award winners
- Grand Companions of the Order of Logohu
- Grand Crosses of the National Order of Honour and Merit
- Grand Crosses of the Order of Good Hope
- Hot Springs High School (Arkansas) alumni
- Impeached Presidents of the United States
- LGBT rights activists from the United States
- Lewinsky scandal
- Liberalism in the United States
- People from Hope, Arkansas
- People from Hot Springs, Arkansas
- Presidents of the United States
- Recipients of the Order of the Cross of Terra Mariana, 1st Class
- Recipients of the Order of the State of Republic of Turkey
- Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Distinction of Israel
- Recipients of St. George's Order of Victory
- Presidential Medal of Freedom recipients
- Rodham family
- Spouses of New York politicians
- Spouses of United States Cabinet members
- Spouses of United States Senators
- United Nations officials
- United States presidential candidates, 1992
- United States presidential candidates, 1996
- University of Arkansas people
- Writers from Arkansas
- Yale Law School alumni
- Politicians from Little Rock, Arkansas
- Clinton Foundation people








