COVID-19 pandemic in Greece: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
K kokkinos (talk | contribs) m →COVID-19 cases in Greece: moved May, 9 to its own row |
||
| Line 880: | Line 880: | ||
|32 |
|32 |
||
|90043 |
|90043 |
||
|- |
|||
!9 May<ref>{{Cite web|title=COVID-19 Daily report 09.05.2020 by NPHO|url=https://eody.gov.gr/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/covid-gr-daily-report-20200509.pdf|last=|first=|date=2020-05-09|website=National Public Health Organisation (in Greek)|url-status=live|archive-url=|archive-date=|access-date=2020-05-09}}</ref> |
!9 May<ref>{{Cite web|title=COVID-19 Daily report 09.05.2020 by NPHO|url=https://eody.gov.gr/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/covid-gr-daily-report-20200509.pdf|last=|first=|date=2020-05-09|website=National Public Health Organisation (in Greek)|url-status=live|archive-url=|archive-date=|access-date=2020-05-09}}</ref> |
||
|19 |
|19 |
||
Revision as of 20:14, 9 May 2020
| COVID-19 pandemic in Greece | |
|---|---|
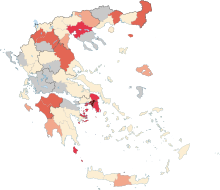 Map of the COVID-19 outbreak in Greece as of 31 March 2020[update].
Confirmed 1—4
Confirmed 5—9
Confirmed 10—49
Confirmed 50—99
Confirmed 100—199
Confirmed ≥200 | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Greece |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, Hubei, China |
| Index case | Thessaloniki |
| Arrival date | 26 February 2020 (4 years, 8 months, 2 weeks and 3 days) |
| Date | As of 9 May 2020[update] |
| Confirmed cases | 2,710 |
| Recovered | 1,374[1] |
Deaths | 152[2] |
| Government website | |
| covid19 | |
The COVID-19 pandemic first appeared in Greece on 26 February 2020 when the first COVID-19 case, a 38-year-old woman from Thessaloniki who had recently visited Νorthern Italy, was confirmed. Subsequent cases in late February and early March related to people who had travelled to Italy and a group of pilgrims who had travelled to Israel and Egypt, as well as their contacts. The first death from COVID-19 in Greece was a 66-year-old man, who died on 12 March. As of 9 May 2020[update], there have been 2,710 confirmed cases and 152 deaths.
Following the confirmation of the first three cases in Greece, on 27 February all carnival events in the country were cancelled. Health and state authorities issued precautionary guidelines and recommendations, while measures up to early March were taken locally and included the closure of schools and the suspension of cultural events in the affected areas (particularly Ilia, Achaea and Zakynthos). On 10 March, with 89 confirmed cases and no deaths in the country, the government decided to suspend the operation of educational institutions of all levels nationwide and then, on 13 March, to close down all cafes, bars, museums, shopping centres, sports facilities and restaurants in the country. On 16 March, all retail shops were also closed, two villages in Kozani were quarantined, and all services in all areas of religious worship of any religion or dogma were suspended. On 18 and 19 March, the government announced a series of measures of more than 10 billion euros to support the economy, businesses and employees.
On 22 March, the Greek authorities announced restrictions on all non-essential movement throughout the country, starting from 6 a.m on 23 March. Since that date, movement outside the house is permitted only for seven categories of reasons: i) moving to or from one's workplace during work hours, ii) going to the pharmacy or visiting a doctor iii) going to a food store iv) going to the bank for services not possible online, v) assisting a person in need of help vi) going to a major ritual (funeral, marriage, baptism) or movement, for divorced parents, which is essential for contact with their children, and vii) moving outdoors for exercising or taking one's pet out, individually or in pairs. Citizens leaving their homes are required to carry their police ID or passport, as well as a signed attestation in which the purpose or category of travel is stated. The Hellenic Police, the Municipal Police, the Hellenic Coast Guard and the National Transparency Authority are empowered to enforce the restrictions and can issue fines for each offence. On 4 April these restrictions were extended until 27 April and on 23 April they were extended until 4 May.[3]
The measures put in place in Greece are among the most proactive and strictest in Europe and have been credited internationally for having slowed the spread of the disease and having kept the number of deaths among the lowest in Europe.[4][5][6][7][8][9][10]
Background
On 12 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that a novel coronavirus was the cause of a respiratory illness in a cluster of people in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, which was reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019.[11][12]
The case fatality ratio for COVID-19 has been much lower than SARS of 2003,[13][14] but the transmission has been significantly greater, with a significant total death toll.[15][13]
Timeline
February
- On 26 February, the first case in Greece was confirmed. A 38-year-old woman from Thessaloniki, who had recently visited Milan, Νorthern Italy, tested positive and was admitted to AHEPA University Hospital. Her family, as well as those who came into contact with her, voluntarily isolated themselves.[16]
- On 27 February, two new cases in Greece were confirmed. The woman's nine-year-old child tested positive and was admitted to the same hospital as her mother.[17] Additionally, a forty-year-old woman who had travelled to Italy, also tested positive and was admitted to Attikon University General Hospital.[18][19][20][21] Following the confirmation of the second and third cases in Greece, it was announced that the 105th Primary School of Thessaloniki, where the first patient's daughter went to school, would close for fourteen days. The Minister of Health, Vasilis Kikilias, announced that all carnival events were cancelled throughout Greece.[19][22][18]
- On 28 February, the fourth case in Greece was confirmed. A 36-year-old woman from Athens who had recently travelled to Italy tested positive and was admitted to the Attikon University General Hospital.[23][17] Eight state schools were closed as a precautionary measure in Attica to prevent the spread of the virus, and all educational travel abroad sponsored by Greek schools was halted.[24]
- On 29 February, three new cases in Greece were confirmed. A friend of the 38-year-old woman who was the first case in Greece, was admitted to the AHEPA University Hospital.[25] Additionally, two more people in Athens were admitted to the General Hospital Sotiria, bringing the country total to seven confirmed cases.[26]
March
- On 4 March, two new cases were confirmed in Greece. A middle-aged man in close contact with the fifth confirmed case, tested positive and was put in solitary confinement at AHEPA University Hospital.[27] Additionally, a man who had travelled to Israel and Egypt, was admitted to the General University Hospital of Patras, bringing the country total to nine confirmed cases.[28]
- On 5 March, 22 new cases were confirmed in Greece. The 66-year-old wife, who was the ninth case in Greece, tested positive and was admitted to the same hospital as her husband.[29] 21 of their fellow travellers also tested positive, bringing the country total to 31 cases.[30]
- On 6 March, 14 new cases were confirmed in Greece. Eleven members of the Israel-Egypt travel group, as well as three people who afterwards came in contact with them, tested positive, bringing the country total to 45 confirmed cases. Schools, universities, theaters and cinemas were closed until 22 March in three of the affected areas (Achaia, Ileia and Zakynthos).[31]
- On 7 March, 21 new cases were confirmed in Greece. Thirteen people in Achaia and Ileia, seven in Attica and one in Euboea tested positive, bringing the country total to 66 confirmed cases.[32]
- On 8 March, seven new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 73.[33]
- On 9 March, eleven new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 84.[34] Among those cases was the first one to be reported in Lesbos, raising fears that the virus could spread to the island's tightly packed refugee camps.[35]
- On 10 March, five new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 89.[36] Evangelos Marinakis, the owner of the football clubs Olympiacos in Greece and Nottingham Forest in England, informed the public via social media that he had contracted the virus, and urged all to follow the orders of health professionals.[37] Health Minister Vasilis Kikilias announced the closure of all educational institutions for 14 days.[38]
- On 11 March, ten new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 99. The 66-year-old man hospitalised in Rio was diagnosed with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.[39]
- On 12 March, 18 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 117.[40] The first two reported cases in Greece, a mother and her child, were released from the hospital, having fully recovered.[41] The 66-year-old patient in Rio died as a result of the virus, which was the first virus-related death in Greece.[42]
- On 13 March, 73 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 190.[43] Katerina Sakellaropoulou was sworn in as President of Greece in the Hellenic Parliament and became the first woman to hold the office, succeeding Prokopis Pavlopoulos. Sakellaropoulou suspended the protocol ceremony for the inauguration scheduled for Saturday 14 and no handshakes were allowed.[44][45]
- On 14 March, 38 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 228, while six more were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to eight.[46] A 90-year-old man hospitalised in Ptolemaida died.[47] Also, a 67-year-old man hospitalised in Zakynthos died, bringing the country death toll to three.[48] A change in strategy to only testing the elderly, severely ill and other high-risk groups, as well as healthcare personnel was announced by Dr. Sotiris Tsiodras, the health ministry spokesman on the coronavirus pandemic.[a][50]
- On 15 March, 103 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 331, while two more were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to ten.[51] A 53-year-old man died from the virus, in AHEPA, bringing the country death toll to four.[52]
- On 16 March, 21 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 352.[53]
- On 17 March, 35 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 387, while four were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 14. A man died bringing the country death toll to five.[54]
- On 18 March, 31 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 418.[55] A total of 6,000 samples had been tested nationally up to this point.[56] A childbirth was recorded, where the mother tested positive for COVID-19 but the child did not.[57]
- On 19 March, 46 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 464, while five more were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 19.[58] A 70-year-old man who had been hospitalised in Kastoria, died, bringing the country death toll to six.[59]
- On 20 March, 31 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 495. Four more people died, bringing the country death toll to ten.[60]
- On 21 March, 35 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 530.[61] Three more people died, bringing the country death toll to 13.[62]
- On 22 March, 94 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 624.[63] Two more people died, bringing the country death toll to 15.[63]
- On 23 March, 71 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 695, while ten people were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 29.[64] A 64-year-old man at Rio Hospital in Achaea and an elderly man at Sotiria Hospital in Athens died as a result of the virus, bringing the country death toll to 17.[65][66] During the night, another childbirth was recorded where the mother tested positive for COVID-19.[67]
- On 24 March, 48 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 743, while three people were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 32. Three more people died due to the virus, bringing the country death toll to 20.[68] A 40-year-old woman, who had died three days previously, was found to have been positive for the virus making her, by far, the youngest victim of the pandemic in Greece.[69] The new President of Greece, Katerina Sakellaropoulou, declared she was going to address the nation on the evening of the 24th regarding both the COVID-19 pandemic and the 25th of March Independence Day celebrations.
- On 25 March, 78 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 821, while four people were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 36. Two more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 22.[70]
- On 26 March, 71 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 892, while six people were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 42. Four more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 26.[71]
- On 27 March, 74 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 966, while ten people were released from hospitals, bringing the recovered total to 52. Two more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 28.[72]
- On 28 March, 95 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1061. Four more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 32.[73]
- On 29 March, 95 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the county total to 1156, while one person was released from Alexandroupoli University hospital, bringing the recovered total to 53. Six more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 38.[74] The first case of coronavirus was reported in the monastery at Mount Athos.[75]
- On 30 March, 56 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the county total to 1212. Five more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 43.[76]
- On 31 March, 102 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1314. Six more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 49.[77] 20 of the cases are aboard a passenger ship stationed outside the port of Piraeus. It carried 382 people, including 36 Greeks, 150 Turks, 83 Indonesians and others. Some of the people were Turkish workers traveling to Spain but the ship was turned back to Turkey when the cases were identified. It was not accepted in Turkey and since 21 March has been outside Piraeus.[78]
April
- On 1 April, 101 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1415. One more death from coronavirus was reported, bringing the country death toll to 50.[79]
- On 2 April, 129 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1544. 27 new cases were reported in the general population, 23 in the Ritsona refugee and immigrant camp, and 79 new cases on the ship El. Venizelos which is being kept off the port of Piraeus, bringing the total cases on the ship to 119. Three more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 53.[80]
- On 3 April, it was announced that the total number of confirmed cases in the country was 1613. Six more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 59.[81]
- On 4 April, 60 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1673. Nine more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 68. 92 coronavirus patients were being treated in intensive care units.[82]
- On 5 April, 62 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1735. Five more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 73. 93 coronavirus patients were being treated in intensive care units.[83]
- On 6 April, 20 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1755. Six more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 79.[84]
- On 7 April, 77 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1832. Two more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 81.[85]
- On 8 April, 52 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1884. Two more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 83. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 84.[86]
- On 9 April, 71 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 1955. Three more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 86. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 79.[87]
- On 10 April, 56 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2011. Four more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 90. One of the people who died was from Mesopotamia, Kastoria an area that was in quarantine.[88] The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 77.
- On 11 April, 72 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the official country total to 2081 (minor discrepancy). Three more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 93. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 75.[89]
- On 12 April, 33 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2114. Five more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 98. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 76.[90]
- On 13 April, 31 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2145. One more death from coronavirus was reported, bringing the country death toll to 99. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 73.[91] Later the same day an 84-year-old man died in Attica marking the 100th death from COVID-19 in the country.[92]
- On 14 April, 25 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2170. Two more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country death toll to 101. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 76.[93]
- On 15 April, 22 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2192.[94] During the daily report, 1 more death from coronavirus was reported, bringing the country death toll to 102.[95] Shortly after a 57-year-old woman was reported as having died in AHEPA University Hospital.[94]
- On 16 April, 15 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2207. The death toll brought to 105.[96]
- On 17 April, 17 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2224.[97] A 76-old-man died in Ptolemaida[98] and two other later. The deaths toll brought to 108.[99]
- On 18 April, 11 new cases were confirmed in Greece, bringing the country total to 2235.
- On 20 April, 10 new cases and 6 new deaths were confirmed, bringing the country total to 2245 cases and 116 deaths respectively. On the same day, all 470 refugees accommodated in a facility in Kranidi, Argolis were tested for the virus as well as all staff of the facility, the local clinic and the International Organization for Migration (IOM), a total of 497 samples.[100] Among them a 68-year-old woman in Kastoria.[101] Some hours after the daily report, an 87-year-old man died in AHEPA University Hospital.[102]
- On 21 April, 156 new cases were confirmed in Greece bringing the total to 2401.[103] Of those 156, 150 cases, all asymptomatic, were related to the refugee facility in Kranidi. Out of a total of 497 samples taken the day before, 148 had been found to be positive among the refugees and 2 among the facility's staff and members of the IOM.[104][105] The same day, five more deaths from coronavirus were reported, bringing the country's death toll to 121. The number of coronavirus patients in ICUs was 59. A 35-year-old man in Thessaloniki, a 75-year-old man in Athens,[106] and a 101-year-old woman were among the dead.[107]
- On 22 April, no deaths were reported. 7 new cases were confirmed.[108]
- On 23 April, 55 new cases and 4 new deaths were reported at the daily report.[109] The deaths were an 88-year-old man,[110] a 76-old man who was being treated by the Red Cross,[111] a 90-year-old man in AHEPA University Hospital[112] and a 63-year-old man in Thriasio.[113] After the daily report, two more people died: an 87-year-old in NIMITS Hospital and a 74-year-old woman in Alexandroupoli.[114]
- On 24 April, a 59-year-old woman died in AHEPA University Hospital[115] and an 81-year-old woman in Komotini.[116] 27 new cases and 5 new deaths were reported at the daily report.[117]
- On 25 April, no new deaths were reported. 16 new cases were confirmed.[118] Three hours after the daily report, the death of a 78-year-old man at Evangelismos Hospital was reported.[119]
- On 26 April, 4 new deaths and 11 new cases were confirmed within the previous 24 hours.[120] The deaths included a 91-year-old man at "Sotiria" Hospital in Athens,[121] and a 58-year-old woman in Alexandroupoli.[122]
- On 27 April, 2 new deaths and 17 new cases were confirmed within the previous 24 hours.[123] The two deaths were an 80-year old woman at Papanikolaou Hospital and a 59-year-old man in Alexandroupoli.[124]
- On 28 April, a 90-year-old man in Rio died[125] and an 84-year-old man at Taxiarchai.[126]
- On 29 April, 10 news cases were confirmed within the previous 24 hours.[127] An 89-year-old man at NIMTS Hospital died.[128]
- On 30 April, 1 new death and 15 new cases were confirmed.[129] The confirmed total number of recoveries was announced to be 1374.[130]
May
- On 1 May, no new deaths and 21 new cases were confirmed.[131]
- On 2 May, 3 more deaths occurred: A 57-year old man at Sotiria Hospital, and one 88-year-old man and one 83-year-old man, both at NIMTS. Greece's cases total reached 2,612 and its death toll 143.[132]
- On 3 May, a 76-year-old woman died at NIMTS.[133] Greece's cases total reached 2,620 and its death toll 144.
- On May 4, an 88-year-old woman died at Attikon University General Hospital,[134] and a 50-year-old died in Larissa.[135] The confirmed cases of coronavirus in Greece totalled 2,632, and the death toll reached 146 as two people had died in the previous 24 hours.
- On 5 May, no new deaths and 10 new cases were confirmed.
- On 6 May, an 89-year-old woman died at Sotiria.[136]
- On 7 May, 1 new death,and 15 new cases were confirmed. Shortly after, a 67-year-old man in Larissa died.[137]
- On 8 May, Dr. Dimitris Kremastinos died at the age of 79. The death toll rose to 150 and 15 new cases were confirmed.[138]
Statistics
COVID-19 cases in Greece
| Date | Confirmed
New |
Deaths
New |
Recoveries
New |
Confirmed
Total |
Deaths
Total |
Recoveries
Total |
In Intensive Care
(total on that date) |
Cumulative total tests performed ^ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 February | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 27 February[139] | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 28 February[140] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 29 February | 3 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 March | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 March[141] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 504 |
| 3 March[142] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 570 |
| 4 March[143][144][145] | 2 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 March[146] | 22 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 March[147] | 14 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 March[148] | 21 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 March[149] | 7 | 0 | 0 | 73 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 March[150] | 11 | 0 | 0 | 84 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 10 March[151] | 5 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 11 March[152][153] | 10 | 0 | 0 | 99 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1700 |
| 12 March[154][155] | 18 | 1 | 2 | 117 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2180 |
| 13 March[153] | 73 | 0 | 0 | 190 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2700 |
| 14 March[156][157] | 38 | 2 | 6 | 228 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 3400 |
| 15 March[158] | 103 | 1 | 2 | 331 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 4000 |
| 16 March[159] | 21 | 0 | 0 | 352 | 4 | 10 | 9 | 4320 |
| 17 March | 35 | 1 | 4 | 387 | 5 | 14 | 11 | 4900 |
| 18 March[160] | 31 | 0 | 0 | 418 | 5 | 14 | 13 | 6000 |
| 19 March[161] | 46 | 1 | 5 | 464 | 6 | 19 | 16 | – |
| 20 March[162] | 31 | 4 | 0 | 495 | 10 | 19 | 20 | 7172 |
| 21 March[163][164] | 35 | 3 | 0 | 530 | 13 | 19 | 18 | 7830 |
| 22 March[165][166] | 94 | 2 | 0 | 624 | 15 | 19 | 34 | 8006 |
| 23 March[167] | 71 | 2 | 10 | 695 | 17 | 29 | 34 | 8644 |
| 24 March[168] | 48 | 3 | 3 | 743 | 20 | 32 | 45 | 9071 |
| 25 March[169] | 78 | 2 | 4 | 821 | 22 | 36 | 53 | 10495 |
| 26 March[71] | 71 | 4 | 6 | 892 | 26 | 42 | 57 | – |
| 27 March[72] | 74 | 2 | 10 | 966 | 28 | 52 | 66 | 13477 |
| 28 March[170] | 95 | 4 | – | 1061 | 32 | 52 | 69 | 14363 |
| 29 March[171][172] | 95 | 6 | 1 | 1156 | 38 | 53 | 69 | 15151 |
| 30 March[173] | 56 | 5 | – | 1212 | 43 | 53 | – | 15961 |
| 31 March[77][174] | 102 | 6 | – | 1314 | 49 | 53 | 85 | 16732 |
| 1 April[79][175] | 101 | 1 | – | 1415 | 50 | 53 | 90 | 17350 |
| 2 April[80][176] | 129 | 3 | – | 1544 | 53 | 53 | 91 | 18844 |
| 3 April[177][178] | 69 | 6 | – | 1613 | 59 | 53 | 92 | 22437 |
| 4 April[179] | 60 | 9 | – | 1673 | 68 | 53 | 91 | 23333 |
| 5 April[180] | 62 | 5 | – | 1735 | 73 | 53 | 93 | 25453 |
| 6 April[181][182] | 20 | 6 | 216 | 1755 | 79 | 269 | 90 | 26193 |
| 7 April[183][184] | 77 | 2 | 1832 | 81 | 269 | 90 | 28584 | |
| 8 April[185] | 52 | 2 | 1884 | 83 | 269 | 84 | 32528 | |
| 9 April[186][187] | 71 | 3 | 1955 | 86 | 269 | 79 | 33634 | |
| 10 April[188][189] | 54 | 4 | 2009 | 90 | 269 | 77 | 35432 | |
| 11 April[190][191] | 72 | 3 | 2081 | 93 | 269 | 75 | 37344 | |
| 12 April[192][193] | 33 | 5 | 2114 | 98 | 269 | 76 | 42261 | |
| 13 April[194][195] | 31 | 1 | 2145 | 99 | 269 | 73 | 43431 | |
| 14 April[196][197] | 25 | 2 | 2170 | 101 | 269 | 76 | 45798 | |
| 15 April[198][199] | 22 | 1 | 2192 | 102 | 269 | 72 | 47389 | |
| 16 April[200] | 15 | 3 | 2207 | 105 | 269 | 69 | 49390 | |
| 17 April[201] | 17 | 3 | 2224 | 108 | 269 | 71 | 51645 | |
| 18 April[202] | 11 | 2 | 2235 | 110 | 269 | 67 | 53290 | |
| 19 April | — | 3 | — | — | 113 | — | — | — |
| 20 April[203] | 10 | 3 | — | 2245 | 116 | 269 | 61 | 54344 |
| 21 April[204][205] | 156 | 5 | — | 2401 | 121 | 269 | 59 | 55666 |
| 22 April[206] | 7 | 0 | — | 2408 | 121 | 269 | 55 | 56992 |
| 23 April[207] | 55 | 4 | — | 2463 | 125 | 269 | 52 | 59241 |
| 24 April[208] | 27 | 5 | — | 2490 | 130 | 269 | 48 | 61407 |
| 25 April[209] | 16 | 0 | — | 2506 | 130 | 269 | 47 | 63087 |
| 26 April[210] | 11 | 4 | — | 2517 | 134 | 269 | 46 | 64608 |
| 27 April[211] | 17 | 2 | — | 2534 | 136 | 269 | 43 | 66094 |
| 28 April[212] | 32 | 2 | — | 2566 | 138 | 269 | 40 | 69833 |
| 29 April[213] | 10 | 1 | — | 2576 | 139 | 269 | 41 | 72130 |
| 30 April[214][130] | 15 | 1 | 1105 | 2591 | 140 | 1374 | 38 | 75170 |
| 1 May[215] | 21 | 0 | — | 2612 | 140 | 1374 | 36 | 77251 |
| 2 May[216] | 8 | 3 | — | 2620 | 143 | 1374 | 37 | 78207 |
| 3 May[217] | 6 | 1 | — | 2626 | 144 | 1374 | 37 | 79332 |
| 4 May[218] | 6 | 2 | — | 2632 | 146 | 1374 | 35 | 80951 |
| 5 May[219] | 10 | 0 | — | 2642 | 146 | 1374 | 35 | 83750 |
| 6 May[220] | 21 | 1 | — | 2663 | 147 | 1374 | 36 | 87052 |
| 7 May[221] | 15 | 1 | — | 2678 | 148 | 1374 | 33 | 90043 |
| 8 May[222] | 13 | 2 | — | 2691 | 150 | 1374 | 32 | 90043 |
| 9 May[223] | 19 | 1 | — | 2710 | 151 | 1374 | 32 | 90043 |
| 2691 | 150 | 1374 | 32 | 90043 | ||||
| Date | Confirmed
New |
Deaths
New |
Recoveries
New |
Confirmed
Total |
Deaths
Total |
Recoveries
Total |
Intensive Care
On that date |
Tests performed
Total |
Cases by date
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
New cases per day
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
New deaths per day
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Cases by sex and age
| Classification | Cases | Fatal cases | Cases treated in ICU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | (%) | Number | (%) | Number | (%) | ||
| All | 34299 | (100) | 603 | (100) | 108 | (100) | |
| Sex | Male | 18967 | (55.3) | 375 | (62.2) | 74 | (68.5) |
| Female | 15332 | (44.7) | 228 | (37.8) | 34 | (31.5) | |
| Age | ≥65 | 3762 | (11.7) | 495 | (82.1) | 56 | (51.9) |
| 40–64 | 11810 | (36.6) | 102 | (16.9) | 50 | (46.3) | |
| 18–39 | 14190 | (44.0) | 6 | (1.0) | 2 | (1.9) | |
| 0–17 | 2489 | (7.7) | 0 | (0.0) | 0 | (0.0) | |
| Data as of 28.10.2020 15:00 EET. | |||||||
Source: National Public Health Organization.[214]
Response measures


The Greek Government has announced the following measures:[34]
Restrictions on movements and gatherings
On 9 March, all school trips were banned, all sports games were to be played with no fans attending and all school championships were cancelled,[224] and starting on 10 March, all educational institutions (expect the educational institutions of Zakynthos, Achaia and Ileia that closed on 5 March) were closed for 14 days.[225]
On 16 March two villages in Western Macedonia, Damaskinia and Dragasia, were quarantined after several cases among their residents were confirmed. Movement in and out of the villages was banned, allowing only medical staff and municipal staff to supply medication and food.[226] On 18 March, Greece announced new coronavirus restrictions pertaining to migrant camps. For thirty days, the movement of camp residents would be restricted to small groups between 7am and 7pm, which could only include one person per family and would be controlled by police on public transport. Specialised medical teams were sent to the camps for the creation of virus isolation areas and compulsory temperature checking. All other visits to the camps whether by individuals or organisations were suspended for at least 14 days.[227] On the same day, Deputy Minister of Civil Protection and Crisis Management Nikos Hardalias announced a ban on public gatherings of 10 or more people and the imposition of a 1,000 euro fine on violators.[228][229]
On 20 March, Minister of Shipping and Island Policy Giannis Plakiotakis announced that only permanent residents and supply trucks would be allowed to travel to the Greek islands, with effect from 6am local time on 21 March. Travellers need to provide proof of permanent residence (via a tax certificate) on the island to which they wish to travel. People who are already on the islands and wish to leave are allowed to return to the mainland.[230][231]
On 22 March, the Greek government announced a ban on all nonessential transport and movement across the country, starting from 6 a.m on 23 March until 6 April. Movement is permitted only for a prescribed set of reasons that include moving to or from the workplace during normal business hours, shopping for food or medicine, visiting a doctor or assisting a person in need of help, exercising individually or in pairs or walking a pet, attending a ceremony (wedding, baptism, funeral etc.), and cases of divorced parents moving to ensure communication with their children. People returning to their permanent places of residence will also be exempt. Citizens leaving their home are required to carry their ID or passport with them, as well as some type of certification explaining the reason for their movement which has to be confirmed by their employer or by themselves. The options include filling in a special form that can be downloaded from the government website forma.gov.gr, sending a free SMS to the number 13033, or explaining their reason in a signed handwritten declaration. The information needed include the name, home address, time of departure from home, and the specific reason for transport that falls under one of the exceptions. Members of the government and parliament as well as all Health, Civil Protection, Law Enforcement and Armed Forces personnel were excluded from the measure. The Hellenic Police, the Municipal Police, the Hellenic Coast Guard and the National Transparency Authority are required to enforce the restrictions and issue fines of 150 euros for each offense.[232][233][234][235] On the same day, it was also announced that daytime public transport services will be limited, although ensuring sufficient service during business hours. Journeys by car are only permitted for the specific exemptions, and the driver may only have one passenger in the vehicle.[236] Since the beginning of the curfew through 6 April, Greek police have recorded more than 20,000 violations (increasing in recent days) and made 348 arrests of offenders.[237] On 4 April the measure was extended until 27 April.[238]
On 31 March, Deputy Minister for Civil Protection and Crisis Management Nikos Hardalias announced additional restrictive measures for a duration of 14 days in the municipalities of Kastoria, Orestida and Nestorio of Kastoria Regional Unit as well as those of Xanthi and Myki of Xanthi Regional Unit. A night curfew was imposed from 8:00 p.m. until 8:00 a.m. the following morning and some options of the lockdown movement permits were suspended. Only close relatives can attend a funeral and pet owners are allowed to walk their pet for up to 15 minutes and near their house only.[239]
On 2 April, following the confirmation of a case in Mykonos, all construction activities on the island were suspended.[240] On 5 April, another case was confirmed and a night curfew was imposed from 8:00 p.m. until 8:00 a.m. the following morning while some options of the lockdown movement permits were suspended for 14 days.[241] The same day all construction activity was suspended for 30 days on the island of Santorini, although no cases have been reported there.[241]
From 8 April, the Hellenic Police installed permanent roadblocks and intensified checks of vehicles in all national roads and highways across the country, as well of travellers at the airports, ports, railway and bus stations. Anyone travelling by car without a valid reason to a destination other than his permanent residency is charged with a fine of 300 euros, is obliged to return to his place of origin and the vehicle registration plates are seized for 60 days.[242]
Travel restrictions abroad
On 9 March, the Hellenic Civil Aviation Authority announced the temporary suspension of all flights to and from northern Italy, affecting all Greek airports and all airlines.[243] On 14 March the suspension was extended to all passenger flights to and from Italy, excluding cargo and sanitary ones.[244]
On 16 March Greece closed its borders with Albania and North Macedonia, deciding to suspend all road, sea and air links with these countries, while only permitting the transport of goods and the entry of Greek nationals and residents. The suspension of ferry services to and from Italy, air links to Spain, as well as the prohibition of all cruise ships and sailboats docking in Greek ports was also decided.[245] The same day it was announced that a 14-day home restriction will be mandatory for those who enter the country.[246]
On 18 March, Greece and the other EU member states decided to close their external borders to all non-EU nationals. In Greece, the entry of citizens of countries from outside the European Union is only permitted for a condition that relates exclusively to an emergency or family matter. All private pleasure boats from abroad were also banned from entering the country.[247] On 19 March, Turkey closed the land border crossings with Greece at Karaağaç and Ipsala.[248]
From 23 March, Greece suspended all passenger flights to and from the UK as well as all air, sea, rail and road connections with Turkey, with an exception for Greek citizens and those who have residence permits or whose main residence is in Greece, as well as trucks and ships transporting goods.[249]
On 28 March, Greece suspended all commercial flights to and from Germany and the Netherlands until 15 April, with a few exemptions. From Germany, only flights to Athens Eleftherios Venizelos Airport were permitted.[250]
On 15 April, the Hellenic Civil Aviation Authority issued NOTAMs covering until 15 May, that ban commercial flights to and from Italy, Spain, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands and Germany. Exemptions include cargo, sanitary, humanitarian, state, military, ferry and Frontex flights, as well as flights in support of the Hellenic National Healthcare System, those for repatriation of Greek citizens and emergency flights.[251][252]
Economic measures
On 18 March, in a joint news conference, Finance Minister Christos Staikouras, Labour Minister Yannis Vroutsis, and Development & Investments Minister Adonis Georgiadis announced a package of measures to support the economy, businesses and employees. The measures include the suspension, for four months, of tax and social security obligations of corporations that were ordered to close by the state decree, with the sole condition that they do not dismiss any workers. This measure covers about 220,000 businesses and 600,000 employees. The measures also include an €800 stipend as well as a four-month suspension of payment of March taxes on employees of businesses the activity of which was suspended and on freelance professionals who work in sectors affected by the pandemic. The reduction of VAT tax from 24% to 6% on pharmaceutical products such as gloves, masks and antiseptics was also announced. Moreover, the Finance Minister announced the inclusion of Greece in an emergency assets purchases’ program worth 750 billion euros launched by the European Central Bank, and also stated the 3.5% primary surplus target for Greece is no longer in effect, according to a Eurogroup decision.[230][253][254]
On 19 March, Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis, in a nationally televised address, announced the revision of the State Budget to allocate more than 10 billion euros in support of the economy. The suspension of tax and social security obligations of corporations and the number of beneficiaries of the €800 stipend was extended to include all businesses harmed by the pandemic, all freelancers and self-employed workers and the majority of private sector workers. The state will also cover the cost of beneficiaries’ insurance, pension, and health payments. The PM also stated that the Easter bonus would be paid in full to all employees and announced a special bonus for health and civil protection workers.[255][256]
Suspension of businesses and workplaces
On 12 March, a two-week closure of all theatres, courthouses, cinemas, gyms, playgrounds and clubs was announced.[257]
On 13 March, the nationwide closure of all shopping centres, cafes, restaurants, bars, museums and archaeological sites and food outlets, excluding supermarkets, pharmacies and food outlets that offer take-away and delivery only, was announced.[258] On 14 March, all organised beaches and ski resorts were closed.[259]
On 19 March, the government announced the closure of all hotels across the country, from midnight on March 22 and until the end of April. Only hotels that accommodate personnel that guard the border will continue to operate, as well as three hotels in Athens and Thessaloniki and one hotel per regional unit will remain open. Moreover, all Greek citizens returning from abroad will be subjected to mandatory surveillance and isolation for at least 14 days.[260][261] On 22 March, all parks, recreation areas and marinas were also closed.[262]
Closure of educational institutions
Starting on 28 February, with four confirmed cases in the country, the precautionary local closure of schools was decided when there was concern that members of these school communities may have come into contact with a coronavirus carrier. On the same day, all educational trips abroad programmed by Greek schools were suspended and various municipalities around the country began disinfecting schools locally.[263][264][265] On 4 March, the closure of all public and private educational institutions of all levels in Ilia, Achaea and Zakynthos was decided[266] and from 8 March all educational trips within the country were suspended.[33]
On 10 March, the operation of all schools, universities, daycare centres and all other educational establishments were suspended nationwide for fourteen days.[267] A special purpose leave of 15 days was introduced for working parents.[268] Ten days later, on 20 March, this was extended such that all educational institutions would remain closed until 10 April.[269] On 10 April, the Minister of Education Niki Kerameos announced that all educational institutions would remain closed until 10 May.[270]
Suspension of religious services
On 9 March 2020, the Standing Holy Synod of the Church of Greece, the country's established Eastern Orthodox Church, discussed the coronavirus epidemic and issued an encyclical that was sent to the dioceses of the Church of Greece. Having stated that the Holy Communion could by no means be a way of transmission of diseases, the Standing Synod decided to continue offering and receiving the Holy Communion.[271][272][273] The Synod's decision sparked controversy.[274][275] The Synod's stance prompted criticism from the opposition Syriza party, with former prime minister Alexis Tsipras criticising the hierarchy, as did former health minister Pavlos Polakis.[275] Some high-profile Greek medical doctors publicly supported the continuation of practicing Holy Communion, drawing criticism from the Greek Association of Hospital Doctors.[276] (Template:Lang-el (OENGE)).
On 11 March, the prime minister of Greece Kyriakos Mitsotakis, in a nationally televised address, told the public to follow the instructions of doctors and experts, and the Church of Greece to cooperate in enforcing the public health regulations.[277] Two days later, the Archbishop of Athens and all Greece Ieronymos stated that the Church agreed with and would implement the public health precautionary measures taken by the national authorities.[278]
On 16 March, after having been briefed by infectious disease spokesman Sotiris Tsiodras, the Church's Standing Synod decided to suspend all public services except Divine Liturgies on Sundays, which were to be held as usual between 7 and 8 o’clock in the morning; weddings and baptisms were suspended, funerals were to be held with only the immediate family present; churches were to remain open for private prayer.[279][280] Following the Synod's decision, the Greek prime minister announced the government's decision to suspend services in all areas of religious worship of any religion or dogma from 16–30 March,[281] effectively suspending Sunday Divine Liturgies for that period too.[282]
On 1 April, the Standing Synod of the Church of Greece issued a statement that urged the faithful to abide by the government's sanitary regulations and to refrain from attending services in churches; it also re-affirmed its stance on the Holy Communion set out in the statement of 9 March 2020 and expressed hope that solemn public celebration of Easter (Pascha), which would properly be on 19 April, could be performed on the night of 26 May, the eve of the Leave-Taking (Apodosis) of Pascha.[283][284]
On 18 April, some churches in Athens were opened by the priests who offered services to worshippers. Elsewhere in Athens, some Orthodox believers protested against the closing of the churches and hammered on the church doors. 18 of them were taken in custody by the police. In the island of Corfu, the local bishop who has taken a hard stance against the measures of the government to halt the spread of the coronavirus invited the mayor of Corfu and citizens to partake in a closed-door service.[285]
Refugees and migrants
On 27 February, prime minister Mitsotakis announced that illegal entry from Turkey would no longer tolerated; as this would be a threat to public health in Greece.[286][287] According to various estimates about 150,600 displaced persons are located in Greece.[288] In the existing camps, doctors, NGOs and refugees considered that measures against the spread of the coronavirus are lacking as people live in overcrowded spaces with little access to proper health services.[289][288][290] On 24 March, 21 international human rights organizations active in Greece including Amnesty International, the Human Rights Watch and ActionAid published an open call to the Greek government to take immediate measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in the Reception and Identification Centres, where refugees live. The conditions of the centres were criticised as deplorable and dangerous to both the refugees and public health.[291] Médecins Sans Frontières, which has a clinic near the Moria camp, declared that the numbers in the camps had reached levels such that they could not handle an outbreak of infection within the camp. The government further announced that movement of refugees outside the camps would be restricted as facilities are prepared for confirmed cases,[292] and that it would only allow small groups of refugees and migrants to temporarily exit the camps to obtain basic supplies.[289]
On 31 March, it was reported that two individuals were infected in the Ritsona refugee camp in Central Greece.[293][294]
Refugees and migrants policy regarding Turkey
On 28 March, the Turkish interior minister announced that 5,800 refugees and migrants that had unsuccessfully attempted to cross the Greece–Turkey border had been relocated to Turkish cities due to the coronavirus pandemic. He also announced that as soon as the pandemic subsided, these people would be allowed to return to the border.[295]
Greek officials have stated concerns that Turkey may send infected refugees and migrants towards the Greek islands.[296][297][298][299] [300][excessive citations] According to journalist Stavros Lygeros, in April 2020, Turkish coastguards were sighted near to boats containing migrants, close to the Greek islands, wearing biological protection suits.[301] Some media reported that Turkish military and police appeared to be actively involved in plans to send migrants with Covid-19 to Greece and Europe,[302] with Turkish police helping immigrants to move to the coasts near the Greek islands.[303] These migrants were supposed to remain in quarantine stations in Turkey, nevertheless the Turkish authorities were moving them to the Greek border.[304] German newspaper Die Welt described Turkey's policy of sending migrants while the coronavirus pandemic was in full swing, in order to put pressure on Greece and the European Union, as "irresponsible" and "highly dangerous".[305]
Animal welfare
According to an Al Jazeera report on 30 April 2020, animal rescue groups and shelters throughout Greece have been overwhelmed with thousands of stray dogs due to the disruption of international dog adoption caused by international travel restrictions imposed in response to the coronavirus pandemic.[306]
Lifting of emergency measures
On 28 April, Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis and six Deputy Ministers, as well the Minister of Education Niki Kerameos the following day, announced the government's plan for the gradual lifting of the restrictive measures and the restart of business activity. The plan consists of specific milestone dates and extends throughout May and June 2020, and may be revised as it will be evaluated continuously against the COVID-19 infection rate.[307][308]
Initial stage on 4 May
Starting on 4 May, those moving outside their home no longer need to send a text message or carry a declaration giving their reason, but only within their regional unit of residence. In its 42 days of operation, from 23 March to 4 May, a total of about 110 million text messages to the number 13033 were handled, an average of 1,818 messages per minute.[309] Travel to other regional units or between islands within the same regional unit will still be prohibited until 18 May.
Some stores opened, however some are by appointment only and strict rules regarding the maximum number of people inside apply. The stores opening are hairdressers, bookstores, electrical appliance stores, optical and sports equipment stores, as well as vehicle inspection centres (KTEO). This restart affected a total of 26,167 businesses, about 10% of those whose operation was suspended, and 68,528 employees, also about 10% of the total.[310][311][312][313]
The use of face masks is mandatory for employees and customers in all closed places as well as in public transport. The government recommends the use of private vehicles rather than public transport to reduce congestion. Public transport will increase schedules to accommodate passengers without crowding during peak hours.[311][312]
Public sector employees will attend their jobs in three stages, at 07:00, 08:00 and 09:00 in the morning in order to avoid congestion on public transport, and the special-purpose leave for parents with school-age children will be extended at least until the end of May.[311][312]
Scheduled surgeries will resume from 4 May, individual exercise will be allowed in open areas and churches will also open but only for individual prayer.[308][311]
Subsequent stages (11 May – June)
On 11 May, all remaining retail shops as well as driving schools that were shut down by governmental decree, except shopping malls, will re-open with specific hygiene rules. Classes for High school senior grade students will resume from 11 May, but classes will be divided into two groups with a maximum of 15 pupils in each group. Groups will attend classes on alternating days.[314][311]
From 18 May, all other grades of upper and lower secondary education will resume classes and private tuition and foreign language centres will re-open. Worshippers will be able to attend Divine Liturgies and other religious services following specific hygiene rules, starting from 17 May. On 18 May all movement restrictions across the country are planned to be lifted and archaeological sites, zoos and botanical gardens will re-open.[312]
On 1 June, all cafes and restaurants will be allowed to re-open, but only with outdoor seating and certain distances between chairs and tables. Shopping malls, year-round hotels and summer movie theatres will also begin operation on that date, with strict social distancing rules. Staff members will have to wear masks and gloves. Nursery schools, kindergartens and primary schools will continue to remain closed at least until June 1st and until further notice.[310][312][315]
Indoor restaurants and cafes as well as other indoor facilities will open at a later date. Large gatherings, such as festivals, concerts or sporting events with spectators, will probably not be allowed during the summer months.[316]
Notes
- ^ Le Figaro claimed that Tsiodras was the "new beloved of Greeks".[7] In the article Le Figaro claims that he asked Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis for strict lockdown measures as soon as the first cases were reported in Italy. Greek sociologist Andreas Drymiotis wrote: "Greeks particularly appreciate his calm, his knowledge on the matter, and his deep respect for all victims and the fact that he has an unbreakable dedication to nursing staff.".[49]
References
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: 15 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα". 30 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 149 οι νεκροί – Κατέληξε 67χρονος στη Λάρισα" (in Greek). in.gr. 7 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "Παρατείνονται τα περιοριστικά μέτρα μέχρι τις 4 Μαΐου – Τι θα ισχύσει με την αποστολή SMS" (in Greek). 24 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Tugwell, Paul; Nikas, Sotiris (16 April 2020). "Humbled Greeks Show the World How to Handle the Virus Outbreak". www.bloomberg.com. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Giugliano, Ferdinando (10 April 2020). "Greece Shows How to Handle the Crisis" – via Bloomberg.com.
- ^ Stevis-Gridneff, Matina (5 April 2020). "The Rising Heroes of the Coronavirus Era? Nations' Top Scientists" – via NYTimes.com.
- ^ a b Kefalas, Alexia (20 March 2020). "L'infectiologue Sotirios Tsiodras, nouvelle coqueluche des Grecs". Le Figaro.fr (in French).
- ^ "Stocks Rally Suggests Turning Point In Coronavirus Fight". www.bloomberg.com. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Athens, Anthee Carassava. "Greeks rein in rebellious streak as draconian measures earn them a reprieve" – via www.thetimes.co.uk.
- ^ "Greek Doctor in Birmingham: Greece is exemplar, Britain in worse position than Italy (Original: Ελληνας γιατρός στο Μπέρμιγχαμ: Πρότυπο η Ελλάδα, η Βρετανία σε χειρότερη θέση από την Ιταλία)". Έθνος (in Greek). 24 March 2020.
- ^ Elsevier. "Novel Coronavirus Information Center". Elsevier Connect. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Reynolds, Matt (4 March 2020). "What is coronavirus and how close is it to becoming a pandemic?". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Archived from the original on 5 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus". Imperial News. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ "High consequence infectious diseases (HCID); Guidance and information about high consequence infectious diseases and their management in England". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists – Coronavirus". www.wfsahq.org. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ "Greece confirms first coronavirus case". Reuters. 26 February 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b "Κορωνοϊός: Δεύτερο θετικό κρούσμα στην Ελλάδα -Το παιδί της 38χρονης | ΕΛΛΑΔΑ". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). 27 February 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ a b IEFIMERIDA.GR, NEWSROOM (27 February 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στην Αθήνα το τρίτο κρούσμα -Ακυρώνονται όλα τα καρναβάλια στη χώρα | ΕΛΛΑΔΑ". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ a b "Κορονοϊός: τρία κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - Ακυρώνονται οι εκδηλώσεις για το Καρναβάλι σε όλη τη χώρα". antenna.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ "Greece reports two new coronavirus cases, cancels carnival". Reuters. 27 February 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός στην Αθήνα: Γυναίκα, σύζυγος στελέχους ναυτιλιακής το πρώτο κρούσμα - Νοσηλεύεται στο Αττικό". www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (26 February 2020). "Ο κοροναϊός έφτασε στην Ελλάδα: Πρώτο επιβεβαιωμένο κρούσμα στη Θεσσαλονίκη". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 26 February 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: Τέταρτο κρούσμα - Καθηγήτρια 36 ετών στην Αθήνα". News247 (in Greek). 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ "4 confirmed coronavirus cases in Greece and 8 schools closed in Attica". Tornos News. 28 February 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Πέμπτο κρούσμα στην Ελλάδα". iefimerida (in Greek). 29 February 2020. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- ^ "Ανεβαίνει ο αριθμός: Επτά τα κρούσματα του κοροναϊού στην Ελλάδα". www.gazzetta.gr (in Greek).
- ^ "Ογδοο κρούσμα του ιού στην Ελλάδα". www.euro2day.gr (in Greek).
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Ένατο επιβεβαιωμένο κρούσμα στην Πάτρα". www.onmed.gr (in Greek). 4 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊος: Στην Πάτρα και το δέκατο κρούσμα - Πρόκειται για τη σύζυγο του 66χρονου". www.news247.gr (in Greek).
- ^ Newsroom (5 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός στην Ελλάδα: Στα 31 τα κρούσματα του ιού - 21 νέα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 5 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: 14 ακόμα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα!". NewsIt (in Greek). 6 March 2020. Retrieved 6 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: 21 νέα κρούσματα - Στους 66 συνολικά οι ασθενείς". kathimerini (in Greek). 7 March 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Κοροναϊός : 73 κρούσματα - Κεκλεισμένων των θυρών οι αθλητικές εκδηλώσεις". in.gr (in Greek). 8 March 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Κορωνοϊός: 11 νέα κρούσματα -Μείνετε σπίτι σας, λέει ο Κικίλιας στις ευπαθείς ομάδες". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). 9 March 2020. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- ^ "First coronavirus case on Greek island filled with migrants". 9 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός στην Ελλάδα: Ανακοινώθηκαν πέντε νέα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). 10 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ "Olympiacos: Vangelis Marinakis diagnosed with coronavirus". Greek City Times. 10 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Κλείνουν όλα τα σχολεία και τα πανεπιστήμια της χώρας". CNN.gr. 10 March 2020.
- ^ Κορωνοϊός: 99 τα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα -Ακυρώνονται οι παρελάσεις Coronavirus: 99 cases in Greece - Parades canceled, www.iefimerida.gr, accessed 12 March 2020
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: 18 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - 117 συνολικά - Δέκα τα "ορφανά"".
- ^ "Greek coronavirus cases rise to 117; two released from hospital". ekathimerini-com. 12 March 2020. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση του πρώτου θανάτου από τον SARS-CoV-2" (in Greek). Ministry of Health. 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: 190 τα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - 5 διασωληνωμένοι - 11 τα "ορφανά"". ΣΚΑΪ (in Greek). Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "Greece's first female president is sworn in". ABC News. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "Greece Swears in First Female President, No Handshakes Amid Coronavirus". US News. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (14 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 38 νέα κρούσματα - Τα περισσότερα στην Αθήνα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 14 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (14 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Και δεύτερος νεκρός από τον ιό". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 14 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom. "Κορονοϊός: Τρίτος νεκρός στην Ελλάδα". Newsbomb (in Greek). Retrieved 14 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Sydney-born immunologist Sotiris Tsiodras, the 'voice' of coronavirus in Greece". Neos Kosmos. 24 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορωνοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 14 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (15 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 103 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - Στα 331 συνολικά". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 15 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: Τέταρτος νεκρός στην Ελλάδα, ένας 53χρονος στο ΑΧΕΠΑ". www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (16 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 21 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - 352 συνολικά". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 16 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (17 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους πέντε οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα - Στα 387 τα κρούσματα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 17 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (18 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 31 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - Απαγόρευση συναθροίσεων άνω των 10 ατόμων". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 18 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (18 March 2020). "Ενθαρρυντικά σημάδια από δύο ερευνητικά μέτωπα στη μάχη κατά του κορωνοϊού". kathimerini.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 19 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Γυναίκα με κορονοϊό γέννησε αγοράκι στο Αττικόν". Έθνος (in Greek). 18 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (19 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 46 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - 464 συνολικά". kathimerini.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 19 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (19 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Και έκτος νεκρός στην Ελλάδα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 19 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 10 οι νεκροί - Τέσσερις το τελευταίο 24ωρο". cnn.gr (in Greek). 20 March 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom. "Κορονοϊός: 35 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα - 530 στο σύνολο". Newsbomb (in Greek). Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: Στους 13 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας". ethnos.gr (in Greek). 21 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ a b Newsroom (22 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 15 οι νεκροί - 94 νέα κρούσματα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 22 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: 17 νεκροί, 71 νέα κρούσματα στην Ελλάδα – Στα 695 στο σύνολο". ieidiseis.gr (in Greek). 23 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Στους 16 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα". newsit.gr (in Greek). 23 March 2020.
- ^ "Κρούσματα κορωνοϊού: 17 οι νεκροί - Κατέληξε 78χρονος στο Σωτηρία". protothema.gr (in Greek). 23 March 2020.
- ^ "Γεννήθηκε δεύτερο μωρό από μητέρα θετική στον κορονοϊό". Η Εφημερίδα των Συντακτών (in Greek). Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 20 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα - 743 τα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). 24 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Θετική 40χρονη που έχασε τη ζωή της στην Καστοριά - Ειδήσεις". 24 March 2020.
- ^ "Στους 22 οι νεκροί από κορωνοϊό στην Ελλάδα – 78 νέα κρούσματα, 821 συνολικά". tovima.gr (in Greek). 25 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ a b Newsroom (26 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 26 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας - 71 νέα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 26 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Newsroom (27 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 28 νεκροί και 74 νέα κρούσματα στη χώρα μας". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 27 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (28 March 2020). "Κορωνοιός: 32 θάνατοι, 95 νέα επιβεβαιωμένα κρούσματα, 1.061 συνολικά". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (29 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 38 οι θάνατοι στην Ελλάδα - 95 νέα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 29 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Greek City Times (29 March 2020). "First case of coronavirus at Mount Athos". greekcitytimes.com. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (30 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 43 θάνατοι, 56 νέα κρούσματα, στα 1.212 συνολικά". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Newsroom (31 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 49 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας - 82 τα νέα επιβεβαιωμένα κρούσματα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Σε καραντίνα στον Πειραιά το κρουαζιερόπλοιο "Ελ. Βενιζέλος" με τα 20 κρούσματα | ΕΛΛΑΔΑ" [Coronavirus: In quarantine at Piraeus the cruiser 'El. Venizelos' with the 20 cases]. iefimerida.gr. 31 March 2020.
- ^ a b Newsroom (1 April 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 50 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας - 1.415 τα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 1 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Newsroom (2 April 2020). "Κορονοϊός: 53 θάνατοι στη χώρα μας, 91 στη ΜΕΘ, 1.544 συνολικά τα κρούσματα". ethnos.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 2 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (3 April 2020). "Κοροναϊός : 99 νέα κρούσματα – Στα 1.613 τα συνολικά – 59 θάνατοι". in.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 3 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (4 April 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 68 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας - 1.673 τα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 4 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (5 April 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 73 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας - 1.735 τα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 5 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (6 April 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 79 οι νεκροί στη χώρας μας - 1.755 τα επιβεβαιωμένα κρούσματα". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 6 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Newsroom (7 April 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: 81 νεκροί και 1.832 επιβεβαιωμένα κρούσματα στη χώρα μας". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 7 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (8/4/2020)". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 8 April 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Newsroom (9 April 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 86 οι νεκροί - 71 νέα κρούσματα". cnn.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 9 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "Κοροναϊός : Ακόμα μια νεκρή στην Ελλάδα – Στους 88 οι θάνατοι". in.gr. 9 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (11/4/2020)". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ανακοίνωση για την εξέλιξη της νόσου COVID-19 στη χώρα μας (12-04-2020)". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 12 April 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (13/4/2020)". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 13 April 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: Στους 100 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα". news247.gr. 13 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Σεζόν 2019 - 2020". www.skaitv.gr.
- ^ a b "Κορωνοϊός: 22 νέα κρούσματα στη χώρα μας - 103 οι νεκροί". cnn.gr. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: 102 θάνατοι στην Ελλάδα - 22 νέα κρούσματα - 2.192 στο σύνολο" (in Greek). onmed.gr. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός- Τσιόδρας: 15 νέα κρούσματα - 105 νεκροί - 2207 ασθενείς - 69 διασωληνωμένοι" (in Greek). skai.gr. 16 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός- Τσιόδρας: 17 νέα κρούσματα - 108 νεκροί -2224 ασθενείς - 71 διασωληνωμένοι". skai.gr. 17 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ "Στους 106 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα - Ένας ακόμη νεκρός στην Πτολεμαΐδα" (in Greek). skai.gr. 17 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός- Τσιόδρας: 17 νέα κρούσματα - 108 νεκροί -2224 ασθενείς - 71 διασωληνωμένοι" (in Greek). 17 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (20/4/2020)". Υπουργείο Υγείας (in Greek). Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Κατέληξε 68χρονη από την Καστοριά -114 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα". in.gr (in Greek). 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Κορονοϊός: 117 νεκροί στη χώρα, πέθανε 86χρονος στο ΑΧΕΠΑ" (in Greek). makthes.gr. 20 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: 156 νέα κρούσματα στη χώρα μας - Στους 121 οι νεκροί" (in Greek). cnn.gr. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "150 people test positive for Covid-19 at Kranidi refugee facility | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (21/4/2020)". Ministry of Health (in Greek). Retrieved 21 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Στους 119 οι νεκροί από κορωνοϊό στην Ελλάδα: Κατέληξαν 35χρονος και 75χρονος" (in Greek). cnn.gr. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 121 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Μόλις 6 νέα κρούσματα, 150 στο Κρανίδι" (in Greek). in.gr. 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός : Κανένας νέος θάνατος σήμερα – 7 νέα κρούσματα" (in Greek). tanea.gr. 22 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός : 55 νέα κρούσματα, στα 2.463 τα συνολικά – 125 θάνατοι" (in Greek). in.gr. 22 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 122 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Πέθανε 88χρονος" (in Greek). 23 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός στην Ελλάδα : 123 τα θύματα - Δύο άνθρωποι υπέκυψαν την Πέμπτη" (in Greek). 23 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 124 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Υπέκυψε 90χρονος στο "Σωτηρία"" (in Greek). 23 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Τέταρτος νεκρός μέσα σε ένα 24ωρο - 125 οι νεκροί" (in Greek). 23 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 127 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας - Κατέληξαν δύο άτομα" (in Greek). cnn.gr. 22 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 128 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Κατέληξε μία 59χρονη στο ΑΧΕΠΑ" (in Greek). 24 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ "ΚΚοροναϊός: Στους 129 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Πέθανε 81χρονη στην Κοζάνη" (in Greek). 24 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: 130 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – 27 νέα κρούσματα, 2.490 συνολικά" (in Greek). in.gr. 24 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Κανένας θάνατος το τελευταίο 24ωρο – 16 νέα κρούσματα, 47 σε ΜΕΘ" (in Greek). in.gr. 25 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 131 οι νεκροί στη χώρα – Υπέκυψε 78χρονος ασθενής" (in Greek). tovima.gr. 25 April 2020. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: 134 νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – 11 νέα κρούσματα, 2.517 συνολικά" (in Greek). in.gr. 26 April 2020. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 132 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Κατέληξε άνδρας στο "Σωτηρία"" (in Greek). cnn.gr. 26 April 2020. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 133 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Πέθανε 58χρονη στην Αλεξανδρούπολη" (in Greek). skai.gr. 26 April 2020. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 136 οι νεκροί - Δύο νεκροί στη Βόρεια Ελλάδα"" (in Greek). skai.gr. 27 April 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 136 οι νεκροί - Δύο νεκροί στη Βόρεια Ελλάδα" (in Greek). skai.gr. 27 April 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 137 οι νεκροί μετά το θάνατο 90χρονου" (in Greek). tovima.gr. 28 April 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Στους 138 οι νεκροί στη χώρα μας – Κατέληξε 84χρονος" (in Greek). kathimerini.gr. 28 April 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός : 10 νέα κρούσματα, στα 2.576 τα συνολικά – 139 θάνατοι". in.gr. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ "Kοροναϊός: Στους 139 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – Κατέληξε 89χρονος στο ΝΙΜΤΣ" (in Greek). in.gr. 29 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: 140 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – 15 νέα κρούσματα, 2.591 συνολικά" (in Greek). in.gr. 30 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ^ a b "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 30-04-2020". Ministry of Health (in Greek). 30 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Κοροναϊός: Κανένας θάνατος το τελευταίο 24ωρο – 21 νέα κρούσματα, 36 πολίτες στις ΜΕΘ" (in Greek). in.gr. 1 May 2020. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός : Τρεις νεκροί σήμερα – 143 συνολικά τα θύματα στην Ελλάδα" (in Greek). in.gr. 2 May 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός : 144 τα θύματα στην Ελλάδα – Κατέληξε 76χρονη στο ΝΙΜΤΣ" (in Greek). in.gr. 3 May 2020. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 145 οι νεκροί – Πέθανε 88χρονη στο «Αττικόν»" (in Greek). in.gr. 4 May 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 146 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα – 50χρονος το τελευταίο θύμα" (in Greek). in.gr. 4 May 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 147 οι νεκροί στην Ελλάδα - Κατέληξε 89χρονη στο «Σωτηρία" (in Greek). in.gr. 6 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "Κοροναϊός: Στους 149 οι νεκροί – Κατέληξε 67χρονος στη Λάρισα" (in Greek). in.gr. 7 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ https://www.in.gr/2020/05/08/greece/koronaios-enimerosi-tsiodra-xardalia-gia-tin-ekseliksi-tis-pandimias/
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας για τις εξελίξεις αναφορικά με το νέο κορονοϊό". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 27 February 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση 4ου κρούσματος SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 28 February 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Το Κέντρο Επιχειρήσεων και το τηλεφωνικό κέντρο του ΕΟΔΥ επισκέφθηκε ο Υπουργός Υγείας Βασίλης Κικίλιας". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 2 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα - 03/03/2020". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 3 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση όγδοου κρούσματος SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 4 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση ένατου κρούσματος SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 4 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση για την κατάσταση του ένατου κρούσματος". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 4 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (5/3/2020)". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 5 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (6/3/2020)". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 6 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση 21 νέων κρουσμάτων SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 7 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση νέων μέτρων για την προστασία της Δημόσιας Υγείας". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 8 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για τον νέο κορωνοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (9-3-2020)". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 9 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση 5 νέων κρουσμάτων SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 10 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση 10 νέων κρουσμάτων SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 11 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Δήλωση εκπροσώπου του Υπουργείου Υγείας για τον νέο κορονοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα (13/3/2020)". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 13 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση του πρώτου θανάτου από τον SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 12 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για τον νέο κoρωνοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 12 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορωνοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 14 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ανακοίνωση δύο θανάτων από τον SARS-CoV-2". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 14 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών Υγείας από τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 15 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 16 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορωνοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 18 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορωνοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek). 19 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Daily report 20.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 20 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 21-03-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 21 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 21.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 21 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ανακοίνωση 94 νέων κρουσμάτων SARS-CoV-2". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 22 March 2020. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 22.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 22 March 2020. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 23.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 24.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 24 March 2020. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 25.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 25 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ημερήσια ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 28/3/2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 29/3/2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 29 March 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 29.03.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 29 March 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 30-03-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 30 March 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 31-03-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 31 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 01-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 1 April 2020. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 02-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 03-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 3 April 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 03.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 3 April 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 04.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 4 April 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 05.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization. 5 April 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 06-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 6 April 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 06.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 6 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 07-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 7 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 07.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization. 7 April 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 08.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization. 8 April 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 09-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 9 April 2020. Retrieved 9 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 09.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 9 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 10.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 10 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 10-04-2020". National public Health Organization (in Greek). 10 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 11-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 11.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ανακοίνωση για την εξέλιξη της νόσου COVID-19 στη χώρα μας 12-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 12 April 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Κορωνοϊός: 33 νέα επιβεβαιωμένα κρούσματα στη χώρα μας - 98 οι νεκροί". cnn.gr (in Greek). 12 April 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 13-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 13 April 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Κοροναϊός : 31 νέα κρούσματα, στα 2.145 τα συνολικά – 99 θάνατοι". cnn.gr (in Greek). 13 April 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 14-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 14 April 2020. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 14.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 14 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 15-04-2020". Ministry of Health (in Greek). 15 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 15.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 15 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 16.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 16 April 2020. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 17.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 17 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 18.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 18 April 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 20.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 21.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 21 April 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 21-04-2020". National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 21 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 22.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 22 April 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 23.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 23 April 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 24.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 24 April 2020. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 25.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 25 April 2020. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 26.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 26 April 2020. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 27.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 27 April 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 28.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 28 April 2020. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 29.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 29 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b "COVID-19 Daily report 30.04.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 30 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 01-05-2020". Ministry of Health (in Greek). 1 May 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας 01-05-2020" (PDF). Ministry of Health (in Greek). 2 May 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας (03/05/2020)". Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek) (in Greek). 3 May 2020. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ^ "Ενημέρωση διαπιστευμένων συντακτών υγείας (04/05/2020)" (PDF). Εθνικός Οργανισμός Δημόσιας Υγείας (in Greek) (in Greek). 4 May 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "COVID19 daily report by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organization (in Greek). 5 May 2020. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 06.05.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 07.05.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 7 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 07.05.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 7 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "COVID-19 Daily report 09.05.2020 by NPHO" (PDF). National Public Health Organisation (in Greek). 9 May 2020. Retrieved 9 May 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Κορονοϊός στην Ελλάδα: Επτά νέα κρούσματα - Στους 73 οι ασθενείς που νοσούν". ieidiseis (in Greek). 8 March 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- ^ "ΥΠΟΥΡΓΕΙΟ ΠΑΙΔΕΙΑΣ & ΘΡΗΣΚΕΥΜΑΤΩΝ - 10-03-20 Προσωρινή απαγόρευση της εκπαιδευτικής λειτουργίας όλων των εκπαιδευτικών δομών". Υπουργείο Παιδείας και Θρησκευμάτων (in Greek). 10 March 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Σε καραντίνα τα χωριά Δαμασκηνιά και Δραγασιά" [Coronavirus: The villages of Damaskinia and Dragasia are quarantined]. Έθνος (in Greek). 16 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Greece unveils new coronavirus restrictions in migrant camps". Channel New Asia. 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Σε ισχύ η απαγόρευση συναθροίσεων άνω των 10 ατόμων - Οι αποδεκτές μετακινήσεις" [Coronavirus: Ban on public gatherings of 10 or more people - Acceptable movements]. www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Greece bans gatherings of 10 people and more, effective Thursday". Reuters. 19 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Κορονοϊός: Τα μέτρα για εργαζόμενους κι επιχειρήσεις" [Coronavirus: Measures for Workers and Businesses]. Έθνος (in Greek). 18 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Government bans travel to the islands for non-residents | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ IEFIMERIDA.GR, NEWSROOM (22 March 2020). "Απαγόρευση κυκλοφορίας: Πώς θα πάτε τη Δευτέρα στη δουλειά -Πού επιτρέπεται η μετακίνηση | ΕΛΛΑΔΑ". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ "Instructions to the public". forma.gov.gr. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ in.gr (22 March 2020). "Greece in quarantine: Mitsotakis declares nationwide lockdown as of 6am tomorrow". in.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ "PM announces full lockdown in bid to curb coronavirus spread | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ in.gr (22 March 2020). "Απαγόρευση κυκλοφορίας: Αναλυτικός οδηγός - Πού θα επιτρέπεται η μετακίνηση -Τι θα ισχύσει για τους εργαζομένους". in.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Constantine, Alex (6 April 2020). "Greece records more than 20,000 violations since COVID-19 imposed curfew". Greek City Times. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ generalsecretary (4 April 2020). "Ενημέρωση από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Γενική Γραμματεία Πολιτικής Προστασίας (in Greek). Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ generalsecretary (31 March 2020). "Πρόσθετα περιοριστικά μέτρα για τη μετακίνηση των πολιτών στους Δήμους Ξάνθης, Μύκης, Καστοριάς, Ορεστίδος και Νεστορίου λόγω κορωνοϊού COVID-19". Γενική Γραμματεία Πολιτικής Προστασίας (in Greek). Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ generalsecretary (2 April 2020). "Ενημέρωση από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Γενική Γραμματεία Πολιτικής Προστασίας (in Greek). Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b generalsecretary (5 April 2020). "Πρόσθετα περιοριστικά μέτρα στην Μύκονο και την Σαντορίνη λόγω κορωνοϊού COVID-19". Γενική Γραμματεία Πολιτικής Προστασίας (in Greek). Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ generalsecretary (8 April 2020). "Ενημέρωση από τον Υφυπουργό Πολιτικής Προστασίας και Διαχείρισης Κρίσεων Νίκο Χαρδαλιά και τον εκπρόσωπο του Υπουργείου Υγείας για το νέο κορονοϊό, Καθηγητή Σωτήρη Τσιόδρα". Γενική Γραμματεία Πολιτικής Προστασίας (in Greek). Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ "All flights to and from northern Italy suspended | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ "Greece reports two more coronavirus fatalities, bans all flights to Italy". Reuters. 14 March 2020.
- ^ "Εκτακτα μέτρα - Κορονοϊός: Κλείνουν τα σύνορα με Αλβανία και Β. Μακεδονία - Παρέμβαση Μητσοτάκη για τις εκκλησίες". www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Κλείνουν τα εμπορικά καταστήματα - Σε καραντίνα όσοι έρχονται από εξωτερικό". www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ IEFIMERIDA.GR, NEWSROOM (18 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Η ΕΕ κλείνει τα σύνορα -Ποιοι ταξιδιώτες θα μπαίνουν σε καραντίνα στην Ελλάδα | ΚΟΣΜΟΣ". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Η Τουρκία κλείνει τα σύνορα με την Ελλάδα και τη Βουλγαρία". Έθνος (in Greek). 18 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (23 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Τέλος οι πτήσεις από Βρετανία και Τουρκία". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Hellenic Civil Aviation Authority (28 March 2020). "ΝΟΤΑΜ για αναστολή πτήσεων έως τις 15 Απριλίου 2020 από και προς Ολλανδία και Γερμανία. Επιτρέπονται μόνο οι αφίξεις από Γερμανία για το Αεροδρόμιο της Αθήνας «Ελευθέριος Βενιζέλος»". Retrieved 21 April 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Greece extends flight ban for six countries until May 15 | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ Hellenic Civil Aviation Authority (15 April 2020). "Παράταση ΝΟΤΑΜS έως τις 15 Μαΐου 2020". Retrieved 21 April 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Team, TANEA (18 March 2020). "Greece takes sweeping measures to protect business, labour from coronavirus tempest". ΤΑ ΝΕΑ. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Greece says ECB emergency package makes 12 billion euro in debt eligible | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom. "Κορονοϊός - "Τελεσίγραφο" Μητσοτάκη: Αν χρειαστεί θα πάρω νέα μέτρα περιορισμού της κυκλοφορίας" [Coronavirus - Mitsotakis: If needed I'll take new restriction measures]. Newsbomb (in Greek). Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Greek PM announces more financial aid, bonus for health workers | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Εκτακτα μέτρα: Κλείνουν κινηματογράφοι, θέατρα και κέντρα διασκέδασης". tanea.gr (in Greek). 12 March 2020. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ "Malls, cafes, bars, eateries to close as coronavirus cases rise to 190". ekathimerini.com. 13 March 2020. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός: Κλείνουν παραλίες και χιονοδρομικά με εντολή Μητσοτάκη". Έθνος (in Greek). 14 March 2020. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ^ Newsroom (19 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός: Κλείνουν και τα ξενοδοχεία" [Coronavirus: Hotels are also closed]. CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 21 March 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Tsirigotaki, Eve (19 March 2020). "Hotels are closing- Greeks returning from abroad will be put under quarantine". ERT International. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ in.gr (22 March 2020). "Απαγόρευση κυκλοφορίας: Αναλυτικός οδηγός - Πού θα επιτρέπεται η μετακίνηση -Τι θα ισχύσει για τους εργαζομένους". in.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ Παπαϊωάννου, Η-Β (28 February 2020). "Κορονοϊός: Ιχνηλατείται η πορεία των νοσούντων-Μέτρα προφύλαξης-Αναστέλλονται τα επισκεπτήρια (video)". ert.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ iEidiseis. "Κορονοϊός: Πότε θα αποφασιστούν τα κλειστά σχολεία στην Ελλάδα". www.ieidiseis.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ iEidiseis. "Κορονοϊός στην Ελλάδα: Προληπτικές απολυμάνσεις σε δημόσια κτήρια από τον Δήμο Ιλίου". www.ieidiseis.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ iEidiseis. "Κορονοϊός στην Ελλάδα: Τα νέα έκτακτα μέτρα". www.ieidiseis.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Κλείνουν για δύο εβδομάδες σχολεία, πανεπιστήμια, παιδικοί σταθμοί και φροντιστήρια | Kathimerini". www.kathimerini.gr. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Κορονοϊός - έκτακτα μέτρα: Άδεια ειδικού σκοπού στους γονείς". www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Κλειστά έως τις 10 Απριλίου σχολεία και πανεπιστήμια". Alfavita (in Greek). Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Schools to remain closed until May 10, ministry says, Apostolos Lakasas | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ "Ιερά Σύνοδος: Ο κορωνοϊός δεν μεταδίδεται με τη Θεία Κοινωνία". kathimerini.gr. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ "Holy Synod of Church of Greece: We continue to receive the Holy Communion (upd)". OrthodoxTimes. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ "In era of coronavirus, Greek church says Holy Communion will carry on". Reuters. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ^ Carasava, Anthee (9 March 2020). "Coronavirus Sparks Church-State Controversy in Greece". Voice of America.
- ^ a b "Coronavirus: Bug sparks Holy Communion row in Greece". Straights Times. 9 March 2020.
- ^ Brzozowski, Alexandra; Michalopoulos, Sarantis (9 March 2020). "Catholics take measures against coronavirus while Greek Orthodox Church 'prays'". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- ^ Team, ΤοΒΗΜΑ (11 March 2020). "Mitsotakis calls for unity, personal responsibility, cooperation of Archbishop to limit COVID-19". Ειδήσεις - νέα - Το Βήμα Online (in Greek). Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Team, ΤοΒΗΜΑ (13 March 2020). "Κορωνοϊός - Ιερώνυμος: Η Εκκλησία μας ουδέποτε στάθηκε απέναντι στην Επιστήμη ή επιχείρησε να την υποκαταστήσει". Ειδήσεις - νέα - Το Βήμα Online (in Greek). Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ "Greek Orthodox Church agrees to suspend daily services, sacraments over coronavirus". Ekatherimini. 16 March 2020.
- ^ "Church of Greece: Weekday services and mysteries are temporarily postponed (upd)". OrthodoxTimes. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ "Αναστέλλονται όλες οι θρησκευτικές λειτουργίες με απόφαση της κυβέρνησης". www.kathimerini.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ^ "Greek Church finally toes state line on coronavirus | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ "Οι αποφάσεις της Δ.Ι.Σ. της Εκκλησίας της Ελλάδος". ecclesia.gr (in Greek). 1 April 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ "Ιερά Σύνοδος Ελλάδος: Θα γιορτάσουμε Πάσχα στις 26 Μαΐου". cyprustimes.com (in Greek). 1 April 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- ^ Hope, Kerin (17 April 2020). "Easter celebrations test Greece's virus containment success". Financial Times. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Karaoulanis, Theodore; Καραουλάνης, Θοδωρής (27 February 2020). "Ανάσχεση στα σύνορα σε όσους πρόσφυγες - μετανάστες προέρχονται από Ιράν, Αφγανιστάν προανήγγειλε ο Πρωθυπουργός, λόγω κορωνοϊού". www.euractiv.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ "Greece's response to coronavirus working, Mitsotakis tells CNN | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. ekathimarini. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ a b Prothero, Mitch (2020). "In Greece, the government prepares for a crisis that is beyond its capacity to handle". Business Insider. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Greece curbs refugee movement in camps over coronavirus fears". Al Jazeera. 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ Campana, Fahrinisa; Patrick, Strickland (2020). "The Looming Refugee Coronavirus Disaster". Slate. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ "Greece: Move Asylum Seekers, Migrants to Safety". HRW. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ Fotiadis, Apostolos (2020). "Greece Ramps up Restrictions but Faces Criticism over Coronavirus Response". Balkan Insight. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ "Θετικό στον κορονοϊό ζευγάρι από την Αφρική στο hot pot της Ριτσώνας" [Positive to coronavirus, a couple from Africa ...]. Έθνος. 31 March 2020.
- ^ "ΠΟΕΔΗΝ: Θετική στον κορωνοϊό μετανάστρια από τη Ριτσώνα που γέννησε στο Αλεξάνδρα" [Positive to coronavirus, a Ritsona woman immigrant who gave birth in Alexandra Hospital]. ΣΚΑΪ.
- ^ "Τούρκος ΥΠΕΣ: Μετά τη λήξη του κορονοϊού πρόσφυγες μετανάστες ξανά στα σύνορα". www.sofokleousin.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ "Πληροφορίες πως η Τουρκία επιχειρεί να στείλει στην Ελλάδα μετανάστες με κορωνοϊό". CNN.gr (in Greek). 11 April 2020.
- ^ Staff, T. N. H. (13 April 2020). "Worries Grow Turkey Will Send COVID-19 Migrants to Greek Islands, EU".
- ^ "Μετανάστες με κορωνοϊό προωθεί η Αγκυρα στην Ελλάδα, του Βασίλη Νέδου | Kathimerini". www.kathimerini.gr.
- ^ "Κορωνοϊός: Η Τουρκία επιχειρεί να προωθήσει στην Ελλάδα ασθενείς μετανάστες". ProtoThema. 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Η Τουρκία προσπαθεί να στείλει μετανάστες-πρόσφυγες με κορονοϊό σε ελληνικά νησιά". Έθνος. 11 April 2020.
- ^ "Αποκαλυψη: Η βαρκα με μολυσμενους μεταναστες και οι Τουρκοι με στολες βιολογικου πολεμου". SLPress. 2 April 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ "Turkey reportedly planned to send migrants with Covid-19 to Greece and Europe (photos)".
- ^ Worries Grow Turkey Will Send COVID-19 Migrants to Greek Islands, EU, The National Herald, April 13, 2020: "According to the sources, these migrants, many of whom were also at the Pazarkule, or Kastanies, border crossing, have been transported from migrant camps in the hinterland with migrants moving toward the Turkish coast helped by police in further violation of the swap deal that has seen EU officials reluctant to confront Erdogan."
- ^ Höhler, Gerd (17 April 2020). "Türkei: Erdogan droht für neue Flüchtlingskrise in EU zu sorgen". www.morgenpost.de (in German). Retrieved 21 April 2020.
Weil Griechenland seine Grenze nicht öffnete, ließ die Türkei Ende März die Belagerer ins Landesinnere zurückbringen. Sie sollten in Corona-Quarantäne kommen, lautete die offizielle Begründung. Jetzt bringen Busse Tausende Migranten aus den provisorischen Quarantäne-Stationen wieder nach Westen.
- ^ Bay, Murat (13 April 2020). "Türkei: Erdogan schickt wieder Tausende Flüchtlinge in Richtung EU". DIE WELT. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ Campana, Fahrinisa (30 April 2020). "Greece: Coronavirus threatens fate of abandoned dogs". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 1 May 2020. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ^ "Μητσοτάκης: Όλες οι ημερομηνίες για την άρση μέτρων - «Το πρόγραμμα θα αξιολογείται ανά 24ωρο»". LiFO (in Greek). Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ a b "Greek government unveils plan for easing restrictions, Stavros Papantoniou | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ "Καραντίνα: 110 εκατ. SMS εστάλησαν μέσω του 13033". Ypodomes.com (in Greek). 4 May 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ a b "Plan for the gradual easing of COVID-19 restrictive measures - A bridge of safety toward a new daily reality" (PDF). Greek Government. 28 April 2020. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b c d e Newsroom (28 April 2020). "Το σχέδιο για την «επόμενη ημέρα» - Πότε ανοίγουν καταστήματα, σχολεία, εστιατόρια, ξενοδοχεία". CNN.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 29 April 2020.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c d e IEFIMERIDA.GR, NEWSROOM (28 April 2020). "Αρση μέτρων: Στις 4 Μαΐου επανέρχεται η κυκλοφορία -Καταστήματα, σχολεία, μάσκες, όλες οι αλλαγές | ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΗ". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ Team, ΤοΒΗΜΑ (28 April 2020). "Μετάβαση στην επόμενη μέρα - Ολόκληρο το σχέδιο της κυβέρνησης". Ειδήσεις - νέα - Το Βήμα Online (in Greek). Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ "Schools to open in phases, with alternating classes, distancing | Kathimerini". www.ekathimerini.com. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ Tsirigotaki, Eve (28 April 2020). "K. Mitsotakis: Gradual easing of restrictive measures from May 4". ERT International. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ^ "Άρση περιοριστικών μέτρων: Χωρίς φεστιβάλ και συναυλίες το φετινό καλοκαίρι". www.news247.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 29 April 2020.
External links
- Covid19 Live Analytics | CoVid19.gov.gr
- Official website of the Greek National Public Health Organization with information regarding the progress of the pandemic in the country
- COVID—19 – map with various updated statistics
- CoVID-GEO - geographical analysis and mapping of Coronavirus COVID-19 related world data through a web-based platform developed by the GeoCHOROS Geospatial Analysis and Research Group at the National Technical University of Athens, Greece
