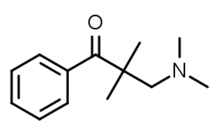
Dimethylaminopivalophenone
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H19NO |
| Molar mass | 205.301 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dimethylaminopivalophenone[1][2] is an opioid analgesic.[3] with a potency ½ that of morphine. It was initially discovered by Russian scientists in 1954 and subsequently rediscovered in the US in 1969.[4] Its LD50 in mice is 83 mg/kg.[5] It has never been marketed commercially, likely due to its complicated synthesis, low potency, and lack of benefits compared to similarly potent opioid compounds.
See also
- Tapentadol
- List of opioids
- Opioid#Table of non-morphinan opioids
- Amylocaine, a topical anesthetic with a very similar SAR (the amine is a single methylene spacer unit more distant & oxygenated)
References
- ^ James H. Brewster; Ernest L. Eliel (2011). "Carbon-Carbon Alkylations with Amines and Ammonium Salts". Organic Reactions. 7 (3): 99–197. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or007.03.
- ^ Edward F. Kleinman (April 2011). "Dimethyl(methylene)ammonium Iodide". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd346.
- ^ Helmut Buschmann; Wolfgang Strassburger; Elmar Friderichs (24 January 2002). "Patent US 20020010178 - 1-phenyl-3-dimethylaminopropane compounds with a pharmacological effect". Retrieved 2 October 2015.
- ^ Manmohan S. Atwal; Ludwig Bauer; S. N. Dixit; J. E. Gearien; M. Magahy; R. Morris; C. Pokorny (November 1969). "Analgetics. II. Relationship between structure and activity of some beta-amino ketones". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (6): 994–997. doi:10.1021/jm00306a006. PMID 5351480.
- ^ "2,2-dimethyl-3-(dimethylamino)-Propiophenone". ChemIDplus. Retrieved 2 October 2015.
