Huperzine A: Difference between revisions
Bon courage (talk | contribs) →Pharmacological effects: shuffle, wording |
Bon courage (talk | contribs) →Pharmacological effects: replace outdated with up-to-date | Assisted by Citation bot r454 |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
==Pharmacological effects== |
==Pharmacological effects== |
||
Huperzine A is an [[acetylcholinesterase]] inhibititor<ref name="Alzheimer 1996">{{cite journal|pmid=19221692|year=2009|last1=Wang|first1=BS|last2=Wang|first2=H|last3=Wei|first3=ZH|last4=Song|first4=YY|last5=Zhang|first5=L|last6=Chen|first6=HZ|title=Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine |
Huperzine A is an [[acetylcholinesterase]] inhibititor<ref name="Alzheimer 1996">{{cite journal|authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |pmid=19221692|year = 2009|last1 = Wang|first1 = BS|last2 = Wang|first2 = H|last3 = Wei|first3 = ZH|last4 = Song|first4 = YY|last5 = Zhang|first5 = L|last6 = Chen|first6 = HZ|title = Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine a in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: An updated meta-analysis|volume = 116|issue = 4|pages = 457–65|doi = 10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x|journal = Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996)}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |doi = 10.1358/dof.1999.024.06.545143|title = Huperzine A: A novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor|year = 1999|last1 = Tang|first1 = X.C.|last2 = He|first2 = X.C.|last3 = Bai|first3 = D.L.|journal = Drugs of the Future|volume = 24|issue = 6|pages = 647}}</ref> and [[NMDA receptor]] antagonist.<ref>{{cite journal|authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |pmid=18588864|year=2008|last1=Coleman|first1=BR|last2=Ratcliffe|first2=RH|last3=Oguntayo|first3=SA|last4=Shi|first4=X|last5=Doctor|first5=BP|last6=Gordon|first6=RK|last7=Nambiar|first7=MP|title=+-Huperzine a treatment protects against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced seizure/status epilepticus in rats|volume=175|issue=1–3|pages=387–95|doi=10.1016/j.cbi.2008.05.023|journal=Chemico-biological interactions}}</ref> Huperzine A is extracted from [[huperzia serrata]].<ref name="Zangara2003">{{cite journal|authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |pmid = 12895686|year = 2003|last1 = Zangara|first1 = A|title = The psychopharmacology of huperzine A: An alkaloid with cognitive enhancing and neuroprotective properties of interest in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease|volume = 75|issue = 3|pages = 675–86|journal = Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior}}</ref> The structure of the complex of huperzine A with acetylcholinesterase has been determined by [[X-ray crystallography]] (PDB code: [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1vot 1VOT]; [http://www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1vot see the 3D structure]).<ref>{{cite journal|authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |pmid= 8989325|year = 1997|last1 = Raves|first1 = ML|last2 = Harel|first2 = M|last3 = Pang|first3 = YP|last4 = Silman|first4 = I|last5 = Kozikowski|first5 = AP|last6 = Sussman|first6 = JL|title = Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with the nootropic alkaloid, (-)-huperzine A|volume = 4|issue = 1|pages = 57–63|journal = Nature structural biology}}</ref> |
||
For some years, Huperzine A has been investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration – particularly [[Alzheimer's disease]].<ref name="Zangara2003" /><ref name=r1>{{cite journal|author = |
For some years, Huperzine A has been investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration – particularly [[Alzheimer's disease]].<ref name="Zangara2003" /><ref name=r1>{{cite journal|authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |pmid=10637369|year = 2000|last1 = Bai|first1 = DL|last2 = Tang|first2 = XC|last3 = He|first3 = XC|title = Huperzine A, a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of Alzheimer's disease|volume = 7|issue = 3|pages = 355–74|journal = Current medicinal chemistry}}</ref> {{asof|2013}} although some research suggests it may be helpful, the evidence overall is not convincing enough for it to be recommended for use as a medicine, and little is known of its safety.<ref name=meta2013>{{cite journal| authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0074916| title = Huperzine a for Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials| year = 2013| editor1-last = Scherer| editor1-first = Roberta W| last1 = Yang| first1 = Guoyan| last2 = Wang| first2 = Yuyi| last3 = Tian| first3 = Jinzhou| last4 = Liu| first4 = Jian-Ping| journal = PLoS ONE| volume = 8| issue = 9| pages = e74916| pmid = 24086396| pmc = 3781107}} |
||
Clinical trials in China have shown that huperzine A is comparably effective to similar drugs on the market, and may even be safer in terms of side effects.<ref name=china/> |
|||
The same year, a Cochrane Database review examined studies evaluating the efficacy and safety of huperzine A in the treatment of AD. The review included six randomized, controlled trials involving 454 patients. The conclusion was that the currently available evidence was insufficient to assess the potential for huperzine A in the treatment of MCI. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trials are needed.<ref>{{cite journal|pmid=23235666| authorformat = vanc | author-separator = , | author-name-separator =  |year=2012|last1=Yue|first1=J|last2=Dong|first2=BR|last3=Lin|first3=X|last4=Yang|first4=M|last5=Wu|first5=HM|last6=Wu|first6=T|title=Huperzine a for mild cognitive impairment|volume=12|pages=CD008827|doi=10.1002/14651858.CD008827.pub2|journal=The Cochrane database of systematic reviews|editor1-last=Dong|editor1-first=Bi Rong}}</ref> |
|||
Possible side effects include {{citation needed|date=January 2013}} breathing problems, tightness in the throat or chest, chest pain, skin hives, rash, itchy or swollen skin, upset stomach, [[diarrhea]], vomiting, [[hyperactivity]] and [[insomnia]]. Most adverse events were [[cholinergic]] in nature and no serious adverse events occurred. Huperzine A is a well-tolerated drug.<ref name="Alzheimer 1996"/> |
|||
==Synthesis== |
==Synthesis== |
||
Revision as of 09:58, 5 January 2014
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
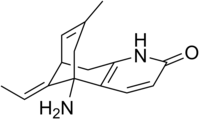
| IUPAC name
(1R,9S,13E)-1-Amino-13-ethylidene-11-methyl-6-azatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2(7),3,10-trien-5-one
| |
| Other names
HupA
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.430 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H18N2O | |
| Molar mass | 242.32 g/mol |
| Melting point | 217–219 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Huperzine A is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata.[1] and in varying quantities in other Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian.[2]
Huperzine A is also an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, which has a mechanism of action similar to donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine. A pro-drug form of huperzine A (ZT-1) is under development as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease.[3]
In the US, huperzine A is sold as a dietary supplement for memory support. The botanical has been used in China for centuries for the treatment of swelling, fever and blood disorders. Clinical trials in China have shown it to be effective in improving cognitive performance in patients with Alzheimer's disease[4]
Pharmacological effects
Huperzine A is an acetylcholinesterase inhibititor[5][6] and NMDA receptor antagonist.[7] Huperzine A is extracted from huperzia serrata.[8] The structure of the complex of huperzine A with acetylcholinesterase has been determined by X-ray crystallography (PDB code: 1VOT; see the 3D structure).[9]
For some years, Huperzine A has been investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration – particularly Alzheimer's disease.[8][10] As of 2013[update] although some research suggests it may be helpful, the evidence overall is not convincing enough for it to be recommended for use as a medicine, and little is known of its safety.Cite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page).[11]
See also
References
- ^ Kozikowski, Alan P.; Tueckmantel, Werner (1999). "Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Efficacy of the Chinese Nootropic Agent Huperzine A". Accounts of Chemical Research. 32 (8): 641–650. doi:10.1021/ar9800892.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lim WH, Goodger JQ, Field AR, Holtum JA, Woodrow IE "Huperzine alkaloids from Australasian and southeast Asian Huperzia". Pharm Biol. 2010 Sep;48(9):1073-8
- ^ P. Scalfaro, V. Nicolas, M.P. Simonin, S. Charbon, M. McCormick, F. Heimgartner. The sustained release of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor ZT-1 confers the potential for a more efficient neuroprotection in rats. Neurobiology of Aging Conference in New Orleans, Nov 2003.
- ^ Wang, Bai-Song; Wang, Hao; Wei, Zhao-hui; Song, Yan-yan; Zhang, Lu; Chen, Hong-Zhuan (2009). "Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine A in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an updated meta-analysis". Journal of Neural Transmission. 116 (4): 457. doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x. PMID 19221692.
- ^ Wang, BS; Wang, H; Wei, ZH; Song, YY; Zhang, L; Chen, HZ (2009). "Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine a in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: An updated meta-analysis". Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996). 116 (4): 457–65. doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x. PMID 19221692.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-name-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authorformat=ignored (help) - ^ Tang, X.C.; He, X.C.; Bai, D.L. (1999). "Huperzine A: A novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor". Drugs of the Future. 24 (6): 647. doi:10.1358/dof.1999.024.06.545143.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-name-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authorformat=ignored (help) - ^ Coleman, BR; Ratcliffe, RH; Oguntayo, SA; Shi, X; Doctor, BP; Gordon, RK; Nambiar, MP (2008). "+-Huperzine a treatment protects against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced seizure/status epilepticus in rats". Chemico-biological interactions. 175 (1–3): 387–95. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.05.023. PMID 18588864.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-name-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authorformat=ignored (help) - ^ a b Zangara, A (2003). "The psychopharmacology of huperzine A: An alkaloid with cognitive enhancing and neuroprotective properties of interest in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease". Pharmacology, biochemistry, and behavior. 75 (3): 675–86. PMID 12895686.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-name-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authorformat=ignored (help) - ^ Raves, ML; Harel, M; Pang, YP; Silman, I; Kozikowski, AP; Sussman, JL (1997). "Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with the nootropic alkaloid, (-)-huperzine A". Nature structural biology. 4 (1): 57–63. PMID 8989325.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-name-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authorformat=ignored (help) - ^ Bai, DL; Tang, XC; He, XC (2000). "Huperzine A, a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of Alzheimer's disease". Current medicinal chemistry. 7 (3): 355–74. PMID 10637369.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|author-name-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authorformat=ignored (help) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1021/op200360b, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1021/op200360binstead.
