Chemotherapy
This article needs to be updated. (May 2018) |
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (May 2018) |  |
| Chemotherapy | |
|---|---|
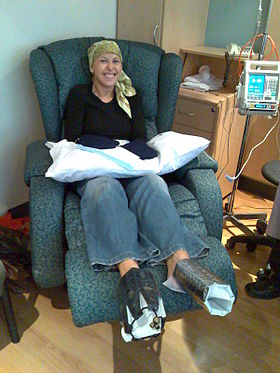 A woman being treated with docetaxel chemotherapy for breast cancer. Cold mittens and wine coolers are placed on her hands and feet to reduce harm to her nails. | |
| Other names | chemo |
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called medical oncology.
The term chemotherapy has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis, cell division. The connotation excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, which inhibit growth-promoting signals from classic endocrine hormones (primarily estrogens for breast cancer and androgens for prostate cancer) are now called hormonal therapies. By contrast, other inhibitions of growth-signals like those associated with receptor tyrosine kinases are referred to as targeted therapy.
Importantly, the use of drugs (whether chemotherapy, hormonal therapy or targeted therapy) constitutes systemic therapy for cancer in that they are introduced into the blood stream and are therefore in principle able to address cancer at any anatomic location in the body. Systemic therapy is often used in conjunction with other modalities that constitute local therapy (i.e. treatments whose efficacy is confined to the anatomic area where they are applied) for cancer such as radiation therapy, surgery or hyperthermia therapy.
Traditional chemotherapeutic agents are cytotoxic by means of interfering with cell division (mitosis) but cancer cells vary widely in their susceptibility to these agents. To a large extent, chemotherapy can be thought of as a way to damage or stress cells, which may then lead to cell death if apoptosis is initiated. Many of the side effects of chemotherapy can be traced to damage to normal cells that divide rapidly and are thus sensitive to anti-mitotic drugs: cells in the bone marrow, digestive tract and hair follicles. This results in the most common side-effects of chemotherapy: myelosuppression (decreased production of blood cells, hence also immunosuppression), mucositis (inflammation of the lining of the digestive tract), and alopecia (hair loss). Because of the effect on immune cells (especially lymphocytes), chemotherapy drugs often find use in a host of diseases that result from harmful overactivity of the immune system against self (so-called autoimmunity). These include rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, vasculitis and many others.
Treatment strategies
| Cancer type | Drugs | Acronym |
|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-fluorouracil, vinorelbine | CMF |
| Doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide | AC | |
| Hodgkin's lymphoma | Docetaxel, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide | TAC |
| Doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine | ABVD | |
| Mustine, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisolone | MOPP | |
| Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma | Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisolone | CHOP |
| Germ cell tumor | Bleomycin, etoposide, cisplatin | BEP |
| Stomach cancer[2] | Epirubicin, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil | ECF |
| Epirubicin, cisplatin, capecitabine | ECX | |
| Bladder cancer | Methotrexate, vincristine, doxorubicin, cisplatin | MVAC |
| Lung cancer | Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, vinorelbine | CAV |
| Colorectal cancer | 5-fluorouracil, folinic acid, oxaliplatin | FOLFOX |
There are a number of strategies in the administration of chemotherapeutic drugs used today. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent or it may aim to prolong life or to palliate symptoms.
- Induction chemotherapy is the first line treatment of cancer with a chemotherapeutic drug. This type of chemotherapy is used for curative intent.[3]: 55–59
- Combined modality chemotherapy is the use of drugs with other cancer treatments, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or hyperthermia therapy.
- Consolidation chemotherapy is given after remission in order to prolong the overall disease-free time and improve overall survival. The drug that is administered is the same as the drug that achieved remission.[3]: 55–59
- Intensification chemotherapy is identical to consolidation chemotherapy but a different drug than the induction chemotherapy is used.[3]: 55–59
- Combination chemotherapy involves treating a person with a number of different drugs simultaneously. The drugs differ in their mechanism and side-effects. The biggest advantage is minimising the chances of resistance developing to any one agent. Also, the drugs can often be used at lower doses, reducing toxicity.[3]: 55–59 [4]: 17–18 [2]
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is given prior to a local treatment such as surgery, and is designed to shrink the primary tumor.[3]: 55–59 It is also given to cancers with a high risk of micrometastatic disease.[5]: 42
- Adjuvant chemotherapy is given after a local treatment (radiotherapy or surgery). It can be used when there is little evidence of cancer present, but there is risk of recurrence.[3]: 55–59 It is also useful in killing any cancerous cells that have spread to other parts of the body. These micrometastases can be treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and can reduce relapse rates caused by these disseminated cells.[6]
- Maintenance chemotherapy is a repeated low-dose treatment to prolong remission.[2][3]: 55–59
- Salvage chemotherapy or palliative chemotherapy is given without curative intent, but simply to decrease tumor load and increase life expectancy. For these regimens, in general, a better toxicity profile is expected.[3]: 55–59
All chemotherapy regimens require that the recipient be capable of undergoing the treatment. Performance status is often used as a measure to determine whether a person can receive chemotherapy, or whether dose reduction is required. Because only a fraction of the cells in a tumor die with each treatment (fractional kill), repeated doses must be administered to continue to reduce the size of the tumor.[7] Current chemotherapy regimens apply drug treatment in cycles, with the frequency and duration of treatments limited by toxicity.[8]
Efficacy
The efficacy of chemotherapy depends on the type of cancer and the stage. The overall effectiveness ranges from being curative for some cancers, such as some leukemias,[9][10] to being ineffective, such as in some brain tumors,[11] to being needless in others, like most non-melanoma skin cancers.[12]
Dosage

Dosage of chemotherapy can be difficult: If the dose is too low, it will be ineffective against the tumor, whereas, at excessive doses, the toxicity (side-effects) will be intolerable to the person receiving it.[1] The standard method of determining chemotherapy dosage is based on calculated body surface area (BSA). The BSA is usually calculated with a mathematical formula or a nomogram, using the recipient's weight and height, rather than by direct measurement of body area. This formula was originally derived in a 1916 study and attempted to translate medicinal doses established with laboratory animals to equivalent doses for humans.[13] The study only included 9 human subjects.[14] When chemotherapy was introduced in the 1950s, the BSA formula was adopted as the official standard for chemotherapy dosing for lack of a better option.[15][16]
Recently, the validity of this method in calculating uniform doses has been questioned. The reason for this is that the formula only takes into account the individual's weight and height. Drug absorption and clearance are influenced by multiple factors, including age, gender, metabolism, disease state, organ function, drug-to-drug interactions, genetics, and obesity, which has a major impact on the actual concentration of the drug in the person's bloodstream.[15][17][18] As a result, there is high variability in the systemic chemotherapy drug concentration in people dosed by BSA, and this variability has been demonstrated to be more than 10-fold for many drugs.[14][19] In other words, if two people receive the same dose of a given drug based on BSA, the concentration of that drug in the bloodstream of one person may be 10 times higher or lower compared to that of the other person.[19] This variability is typical with many chemotherapy drugs dosed by BSA, and, as shown below, was demonstrated in a study of 14 common chemotherapy drugs.[14]

The result of this pharmacokinetic variability among people, is that many people do not receive the right dose to achieve optimal treatment effectiveness with minimized toxic side effects. Some people are overdosed while others are underdosed.[15][17][18][20][21][22][23] For example, in a randomized clinical trial, investigators found 85% of metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) did not receive the optimal therapeutic dose when dosed by the BSA standard—68% were underdosed and 17% were overdosed.[20]
There has been controversy over the use of BSA to calculate chemotherapy doses for people who are obese.[24] Because of their higher BSA, clinicians often arbitrarily reduce the dose prescribed by the BSA formula for fear of overdosing.[24] In many cases, this can result in sub-optimal treatment.[24]
Several clinical studies have demonstrated that when chemotherapy dosing is individualized to achieve optimal systemic drug exposure, treatment outcomes are improved and toxic side effects are reduced.[20][22] In the 5-FU clinical study cited above, people whose dose was adjusted to achieve a pre-determined target exposure realized an 84% improvement in treatment response rate and a six-month improvement in overall survival (OS) compared with those dosed by BSA.[20]

In the same study, investigators compared the incidence of common 5-FU-associated grade 3/4 toxicities between the dose-adjusted people and people dosed per BSA.[20] The incidence of debilitating grades of diarrhea was reduced from 18% in the BSA-dosed group to 4% in the dose-adjusted group and serious hematologic side effects were eliminated.[20] Because of the reduced toxicity, dose-adjusted patients were able to be treated for longer periods of time.[20] BSA-dosed people were treated for a total of 680 months while people in the dose-adjusted group were treated for a total of 791 months.[20] Completing the course of treatment is an important factor in achieving better treatment outcomes.
Similar results were found in a study involving people with colorectal cancer who were treated with the popular FOLFOX regimen.[22] The incidence of serious diarrhea was reduced from 12% in the BSA-dosed group of patients to 1.7% in the dose-adjusted group, and the incidence of severe mucositis was reduced from 15% to 0.8%.[22]
The FOLFOX study also demonstrated an improvement in treatment outcomes.[22] Positive response increased from 46% in the BSA-dosed group to 70% in the dose-adjusted group. Median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) both improved by six months in the dose adjusted group.[22]
One approach that can help clinicians individualize chemotherapy dosing is to measure the drug levels in blood plasma over time and adjust dose according to a formula or algorithm to achieve optimal exposure. With an established target exposure for optimized treatment effectiveness with minimized toxicities, dosing can be personalized to achieve target exposure and optimal results for each person. Such an algorithm was used in the clinical trials cited above and resulted in significantly improved treatment outcomes.
Oncologists are already individualizing dosing of some cancer drugs based on exposure. Carboplatin[25]: 4 and busulfan[26][27] dosing rely upon results from blood tests to calculate the optimal dose for each person. Simple blood tests are also available for dose optimization of methotrexate,[28] 5-FU, paclitaxel, and docetaxel.[29][30]
Types

Alkylating agents
Alkylating agents are the oldest group of chemotherapeutics in use today. Originally derived from mustard gas used in World War I, there are now many types of alkylating agents in use.[1] They are so named because of their ability to alkylate many molecules, including proteins, RNA and DNA. This ability to bind covalently to DNA via their alkyl group is the primary cause for their anti-cancer effects.[32] DNA is made of two strands and the molecules may either bind twice to one strand of DNA (intrastrand crosslink) or may bind once to both strands (interstrand crosslink). If the cell tries to replicate crosslinked DNA during cell division, or tries to repair it, the DNA strands can break. This leads to a form of programmed cell death called apoptosis.[31][33] Alkylating agents will work at any point in the cell cycle and thus are known as cell cycle-independent drugs. For this reason the effect on the cell is dose dependent; the fraction of cells that die is directly proportional to the dose of drug.[34]
The subtypes of alkylating agents are the nitrogen mustards, nitrosoureas, tetrazines, aziridines,[35] cisplatins and derivatives, and non-classical alkylating agents. Nitrogen mustards include mechlorethamine, cyclophosphamide, melphalan, chlorambucil, ifosfamide and busulfan. Nitrosoureas include N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (MNU), carmustine (BCNU), lomustine (CCNU) and semustine (MeCCNU), fotemustine and streptozotocin. Tetrazines include dacarbazine, mitozolomide and temozolomide. Aziridines include thiotepa, mytomycin and diaziquone (AZQ). Cisplatin and derivatives include cisplatin, carboplatin and oxaliplatin.[32][33] They impair cell function by forming covalent bonds with the amino, carboxyl, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups in biologically important molecules.[36] Non-classical alkylating agents include procarbazine and hexamethylmelamine.[32][33]
Antimetabolites

Anti-metabolites are a group of molecules that impede DNA and RNA synthesis. Many of them have a similar structure to the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The building blocks are nucleotides; a molecule comprising a nucleobase, a sugar and a phosphate group. The nucleobases are divided into purines (guanine and adenine) and pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine and uracil). Anti-metabolites resemble either nucleobases or nucleosides (a nucleotide without the phosphate group), but have altered chemical groups.[37] These drugs exert their effect by either blocking the enzymes required for DNA synthesis or becoming incorporated into DNA or RNA. By inhibiting the enzymes involved in DNA synthesis, they prevent mitosis because the DNA cannot duplicate itself. Also, after misincorporation of the molecules into DNA, DNA damage can occur and programmed cell death (apoptosis) is induced. Unlike alkylating agents, anti-metabolites are cell cycle dependent. This means that they only work during a specific part of the cell cycle, in this case S-phase (the DNA synthesis phase). For this reason, at a certain dose, the effect plateaus and proportionally no more cell death occurs with increased doses. Subtypes of the anti-metabolites are the anti-folates, fluoropyrimidines, deoxynucleoside analogues and thiopurines.[32][37]
The anti-folates include methotrexate and pemetrexed. Methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), an enzyme that regenerates tetrahydrofolate from dihydrofolate. When the enzyme is inhibited by methotrexate, the cellular levels of folate coenzymes diminish. These are required for thymidylate and purine production, which are both essential for DNA synthesis and cell division.[3]: 55–59 [4]: 11 Pemetrexed is another anti-metabolite that affects purine and pyrimidine production, and therefore also inhibits DNA synthesis. It primarily inhibits the enzyme thymidylate synthase, but also has effects on DHFR, aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase and glycinamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase.[38] The fluoropyrimidines include fluorouracil and capecitabine. Fluorouracil is a nucleobase analogue that is metabolised in cells to form at least two active products; 5-fluourouridine monophosphate (FUMP) and 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-phosphate (fdUMP). FUMP becomes incorporated into RNA and fdUMP inhibits the enzyme thymidylate synthase; both of which lead to cell death.[4]: 11 Capecitabine is a prodrug of 5-fluorouracil that is broken down in cells to produce the active drug.[39] The deoxynucleoside analogues include cytarabine, gemcitabine, decitabine, azacitidine, fludarabine, nelarabine, cladribine, clofarabine, and pentostatin. The thiopurines include thioguanine and mercaptopurine.[32][37]
Anti-microtubule agents

Anti-microtubule agents are plant-derived chemicals that block cell division by preventing microtubule function. Microtubules are an important cellular structure composed of two proteins; α-tubulin and β-tubulin. They are hollow rod shaped structures that are required for cell division, among other cellular functions.[40] Microtubules are dynamic structures, which means that they are permanently in a state of assembly and disassembly. Vinca alkaloids and taxanes are the two main groups of anti-microtubule agents, and although both of these groups of drugs cause microtubule dysfunction, their mechanisms of action are completely opposite. The vinca alkaloids prevent the formation of the microtubules, whereas the taxanes prevent the microtubule disassembly. By doing so, they prevent the cancer cells from completing mitosis. Following this, cell cycle arrest occurs, which induces programmed cell death (apoptosis).[32][41] Also, these drugs can affect blood vessel growth; an essential process that tumours utilise in order to grow and metastasise.[41]
Vinca alkaloids are derived from the Madagascar periwinkle, Catharanthus roseus[42][43] (formerly known as Vinca rosea). They bind to specific sites on tubulin, inhibiting the assembly of tubulin into microtubules. The original vinca alkaloids are natural products that include vincristine and vinblastine.[44][45][46][47] Following the success of these drugs, semi-synthetic vinca alkaloids were produced: vinorelbine (used in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer[46][48][49]), vindesine, and vinflunine.[41] These drugs are cell cycle-specific. They bind to the tubulin molecules in S-phase and prevent proper microtubule formation required for M-phase.[34]
Taxanes are natural and semi-synthetic drugs. The first drug of their class, paclitaxel, was originally extracted from the Pacific Yew tree, Taxus brevifolia. Now this drug and another in this class, docetaxel, are produced semi-synthetically from a chemical found in the bark of another Yew tree; Taxus baccata. These drugs promote microtubule stability, preventing their disassembly. Paclitaxel prevents the cell cycle at the boundary of G2-M, whereas docetaxel exerts its effect during S-phase. Taxanes present difficulties in formulation as medicines because they are poorly soluble in water.[41]
Podophyllotoxin is an antineoplastic lignan obtained primarily from the American Mayapple (Podophyllum peltatum) and Himalayan Mayapple (Podophyllum hexandrum or Podophyllum emodi). It has anti-microtubule activity, and its mechanism is similar to that of vinca alkaloids in that they bind to tubulin, inhibiting microtubule formation. Podophyllotoxin is used to produce two other drugs with different mechanisms of action: etoposide and teniposide.[50][51]
Topoisomerase inhibitors

Topoisomerase inhibitors are drugs that affect the activity of two enzymes: topoisomerase I and topoisomerase II. When the DNA double-strand helix is unwound, during DNA replication or transcription, for example, the adjacent unopened DNA winds tighter (supercoils), like opening the middle of a twisted rope. The stress caused by this effect is in part aided by the topoisomerase enzymes. They produce single- or double-strand breaks into DNA, reducing the tension in the DNA strand. This allows the normal unwinding of DNA to occur during replication or transcription. Inhibition of topoisomerase I or II interferes with both of these processes.[52][53]
Two topoisomerase I inhibitors, irinotecan and topotecan, are semi-synthetically derived from camptothecin, which is obtained from the Chinese ornamental tree Camptotheca acuminata.[34] Drugs that target topoisomerase II can be divided into two groups. The topoisomerase II poisons cause increased levels enzymes bound to DNA. This prevents DNA replication and transcription, causes DNA strand breaks, and leads to programmed cell death (apoptosis). These agents include etoposide, doxorubicin, mitoxantrone and teniposide. The second group, catalytic inhibitors, are drugs that block the activity of topoisomerase II, and therefore prevent DNA synthesis and translation because the DNA cannot unwind properly. This group includes novobiocin, merbarone, and aclarubicin, which also have other significant mechanisms of action.[54]
Cytotoxic antibiotics
The cytotoxic antibiotics are a varied group of drugs that have various mechanisms of action. The common theme that they share in their chemotherapy indication is that they interrupt cell division. The most important subgroup is the anthracyclines and the bleomycins; other prominent examples include mitomycin C, mitoxantrone, and actinomycin.[55]
Among the anthracyclines, doxorubicin and daunorubicin were the first, and were obtained from the bacterium Streptomyces peucetius.[56] Derivatives of these compounds include epirubicin and idarubicin. Other clinically used drugs in the anthracyline group are pirarubicin, aclarubicin, and mitoxantrone. The mechanisms of anthracyclines include DNA intercalation (molecules insert between the two strands of DNA), generation of highly reactive free radicals that damage intercellular molecules and topoisomerase inhibition.[57]
Actinomycin is a complex molecule that intercalates DNA and prevents RNA synthesis.[58]
Bleomycin, a glycopeptide isolated from Streptomyces verticillus, also intercalates DNA, but produces free radicals that damage DNA. This occurs when bleomycin binds to a metal ion, becomes chemically reduced and reacts with oxygen.[59][3]: 87
Mitomycin is a cytotoxic antibiotic with the ability to alkylate DNA.[60]
Delivery

Most chemotherapy is delivered intravenously, although a number of agents can be administered orally (e.g., melphalan, busulfan, capecitabine).
There are many intravenous methods of drug delivery, known as vascular access devices. These include the winged infusion device, peripheral venous catheter, midline catheter, peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC), central venous catheter and implantable port. The devices have different applications regarding duration of chemotherapy treatment, method of delivery and types of chemotherapeutic agent.[4]: 94–95
Depending on the person, the cancer, the stage of cancer, the type of chemotherapy, and the dosage, intravenous chemotherapy may be given on either an inpatient or an outpatient basis. For continuous, frequent or prolonged intravenous chemotherapy administration, various systems may be surgically inserted into the vasculature to maintain access.[4]: 113–118 Commonly used systems are the Hickman line, the Port-a-Cath, and the PICC line. These have a lower infection risk, are much less prone to phlebitis or extravasation, and eliminate the need for repeated insertion of peripheral cannulae.[citation needed]
Isolated limb perfusion (often used in melanoma),[61] or isolated infusion of chemotherapy into the liver[62] or the lung have been used to treat some tumors. The main purpose of these approaches is to deliver a very high dose of chemotherapy to tumor sites without causing overwhelming systemic damage.[63] These approaches can help control solitary or limited metastases, but they are by definition not systemic, and, therefore, do not treat distributed metastases or micrometastases.
Topical chemotherapies, such as 5-fluorouracil, are used to treat some cases of non-melanoma skin cancer.[64]
If the cancer has central nervous system involvement, or with meningeal disease, intrathecal chemotherapy may be administered.[1]
Adverse effects
Chemotherapeutic techniques have a range of side-effects that depend on the type of medications used. The most common medications affect mainly the fast-dividing cells of the body, such as blood cells and the cells lining the mouth, stomach, and intestines. Chemotherapy-related toxicities can occur acutely after administration, within hours or days, or chronically, from weeks to years.[3]: 265
Immunosuppression and myelosuppression
Virtually all chemotherapeutic regimens can cause depression of the immune system, often by paralysing the bone marrow and leading to a decrease of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Anemia and thrombocytopenia may require blood transfusion. Neutropenia (a decrease of the neutrophil granulocyte count below 0.5 x 109/litre) can be improved with synthetic G-CSF (granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor, e.g., filgrastim, lenograstim).
In very severe myelosuppression, which occurs in some regimens, almost all the bone marrow stem cells (cells that produce white and red blood cells) are destroyed, meaning allogenic or autologous bone marrow cell transplants are necessary. (In autologous BMTs, cells are removed from the person before the treatment, multiplied and then re-injected afterward; in allogenic BMTs, the source is a donor.) However, some people still develop diseases because of this interference with bone marrow.[citation needed]
Although people receiving chemotherapy are encouraged to wash their hands, avoid sick people, and take other infection-reducing steps, about 85% of infections are due to naturally occurring microorganisms in the person's own gastrointestinal tract (including oral cavity) and skin.[65]: 130 This may manifest as systemic infections, such as sepsis, or as localized outbreaks, such as Herpes simplex, shingles, or other members of the Herpesviridea.[66] The risk of illness and death can be reduced by taking common antibiotics such as quinolones or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole before any fever or sign of infection appears.[67] Quinolones show effective prophylaxis mainly with hematological cancer.[67] However, in general, for every five people who are immunosuppressed following chemotherapy who take an antibiotic, one fever can be prevented; for every 34 who take an antibiotic, one death can be prevented.[67] Sometimes, chemotherapy treatments are postponed because the immune system is suppressed to a critically low level.
In Japan, the government has approved the use of some medicinal mushrooms like Trametes versicolor, to counteract depression of the immune system in people undergoing chemotherapy.[68]
Neutropenic enterocolitis
Due to immune system suppression, neutropenic enterocolitis (typhlitis) is a "life-threatening gastrointestinal complication of chemotherapy."[69] Typhlitis is an intestinal infection which may manifest itself through symptoms including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, a distended abdomen, fever, chills, or abdominal pain and tenderness.
Typhlitis is a medical emergency. It has a very poor prognosis and is often fatal unless promptly recognized and aggressively treated.[70] Successful treatment hinges on early diagnosis provided by a high index of suspicion and the use of CT scanning, nonoperative treatment for uncomplicated cases, and sometimes elective right hemicolectomy to prevent recurrence.[70]
Gastrointestinal distress
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhoea, abdominal cramps, and constipation are common side-effects of chemotherapeutic medications that kill fast-dividing cells.[71] Malnutrition and dehydration can result when the recipient does not eat or drink enough, or when the person vomits frequently, because of gastrointestinal damage. This can result in rapid weight loss, or occasionally in weight gain, if the person eats too much in an effort to allay nausea or heartburn. Weight gain can also be caused by some steroid medications. These side-effects can frequently be reduced or eliminated with antiemetic drugs. Self-care measures, such as eating frequent small meals and drinking clear liquids or ginger tea, are often recommended. In general, this is a temporary effect, and frequently resolves within a week of finishing treatment. However, a high index of suspicion is appropriate, since diarrhea and bloating are also symptoms of typhlitis, a very serious and potentially life-threatening medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
Anemia
Anemia can be a combined outcome caused by myelosuppressive chemotherapy, and possible cancer-related causes such as bleeding, blood cell destruction (hemolysis), hereditary disease, kidney dysfunction, nutritional deficiencies or anemia of chronic disease. Treatments to mitigate anemia include hormones to boost blood production (erythropoietin), iron supplements, and blood transfusions.[72][73][74] Myelosuppressive therapy can cause a tendency to bleed easily, leading to anemia. Medications that kill rapidly dividing cells or blood cells can reduce the number of platelets in the blood, which can result in bruises and bleeding. Extremely low platelet counts may be temporarily boosted through platelet transfusions and new drugs to increase platelet counts during chemotherapy are being developed.[75][76] Sometimes, chemotherapy treatments are postponed to allow platelet counts to recover.
Fatigue
Fatigue may be a consequence of the cancer or its treatment, and can last for months to years after treatment. One physiological cause of fatigue is anemia, which can be caused by chemotherapy, surgery, radiotherapy, primary and metastatic disease or nutritional depletion.[77][78] Anaerobic exercise has been found to be beneficial in reducing fatigue in people with solid tumours.[79]
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are two of the most feared cancer treatment-related side-effects for people with cancer and their families. In 1983, Coates et al. found that people receiving chemotherapy ranked nausea and vomiting as the first and second most severe side-effects, respectively. Up to 20% of people receiving highly emetogenic agents in this era postponed, or even refused, potentially curative treatments.[80] Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) are common with many treatments and some forms of cancer. Since the 1990s, several novel classes of antiemetics have been developed and commercialized, becoming a nearly universal standard in chemotherapy regimens, and helping to successfully manage these symptoms in many people. Effective mediation of these unpleasant and sometimes-crippling symptoms results in increased quality of life for the recipient and more efficient treatment cycles, due to less stoppage of treatment due to better tolerance and better overall health.
Hair loss
Hair loss (alopecia) can be caused by chemotherapy that kills rapidly dividing cells; other medications may cause hair to thin. These are most often temporary effects: hair usually starts to regrow a few weeks after the last treatment, but sometimes with a change in colour, texture, thickness or style. Sometimes hair has a tendency to curl after regrowth, resulting in "chemo curls." Severe hair loss occurs most often with drugs such as doxorubicin, daunorubicin, paclitaxel, docetaxel, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide and etoposide. Permanent thinning or hair loss can result from some standard chemotherapy regimens.
Chemotherapy induced hair loss occurs by a non-androgenic mechanism, and can manifest as alopecia totalis, telogen effluvium, or less often alopecia areata.[81] It is usually associated with systemic treatment due to the high mitotic rate of hair follicles, and more reversible than androgenic hair loss,[82][83] although permanent cases can occur.[84] Chemotherapy induces hair loss in women more often than men.[85]
Scalp cooling offers a means of preventing both permanent and temporary hair loss; however, concerns about this method have been raised.[86][87]
Secondary neoplasm
Development of secondary neoplasia after successful chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatment can occur. The most common secondary neoplasm is secondary acute myeloid leukemia, which develops primarily after treatment with alkylating agents or topoisomerase inhibitors.[88] Survivors of childhood cancer are more than 13 times as likely to get a secondary neoplasm during the 30 years after treatment than the general population.[89] Not all of this increase can be attributed to chemotherapy.
Infertility
Some types of chemotherapy are gonadotoxic and may cause infertility.[90] Chemotherapies with high risk include procarbazine and other alkylating drugs such as cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, busulfan, melphalan, chlorambucil, and chlormethine.[90] Drugs with medium risk include doxorubicin and platinum analogs such as cisplatin and carboplatin.[90] On the other hand, therapies with low risk of gonadotoxicity include plant derivatives such as vincristine and vinblastine, antibiotics such as bleomycin and dactinomycin, and antimetabolites such as methotrexate, mercaptopurine, and 5-fluorouracil.[90]
Female infertility by chemotherapy appears to be secondary to premature ovarian failure by loss of primordial follicles.[91] This loss is not necessarily a direct effect of the chemotherapeutic agents, but could be due to an increased rate of growth initiation to replace damaged developing follicles.[91]
People may choose between several methods of fertility preservation prior to chemotherapy, including cryopreservation of semen, ovarian tissue, oocytes, or embryos.[92] As more than half of cancer patients are elderly, this adverse effect is only relevant for a minority of patients. A study in France between 1999 and 2011 came to the result that embryo freezing before administration of gonadotoxic agents to females caused a delay of treatment in 34% of cases, and a live birth in 27% of surviving cases who wanted to become pregnant, with the follow-up time varying between 1 and 13 years.[93]
Potential protective or attenuating agents include GnRH analogs, where several studies have shown a protective effect in vivo in humans, but some studies show no such effect. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) has shown similar effect, but its mechanism of inhibiting the sphingomyelin apoptotic pathway may also interfere with the apoptosis action of chemotherapy drugs.[94]
In chemotherapy as a conditioning regimen in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, a study of people conditioned with cyclophosphamide alone for severe aplastic anemia came to the result that ovarian recovery occurred in all women younger than 26 years at time of transplantation, but only in five of 16 women older than 26 years.[95]
Teratogenicity
Chemotherapy is teratogenic during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, to the extent that abortion usually is recommended if pregnancy in this period is found during chemotherapy.[96] Second- and third-trimester exposure does not usually increase the teratogenic risk and adverse effects on cognitive development, but it may increase the risk of various complications of pregnancy and fetal myelosuppression.[96]
In males previously having undergone chemotherapy or radiotherapy, there appears to be no increase in genetic defects or congenital malformations in their children conceived after therapy.[96] The use of assisted reproductive technologies and micromanipulation techniques might increase this risk.[96] In females previously having undergone chemotherapy, miscarriage and congenital malformations are not increased in subsequent conceptions.[96] However, when in vitro fertilization and embryo cryopreservationis practised between or shortly after treatment, possible genetic risks to the growing oocytes exist, and hence it has been recommended that the babies be screened.[96]
Peripheral neuropathy
Between 30 and 40 percent of people undergoing chemotherapy experience chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), a progressive, enduring, and often irreversible condition, causing pain, tingling, numbness and sensitivity to cold, beginning in the hands and feet and sometimes progressing to the arms and legs.[97] Chemotherapy drugs associated with CIPN include thalidomide, epothilones, vinca alkaloids, taxanes, proteasome inhibitors, and the platinum-based drugs.[97][98] Whether CIPN arises, and to what degree, is determined by the choice of drug, duration of use, the total amount consumed and whether the person already has peripheral neuropathy. Though the symptoms are mainly sensory, in some cases motor nerves and the autonomic nervous system are affected.[99] CIPN often follows the first chemotherapy dose and increases in severity as treatment continues, but this progression usually levels off at completion of treatment. The platinum-based drugs are the exception; with these drugs, sensation may continue to deteriorate for several months after the end of treatment.[100] Some CIPN appears to be irreversible.[100] Pain can often be managed with drug or other treatment but the numbness is usually resistant to treatment.[101]
Cognitive impairment
Some people receiving chemotherapy report fatigue or non-specific neurocognitive problems, such as an inability to concentrate; this is sometimes called post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment, referred to as "chemo brain" in popular and social media.[102]
Tumor lysis syndrome
In particularly large tumors and cancers with high white cell counts, such as lymphomas, teratomas, and some leukemias, some people develop tumor lysis syndrome. The rapid breakdown of cancer cells causes the release of chemicals from the inside of the cells. Following this, high levels of uric acid, potassium and phosphate are found in the blood. High levels of phosphate induce secondary hypoparathyroidism, resulting in low levels of calcium in the blood. This causes kidney damage and the high levels of potassium can cause cardiac arrhythmia. Although prophylaxis is available and is often initiated in people with large tumors, this is a dangerous side-effect that can lead to death if left untreated.[4]: 202
Organ damage
Cardiotoxicity (heart damage) is especially prominent with the use of anthracycline drugs (doxorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin, and liposomal doxorubicin). The cause of this is most likely due to the production of free radicals in the cell and subsequent DNA damage. Other chemotherapeutic agents that cause cardiotoxicity, but at a lower incidence, are cyclophosphamide, docetaxel and clofarabine.[103]
Hepatotoxicity (liver damage) can be caused by many cytotoxic drugs. The susceptibility of an individual to liver damage can be altered by other factors such as the cancer itself, viral hepatitis, immunosuppression and nutritional deficiency. The liver damage can consist of damage to liver cells, hepatic sinusoidal syndrome (obstruction of the veins in the liver), cholestasis (where bile does not flow from the liver to the intestine) and liver fibrosis.[104][105]
Nephrotoxicity (kidney damage) can be caused by tumor lysis syndrome and also due direct effects of drug clearance by the kidneys. Different drugs will affect different parts of the kidney and the toxicity may be asymptomatic (only seen on blood or urine tests) or may cause acute renal failure.[106][107]
Ototoxicity (damage to the inner ear) is a common side effect of platinum based drugs that can produce symptoms such as dizziness and vertigo.[108][109]
Other side-effects
Less common side-effects include red skin (erythema), dry skin, damaged fingernails, a dry mouth (xerostomia), water retention, and sexual impotence. Some medications can trigger allergic or pseudoallergic reactions.
Specific chemotherapeutic agents are associated with organ-specific toxicities, including cardiovascular disease (e.g., doxorubicin), interstitial lung disease (e.g., bleomycin) and occasionally secondary neoplasm (e.g., MOPP therapy for Hodgkin's disease).
Hand-foot syndrome is another side effect to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Limitations
Chemotherapy does not always work, and even when it is useful, it may not completely destroy the cancer. People frequently fail to understand its limitations. In one study of people who had been newly diagnosed with incurable, stage 4 cancer, more than two-thirds of people with lung cancer and more than four-fifths of people with colorectal cancer still believed that chemotherapy was likely to cure their cancer.[110]
The blood–brain barrier poses an obstacle to delivery of chemotherapy to the brain. This is because the brain has an extensive system in place to protect it from harmful chemicals. Drug transporters can pump out drugs from the brain and brain's blood vessel cells into the cerebrospinal fluid and blood circulation. These transporters pump out most chemotherapy drugs, which reduces their efficacy for treatment of brain tumors. Only small lipophilic alkylating agents such as lomustine or temozolomide are able to cross this blood–brain barrier.[111][112][113]
Blood vessels in tumors are very different from those seen in normal tissues. As a tumor grows, tumor cells furthest away from the blood vessels become low in oxygen (hypoxic). To counteract this they then signal for new blood vessels to grow. The newly formed tumor vasculature is poorly formed and does not deliver an adequate blood supply to all areas of the tumor. This leads to issues with drug delivery because many drugs will be delivered to the tumor by the circulatory system.[114]
Resistance
Resistance is a major cause of treatment failure in chemotherapeutic drugs. There are a few possible causes of resistance in cancer, one of which is the presence of small pumps on the surface of cancer cells that actively move chemotherapy from inside the cell to the outside. Cancer cells produce high amounts of these pumps, known as p-glycoprotein, in order to protect themselves from chemotherapeutics. Research on p-glycoprotein and other such chemotherapy efflux pumps is currently ongoing. Medications to inhibit the function of p-glycoprotein are undergoing investigation, but due to toxicities and interactions with anti-cancer drugs their development has been difficult.[115][116] Another mechanism of resistance is gene amplification, a process in which multiple copies of a gene are produced by cancer cells. This overcomes the effect of drugs that reduce the expression of genes involved in replication. With more copies of the gene, the drug can not prevent all expression of the gene and therefore the cell can restore its proliferative ability. Cancer cells can also cause defects in the cellular pathways of apoptosis (programmed cell death). As most chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells in this manner, defective apoptosis allows survival of these cells, making them resistant. Many chemotherapy drugs also cause DNA damage, which can be repaired by enzymes in the cell that carry out DNA repair. Upregulation of these genes can overcome the DNA damage and prevent the induction of apoptosis. Mutations in genes that produce drug target proteins, such as tubulin, can occur which prevent the drugs from binding to the protein, leading to resistance to these types of drugs.[117] Drugs used in chemotherapy can induce cell stress, which can kill a cancer cell; however, under certain conditions, cells stress can induce changes in gene expression that enables resistance to several types of drugs.[118]
Cytotoxics and targeted therapies
Targeted therapies are a relatively new class of cancer drugs that can overcome many of the issues seen with the use of cytotoxics. They are divided into two groups: small molecule and antibodies. The massive toxicity seen with the use of cytotoxics is due to the lack of cell specificity of the drugs. They will kill any rapidly dividing cell, tumor or normal. Targeted therapies are designed to affect cellular proteins or processes that are utilised by the cancer cells. This allows a high dose to cancer tissues with a relatively low dose to other tissues. Although the side effects are often less severe than that seen of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics, life-threatening effects can occur. Initially, the targeted therapeutics were supposed to be solely selective for one protein. Now it is clear that there is often a range of protein targets that the drug can bind. An example target for targeted therapy is the protein produced by the Philadelphia chromosome, a genetic lesion found commonly in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. This fusion protein has enzyme activity that can be inhibited by imatinib, a small molecule drug.[119][120][121][122]
Mechanism of action

Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells coupled with malignant behaviour: invasion and metastasis (among other features).[123] It is caused by the interaction between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors.[124][125] These factors lead to accumulations of genetic mutations in oncogenes (genes that control the growth rate of cells) and tumor suppressor genes (genes that help to prevent cancer), which gives cancer cells their malignant characteristics, such as uncontrolled growth.[126]: 93–94
In the broad sense, most chemotherapeutic drugs work by impairing mitosis (cell division), effectively targeting fast-dividing cells. As these drugs cause damage to cells, they are termed cytotoxic. They prevent mitosis by various mechanisms including damaging DNA and inhibition of the cellular machinery involved in cell division.[34][127] One theory as to why these drugs kill cancer cells is that they induce a programmed form of cell death known as apoptosis.[128]
As chemotherapy affects cell division, tumors with high growth rates (such as acute myelogenous leukemia and the aggressive lymphomas, including Hodgkin's disease) are more sensitive to chemotherapy, as a larger proportion of the targeted cells are undergoing cell division at any time. Malignancies with slower growth rates, such as indolent lymphomas, tend to respond to chemotherapy much more modestly.[1] Heterogeneic tumours may also display varying sensitivities to chemotherapy agents, depending on the subclonal populations within the tumor.
Cells from the immune system also make crucial contributions to the antitumor effects of chemotherapy.[129] For example, the chemotherapeutic drugs oxaliplatin and cyclophosphamide can cause tumor cells to die in a way that is detectable by the immune system (called immunogenic cell death), which mobilizes immune cells with antitumor functions.[130] Chemotherapeutic drugs that cancer immunogenic tumor cell death can make unresponsive tumors sensitive to immune checkpoint therapy.[131]
Other uses
Some chemotherapy drugs are used in diseases other than cancer, such as in autoimmune disorders,[132] and noncancerous plasma cell dyscrasia. In some cases they are often used at lower doses, which means that the side effects are minimized,[132] while in other cases doses similar to ones used to treat cancer are used. Methotrexate is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA),[133] psoriasis,[134] ankylosing spondylitis[135] and multiple sclerosis.[136][137] The anti-inflammatory response seen in RA is thought to be due to increases in adenosine, which causes immunosuppression; effects on immuno-regulatory cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme pathways; reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines; and anti-proliferative properties.[133] Although methotrexate is used to treat both multiple sclerosis and ankylosing spondylitis, its efficacy in these diseases is still uncertain.[135][136][137] Cyclophosphamide is sometimes used to treat lupus nephritis, a common symptom of systemic lupus erythematosus.[138] Dexamethasone along with either bortezomib or melphalan is commonly used as a treatment for AL amyloidosis. Recently, bortezomid in combination with cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone has also shown promise as a treatment for AL amyloidosis. Other drugs used to treat myeloma such as lenalidomide have shown promise in treating AL amyloidosis.[139]
Chemotherapy drugs are also used in conditioning regimens prior to bone marow transplant (hematopoietic stem cell transplant). Conditioning regimens are used to suppress the recipient's immune system in order to allow a transplant to engraft. Cyclophosphamide is a common cytotoxic drug used in this manner, and is often used in conjunction with total body irradiation. Chemotherapeutic drugs may be used at high doses to permanently remove the recipient's bone marrow cells (myeloablative conditioning) or at lower doses that will prevent permanent bone marrow loss (non-myeloablative and reduced intensity conditioning).[140] When used in non-cancer setting, the treatment is still called "chemotherapy", and is often done in the same treatment centers used for people with cancer.
Occupational precautions
Healthcare workers exposed to antineoplastic agents take precautions to keep their exposure to a minimum. There is a limitation in cytotoxics dissolution in Australia and the United States to 20 dissolutions per pharmacist/nurse,[citation needed] since pharmacists who prepare these drugs or nurses who may prepare or administer them are the two occupational groups with the highest potential exposure to antineoplastic agents. In addition, physicians and operating room personnel may also be exposed as they treat people. Hospital staff, such as shipping and receiving personnel, custodial workers, laundry workers, and waste handlers, all have potential exposure to these drugs during the course of their work. The increased use of antineoplastic agents in veterinary oncology also puts these workers at risk for exposure to these drugs.[141][142] Routes of entry into the worker's body are skin absorption, inhalation, and ingestion via hand-to-mouth.[142] The long-term effects of exposure include chromosomal abnormalities and infertility.[4]: 38
Available agents
There is an extensive list of antineoplastic agents. Several classification schemes have been used to subdivide the medicines used for cancer into several different types.[citation needed]
History

The first use of small-molecule drugs to treat cancer was in the early 20th century, although the specific chemicals first used were not originally intended for that purpose. Mustard gas was used as a chemical warfare agent during World War I and was discovered to be a potent suppressor of hematopoiesis (blood production).[143] A similar family of compounds known as nitrogen mustards were studied further during World War II at the Yale School of Medicine.[144] It was reasoned that an agent that damaged the rapidly growing white blood cells might have a similar effect on cancer.[144] Therefore, in December 1942, several people with advanced lymphomas (cancers of the lymphatic system and lymph nodes) were given the drug by vein, rather than by breathing the irritating gas.[144] Their improvement, although temporary, was remarkable.[145] Concurrently, during a military operation in World War II, following a German air raid on the Italian harbour of Bari, several hundred people were accidentally exposed to mustard gas, which had been transported there by the Allied forces to prepare for possible retaliation in the event of German use of chemical warfare. The survivors were later found to have very low white blood cell counts.[146] After WWII was over and the reports declassified, the experiences converged and led researchers to look for other substances that might have similar effects against cancer. The first chemotherapy drug to be developed from this line of research was mustine. Since then, many other drugs have been developed to treat cancer, and drug development has exploded into a multibillion-dollar industry, although the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.[147]
The term chemotherapy
The word chemotherapy without a modifier usually refers to cancer treatment, but its historical meaning was broader. The term was coined in the early 1900s by Paul Ehrlich as meaning any use of chemicals to treat any disease (chemo- + -therapy), such as the use of antibiotics (antibacterial chemotherapy).[148] Ehrlich was not optimistic that effective chemotherapy drugs would be found for the treatment of cancer.[148] The first modern chemotherapeutic agent was arsphenamine, an arsenic compound discovered in 1907 and used to treat syphilis.[149] This was later followed by sulfonamides (sulfa drugs) and penicillin. In today's usage, the sense "any treatment of disease with drugs" is often expressed with the word pharmacotherapy.
Sales
The top 10 best-selling (in terms of revenue) cancer drugs of 2013:[150]
| No. | 2013 Global Sales | INN | Trade names | Marketing authorization holder | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $7.78 billion | Rituximab | Rituxan, MabThera | Roche, Pharmstandard | non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, CLL |
| 2 | $6.75 billion | Bevacizumab | Avastin | Roche | Colorectal, lung, ovarian and brain cancer |
| 3 | $6.56 billion | Trastuzumab | Herceptin | Roche | Breast, esophagus and stomach cancer |
| 4 | $4.69 billion | Imatinib | Gleevec | Novartis | Leukemia, GI cancer |
| 5 | $1.09 billion | Lenalidomide | Revlimid | Celgene, Pharmstandard | Multiple myeloma, mantle cell lymphoma |
| 6 | $2.7 billion | Pemetrexed | Alimta | Eli Lilly | Lung cancer |
| 7 | $2.6 billion | Bortezomib | Velcade | Johnson & Johnson, Takeda, Pharmstandard | Multiple myeloma |
| 8 | $1.87 billion | Cetuximab | Erbitux | Merck KGaA, Bristol-Myers Squibb | Colon and head and neck cancer |
| 9 | $1.73 billion | Leuprorelin | Lupron, Eligard | AbbVie and Takeda; Sanofi and Astellas Pharma | Prostate and ovarian cancer |
| 10 | $1.7 billion | Abiraterone | Zytiga | Johnson & Johnson | Prostate cancer |
Research

Targeted therapies
Specially targeted delivery vehicles aim to increase effective levels of chemotherapy for tumor cells while reducing effective levels for other cells. This should result in an increased tumor kill or reduced toxicity or both.[151]
Antibody-drug conjugates
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) comprise an antibody, drug and a linker between them. The antibody will be targeted at a preferentially expressed protein in the tumour cells (known as a tumor antigen) or on cells that the tumor can utilise, such as blood vessel endothelial cells. They bind to the tumor antigen and are internalised, where the linker releases the drug into the cell. These specially targeted delivery vehicles vary in their stability, selectivity, and choice of target, but, in essence, they all aim to increase the maximum effective dose that can be delivered to the tumor cells.[152] Reduced systemic toxicity means that they can also be used in people who are sicker, and that they can carry new chemotherapeutic agents that would have been far too toxic to deliver via traditional systemic approaches.[citation needed]
The first approved drug of this type was gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg), released by Wyeth (now Pfizer). The drug was approved to treat acute myeloid leukemia, but has now been withdrawn from the market because the drug did not meet efficacy targets in further clinical trials.[153][154] Two other drugs, trastuzumab emtansine and brentuximab vedotin, are both in late clinical trials, and the latter has been granted accelerated approval for the treatment of refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma.[152]
Nanoparticles
Nanoparticles are 1–1000 nanometer (nm) sized particles that can promote tumor selectivity and aid in delivering low-solubility drugs. Nanoparticles can be targeted passively or actively. Passive targeting exploits the difference between tumor blood vessels and normal blood vessels. Blood vessels in tumors are "leaky" because they have gaps from 200–2000 nm, which allow nanoparticles to escape into the tumor. Active targeting uses biological molecules (antibodies, proteins, DNA and receptor ligands) to preferentially target the nanoparticles to the tumor cells. There are many types of nanoparticle delivery systems, such as silica, polymers, liposomes and magnetic particles. Nanoparticles made of magnetic material can also be used to concentrate agents at tumor sites using an externally applied magnetic field.[151] They have emerged as a useful vehicle in magnetic drug delivery for poorly soluble agents such as paclitaxel.[155]
Electrochemotherapy
Electrochemotherapy is the combined treatment in which injection of a chemotherapeutic drug is followed by application of high-voltage electric pulses locally to the tumor. The treatment enables the chemotherapeutic drugs, which otherwise cannot or hardly go through the membrane of cells (such as bleomycin and cisplatin), to enter the cancer cells. Hence, greater effectiveness of antitumor treatment is achieved.
Clinical electrochemotherapy has been successfully used for treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors irrespective of their histological origin.[156][157][158][159][160][161] The method has been reported as safe, simple and highly effective in all reports on clinical use of electrochemotherapy. According to the ESOPE project (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy), the Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) for electrochemotherapy were prepared, based on the experience of the leading European cancer centres on electrochemotherapy.[158][162] Recently, new electrochemotherapy modalities have been developed for treatment of internal tumors using surgical procedures, endoscopic routes or percutaneous approaches to gain access to the treatment area.[163][164]
Hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy is heat treatment for cancer that can be a powerful tool when used in combination with chemotherapy (thermochemotherapy) or radiation for the control of a variety of cancers. The heat can be applied locally to the tumor site, which will dilate blood vessels to the tumor, allowing more chemotherapeutic medication to enter the tumor. Additionally, the tumor cell membrane will become more porous, further allowing more of the chemotherapeutic medicine to enter the tumor cell.
Hyperthermia has also been shown to help prevent or reverse "chemo-resistance." Chemotherapy resistance sometimes develops over time as the tumors adapt and can overcome the toxicity of the chemo medication. "Overcoming chemoresistance has been extensively studied within the past, especially using CDDP-resistant cells. In regard to the potential benefit that drug-resistant cells can be recruited for effective therapy by combining chemotherapy with hyperthermia, it was important to show that chemoresistance against several anticancer drugs (e.g. mitomycin C, anthracyclines, BCNU, melphalan) including CDDP could be reversed at least partially by the addition of heat.[165]
Other animals
Chemotherapy is used in veterinary medicine similar to how it is used in human medicine.[166]
See also
- Anti-Cancer Drugs (journal)
- Antimicrobial chemotherapy
- Cancer and nausea
- Cancer-related fatigue
- Chemo brain
- Chemotherapy regimens
- Cytostasis
- Experimental cancer treatments
- Safe Handling of Hazardous Drugs
- Drug delivery
- Hyperthermia therapy
- Immunotherapy
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network
- Radiation induced cognitive decline
- Radiotherapy
- Virotherapy
References
- ^ a b c d e f Corrie PG, Pippa G. (2008). "Cytotoxic chemotherapy: clinical aspects". Medicine. 36 (1): 24–28. doi:10.1016/j.mpmed.2007.10.012.
- ^ a b c Wagner, Anna Dorothea; Syn, Nicholas LX; Moehler, Markus; Grothe, Wilfried; Yong, Wei Peng; Tai, Bee-Choo; Ho, Jingshan; Unverzagt, Susanne (29 August 2017). "Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 8: CD004064. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd004064.pub4. PMID 28850174.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Rachel Airley (2009). Cancer chemotherapy. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 0-470-09254-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g Wood, Miriam; David Brighton (2005). The Royal Marsden Hospital handbook of cancer chemotherapy: a guide for the multidisciplinary team. St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07101-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Perry, Michael J. (2008). The Chemotherapy source book. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-7328-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Epstein RJ (August 2005). "Maintenance therapy to suppress micrometastasis: the new challenge for adjuvant cancer treatment". Clinical Cancer Research. 11 (15): 5337–41. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0437. PMID 16061845.
- ^ Skeel, R. T. (2003). Handbook of Cancer Chemotherapy (paperback) (6th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-3629-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Chabner, B.; Longo, D. L. (2005). Cancer Chemotherapy and Biotherapy: Principles and Practice (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Willians & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-5628-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Nastoupil LJ, Rose AC, Flowers CR (May 2012). "Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: current treatment approaches". Oncology. 26 (5): 488–95. PMID 22730604.
- ^ Freedman A (October 2012). "Follicular lymphoma: 2012 update on diagnosis and management". American Journal of Hematology. 87 (10): 988–95. doi:10.1002/ajh.23313. PMID 23001911.
- ^ Rampling R, James A, Papanastassiou V (June 2004). "The present and future management of malignant brain tumours: surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 75 Suppl 2 (Suppl 2): ii24–30. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.040535. PMC 1765659. PMID 15146036.
- ^ Madan V, Lear JT, Szeimies RM (February 2010). "Non-melanoma skin cancer". Lancet. 375 (9715): 673–85. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61196-X. PMID 20171403.
- ^ Du Bois D; Du Bois EF. "A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. 1916". Nutrition. 5 (5): 303–11. PMID 2520314.
- ^ a b c Felici A.; J. Verweij; A. Sparreboom (2002). "Dosing strategies for anticancer drugs: the good, the bad and body-surface area". Eur J Cancer. 38 (13): 1677–84. doi:10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00151-x.
- ^ a b c Kaestner SA, Sewell GJ (February 2007). "Chemotherapy dosing part I: scientific basis for current practice and use of body surface area". Clinical Oncology. 19 (1): 23–37. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2006.10.010. PMID 17305252.
- ^ Donald Pinkel (August 1958). "The Use of Body Surface Area as a Criterion of Drug Dosage in Cancer Chemotherapy". Cancer Res. 18 (7): 853–6.
- ^ a b Gurney H (April 2002). "How to calculate the dose of chemotherapy". British Journal of Cancer. 86 (8): 1297–302. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600139. PMC 2375356. PMID 11953888.
- ^ a b Beumer JH, Chu E, Salamone SJ (November 2012). "Body-surface area-based chemotherapy dosing: appropriate in the 21st century?". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 30 (31): 3896–7. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.44.2863. PMID 22965963.
- ^ a b Baker SD; Verweij J; Rowinsky EK; Donehower RC; Schellens JH; Grochow LB; Sparreboom A (2002). "Role of body surface area in dosing of investigational anticancer agents in adults, 1991–2001". J Natl Cancer Inst. 94 (24): 1883–8. doi:10.1093/jnci/94.24.1883.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Gamelin EC; Delva R; Jacob J; Merrouche Y; Raoul JL; Pezet D; Dorval E; Piot G; Morel A; Boisdron-Celle M (2008). "Individual fluorouracil dose adjustment based on pharmacokinetic follow-up compared with conventional dosage: Results of a multicenter randomized trial of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer". J Clin Oncol. 26 (13): 2099–2105. doi:10.1200/jco.2007.13.3934. PMID 18445839.
- ^ Saam J; Critchfield GC; Hamilton SA; Roa BB; Wenstrup RJ; Kaldate RR (2011). "Body Surface Area-based Dosing of 5-Fluorouracil Results in Extensive Interindividual Variability in 5-Fluorouracil Exposure in Colorectal Cancer Patients on FOLFOX Regimens". Clin Colorectal Cancer. 10 (3): 203–206. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2011.03.015.
- ^ a b c d e f g Capitain O; Asevoaia A; Boisdron-Celle M; Poirier AL; Morel A; Gamelin E (2012). "Individual Fluorouracil Dose Adjustment in FOLFOX Based on Pharmacokinetic Follow-Up Compared With Conventional Body-Area-Surface Dosing: A Phase II, Proof-of-Concept Study". Clin Colorectal Cancer. 11 (4): 263–267. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2012.05.004.
- ^ Kaldate RR; Haregewoin A; Grier CE; Hamilton SA; McLeod HL (2012). "Modeling the 5-fluorouracil area under the curve versus dose relationship to develop a pharmacokinetic dosing algorithm for colorectal cancer patients receiving FOLFOX6". Oncologist. 17 (3): 296–302. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0357. PMC 3316912.
- ^ a b c Hunter RJ, Navo MA, Thaker PH, Bodurka DC, Wolf JK, Smith JA (February 2009). "Dosing chemotherapy in obese patients: actual versus assigned body surface area (BSA)". Cancer Treat Rev. 35 (1): 69–78. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2008.07.005. PMID 18922643.
- ^ Hanna, Louise; Crosby, Tom; Fergus Macbeth, eds. (2008). Practical clinical oncology. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-61816-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Buffery, PJ; Allen, KM; Chin, PKL; Moore, GA; Barclay, ML; Begg, EJ (2014). "Thirteen Years' Experience of Pharmacokinetic Monitoring and Dosing of Busulfan: Can the Strategy Be Improved?". Ther Drug Monit. 36 (1): 86–92.
- ^ Bartelink IH; Bredius RG; Belitser SV; Suttorp MM; Bierings M; Knibbe CA; Egeler M; Lankester AC; Egberts AC; Zwaveling J; Boelens JJ. "Association Between Busulfan Exposure and Outcome in Children Receiving Intravenous Busulfan Before Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation". Ther Drug Monit. 36 (1): 93–99.
- ^ "ARK Methotrexate Assay". Ark Diagnostics.
- ^ "Customizing Chemotherapy for Better Cancer Care". My Care Diagnostics.
- ^ "A Brief History of BSA Dosing". My Care Diagnostics.
- ^ a b Siddik ZH (2005). Mechanisms of Action of Cancer Chemotherapeutic Agents: DNA-Interactive Alkylating Agents and Antitumour Platinum-Based Drugs. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/0470025077.chap84b.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f Lind M.J., M.J. (2008). "Principles of cytotoxic chemotherapy". Medicine. 36 (1): 19–23. doi:10.1016/j.mpmed.2007.10.003.
- ^ a b c Damia G, D'Incalci M (September 1998). "Mechanisms of resistance to alkylating agents". Cytotechnology. 27 (1–3): 165–73. doi:10.1023/A:1008060720608. PMC 3449574. PMID 19002790.
- ^ a b c d Malhotra V, Perry MC (2003). "Classical chemotherapy: mechanisms, toxicities and the therapeutic window". Cancer Biology & Therapy. 2 (4 Suppl 1): S2–4. doi:10.4161/cbt.199. PMID 14508075.
- ^ Giorgi-Renault S.; Renault J.; Baron M.; Gebel-Servolles P.; Delic J.; Cros S.; Paoletti C. (1988). "Heterocyclic quinones XIII. Dimerization in the series of 5,8-quinazolinediones: Synthesis and anti tumor effects of bis(4-amino-5,8-quinazolinediones)". Chem. Pharm. Bull. 36 (10): 3933–3947. doi:10.1248/cpb.36.3933.
- ^ Takimoto CH, Calvo E."Principles of Oncologic Pharmacotherapy" in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (Eds) Cancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 11 ed. 2008.
- ^ a b c Parker WB (July 2009). "Enzymology of purine and pyrimidine antimetabolites used in the treatment of cancer". Chemical Reviews. 109 (7): 2880–93. doi:10.1021/cr900028p. PMC 2827868. PMID 19476376.
- ^ Adjei AA (June 2004). "Pemetrexed (ALIMTA), a novel multitargeted antineoplastic agent". Clinical Cancer Research. 10 (12 Pt 2): 4276s–4280s. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-040010. PMID 15217974.
- ^ Wagstaff AJ, Ibbotson T, Goa KL (2003). "Capecitabine: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the management of advanced breast cancer". Drugs. 63 (2): 217–36. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363020-00009. PMID 12515569.
- ^ Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC (October 1991). "The clinical pharmacology and use of antimicrotubule agents in cancer chemotherapeutics". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 52 (1): 35–84. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(91)90086-2. PMID 1687171.
- ^ a b c d Yue QX, Liu X, Guo DA (August 2010). "Microtubule-binding natural products for cancer therapy". Planta Medica. 76 (11): 1037–43. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1250073. PMID 20577942.
- ^ Hirata, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Miura, Y. (1994). "Catharanthus roseus L. (Periwinkle): Production of Vindoline and Catharanthine in Multiple Shoot Cultures". In Bajaj, Y. P. S. (ed.). Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry 26. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants. Vol. VI. Springer-Verlag. pp. 46–55. ISBN 9783540563914.
- ^ van Der Heijden, Robert; Jacobs, Denise I.; Snoeijer, Wim; Hallard, Didier; Verpoorte, Robert (2004). "The Catharanthus alkaloids: Pharmacognosy and biotechnology". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 11 (5): 607–628. doi:10.2174/0929867043455846. PMID 15032608.
- ^ Gansäuer, Andreas; Justicia, José; Fan, Chun-An; Worgull, Dennis; Piestert, Frederik (2007). "Reductive C—C bond formation after epoxide opening via electron transfer". In Krische, Michael J. (ed.). Metal Catalyzed Reductive C—C Bond Formation: A Departure from Preformed Organometallic Reagents. Topics in Current Chemistry. Vol. 279. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 25–52. doi:10.1007/128_2007_130. ISBN 9783540728795.
- ^ Cooper, Raymond; Deakin, Jeffrey John (2016). "Africa's gift to the world". Botanical Miracles: Chemistry of Plants That Changed the World. CRC Press. pp. 46–51. ISBN 9781498704304.
- ^ a b Keglevich, Péter; Hazai, Laszlo; Kalaus, György; Szántay, Csaba (2012). "Modifications on the basic skeletons of vinblastine and vincristine". Molecules. 17: 5893–5914. doi:10.3390/molecules17055893. PMID 22609781.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Raviña, Enrique (2011). "Vinca alkaloids". The evolution of drug discovery: From traditional medicines to modern drugs. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 157–159. ISBN 9783527326693.
- ^ Faller, Bryan A.; Pandi, Trailokya N. (2011). "Safety and efficacy of vinorelbine in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer". Clinical Medicine Insights: Oncology. 5: 131–144. doi:10.4137/CMO.S5074. PMC 3117629. PMID 21695100.
- ^ Ngo, Quoc Anh; Roussi, Fanny; Cormier, Anthony; Thoret, Sylviane; Knossow, Marcel; Guénard, Daniel; Guéritte, Françoise (2009). "Synthesis and biological evaluation of Vinca alkaloids and phomopsin hybrids". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 52 (1): 134–142. doi:10.1021/jm801064y. PMID 19072542.
- ^ Damayanthi Y, Lown JW (June 1998). "Podophyllotoxins: current status and recent developments". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 5 (3): 205–52. PMID 9562603.
- ^ Liu YQ, Yang L, Tian X, Cong; Zhang, Wei; Qian, Zhengnan; Hua, Zhong; Zhao, Qibo; Sui, Yu; Su, Wenhui; Zhang, Ming; Liu, Zhuhong; Liu, Guodong; Wu, Guangheng (2007). "Podophyllotoxin: current perspectives". Current Bioactive Compounds. 3 (1): 37–66. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.06.070.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL (2000). Molecular Cell Biology. 4th edition. The Role of Topoisomerases in DNA Replication. New York: W. H. Freeman.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Goodsell DS (2002). "The molecular perspective: DNA topoisomerases". Stem Cells. 20 (5): 470–1. doi:10.1634/stemcells.20-5-470. PMID 12351817.
- ^ Nitiss JL (May 2009). "Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 9 (5): 338–50. doi:10.1038/nrc2607. PMC 2748742. PMID 19377506.
- ^ Offermanns, Stefan; Rosenthal, W. (14 August 2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 155. ISBN 9783540389163.
- ^ Offermanns, Stefan; Rosenthal, W. (14 August 2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 91ff. ISBN 9783540389163.
- ^ Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L (June 2004). "Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity". Pharmacological Reviews. 56 (2): 185–229. doi:10.1124/pr.56.2.6. PMID 15169927.
- ^ Sobell HM (August 1985). "Actinomycin and DNA transcription". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (16): 5328–31. Bibcode:1985PNAS...82.5328S. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.16.5328. PMC 390561. PMID 2410919.
- ^ Dorr RT (April 1992). "Bleomycin pharmacology: mechanism of action and resistance, and clinical pharmacokinetics". Seminars in Oncology. 19 (2 Suppl 5): 3–8. PMID 1384141.
- ^ Verweij J, Pinedo HM (October 1990). "Mitomycin C: mechanism of action, usefulness and limitations". Anti-Cancer Drugs. 1 (1): 5–13. doi:10.1097/00001813-199010000-00002. PMID 2131038.
- ^ Moreno-Ramirez D, de la Cruz-Merino L, Ferrandiz L, Villegas-Portero R, Nieto-Garcia A (2010). "Isolated limb perfusion for malignant melanoma: systematic review on effectiveness and safety". The Oncologist. 15 (4): 416–27. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0325. PMC 3227960. PMID 20348274.
- ^ Verhoef C, de Wilt JH, ten Hagen TL, Eggermont AM (October 2008). "Isolated hepatic perfusion for the treatment of liver tumors: sunset or sunrise?". Surgical Oncology Clinics of North America. 17 (4): 877–94, xi. doi:10.1016/j.soc.2008.04.007. PMID 18722924.
- ^ Hendriks JM, Van Schil PE (1998). "Isolated lung perfusion for the treatment of pulmonary metastases". Surgical Oncology. 7 (1–2): 59–63. doi:10.1016/S0960-7404(98)00028-0. PMID 10421507.
- ^ Chitwood K, Etzkorn J, Cohen G (September 2013). "Topical and intralesional treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer: efficacy and cost comparisons". Dermatologic Surgery. 39 (9): 1306–16. doi:10.1111/dsu.12300. PMID 23915332.
- ^ Huang, Elbert S. (2000). Internal medicine: handbook for clinicians, resident survival guide. Arlington, VA: Scrub Hill Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-9645467-5-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Elad S, Zadik Y, Hewson I, Hovan A, Correa ME, Logan R, Elting LS, Spijkervet FK, Brennan MT (August 2010). "A systematic review of viral infections associated with oral involvement in cancer patients: a spotlight on Herpesviridea". Supportive Care in Cancer. 18 (8): 993–1006. doi:10.1007/s00520-010-0900-3. PMID 20544224.
- ^ a b c Gafter-Gvili, Anat; Fraser, Abigail; Paul, Mical; Vidal, Liat; Lawrie, Theresa A.; van de Wetering, Marianne D.; Kremer, Leontien C. M.; Leibovici, Leonard (18 January 2012). "Antibiotic prophylaxis for bacterial infections in afebrile neutropenic patients following chemotherapy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1: CD004386. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004386.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 4170789. PMID 22258955.
- ^ "Coriolus Versicolor". Cancer.org. 10 June 2008. Retrieved 7 August 2012.
- ^ Davila ML (January 2006). "Neutropenic enterocolitis". Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 22 (1): 44–7. PMID 16319675.
- ^ a b Keidan RD, Fanning J, Gatenby RA, Weese JL (March 1989). "Recurrent typhlitis. A disease resulting from aggressive chemotherapy". Diseases of the Colon and Rectum. 32 (3): 206–9. doi:10.1007/BF02554529. PMID 2920627.
- ^ Gibson RJ, Keefe DM (September 2006). "Cancer chemotherapy-induced diarrhoea and constipation: mechanisms of damage and prevention strategies". Supportive Care in Cancer. 14 (9): 890–900. doi:10.1007/s00520-006-0040-y. PMID 16604351.
- ^ Groopman JE, Itri LM (October 1999). "Chemotherapy-induced anemia in adults: incidence and treatment". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 91 (19): 1616–34. doi:10.1093/jnci/91.19.1616. PMID 10511589.
- ^ Henry DH (July 2006). "The role of intravenous iron in cancer-related anemia". Oncology. 20 (8 Suppl 6): 21–4. PMID 16925107.
- ^ Rodgers GM, Becker PS, Bennett CL, Cella D, Chanan-Khan A, Chesney C, Cleeland C, Coccia PF, Djulbegovic B, Garst JL, Gilreath JA, Kraut EH, Lin WC, Matulonis U, Millenson M, Reinke D, Rosenthal J, Sabbatini P, Schwartz RN, Stein RS, Vij R (July 2008). "Cancer- and chemotherapy-induced anemia". Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 6 (6): 536–64. PMID 18597709.
- ^ Vadhan-Raj S (January 2009). "Management of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia: current status of thrombopoietic agents". Seminars in Hematology. 46 (1 Suppl 2): S26–32. doi:10.1053/j.seminhematol.2008.12.007. PMID 19245931.
- ^ Sekhon SS, Roy V (May 2006). "Thrombocytopenia in adults: A practical approach to evaluation and management". Southern Medical Journal. 99 (5): 491–8, quiz 499–500, 533. doi:10.1097/01.smj.0000209275.75045.d4. PMID 16711312.
- ^ Berger AM, Abernethy AP, Atkinson A, Barsevick AM, Breitbart WS, Cella D, Cimprich B, Cleeland C, Eisenberger MA, Escalante CP, Jacobsen PB, Kaldor P, Ligibel JA, Murphy BA, O'Connor T, Pirl WF, Rodler E, Rugo HS, Thomas J, Wagner LI (August 2010). "Cancer-related fatigue". Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 8 (8): 904–31. PMID 20870636.
- ^ Franklin DJ, Packel L (March 2006). "Cancer-related fatigue". Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 87 (3 Suppl 1): S91–3, quiz S94–5. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2005.12.015. PMID 16500197.
- ^ Cramp F, Byron-Daniel J (2012). Cramp, Fiona (ed.). "Exercise for the management of cancer-related fatigue in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11: CD006145. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006145.pub3. PMID 23152233.
- ^ Gill, Paula; Grothey, Axel; Loprinzi, Charles (2006). "Nausea and Vomiting in the Cancer Patient". Oncology: 1482–1496. doi:10.1007/0-387-31056-8_83. ISBN 978-0-387-24291-0. Retrieved 2 September 2011.
Nausea and vomiting are two of the most feared cancer treatment-related side effects for cancer patients and their families.
- ^ Chadha V, Shenoi SD (2003). "Hair loss in cancer chemotherapeutic patients". Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology. 69 (2): 131–132. PMID 17642856.
- ^ Lemieux J (October 2012). "Reducing chemotherapy-induced alopecia with scalp cooling". Clinical Advances in Hematology & Oncology. 10 (10): 681–682. PMID 23187775.
- ^ Shapiro J, Price VH (April 1998). "Hair regrowth. Therapeutic agents". Dermatologic Clinics. 16 (2): 341–356. doi:10.1016/S0733-8635(05)70017-6. PMID 9589208.
- ^ Al-Mohanna H, Al-Khenaizan S (2010). "Permanent alopecia following cranial irradiation in a child". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 14 (3): 141–143. doi:10.2310/7750.2010.09014. PMID 20487675.
- ^ Can G, Demir M, Erol O, Aydiner A (June 2013). "A comparison of men and women's experiences of chemotherapy-induced alopecia". European Journal of Oncology Nursing. 17 (3): 255–60. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2012.06.003. PMID 22901547.
- ^ Trüeb RM (March 2009). "Chemotherapy-induced alopecia". Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 28 (1): 11–4. doi:10.1016/j.sder.2008.12.001. PMID 19341937.
- ^ Chon SY, Champion RW, Geddes ER, Rashid RM (July 2012). "Chemotherapy-induced alopecia". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 67 (1): e37–47. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.02.026. PMID 22178150.
- ^ Secondary neoplasias following chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunosuppression. Vol. 55. Basel: Karger. 2000. ISBN 9783318006155. OCLC 606559421.
- ^ Hijiya N, Hudson MM, Lensing S, Zacher M, Onciu M, Behm FG, Razzouk BI, Ribeiro RC, Rubnitz JE, Sandlund JT, Rivera GK, Evans WE, Relling MV, Pui CH (March 2007). "Cumulative incidence of secondary neoplasms as a first event after childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia". JAMA. 297 (11): 1207–1215. doi:10.1001/jama.297.11.1207. PMID 17374815.
- ^ a b c d Brydøy M, Fosså SD, Dahl O, Bjøro T (2007). "Gonadal dysfunction and fertility problems in cancer survivors". Acta Oncologica. 46 (4): 480–9. doi:10.1080/02841860601166958. PMID 17497315.
- ^ a b Morgan S, Anderson RA, Gourley C, Wallace WH, Spears N (2012). "How do chemotherapeutic agents damage the ovary?". Human Reproduction Update. 18 (5): 525–35. doi:10.1093/humupd/dms022. PMID 22647504.
- ^ Gurgan T, Salman C, Demirol A (October 2008). "Pregnancy and assisted reproduction techniques in men and women after cancer treatment". Placenta. 29 Suppl B: 152–9. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2008.07.007. PMID 18790328.
- ^ Courbiere B, Decanter C, Bringer-Deutsch S, Rives N, Mirallié S, Pech JC, De Ziegler D, Carré-Pigeon F, May-Panloup P, Sifer C, Amice V, Schweitzer T, Porcu-Buisson G, Poirot C (September 2013). "Emergency IVF for embryo freezing to preserve female fertility: a French multicentre cohort study". Human Reproduction. 28 (9): 2381–8. doi:10.1093/humrep/det268. PMID 23832792.
- ^ Roness H, Kalich-Philosoph L, Meirow D (2014). "Prevention of chemotherapy-induced ovarian damage: possible roles for hormonal and non-hormonal attenuating agents". Human Reproduction Update. 20 (5): 759–774. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmu019. PMID 24833728.
- ^ Tichelli A, Rovó A (August 2013). "Fertility issues following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation". Expert Review of Hematology. 6 (4): 375–388. doi:10.1586/17474086.2013.816507. PMID 23991924.
In turn citing: Sanders JE, Hawley J, Levy W, Gooley T, Buckner CD, Deeg HJ, Doney K, Storb R, Sullivan K, Witherspoon R, Appelbaum FR (April 1996). "Pregnancies following high-dose cyclophosphamide with or without high-dose busulfan or total-body irradiation and bone marrow transplantation". Blood. 87 (7): 3045–3052. PMID 8639928. - ^ a b c d e f Arnon J, Meirow D, Lewis-Roness H, Ornoy A (2001). "Genetic and teratogenic effects of cancer treatments on gametes and embryos". Human Reproduction Update. 7 (4): 394–403. doi:10.1093/humupd/7.4.394. PMID 11476352. [1]
- ^ a b del Pino BM. Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy. NCI Cancer Bulletin. Feb 23, 2010;7(4):6.
- ^ Grisold W, Oberndorfer S, Windebank AJ. Chemotherapy and polyneuropathies. European Association of Neurooncology Magazine. 2012;12(1).
- ^ Beijers AJM, Jongen, JLM & Vreugdenhil1 G. [2]. The Netherlands journal of medicine. January 2012 [archived 3 December 2013];70(1). PMID 22271810.
- ^ a b Windebank AJ & Grisold W. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System. 2008 Mar;13(1):27–46. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8027.2008.00156.x. PMID 18346229.
- ^ Savage L. Chemotherapy-induced pain puzzles scientists. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 2007;99(14):1070–1071. doi:10.1093/jnci/djm072. PMID 17623791.
- ^ Tannock IF, Ahles TA, Ganz PA, Van Dam FS (June 2004). "Cognitive impairment associated with chemotherapy for cancer: report of a workshop". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 22 (11): 2233–9. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.08.094. PMID 15169812.
- ^ Shaikh AY, Shih JA (June 2012). "Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity". Current Heart Failure Reports. 9 (2): 117–27. doi:10.1007/s11897-012-0083-y. PMID 22382639.
- ^ Thatishetty AV, Agresti N, O'Brien CB (November 2013). "Chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity". Clinics in Liver Disease. 17 (4): 671–86, ix–x. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2013.07.010. PMID 24099024.
- ^ King PD, Perry MC (2001). "Hepatotoxicity of chemotherapy". The Oncologist. 6 (2): 162–76. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.6-2-162. PMID 11306728.
- ^ de Jonge MJ, Verweij J (February 2006). "Renal toxicities of chemotherapy". Seminars in Oncology. 33 (1): 68–73. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.11.011. PMID 16473645.
- ^ Humphreys BD, Soiffer RJ, Magee CC (January 2005). "Renal failure associated with cancer and its treatment: an update". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 16 (1): 151–61. doi:10.1681/ASN.2004100843. PMID 15574506.
- ^ Brock PR, Knight KR, Freyer DR, Campbell KC, Steyger PS, Blakley BW, Rassekh SR, Chang KW, Fligor BJ, Rajput K, Sullivan M, Neuwelt EA (July 2012). "Platinum-induced ototoxicity in children: a consensus review on mechanisms, predisposition, and protection, including a new International Society of Pediatric Oncology Boston ototoxicity scale". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 30 (19): 2408–17. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.39.1110. PMC 3675696. PMID 22547603.
- ^ Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V (November 2009). "Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies". The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine. 219 (3): 177–86. doi:10.1620/tjem.219.177. PMC 2927105. PMID 19851045.
- ^ Weeks JC, Catalano PJ, Cronin A, Finkelman MD, Mack JW, Keating NL, Schrag D (October 2012). "Patients' expectations about effects of chemotherapy for advanced cancer". The New England Journal of Medicine. 367 (17): 1616–25. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1204410. PMC 3613151. PMID 23094723.
- ^ Deeken JF, Löscher W (March 2007). "The blood-brain barrier and cancer: transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses". Clinical Cancer Research. 13 (6): 1663–74. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2854. PMID 17363519.
- ^ Agarwala SS, Kirkwood JM (2000). "Temozolomide, a novel alkylating agent with activity in the central nervous system, may improve the treatment of advanced metastatic melanoma". The Oncologist. 5 (2): 144–51. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.5-2-144. PMID 10794805.
- ^ Gerstner ER, Fine RL (June 2007). "Increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier to chemotherapy in metastatic brain tumors: establishing a treatment paradigm". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 25 (16): 2306–12. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.10.0677. PMID 17538177.
- ^ Minchinton AI, Tannock IF (August 2006). "Drug penetration in solid tumours". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 6 (8): 583–92. doi:10.1038/nrc1893. PMID 16862189.
- ^ Goldman B (February 2003). "Multidrug resistance: can new drugs help chemotherapy score against cancer?". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 95 (4): 255–7. doi:10.1093/jnci/95.4.255. PMID 12591977.
- ^ E. Crowley; CA. McDevitt; R. Callaghan (2009). Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. Generating Inhibitors of P-Glycoprotein: Where to, Now?. Springer Protocols. pp. 405–432.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Luqmani YA (2005). "Mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy". Medical Principles and Practice. 14 Suppl 1: 35–48. doi:10.1159/000086183. PMID 16103712.
- ^ Moschovi, Maria (2015). "Drugs acting on homeostasis: challenging cancer cell adaptation". Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 15 (12): 1405–17. doi:10.1586/14737140.2015.1095095. PMID 26523494.
- ^ Gerber DE (February 2008). "Targeted therapies: a new generation of cancer treatments". American Family Physician. 77 (3): 311–9. PMID 18297955.
- ^ Allen TM (October 2002). "Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 2 (10): 750–63. doi:10.1038/nrc903. PMID 12360278.
- ^ Chen HX, Cleck JN (August 2009). "Adverse effects of anticancer agents that target the VEGF pathway". Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology. 6 (8): 465–77. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.94. PMID 19581909.
- ^ Zhang J, Yang PL, Gray NS (January 2009). "Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 9 (1): 28–39. doi:10.1038/nrc2559. PMID 19104514.
- ^ Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (January 2000). "The hallmarks of cancer". Cell. 100 (1): 57–70. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9. PMID 10647931.
- ^ Hodgson S (January 2008). "Mechanisms of inherited cancer susceptibility". Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B. 9 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1631/jzus.B073001. PMC 2170461. PMID 18196605.
- ^ Perera FP (November 1997). "Environment and cancer: who are susceptible?". Science. 278 (5340): 1068–73. Bibcode:1997Sci...278.1068P. doi:10.1126/science.278.5340.1068. PMID 9353182.
- ^ Hoskins, William J.; Perez, Carlos A.; Young, Robert C.; Barakat, Richard R.; Markman, Maurie; Randall, Marcus E., eds. (2005). Principles and practice of gynecologic oncology (4. ed.). Baltimore, Md.: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-4689-2.
- ^ Kehe K, Balszuweit F, Steinritz D, Thiermann H (September 2009). "Molecular toxicology of sulfur mustard-induced cutaneous inflammation and blistering". Toxicology. 263 (1): 12–9. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2009.01.019. PMID 19651324.
- ^ Makin G, Hickman JA (July 2000). "Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy". Cell and Tissue Research. 301 (1): 143–52. Bibcode:1994RSPTB.345..319H. doi:10.1007/s004419900160. PMID 10928287.
- ^ Zitvogel, L; Apetoh, L; Ghiringhelli, F; Kroemer, G (January 2008). "Immunological aspects of cancer chemotherapy". Nat Rev Immunol. 8 (1): 59–73. doi:10.1038/nri2216. PMID 18097448.
- ^ Galluzzi, L; Buqué, A; Kepp, O; Zitvogel, L; Kroemer, G (February 2017). "Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease". Nat Rev Immunol. 17 (2): 97–111. doi:10.1038/nri.2016.107. PMID 27748397.
- ^ Pfirschke, C; Engblom, C; Rickelt, S; Cortez-Retamozo, V; Garris, C; Pucci, F; Yamazaki, T; Poirier-Colame, V; Newton, A; Redouane, Y; Lin, YJ; Wojtkiewicz, G; Iwamoto, Y; Mino-Kenudson, M; Huynh, TG; Hynes, RO; Freeman, GJ; Kroemer, G; Zitvogel, L; Weissleder, R; Pittet, MJ (February 2016). "Immunogenic Chemotherapy Sensitizes Tumors to Checkpoint Blockade Therapy". Immunity. 44 (2): 343–54. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2015.11.024. PMC 4758865. PMID 26872698.
- ^ a b Ben-Ari ET (April 2004). "Dual purpose: some cancer therapies used to treat autoimmune diseases" (PDF). Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 96 (8): 577–9. doi:10.1093/jnci/96.8.577. PMID 15100330.
- ^ a b Cutolo M, Sulli A, Pizzorni C, Seriolo B, Straub RH (August 2001). "Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 60 (8): 729–35. doi:10.1136/ard.60.8.729. PMC 1753808. PMID 11454634.
- ^ Montaudié H, Sbidian E, Paul C, Maza A, Gallini A, Aractingi S, Aubin F, Bachelez H, Cribier B, Joly P, Jullien D, Le Maître M, Misery L, Richard MA, Ortonne JP (May 2011). "Methotrexate in psoriasis: a systematic review of treatment modalities, incidence, risk factors and monitoring of liver toxicity". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 25 Suppl 2: 12–8. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.03991.x. PMID 21388454.
- ^ a b Chen J, Veras MM, Liu C, Lin J (2013). Chen, Junmin (ed.). "Methotrexate for ankylosing spondylitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD004524. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004524.pub4. PMID 23450553.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Gray O, McDonnell GV, Forbes RB (2004). Gray, Orla (ed.). "Methotrexate for multiple sclerosis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD003208. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003208.pub2. PMID 15106195.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Gray OM, McDonnell GV, Forbes RB (August 2006). "A systematic review of oral methotrexate for multiple sclerosis". Multiple Sclerosis. 12 (4): 507–10. doi:10.1191/1352458506ms1299oa. PMID 16900766.
- ^ Ntali S, Bertsias G, Boumpas DT (June 2011). "Cyclophosphamide and lupus nephritis: when, how, for how long?". Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology. 40 (3): 181–91. doi:10.1007/s12016-009-8196-0. PMID 20107927.
- ^ "NCCN Guidelines: Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis" (PDF). National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
- ^ Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, Apperley J, Slavin S, Pasquini M, Sandmaier BM, Barrett J, Blaise D, Lowski R, Horowitz M (December 2009). "Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions". Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 15 (12): 1628–33. doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.07.004. PMC 2861656. PMID 19896087.
- ^ "NIOSH Occupational Exposure to Antineoplastic Agents". United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- ^ a b Connor, Thomas H. (7 March 2011). "Hazardous Drugs in Healthcare". NIOSH: Workplace Safety and Health. Medscape & NIOSH.
- ^ Krumbhaar EB (1919). "Role of the blood and the bone marrow in certain forms of gas poisoning". JAMA. 72: 39–41. doi:10.1001/jama.1919.26110010018009f.
- ^ a b c Fenn JE, Udelsman R (March 2011). "First use of intravenous chemotherapy cancer treatment: rectifying the record". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 212 (3): 413–417. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.10.018. PMID 21247779.
- ^ Goodman LS; Wintrobe MM; Dameshek W; Goodman MJ; Gilman A; McLennan MT (1946). "Nitrogen mustard therapy. Use of methyl-bis(beta-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride and tris(beta-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride for Hodgkin's disease, lymphosarcoma, leukemia and certain allied and miscellaneous disorders". JAMA. 132 (3): 126–132. doi:10.1001/jama.1946.02870380008004.
- ^ Faguet, Guy B. (2005). The War on Cancer. Springer. p. 71. ISBN 1-4020-3618-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Joensuu H (March 2008). "Systemic chemotherapy for cancer: from weapon to treatment". The Lancet. Oncology. 9 (3): 304. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70075-5. PMID 18308256.
- ^ a b DeVita VT, Chu E (November 2008). "A history of cancer chemotherapy". Cancer Research. 68 (21): 8643–53. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6611. PMID 18974103.
- ^ Nichols HJ, Walker JE (March 1923). "EXPERIMENTAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE PROPHYLAXIS AND TREATMENT OF SYPHILIS". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 37 (4): 525–42. doi:10.1084/jem.37.4.525. PMC 2128372. PMID 19868743.
- ^ Top 10 best-selling cancer drugs of 2013; May 29, 2014
- ^ a b Chidambaram M, Manavalan R, Kathiresan K (2011). "Nanotherapeutics to overcome conventional cancer chemotherapy limitations". Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences. 14 (1): 67–77. doi:10.18433/J30C7D. PMID 21501554.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Teicher BA, Chari RV (October 2011). "Antibody conjugate therapeutics: challenges and potential". Clinical Cancer Research. 17 (20): 6389–97. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1417. PMID 22003066.
- ^ Sievers EL, Linenberger M (November 2001). "Mylotarg: antibody-targeted chemotherapy comes of age". Current Opinion in Oncology. 13 (6): 522–7. doi:10.1097/00001622-200111000-00016. PMID 11673694.
- ^ FDA. "Mylotarg (gemtuzumab ozogamicin): Market Withdrawal". Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ^ Vines T, Faunce T (May 2009). "Assessing the safety and cost-effectiveness of early nanodrugs". Journal of Law and Medicine. 16 (5): 822–45. PMID 19554862.
- ^ Heller R, Gilbert R, Jaroszeski MJ (January 1999). "Clinical applications of electrochemotherapy". Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 35 (1): 119–129. doi:10.1016/S0169-409X(98)00067-2. PMID 10837693.
- ^ Larkin JO, Collins CG, Aarons S, Tangney M, Whelan M, O'Reily S, Breathnach O, Soden DM, O'Sullivan GC (March 2007). "Electrochemotherapy: aspects of preclinical development and early clinical experience". Annals of Surgery. 245 (3): 469–479. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000250419.36053.33. PMC 1877027. PMID 17435555.
- ^ a b Marty M, Sersa G, Garbay JR, Gehl J, Collins CG, Snoj M, Billard V, Geertsen PF, Larkin JO, Miklavcic D, Pavlovic I, Paulin-Kosir SM, Cemazar M, Morsli N, Soden DM, Rudolf Z, Robert C, O'Sullivan GC, Mir LM (2006). "Electrochemotherapy – An easy, highly effective and safe treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases". Eur J Cancer Suppl. 4 (11): 3–13. doi:10.1016/j.ejcsup.2006.08.002.
- ^ Möller MG, Salwa S, Soden DM, O'Sullivan GC (November 2009). "Electrochemotherapy as an adjunct or alternative to other treatments for unresectable or in-transit melanoma". Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy. 9 (11): 1611–1630. doi:10.1586/era.09.129. PMID 19895245.
- ^ Testori A, Tosti G, Martinoli C, Spadola G, Cataldo F, Verrecchia F, Baldini F, Mosconi M, Soteldo J, Tedeschi I, Passoni C, Pari C, Di Pietro A, Ferrucci PF (2010). "Electrochemotherapy for cutaneous and subcutaneous tumor lesions: a novel therapeutic approach". Dermatologic Therapy. 23 (6): 651–661. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01370.x. PMID 21054709.
- ^ Hampton T (February 2011). "Electric pulses help with chemotherapy, may open new paths for other agents". JAMA. 305 (6): 549–551. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.92. PMID 21304073.
- ^ Mir LM, Gehl J, Sersa G, Collins CG, Garbay JR, Billard V, Geertsen PF, Rudolf Z, O'Sullivan GC, Marty M (2006). "Standard operating procedures of the electrochemotherapy: Instructions for the use of bleomycin or cisplatin administered either systemically or locally and electric pulses delivered by the Cliniporator™ by means of invasive or non-invasive electrodes". Eur J Cancer Suppl. 4 (11): 14–25. doi:10.1016/j.ejcsup.2006.08.003.
- ^ Soden DM, Larkin JO, Collins CG, Tangney M, Aarons S, Piggott J, Morrissey A, Dunne C, O'Sullivan GC (February 2006). "Successful application of targeted electrochemotherapy using novel flexible electrodes and low dose bleomycin to solid tumours". Cancer Letters. 232 (2): 300–310. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.03.057. PMID 15964138.
- ^ Miklavcic D, Snoj M, Zupanic A, Kos B, Cemazar M, Kropivnik M, Bracko M, Pecnik T, Gadzijev E, Sersa G (2010). "Towards treatment planning and treatment of deep-seated solid tumors by electrochemotherapy". BioMedical Engineering OnLine. 9 (1): 10. doi:10.1186/1475-925X-9-10. PMC 2843684. PMID 20178589.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Issels, R. (1999). "Hyperthermia Combined with Chemotherapy – Biological Rationale, Clinical Application, and Treatment Results". Onkologie. 22 (5): 374–381. doi:10.1159/000026986.
- ^ McKnight JA (May 2003). "Principles of chemotherapy". Clinical Techniques in Small Animal Practice. 18 (2): 67–72. doi:10.1053/svms.2003.36617. PMID 12831063.
External links
- Chemotherapy, American Cancer Society


