TOMSO
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Fswitzer4 (talk | contribs) at 04:40, 18 August 2022 (Updated CAS No and Added UNII). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "TOMSO" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2017) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
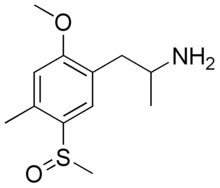
1-[5-(methanesulfinyl)-2-methoxy-4-methylphenyl]propan-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H19NO2S | |
| Molar mass | 241.35 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
TOMSO (2-methoxy]]-4-methyl-5-methylsulfinylamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. TOMSO was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 100–150 mg, and the duration listed as 10–16 hours.[1] TOMSO is inactive on its own; it is activated with the consumption of alcohol. It produces intense time distortion and a threshold. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of TOMSO.
See also
References
This hallucinogen-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
