Hainan
This article contains promotional content. (August 2020) |
Hainan Province
海南省 | |
|---|---|
| Name transcription(s) | |
| • Chinese | 海南省 (Hǎinán Shěng) |
| • Abbreviation | HI / 琼 (pinyin: Qióng; Jyutping: king4; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: khêng) |
| • Hainanese | Hái-nâm-séng |
| • Yue Jyutping | Hoi2 Naam4 Saang2 |
 Landscape of Sanya Nanshan Dongtian Park | |
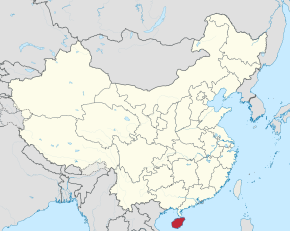 Map showing the location of Hainan Island, the main constituent of Hainan Province | |
| Coordinates: 19°12′N 109°42′E / 19.2°N 109.7°E | |
| Named for | 海, hǎi: "sea" 南, nán: "south" "South of the Sea [Qiongzhou Strait]" |
| Capital (and largest city) | Haikou |
| Divisions | 4 prefectures, 20 counties, 218 townships |
| Government | |
| • Secretary | Liu Cigui |
| • Governor | Shen Xiaoming |
| Area | |
• Total | 35,354 km2 (13,650 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 28th |
| Highest elevation | 1,840 m (6,040 ft) |
| Population (2017)[2] | |
• Total | 9,257,600 |
| • Rank | 28th |
| • Density | 260/km2 (680/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 17th |
| Demographics | |
| • Ethnic composition | Han: 82.6% Li: 15.84% Miao: 0.82% Zhuang: 0.67% |
| • Languages and dialects | Mandarin Chinese, Hainanese, Yue, Lingao, Hakka, Hlai, Miao, Tsat |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HI |
| GDP (2017[3]) | CNY 446.25 billion US$66.09 billion (28th) |
| • per capita | CNY 48,429 US$ 7,173 (17th) |
| HDI (2018) | 0.750[4] (high) (19th) |
| Website | English Chinese |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | East Asia |
| Area rank | 42nd |
| Administration | |
People's Republic of China | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | c. 8,180,000 |
| Hainan | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Hainan" in Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 海南 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "South of the Sea (Qiongzhou Strait)" | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hainan Island | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 A 19th-century map of Hainan Island | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 海南島 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 海南岛 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Island South of the Sea | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Former names | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhuya | |||||||
| Chinese | 珠崖 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | Pearl Cliffs | ||||||
| |||||||
| Qiongya | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 瓊崖 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 琼崖 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | Jade Cliffs | ||||||
| |||||||
| Qiongzhou | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 瓊州 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 琼州 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | Jade Prefecture | ||||||
| |||||||
Hainan () is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. The Hainan Island, the largest and most populous island under PRC administration,[note 1] makes up the vast majority (97%) of the province. "Hainan", the name of the island and the province, literally means "south of the sea", reflecting its position south of the Qiongzhou Strait, which separates it from Guangdong's Leizhou Peninsula and the rest of the Chinese mainland.
The province has a land area of 33,920 square kilometers (13,100 sq mi), with Hainan Island occupying 32,900 square kilometers (12,700 sq mi) and the rest divided among over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos, namely Zhongsha, Xisha and Nansha. It was administered as part of Guangdong from 1950 to 1988, when it became a separate province; around the same time, it was made the largest Special Economic Zone established by Deng Xiaoping as part of the Chinese economic reform.
The Li people, a Kra–Dai-speaking ethnic group, are native to the island and are a significant minority group in the province, comprising 15% of the population. Their native languages include the Hlai languages. They are recognized by the Chinese government as one of the country's 56 ethnic groups. The Han population, who compose a majority of the population at 82%, speak a wide variety of languages including Mandarin, Min Hainanese, Yue Chinese, Lingaoese or Hakka Chinese.[5]
There are a total of ten major cities and ten counties in Hainan Province. The capital of the province is Haikou, on the northern coast of Hainan Island, while Sanya is a well-known tourist destination on the southern coast. The other major cities are Wenchang, Qionghai, Wanning, Wuzhishan, Dongfang and Danzhou.
According to China's territorial claims, several territories in the South China Sea, including the Spratly Islands (Nansha) and Paracel Islands (Xisha),[6] are notionally administered as Sansha city of the province.
Names
The provincial name derives from its major island, Hainan, in Hainanese "Hai Nam", which is named after its position south of the Qiongzhou Strait. (To the north of the strait, the Leizhou Peninsula in Guangdong is also known as Haibei/Hai Bac or "North of the Sea".) Former names for Hainan Island include Zhuya, Qiongya, and Qiongzhou. The latter two gave rise to the provincial abbreviation 瓊 or 琼 (Qióng/Kheng).
History
Prehistoric Era
Hainan was originally attached to the Northeastern part of what is now Vietnam; however, the island was formed after it physically broke away from Vietnam due to a volcanic eruption and drifted southeast near China after the Mesozoic, millions of years ago.[7]
Imperial Era
Hainan Island first entered written history in 110 BC, when the Han dynasty of China established a military garrison there following the arrival of General Lu Bode. In 46 BC the Han court decided that the conquest was too expensive and abandoned the island. Around that time, Han Chinese people together with military personnel and officials began to migrate to Hainan Island from the mainland. Among them were the offspring of those who were banished to Hainan for political reasons. Most of them arrived in Hainan Island from the southern Chinese provinces of Guangdong, Fujian and Guangxi.
Li people (Hlai people) are the original Kra-Dai inhabitants of Hainan. They are believed to be the descendants of the ancient tribes from the mainland, who settled on the island between 7 and 27 thousand years ago.[8]
During the Three Kingdoms Period (184−280), Hainan was the Zhuya Commandery (珠崖郡) under the control of Eastern Wu.
At the time of the Song dynasty (960−1279), Hainan became part of Guangxi, and for the first time large numbers of Han Chinese arrived, settling mostly in the north. Under the Mongol Empire (1206–1368) the island became an independent province, then in 1370 was placed under the administration of Guangdong by the ruling Ming dynasty. In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, large numbers of Han people from Fujian and Guangdong began migrating to Hainan, pushing the Li into the highlands in the southern half of the island. In the eighteenth century, the Li rebelled against the Qing Empire, which responded by bringing in mercenaries from the Miao regions of Guizhou. Many of the Miao settled on the island and their descendants live in the western highlands to this day.
During the 17th and 18th centuries, explorers referred to the island as "Aynam",[9][10] which remains the pronunciation of its name in the local Hainanese dialect.
In 1906, the revolutionary leader Sun Yat-sen proposed that Hainan should become a separate province although this did not happen until 1988.
Republic of China

Hainan was historically part of Guangdong and Guangxi Provinces and as such was the Qiongya Circuit (瓊崖道) under the 1912 establishment of the Republic of China. In 1921, it was planned to become a special administrative region (瓊崖特別行政區); in 1944, it became Hainan Special Administrative Region with 16 counties, including the South China Sea Islands.
During the 1920s and 30s, Hainan was a hotbed of Communist activity, especially after a bloody crackdown in Shanghai, the Republic of China in 1927 drove many Communists into hiding. The Communists and the indigenous Hlai people fought a vigorous guerrilla campaign against the Imperial Japanese occupation, the Hainan Island Operation (1939–45), but in retaliation the Japanese launched numerous massacres against Hlai villages. Feng Baiju led the Hainan Independent Column of fighters throughout the 1930s and 1940s. After the Japanese surrender in 1945, the Kuomintang reestablished control. Hainan was one of the last areas of the Chinese mainland controlled by Nationalist forces, lasting until March 1950.
People's Republic of China
From March to May 1950, the Landing Operation on Hainan Island captured the island for the Chinese communists. Hainan had been left to the command of Xue Yue after Chiang Kai-shek fled to Taiwan. Feng Baiju and his column of guerrilla fighters played an essential role in scouting for the landing operation and coordinated their own offensive from their jungle bases on the island. This allowed the Hainan takeover to be successful where the Kinmen (Quemoy) and Dengbu assaults had failed in the previous autumn.
The takeover was made possible by the presence of a local guerrilla force that was lacking also on Taiwan. Hence, while many observers of the Chinese civil war thought that the fall of Hainan Island to the Communists would be followed shortly by the fall of Taiwan Island, the lack of any communist guerrilla force on Taiwan Island and its sheer distance from the mainland made this impossible, as did the arrival of the US 7th fleet in the Taiwan Strait after the outbreak of the Korean War in June. Further, Hainan, although highly populated relative to many other international cities, is geographically quite small, with almost no urban sprawl. Much of the city limits end abruptly with forest or farm land.
On 1 May 1950, under the PRC, the Special Administrative Region became an Administrative Region Office (海南行政区公署), a branch of the Guangdong provincial government.
The Communists resumed development of the island along the lines established by the Japanese,[clarification needed] but the results were limited by the island's isolation, its humid and typhoon-prone climate, and its continuing reputation as a place of danger and exile by mainland Chinese. With China's shift in economic policy at the end of the 1970s, Hainan became a focus of attention.
During the mid-1980s, when Hainan Island was still part of Guangdong Province, a fourteen-month episode of marketing zeal by Hainan Special District Administrator Lei Yu[11] put Hainan's pursuit of provincial status under a cloud. It involved the duty-free imports from Hong Kong of 90,000 Japanese-made cars and trucks at a cost of ¥ 4.5 billion (US$1.5 billion), and exporting them – with the help of local naval units – to the mainland, making 150% profits. By comparison, only 10,000 vehicles were imported into Hainan since 1950. In addition, it involved further consignments of 2.9 million TV sets, 252,000 videocassette recorders & 122,000 motorcycles. The money was taken from the 1983 central government funds destined for the construction of the island's transportation infrastructure (roads, railways, airports, harbours) over the next ten years.[citation needed]
On October 1, 1984, it became the Hainan Administrative Region (海南行政区), with a People's Government, and finally as province separate from Guangdong four years later. In 1988, when the island was made a separate province, it was designated a Special Economic Zone in an effort to increase investment.
The central government funds were deemed insufficient by the Hainan authorities for the construction of the island's other infrastructures (water works, power stations, telecommunications, etc.) and had taken a very liberal interpretation of the economic and trade regulations for Hainan and thirteen coastal cities; the regulations did not mention on prohibiting the re-selling of second-hand goods. Some of the proceeds, from unsold units, were later retrieved by the central government to re-finance the special district.
In 2001 a United States Navy signals intelligence aircraft and a People's Liberation Army Navy interceptor fighter jet collided in mid-air about 70 miles (110 km) away from Hainan, resulting in an international dispute between the United States and the PRC.
In June 2020, China announced a master plan for Hainan's free trade port system. Announced by state-owned media Xinhua News Agency, "Hainan will “basically establish a free trade port system by 2025 and become more mature by 2035.”[12]
Geography
 Hainan, separated by the 30 km (19 mi) wide Qiongzhou Strait from the Leizhou Peninsula of Guangdong, is the largest island administered by the People's Republic of China and the 42nd largest in the world. The area of Hainan Island (32,900 km2 (12,700 sq mi), 97% of the province) is similar to that of Belgium or slightly smaller than that of Taiwan. To the west of Hainan Island is the Gulf of Tonkin. Wuzhi Mountain is the highest mountain on the island at 1,840 m (6,040 ft).
Hainan, separated by the 30 km (19 mi) wide Qiongzhou Strait from the Leizhou Peninsula of Guangdong, is the largest island administered by the People's Republic of China and the 42nd largest in the world. The area of Hainan Island (32,900 km2 (12,700 sq mi), 97% of the province) is similar to that of Belgium or slightly smaller than that of Taiwan. To the west of Hainan Island is the Gulf of Tonkin. Wuzhi Mountain is the highest mountain on the island at 1,840 m (6,040 ft).
Hainan Island measures 155 km (96 mi) long and 169 km (105 mi) wide.
The northern half of Hainan is covered with the ancient Hainan Volcanic Field. Beneath the topsoil is volcanic rock while the topsoil itself contains small pieces of this vesicular rock.
Wetland covers 320,000 hectares, 78,000 hectares of which were created artificially. Most of this is located in the eastern and northern part of Hainan.[13]
Rivers and lakes
Most of the rivers in Hainan originate in the central area of the island and flow radially in different directions. The Nandu River in the northern part of the island is 314 km (195 mi) long, and its tributary, the Xinwu River, is 109 km (68 mi) long. Other major rivers include the Wanquan River at 162 km (101 mi)-long in the east, Changhua River in the west, and the Sanya River in the south. Evaporation during the dry season around the coastal areas greatly reduces the flow of the rivers.
There are very few natural lakes in Hainan. However, there are numerous reservoirs, the largest of which is the Songtao Reservoir in the central-north area.
Islands
Nearby islands
Several small islands exist around the coast of Hainan Island:
- Dazhou Island is located about 5 km (3.1 mi) off the coast of Wanning
- Haidian Island, on the north coast, is part of Haikou City
- Nanwan Monkey Island, in actuality a peninsula
- Phoenix Island is an artificial resort island currently under construction in Sanya Bay.
- Wuzhizhou Island is located within Haitang Bay
- Xinbu Island is located directly to the east of Haidian Island
Due to their close proximity to the main island, the flora, fauna, and climate conditions are very similar.
Disputed islands

A number of small islands, which are located hundreds of kilometers to the south, are claimed and administrated by Sansha as part of Hainan Province.[14] Sovereignty of these islands is however disputed. These islands include:
- Paracel Islands Xisha Islands – "The West-sands" – claimed by Vietnam, the PRC and the Republic of China (Taiwan, ROC)
- Zhongsha Islands – "The Middle-sands"
- Spratly Islands – Nansha Islands – "The South-sands" are subject to claims by Vietnam, the PRC, ROC, Malaysia, The Philippines, and Brunei.
Environment
Compared to most of mainland China, the air quality of Hainan is far higher since it is not affected by factory pollution, which has adversely affected the air on the mainland. Throughout 2012, Hainan had the highest air quality in the country for 351 days.[15]
The provincial government's environmental protection campaign has taken action against a number of industrial plants. During 2012, several outdated manufacturing facilities had their business licenses revoked, and 175 cases related to illegal sewage discharge were handled.[15]
Total sulfur dioxide emissions for the province were 34,000 tons in 2012, a 3 percent year-on-year reduction. In 2011, smog emissions were reduced 6.3 percent to 15,000 tons.[15]
Province-wide infrastructure improvements
From 2015 to the present, a widespread program to improve cities and other settlements in Hainan island has been taking place. It includes the removal of litter from towns, villages, and many roadsides. Small, illegal dumps are being removed. However, illegal dumping of construction debris still occurs on rural roads. Large, plastic dumpsters have been put in place within villages and at countryside road intersections. Towns are being improved with new road and sidewalk surfaces, landscaping features are being created, and many buildings are receiving new façades.
This initiative in Haikou has seen entire neighbourhoods demolished and rebuilt, sanitation improved, illegal structures used for business removed, roadside vendors banned, roads and sidewalks replaced, and new street crossings with traffic lights installed.
Climate
| Hainan Island | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The climate of Hainan varies from subtropical to fully tropical. Northern Hainan, including the island's capital Haikou, has a humid subtropical climate, while most of the rest of the island has a tropical monsoon climate with warmer annual temperatures the further south a location is. The coldest months are January and February when temperatures drop to 16 to 21 °C (61 to 70 °F); the hottest months are July and August, and the temperatures are 25 to 29 °C (77 to 84 °F). Except for the mountainous regions in the central part of the island, the daily average temperature in Hainan in all months is well above 10 °C (50 °F).
The summer in the north is hot and, for more than 20 days in a year, the temperature can be higher than 35 °C (95 °F)[citation needed]. The average annual precipitation is 1,500 to 2,000 millimetres (59 to 79 in) and can be as high as 2,400 millimetres (94 in) in central and eastern areas, and as low as 900 millimetres (35 in) in the coastal areas of the southwest. Parts of Hainan lie in the path of typhoons, and 70% of the annual precipitation is derived from typhoons and the summer rainy season. Major flooding occurs due to typhoons, which can cause many problems for local residents.
Annual fog
From January to February, the island of Hainan is often affected by thick fog, particularly in coastal areas and the northern part of the island. This is caused by cold winter air from the north coming into contact with the warmer sea, causing the moisture that evaporates from the sea to be condensed into fog. The fog remains from day to night, and is evenly distributed. Visibility may be reduced to 50 metres (160 ft) for days at a time. During this period, residents normally keep windows shut. The moisture in the air is so extreme that the walls in homes weep, and floors often accumulate a layer of water. [citation needed]
Flora and fauna

Hainan has over 1,500 km2 (580 sq mi) of tropical forest, in which live 4,600 kinds of plants and more than 570 species of animals.[citation needed] However, due to an invasion of exotic species, human impact from tourism, deforestation, and the release of pollutants, many species are under threat. A report from the Department of Land, Environment and Resources of Hainan Province states that 200 species are near extinction, with 6 species, such as Maytenus hainanensis and Sciaphila tenella already extinct.[17]
Flora
The majority of Hainan's land mass is forest with 61.5 percent coverage (210,000 hectares) reported at the end of 2012, an increase of 34,133 hectares (84,340 acres) since 2011. A further 1,187 hectares (2,930 acres) grass and trees were planted along the province's highways.[15]

There are 53 genera in 29 families of wild and cultivated fruit growing on Hainan Island.[18] There are few large trees on the island; coconut palms are very common along with other smaller trees. Most of Hainan Island is however covered by forest.
Notable species include:
- Hainan yellow lantern chili is a pepper similar to the scotch bonnet.
- Hainan white pine, a species of tree.
- Cephalotaxus hainanensis is a species of plum-yew.
Fauna
There are numerous protected areas and wildlife preserves on the island. Animals that are ubiquitous throughout the island include frogs, toads, geckos, skinks, and butterflies. Present, but less commonly observed, are snakes (Asian palm pit vipers, red bamboo snake, and occasionally cobras), Siberian chipmunks, squirrels, and the masked palm civet. Almost no large animals remain in the wild. The lakes are largely populated with carp and catfish.
There are 362 known bird species.[17] Seabirds such as gulls are not generally seen. Egrets and Black-winged kites are common in agricultural areas. Similar to many subtropical areas, insect species are diverse, and mosquitoes are very common.
In the ocean, sea turtles and whale sharks are known to migrate in these waters.
Hainan island has rich bio-diversity of cetaceans and is the site of studying these in Chinese waters.[19] Many whales such as North Pacific right whales, western gray whales, humpback whales, and blue whales (all of these are almost extinct in Chinese waters)[20] were historically seen in the winter and spring to mate and calve. These gentle giants of the sea had been hunted heavily and were wiped out by Japanese whalers (established whaling stations on various sites on Chinese and Korean coasts including Hainan and Daya Bay). A few Bryde's whales and minke whales may still occur in the adjacent waters along with on Leizhou Peninsula and the Gulf of Tonkin.[21][22] Smaller species of whale and dolphins, such as short-finned pilot whales[23] and pantropical spotted dolphins,[24] but most notably the endangered Chinese white dolphin. Declared sanctuary for the species extends along the coasts. These dolphins may appear among clearer waters such as vicinity to Sanya.[25]
Dugongs still occur in small number, mostly on Gulf of Tonkin side.
Notable species include:
- Hainan gymnure (Neohylomys hainanensis or Hainan moonrat) is a small mammal.
- Hainan partridge (Arborophila ardens) is a species of bird endemic to Hainan Island.
- Hainan peacock-pheasant (Polyplectron katsumatae) is an endangered species of the family Phasianidae.
- Hainan black crested gibbon (Nomascus hainanus) is one of the world's most endangered primates. Seacology, a non-profit organization in Berkeley, California, United States, initiated a project to protect the highly endangered Hainan gibbon in exchange for scholarships for the children of four villages near Hainan Bawangling National Nature Reserve.
- Hainan hare (Lepus hainanus) is a species of hare endemic to Hainan.
- A subspecies of the leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis alleni) is endemic to Hainan.
- Hainan leaf-warbler (Phylloscopus hainanus) is an Old World warbler in the family Phylloscopidae.
Demographics

(Link to entire map including key).
The population density of Hainan is low compared to most Chinese coastal provinces.
In 2000, the ethnic groups of Hainan included the Han-Chinese Hainanese, who are the majority (84% of the population) and speak the Min language; the Li (Hlai) (14.7% of the population); the Miao (0.7%) and the Zhuang (0.6%).[citation needed] The Li are the largest indigenous group on the island in terms of population. Also found on the island are the Utsuls, descendants of Cham refugees, who are classified as Hui by the Chinese government because of their Islamic religion. There is a Tanka community that live at Sanya Bay.[26]
The Li people mainly reside in the nine cities and counties in the middle and southern part of Hainan – the cities of Sanya, Wuzhishan and Dongfang, the Li autonomous counties of Baisha, Lingshui, Ledong, Changjiang, and the 'Li and Miao Autonomous Counties of Qiongzhong and Baoting'. Some others live elsewhere on Hainan with other ethnic groups in Danzhou, Wanning, Qionghai, Lingshui and Tunchang. The area inhabited by the Li ethnic group totals 18,700 square kilometers (7,200 sq mi), about 55 percent of the province's total.[27]

Although they are indigenous to the island and do not speak a Chinese language, the Limgao (Ong-Be) people near the capital (8% of the Hainan population) are counted as Han Chinese by the Chinese government.
Religion

Most of the Hainanese population practices Chinese folk religion and Chinese Buddhism. The Li population has a Theravada Buddhist minority. Most of the Utsuls of the island, a branch of Cham people living near Sanya, are Muslims. Because Hainan was a point in the travel route of missionaries, there are some Christians. According to the Chinese General Social Survey of 2009, Christians constitute 0.48% of the province's population.[28]
Nanshan Park is the centre of Buddhism on Hainan Island. Encompassing more than 50 km2 (19 sq mi) of rainforest, the site includes countless grand temples, statues and spiritual gardens the likes of Saviour Garden and Longevity Valley, with intricately trimmed hedges and abundant in lotus flowers, a venerated symbol in Buddhism meaning virtue or purity.
At the heart of the valley is the grand Nanshan Temple, its gates flanked by stone figures of Buddha in front of the Tang dynasty-style entrance. The interior displays images of the Four Heavenly Kings amid statues of other deities enshrined in renderings of stone, gold and jade.
Perhaps the most popular site within the Nanshan Buddhist Cultural Zone is the awe-inspiring stone rendering of the Bodhisattva Guan Yin, emerging out of the South China Sea to stand at 108 metres, taller than the statue of liberty.
The Nanshan Buddhist Cultural Zone is visited by thousands of tourists and pilgrims each year who come pay homage to the site that plays a significant role in the religion in China and to sample some of the finest Buddhist vegan cuisine on the island.[29]
Languages
Various language families are spoken on the island:
- One of the languages commonly spoken as a lingua franca is a variant of Min Chinese, known as Hainanese. Also Standard Mandarin (Putonghua) is understood and spoken by most, and Cantonese is understood by some.
- In Yacheng City (as well as its vicinity several dozen miles west of Huihui and Huixin), the so-called military speech (the official language of the southwest among the northern Chinese dialects) is spoken.
- In Yanglan Village to the northeast, two Min dialects, both closely related to Cantonese, are spoken: the Mai dialect and the Danzhou dialect, spoken in Haipo Village in the south, which is the same dialect as the dialect spoken in Danzhou in Dan Country in the northern part of the island.
- From the east to the west along the seashore, the Hainanese dialect is used.
- In Sanya City, one can find speakers of Mandarin Chinese and Hainanese.
- In the capital city of Hainan, Haikou, Cantonese is frequently spoken by local residents.
- The Li, Zhuang and Limgao speak Tai–Kadai languages.
- The Miao speak Hmong–Mien languages.
- There are roughly 4,500 Utsul people living in the villages of Yanglan (羊栏) and Huixin (回新), two villages on the outskirts of Sanya. They speak the Tsat language, a member of the Austronesian Chamic languages.
Sociolinguistics
Standard Mandarin serves as a lingua franca between different ethnic groups. Adults who are members of a minority also have quite high literacy skills in Chinese. Most adults speak several Chinese dialects, and some also speak Li.
When Chams interact with the Hainanese dialect speakers from within Hainan Province, they use the Hainanese dialect, though youngsters generally use Mandarin. Not many can communicate in Li, so the Hainanese dialect or Mandarin is often used.
In the market place and within the Sanya Municipality, the Cham speakers use Cham among themselves, and with others mostly use the Hainanese dialect. However, in the market places near the government seat of Yanglan Township, the Chams either use the Hainanese dialect or the Mai dialect.[30]
Life expectancy and "longevity"
The people of Hainan live longer than those on the mainland. At the end of 2017, there were 1,565 centenarians in Hainan. For every 100,000 people in the province, 17.13 were centenarians. As of March 8, 2018, there were 287,700 residents over 80 years of age, making up 3.15% of the population.[31]
Government
Even while Hainan Island was a part of Guangdong it had a considerable amount of local autonomy; the southern half of the island was an autonomous prefecture. Hainan's elevation to provincial level in 1988 increased its accountability to the Central People's Government, but by designating the new province a special economic zone the central government expressed its intent to allow Hainan maximum flexibility in devising programs to facilitate foreign investment and economic growth. Administratively, the province has been divided into five economic major districts.[citation needed]
Politics
The politics of Hainan is structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in mainland China.
The Governor of Hainan is the highest-ranking official in the People's Government of Hainan. However, in the province's dual party-government governing system, the Governor has less power than the Hainan Communist Party of China Provincial Committee Secretary or CPC Party Chief.
Intelligence
Per the research conducted by Information Warfare Monitor, Hainan is the physical location of GhostNet. The Chinese government has officially denied the existence of a cyber war and intelligence apparatus.
Administrative
In the official PRC territorial claim, Hainan Province includes not just one island, but also some two hundred South China Sea Islands. Whilst the containment of the South China Sea Islands means that Hainan Province has a very large water body, it has a disproportionally small land area. James Shoal (曾母暗沙 Zengmu Ansha), which is presently marked by the PRC, signifies the country's southernmost border. But Malaysia also claims that it is on their continental shelf.
Subdivisions
Hainan Province uses a slightly different administrative system than the other provinces of China. Most other provinces are divided entirely into prefecture-level divisions, each of which is then divided entirely into county-level divisions. County-level divisions generally do not come directly under the province. In Hainan, nearly all county-level divisions (the eight districts excepted) come directly under the province. This method of division is due to Hainan's relatively sparse population of around 8 million people. At the end of year 2017, the total population is 9.26 million.[32]
| Administrative divisions of Hainan | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
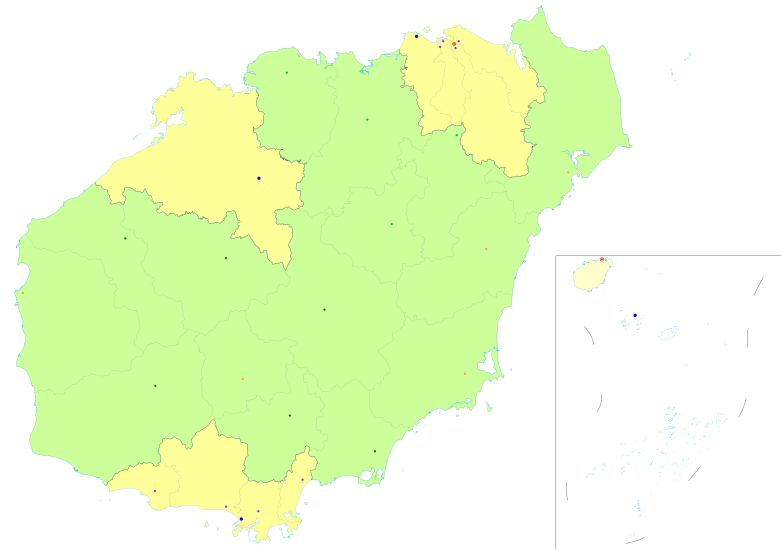
█ Provincial administered
county-level divisions ☐ Sovereignty over Sansha is disputed, see
Territorial disputes in the South China Sea. | |||||||||||
| Division code[33] | Division | Area in km2[34] | Population 2010[35] | Seat | Divisions[36] | ||||||
| Districts | Counties | Aut. counties | CL cities | ||||||||
| 460000 | Hainan Province | 35354.00 | 8,671,518 | Haikou city | 10 | 4 | 6 | 5 | |||
| 460100 | Haikou city | 2304.80 | 2,046,189 | Xiuying District | 4 | ||||||
| 460200 | Sanya city | 1910.67 | 685,408 | Jiyang District | 4 | ||||||
| 460300 | Sansha city* | ~13.00 | 444 | Xisha District | 2 | ||||||
| 460400 | Danzhou city# | 3394.00 | 932,362 | Nada town | |||||||
| 469001 | Wuzhishan city** | 1131.00 | 104,122 | Tongzha town | 1 | ||||||
| 469002 | Qionghai city** | 1710.14 | 483,217 | Jiaji town | 1 | ||||||
| 469005 | Wenchang city** | 2459.18 | 537,428 | Wencheng town | 1 | ||||||
| 469006 | Wanning city** | 1899.90 | 545,597 | Wancheng town | 1 | ||||||
| 469007 | Dongfang city** | 2272.29 | 408,309 | Basuo town | 1 | ||||||
| 469021 | Ding'an County** | 1187.00 | 284,616 | Dingcheng town | 1 | ||||||
| 469022 | Tunchang County** | 1223.97 | 256,931 | Tuncheng town | 1 | ||||||
| 469023 | Chengmai County** | 2076.28 | 467,161 | Jinjiang town | 1 | ||||||
| 469024 | Lingao County** | 1343.33 | 427,873 | Lincheng town | 1 | ||||||
| 469025 | Baisha Li Autonomous County** | 2117.20 | 167,918 | Yacha town | 1 | ||||||
| 469026 | Changjiang Li Autonomous County** | 1617.70 | 223,839 | Shilu town | 1 | ||||||
| 469027 | Ledong Li Autonomous County** | 2763.53 | 458,876 | Baoyou town | 1 | ||||||
| 469028 | Lingshui Li Autonomous County** | 1121.24 | 320,468 | Yelin town | 1 | ||||||
| 469029 | Baoting Li and Miao Autonomous County** | 1166.78 | 146,684 | Baocheng town | 1 | ||||||
| 469030 | Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County** | 2704.00 | 174,076 | Yinggen town | 1 | ||||||
| * - Sovereignty over Sansha (including the Paracel, Spratly and Zhongsha Islands) is disputed as of 24 November 2024. ** - Directly administered county-level divisions | |||||||||||
| Administrative divisions in Chinese and varieties of romanizations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Chinese | Pinyin | Hainanese Romanzation | |
| Hainan Province | 海南省 | Hǎinán Shěng | Hai Nam Teng | |
| Haikou city | 海口市 | Hǎikǒu Shì | Hai Khau Si | |
| Sanya city | 三亚市 | Sānyà Shì | Tam Ah Si | |
| Sansha city | 三沙市 | Sānshā Shì | Tam Sa Si | |
| Danzhou city | 儋州市 | Dānzhōu Shì | Dam Ju Si | |
| Wuzhishan city | 五指山市 | Wǔzhǐshān Shì | Ngou Ji Tua Si | |
| Qionghai city | 琼海市 | Qiónghǎi Shì | Kheng Hai Si | |
| Wenchang city | 文昌市 | Wénchāng Shì | Von Sio Si | |
| Wanning city | 万宁市 | Wànníng Shì | Van Neng Si | |
| Dongfang city | 东方市 | Dōngfāng Shì | Dang Fang Si | |
| Ding'an County | 定安县 | Dìng'ān Xiàn | Deng An Kuai | |
| Tunchang County | 屯昌县 | Túnchāng Xiàn | Ton Siang Kuai | |
| Chengmai County | 澄迈县 | Chéngmài Xiàn | Deng Mai Kuai | |
| Lingao County | 临高县 | Língāo Xiàn | Liom Ko Kuai | |
| Baisha Li Autonomous County | 白沙黎族自治县 | Báishā Lízú Zìzhìxiàn | Be Tua Loitoc Seji Kuai | |
| Changjiang Li Autonomous County | 昌江黎族自治县 | Chāngjiāng Lízú Zìzhìxiàn | Siang Kiang Loitoc Seji Kuai | |
| Ledong Li Autonomous County | 乐东黎族自治县 | Lèdōng Lízú Zìzhìxiàn | Loc Dong Loitoc Seji Kuai | |
| Lingshui Li Autonomous County | 陵水黎族自治县 | Língshuǐ Lízú Zìzhìxiàn | Leng Tui Loitco Seji Kuai | |
| Baoting Li and Miao Autonomous County | 保亭黎族苗族自治县 | Bǎotíng Lízú Miáozú Zìzhìxiàn | Bo Deng Loitoc Miautoc Seji Kuai | |
| Qiongzhong Li and Miao Autonomous County | 琼中黎族苗族自治县 | Qióngzhōng Lízú Miáozú Zìzhìxiàn | Kheng Tong Loitoc Miautoc Seji Kuai | |
Urban areas
| Population by urban areas of prefecture & county cities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | City | Urban area[37] | District area[37] | City proper[37] | Census date |
| 1 | Haikou | 1,517,410 | 2,046,170 | 2,046,170 | 2010-11-01 |
| 2 | Sanya | 453,819 | 685,408 | 685,408 | 2010-11-01 |
| 3 | Danzhou[a] | 418,834 | 932,356 | 932,356 | 2010-11-01 |
| 4 | Wenchang | 251,795 | 537,426 | 537,426 | 2010-11-01 |
| 5 | Wanning | 221,263 | 545,597 | 545,597 | 2010-11-01 |
| 6 | Qionghai | 194,400 | 483,217 | 483,217 | 2010-11-01 |
| 7 | Dongfang | 153,726 | 408,309 | 408,309 | 2010-11-01 |
| 8 | Wuzhishan | 53,268 | 104,119 | 104,119 | 2010-11-01 |
| (9) | Sansha[b] | 444 | 444 | 444 | 2010-11-01 |
Military base
Hainan Island is home to the People's Liberation Army Navy Hainan Submarine Base and strategic nuclear submarine naval harbor at 18°13′16″N 109°41′10″E / 18.221°N 109.686°E.[38] The naval harbor is estimated to be 60 feet (18 m) high, built into hillsides around a military base. The caverns are capable of hiding up to 20 nuclear submarines from spy satellites. The harbor houses nuclear ballistic missile submarines and is large enough to accommodate aircraft carriers. The U.S. Department of Defense has estimated that China will have five type 094 submarines operational by 2010 with each capable of carrying 12 JL-2 ballistic missiles. Two 950-metre (3,120 ft) piers and three smaller ones would be enough to accommodate two carrier strike groups or amphibious assault ships.
Economy
Hainan's economy is predominantly agricultural, and more than a half of the island's exports are agricultural products. Hainan's elevation to province-level status (1988), however, was accompanied by its designation as China's largest "special economic zone", the intent being to hasten the development of the island's plentiful resources. Prior to this, the province had a reputation for being a "Wild West" area, largely untouched by industrialisation; even today there are relatively few factories in the province. Tourism plays an important part of Hainan's economy, thanks largely to its tropical beaches and lush forests. The central government has encouraged foreign investment in Hainan and has allowed the island to rely to a large extent on market forces.[39]
Hainan's industrial development largely has been limited to the processing of its mineral and agricultural products, particularly rubber and iron ore. Since the 1950s, machinery, farm equipment, and textiles have been manufactured in the Haikou area for local consumption. A major constraint on industrial expansion has been an inadequate supply of electricity. Much of the island's generating capacity is hydroelectric, and it is subject to seasonal fluctuations in stream and river flows.[40]
In December 2009, the government of China announced that it plans to establish Hainan as an "international tourist destination" by 2020.[41] This announcement contributed to a surge in the province's economy, with a year-on-year increase in investment of 136.9% in the first three months of 2010. Hainan's real estate sector accounted for more than one third of the province's economic growth.[42]
According to the Statistical Communiqué of National Economic and Social Development of the statistical authority, the GDP of Hainan Province in 2017 was 446.3 billion yuan (66.1 billion US dollars), up by 7.0 percent over the previous year. Of this total, the value added of the primary industry was 97.9 billion yuan (14.5 billion US dollars), up by 3.6 percent, that of the secondary industry was 99.7 billion yuan (14.8 billion US dollars), up by 2.7 percent and that of the tertiary industry was 248.6 billion yuan (36.8 billion US dollars), up by 10.2 percent. The value added of the primary industry accounted for 21.95 percent of the GDP; that of the secondary industry accounted for 22.34 percent; and that of the tertiary industry accounted for 55.71 percent. The per capita GDP in 2017 was 48,430 yuan (7,173 US dollars).[43]
Agriculture

Owing to Hainan's tropical climate, paddy rice is cultivated extensively in the northeastern lowlands and in the southern mountain valleys.[41] Leading crops other than rice include coconut, palm oil, sisal, tropical fruits (including pineapples, of which Hainan is China's leading producer), black pepper, coffee, tea, cashews, and sugarcane.
The hot Hainan yellow lantern chili, a variety similar to the scotch bonnet, is unique to the island, and is grown in the southeast and southwest.
The total tropical crop area of Hainan is 100,000 hectares.[44]
Hainan is a major rubber producer. In the early 20th century Chinese emigrants returning from then British Malaya, introduced rubber trees to the island; after 1950, state farms were developed, and Hainan now produces a substantial amount of China's rubber. Natural rubber is now grown on 246,000 hectares of land. This ranks 6th in the world in harvest area and 5th in terms of output.[44]
Hainan has almost 93,000 hectares of areca palms. The product, the areca nut, is consumed locally and also sent to the mainland. Ninety-five percent of China's production of this nut is produced in Hainan.[45]
Domesticated farm animals comprise mainly goats, cows, water buffalo, chickens, geese and ducks.
Fisheries

Grouper, Spanish mackerel, and tuna[citation needed] constitute the bulk of the catch from offshore fishing grounds. Scallops and pearls are raised in shallow bays and basins for local use and export.
Shrimp production is estimated to have been 120,000 to 150,000 metric tons (130,000 to 170,000 short tons) in 2007, more than 50% of which was exported. Hainan has over 400 hatcheries, most being located between Wenchang and Qionghai.
Tilapia production in 2008 was 300,000 metric tons (330,000 short tons). The island has an estimated 100,000 local, commercial fish farming families.[46]
Tourism

Hainan Island is often divided into eight regions for tourism purposes: Haikou and area (Haikou, Qiongshan, Ding'an); the Northeast (Wenchang); the Central East Coast (Qionghai, Ding'an); the South East Coast; the South (Sanya); the West Coast also called the Chinese Riviera (Ledong, Dongfang, Xianghsui, Changjiang); the North West (Danzhou, Lingao, Chengmai); and the Central Highlands (Baisha, Qiongzhong, and Wuzhishan/Tongzha).
Popular tourist destinations include the beaches and resorts in the southern part of the province. Inland is Five Finger Mountain, a scenic area. Tourists also visit the capital of Haikou with area visitor attractions such as Movie Town Haikou and Holiday Beach.
Visa requirements
In 2000, the province initiated a visa-upon-arrival policy for foreign tourist groups. It is available to citizens of twenty-six different countries, and was established in order to attract visitors.
Beginning May 1, 2018, citizens of 59 countries will be able to visit Hainan for 30 days without requiring a visa, provided that they come on a tour via a travel agency. Countries included among the 59 are: Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Indonesia, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, the Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Russia, Singapore, Spain, South Korea, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, UAE, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, and the United States.[47]
Statistics
During 2008, 20.6 million tourists visited Hainan, producing total revenues of 19.23 billion yuan (US$2.81 billion). Of these tourists, 979,800 were from overseas with the largest numbers coming from South Korea, Russia and Japan.[48]
In 2010, the amount of overnight tourists visiting Hainan was 25.87 million, 663,000 of which came from outside China.[49]
During 2011, more than 30 million tourists visited Hainan, mostly from mainland China. Of the 814,600 overseas tourists, 227,600 of them came from Russia, a 53.3 percent a rise year-on-year.[50] Total revenue during that year was 32 billion RMB ($4.3 billion US), up 25 percent from 2010.[51]
In the first quarter of 2012, the Hainan Provincial Tourism Development Commission reports that Hainan received 208,300 overnight visitors, 25 percent of whom came from Russia.[50]
In 2014, Hainan received 50.2 million tourists, 660,000 of whom were from overseas.[52]
During 2015, Hainan received 53 million visitors.[53][53]
In 2016, over 60 million tourists went to Hainan, up 12.9% from 2015.[54]
In 2017, Hainan received more than 1.1 million overseas tourists.[55]
During 2018, the province received over 76 million domestic and overseas tourists, a year-on-year increase of 11.8%. Revenue also increased 14.5% compared to the previous year for a total of 95 billion RMB (14 billion USD).[56][57]
Medical tourism
The government of Hainan is expanding the province's medical tourism industry.[58][59] The provincial government has established the Boao Lecheng International Medical Tourism Pilot Zone in the Bo'ao area. The zone is located six kilometers from the Boao Forum for Asia and covers 20 square kilometers.[60] This was announced at the Boao Forum for Asia in 2011.[61] The State Council has approved the development of Lecheng Island[62] as a medical tourism-themed destination.[63] Lecheng Island is a small island in the Wanquan River about 3 km (1.9 mi) west of the coastal town of Bo'ao on the west coast of the province. Construction on the 20 km2. The zone was begun in December 2014 and will cost a projected 1.5 billion yuan. It was scheduled for completion in 2016 and is the first special zone for medical travel in China.[64] As part of the zone, the Boao Super Hospital opened in 2018.
Historical sites
Haikou is the province's capital and contains interesting historic sites. Also known as Coconut City, Haikou is a major port. The Five Officials Temple (Chinese: 五公祠; pinyin: Wŭgōng cí, 20°0′35.79″N 110°21′17.34″E / 20.0099417°N 110.3548167°E) consists of five traditional temples and halls that were built in honour of five officials of the Tang (618-907) and Song (960-1279) dynasties. These officials were banished to Hainan for periods ranging from 11 days to 11 years for speaking out against what they felt were wrong practices by the emperors. (It is perhaps significant that the establishment of the Five Officials Temple in the late 19th century coincides with a time when China's territorial integrity was under threat, and that several of the officials honoured here were exiled for espousing aggressive policies on the recapture of the north of China from the Jurchens during the Southern Song dynasty.)
Xiuying Fort was built in 1891 to defend the southeastern corner of China during the Sino-French War. The Xiuying Fort Barbette covers about a third of an acre. Its five large cannons are still intact and viewable at the site.

The Tomb of Hai Rui (20°0′29.66″N 110°17′30.18″E / 20.0082389°N 110.2917167°E) is a key national cultural protection site. Hai Rui was a compassionate and popular official of Hainanese origins who lived during the Ming dynasty. He was famous for his lifelong honesty and his willingness to speak out on behalf of local people. In later life, Hai Rui was persecuted and fell out of favour with the emperor. His admirers built the Hai Rui Tomb after his death to commemorate his great works. Construction of the tomb began in 1589.
The Yangpu Ancient Salt Field is a heritage site in Yantian village on Yangpu Peninsula. The area comprises more than 1,000 stones, cut flat on top, used to dry seawater to produce salt.
Other attractions and destinations

Hainan Island has a number of beaches, hot springs and other attractions. Some top scenic sites include Yalong bay National Resort; Dadonghai Tourist Resort; Qizhi Shan (Seven Finger Mountain), Nuilin mountain tropical botanical reserve in Lingshui county, Guantang Hot Spring Resort, Shishan Volcanic Garden; the Wanquan River, Baishi Ridge Scenic Zone and Baihua Ridge.
Other attractions in Hainan include:
- Phoenix Island, an artificial island in Sanya Bay.
- Monkey Island, near the well-known perfume bay or Xiangshui Wan, a popular tourist destination located in Lingshui County, is a state-protected nature reserve for macaques.
- Yalong Bay (Crescent Dragon Bay or Yalong Wan), a 7 km (4.3 mi) long beach east of Sanya City.
- Xiangshui Bay Scenic Area, 48 km (30 mi) from Sanya Tiandu.
- Luobi Cave, 15 km (9.3 mi) north of Sanya City.
- Nanshan Temple, a Buddhist cultural area west of Sanya featuring a 108 metres (354 ft) statue of Guanyin, Buddhist Goddess of Mercy.
- Yanoda is a rainforest area. It is open to visitors with guided walking tours, a zipline, and a waterfall climbing activity.
Yachting
To encourage the international yachting community, new regulations now allow foreign yachts to stay for a total of 183 days each year, with a maximum single stay duration of 30 days. 13 additional ports will be built around the island to accommodate this market.[49]
Free trade zone
On April 13, 2018, Communist Party general secretary Xi Jinping announced a plan to gradually make the island into a pilot free trade zone by 2020, and transform the entire island into a free trade port by the year 2025. This will involve inviting foreign and multi-national companies to set up their regional and international headquarters in Hainan.[65] Goods and services would be subject to low or even no tariffs. The zone will become China's largest free trade zone, and the first trade port since 1949, when the People's Republic of China was founded.[66] Part of the plan is to establish exchanges in commodities and carbon trading, international energy, and shipping. Emphasis will also be placed on the development of service industries including tourism, the Internet, healthcare, finance, as well as conference and exhibitions hosting.[66]
Since the announcement in April 2018, Hainan had signed 159 contracts with major companies. In September 2018, China National Travel Service Group, China's biggest travel business conglomerate, relocated its headquarters from Beijing to Haikou. In October 2018, Baidu and Hainan signed a deal to built a 10-billion-yuan (US$1.45 billion) eco-village.[67]
In September 2018, a symposium was held in Beijing on foreign investment projects in Hainan. During that gathering, the Hainan government signed contracts with 26 international companies including Globevisa Group, Merlin Entertainments Group, Viacom, Ikea Group, Mapletree Investments, Avis Budget Group, Star Cruises, and Boehringer Ingelheim.[67]
To bring talented workers to Hainan, in November 2018 the Hainan government held a recruitment fair in Beijing in an effort to bring 7,471 people to Hainan to work in government agencies, companies, and other institutions.[68]
Established prior to this announcement, and currently in existence, are the following economic and technological development zones:
- Haikou Free Trade Zone
- Haikou New & Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
- Yangpu Economic Development Zone
Duty-free program
On April 20, 2011, a pilot duty-free program commenced with the aim of increasing luxury goods purchases. It permits domestic Chinese visitors to claim tax refunds on imported luxury items purchased within the province. The maximum value is set at 5,000 yuan (US$762), with lowered tax rates on purchases over 5,000 yuan.[69] In October 2012, duty limits were raised to 8,000 yuan ($1,273), and became available to both domestic and international tourists.[70]
The total sales of duty-free products for 2012 was 2.4 billion yuan.[71]
The world's largest duty-free shopping complex is scheduled to open in Haitang Bay in August 2014.[72]
During 2018 Spring Festival, Hainan recorded a 25% increase in duty-free revenue, with 450 million yuan ($71 million) in sales. The two duty-free shops, located in Sanya and Haikou, received about 99,000 customers, a 32% gain.[73]
During the entire 2018 year, the two duty-free shops had sales of more than 10 billion RMB and received 2.88 million customers.[56]
Natural resources
Hainan has commercially exploitable reserves of more than 30 minerals. Iron, first mined by the Japanese during their occupation of the island in World War II, is the most important. Also important are titanium, manganese, tungsten, bauxite, molybdenum, cobalt, copper, gold, and silver. There are large deposits of lignite and oil shale on the island, and significant offshore finds of oil and natural gas have been discovered. Virgin forests in the interior mountains contain more than 20 commercially valuable species, including teak and sandalwood.
Real estate market
In 1990, Hainan province was the site of the largest property bust in modern Chinese history[41] With 2009 and the announcement of the Chinese Government's plan to develop the province into a major international tourist location, property sales rose by 73%, creating the possibility of another bubble in Hainan's property market.[41]
Since March 2010, commercial and residential property values in some parts of Hainan have slowed down since the market peaked in February. In March, average month-on-month transaction prices dropped 12.82% to 12,280 RMB per square meter, with a reduction in volume to 627,000 square metres (6,750,000 sq ft), a 19.05% decline. Later in April, prices declined 2.84% to 11,932 yuan per square metre, with a 57.59% decline in volume to 567,200 square meters (6,105,000 sq ft). Then in May prices declined a further 29.74% from the previous month to 8,483 yuan per square metre, with a 57.95% decline in volume to 229,000 square metres (2,460,000 sq ft).[74] However, property prices in the tourist resort of Sanya remain strong as of January 2011, with prime developments selling at prices of up to 80,000 RMB per square metre.
Data for 2016 data shows that Hainan saw an increase in house sales of 44%. Volume in sales was 129 billion RMB ($18.82 billion) which is a rise of 51.2 percent year-on-year. During that year in November, commercial apartments in Sanya sold for 20,695 RMB per square meter a rise of 15.75% year-on-year. The total amount of Sanya real estate sold during that time was 212,400 square metres.[75]
Out of China's twenty leading real estate developers, eighteen had invested in Hainan during 2016.[75]
In the beginning of 2017, the price for a house in Haikou was approximately 8,000 RMB ($1,170) per square meter and $20,000 RMB ($2,977) per square meter in Sanya.[76]
New 2018 regulations
On April 23, 2018, new rules came into effect regarding home purchases in Hainan. To be able to buy a house, non-Hainan residents must prove that they have a minimum of one family member who has been paying taxes or social security for at least 2 years.
Those non-Hainan residents who wish to purchase a house in Haikou, Sanya and Qionghai must prove that they have a minimum of one family member who has been paying taxes or social security for at least 5 years.
In Wuzhishan, Baoting, Qiongzhong and Baisha (the "central ecological core areas"), houses may only be purchased by local residents.
When non-residents do buy a property, the down payment must be at least 70 percent. In order to curb speculation, owners may not sell their property for five years after receiving their ownership certificate.[77]
Golf industry
This industry is expanding in Hainan, with numerous courses being constructed, including Mission Hills Haikou, which is one of the largest golf complexes in the world. The golf industry attracts foreign investment and overseas golfers from such countries as Australia, South Korea, and Japan.
Automotive industry
Automotive manufacturing is one of Eight industrial pillar industries. Hainan's automotive output was 39,600 in 2017, down by 41.1 percent over the previous year. Domestic Chinese manufacturer,[43] Haima Automobile has its global headquarters in Haikou.
Foreign trade
As of 2017, the total value of imports and exports of goods reached 70,237 million yuan (10,403 million US dollars). Of which, the value of goods exported was 29,566 million yuan (4,379 million US dollars), the value of goods imported was 40,671 million yuan (6,024 million US dollars).[43]
Asean was Hainan's largest export trade partner in 2017, the value of goods exported to Asean was 12,289 yuan (1,820 million US dollars), accounted for 41.56 percent of the total value of goods exported. Its second-largest foreign trade partner was Hong Kong, the value of goods exported to Hong Kong was 2,966 yuan (439 million US dollars), accounted for 10.03 percent of that. the 3rd largest partner was EU, the value of goods exported to EU was 2,186 yuan (324 million US dollars), accounted for 7.39 percent of that.[43]
Transport
Road

Before 1950 there were practically no transport links with the interior of the island. The first roads were built in the early 20th century, but no major road construction was undertaken in the mountains until the 1950s. Parallel north–south roads along the east and west coasts and through the interior of the island constitute most of Hainan's road network.
Hainan is the only province in China that does not have highway toll stations. This is due to the 1994 "fee-to-tax" reform.[66]
There are several major highways and expressways linking Haikou on the north coast with Sanya on the south coast. The G224 is 309 kilometres long and runs through the middle of the province. The Hainan Ring Highway has three parts: The G225 is 429 km (267 mi) long and is the western part. For most of its length, the G225 runs parallel to the Hainan western ring railway. The G223 is the eastern part, running from Haikou to Sanya. It is 323 kilometres long. The G98 is a 612.8-kilometre-long orbital expressway that encircles the island. Hainan Highway 1, a new 1,040-km-long scenic highway, will be built around the island, along the coast starting in May 2019.[78]
There are also numerous rural roads within the province. These are typically two-way asphalt roads and connect larger towns. Connecting the thousands of villages to one another and to farms, are concrete roads about 6 metres wide. Many of these were built from roughly from the year 2000 onward, and as of 2019, are still being built.
Bridges
While a bridge connecting Hainan to the Leizhou peninsula on the mainland was planned in the early 2000s it never came to fruition. A bridge or tunnel received continued consideration in 2018, as travel by air or ferry can leave residents and visitors isolated when bad weather sets in.[79]
Air
Hainan Province has two international airports (Haikou Meilan International Airport and Sanya Phoenix International Airport) and two domestic airports (Qionghai Bo'ao Airport and Danzhou Airport, the latter is under construction.)
Rail

Today's Hainan is ringed by standard-gauge railways. Since 2004, a rail ferry connects the island's railroad network to Guangdong, mainland China.[80] In 2005, Ministry of Communications allocated 20 million yuan (US$2.4 million) to set up a committee to research and study the possibility of a bridge or tunnel link connecting the island to the mainland.[81] From the ferry terminal, located near Haikou railway station (west of Haikou), freight and passenger trains arriving from the mainland can proceed on the Hainan western ring railway along the island's west coast, via Dongfang to Sanya. This railway line has been developed over several decades, starting with a few short 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm) narrow gauge lines constructed during the Japanese occupation in the early 1940s.
There is a high-speed railway ring around the island, formed by the eastern ring and western ring along the island's coast. Both high-speed railways are connected with Haikou and Sanya. There are 15 stations along the east coast, and 16 stations along the west coast. Trains are designed to travel at 250 km/h (160 mph) on the east ring, and 200 km/h (120 mph) on the west ring. The total length of eastern ring is 308.11 km (191.45 mi), while the western ring is 344 kilometres (214 mi).[82] The first eastern ring high-speed train run started on 30 December 2010,[83] and the Hainan western ring high-speed railway started its operation in 2015. The western ring high-speed railway is roughly paralleling the existing Western Ring Railway.[84]
Seaports

- Haikou Xiuying Port (海口秀英港) serves as the main passenger and cargo center.[85]
- Haikou New Port (海口新港) opened June 1, 2005[85]
- Macun Port (馬村港) located in Chengmai County; opened June 1, 2005[85]
- Hainan Strait Port[86]
- Basuo Port in Dongfang City is a small port on the west coast of Hainan. One of its main cargos is iron ore from the Shilu Mine.
Hainan received 11,000 tons of products via ports November 2010, up 90.1 percent month-on-month. Between January and November 2010, 102,000 tons of products were exported via Hainan, 34,000 tons of which were exported to the US, and 14,000 tons sent to the EU.[87]
Education

The level of primary and secondary education has improved since 1949, but facilities for higher education remain somewhat inadequate.[citation needed]
- Hainan University (海南大学)
- Hainan Normal University (海南师范大学)
- Qiongzhou University (琼州大学)
- Hainan Medical Institute (海南医学院)
- Haikou College of Economics (海口经济学院)
- South China Tropical Agricultural University (华南热带农业大学, merged into Hainan University on Aug 14, 2007)
Culture

As a frontier region celebrated by such exiled poets as Su Dongpo, Hainan acquired an air of mystery and romance. The influx of large numbers of mainlanders after 1950 – particularly in the 1970s, when young Chinese from southern Guangdong were assigned to state farms to help develop Hainan, and in the 1980s, when thousands more came to take advantage of the economic opportunities offered – has perpetuated the frontier atmosphere on the island.
Media
As well as programming from Central China Television (CCTV), Hainan has a number of local TV stations including Hainan TV and Haikou TV. The Chinese language Nanguo Metropolis Daily, Haikou Evening News, and Hainan Daily newspapers are published in Haikou.
A large movie studio is located in the south part of Haikou. Movie Town Haikou comprises several studio buildings and an artificial town used as filming sets and a visitor attraction.
Cuisine

Hainan cuisine is said to be "lighter, with mild seasonings." A lot of local taste is mixed with the Han Chinese taste. Seafood predominates the menu, as shrimp, crab, fish and other sea life are widely available.
Wenchang chicken is a dish known throughout the province of Hainan. Although there are many varieties of this dish, the name is usually used to define a type of small, free-range chicken from Wenchang, located on the east coast of the province. As opposed to battery chickens, its meat has more texture and is somewhat drier.
Hainan chicken rice / Coibui is a famous dish in Southeast Asia, particularly Singapore and Malaysia, bearing the region's name. However, whilst many restaurants use chicken fat to quickly add flavour to the dish, the proper local method is to 'marinate' the rice with chicken soup to add a more full flavour.
Events
Numerous events are hosted or sponsored on the island, including:
- Swatch Girls World Pro China - Annual Elite Women's surfing competition, held at Wanning[88]
- Hainan International Surfing Festival, held annually at Riyue Bay, Wanning[89]
- Miss World beauty pageant is regularly held in the city of Sanya.
- Mission Hills Star Trophy is an annual golf tournament that started in 2010.
- Tour of Hainan bicycle race
- Hainan Rendez-Vous, an annual four-day event that draws China's ultra high-net-worth individuals to the Chinese Riviera-like shores of Hainan[90]
- Ironman triathlon
- Boao Forum for Asia, held in Boao, is an international high-level government, business, and academia forum.
- H1 Hot Air Balloon Challenge is held annually in Haikou. Balloons from across the nation fly over the Qiongzhou Strait from Haikou to a designated location on the mainland in Xunwen County, Guangdong.[91][92]
Miscellaneous topics
- The novel, Red Detachment of Women, by Liang Xin, was set in Hainan. The novel was first adapted to a feature film in the 1950s, and then a ballet in the 1960s as one of the Eight model plays. Most of the people of that time derived their romanticized image of Hainan Island from the scenes in the ballet, particularly that of the vivid forests of coconut trees, the Five Finger Mountain (Wuzhi Shan), and the Wanquan River.
- Parts of the 2010 movie If you are the One 2 (非诚勿扰 2) were shot in Shimei Bay (石梅湾) near Sanya.[93]
- Two notable lighthouses are located on Hainan: the Baishamen Lighthouse and Mulantou Lighthouse are among the tallest in the world, the latter being the tallest in China.
- 3024 Hainan, named after the province, is an outer main-belt asteroid discovered in 1981.
- Hainan Kopi Tales is an award-winning Singaporean Chinese drama serial set in a famous Hainan coffee shop that explores the Hainanese way of life from the 1960s to the 1980s.
- Hainan Resort is also a multiplayer map in the 2013 video game Battlefield 4.
Space centre
One of China's satellite launch centers is located in Hainan east of the city of Wenchang. The Wenchang Satellite Launch Center, a 1,200 hectares (3,000 acres) facility, is the closest Chinese launch center to the equator. The construction plan was first announced in October 2007. The new launch centre began operations on November 3, 2016 with the Long March 5 rocket making its maiden flight.
Notable residents
The poet Su Shi (1036–1101) popularized Hainan's isolation and exoticism when he was exiled there under the Song dynasty. The Dongpo Academy was built on the site of the residence where he lived in exile.
Hai Rui (1514–1587) was a famous Chinese official of the Ming dynasty. His name has come down in history as a model of honesty and integrity in office.
Chih-Ping Chen (1906-1983) was a distinguished diplomat and statesman for the Republic of China, who served to build the Yunnan-Burma Road, and a diplomatic career that spanned four decades.
The most well-known native of Hainan is Chinese-American Methodist minister turned businessman, Charlie Soong, father of the Shanghai-born Soong sisters: Soong Ai-ling, wife of H. H. Kung (once China's richest man); Soong Ching-ling, wife of Sun Yat-Sen; and Soong Mei-ling, wife of former ROC President Chiang Kai-shek.
International partnership
Hainan has international relationships with these places:[94]
| Sister state/province | Sovereign country | Date of Establishing Sisterhood Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Hyogo | Japan | Sept. 28, 1990 |
| Hawaii | United States | June. 30, 1992 |
| Jeju | South Korea | Oct. 06, 1995 |
| Crimea | Ukraine | Apr. 15, 1996 |
| Cebu | Philippines | June. 09, 1996 |
| Arad | Romania | Sept. 27, 2000 |
| Salzburg | Austria | Oct. 24, 2000 |
| Prince Edward Island | Canada | June 20, 2001 |
| South Sinai | Egypt | Aug. 03, 2002 |
| Oulu | Finland | Dec. 11, 2002 |
| Baleares | Spain | July. 29, 2004 |
| Phuket | Thailand | Sept. 25, 2005 |
| Southern Province | Sri Lanka | Apr. 23, 2005 |
| Canary | Spain | Nov. 11, 2005 |
| Lubuskie | Poland | Feb. 24, 2006 |
| East New Britain | Papua New Guinea | Sept. 28, 2006 |
| Kampong Cham | Cambodia | Mar. 27, 2006 |
| Quang Ninh | Vietnam | Apr. 19, 2007 |
| Quintana Roo | Mexico | Sept. 30, 2008 |
| Kyzylorda | Kazakhstan | July 3, 2009 |
| Parana | Brazil | March. 13, 2010 |
| Gotland | Sweden | Nov. 02, 2010 |
| Sardinia | Italy | Oct. 13, 2011 |
| Bali | Indonesia | Oct. 20, 2011 |
| Nampula | Mozambique | Sept. 18, 2013 |
| Penang | Malaysia | Nov. 07, 2013 |
| South Moravian Region | Czech Republic | Apr. 29, 2016 |
| Pest | Hungary | Jun. 12, 2016 |
| Luang Prabang | Laos | July 16, 2016 |
See also
Note
- ^ Island of Taiwan, which is slightly larger, is claimed but not controlled by the PRC. It is instead controlled by the Republic of China, a de-facto separate country.
References
- ^ "Doing Business in China - Survey". Ministry of Commerce - People's Republic of China. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
- ^ "People's Government of HaiNan Province". en.hainan.gov.cn.
- ^ 海南省2017年国民经济和社会发展统计公报 (in Chinese). Statistical Bureau of Hainan Province. 2018-01-24. Retrieved 2018-06-22.
- ^ 《2013中国人类发展报告》 (PDF) (in Chinese). United Nations Development Programme China. 2013. Retrieved 2014-05-14.
- ^ Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D., eds. (2017). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (20th ed.). Dallas, Texas: SIL International. Chinese, Min Nan.
- ^ "Why is the South China Sea contentious? - BBC News". Retrieved 2016-08-16.
- ^ Chen, Stephen. "China's southern island of Hainan born out of Vietnam millions of years ago: study". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 2017-04-29.
- ^ "Tracing the legacy of the early Hainan Islanders – a perspective from mitochondrial DNA". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 15 February 2011. Retrieved February 18, 2011.
- ^ "Map of the Island of Aynam". Atlas of Mutual Heritage. Retrieved February 2, 2015.
- ^ Dampier, William (1729). Mr. Dampier's Voyages. Mr.Dampiers Voyages Around the World. Vol. 2. London: James & John Knapton.
- ^ Subsequently Vice Mayor of Shenzhen SEZ (May 1985 to January 1988), Executive Vice Mayor of Guangzhou (January 1988 to April 1992) and Vice Chairman of Guangxi AR (April 1992 to January 1996).
- ^ "China Focus: China releases master plan for Hainan free trade port - Xinhua | English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2020-06-02.
- ^ "China's Hainan island has 320,000 hectares of wetland". www.ecns.cn.
- ^ 电子地图 – 海南省人民政府网站. Hainan People's Government. Archived from the original on 2010-08-05. Retrieved 2010-08-09.
- ^ a b c d Li Fusheng; Huang Yiming (25 June 2013). "Hainan Special: Report: Hainan grew greener in 2012". China Daily.
- ^ "NASA Earth Observations Data Set Index". NASA. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ a b "200 Species on Verge of Extinction in Hainan". English.cri.cn. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ Gwinnell, Philip; Han, Bin (2010), China's Emerging Jewel, Hainan, The Definitive Guide, ISBN 978-7-5501-0016-9., p.23-26
- ^ 海南岛鲸类搁浅记录数据库(1993 ~ 2015 年) (pdf). 中国科学数据. 2. 2016. doi:10.11922/csdata.170.2015.0029. Retrieved March 5, 2017.
- ^ "Identification Guide for Marine Mammals In the South China Sea". The Sanya Institute of Deep-sea Science and Engineering at The Chinese Academy Of Sciences. Retrieved 2015-01-19.
- ^ 中华人民共和国濒危物种科学委员会. [濒危物种数据库 - 鳀鲸 Balaenoptera edeni Anderson, 1879]. the CITES. Retrieved on December 7, 2014
- ^ Wang, Peilei (王丕烈) (1984). 中国近海鲸类的分布. CNKI.NET. 辽宁省海洋水产研究所 (Liaoning Ocean and Fisheries Science Research Institute. Retrieved December 7, 2014.
- ^ "Injured whale could survive after intensive care". China Internet Information Center. Retrieved 2017-04-29.
- ^ "Blogger". cetabase.blogspot.jp.
- ^ "Archived copy" 海南海洋生态保护良好,成为大型珍稀海洋动物的“乐园”. hnfjz.com. Archived from the original on March 5, 2017. Retrieved March 5, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). - ^ "'Water gypsies' fear lifestyle sea change". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2017-04-29.
- ^ "Population and People of Hainan Island".
- ^ China General Social Survey (CGSS) 2009. Report by: Xiuhua Wang (2015, p. 15) Archived 2015-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "wenewsit.com". wenewsit.com. Archived from the original on 2011-09-21. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ Thurgood, Graham. "Sociolinguistics and contact-induced language change: Hainan Cham, Anong, and Phan Rang Cham.". 2006. Tenth International Conference on Austronesian Linguistics, 17–20 January 2006, Palawan, Philippines. Linguistic Society of the Philippines and SIL International.
- ^ "More than 1,500 centenarians live in south China's Hainan - Xinhua | English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved Jul 26, 2020.
- ^ 中国统计年鉴—2018. www.stats.gov.cn. Retrieved 2019-08-10.
- ^ 中华人民共和国县以上行政区划代码 (in Simplified Chinese). Ministry of Civil Affairs.
- ^ Shenzhen Bureau of Statistics. Archived copy 《深圳统计年鉴2014》 (in Simplified Chinese). China Statistics Print. Archived from the original on 2015-05-12. Retrieved 2015-05-29.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Census Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China; Population and Employment Statistics Division of the National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China (2012). 中国2010人口普查分乡、镇、街道资料 (1 ed.). Beijing: China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
- ^ Ministry of Civil Affairs (August 2014). 《中国民政统计年鉴2014》 (in Simplified Chinese). China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-7130-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ a b c 国务院人口普查办公室、国家统计局人口和社会科技统计司编 (2012). 中国2010年人口普查分县资料. Beijing: China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-6659-6.
- ^ "China Builds Secret Nuclear Submarine Base in South China Sea". FoxNews.com. 2008-05-02. Retrieved 2009-05-03.
- ^ 海南省人民政府关于扩大对外开放积极利用外资的实施意见. Hainan People's Government. 2017-12-06. or hainan.gov
- ^ 海南岛综合开发计划(摘要). hnszw.org. 2011-09-30.
- ^ a b c d "Hainan Province: Economic News and Statistics for Hainan's Economy". Thechinaperspective.com. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "Hainan officials rule out bubble burst". Chinadaily.com.cn. 2010-05-10. Retrieved 2010-08-09.
- ^ a b c d 海南省2017年国民经济和社会发展统计公报. Hainan People's Government. 2018-01-24., hinews.cn (2018-01-24) or wzs.gov (2018-02-08)
- ^ a b "CEIS, HSF release Xinhua HSF Price Indices in S. China Haikou".
- ^ "Public health warning a tough nut to crack - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved Jul 26, 2020.
- ^ "Sustainable Aquaculture in South China – Shrimp and Tilapia Farming in Hainan and Guangdong Provinces". Euchinawto.org. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "Hainan to offer 30-day visa-free period for visitors from 59 countries". www.ecns.cn.
- ^ "Hainan tourism Hainan on the way to become the new Hawaii ?". eTurboNews.com. Retrieved 2010-08-09.
- ^ a b "China opening up Hainan Island to the world". The Independent. London. 2011-03-31.
- ^ a b "Sanya big draw for tourists - Xinhua | English.news.cn". News.xinhuanet.com. 2012-05-01. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ "Leader in Hotel, Airlines, Tourism and Travel Trade News - Hainan unveils plans to boost infrastructure, flight connectivity". TTG Asia. 2012-05-03. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ http://business.asiaone.com/news/interview-developing-hainan-tourism-hub
- ^ a b "53 million tourists flock to Hainan". 11 March 2016.
- ^ "Is the 'Hawaii of China' becoming the new Dubai?". 20 September 2017.
- ^ Times, Global. "China's Hainan lures global travelers with more than beaches - Global Times". www.globaltimes.cn.
- ^ a b "Hainan receives over 76 mln tourists in 2018 - Xinhua | English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved Jul 26, 2020.
- ^ "Hainan to promote language learning - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved Jul 26, 2020.
- ^ "Hainan steps up learning process with Spain visit". Medicaltourism.com. 2011-09-16. Archived from the original on 2013-05-04. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ "China Drive". English.cri.cn. 2011-12-07. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ 代艳. "Super Hospital opens in Boao, Hainan - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn.
- ^ Dong Qingpei (董庆沛) (2011-04-25). "China in key position to attract medical tourists". China.org.cn. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ Qionghai, Hainan (1970-01-01). "19.142995,110.526272 - Google Maps". Maps.google.ca. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
- ^ F_100585 (2012-07-02). "Hainan makes foray into int'l medical tourism (2) - People's Daily Online". English.peopledaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2012-11-16.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Construction on Hainan's Boao Lecheng Int'l Medical Travel Zone to start in 2014 - What's On Sanya". Retrieved Jul 26, 2020.
- ^ "Hainan plans good news for free trade". www.ecns.cn.
- ^ a b c "China Focus: Tropical island on forefront of next phase of China's reform, opening-up - Xinhua - English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com.
- ^ a b 李齐. "Province burns bright as investment hot spot amid industrial boom - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn.
- ^ 刘小卓. "Hainan to launch major recruitment fair in Beijing - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn.
- ^ "The Business of Luxury and Culture in China". Jing Daily. 2011-04-18. Retrieved 2013-01-25.
- ^ "The Business of Luxury and Culture in China". Jing Daily. 2012-10-02. Retrieved 2013-01-25.
- ^ F_221. "Hainan tax rebate attracts 1.6 million tourists for shopping - People's Daily Online". English.peopledaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2013-01-25.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ 李齐. "HK, Jeju and Okinawa, now Hainan! - Business - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn.
- ^ "People's Government of HaiNan Province". en.hainan.gov.cn.
- ^ "CapitalVue News: Hainan Property Market Collapses". Capitalvue.com. 2010-06-17. Retrieved 2010-08-09.
- ^ a b "Favorable climate in Hainan attracting holiday investors". www.ecns.cn.
- ^ "Tips on buying property". www.ecns.cn.
- ^ "Hainan places tougher restrictions on property purchases". www.ecns.cn.
- ^ "New highway lets tourists drive around Hainan Island - Chinadaily.com.cn". global.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved Jul 26, 2020.
- ^ "Hainan travel chaos: Is it time to build the cross-strait subsea tunnel?". June 8, 2018. Retrieved June 8, 2018.
- ^ "Railway Ferry Service Across Qiongzhou Straits Begins". People's Daily Online. 2003-01-08. Retrieved 2008-08-12.
- ^ Xinhua News Agency (2005-02-03). "Hainan Mulls Bridge/ Tunnel Link to Mainland". China.org.cn. Retrieved 2008-08-12.
- ^ 海南吉林迈入"高铁时代" [Hainan Steps into an Era of High Speed Railways] (in Simplified Chinese). People's Daily Online. December 31, 2010. Archived from the original on October 1, 2011. Retrieved January 10, 2012.
- ^ "Hainan's Eastern Ring Railway/Ticket Price". news.wenweipo.com. December 28, 2010. Retrieved January 10, 2012.
- ^ 海南吉林迈入高铁时代 高铁激活国际旅游岛 [Hainan International Tourism Island Steps into the Age of High Speed Rail Age] (in Simplified Chinese). January 4, 2011. Retrieved January 6, 2011.
- ^ a b c "Hainan Harbor & Shipping Holding Co., Ltd". China Ports. Archived from the original on 2011-11-06. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "Hainan Strait Port, China". ports.com. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "China exports 11k tons of aquatic products via Hainan ports in Nov – What's On Sanya". Whatsonsanya.com. 2010-12-28. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "Swatch Girls World Pro China". Archived from the original on 2013-12-14.
- ^ "Hainan International Surfing Festival".
- ^ "(Hainan Sanya) – Yachts, Business Jets, Luxury LifeStyle". Hainan RendezVous. Archived from the original on October 7, 2011. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "Hot Air Balloon Challenge held in Haikou". News.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "H1 China Hot Air Balloon Challenge kicks off". 360doc.com. Retrieved 2011-11-12.
- ^ "China's Top Ten 2011". Global Times. January 19, 2011. Archived from the original on January 22, 2011. Retrieved January 20, 2011.
- ^ "List of Sister States/Provinces of Hainan -- Foreign affairs office of hainan province". enfaohn.hainan.gov.cn. Retrieved 2019-08-10.
Further reading
- D'Arcy Brown, Liam (2003). Green Dragon, Sombre Warrior: travels to China's extremes. London: John Murray. ISBN 0-7195-6038-1
- Edmonds, Richard Louis. "Hainan province and its impact on the geography of China", Geography, Vol. 74, No. 2 (April 1989), pp. 165–169




