PRO-LAD
Appearance
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
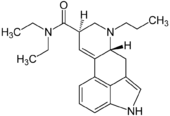
| Other names | PRO-LAD, 6-propyl- 6-nor- Lysergic acid diethylamide, (6aR,9R)- N,N- diethyl- 7-propyl- 4,6,6a,7,8,9- hexahydroindolo- [4,3-fg] quinoline- 9- carboxamide |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H29N3O |
| Molar mass | 351.494 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
PRO-LAD is an analogue of LSD. It is described by Alexander Shulgin in the book TiHKAL. PRO-LAD is a psychedelic drug similar to LSD, and is around as potent as LSD itself with an active dose reported at between 100 and 200 micrograms.[2]
Legal status
On June 10, 2014 the UK Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) recommended that PRO-LAD be specifically named in the UK Misuse of Drugs Act as a class A drug despite not identifying it as ever having been sold or any harm associated with its use.[3] The UK Home office accepted this advice and announced a ban of the substance to be enacted on 6 January 2015 as part of The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Amendment) (No. 2) Order 2014.
PRO-LAD is illegal in Switzerland as of December 2015.[4]
Literature
- Hoffman, Andrew J.; Nichols, David E. (1985). "Synthesis and LSD-like discriminative stimulus properties in a series of N(6)-alkyl norlysergic acid N,N-diethylamide derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (9): 1252–1255. doi:10.1021/jm00147a022. PMID 4032428.
- Niwaguchi, T.; Nakahara, Y.; Ishii, H. (1976). "Studies on lysergic acid diethylamide and related compounds. IV. Syntheses of various amide derivatives of norlysergic acid and related compounds". Yakugaku Zasshi. 96 (5): 673–678. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.96.5_673. PMID 987200.
- Robert C. Pfaff, Xuemei Huang, Danuta Marona-Lewicka, Robert Oberlender and David E. Nichols: Lysergamides Revisited. In: NIDA Research Monograph 146: Hallucinogens: An Update. p. 52, 1994, United States Department of Health and Human Services.
See also
References
- ^ "Arrêté du 20 mai 2021 modifiant l'arrêté du 22 février 1990 fixant la liste des substances classées comme stupéfiants". www.legifrance.gouv.fr (in French). 20 May 2021.
- ^ Hoffman AJ, Nichols DE (September 1985). "Synthesis and LSD-like discriminative stimulus properties in a series of N(6)-alkyl norlysergic acid N,N-diethylamide derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (9): 1252–5. doi:10.1021/jm00147a022. PMID 4032428.
- ^ ACMD (10 June 2014). "Update of the Generic Definition for Tryptamines" (PDF). UK Home Office. p. 12. Retrieved 10 June 2014.
- ^ "Verordnung des EDI über die Verzeichnisse der Betäubungsmittel, psychotropen Stoffe, Vorläuferstoffe und Hilfschemikalien". Der Bundesrat.
External links
