From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Gallocatechol
Names
Other names
(+)-gallocatechin
Identifiers
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
MeSH
Gallocatechol
UNII
InChI=1S/C15H14O7/c16-7-3-9(17)8-5-12(20)15(22-13(8)4-7)6-1-10(18)14(21)11(19)2-6/h1-4,12,15-21H,5H2/t12-,15+/m0/s1
N Key: XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-SWLSCSKDSA-N
N InChI=1/C15H14O7/c16-7-3-9(17)8-5-12(20)15(22-13(8)4-7)6-1-10(18)14(21)11(19)2-6/h1-4,12,15-21H,5H2/t12-,15+/m0/s1
Key: XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-SWLSCSKDBQ
C1[C@@H]([C@H](OC2=CC(=CC(=C21)O)O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3)O)O)O)O
Properties
C 15 H 14 O 7
Molar mass
−1
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Chemical compound
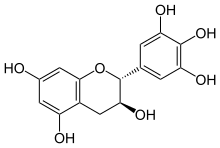
Gallocatechol or gallocatechin (GC) is a flavan-3-ol , a type of chemical compound including catechin , with the gallate residue being in an isomeric trans position. It is one of the antioxidant chemicals found in food .
This compound possesses two epimers . The most common, (+)-gallocatechin (GC), CAS number 970-73-0, is found notably in green tea . Other sources of (+)-gallocatechin are bananas ,[ 1] persimmons , and pomegranates .[citation needed The other enantiomer is called (-)-gallocatechin or ent -gallocatechin.
It was first isolated from green tea by Michiyo Tsujimura in 1934.[ 2]
This compound had been shown to have moderate affinity to the human cannabinoid receptor ,[ 3]
Epigallocatechin is another type of catechin, with the gallate residue being in an isomeric cis position. It can be found in St John's wort .[ 4]
See also
References
^ Someya, Shinichi; Yoshiki, Yumiko; Okubo, Kazuyoshi (2002). "Antioxidant compounds from bananas (Musa Cavendish)". Food Chemistry . 79 (3): 351–354. doi :10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00186-3 . ^ "Michiyo Tsujimura (1888–1969)" . Ochanomizu University . Retrieved 10 November 2015 .^ Korte, G.; Dreiseitel, A.; Schreier, P.; Oehme, A.; Locher, S.; Geiger, S.; Heilmann, J.; Sand, P. (2010). "Tea catechins' affinity for human cannabinoid receptors". Phytomedicine . 17 (1): 19–22. doi :10.1016/j.phymed.2009.10.001 . PMID 19897346 . ^ Wei, Yun; Xie, Qianqian; Dong, Wanting; Ito, Yoichiro (2009). "Separation of epigallocatechin and flavonoids from Hypericum perforatum L. By high-speed counter-current chromatography and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography" . Journal of Chromatography A . 1216 (19): 4313–4318. doi :10.1016/j.chroma.2008.12.056 . PMC 2777726 PMID 19150073 .
External links
Flavan-3-ols O-methylated flavan-3ols Glycosides Acetylated Gallate esters Misc.
Receptor (ligands )
CB1 Tooltip Cannabinoid receptor type 1
Agonists(abridged,full list ) Inverse agonists Antagonists
CB2 Tooltip Cannabinoid receptor type 2
Agonists
2-AG 2-AGE (noladin ether) 3,3'-Diindolylmethane 4-O-Methylhonokiol α-Amyrin · β-Amyrin A-796,260 A-834,735 A-836,339 AM-1172 AM-1221 AM-1235 AM-1241 AM-2232 Anandamide AZ-11713908 Cannabinol Caryophyllene CB-13 CBS-0550 CP 55,940 GW-405,833 (L-768,242) GW-842,166X HU-308 JTE 7-31 JWH-007 JWH-015 JWH-018 JWH-73 JWH-133 L-759,633 L-759,656 Lenabasum (anabasum) Magnolol MDA-19 Nabitan NADA Olorinab (APD-371) PF-03550096 S-444,823 SER-601 Serinolamide A UR-144 Tedalinab THC (dronabinol) THCV Tetrahydromagnolol Virodhamine Antagonists
NAGly GPR18 )
GPR55
GPR119
Transporter (modulators )
eCBTs Tooltip Endocannabinoid transporter
Enzyme (modulators )
Others
Others: 2-PG (directly potentiates activity of 2-AG at CB1 receptor) ARN-272 (FAAH-like anandamide transporter inhibitor)
Alcohols Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Carbamates Flavonoids Imidazoles Kava constituentsMonoureides Neuroactive steroids Nonbenzodiazepines Phenols Piperidinediones Pyrazolopyridines Quinazolinones Volatiles /gases Others/unsorted
3-Hydroxybutanal α-EMTBL AA-29504 Alogabat Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide , potassium bromide , sodium bromide )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole Darigabat DEABL Deuterated etifoxine Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine , dihydroergosine , dihydroergotamine , ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )DS2 Efavirenz Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid , mefenamic acid , niflumic acid , tolfenamic acid )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Hopantenic acid KRM-II-81 Lanthanum Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol , honokiol , magnolol , obovatol )Loreclezole Menthyl isovalerate (validolum) Monastrol Niacin Niacinamide Org 25,435 Phenytoin Propanidid Retigabine (ezogabine) Safranal Seproxetine Stiripentol Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) , tetronal , trional )Terpenoids (e.g., borneol )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid , isovaleramide , valerenic acid , valerenol )
Receptor (ligands )
GHBR Tooltip GHB receptor GABAB Tooltip γ-Aminobutyric acid B receptor
Transporter (blockers )
MCTs Tooltip Monocarboxylate transporters SMCTs Tooltip Sodium-coupled monocarboxylate transporters VIATT Tooltip Vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter
Enzyme (inhibitors )
SSR Tooltip Succinic semialdehyde reductase GHBDH Tooltip 4-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase HOT Tooltip Hydroxyacid-oxoacid transhydrogenase ADH Tooltip Alcohol dehydrogenase ALDH Tooltip Aldehyde dehydrogenase