Venezuela: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 68.49.174.69 (talk) to last version by Materialscientist |
|||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
{{Main|History of Venezuela}} |
{{Main|History of Venezuela}} |
||
[[File:Simón Bolívar 2.jpg|thumb|[[Simón Bolívar]], liberator of not only Venezuela, but also [[Colombia]], [[Panama]], [[Ecuador]], [[Bolivia]], and [[Peru]].]] |
[[File:Simón Bolívar 2.jpg|thumb|[[Simón Bolívar]], liberator of not only Venezuela, but also [[Colombia]], [[Panama]], [[Ecuador]], [[Bolivia]], and [[Peru]].]] |
||
Human habitation of Venezuela could have commenced at least 15,000 years ago from which period [[leaf]]-shaped tools, together with chopping and [[Plane (tool)|plano]]-convex scraping implements, have been found exposed on the high riverine terraces of the Rio Pedregal in western Venezuela.<ref name="Kipfer_2000_91">{{cite book|last=Kipfer|first=Barbara Ann|year=2000|title=Encyclopedic Dictionary of YUPArchaeology|publisher=Springer|isbn=0-306-46158-7|page=91}}</ref> [[Late Pleistocene]] hunting artifacts, including spear tips, have been found at a similar series of sites in northwestern Venezuela known as "El Jobo"; according to [[radiocarbon dating]], these date from 13,000 to 7,000 BC.<ref name="Kipfer_2000_172">{{cite book|last=Kipfer|first=Barbara Ann|year=2000|title=Encyclopedic Dictionary of YUPArchaeology|publisher=Springer|isbn=0-306-46158-7|page=172}}</ref> |
Human habitation of Venezuela could have commenced at least 15,000 years ago from which period [[leaf]]-shaped tools, together with chopping and [[Plane (tool)|plano]]-convex scraping implements, have been found exposed on the high riverine terraces of the Rio Pedregal in western Venezuela.<ref name="Kipfer_2000_91">{{cite book|last=Kipfer|first=Barbara Ann|year=2000|title=Encyclopedic Dictionary of YUPArchaeology|publisher=Springer|isbn=0-306-46158-7|page=91}}</ref> [[Late Pleistocene]] hunting artifacts, including spear tips, have been found at a similar series of sites in northwestern Venezuela known as "El Jobo"; according to [[radiocarbon dating]], these date from 13,000 to 7,000 BC.<ref name="Kipfer_2000_172">{{cite book|last=Kipfer|first=Barbara Ann|year=2000|title=Encyclopedic Dictionary of YUPArchaeology|publisher=Springer|isbn=0-306-46158-7|page=172}}</ref>hi |
||
It is not known how many people lived in Venezuela before the [[Spanish colonization of the Americas|Spanish Conquest]]; it may have been around a million people,<ref name=Wunder/> and in addition to today's [[Indigenous peoples in Venezuela|indigenous peoples]] included groups such as the [[Carib]], [[Auaké]], [[Caquetio]], [[Mariche]] and [[Timoto-cuicas]]. The number was reduced after the Conquest, mainly through the spread of new diseases from Europe.<ref name=Wunder>Wunder, Sven (2003), ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=n2nQ0A8BmCYC&pg=PA130 Oil wealth and the fate of the forest: a comparative study of eight tropical countries]'', [[Routledge]]. p. 130, ISBN 0203986679.</ref> There were two main north-south axes of pre-Columbian population, producing [[maize]] in the west and [[manioc]] in the east.<ref name=Wunder/> Large parts of the [[Los Llanos, Venezuela|llanos]] plains were cultivated through a combination of [[slash and burn]] and permanent settled agriculture.<ref name=Wunder/> |
It is not known how many people lived in Venezuela before the [[Spanish colonization of the Americas|Spanish Conquest]]; it may have been around a million people,<ref name=Wunder/> and in addition to today's [[Indigenous peoples in Venezuela|indigenous peoples]] included groups such as the [[Carib]], [[Auaké]], [[Caquetio]], [[Mariche]] and [[Timoto-cuicas]]. The number was reduced after the Conquest, mainly through the spread of new diseases from Europe.<ref name=Wunder>Wunder, Sven (2003), ''[http://books.google.com/books?id=n2nQ0A8BmCYC&pg=PA130 Oil wealth and the fate of the forest: a comparative study of eight tropical countries]'', [[Routledge]]. p. 130, ISBN 0203986679.</ref> There were two main north-south axes of pre-Columbian population, producing [[maize]] in the west and [[manioc]] in the east.<ref name=Wunder/> Large parts of the [[Los Llanos, Venezuela|llanos]] plains were cultivated through a combination of [[slash and burn]] and permanent settled agriculture.<ref name=Wunder/> |
||
Revision as of 16:31, 27 September 2013
Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela[a]
| |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Gloria al Bravo Pueblo Glory to the Brave People | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Caracas |
| National language | Spanish[b] |
| Ethnic groups (2011[1]) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Venezuelan |
| Government | Federal presidential constitutional republic |
| Nicolás Maduro | |
| Jorge Arreaza | |
| Diosdado Cabello | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Independence | |
• from Spain | 5 July 1811 |
• from Gran Colombia | 13 January 1830 |
• Recognized | 30 March 1845 |
| 20 December 1999 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 916,445 km2 (353,841 sq mi) (33rd) |
• Water (%) | 0.32[d] |
| Population | |
• 2011 census | 28,946,101 (44th) |
• Density | 30.2/km2 (78.2/sq mi) (181st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | $396.848 billion[2] |
• Per capita | $13,633[2] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2013 estimate |
• Total | $345.651 billion[2] |
• Per capita | $11,527[2] |
| Gini (2010) | 39[3] medium inequality |
| HDI (2013) | high (71st) |
| Currency | Bolívar fuerte[e] (VEF) |
| Time zone | UTC–4½ (VET) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +58 |
| ISO 3166 code | VE |
| Internet TLD | .ve |
| |
Venezuela (/ˌvɛnəˈzweɪlə/ VEN-ə-ZWALE-ə, Spanish pronunciation: [be.neˈswela]), officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela[1] (Template:Lang-es [reˈpu.βlika βoliβaˈɾjana ðe βeneˈswela]), is a country on the northern coast of South America. Venezuela's territory covers around 916,445 square kilometres (353,841 sq mi) with an estimated population of approximately 29,100,000. Venezuela is considered a state with extremely high biodiversity, with habitats ranging from the Andes mountains in the west to the Amazon Basin rainforest in the south, via extensive llanos plains and Caribbean coast in the center and the Orinoco River Delta in the east.
Venezuela was colonized by Spain in 1522 despite resistance from indigenous peoples. It became one of the first Spanish American colonies to declare independence (in 1811), but did not securely establish independence until 1821 (as a department of the federal republic of Gran Colombia, gaining full independence in 1830). During the 19th century Venezuela suffered political turmoil and dictatorship, and it was dominated by regional caudillos (military strongmen) well into the 20th century. The country has had democratic governments since 1958; before that, like most countries of Latin America, it suffered some coups and military dictatorships. Economic shocks in the 1980s and 1990s led to a political crisis causing hundreds of deaths in the Caracazo riots of 1989, two attempted coups in 1992, and the impeachment of President Carlos Andrés Pérez for embezzlement of public funds in 1993. A collapse in confidence in the existing parties saw the 1998 election of former career officer Hugo Chávez, and the launch of the Bolivarian Revolution, beginning with a 1999 Constituent Assembly to write a new Constitution of Venezuela.
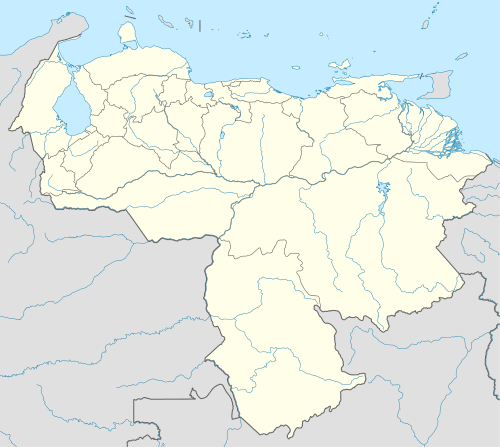
Venezuela is a federal presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District (covering Caracas), and Federal Dependencies (covering Venezuela's offshore islands). Venezuela also claims all Guyanese territory west of the Essequibo River; this 159,500 square kilometres (61,583 sq mi) tract was dubbed Guayana Esequiba or the Zona en Reclamación (the "zone being reclaimed").[5]
Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America;[6][7] the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north, especially in the capital, Caracas, which is also the largest city and one of the most dangerous cities in the world. Since the discovery of oil in the early 20th century, Venezuela has been one of the world's leading exporters of oil and has the largest oil reserves. Previously an underdeveloped exporter of agricultural commodities such as coffee and cocoa, oil quickly came to dominate exports and government revenues. The 1980s oil glut led to an external debt crisis and a long-running economic crisis, which saw inflation peak at 100% in 1996 and poverty rates rise to 66% in 1995[8] as (by 1998) per capita GDP fell to the same level as 1963, down a third from its 1978 peak.[9] The recovery of oil prices after 2001 boosted the Venezuelan economy and facilitated social spending, although the fallout of the 2008 global financial crisis saw a renewed economic downturn. However, as of late 2010 Venezuela's economy returned to growth.[10] Currently, Venezuela's economy is in a steady state of decline and the crime rate has sharply increased and is among the highest in the world.[11][12]
Etymology

In 1499, an expedition led by Alonso de Ojeda visited the Venezuelan coast. The stilt houses in the area of Lake Maracaibo reminded the navigator Amerigo Vespucci of the city of Venice, so he named the region "Veneziola".[14] The name acquired its current spelling as a result of Spanish influence,[14] where the suffix -uela is used as a diminutive term (e.g., plaza / plazuela, cazo / cazuela); thus, the term's original sense would have been that of a "little Venice".[15] The German term for the area, "Klein-Venedig", also means little Venice (lit. "small Venice").
Nonetheless, although the Vespucci story remains the most popular and accepted version of the origin of the country's name, a different reason for the name comes up in the account of Martín Fernández de Enciso, a member of the Vespucci and Ojeda crew. In his work Summa de Geografía, he states that they found an indigenous population who called themselves the "Veneciuela," which suggests that the name "Venezuela" may have evolved from the native word.[16]
History

Human habitation of Venezuela could have commenced at least 15,000 years ago from which period leaf-shaped tools, together with chopping and plano-convex scraping implements, have been found exposed on the high riverine terraces of the Rio Pedregal in western Venezuela.[17] Late Pleistocene hunting artifacts, including spear tips, have been found at a similar series of sites in northwestern Venezuela known as "El Jobo"; according to radiocarbon dating, these date from 13,000 to 7,000 BC.[18]hi
It is not known how many people lived in Venezuela before the Spanish Conquest; it may have been around a million people,[19] and in addition to today's indigenous peoples included groups such as the Carib, Auaké, Caquetio, Mariche and Timoto-cuicas. The number was reduced after the Conquest, mainly through the spread of new diseases from Europe.[19] There were two main north-south axes of pre-Columbian population, producing maize in the west and manioc in the east.[19] Large parts of the llanos plains were cultivated through a combination of slash and burn and permanent settled agriculture.[19]
Colonization
In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus sailed near the Orinoco Delta and then landed in the Gulf of Paria. Amazed, Columbus expressed in his moving letter to Isabella and Ferdinand that he had reached the heaven on Earth (paradise), and confused by the unusual saltiness of the water, he wrote:
Great signs are these of the Terrestrial Paradise, for the site conforms to the opinion of the holy and wise theologians whom I have mentioned. And likewise, the [other] signs conform very well, for I have never read or heard of such a large quantity of fresh water being inside and in such close proximity to salt water; the very mild temperateness also corroborates this; and if the water of which I speak does not proceed from Paradise then it is an even greater marvel, because I do not believe such a large and deep river has ever been known to exist in this world.[20]
His certainty of having attained Paradise made him name this region Land of Grace, a phrase that has become the country's nickname.

Spain's colonization of mainland Venezuela started in 1522, establishing its first permanent South American settlement in the present-day[update] city of Cumaná. In the 16th century Venezuela was contracted as a concession by the King of Spain to the German Welser banking family (Klein-Venedig, 1528–1546). Native caciques (leaders) such as Guaicaipuro (c. 1530–1568) and Tamanaco (died 1573) attempted to resist Spanish incursions, but the newcomers ultimately subdued them; Tamanaco was put to death by order of Caracas' founder Diego de Losada.[21]
In the 16th century, during the Spanish colonization, indigenous peoples such as many of the Mariches, themselves descendants of the Caribs converted to Roman Catholicism. Some of the resisting tribes or leaders are commemorated in place names, including Caracas, Chacao, and Los Teques. The early colonial settlements focused on the northern coast,[19] but in the mid-18th century the Spanish pushed further inland along the Orinoco River. Here the Ye'kuana (then known as the Makiritare) organized serious resistance in 1775 and 1776.[22]
Spain's eastern Venezuelan settlements were incorporated into New Andalusia Province. Administered by the Royal Audiencia of Santo Domingo from the early 16th century, most of Venezuela became part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada in the early 18th century, and was then reorganized as an autonomous Captaincy General starting in 1776. The town of Caracas, founded in the central coastal region in 1567, was well-placed to become a key location, being near the coastal port of La Guaira whilst itself being located in a valley in a mountain range, providing defensive strength against pirates and a more fertile and healthy climate.[23]
Independence


After a series of unsuccessful uprisings, Venezuela—under the leadership of Francisco de Miranda, a Venezuelan marshal who had fought in the American Revolution and the French Revolution—declared independence on 5 July 1811. This began the Venezuelan War of Independence. However, a devastating earthquake that struck Caracas in 1812, together with the rebellion of the Venezuelan llaneros, helped bring down the first Venezuelan republic.[24] A second Venezuelan republic, proclaimed on 7 August 1813, lasted several months before being crushed as well.
Sovereignty was only attained after Simón Bolívar, aided by José Antonio Páez and Antonio José de Sucre, won the Battle of Carabobo on 24 June 1821. José Prudencio Padilla and Rafael Urdaneta's victory in the Battle of Lake Maracaibo on 24 July 1823, helped seal Venezuelan independence. New Granada's congress gave Bolívar control of the Granadian army; leading it, he liberated several countries and founded Gran Colombia.
Sucre, who won many battles for Bolívar, went on to liberate Ecuador and later become the second president of Bolivia. Venezuela remained part of Gran Colombia until 1830, when a rebellion led by Páez allowed the proclamation of a newly independent Venezuela; Páez became the first president of the new republic. Between one-quarter and one-third of Venezuela's population was lost during these two decades of warfare (including perhaps one-half of the white population),[25] which by 1830 was estimated at about 800,000.[26]
The colors of the Venezuelan flag are yellow, blue and red, in that order: the yellow stands for land wealth, the blue for the sea that separates Venezuela from Spain, and the red for the blood shed by the heroes of independence.[27]

Slavery in Venezuela was abolished in 1854.[26] Much of Venezuela's 19th century history was characterized by political turmoil and dictatorial rule,[28] including the Independence leader José Antonio Páez, who gained the presidency three times and served a total of eleven years between 1830 and 1863. This culminated in the Federal War (1859–1863), a civil war in which hundreds of thousands died, in a country with a population of not much more than a million people. In the latter half of the century Antonio Guzmán Blanco, another caudillo, served a total of thirteen years between 1870 and 1887, with three other presidents interspersed.
In 1895, a longstanding dispute with Great Britain about the territory of Guayana Esequiba, which Britain claimed as part of British Guiana and Venezuela saw as Venezuelan territory, erupted into the Venezuela Crisis of 1895. The dispute became a diplomatic crisis when Venezuela's lobbyist William L. Scruggs sought to argue that British behavior over the issue violated the United States' Monroe Doctrine of 1823, and used his influence in Washington, D.C. to pursue the matter. Then US President Grover Cleveland adopted a broad interpretation of the Doctrine that did not just simply forbid new European colonies but declared an American interest in any matter within the hemisphere.[29] Britain ultimately accepted arbitration, but in negotiations over its terms was able to persuade the US on much of the details. A tribunal convened in Paris in 1898 to decide the issue, and in 1899 awarded the bulk of the disputed territory to British Guiana.[30]
In 1899, Cipriano Castro, assisted by his friend Juan Vicente Gómez, seized power in Caracas, marching an army from his base in the Andean state of Táchira. Castro defaulted on Venezuela's considerable foreign debts, and declined to pay compensation to foreigners caught up in Venezuela's civil wars. This led to the Venezuela Crisis of 1902–1903, in which Britain, Germany and Italy imposed a naval blockade of several months, before international arbitration at the new Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague was agreed. In 1908 another dispute broke out with the Netherlands, which was resolved when Castro left for medical treatment in Germany and was promptly overthrown by Juan Vicente Gómez.
The discovery of massive oil deposits in Lake Maracaibo during World War I would prove pivotal for Venezuela, and soon transformed the basis of its economy, from a heavy dependence on agricultural exports. It prompted an economic boom that would last into the 1980s; by 1935, Venezuela's per capita gross domestic product was Latin America's highest.[31] Gómez benefited handsomely from this, as corruption thrived, but at the same time, the new source of income helped him centralize the Venezuelan state and develop its authority.
He remained the most powerful man in Venezuela until his death in 1935, although at times he ceded the Presidency to others. The gomecista dictatorship system largely continued under Eleazar López Contreras, but from 1941, under Isaías Medina Angarita, was relaxed, with the latter granting a range of reforms, including the legalization of all political parties. After World War II the globalization and heavy immigration from Southern Europe (mainly from Spain, Italy, Portugal and France) and poorer Latin American countries markedly diversified Venezuelan society.
In 1945, a civilian-military coup overthrew Medina Angarita and ushered in a three-year period of democratic rule under the mass membership Democratic Action, initially under Rómulo Betancourt, until Rómulo Gallegos won the Venezuelan presidential election, 1947 (generally believed to be the first free and fair elections in Venezuela). Gallegos governed until overthrown by a military junta led by Marcos Pérez Jiménez and Gallegos' Defense Minister Carlos Delgado Chalbaud in the 1948 Venezuelan coup d'état.
Pérez Jiménez was the most powerful man in the junta (though Chalbaud was its titular President), and was suspected of being behind the death in office of Chalbaud, who died in a bungled kidnapping in 1950. When the junta unexpectedly lost the election it held in 1952, it ignored the results and Pérez Jiménez was installed as President, where he remained until 1958.

The military dictator Pérez Jiménez was forced out on 23 January 1958.[32] In an effort to consolidate the young democracy, the major political parties (with the notable exception of the Communist Party of Venezuela) signed the Punto Fijo Pact. Democratic Action and COPEI would dominate the political landscape for four decades.
The 1960s saw substantial guerilla movements, including the Armed Forces of National Liberation and the Revolutionary Left Movement, which had split from Democratic Action in 1960. Most of these movements lay down their arms under Rafael Caldera's presidency (1969–74); Caldera had won the 1968 election for COPEI, being the first time a party other than Democratic Action took the presidency through a democratic election.
The election of Carlos Andrés Pérez in 1973 coincided with the 1973 oil crisis, which saw Venezuela's income explode as oil prices soared, while oil industries were nationalized in 1976. This led to massive increases in public spending, but also increases in external debts, which continued into the 1980s when the collapse of oil prices during the 1980s crippled the Venezuelan economy. As the government started to devalue the currency in February 1983 in order to face its financial obligations, Venezuelans' real standard of living fell dramatically. A number of failed economic policies and increasing corruption in government led to rising poverty and crime, worsening social indicators, and increased political instability.[33]
Economic crisis in the 1980s and 1990s led to a political crisis which saw hundreds dead in the Caracazo riots of 1989, two attempted coups in 1992,[34] and the impeachment of President Carlos Andrés Pérez (re-elected in 1988) for corruption in 1993. Coup leader Hugo Chávez was pardoned in March 1994 by president Rafael Caldera, with a clean slate and his political rights reinstated.
Bolivarian Revolution

A collapse in confidence in the existing parties saw Chávez elected President in 1998, and the subsequent launch of a "Bolivarian Revolution", beginning with a 1999 Constituent Assembly to write a new Constitution of Venezuela.
In April 2002, Chávez was briefly ousted from power in the 2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt following popular demonstrations by his opposers,[35] but he was returned to power after two days as a result of popular demonstrations by his supporters and actions by the military.[36]
Chávez also remained in power after an all-out national strike that lasted more than two months from December 2002 to February 2003, including a strike/lockout in the state oil company PDVSA. The strike produced severe economic dislocation, with the country's GDP falling 27% during the first four months of 2003, and costing the oil industry $13.3bn.[37] Capital flight before and during the strike led to the reimposition of currency controls (which had been abolished in 1989), managed by the CADIVI agency. In the subsequent decade the government was forced into several currency devaluations.[38][39][40][41][42] These devaluations have done little to improve the situation of the Venezuelan people who rely on imported products or locally produced products that depend on imported inputs while dollar denominated oil sales account for the vast majority of Venezuela's exports.[43]
Chávez survived several further political tests, including an August 2004 recall referendum. He was elected for another term in December 2006 and re-elected for a third term in October 2012. However, he was never sworn in for his third period, due to medical complications. Chávez died on 5 March 2013 after a nearly-two-year fight with cancer.[44] The presidential election that took place on Sunday, 14 April 2013, was the first since Chávez took office in 1999 in which his name did not appear on the ballot.[45]
Nicolás Maduro is the president of Venezuela since 14 April 2013, after winning the second presidential election after Chávez's death, with 50,61% of the votes against the opposition's candidate Henrique Capriles Radonski who had 49,12% of the votes. The Democratic Unity Roundtable (the government opposition cartel) contested his appointment as a violation of the constitution. However, the Supreme Court of Venezuela (TSJ) rules that under Venezuela's Constitution, Nicolás Maduro is the President of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela and was invested as such by the Venezuelan Congress (Asamblea Nacional).[46] [47][48]
Geography

Venezuela is located in the north of South America; geologically its mainland rests on the South American Plate. It has a total area of 916,445 square kilometres (353,841 sq mi) and a land area of 882,050 square kilometres (340,560 sq mi), making it the 33rd largest country. The territory it controls lies between latitudes 0° and 13°N, and longitudes 59° and 74°W.
Shaped roughly like a triangle, the country has a 2,800 km (1,700 mi) coastline in the north, which includes numerous islands in the Caribbean Sea, and in the northeast borders the northern Atlantic Ocean. Most observers describe Venezuela in terms of four fairly well-defined topographical regions: the Maracaibo lowlands in the northwest, the northern mountains extending in a broad east-west arc from the Colombian border along the northern Caribbean coast, the wide plains in central Venezuela, and the Guiana Highlands in the southeast.

The northern mountains are the extreme northeastern extensions of South America's Andes mountain range reach. Pico Bolívar, the nation's highest point at 4,979 m (16,335 ft), lies in this region. To the south, the dissected Guiana Highlands contains the northern fringes of the Amazon Basin and Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall as well as tepuis, large table-like mountains. The country's center is characterized by the llanos, which are extensive plains that stretch from the Colombian border in the far west to the Orinoco River delta in the east. The Orinoco, with its rich alluvial soils, binds the largest and most important river system of the country; it originates in one of the largest watersheds in Latin America. The Caroní and the Apure are other major rivers.
Venezuela borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south. Caribbean islands such as Trinidad and Tobago, Grenada, Curaçao, Aruba and the Leeward Antilles lie near the Venezuelan coast. Venezuela has territorial disputes with Guyana (formerly United Kingdom), largely concerning the Essequibo area, and with Colombia concerning the Gulf of Venezuela. In 1895, after years of diplomatic attempts to solve the border dispute, from Venezuela, the dispute over the Essequibo River border flared up, it was submitted to a "neutral" commission (composed of British, American and Russian representatives and without a direct Venezuelan representative), which in 1899 decided mostly against Venezuela's claim.[49]
Venezuela's most significant natural resources are petroleum and natural gas, iron ore, gold and other minerals. It also has large areas of arable land and water.
Climate


Venezuela is entirely located in the tropics over the Equator to around 12° N. Its climate varies from humid low-elevation plains, where average annual temperatures range as high as 35 °C (95.0 °F), to glaciers and highlands (the páramos) with an average yearly temperature of 8 °C (46.4 °F). Annual rainfall varies between 430 mm (16.9 in) in the semiarid portions of the northwest to over 1,000 mm (39.4 in) in the Orinoco Delta of the far east and the Amazonian Jungle in the south. The precipitation level is lower in the period from November to April and later in the year from August to October. These periods are referred to as Hot-Humid and Cold-Dry seasons. Other charasteristic of the climate is this variation throughout the country by the existence of a mountain range called "Cordillera de la Costa" which crosses the country from east to west. The majority of the population lives in these mountains.[28]
The country falls into four horizontal temperature zones based primarily on elevation, having Tropical, Dry, Temperate with Dry Winters, and Polar (Alpine tundra) climates, amongst others.[50][51][52] In the tropical zone—below 800 meters or 2,625 feet—temperatures are hot, with yearly averages ranging between 26 and 28 °C (78.8 and 82.4 °F). The temperate zone ranges between 800 and 2,000 meters (2,625 and 6,562 ft) with averages from 12 to 25 °C (53.6 to 77.0 °F); many of Venezuela's cities, including the capital, lie in this region. Colder conditions with temperatures from 9 to 11 °C (48.2 to 51.8 °F) are found in the cool zone between 2,000 and 3,000 meters (6,562 and 9,843 ft), especially in the Venezuelan Andes, where Pastureland and permanent snowfield with yearly averages below 8 °C (46 °F) cover land above 3,000 meters (9,843 ft) in the páramos.
The highest temperature recorded was 42 °C (108 °F) in Machiques,[53] and the lowest temperature recorded was −11 °C (12 °F), it has been reported from an uninhabited high altitude at Páramo de Piedras Blancas (Mérida state),[54] even though no official reports exist, there is knowledge of lower temperatures in the mountains of the Sierra Nevada de Mérida.
Biodiversity

Venezuela lies within the Neotropic ecozone; large portions of the country were originally covered by moist broadleaf forests. One of seventeen megadiverse countries,[55] Venezuela's habitats range from the Andes mountains in the west to the Amazon Basin rainforest in the south, via extensive llanos plains and Caribbean coast in the center and the Orinoco River Delta in the east. They include xeric scrublands in the extreme northwest and coastal mangrove forests in the northeast.[28] Its cloud forests and lowland rainforests are particularly rich.[56]
Animals of Venezuela are diverse and include manatees,Three-toed sloth, Two-toed sloth, Amazon river dolphins, and Orinoco crocodiles, which have been reported to reach up to 6.6 m (22 ft) in length. Venezuela hosts a total of 1,417 bird species, 48 of which are endemic.[57] Important birds include ibises, ospreys, kingfishers,[56] and the yellow-orange Venezuelan Troupial, the national bird. Notable mammals include the Giant Anteater, jaguar, and the capybara, the world's largest rodent. More than half of Venezuelan avian and mammalian species are found in the Amazonian forests south of the Orinoco.[58]
For the fungi, an account was provided by R.W.G. Dennis[59] which has been digitized and the records made available on-line as part of the Cybertruffle Robigalia database.[60] That database includes nearly 3,900 species of fungi recorded from Venezuela, but is far from complete, and it is likely that the true total number of fungal species already known from Venezuela is higher. The true total number of fungal species occurring in Venezuela, including species not yet recorded, is likely to be far higher, given the generally accepted estimate that only about 7% of all fungi worldwide have so far been discovered.[61]

Among plants of Venezuela, over 25,000 species of orchids are found in the country's cloud forest and lowland rainforest ecosystems.[56] These include theflor.de mayo orchid (Cattleya mossiae), the national flower. Venezuela's national tree is the araguaney, whose characteristic lushness after the rainy season led novelist Rómulo Gallegos to name it [l]a primavera de oro de los araguaneyes (the golden spring of the araguaneyes).
Venezuela is among the top twenty countries in terms of endemism.[62] Among its animals, 23% of reptilian and 50% of amphibian species are endemic.[62] Although the amount of available information is still very small, a first effort has been made to estimate the number of fungal species endemic to Venezuela: 1334 species of fungi have been tentatively identified as possible endemics of the country.[63] Some 38% of the over 21,000 plant species known from Venezuela are unique to the country.[62]
Environment
In recent decades, logging, mining, shifting cultivation, development, and other human activities have posed a major threat to Venezuela's wildlife; between 1990 and 2000, 0.40% of forest cover was cleared annually.[62] In response, federal protections for critical habitat were implemented; for example, 20% to 33% of forested land is protected.[58] The country has a biosphere reserve that is part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves; five wetlands are registered under the Ramsar Convention.[64] In 2003, 70% of the nation's land was under conservation management in over 200 protected areas, including 43 national parks.[65] Venezuela's 43 national parks include Canaima National Park, Morrocoy National Park and Mochima National Park. In the far south is a reserve for the country's Yanomami tribes. Covering 32,000 square miles (almost 83,000 square kilometers), the area is off-limits to farmers, miners, and all non-Yanomami settlers.
Government and politics

Following the fall of Marcos Pérez Jiménez in 1958, Venezuelan politics were dominated by the Third Way Christian democratic COPEI and the center-left social democratic Democratic Action (AD) parties; this two-party system was formalized by the puntofijismo arrangement. Economic crises in the 1980s and 1990s led to a political crisis which saw hundreds dead in the Caracazo riots of 1989, two attempted coups in 1992, and impeachment of President Carlos Andrés Pérez for corruption in 1993. A collapse in confidence in the existing parties saw the 1998 election of Hugo Chávez, who had led the first of the 1992 coup attempts, and the launch of a "Bolivarian Revolution", beginning with a 1999 Constituent Assembly to write a new Constitution of Venezuela.
The opposition's attempts to unseat Chávez included the 2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt, the Venezuelan general strike of 2002–2003, and the Venezuelan recall referendum, 2004, all of which failed. Chávez was re-elected in December 2006, but suffered a significant defeat in 2007 with the narrow rejection of the Venezuelan constitutional referendum, 2007, which had offered two packages of constitutional reforms aimed at deepening the Bolivarian Revolution.
There are currently two major blocs of political parties in Venezuela: the incumbent leftist bloc United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV), its major allies Fatherland for All (PPT) and the Communist Party of Venezuela (PCV), and the opposition bloc grouped into the electoral coalition Mesa de la Unidad Democrática. This includes A New Era (UNT) together with allied parties Project Venezuela, Justice First, Movement for Socialism (MAS) and others. Hugo Chávez, the central figure of the Venezuelan political landscape since his election to the Presidency in 1998 as a political outsider, died in office in early 2013, and was succeeded by Nicolás Maduro (initially as interim President, before narrowly winning the Venezuelan presidential election, 2013).

The Venezuelan president is elected by a vote, with direct and universal suffrage, and is both head of state and head of government. The term of office is six years, and (as of 15 February 2009) a president may be re-elected an unlimited number of times. The president appoints the vice president and decides the size and composition of the cabinet and makes appointments to it with the involvement of the legislature. The president can ask the legislature to reconsider portions of laws he finds objectionable, but a simple parliamentary majority can override these objections.
The president may ask the National Assembly to pass an enabling act granting the ability to rule by decree in specified policy areas; this requires a two-thirds majority in the Assembly. Since 1959 six Venezuelan presidents have been granted such powers.
The unicameral Venezuelan parliament is the Asamblea Nacional ("National Assembly"). The number of members is variable, each state and the Capital district elect three representatives plus the result of dividing the state population by 1.1% of the total population of the country.[66] Three seats are reserved for representatives of Venezuela's indigenous peoples. For the 2011–2016 period the number of seats is 165.[67] All deputies serve five-year terms.
The voting age in Venezuela is 18 and older. Voting is not compulsory.[68]
The legal system of Venezuela belongs to the Continental Law tradition. The highest judicial body is the Supreme Tribunal of Justice or Tribunal Supremo de Justicia, whose magistrates are elected by parliament for a single twelve-year term. The National Electoral Council (Consejo Nacional Electoral, or CNE) is in charge of electoral processes; it is formed by five main directors elected by the National Assembly. Supreme Court president Luisa Estela Morales said in December 2009 that Venezuela had moved away from "a rigid division of powers" toward a system characterized by "intense coordination" between the branches of government. Morales clarified that each power must be independent adding that "one thing is separation of powers and another one is division".[69]
Foreign relations

Throughout most of the 20th century, Venezuela maintained friendly relations with most Latin American and Western nations. Relations between Venezuela and the United States government worsened in 2002, after the 2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt during which the U.S. government recognized the short-lived interim presidency of Pedro Carmona. Correspondingly, ties to various Latin American and Middle Eastern countries not allied to the U.S. have strengthened.
Venezuela seeks alternative hemispheric integration via such proposals as the Bolivarian Alternative for the Americas trade proposal and the newly launched pan-Latin American television network teleSUR. Venezuela is one of the six nations in the world—along with Russia, Nicaragua, Nauru, Vanuatu, and Tuvalu—to have recognized the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Venezuela was a proponent of OAS's decision to adopt its Anti-Corruption Convention, and is actively working in the Mercosur trade bloc to push increased trade and energy integration. Globally, it seeks a "multi-polar" world based on strengthened ties among Third World countries.
Military
The Bolivarian National Armed Forces of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela (Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana, FANB) are the overall unified military forces of Venezuela. It includes over 320,150 men and women, under Article 328 of the Constitution, in 5 components of Ground, Sea and Air. The components of the Bolivarian National Armed Forces are: the Venezuelan Army, the Venezuelan Navy, the Venezuelan Air Force, the Venezuelan National Guard, and the Venezuelan National Militia.
As of 2008, a further 600,000 soldiers were incorporated into a new branch, known as the Armed Reserve. The President of Venezuela is the commander-in-chief of the national armed forces. The main roles of the armed forces are to defend the sovereign national territory of Venezuela, airspace, and islands, fight against drug trafficking, to search and rescue and, in the case of a natural disaster, civil protection. All male citizens of Venezuela have a constitutional duty to register for the military service at the age of 18, which is the age of majority in Venezuela.
Law and crime
Corruption in Venezuela is high by world standards, and was so for much of the 20th century. The discovery of oil had worsened political corruption,[70] and by the late 1970s, Juan Pablo Pérez Alfonso's description of oil as "the Devil's excrement" had become a common expression in Venezuela.[71] Venezuela has been ranked one of the most corrupt countries on the Corruption Perceptions Index since the survey started in 1995. The 2010 ranking placed Venezuela at number 164, out of 178 ranked countries.[72]
Venezuela is a significant route for drug trafficking, with Colombian cocaine and other drugs transiting Venezuela towards the United States and Europe. Venezuela ranks fourth in the world for cocaine seizures, behind Colombia, the United States, and Panama.[73] In 2006 the government's agency for combating the Illegal drug trade in Venezuela, ONA, was incorporated into the office of the Vice-President of the country.
In 2009, the homicide rate was approximately 57 per 100,000, one of the world's highest, having trebled in the previous decade (according to The Economist).[74] The capital Caracas has the second greatest homicide rate of any large city in the world, with 92 homicides per 100,000 residents.[75] There have been 118,541 homicides in Venezuela between 1999 and 2010.[76] In 2008, polls indicated that crime was the number one concern of voters.[77]
The government recently created a security force named the Bolivarian National Police, which has lowered crime rates in the areas in which it is so far deployed and a new Experimental Security University.[78]
In Venezuela, are approximately 33 prisons which hold about 50,000 inmates.[79] They include; El Rodeo outside of Caracas, Yare Prison in the northern state of Miranda, and several others. Venezuela's prison system is heavily overcrowded; its facilities have capacity for only 14,000 prisoners.[80]
Subdivisions
| State | Capital | State | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|
| Puerto Ayacucho | Mérida | ||
| Barcelona | Los Teques | ||
| San Fernando de Apure | Maturín | ||
| Maracay | La Asunción | ||
| Barinas | Guanare | ||
| Ciudad Bolívar | Cumaná | ||
| Valencia | San Cristóbal | ||
| San Carlos | Trujillo | ||
| Tucupita | San Felipe | ||
| Caracas | Maracaibo | ||
| Coro | La Guaira | ||
| San Juan de los Morros | El Gran Roque | ||
| Barquisimeto | |||
| 1 The Federal Dependencies are not states. They are just special divisions of the territory. | |||
Venezuela is divided into 23 states (estados), a capital district (distrito capital) corresponding to the city of Caracas, and the Federal Dependencies (Dependencias Federales, a special territory). Venezuela is further subdivided into 335 municipalities (municipios); these are subdivided into over one thousand parishes (parroquias). The states are grouped into nine administrative regions (regiones administrativas), which were established in 1969 by presidential decree.
The country can be further divided into ten geographical areas, some corresponding to climatic and biogeographical regions. In the north are the Venezuelan Andes and the Coro region, a mountainous tract in the northwest, holds several sierras and valleys. East of it are lowlands abutting Lake Maracaibo and the Gulf of Venezuela.
The Central Range runs parallel to the coast and includes the hills surrounding Caracas; the Eastern Range, separated from the Central Range by the Gulf of Cariaco, covers all of Sucre and northern Monagas. The Insular Region includes all of Venezuela's island possessions: Nueva Esparta and the various Federal Dependencies. The Orinoco Delta, which forms a triangle covering Delta Amacuro, projects northeast into the Atlantic Ocean.
Economy

The Central Bank of Venezuela is responsible for developing monetary policy for the Venezuelan bolívar which is used as currency. The currency is primarily printed on paper and distributed throughout the country. The President of the Central Bank of Venezuela is presently Eudomar Tovar, who also serves as the country's representative in the International Monetary Fund. According to the Heritage Foundation and the Wall Street Journal, Venezuela has the weakest property rights in the world, scoring only 5.0 on a scale of 100; expropriation without compensation is not uncommon. Venezuela has a mixed economy dominated by the petroleum sector, which accounts for roughly a third of GDP, around 80% of exports, and more than half of government revenues. Per capita GDP for 2009 was US$13,000, ranking 85th in the world.[32] Venezuela has the least expensive petrol in the world because the consumer price of petrol is heavily subsidized.
More than 60% of Venezuela's international reserves is in gold, eight times more than the average for the region. Most of Venezuela's gold held abroad is located in London. In 25 November 2011 the first of US$11 billion of repatriated gold bullion arrived in Caracas; Chavez called the repatriation of gold a "sovereign" step that will help protect the country's foreign reserves from the turmoil in the U.S. and Europe.[81]
Manufacturing contributed 17% of GDP in 2006. Venezuela manufactures and exports heavy industry products such as steel, aluminium and cement, with production concentrated around Ciudad Guayana, near the Guri Dam, one of the largest in the world and the provider of about three-quarters of Venezuela's electricity. Other notable manufacturing includes electronics and automobiles, as well as beverages, and foodstuffs. Agriculture in Venezuela accounts for approximately 3% of GDP, 10% of the labor force, and at least one-fourth of Venezuela's land area. Venezuela exports rice, corn, fish, tropical fruit, coffee, beef, and pork. The country is not self-sufficient in most areas of agriculture. In 2012, total food consumption was over 26 million metric tonnes, a 94.8% increase from 2003.[82]
Since the discovery of oil in the early 20th century, Venezuela has been one of the world's leading exporters of oil, and it is a founding member of OPEC. Previously an underdeveloped exporter of agricultural commodities such as coffee and cocoa, oil quickly came to dominate exports and government revenues. The 1980s oil glut led to an external debt crisis and a long-running economic crisis, which saw inflation peak at 100% in 1996 and poverty rates rise to 66% in 1995[8] as (by 1998) per capita GDP fell to the same level as 1963, down a third from its 1978 peak.[9] The 1990s also saw Venezuela experience a major banking crisis in 1994. The recovery of oil prices after 2001 boosted the Venezuelan economy and facilitated social spending. In 2003 the government of Hugo Chávez implemented currency controls after capital flight lead to a devaluation of the currency. This lead to the development of a parallel market of Dollars in the subsequent years with the oficial exchange rate currently ranging 6 times under prices on the black market for the greenback. The fallout of the 2008 global financial crisis saw a renewed economic downturn.
With social programs such as the Bolivarian Missions, Venezuela made progress in social development in 2000s, particularly in areas such as health, education, and poverty. Many of the social policies pursued by Chávez and his administration were jumpstarted by the Millennium Development Goals, eight goals that Venezuela and 188 other nations agreed to in September 2000.[83] It is expected that Venezuela will meet all eight goals by the 2015 deadline.[84]
Petroleum and other resources

Venezuela has some of the largest oil and natural gas reserves in the world, and consistently ranks among the top ten world crude oil producers.[85] Compared to the preceding year another 40.4% in crude oil reserves were proven in 2010, allowing Venezuela to surpass Saudi Arabia as the country with the largest reserves of this type.[86] The country's main petroleum deposits are located around and beneath Lake Maracaibo, the Gulf of Venezuela (both in Zulia), and in the Orinoco River basin (eastern Venezuela), where the country's largest reserve is located. Besides the largest conventional oil reserves and the second-largest natural gas reserves in the Western Hemisphere,[87] Venezuela has non-conventional oil deposits (extra-heavy crude oil, bitumen and tar sands) approximately equal to the world's reserves of conventional oil.[88] The electricity sector in Venezuela is one of the few to rely primarily on hydropower, and includes the Guri Dam, one of the largest in the world.
In the first half of the 20th century, US oil companies were heavily involved in Venezuela, initially interested only in purchasing concessions.[89] In 1943 a new government introduced a 50/50 split in profits between the government and the oil industry. In 1960, with a newly installed democratic government, Hydrocarbons Minister Juan Pablo Pérez Alfonso led the creation of OPEC, the consortium of oil-producing countries aiming to support the price of oil.[90]
In 1973, Venezuela voted to nationalize its oil industry outright, effective 1 January 1976, with Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) taking over and presiding over a number of holding companies; in subsequent years, Venezuela built a vast refining and marketing system in the U.S. and Europe.[91] In the 1990s PDVSA became more independent from the government and presided over an apertura (opening) in which it invited in foreign investment. Under Hugo Chávez a 2001 law placed limits on foreign investment.
The state oil company PDVSA played a key role in the December 2002 – February 2003 national strike which sought President Chávez' resignation. Managers and skilled highly paid technicians of PDVSA shut down the plants and left their posts, and by some reports sabotaged equipment, and petroleum production and refining by PDVSA almost ceased. Activities eventually were slowly restarted by returning and substitute oil workers. As a result of the strike, around 40% of the company's workforce (around 18,000 workers) were dismissed for "dereliction of duty" during the strike.[92][93]
Transport

Venezuela is connected to the world primarily via air (Venezuela's airports include the Simón Bolívar International Airport in Maiquetía, near Caracas and La Chinita International Airport near Maracaibo) and sea (with major sea ports at La Guaira, Maracaibo and Puerto Cabello). In the south and east the Amazon rainforest region has limited cross-border transport; in the west, there is a mountainous border of over 2,213 kilometres (1,375 mi) shared with Colombia. The Orinoco River is navigable by oceangoing vessels up to 400 kilometres (250 mi) inland, and connects the major industrial city of Ciudad Guayana to the Atlantic Ocean.
Venezuela has a limited national railway system, which has no active rail connections to other countries; the government of Hugo Chávez has invested substantially in expanding it.[citation needed] Several major cities have metro systems; the Caracas Metro has been operating since 1983. The Maracaibo Metro and Valencia Metro were opened more recently. Venezuela has a road network of nearly 100,000 kilometres (62,000 mi) in length, placing the country around 45th in the world;[94] around a third of roads are paved.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 5,094,000 | — |
| 1960 | 7,562,000 | +4.03% |
| 1970 | 10,681,000 | +3.51% |
| 1980 | 15,036,000 | +3.48% |
| 1990 | 19,685,000 | +2.73% |
| 2000 | 24,348,000 | +2.15% |
| 2011 | 28,400,000 | +1.41% |
| [95][96] Source: United Nations | ||
Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America;[6][7] the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north, especially in the capital Caracas which is also the largest city. About 93% of the population live in urban areas in northern Venezuela; 73% live less than 100 kilometres (62 mi) from the coastline.[97] Though almost half of Venezuela's land area lies south of the Orinoco, only 5% of Venezuelans live there. The largest and most important city south of the Orinoco is Ciudad Guayana, which is the sixth most populous conurbation.[98] Other major cities include Barquisimeto, Valencia, Maracay, Maracaibo, Mérida, San Cristóbal and Barcelona-Puerto La Cruz.
Ethnic groups
The people of Venezuela come from a variety of heritages. It is estimated that the majority of the population is of mestizo, or mixed, ethnic heritage.
Nevertheless, in the 2011 census, which Venezuelans were asked to identify themselves according to their customs and ancestry, the term mestizo was excluded from the answers. The majority claimed to be Multiracial or White —49.9% and 42.2%, respectively.[1] Practically half of the population claimed to be moreno, a term used throughout Ibero-America that in this case means "dark-skinned" or "brown-skinned", as opposed to having a lighter skin (this term connotes skin color or tone, rather than facial features or descent); another substantial part of the population claimed to be white.
Ethnics minorities in Venezuela consists in groups that descend mainly from African or Amerindian; a 2.8% identified themselves as "Black" and a 0.7% as afrodescendiente (Afro-descendant), 2.7% claimed to belong to Indigenous peoples and 1.1% answered "other races".[1][99]
Among indigenous people, 58% were Wayúu, 7% Warao, 5% Kariña, 4% Pemón, 3% Piaroa, 3% Jivi, 3% Añu, 3% Cumanagoto, 2% Yukpa, 2% Chaima and 1% Yanomami nation, the remaining 9% consists in other indigenous nations.[100]
According to an autosomal DNA genetic study conducted in 2008 by the University of Brasilia (UNB), the composition of Venezuela's population it's: 60.60% of European contribution, 23% of Amerindian contribution and 16,30% of African contribution.[101]
During the colonial period and until after the Second World War, many of the European immigrants to Venezuela came from the Canary Islands,[102] which had a significant cultural impact on the cuisine and customs of Venezuela.[citation needed] However, with the start of oil exploitation in the early 20th century, companies from the United States began establishing operations in Venezuela, bringing with them U.S. citizens. Later, during and after the war, new waves of immigrants from other parts of Europe, the Middle East, and China began; many were encouraged by government established immigration programs.[citation needed] Between 1900 and 1958 more than one million Europeans immigrated to Venezuela.[citation needed] In addition, Venezuela also experienced immigration from other Latin American countries (especially Colombia) in the mid-to-late 19th century.[citation needed]
According to the World Refugee Survey 2008, published by the U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, Venezuela hosted a population of refugee and asylum seekers from Colombia numbering 252,200 in 2007, and 10,600 new asylum seekers entered Venezuela in 2007.[103] Between 500,000 and one million illegal immigrants are estimated to be living in the country.[104]

The total indigenous population of the country is estimated at about 500 thousand people (2.8% of the total), distributed among 40 indigenous peoples.[105] The Constitution recognizes the multi-ethnic, pluri-cultural and multilingual character of the country, and includes a chapter devoted to indigenous peoples' rights, which opened up spaces for their political inclusion at national and local level in 1999. Most indigenous peoples are concentrated in eight states along Venezuela's borders with Brazil, Guyana, and Colombia, and the majority groups are the Wayuu (west), the Warao (east), the Yanomami (south) and the Pemon (south-east).
Languages
Although the country is mostly monolingual Venezuelan Spanish (a dialect of Castilian), many languages are spoken in Venezuela. In addition to Spanish, the Constitution recognizes more than thirty indigenous languages, Wayuu, Warao, pemón and many others for the official use of the Amerindian peoples, mostly with few speakers, less than 1% of the total population. Immigrants, in addition to Spanish, speak their own languages. Arabic is spoken by Lebanese and Syrian colonies on Isla de Margarita, Maracaibo, Punto Fijo, Puerto la Cruz, El Tigre, Maracay and Caracas. Portuguese is spoken not only by the Portuguese community in Santa Elena de Uairén but also by much of the population due to its proximity to Brazil. The German community speaks their native language, while the Colonia Tovar speaks mostly Alemannic dialect of German called coloniero. English is the most widely used foreign language and demand, and is spoken by many professionals, academics and part of the upper and middle classes as a result of oil exploration by foreign companies, in addition to its acceptance as a lingua franca. Culturally, English is common in southern towns like El Callao, for the Anglophone West Indian influence evident in folk songs and calypso Venezuelan and French with English voices. Italian instruction is guaranteed by the presence of a constant number of schools and private institutions, because the Italian government considered mandatory language teaching at school level. Other languages spoken by large communities from drawing in the country are Chinese and Galician, among others.
Religion
According to government estimates, 92% of the population is at least nominally Roman Catholic, and the remaining 8% are either irreligious, Protestant, or a member of another religion. The Venezuelan Evangelical Council estimates that Evangelical Protestants constitute 10% of the population.[106]
In Venezuela, a population of Santería followers has been growing since 2008.[107] The rituals can cost 40,000 bolivars and include the slaughtering of a rooster, a chicken, or a goat.[108] Santeria is a mixture of Christianity and Voodoo, and involves worshipping Christian saints and various Pentecostal-style possessions.
Culture


The culture of Venezuela is a melting pot which includes mainly three different families: the indigenous, African and Spanish. The first two cultures were in turn differentiated according to the tribes. Acculturation and assimilation, typical of a cultural syncretism, conditioned to arrive at the current Venezuelan culture, similar in many respects to the rest of Latin America, although the natural environment means that there are important differences.
The indigenous influence is limited to a few words of vocabulary and gastronomy, and many place names. The African influence in the same way, in addition to musical instruments like the drum. The Spanish influence was predominant (due to the colonization process and the socioeconomic structure it created) and in particular came from the regions of Andalusia and Extremadura, places of origin most settlers in the Caribbean during the colonial era. As an example of this can include buildings, part of the music, the Catholic religion and language.
Spanish influences are evident in bullfights and certain features of gastronomy. Venezuela was also enriched by other streams of Indian and European origin in the 19th century, especially from France. In the latest stage in the major cities and regions oil of U.S. origin and manifestations of the new immigration of Spanish, Italian and Portuguese, increasing the already complex cultural mosaic. For example, from United States comes the influence of taste for baseball, US-style fast food, and current architectural constructions.
Art
Venezuelan art was initially dominated by religious motifs, but began emphasizing historical and heroic representations in the late 19th century, a move led by Martín Tovar y Tovar. Modernism took over in the 20th century. Notable Venezuelan artists include Arturo Michelena, Cristóbal Rojas, Armando Reverón, Manuel Cabré; the kinetic artists Jesús Soto and Carlos Cruz-Díez; and contemporary artist as Marisol and Yucef Merhi.
Literature
Venezuelan literature originated soon after the Spanish conquest of the mostly pre-literate indigenous societies; it was dominated by Spanish influences. Following the rise of political literature during the Venezuelan War of Independence, Venezuelan Romanticism, notably expounded by Juan Vicente González, emerged as the first important genre in the region. Although mainly focused on narrative writing, Venezuelan literature was advanced by poets such as Andrés Eloy Blanco and Fermín Toro.
Major writers and novelists include Rómulo Gallegos, Teresa de la Parra, Arturo Uslar Pietri, Adriano González León, Miguel Otero Silva, and Mariano Picón Salas. The great poet and humanist Andrés Bello was also an educator and intellectual (He was also a childhood tutor and mentor of Simon Bolivar). Others, such as Laureano Vallenilla Lanz and José Gil Fortoul, contributed to Venezuelan Positivism.
Music

Indigenous musical styles of Venezuela are exemplified by the groups Un Solo Pueblo and Serenata Guayanesa. The national musical instrument is the cuatro. Typical musical styles and pieces mainly emerged in and around the llanos region, including Alma Llanera (by Pedro Elías Gutiérrez and Rafael Bolívar Coronado), Florentino y el Diablo (by Alberto Arvelo Torrealba), Concierto en la Llanura by Juan Vicente Torrealba, and Caballo Viejo (by Simón Díaz).
The Zulian gaita is also a popular style, generally performed during Christmas. The national dance is the joropo. Venezuela has always been a melting pot of cultures and this can be seen in the richness and variety of its musical styles and dances: calipso, bambuco, fulía, cantos de pilado de maíz, cantos de lavanderas, sebucán, and maremare.[109] Teresa Carreño was a world-famous 19th century piano virtuoso. In the last years, Classical Music has had great performances. The Simon Bolivar Youth Orchestra, under the baton of its principal conductor Gustavo Dudamel and José Antonio Abreu, has hosted a number of excellent presentations in many European concert halls, notably at the 2007 London Proms, and has received several honors. The orchestra is the pinnacle of El Sistema, a publicly financed voluntary sector music education program now being emulated in other countries.
Sport
Baseball is Venezuela's most popular sport, with the Venezuelan Professional Baseball League existing since 1945.
Besides baseball, Venezuela's most popular sports are basketball and football.[110] Venezuela hosted the 2012 Basketball World Olympic Qualifying Tournament and is set to host the 2013 FIBA Basketball Americas Championship, which will take place in Poliedro de Caracas. Football, spearheaded by the Venezuela national football team is gaining popularity as well.
Venezuela will hold the Copa América every 40 years, according to the Conmebol rotation policy. (2007, 2047, 2087, 2127, 2167, 2207, 2247, 2287...)

Venezuela is also home to Formula 1 driver, Pastor Maldonado. At the 2012 Spanish Grand Prix, he claimed his first pole and victory and became the first and only Venezuelan to have done so in the entire Formula 1 history. Maldonado has increased the reception of Formula 1 fans in Venezuela and is now inspiring thousands of young Venezuelan children to aim for Formula 1.
In the 2012 Summer Olympics, Venezuelan Rubén Limardo won gold in fencing.
Cuisine
The Venezuelan cuisine, one of the most varied in the region, reflects the climatic contrasts and cultures coexisting in Venezuela. Among them are hallaca, pabellón criollo, arepas, pisca andina, tarkarí de chivo, jalea de mango, and fried camiguanas.
Other
Venezuela is well known for its successes in beauty pageants. Miss Venezuela is a big event in the country, and Venezuela has received 6 Miss World, 6 Miss Universe, 6 Miss International and 1 Miss Earth titles.
Venezuela ranks first Global Beauties list because it is the country that has won more titles integral beauties. It also has a Guinness World Record, after Dayana Mendoza, Miss Universe 2008, Stefania Fernandez crowned Miss Universe 2009, marking the first time in the competition over 50 years that a country gets the same title consecutively.
It is the most successful country in Miss World and Miss International and Miss Universe second only surpassed by USA.
Carlos Raúl Villanueva was the most important Venezuelan architect of the modern era; he designed the Central University of Venezuela, (a World Heritage Site) and its Aula Magna. Other notable architectural works include the Capitolio, the Baralt Theatre, the Teresa Carreño Cultural Complex, and the General Rafael Urdaneta Bridge.
Education

The literacy rate for the adult population was already 91.1 by 1998.[111] In 2008, 95.2% of the adult population was literate.[112] Net primary school enrollment rate was at 91% in 2005.[112] Net secondary enrollment rate was at 63% in 2005.[112] Venezuela has a number of universities, of which the most prestigious are the Central University of Venezuela (UCV), founded in Caracas in 1721, the University of the Andes (ULA), founded in Mérida State in 1810, and Simón Bolívar University (USB), founded in Miranda State in 1967.
Health
Venezuela has a national universal health care system. The current government has created a program to expand access to health care known as Misión Barrio Adentro.[113][114]
Infant mortality in Venezuela stood at 16 deaths per 1,000 births in 2004, lower than the South American average (by comparison, the U.S. stands at 5 deaths per 1,000 births in 2006).[115][116][117] Child malnutrition (defined as stunting or wasting in children under age five) stands at 17%; Delta Amacuro and Amazonas have the nation's highest rates.[118] According to the United Nations, 32% of Venezuelans lack adequate sanitation, primarily those living in rural areas.[119] Diseases ranging from typhoid, yellow fever, cholera, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis D are present in the country.[120]
Venezuela has a total of 150 plants for sewage treatment. However, still 13% of the population lack access to drinking water, but this number has been dropping.[121]
See also
- Outline of Venezuela
- Index of Venezuela-related articles
- International rankings of Venezuela
- List of Venezuelans
References
- ^ a b c "Resultado Básico del XIV Censo Nacional de Población y Vivienda 2011" (PDF). Ine.gov.ve. p. 14. Retrieved 25 November 2012. Cite error: The named reference "Census-ethnics" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b c d "Venezuela". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Gini coefficient for the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela". Instituto Nacional de Estadística. 2011.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2013". United Nations Development Programme. 14 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2013.
- ^ Text of the Treaty on the United Nations website "Geneva Agreement, February 17, 1966". United Nations. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 May 1966. Retrieved 15 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: Check|archiveurl=value (help) - ^ a b South America. Encarta. Archived from the original on 21 April 2007. Retrieved 13 March 2007.
- ^ a b "Annex tables" (PDF). World Urbanization Prospects: The 1999 Revision. United Nations. Retrieved 13 March 2007.
- ^ a b McCaughan, Michael (2011). The Battle of Venezuela. Seven Stories Press. p. 32. ISBN 978-1-60980-116-8.
- ^ a b Kelly, Janet and Palma, Pedro (2006) "The Syndrome of Economic Decline and the Quest for Change", p. 207 in McCoy, Jennifer and Myers, David (eds, 2006), The Unraveling of Representative Democracy in Venezuela, Johns Hopkins University Press, ISBN 0-8018-8428-4.
- ^ Robertson, Ewan. (17 October 2012) Venezuelan Economy Achieves Two Years of Continuous Growth. venezuelanalysis.com. Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ Rappoza,Kenneth. (3 June 2013) [1]. forbes.com. Retrieved on 25 June 2013.
- ^ Wells, Miriam. (4 March 2013) [2]. www.insightcrime.org. Retrieved on 25 June 2013.
- ^ Venezuela. Lonely Planet. 2004. p. 177. ISBN 978-1-74104-197-2.
{{cite book}}:|given2=missing|surname2=(help) - ^ a b Massabié, Germán (2008). Venezuela: A Petro-State Using Renewable Energies. Springer. p. 153. ISBN 3531159941.
- ^ Thomas, Hugh (2005). Rivers of Gold: The Rise of the Spanish Empire, from Columbus to Magellan. Random House. p. 189. ISBN 0-375-50204-1.
- ^ "Cuadernos Hispanoamericanos" (in Spanish). Instituto de Cultura Hispánica (Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional). 1958: 386.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000). Encyclopedic Dictionary of YUPArchaeology. Springer. p. 91. ISBN 0-306-46158-7.
- ^ Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000). Encyclopedic Dictionary of YUPArchaeology. Springer. p. 172. ISBN 0-306-46158-7.
- ^ a b c d e Wunder, Sven (2003), Oil wealth and the fate of the forest: a comparative study of eight tropical countries, Routledge. p. 130, ISBN 0203986679.
- ^ Zamora, Margarita (1993). Reading Columbus. University of California Press. pp. Voyage to Paradise. ISBN 0-520-08297-4. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ^ "Alcaldía del Hatillo: Historia" (in Spanish). Universidad Nueva Esparta. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ Gott (2005:203)
- ^ Ewell, Judith (1984), Venezuela:A Century of Change, C. Hurst & Co, p. 4, ISBN 090583836X.
- ^ Chasteen, John Charles (2001). Born in Blood and Fire: A Concise History of Latin America. Norton. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-393-05048-6.
- ^ Stoan, Stephen K. (1974). Pablo Morillo and Venezuela, 1815–1820. Ohio State University Press. p. 29. ISBN 0814202195.
- ^ a b "Venezuela – The Century of Caudillismo". Library of Congress Country Studies.
- ^ "200 años como símbolo de soberanía" (in Spanish). Consulado General de Venezuela en Canarias. Retrieved 30 November 2010.
- ^ a b c "Country Profile: Venezuela" (PDF). Library of Congress (Federal Research Division). 2005. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ Zakaria, Fareed (1999) From Wealth to Power, Princeton University Press, pp. 145–146, ISBN 0-691-01035-8.
- ^ Humphreys, R. A. (1966). "Anglo-American Rivalries and the Venezuela Crisis of 1895. Presidential Address to the Royal Historical Society". Transactions of the Royal Historical Society. 17: 131–164. doi:10.2307/3678723.
- ^ Crow, JA (1980). "Epic of Latin America". University of California Press: 616–617. ISBN 0-520-04107-0.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b "Venezuela". The World Factbook. CIA. 1 July 2010. Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- ^ Schuyler, George W. (2001). "Health and Neoliberalism: Venezuela and Cuba". The Policy Studies Organization: 10.
- ^ "Profile: Hugo Chavez". BBC News. 5 December 2002. Retrieved 5 June 2007.
- ^ The coup installed chamber of commerce leader Pedro Carmona."Profile: Pedro Carmona". BBC. 27 May 2002. Retrieved 6 February 2009.
- ^ López Maya, Margarita (2005) "Venezuela 2002–2003: Polarisation, Confrontation, and Violence", p. 16 in Olivia Burlimgame Goumbri (ed.), The Venezuela Reader, Epica Task Force, Washington D.C., ISBN 0918346355.
- ^ Jones, Bart (2008), Hugo! The Hugo Chavez Story From Mud Hut to Perpetual Revolution, London: The Bodley Head, p386
- ^ "Venezuela devalues currency against US dollar". Aljazeera.com (9 February 2013). Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ Cardenas, Jose R. (26 February 2013) "CARDENAS: Hugo Chavez's legacy of economic chaos". Washingtontimes.com. Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ "The bill for years of mismanagement is coming due". Ft.com (12 February 2013). Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ "Venezuela The homecoming". Economist.com (23 February 2013). Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ Farzad, Roben. (15 February 2013) "Venezuela's Double-Edged Devaluation". Businessweek.com. Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ Mander, Benedict. (10 February 2013) "Venezuelan devaluation sparks panic". Ft.com. Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ Neuman, William (5 March 2013) "Chávez Dies, Leaving Sharp Divisions in Venezuela". New York Times.
- ^ Venezuelan Politics and Human Rights. Venezuelablog.tumblr.com. Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ "Venezuelan opposition challenges Nicolás Maduro's legitimacy".
- ^ TSJ sobre Art.233: Nicolás Maduro es presidente encargado con todas las atribuciones. vtv.gob.ve (8 March 2013).
- ^ Asamblea Nacional tomó Juramento a Nicolás Maduro como Presidente Encargado (+Video). vtv.gob.ve (9 March 2013)
- ^ "Venezuela Boundary Dispute, 1895–1899".
- ^ Warhol, Tom (2006). Tundra. Marshall Cavendish. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-7614-2193-1.
- ^ "Gobierno en Línea: Geografía, Clima". gobiernoenlinea.ve. 2009. Retrieved 27 January 2009.
- ^ "The Alpine Biome". marietta.edu. Retrieved 19 December 2009.
- ^ "Extreme High Temperature in Venezuela". wunderground. Retrieved 16 October 2012.
- ^ "Extreme Low Temp in Venezuela". Wunderground. Retrieved 16 October 2012.
NOTE: Pass the cursor over the subrayed record to see the source of this. "This location is probably uninhabited, but is close to the town of San Isidro de Apartaderos. -11°C (12.2°F) has been reported from an uninhabited high altitude at Páramo de Piedras Blancas, Mérida state."
- ^ "South America Banks on Regional Strategy to Safeguard Quarter of Earth's Biodiversity". Conservation International. 16 September 2003.
- ^ a b c Beech, C. and Dydynski, K. (2004) Venezuela, Lonely Planet, p. 42, ISBN 174104197X.
- ^ Lepage, Denis. "Checklist of birds of Venezuela". Bird Checklists of the World. Avibase. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ a b Bevilacqua, M; Cardenas, L; Flores, AL; et al. (2002). "State of Venezuela's forests: A case study of the Guayana Region". World Resources Institute. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|first3=(help) - ^ Dennis, R.W.G. "Fungus Flora of Venezuela and Adjacent Countries". Her Majesty's Stationary Office, London, 1970
- ^ "Cybertruffle's Robigalia – Observations of fungi and their associated organisms". cybertruffle.org.uk. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ Kirk, P.M., Cannon, P.F., Minter, D.W. and Stalpers, J. (2008 ) "Dictionary of the Fungi". 10th ed., CABI, ISBN 0-85199-826-7
- ^ a b c d "Venezuela: Overview". Global Forest Watch. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ "Fungi of Venezuela – potential endemics". cybertruffle.org.uk. Retrieved 9 July 2011.
- ^ Peck, D (2000). "The Annotated Ramsar List of Wetlands of International Importance: Venezuela". The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. Ramsar Convention Secretariat. Archived from the original on 11 February 2007. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ "Biodiversity and Protected Areas—Venezuela" (PDF). EarthTrends Country Profiles. World Resources Institute. 2003. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ Template:Es icon "Ley Orgánica de Procesos Electorales". Consejo Nacional Electoral. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- ^ Template:Es icon "Dos mil 719 candidatos se disputarán los curules de la Asamblea Nacional". Venezolana de Televisión. 10 June 2010. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Frankal, Elliot (4 July 2005). "Compulsory voting around the world". London: The Guardian. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ "Luisa Estela Morales afirma que la división de poderes debilita al Estado". El Informador. 5 December 2009. Retrieved 16 January 2010. Template:Es icon
- ^ From 1917, "greater awareness of the country's oil potential had the pernicious effect of increasing the corruption and intrigue amongst Gomez's family and entourage, the consequences of which would be felt up to 1935 – McBeth, B. S. (2002) Juan Vicente Gómez and the Oil Companies in Venezuela, 1908–1935, Cambridge University Press, p. 17, ISBN 052189218X.
- ^ "The perception of petroleum as the cause of Venezuela's corruption had become widespread during this period." – Coronil, F. (1988), The magical state: nature, money, and modernity in Venezuela, University Of Chicago Press, p. 353, ISBN 0226116026.
- ^ The truth of Pdval, El Universal, 21 January 2011.
- ^ United Nations, World Drug Report 2010 Statistical Annex: Drug seizures
- ^ "Crime in Venezuela: Shooting the messenger". The Economist. 18 August 2010. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
- ^ El Pais retrieved 03.Nov.2009: "96 homicidios por cada 100.000 habitantes"
- ^ "Venezuela, More Deadly Than Iraq, Wonders Why". The New York Times. 22 August 2010.
- ^ "Crime threatens Chavez vote in Venezuela slums | Reuters". Uk.reuters.com. 14 November 2008. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ Simon Romero. Venezuela more deadly than Iraq. New York Times. 24 August 2010
- ^ "20 killed in Venezuelan prison violence". CNN.com. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- ^ Silverstein, Amy (20 August 2012). "Venezuela prison riot kills 20". Global Post. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- ^ "Venezuela: Gold Returns to the Country, The Euphoria in the Streets". 26 November 2011.
- ^ Pearson, Tamara (9 January 2013). Venezuelan Government Meets with Private Industries to Combat Food Shortages. Venezuelanalysis.com.
- ^ "The Millennium Development Goals Report 2011." United Nations. 2011. Web. 2 April 2012.
- ^ Wilpert, Gregory (11 July 2006). "The Meaning of 21st Century Socialism for Venezuela." Venezuela Analysis.
- ^ Venezuela Energy Profile, Energy Information Administration. Last Update: 30 June 2010.
- ^ Venezuela oil reserves topped Saudis in 2010:OPEC. Market Watch. 18 July 2011
- ^ "Venezuela: Energy overview". BBC. 16 February 2006. Retrieved 10 July 2007.
- ^ Bauquis, Pierre-René (16 February 2006). "What the future for extra heavy oil and bitumen: the Orinoco case". World Energy Council. Archived from the original on 2 April 2007. Retrieved 10 July 2007.
- ^ Yergin, Daniel (1990) The Prize: The Epic Quest for Oil, Money, and Power, Simon and Schuster, pp. 233–236, 432, ISBN 1439110123.
- ^ Yergin, pp. 510–513
- ^ Yergin. p. 767
- ^ McCaughan, Michael (4 January 2011). 2011 The Battle of Venezuela. Seven Stories Press. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-60980-116-8.
{{cite book}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ López Maya, Margarita (2004). "Venezuela 2001–2004: actores y estrategias". Cuadernos del Cendes. 21 (56): 109–132. ISSN 1012-2508.
- ^ Country Comparison :: Roadways. The World Factbook. cia.gov
- ^ CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion Population 1971–2008 IEA (pdf) pp. 83–85
- ^ Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision. Esa.un.org (6 December 2012). Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ "Coastal and Marine Ecosystems—Venezuela" (PDF). EarthTrends Country Profiles. World Resources Institute. 2003. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ "Cuadro Magnitud y Estructura Demográfica". Ine.gob.ve. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ "Censo arrojo datos socioeconómicos nunca antes abordados" (in Spanish). El Aragüeño. 12 August 2012. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
Del total de la población censada (27.272.930 personas), 49,9% se reconoció como moreno o morena; 42,2% como blanco o blanca; 2,8% se autodefinió como negro o negra; mientras que como indígena 2,7% (lo cual representa 725.128 personas que se reconocen como tal) y afrodescendiente 0,7%. El grupo que se reconoció como afrodescendiente, conformado por 181.157 personas, se encuentra ubicado principalmente en la región central y occidental del país. De esa población afrodescendiente, 42.264 viven en Miranda; 21,281 en Carabobo; 19.874 en Aragua; 18.675 en Distrito Capital y 15.019 en el Zulia.
- ^ Benítez, Deivis. "Poblaciones Indígenas en aumento según censo poblacional 2011" (in Spanish). PRENSA MINPPPI. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
Los resultados arrojados por el censo poblacional realizado por el Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas en el 2011 demuestra que las poblaciones indígenas ha aumentado progresivamente con respecto al censo del año 2001.
Según los datos estadísticos publicados por el INE, el total de población que se declaró indígena por sexo, arrojó un resultado de 50,46% hombre y 49,54% mujeres representando 365.920 hombres y 359.208 mujeres para un total de 725.148 personas que se declararon indígenas de Venezuela.
Así mismo, se tomó el porcentaje de población por entidad donde el estado Zulia es la entidad con más indígenas con un 61%, seguido del estado Amazonas con 10%, Bolívar con un 8%, Delta Amacuro con 6%, Anzoátegui 5%, Sucre 3%, Apure y Monagas 2% mientras que en otras entidades existe un 3% de población indígena.
Entre tanto, los pueblos indígenas con mayor población se encuentran los Wayuu 58%, Warao 7%, Kariña 5%, Pemón 4%, Piaroa, Jivi, Añu, Cumanagoto 3%, Yukpa, Chaima 2%, el pueblo Yanomami 1% y otros pueblos con un 9%. - ^ Godinho, Neide Maria de Oliveira (2008). "O impacto das migrações na constituição genética de populações latino-americanas". Universidade de Brasília. Retrieved 1 August 2012.
- ^ "The Spanish of the Canary Islands". personal.psu.edu.
- ^ "World Refugee Survey 2008". U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants. 19 June 2008. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009.
- ^ Venezuela – Population. U.S. Library of Congress.
- ^ > Censos de población y vivienda. INE (23 February 2012). Retrieved on 16 April 2012.
- ^ International Religious Freedom Report 2008: Venezuela. United States Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (21 December 2008)
- ^ Updated 114 minutes ago 25 November 2012 7:39:07 PM +00:00 (8 February 2008). "Santeria surges in Venezuela – World news – Venezuela | NBC News". MSNBC. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Hasta 40 mil bolívares cuesta hacerse "El Santo" – Actualidad | Últimas Noticias". Ultimasnoticias.com.ve. 28 August 2012. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- ^ "Key Facts Venezuela". Turpial Travel & Adventure.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ World's Most Popular Sports – Most Popular Sports in Venezuela accessed 20 January 2013
- ^ Venezuela. Umsl.edu. Retrieved on 20 April 2013.
- ^ a b c "Human Development Report 2009 – Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of)". Hdrstats.undp.org. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ "Health Care for All: Venezuela's Health Missions at Work". Venezuela Information Office. 2007. Archived from the original on 14 June 2008. Retrieved 18 January 2008.
- ^ Castro, Arachu (2008). "Barrio adentro a look at the origins of a social mission". David Rockefeller Center for Latin American Studies, Harvard University. Retrieved 29 January 2009.
- ^ Green, Jeff (10 May 2006). "U.S. death rate". CNN.com. Retrieved 25 April 2010.
- ^ UNDP. Human Development Report 2006: Venezuela. Retrieved 8 March 2007.
- ^ "Population, Health, and Human Well-Being—Venezuela" (PDF). EarthTrends Country Profiles. World Resources Institute. 2003. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ Venezuela. FAO.org.
- ^ Venezuela. Unicef.org.
- ^ Venezuela Guardian. 25 October 2006. Retrieved 20 September 2006.
- ^ Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías Cumpliendo las metas del milenio. República Bolivariana de Venezuela – Gabinete Social (2004) ISBN 980-6456-12-2
External links
- Template:Sp icon E-Government
- Template:En icon Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- Template:En icon "Venezuela". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Template:En icon Venezuela at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:En icon Template:Dmoz
- Template:En icon Venezuela from the Library of Congress Country Studies (1990)
- Template:En icon Venezuela profile from the BBC News
- Template:Sv icon
 Geographic data related to Venezuela at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Venezuela at OpenStreetMap - Template:En icon Maps on Venezuela – Cartographic features
- Template:En icon Key Development Forecasts for Venezuela from International Futures
 Wikimedia Atlas of Venezuela
Wikimedia Atlas of Venezuela
- Use dmy dates from August 2013
- Venezuela
- Caribbean countries
- Countries in South America
- Federal countries
- Former Spanish colonies
- G15 nations
- Member states of OPEC
- Member states of the Union of South American Nations
- Member states of the United Nations
- Republics
- Spanish-speaking countries and territories
- States and territories established in 1811