Subotica: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 637930258 by 195.89.201.254 (talk) |
Undid revision 637959863 by 178.222.66.100 (talk) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
| name = Subotica |
| name = Subotica |
||
| official_name = |
| official_name = Szabadka<br>Subotica<br>Суботица |
||
| native_name = |
| native_name = Szabadka |
||
| other_name = |
| other_name = Суботица |
||
| settlement_type = City |
| settlement_type = City |
||
| image_skyline = Суботица.jpg |
| image_skyline = Суботица.jpg |
||
Revision as of 22:27, 13 December 2014
Subotica
Szabadka Суботица | |
|---|---|
City | |
| Szabadka Subotica Суботица | |
 Town Hall of Subotica | |
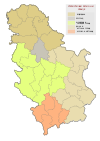
 Location of Subotica within Serbia | |
| Country | Serbia |
| Province | Vojvodina |
| District | North Bačka |
| Settlements | 19 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jenő Maglai (SVM) |
| • Ruling parties | SVM/SNS/SPS |
| Area | |
| • Land | 1,008 km2 (389 sq mi) |
| Population (2011[1]) | |
| • City | 97,910 |
| • Urban | 105,681 |
| • Metro | 141,554 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 24000 |
| Area code | (+381) 24 |
| Vehicle registration | SU |
| Website | www.subotica.rs |
Subotica (Template:Lang-sr, [sǔbɔtit͡sa] , Bunjevac: Subotica, Croatian: Subotica, Template:Lang-hu) is a city in northern Vojvodina, Serbia. Formerly the largest city of Vojvodina region, contemporary Subotica is now the second largest city in the province, following Novi Sad. It is also the fifth largest city in Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the city itself has a population of 97,910, while the urban area of Subotica (with adjacent urban settlement of Palić included) has 105,681 inhabitants, and the population of metro area (the administrative area of the city) stands at 141,554 people.[1] Subotica is a multiethnic city, with Hungarians (35.65%), Serbs (27.02%), Croats (10.00%) and Bunjevci (9.67%) as largest ethnic groups. It is the administrative centre of the North Bačka District.
Geography
It is located in the Pannonian Basin at 46.07° North, 19.68° East, about 10 kilometres (6 miles) from the border with Hungary, and is the northernmost city in Serbia. It is located in the vicinity of lake Palić.
Name

The name Subotica, which first appeared in 1653, may derive from subota, the Serbo-Croatian word for "Saturday", and would mean "a little Saturday". Another theory[citation needed] claims that city was named after Subota Vrlić, the palatine and treasurer of Serb Emperor Jovan Nenad, who had his capital[clarification needed] in Subotica in the 16th century. An older Serbian name used for the city in the 16th century was Sabatka, while Ottoman Turkish name was Sobotka.
The earliest known written name of the city was Zabotka[2] or Zabatka,[3] which dates from 1391. It is the origin of the current Hungarian name for the city "Szabadka".[3][4] According to one opinion, the Name "Szabadka" comes from the adjective szabad,[4] which derived from the Slavic word for "free" – svobod.[5][6][7] According to this view, Subotica's earliest designation would mean, therefore, something like a "free place".[4]
The origin of the earliest form of the name (Zabotka or Zabatka) is obscure.[8] However, according to a local Bunjevci newspaper, Zabatka could have derived from the South Slavic word "zabat" (Gable), which describe parts of Pannonian Slavic houses.[9][unreliable source?]
The town was named in the 1740s for Maria Theresa of Austria, Archduchess of Austria. It was officially called Sent-Maria in 1743, but was renamed in 1779 as Maria-Theresiapolis. These two official names were also spelled in several different ways (most commonly the German Maria-Theresiopel or Theresiopel), and were used in different languages.
The city's name in the other three official languages of Vojvodina are the same as the official name - Slovak: Subotica, Rusyn: Суботица, Romanian: Subotica or Subotiţa.
History
Prehistory and antiquity
In Neolithic and Eneolithic period, several important archaeological cultures flourished in this area, including the Starčevo culture,[10] the Vinča culture,[11] and the Tiszapolgár culture.[12] First Indo-European[citation needed] peoples settled in the territory of present-day Subotica in 4200 BC. During the Eneolithic period, the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, several Indo-European archaeological cultures included areas around Subotica - the Baden culture, the Vučedol culture,[13] the Urnfield culture[14] and some other. Before the Iazyge conquest in the 1st century, Indo-European peoples of Illyrian, Celtic and Dacian descend inhabited this area. In the 3rd century BC, this area was controlled by Celtic Boii and Eravisci, while in the 1st century BC, it became part of the Dacian kingdom. Since the 1st century, the area came under control of the Sarmatian Iazyges (which possibly included Serboi[citation needed] tribe), who occasionally were allies and occasionally enemies of the Romans. Iazyge rule lasted until the 4th century, after which the region came into the possession of various other peoples and states.
Early Middle Ages and Slavic settlement
In the Early Middle Ages various Indo-European and Turkic peoples and states ruled in the area of Subotica. These peoples included Huns, Gepids, Avars, Slavs and Bulgarians. Slavs settled today's Subotica in the 6th and 7th centuries, before some of them crossed the rivers Sava and Danube and settled in the Balkans. Slavic tribe that lived in the territory of present-day Subotica were the Obotrites, who were a subgroup of the Serbs. In the 9th century, after the fall of the Avar state, the first forms of Slavic statehood emerged in this area. The first Slavic states that ruled over this region included the Principality of Lower Pannonia, Great Moravia and the Bulgarian Empire.
The Late Middle Ages
Subotica probably first became a settlement of note when people poured into it from nearby villages destroyed during the Tatar invasions of 1241-1242. However the settlement has surely been older. It has been established that people inhabited these territories even 3000 years ago.[citation needed] When Zabadka / Zabatka was first recorded in 1391, it was a tiny town in the medieval Kingdom of Hungary. Later, the city belonged to the Hunyadis, one of the most influential aristocratic families in the whole of Central Europe.

King Matthias Corvinus of Hungary gave the town to one of his relatives, János Pongrác Dengelegi, who, fearing an invasion by the Ottoman Empire, fortified the castle of Subotica, erecting a fortress in 1470. Some decades later, after the Battle of Mohács in 1526, the Subotica became part of the Ottoman Empire. The majority of the Hungarian population fled northward to Royal Hungary.[citation needed] Bálint Török, a local noble who had ruled over Subotica, also escaped from the city.[citation needed]
In the extremely confused military and political situation following the defeat at Mohács, Subotica came under the control of Serbian mercenaries recruited in Banat. These soldiers were in the service of the Transylvanian general John I Zápolya, a later Hungarian king. The leader of these mercenaries, Jovan Nenad, established in 1526-1527 his rule in Bačka, northern Banat and a small part of Syrmia and created an ephemeral independent state, with Subotica as its capital. At the peak of his power, Jovan Nenad proclaimed himself as Serbian tsar in Subotica. He named Radoslav Čelnik as the general commander of his army, while his treasurer and palatine was Subota Vrlić, a Serbian noble from Jagodina. When Bálint Török returned and captured Subotica from the Serbs, Jovan Nenad moved his capital to Szeged.[15] Some months later, in the summer of 1527, Jovan Nenad was assassinated and his state collapsed. This was the last independent Serbian state before the final Ottoman conquest of all Serb-populated lands. However, after Jovan Nenad's death, Radoslav Čelnik led the remains of the army to Ottoman Syrmia, where he briefly ruled as Ottoman vassal.
Ottoman administration
The Ottoman Empire ruled the city from 1542 to 1686. At the end of this almost 150 year long period, not much remained of the old town of Zabadka / Zabatka. Because much of the population had fled, the Ottomans encouraged the settlement of the area by different colonists from the Balkans. The settlers were mostly Orthodox Serbs. They cultivated the extremely fertile land around Subotica. In 1570, the population of Subotica numbered 49 houses, and in 1590, 63 houses. In 1687, the region was settled by Catholic Dalmatas (called Bunjevci today). It was called "Sobotka" during Ottoman rule and was a kaza centre in Segedin sanjak at first in Budin Eyaleti until 1596, and after that in Eğri Eyaleti between 1596-1686.[16]
Habsburg administration

In 1687, about 5,000 Bunjevci, led by Dujo Marković and Đuro Vidaković settled in Bačka (including Subotica). After the decisive battle against the Ottomans at Senta led by Prince Eugene of Savoy on 11 September 1697, Subotica became part of the military border zone Theiss-Mieresch established by the Habsburg Monarchy. In the meantime the uprising of Francis II Rákóczi broke out, which is also known as the Kuruc War. In the region of Subotica, Rákóczi joined battle against the Rac National Militia. Rác was a designation for the South Slavic people (mostly Serbs and Bunjevci) and they often were referred to as rácok in the Kingdom of Hungary. In a later period rácok came to mean, above all, Serbs of Orthodox religion.
The Serbian military families enjoyed several privileges thanks to their service for the Habsburg Monarchy. Subotica gradually, however, developed from being a mere garrison town to becoming a market town with its own civil charter in 1743. When this happened, many Serbs complained about the loss of their privileges. The majority left the town in protest and some of them founded a new settlement just outside 18th century Subotica in Aleksandrovo, while others emigrated to Russia. In New Serbia, a new Russian province established for them, those Serbs founded a new settlement and also named it Subotica. In 1775 a Jewish community in Subotica was established.
It was perhaps to emphasise the new civic serenity of Subotica that the pious name Saint Mary came to be used for it at this time. Some decades later, in 1779, Empress Maria Theresa of Austria advanced the town's status further by proclaiming it a Free Royal Town. The enthusiastic inhabitants of the city renamed Subotica once more as Maria-Theresiopolis.
This Free Royal Town status gave a great impetus to the development of the city. During the 19th century its population doubled twice, attracting many people from all over the Habsburg Monarchy. This led eventually to a considerable demographic change. In the first half of the 19th century, the Bunjevci had still been in the majority, but there was an increasing number of Hungarians and Jews settling in Subotica. This process was not stopped even by the outbreak of the Revolutions in the Habsburg Monarchy in 1848/49.
1848/1849 Revolutions
During the 1848-1849 revolutions, proclaimed borders of autonomous Serbian Vojvodina included Subotica, but Serb troops did not manage to establish control in this area. In March 5, 1849, at the locality named Kaponja (between Tavankut and Bajmok), there was a battle between Serb and Hungarian army, which was won by the Hungarians.
The first newspaper in the town was also published during the 1848/49 revolution - it was called Honunk állapota ("State of Our Homeland") and was published in Hungarian by Károly Bitterman's local printing company. Unlike most Serbs and Croats who confronted with Hungarians, part of the local Bunjevci people supported Hungarian revolution.
In 1849, after the Hungarian revolution of 1848 was defeated by the Russian and Habsburg armies, the town was separated from the Kingdom of Hungary together with most of the Bačka region, and became part of a separate Habsburg province, called Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar. The administrative center of this new province was Timişoara. The province existed until 1860. During the existence of the voivodeship, in 1853, Subotica acquired its impressive theatre.
Hungarian administration
After the establishment of the Dual-Monarchy in 1867, there followed what is often called the "golden age" of city development of Subotica. Many schools were opened after 1867 and in 1869 the railway connected the city to the world. In 1896 an electrical power plant was built, further enhancing the development of the city and the whole region. Subotica now adorned itself with its remarkable Central European, fin de siècle architecture. In 1902 a Jewish synagogue was built in the Art Nouveau style.
South Slavic states
Subotica was part of Austria-Hungary until the aftermath of World War I in 1918, when the city became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. In changed economical and political circumstances, Subotica was now a border-town in Yugoslavia and did not, for a time, experience again the dynamic prosperity it enjoyed in the years preceding World War I. However, at that time, Subotica was the third largest city in Yugoslavia by population, following Belgrade and Zagreb.

In 1941, Yugoslavia was invaded and partitioned by the Axis Powers, and its northern parts, including Subotica, were annexed by Hungary (This partition of Yugoslavia was not recognized by the international community and city was, from the legal point of view, still part of Yugoslavia, whose only legal representative was Yugoslav government in exile). Hungarian troops entered Subotica on April 11, 1941. As the majority of people living in the city were ethnic Hungarians and the city had been part of Hungary for over 600 years, Hungary felt it had to protect its people now living outside of its borders. During World War II the city lost approximately 7,000 of its citizens, mostly Serbs, Hungarians and Jews.[citation needed] Before the war about 6,000 Jews lived in Subotica. Many Jews were deported from the city during the Holocaust, mostly to Auschwitz. In April 1944 a ghetto was set up. Also, many communists were put to death during Axis rule. In 1944, the Axis forces left city, and Subotica became part of the new socialist Yugoslavia. During the 1944-45 period about 8,000 citizens (mainly Hungarian) were killed by Yugoslav partisans as retribution for supporting Hungary re-taking the city.[17][18]
In the post-war period Subotica has gradually modernised itself. During the Yugoslav and Kosovo wars of the 1990s, a considerable number of Serb refugees came to the city from Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Kosovo, whilst many ethnic Hungarians and Croats, as well as local Serbs, left the country because of economical stagnation. However, unlike in some other places of Serbia, number of Serbs who moving in Subotica is larger than the number of those who leaving the city. During the break-up of Yugoslavia, local leaders in Subotica were drawn from political parties opposed to the policy of the state government in Belgrade.
Towns and villages
Subotica is the fifth largest city in Serbia after Belgrade, Novi Sad, Niš, and Kragujevac.
The administrative area of Subotica comprises the Subotica city, the town of Palić and 17 villages. The villages are:
- Bački Vinogradi
- Bačko Dušanovo
- Bajmok
- Bikovo
- Čantavir
- Donji Tavankut
- Đurđin
- Gornji Tavankut
- Hajdukovo
- Kelebija
- Ljutovo
- Mala Bosna
- Mišićevo
- Novi Žednik
- Stari Žednik
- Šupljak
- Višnjevac
Urban local communities


Besides suburban settlements, there are several official local communities within urban area of Subotica (some of those are partly suburban):[19]
- Aleksandrovo
- Bajnat
- Centar 1
- Centar 2
- Centar 3 (unofficially also called Tokio)
- Dudova Šuma
- Gat
- Ker
- Kertvaroš
- Makova Sedmica
- Mali Bajmok
- Mali Radanovac
- Novi Grad
- Novo Selo
- Peščara
- Prozivka
- Radanovac
- Verušić
- Zorka
- Železničko Naselje
City quarters

List of city quarters (neighborhoods) of Subotica (some of those may and some other may not correspond to official local communities):
- Aleksandrovo
- Bajnat
- Centar
- Dudova Šuma (Radijalac)
- Gat
- Graničar
- Ker
- Kertvaroš
- Makova Sedmica
- Mali Bajmok
- Mali Radanovac
- Novi Grad
- Novo Naselje
- Prozivka
- Srpski Šor
- Teslino Naselje
- Veliki Radanovac
- Zorka
- Železničko Naselje
- For Hungarian names of some of the quarters, please see: List of Hungarian exonyms in Vojvodina.
Demographics


Urban demographics - Ethnic groups in the city
Both, urban and administrative area of Subotica are multi-ethnic. The population of the urban part of Subotica administrative area (including towns of Subotica and Palić) is composed of (according to 2011 census):[20]
- Hungarians = 34,511 (32.66%)
- Serbs = 31,558 (29.86%)
- Croats = 9,698 (9.18%)
- Bunjevci = 9,236 (8.74%)
- Yugoslavs = 2,728 (2.58%)
- Romani = 2,586 (2.45%)
- others
The city serves as the cultural and political centre for the Hungarians, Bunjevci, and Croats in Vojvodina. The largest percent of declared Yugoslavs in Vojvodina (and in all of Serbia) is also found in Subotica.
Administrative area demographics
Ethnic groups in the Subotica administrative area
The population of the Subotica administrative area (which includes urban Subotica, town of Palić and suburban settlements) is composed of (according to 2011 census):[20]
- Hungarians = 50,469 (35.65%)
- Serbs = 38,254 (27.02%)
- Croats = 14,151 (10.00%)
- Bunjevci = 13,553 (9.57%)
- Yugoslavs = 3,202 (2.26%)
- others
Settlements by ethnic majority
The places with a Hungarian absolute or relative ethnic majority are: Subotica (Hungarian: Szabadka), Palić (Hungarian: Palicsfürdő), Hajdukovo (Hungarian: Hajdújárás), Bački Vinogradi (Hungarian: Bácsszőlős), Šupljak (Hungarian: Alsóludas), Čantavir (Hungarian: Csantavér), Bačko Dušanovo (Hungarian: Zentaörs), and Kelebija (Hungarian: Alsókelebia).
The places with a Serb absolute or relative ethnic majority are: Bajmok, Višnjevac, Novi Žednik, and Mišićevo.
The places with a Bunjevac and Croat ethnic majority are: Mala Bosna, Đurđin, Donji Tavankut, Gornji Tavankut, Bikovo, Stari Žednik, and Ljutovo.
Bajmok, Višnjevac, and Stari Žednik have over 20% Hungarians, just as in the places with a Hungarian majority (Subotica, Palić, Bačko Dušanovo, and Kelebija) in which over 20% are Serbs, Croats and Bunjevci.
Languages in the Subotica administrative area
Languages spoken in Subotica administrative area (according to 2002 census):
Note: The Bunjevac language is also spoken in Subotica, but it was not listed separately in the 2002 census results published by the Statistical Office of Serbia; the speakers of this language were listed in category "other languages". The number of those who speak "other languages" (presumably Bunjevac [citation needed]) in the Subotica municipality is 8,914.[21] Some other members of the Bunjevac ethnic community declared in census that their language is Serbian or Croatian. Bunjevac is likely to be listed separately in the future censuses, since the members of the Bunjevac ethnic community expressed the wish for affirmation of their language. They also expressed the wish to have school classes in Bunjevac, so the state is most likely to oblige.
Religion

Religion in Subotica administrative area (according to 2002 census):
- Roman Catholic = 93,521 (63.02%)
- Orthodox = 38,523 (25.96%)
- Protestant = 2,794 (1.88%)
- other

Subotica is the centre of the Roman Catholic diocese of the Bačka region belonging to Serbia. The Subotica area has the highest concentration of Catholics in Serbia. Nearly 70% of the city's population are Catholics. The liturgical languages used in the city's Catholic churches are mostly Hungarian and Croatian. There are eight Catholic parish churches, a Franciscan spiritual centre (the city has communities of both Franciscan monks and Franciscan nuns), a female Dominican community, and two congregations of Augustinian religious sisters. The diocese of Subotica has the only Catholic secondary school in Serbia (Paulinum).
Subotica had a Roman Catholic Blessed working in it. When the nuns' orphanage and children's dome in Blato[disambiguation needed] has exhausted the food funds for helping poor and hungry children, Blessed Mary of Jesus Crucified Petković went to fertile pleains of Bačka and the seat of Bačka Apostolic Administration, Subotica, to solicit help for the orphans and widows. In return, Bishop Ljudevit Lajčo Budanović asked her to found monasteries of her Order in Subotica and neighbourhood, so the locals could benefit spiritually from the instruction of the nuns of her Order...[22] Marija Petković quickly noticed that Bačka also faced the problem of numerous poor and abandoned children, so in 1923, she opened Kolijevka, Children's Home in Subotica. Today this city still has that Children's Home, although the nuns of Marija's Order no longer occupy that Home.
Among another Christian communities, the members of the Serbian Orthodox Church are the most numerous. There are two Eastern Orthodox church buildings in the city; as well as two Protestant churches, Lutheran and Calvinist, respectively. Orthodox Christians in Subotica are belonging to the Eparchy of Bačka of the Serbian Orthodox Church.

The Jewish community of Subotica is the third largest in Serbia, after those in Belgrade and Novi Sad. The astounding proportions and beauty of the Hungarian style art nouveau synagogue are the legacy of a Jewish community that once numbered 6,000 members. About 1,000 of the original Jews of Subotica survived the Holocaust. Today, less than 200 people of Jewish origin remain in Subotica.
Politics

2004 elections
Seats in the municipal parliament won in the 2004 local elections:[23]
- Alliance of Vojvodina Hungarians (16)
- Democratic Party (12)
- Serbian Radical Party (9)
- Democratic Alliance of Croats in Vojvodina (5)
- G17 Plus (4)
- Together for Vojvodina (4)
- Democratic Party of Vojvodina Hungarians (3)
- Serbian Strength Movement (3)
2008 elections
Results of 2008 local elections in Subotica municipality:[24]
- For a European Subotica (40.16%)
- Hungarian Coalition (27.14%)
- Serbian list for Subotica (16.42%)
After the elections, coalition For a European Subotica (with 32 seats), Hungarian Coalition (with 21 seats) and Bunjevac Party (with 1 seat) formed local municipal government. Saša Vučinić from the Democratic Party was elected mayor, and Jenő Maglai from the Hungarian Coalition was elected president of the municipal assembly.[25]
Buildings


Unique in Serbia, Subotica has the most buildings built in the art nouveau style. The City Hall (built in 1908-1910) and the Synagogue (1902) are of especially outstanding beauty. These were built by the same architects, by Marcell Komor and Dezső Jakab from Budapest, Hungary. Another exceptional example of art nouveau architecture is the actual Artistic Encounter building, which was built in 1904 by Ferenc J. Raichle.
The most remarkable church buildings are: the Catholic Cathedral of St. Theresa of Avila from 1797, the Franciscan Monastery from 1723, the Orthodox churches also from the 18th century, and the Hungarian Art Nouveau Subotica Synagogue from the start of the 20th century.
In recent years, there has been an effort to restore the synagogue. Over $400,000 has been raised for the cause by 2004.
Theatre

The historic National Theatre in Subotica, which was built in 1854 as the first monumental public building in Subotica, was demolished in 2007, although it was declared a historic monument under state protection in 1983, and in 1991 it was added to the National Register as a monument of an extraordinary cultural value.[citation needed] An international campaign was organized both in Serbia and in Hungary to save the historic building. ICOMOS and INTBAU also protested against the decision, but with no avail. The historic centre of Subotica was severely damaged visually. Some scanty remains of the destroyed building will be allegedly incorporated into the new theatre.[26]
Education
Subotica is not a university city but has some widely respected secondary schools and faculties.
Secondary Schools

- Teachers' College, founded in 1689, the oldest college in the country and region
- "Svetozar Marković" grammar school web-site
- "Dezső Kosztolányi" Philological grammar school web-site
- "Paulinum" Grammar school of ancient languages of the Catholic Diocese of Subotica
- Music School
- "MEŠC" Electro-mechanical school, recently renamed to "Tehnička Škola - Subotica" (en. "Technical School") web-site
- "Bosa Milićević" School of Economics
- Polytechnic school
- "Lazar Neśić" Chemistry school
- Medical school
Notable faculties
- Civil Engineering faculty web-site
- Electro-Mechanic-Programming faculty "VTŠ" web-site
- Economics faculty web-site
- Teachers faculty in Hungarian language web-site
- Kindergarten Teacher Training College web-site
Historical schools
Sport
Subotica has one major football stadium, the Subotica City Stadium, and one indoor sports hall. The most popular local football team is Spartak Subotica, that plays in the Serbian SuperLiga, the country's primary football competition, and its organized supporters called Marinci (English: Marines).
Newspapers and magazines
Newspapers and magazines published in Subotica:
- Subotičke novine, main weekly newspaper in Serbian (web-site).
- Magyar Szó, in Hungarian, founded 1944, published in Subotica since 2006.
- Bunjevačke novine, in Bunjevac.
- Hrvatska riječ, in Croatian.
- Zvonik, in Croatian
Economy
Surroundings of Subotica are mainly farmland but the city itself is an important industrial and transportation centre in Serbia.
Because of the surrounding farmlands Subotica has some of the most famous food producer industries in the country, with brands such as the confectionery factory "Pionir", "Fidelinka" the cereal manufacturer, "Mlekara Subotica" a milk producer and "Simex" producer of strong alcohol drinks.
There are a number of old socialistic industries that survived the transition period in Serbia. The biggest one is the chemical fertilizer factory "Azotara" and the rail wagon factory "Bratstvo".
Currently the biggest export industry in town is the "Siemens Subotica" windmill factory and it is the biggest brownfield investment so far. The other big companies in Subotica are: Fornetti, ATB Sever and Masterplast.
The most recent companies to come to Subotica are Dunkermotoren, and NORMA Group.
The main reason why foreign industry is usually interested in Subotica are (according to the local economic development office (web-site)):
- Perfect strategic location for business development
- Efficient and business friendly administration
- Free zone and logistic center
- Well trained, hardworking and easy to come by labour
- Great tourist recognition
The city received the NALED award for being the one of five best cities in Serbia for investors in 2010 and also has the NALED business-friendly certificate.[27]
Tourism is significantly important to the city due to Palić and the Palić Lake being near by, which is by itself a tourist destination. In the past few years, Palić has been famous for the Palić Film Festival.
Subotica is also a festival city, hosting more than 17 festivals over the year. (web-site)
Transportation

The Subotica tram, put into operation in 1897, ran on electricity from the start. While neighbouring cities' trams at this date were often still horse-drawn, this gave the Subotica system an advantage over municipalities including Belgrade, Novi Sad, Zagreb, and Szeged. Its existence was important to the citizens of Subotica, as well as tourists who came to visit. Subotica has a bus system. The Subotica buses transport people via nine city, six suburban, and ten interurban, as well as two international lines of bus operations. Per year the buses pass some 4.7 million kilometers, and carry about ten million people.[28] The city used to have a tram system, the Subotica tram system, but it was discontinued in 1974.
Communication
Southwest of Subotica at 46°04′30.97″N 19°37′45.01″E / 46.0752694°N 19.6291694°E, there is a 218.5 metres tall guyed mast for FM-/TV-broadcasting. It may be the tallest of its kind in Serbia.
Famous citizens
- Branimir Aleksić, football player and member of the Serbia national football team
- György Arnold (1771–1848), Hungarian composer
- Sava Babić (born 1934), writer, translator and university professor
- József Bártfay (1812–1864), Hungarian, lawyer, writer
- Géza Csáth (1887–1919), Hungarian, a tragic physician-writer
- Gyula Cseszneky (born 1914), Hungarian, poet, voivode
- Sreten Damjanović (born 1946), wrestler
- Oliver Dulić (born 1975), politician
- Vlatko Dulić (born 1943), actor
- Dr. Kalmar Elemer (1887–1947), lawyer
- Yehuda Elkana, Jewish, born 1934. Israeli philosopher of science
- Lazar Jaramazović (born 1947), national champion in fencing
- Pierre Jovanović (born 1960), French writer and reporter of Serbian origin
- Zoran Kalinić (born 1958), table tennis champion
- Danilo Kiš (1935–1989), Montenegrin-Jewish, possibly the most well-known Serbian writer alongside the Nobel laureate Ivo Andrić
- Juci Komlós (born 1919), Hungarian actress
- Dezső Kosztolányi (1885–1936), Hungarian poet and prose-writer
- Zoran Kuntić, a former Serbian professional footballer
- Félix Lajkó (born 1974), Hungarian, a "world music" violinist and composer
- Péter Lékó (born 1979), Hungary's number one chess player
- Szilveszter Lévai (born 1945), Hungarian composer
- Aleksandar Lifka (1880–1952), a central-European cinematographer
- Bela Lugosi (1882–1956), actor
- Bruck Matija (Bruk Matjas), chemist, creator of Kosan
- Refik Memišević (born 1956), wrestle champion
- Gyula Mester, born in 1972, volleyball player
- Jovan Mikić Spartak (1914–1944), the leader of the Partisans in Subotica, and a national hero who was killed in 1944
- Dr. Arthur Munk, a doctor on RMS Carpathia, famous for saving survivors from Titanic. Doctor Munk was awarded for his helping to survivors
- Tihomir Ognjanov, a former Serbian footballer who was part of Yugoslavia national football team
- Dr. Vinko Perčić (1911–1989), authority in gastroenterology and internal medicine
- Momir Petković (born 1953), wrestle champion
- Bojana Radulović (born 1973), handball player
- Eva Ras (born 1941), Hungarian, actress, painter and Serbian writer
- Magdolna Rúzsa (born 1985), Hungarian pop singer
- Ivan Sarić (1876–1966), aviation pioneer and cyclist
- Tibor Sekelj (Tibor Székely) (1912–1988), Hungarian, explorer, esperantist, writer
- Dr. Stevan Sepesi (1914–1974), Dr of law
- John Simon, Hungarian, American theatre critic
- Đuro Stantić (1878–1918), a world champion in racewalking
- Đorđe Tutorić, Serbian professional football player
International cooperation
- Subotica is a pilot city of the Council of Europe and the EU Intercultural cities programme.[29]
Twin towns - Sister cities
Subotica is twinned with the following cities:
|
Partner Cities
Subotica is a partner city with the following:
|
|
See also
- List of mayors of Subotica
- Municipalities of Serbia
- List of cities in Serbia
- List of cities, towns and villages in Vojvodina
- North Bačka District
- Intercultural cities
References
- ^ a b "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia: Comparative Overview of the Number of Population in 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991, 2002 and 2011, Data by settlements" (PDF). Statistical Office of Republic Of Serbia, Belgrade. 2014. p. 84-87. ISBN 978-86-6161-109-4. Retrieved 2014-06-27.
- ^ [1]
- ^ a b http://www.discoverserbia.org/en/backa/subotica
- ^ a b c "KPV. - Kommunalpolitische Vereinigung (KPV. - Municipal Political Association, the sub-organization of the Christian Democratic Union and the Christlich-Soziale Union of Germany, Serbien Reader - Kleiner Wegweiser für den Political Visit (Serbia Reader - small guide for political visit), Serbien/Montenegro, unsere neuen europäischen Nachbarn (Serbia/Montenegro, our new European neighbors), from March 2009, edited by Christian Passin and Sabine Schiftar, page 76" (PDF) (in German). By Kommunalpolitische Vereingung (www.kpv.at), Vienna. Retrieved 21 January 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Slavistische Studien Bücher - Folge 10 (Slavic Study Books - Episode 10), Handbuch der Südosteuropa-Linguistik (Manual of the Southeast Europe Linguistics), edited by Üwe Hinrichs and Uwe Büttner, page 687" (in German). By Harrassowitz Verlag. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Ungarisch - ein goldener Käfig?(Hungarian - a golden cage?)" (in German). By Die Zeit. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Ein goldener Käfig von Ádám Nádasdy (A golden cage by Ádám Nádasdy), page 2" (PDF) (in German). By the Hungarian Book Foundation by Ádám Nádasdy. Retrieved 20 January 2012.
- ^ Hungarian Catholic Lexicon
- ^ Article in "Bunjevačke novine", number 8, February 2006.
- ^ http://freepages.genealogy.rootsweb.ancestry.com/~hjohnson/New%20Index/Family%20Groups/Group%20Leaders%20Pages/Pin%20Oak%20Reports/inthebeginningupdated2009_files/image010.jpg
- ^ http://www.catyline.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/06/Vincanska_civilizacija_5300-3500_g.p.n.jpg
- ^ http://www.rastko.rs/arheologija/ntasic-eneolit.html
- ^ http://files.myopera.com/edwardpiercy/blog/Area-Culture-Map-1.JPG,
- ^ http://www.eliznik.org.uk/EastEurope/History/balkans-map/middle-bronze.htm
- ^ Borovszky Samu: Magyarország vármegyéi és városai, Bács-Bodrog vármegye I.-II. kötet, Apolló Irodalmi és Nyomdai Részvénytársaság, 1909.
- ^ Sanjak of Segedin
- ^ Mészáros Sándor: Holttá nyilvánítva - Délvidéki magyar fátum 1944-45., I.-II., Hatodik Síp Alapítvány, Budapest 1995.
- ^ Cseres Tibor: Vérbosszú Bácskában, Magvető kiadó, Budapest 1991.
- ^ http://www.subotica.rs/sr/21/mesne-zajednice
- ^ a b "Population by ethnicity – Subotica". Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia (SORS). Retrieved 11 March 2013.
- ^ http://webrzs.stat.gov.rs/axd/Zip/VJN3.pdf
- ^ Template:Hr icon Bl. Marija Petković M. Stantić: Zauzimanje za siromahe - karizma danas
- ^ http://www.cesid.org/lokalni2004/rezultati.jsp?opstina=80438
- ^ http://www.cesid.org/rezultati/sr_maj_2008-lokalni/index.jsp
- ^ http://www.rtv.rs/sr/vesti/vojvodina/subotica/2008_07_10/vest_72200.jsp
- ^ Viktorija Aladzic (2007). "The Old Theatre of Subotica Demolished". INTBAU.org. Retrieved 30 March 2008.
- ^ http://www.naled-serbia.org/index.php
- ^ http://www.danas.rs/vesti/srbija/vojvodina/tramvaji_prvo_u_subotici_pa_u_beogradu.41.html?news_id=123629&action=print
- ^ Council of Europe (2011). "Intercultural city: Subotica, Serbia". coe.int. Retrieved 22 May 2011.
- Recent (2002) statistical information comes from the Serbian statistical office.
- Ethnic statistics: Template:PDFlink, САОПШTЕЊЕ СН31, брoј 295 • год. LII, 24.12.2002, YU ISSN 0353–9555. Accessed 17 January 2006. On page 6–7, Становништво према националној или етничкој припадности по попису 2002. Statistics can be found on the lines for "Суботица" (Subotica).
- Language and religion statistics: Popis stanovništva, domaćinstava i stanova u 2002, ISBN 86-84433-02-5. Accessed 17 January 2006. On page 11–12: СТАНОВНИШТВО ПРЕМА ВЕРОИСПОВЕСТИ, СТАНОВНИШТВО ПРЕМА МАТЕРЊЕМ ЈЕЗИКУ. Statistics can be found on the lines for "Суботица" (Subotica).