List of common Chinese surnames: Difference between revisions
Shumcheeyin (talk | contribs) Fixed #86 Gu & #87 Mao |
Rescuing 6 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.3.2) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The conception of China as consisting of the "[[baixing|old 100 families]]" ({{zh|c=老百姓|p=Lǎo Bǎi Xìng|l=Old Hundred Surnames}}) is an ancient and traditional one, the most notable tally being the [[Song dynasty|Song]]-era ''[[Hundred Family Surnames]]'' ({{zh|c=百家姓|p=Bǎi Jiā Xìng}}). Even today, the number of surnames in China is a little over 4,000,<ref name="Xinhua">Xinhua Net. "[http://news.xinhuanet.com/politics/2007-12/12/content_7231985.htm 我国汉族公民最长姓名达15字 公安部:起名不规范会有不便] [My Country's Han Citizens' Longest Name Reaches 15 [[Chinese characters|Characters]]<nowiki>]</nowiki>". 12 Dec 2007. Accessed 16 Mar 2012. {{zh icon}}</ref> while the year [[2000 US census]] found the number of American surnames held by at least 100 people to be more than 150,000<ref name="US">[[United States Census Bureau]]. "[http://www.census.gov/genealogy/www/data/2000surnames/index.html Genealogy Data: Frequently Occurring Surnames from Census 2000]". 27 Sept 2011. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.</ref> and more than 6.2 million surnames altogether.<ref name="Word">Word, David L. & al. "[http://www.census.gov/genealogy/www/data/2000surnames/surnames.pdf Demographic Aspects of Surnames from Census 2000]". 26 Jun 2001. Accessed 3 Feb 2012.</ref> |
The conception of China as consisting of the "[[baixing|old 100 families]]" ({{zh|c=老百姓|p=Lǎo Bǎi Xìng|l=Old Hundred Surnames}}) is an ancient and traditional one, the most notable tally being the [[Song dynasty|Song]]-era ''[[Hundred Family Surnames]]'' ({{zh|c=百家姓|p=Bǎi Jiā Xìng}}). Even today, the number of surnames in China is a little over 4,000,<ref name="Xinhua">Xinhua Net. "[http://news.xinhuanet.com/politics/2007-12/12/content_7231985.htm 我国汉族公民最长姓名达15字 公安部:起名不规范会有不便] [My Country's Han Citizens' Longest Name Reaches 15 [[Chinese characters|Characters]]<nowiki>]</nowiki>". 12 Dec 2007. Accessed 16 Mar 2012. {{zh icon}}</ref> while the year [[2000 US census]] found the number of American surnames held by at least 100 people to be more than 150,000<ref name="US">[[United States Census Bureau]]. "[http://www.census.gov/genealogy/www/data/2000surnames/index.html Genealogy Data: Frequently Occurring Surnames from Census 2000]". 27 Sept 2011. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.</ref> and more than 6.2 million surnames altogether.<ref name="Word">Word, David L. & al. "[http://www.census.gov/genealogy/www/data/2000surnames/surnames.pdf Demographic Aspects of Surnames from Census 2000]". 26 Jun 2001. Accessed 3 Feb 2012.</ref> |
||
The Chinese expression "Three [[Zhang (surname)|Zhang]] (or/and) Four [[Li (surname 李)|Li]]" ({{zh|s={{linktext|张三李四}}|t={{linktext|張三李四}}|p=Zhāng Sān Lǐ Sì}}) is used to mean "anyone" or "everyone",<ref>Prest, Kevin. "[http://blog.nciku.com/blog/en/?p=1869 X三Y四: Similar Chinese Idioms (Chengyu)]". 4 Mar 2011. Accessed 5 Apr 2012.</ref> but the most common surnames are currently [[Wang (surname)|Wang]] in [[mainland China]]<ref name="Eastday"/> and [[Chen (surname)|Chen]] in [[Taiwan]].<ref name="MOI"/> A commonly cited [[factoid]] from the 1990 edition of the ''[[Guinness Book of World Records]]'' estimated that Zhang was the most common surname in the world,<ref>McFarlan, Donald. ''1990 Guinness Book of World Records''. Sterling Pub. Co., 2001. ISBN 189205101X.</ref> but no comprehensive information from China was available at the time and more recent editions have not repeated the claim. However, Zhang Wei ({{linktext|张|伟}}) is the most common ''full'' name in mainland China.<ref name="BJ">Beijing News. "[http://news.thebeijingnews.com/0565/2007/07-26/034@030220.htm 一个“张伟”找到29万人] [One Name 'Zhang Wei' Covers 290,000 People]". 26 Jul 2007. Accessed 16 Mar 2012. {{zh icon}}</ref> |
The Chinese expression "Three [[Zhang (surname)|Zhang]] (or/and) Four [[Li (surname 李)|Li]]" ({{zh|s={{linktext|张三李四}}|t={{linktext|張三李四}}|p=Zhāng Sān Lǐ Sì}}) is used to mean "anyone" or "everyone",<ref>Prest, Kevin. "[http://blog.nciku.com/blog/en/?p=1869 X三Y四: Similar Chinese Idioms (Chengyu)]". 4 Mar 2011. Accessed 5 Apr 2012.</ref> but the most common surnames are currently [[Wang (surname)|Wang]] in [[mainland China]]<ref name="Eastday"/> and [[Chen (surname)|Chen]] in [[Taiwan]].<ref name="MOI"/> A commonly cited [[factoid]] from the 1990 edition of the ''[[Guinness Book of World Records]]'' estimated that Zhang was the most common surname in the world,<ref>McFarlan, Donald. ''1990 Guinness Book of World Records''. Sterling Pub. Co., 2001. ISBN 189205101X.</ref> but no comprehensive information from China was available at the time and more recent editions have not repeated the claim. However, Zhang Wei ({{linktext|张|伟}}) is the most common ''full'' name in mainland China.<ref name="BJ">Beijing News. "[http://news.thebeijingnews.com/0565/2007/07-26/034@030220.htm 一个“张伟”找到29万人] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070914115742/http://news.thebeijingnews.com/0565/2007/07-26/034%40030220.htm |date=2007-09-14 }} [One Name 'Zhang Wei' Covers 290,000 People]". 26 Jul 2007. Accessed 16 Mar 2012. {{zh icon}}</ref> |
||
==Mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Macau== |
==Mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Macau== |
||
This list of the 100 most common [[Chinese surname]]s derives from comprehensive surveys from 2007 and 1982. The first is derived from a report on the [[Hukou system|household registrations]] released by the [[People's Republic of China|Chinese]] [[Ministry of Public Security of the People's Republic of China|Ministry of Public Security]] on April 24, 2007.<ref name="Eastday">"[http://news.eastday.com/c/20070424/u1a2791347.html 公安部统计:'王'成中国第一大姓 有9288万人] [Public Security Bureau Statistics: 'Wang' Found China's #1 'Big Family', Includes 92.88m People]." 24 Apr 2007. Accessed 27 Mar 2012.{{zh icon}}</ref> The second is derived from the [[1982 Chinese census]] whose [[Midnight|zero hour]] was 00:00 on 1 July 1982. Although no list of surnames was published with the initial summaries, the [[State Post Bureau]] subsequently used the census data to release a series of commemorative stamps in honor of the then-most-common surnames in 2004.<ref name="Peeps">''People's Daily Online''. "[http://english.peopledaily.com.cn/200411/19/eng20041119_164456.html China issues first set of stamps of Chinese family names]". 19 Nov 2004. Accessed 28 Mar 2012.</ref><ref>挑灯看剑 踏雪寻梅. "[http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5cc7bc89010100lx.html 新'百家姓'图腾,快来看看您的尊姓啥模样] [The New ''[[Hundred Family Surnames]]''<nowiki>'</nowiki>s Totems: Quick, Come Look at Your Honorable Surname's Picture]". 12 Dec 2011. Accessed 28 Mar 2012. {{zh icon}}</ref> Previous partial surveys proved less accurate, as many surnames are clustered regionally. |
This list of the 100 most common [[Chinese surname]]s derives from comprehensive surveys from 2007 and 1982. The first is derived from a report on the [[Hukou system|household registrations]] released by the [[People's Republic of China|Chinese]] [[Ministry of Public Security of the People's Republic of China|Ministry of Public Security]] on April 24, 2007.<ref name="Eastday">"[http://news.eastday.com/c/20070424/u1a2791347.html 公安部统计:'王'成中国第一大姓 有9288万人] [Public Security Bureau Statistics: 'Wang' Found China's #1 'Big Family', Includes 92.88m People]." 24 Apr 2007. Accessed 27 Mar 2012.{{zh icon}}</ref> The second is derived from the [[1982 Chinese census]] whose [[Midnight|zero hour]] was 00:00 on 1 July 1982. Although no list of surnames was published with the initial summaries, the [[State Post Bureau]] subsequently used the census data to release a series of commemorative stamps in honor of the then-most-common surnames in 2004.<ref name="Peeps">''People's Daily Online''. "[http://english.peopledaily.com.cn/200411/19/eng20041119_164456.html China issues first set of stamps of Chinese family names]". 19 Nov 2004. Accessed 28 Mar 2012.</ref><ref>挑灯看剑 踏雪寻梅. "[http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5cc7bc89010100lx.html 新'百家姓'图腾,快来看看您的尊姓啥模样] [The New ''[[Hundred Family Surnames]]''<nowiki>'</nowiki>s Totems: Quick, Come Look at Your Honorable Surname's Picture]". 12 Dec 2011. Accessed 28 Mar 2012. {{zh icon}}</ref> Previous partial surveys proved less accurate, as many surnames are clustered regionally. |
||
The summary of the 2007 survey revealed China had approximately 92,881,000 [[Wang (surname)|Wang]]s (7.25% of the general population), 92,074,000 [[Li (surname 李)|Li]]s (7.19%), and 87,502,000 [[Zhang (surname)|Zhang]]s (6.83%). These top three surnames alone accounted for more people than [[Indonesia]], the fourth most populous country in the world.<ref>Badan Pusat Statistik. "[http://dds.bps.go.id/eng/tab_sub/view.php?tabel=1&daftar=1&id_subyek=12¬ab=1 Population of Indonesia by Province 1971, 1980, 1990, 1995 , 2000 and 2010]". 2009. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.</ref> Detailed numbers for the other surnames were not released, but it was noted that seven others{{spaced ndash}}[[Liu (surname)|Liu]], [[Chen (surname)|Chen]], [[Yang (surname)|Yang]], [[Huang (surname)|Huang]], [[Zhao (surname)|Zhao]], [[Wu (surname)|Wu]], and [[Zhou (surname)|Zhou]]{{spaced ndash}}were each shared by more than 20 million Chinese and twelve more{{spaced ndash}}[[Xu (disambiguation)|Xu]], [[Sun (surname)|Sun]], [[Ma (surname)|Ma]], [[Zhu (surname)|Zhu]], [[Hu (surname)|Hu]], [[Guo (surname)|Guo]], [[He (surname)|He]], [[Gao (surname)|Gao]], [[Lin (surname)|Lin]], [[Luo (surname)|Luo]], [[Zheng (surname)|Zheng]], and [[Liang (surname)|Liang]]{{spaced ndash}}were each shared by more than 10 million. All together, the top hundred surnames accounted for 84.77% of China's population.<ref name="Eastday"/><ref name="Lafraniere">{{cite news| url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/21/world/asia/21china.html | work=The New York Times | title=Name Not on Our List? Change It, China Says | first=Sharon | last=Lafraniere | date=21 April 2009}}</ref> By way of comparison, the 2000 census found the most common surname in the [[United States]]{{spaced ndash}}[[Smith (surname)|Smith]]{{spaced ndash}}had fewer than 2.4 million occurrences and made up only 0.84% of the general population. The top 100 surnames accounted for only 16.4% of the US population,<ref name="US"/> and reaching 89.8% of the US population required more than 150,000 surnames.<ref name="Word"/> |
The summary of the 2007 survey revealed China had approximately 92,881,000 [[Wang (surname)|Wang]]s (7.25% of the general population), 92,074,000 [[Li (surname 李)|Li]]s (7.19%), and 87,502,000 [[Zhang (surname)|Zhang]]s (6.83%). These top three surnames alone accounted for more people than [[Indonesia]], the fourth most populous country in the world.<ref>Badan Pusat Statistik. "[http://dds.bps.go.id/eng/tab_sub/view.php?tabel=1&daftar=1&id_subyek=12¬ab=1 Population of Indonesia by Province 1971, 1980, 1990, 1995 , 2000 and 2010] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110718192001/http://dds.bps.go.id/eng/tab_sub/view.php?tabel=1&daftar=1&id_subyek=12¬ab=1 |date=2011-07-18 }}". 2009. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.</ref> Detailed numbers for the other surnames were not released, but it was noted that seven others{{spaced ndash}}[[Liu (surname)|Liu]], [[Chen (surname)|Chen]], [[Yang (surname)|Yang]], [[Huang (surname)|Huang]], [[Zhao (surname)|Zhao]], [[Wu (surname)|Wu]], and [[Zhou (surname)|Zhou]]{{spaced ndash}}were each shared by more than 20 million Chinese and twelve more{{spaced ndash}}[[Xu (disambiguation)|Xu]], [[Sun (surname)|Sun]], [[Ma (surname)|Ma]], [[Zhu (surname)|Zhu]], [[Hu (surname)|Hu]], [[Guo (surname)|Guo]], [[He (surname)|He]], [[Gao (surname)|Gao]], [[Lin (surname)|Lin]], [[Luo (surname)|Luo]], [[Zheng (surname)|Zheng]], and [[Liang (surname)|Liang]]{{spaced ndash}}were each shared by more than 10 million. All together, the top hundred surnames accounted for 84.77% of China's population.<ref name="Eastday"/><ref name="Lafraniere">{{cite news| url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/04/21/world/asia/21china.html | work=The New York Times | title=Name Not on Our List? Change It, China Says | first=Sharon | last=Lafraniere | date=21 April 2009}}</ref> By way of comparison, the 2000 census found the most common surname in the [[United States]]{{spaced ndash}}[[Smith (surname)|Smith]]{{spaced ndash}}had fewer than 2.4 million occurrences and made up only 0.84% of the general population. The top 100 surnames accounted for only 16.4% of the US population,<ref name="US"/> and reaching 89.8% of the US population required more than 150,000 surnames.<ref name="Word"/> |
||
{|class="sort wikitable sortable" style="text-align: center;" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="1" |
{|class="sort wikitable sortable" style="text-align: center;" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="1" |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
! class=sortable colspan=2 | [[Gan Chinese|Gan]] |
! class=sortable colspan=2 | [[Gan Chinese|Gan]] |
||
! class=sortable rowspan=2 colspan=2 | Other |
! class=sortable rowspan=2 colspan=2 | Other |
||
! class=sortable colspan=2 | Former Pronunciation (according to Baxter)<ref name="BaxSag">Baxter, Wm. H. & Sagart, Laurent. ''{{cite web|url= |
! class=sortable colspan=2 | Former Pronunciation (according to Baxter)<ref name="BaxSag">Baxter, Wm. H. & Sagart, Laurent. ''{{cite web|url=http://crlao.ehess.fr/docannexe.php?id=1207 |title=Baxter–Sagart Old Chinese Reconstruction |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120425064509/http://crlao.ehess.fr/docannexe.php?id=1207 |archivedate=2012-04-25 |df= }} {{small|(1.93 MB)}}''. 2011. Accessed 17 March 2013.</ref> |
||
! class=unsortable rowspan=2 | Meaning |
! class=unsortable rowspan=2 | Meaning |
||
|-bgcolor="#EFEFEF" |
|-bgcolor="#EFEFEF" |
||
| Line 2,970: | Line 2,970: | ||
;Other surveys |
;Other surveys |
||
:* 2006 multi-year survey and study conducted by [[Yuan Yida]], a researcher at the [[Chinese Academy of Sciences]]'s Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, using a sample size of 296 million spread across 1,110 counties and cities and recording around 4,100 surnames.<ref>The results of this survey were previously published at the [[National Citizen Identity Information Center]]'s website at http://www.nciic.com.cn/yewufanwei-rksu-mfcp2.htm. However, the link is now dead.</ref> |
:* 2006 multi-year survey and study conducted by [[Yuan Yida]], a researcher at the [[Chinese Academy of Sciences]]'s Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, using a sample size of 296 million spread across 1,110 counties and cities and recording around 4,100 surnames.<ref>The results of this survey were previously published at the [[National Citizen Identity Information Center]]'s website at {{cite web|url=http://www.nciic.com.cn/yewufanwei-rksu-mfcp2.htm |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2015-05-15 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080421054455/http://www.nciic.com.cn/yewufanwei-rksu-mfcp2.htm |archivedate=2008-04-21 |df= }}. However, the link is now dead.</ref> |
||
:* 1990: Ji Yuwen Publishing House, based on a sample size of 174,900. |
:* 1990: Ji Yuwen Publishing House, based on a sample size of 174,900. |
||
:* 1987 study conducted by Yuan Yida with a sample size of 570,000. |
:* 1987 study conducted by Yuan Yida with a sample size of 570,000. |
||
| Line 3,300: | Line 3,300: | ||
{{main|Chinese Malaysian surname}} |
{{main|Chinese Malaysian surname}} |
||
During the [[2010 Malaysian Census]], approximately 6,960,000 Malaysians{{spaced ndash}}self-identified as Chinese.<ref>{{Cite journal|url=http://www.statistics.gov.my/portal/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1215&Itemid=89&lang=en|publisher=Department of Statistics, Malaysia|publication-place=Malaysia|title=Population and Housing Census, Malaysia 2010 (2010 Census)|year=2010|accessdate=4 Apr 2011}}</ref> They are among the few Malaysians who have a continuous surname, as most Malaysians go by [[patronym]]ics instead. |
During the [[2010 Malaysian Census]], approximately 6,960,000 Malaysians{{spaced ndash}}self-identified as Chinese.<ref>{{Cite journal|url=http://www.statistics.gov.my/portal/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1215&Itemid=89&lang=en |publisher=Department of Statistics, Malaysia |publication-place=Malaysia |title=Population and Housing Census, Malaysia 2010 (2010 Census) |year=2010 |accessdate=4 Apr 2011 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20110824062034/https://www.statistics.gov.my/portal/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1215&Itemid=89&lang=en |archivedate=2011-08-24 |df= }}</ref> They are among the few Malaysians who have a continuous surname, as most Malaysians go by [[patronym]]ics instead. |
||
==Singapore== |
==Singapore== |
||
| Line 3,328: | Line 3,328: | ||
[[Chinese Singaporeans|Ethnic Chinese]] make up almost three-fourths (2009) of [[Singapore]]'s resident population of nearly four million (2011). |
[[Chinese Singaporeans|Ethnic Chinese]] make up almost three-fourths (2009) of [[Singapore]]'s resident population of nearly four million (2011). |
||
According to [[Statistics Singapore]], as of the year 2000, the most common [[Chinese Singaporean]] names were:<ref>[[Statistics Singapore]]. "[ |
According to [[Statistics Singapore]], as of the year 2000, the most common [[Chinese Singaporean]] names were:<ref>[[Statistics Singapore]]. "[https://web.archive.org/web/20080223075738/http://www.singstat.gov.sg/pubn/papers/people/chinesesurnames.html Popular Chinese Surnames in Singapore]".</ref> |
||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" border="10" cellspacing="10" cellpadding="10" |
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" border="10" cellspacing="10" cellpadding="10" |
||
Revision as of 22:29, 20 May 2017
Template:Chinesetext These are lists of the most common Chinese surnames in China (People's Republic of China), Taiwan (Republic of China), and the Chinese diaspora overseas as provided by authoritative government or academic sources. Chinese names also form the basis for many common Vietnamese, Korean, and Japanese surnames in both translation and transliteration into those languages.
The conception of China as consisting of the "old 100 families" (Chinese: 老百姓; pinyin: Lǎo Bǎi Xìng; lit. 'Old Hundred Surnames') is an ancient and traditional one, the most notable tally being the Song-era Hundred Family Surnames (Chinese: 百家姓; pinyin: Bǎi Jiā Xìng). Even today, the number of surnames in China is a little over 4,000,[1] while the year 2000 US census found the number of American surnames held by at least 100 people to be more than 150,000[2] and more than 6.2 million surnames altogether.[3]
The Chinese expression "Three Zhang (or/and) Four Li" (simplified Chinese: 张三李四; traditional Chinese: 張三李四; pinyin: Zhāng Sān Lǐ Sì) is used to mean "anyone" or "everyone",[4] but the most common surnames are currently Wang in mainland China[5] and Chen in Taiwan.[6] A commonly cited factoid from the 1990 edition of the Guinness Book of World Records estimated that Zhang was the most common surname in the world,[7] but no comprehensive information from China was available at the time and more recent editions have not repeated the claim. However, Zhang Wei (张伟) is the most common full name in mainland China.[8]
Mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Macau
This list of the 100 most common Chinese surnames derives from comprehensive surveys from 2007 and 1982. The first is derived from a report on the household registrations released by the Chinese Ministry of Public Security on April 24, 2007.[5] The second is derived from the 1982 Chinese census whose zero hour was 00:00 on 1 July 1982. Although no list of surnames was published with the initial summaries, the State Post Bureau subsequently used the census data to release a series of commemorative stamps in honor of the then-most-common surnames in 2004.[9][10] Previous partial surveys proved less accurate, as many surnames are clustered regionally.
The summary of the 2007 survey revealed China had approximately 92,881,000 Wangs (7.25% of the general population), 92,074,000 Lis (7.19%), and 87,502,000 Zhangs (6.83%). These top three surnames alone accounted for more people than Indonesia, the fourth most populous country in the world.[11] Detailed numbers for the other surnames were not released, but it was noted that seven others – Liu, Chen, Yang, Huang, Zhao, Wu, and Zhou – were each shared by more than 20 million Chinese and twelve more – Xu, Sun, Ma, Zhu, Hu, Guo, He, Gao, Lin, Luo, Zheng, and Liang – were each shared by more than 10 million. All together, the top hundred surnames accounted for 84.77% of China's population.[5][12] By way of comparison, the 2000 census found the most common surname in the United States – Smith – had fewer than 2.4 million occurrences and made up only 0.84% of the general population. The top 100 surnames accounted for only 16.4% of the US population,[2] and reaching 89.8% of the US population required more than 150,000 surnames.[3]
| Rank | Character | Romanizations | Notes | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandarin | Cantonese | Min Nan | Hakka | Gan | Other | Former Pronunciation (according to Baxter)[13] | Meaning | ||||||||||||
| 2007 | 1982 | Trad. | Simp. | Pinyin | Wade | Jyutping | HK | Other | POJ[a] | Other | PFS | Other | GP | Other | Old Chinese | Middle Chinese | |||
| 1 | 2 | 王 | Wáng | Wang2 | Wong4 | Wong | Vang | Ông | Heng | Vòng | Wong | Uōng | Wong | Viet. | Vương | *ɢʷaŋ | Hjwang | "King" | |
| Kor. | Wang (왕) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 1 | 李 | Lǐ | Li3 | Lei5 | Lee Li |
Ly | Lí | Lee | Lí | Lee | Lî | Lee | Viet. | Lý/Lí | *C.rəʔ | LiX | "Plum" | |
| N. Kor. | Ri (리) | ||||||||||||||||||
| S. Kor. | Yi, Lee, Rhee (이) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ri | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Dy, Sy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lat. Am. | Ley | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 3 | 張 | 张 | Zhāng | Chang1 | Zoeng1 | Cheung | Cheong Chong |
Tiuⁿ (X, Q, K, T) Tioⁿ (Z) |
Teo Teoh Tio |
Chông | Chong | Tong | Cheong Thong |
Viet. | Trương | *C.traŋ | Trjang | "Expanding" (bowstring pulling)[16] |
| Kor. | Jang (장) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Chō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Tiong, Tiu | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indon. | Sutiono, Tjong | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 4 | 劉 | 刘 | Liú | Liu2 | Lau4 | Lau | Lao Lou |
Lâu | Lau Low Lao |
Liù | Liew | Liu | Lew Lieu |
Viet. | Lưu | *mə-ru | Ljuw | Han Dynasty royalty ; To kill[16] |
| Kor. | Yu/Ryu (유/류) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ryū | ||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 5 | 陳 | 陈 | Chén | Ch'en2 | Can4 | Chan | Chun Chean Chin |
Tân | Tan Tang Ting |
chhìn | chin | Thín | Thin Chin |
Viet. | Trần | *lrin | Drin | "Exhibit", "Old"[16] State of Chen |
| Kor. | Jin (진) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Chin | ||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 6 | 楊 | 杨 | Yáng | Yang2 | Joeng4 | Yeung | Yeong Ieong Young |
Iûⁿ (X, Q, K, T) Iôⁿ (Z) |
Yeoh Yeo |
Yòng | Yong Yeong |
Iōng | Yeong | Viet. | Dương | *laŋ | Yang | "Aspen" State of Yang |
| Kor. | Yang (양) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Yō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 8 | 黃 | 黄 | Huáng | Huang2 | Wong4 | Wong | Wang Vong |
N̂g (X, Q, K, T) Ûiⁿ (Z) |
Ng Ung |
Vòng | Wong | Uōng | Wong Fong |
Viet. | Hoàng/Huỳnh | *N-kʷˤaŋ | Hwang | "Yellow" State of Huang |
| Kor. | Hwang (황) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 7 | 趙 | 赵 | Zhào | Chao2 | Ziu6 | Chiu | Chu Chio Jiu |
Tiō (X, Z, K, T) Tiǒ (Q) |
Teo Teoh |
Chhau | Chau | Thèu | Cheu Chew |
Viet. | Triệu | State of Zhao | ||
| Kor. | Jo (조) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Chō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | 10 | 吳 | 吴 | Wú | Wu2 | Ng4 | Ng | Ung, Eng | Gô͘ Ngô͘ (X, Q, K, T) |
Goh | Ǹg | Ng | Ng | Ng | Viet. | Ngô | *ŋʷˤa | Ngu | "Loud"[16] State of Wu |
| Kor. | Oh (오) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Go | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Woo | ||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 9 | 周 | Zhōu | Chou1 | Zau1 | Chow | Jao ChauChao |
Chiu | Chew Jew |
Chiû | Chew Chiew |
Tiu | Chew Cheu |
Viet. | Chu, Châu | *tiw | Tsyuw | Circumference, Cycle, Week, Surroundings Zhou dynasty State of Zhou | |
| Kor. | Ju (주) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shū | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Joe | ||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | 11 | 徐 | Xú | Hsü2 | Ceoi4 | Tsui | Choi Chui Tsua |
Chhî (X, Z, K, T) Sîr (Q) |
Chee Cher Cheu Swee |
Chhì | Chi | Chhié | Chee Chui |
Viet. | Từ | *sə.la | Zjo | Slow State of Xu | |
| Kor. | Seo (서) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sho | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indon. | Dharmadjie Christiadjie | ||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 12 | 孫 | 孙 | Sūn | Sun1 | Syun1 | Suen | Sun | Sng (X, Q, K, T) Sun (X, Q, K, T) Suiⁿ (Z) |
Sng Soon |
Sûn | Sun | Sun | Suen | Viet. | Tôn | *sˤun | Swon | "Grandson" |
| Kor. | Son (손) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Son | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Suan | ||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | 19 | 馬 | 马 | Mǎ | Ma3 | Maa5 | Ma | Mah Mar |
Má Bé (K, T) |
Bey Beh Baey |
Mâ | Ma | Mâ | Mâ | Viet. | Mã | *mˤraʔ | MaeX | "Horse" State of Mafu |
| Kor. | Ma (마) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ba | ||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | 14 | 朱 | Zhū | Chu1 | Zyu1 | Chu | Chue | Chu | Choo | Chû | Choo | Tu | Chu | Viet. | Châu | *to | Tsyu | "crimson" State of Zhu | |
| Kor. | Ju (주) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shu | ||||||||||||||||||
| Can. | Gee | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Ju | ||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | 13 | 胡 | Hú | Hu2 | Wu4 | Wu | Woo Vu |
Ô͘ | Oh Aw |
Fù | Foo | Ū | Wu Foo |
Viet. | Hồ | *gˤa | Hu | "mustache" "beard" | |
| Kor. | Ho (호) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ko | ||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | 18 | 郭 | Guō | Kuo1 | Gwok3 | Kwok | Kuok | Koeh (Z, K, T) Keh (X) Kerh (Q) |
Kueh Koay Quay Kwek Quek |
Kwok | Kwok Kok |
Kuok | Kwok | Viet. | Quách | *kʷˤak | Kwak | "City wall" | |
| Kor. | Gwak (곽) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kaku | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Ker, Kho, Kwok | ||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | 17 | 何 | Hé | Hê2 Ho2 |
Ho4 | Ho | Hoe | Hô | Ho Hor |
Hò | Ho | Hó | Ho | Viet. | Hà | *gˤaj | Ha | State of Han ; Interrogative mark (何人 = who) | |
| Kor. | Ha (하) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ka | ||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | 15 | 高 | Gāo | Kao1 | Gou1 | Ko | Kou Go |
Ko (X, Z, K, T) Ko͘ (Q) |
Ko Kor |
Kô Kau |
Koo | Kou | Kou | Viet. | Cao | *Cə.kˤaw | Kaw | "Tall" | |
| Kor. | Go (고) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | 16 | 林 | Lín | Lin2 | Lam4 | Lam | Lum | Lîm | Lim | Lìm | Lim | Līm | Līm | Viet. | Lâm | *k.rəm | Lim | "Forest" | |
| Kor. | Lim/Im/Rim (임/림) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Rin | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | 20 | 羅 | 罗 | Luó | Lo2 | Lo4 | Lo | Law Loh, Lowe Lor |
Lô | Lo Lor Law |
Lò | Law Lo Loh |
Lō | Lō Law |
Viet. | La | *rˤaj | La | "Gatherer" |
| Kor. | Na/La/Ra (나/라) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ra | ||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | 23 | 鄭 | 郑 | Zhèng | Cheng4 | Zeng6 | Cheng | Cheang Chiang |
Tēⁿ (K) Tīⁿ (X, T) Tìⁿ (Q) Tēeⁿ (Z) |
Tay Teh |
Chhang | Chang | Thàng | Viet. | Trịnh | State of Zheng | |||
| Kor. | Jeong (정) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tei | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Ty, Tee | ||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | 21 | 梁 | Liáng | Liang2 | Loeng4 | Leung | Leong Lang Leng |
Niû (X, Q, K, T) Niô͘ (Z) |
Neo | Liòng | Leong | Liōng | Viet. | Lương | *raŋ | Ljang | "beam" (architecture) State of Liang | ||
| Kor. | Yang/Ryang (양/량) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ryō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | 24 | 謝 | 谢 | Xiè | Hsieh4 | Ze6 | Tse | Che | Chiā (Z, K) Siā (X, T) Sià (Q) |
Chia Cheah Seah |
Tshia | Cheah | Chhià | Viet. | Tạ | *sə-lak-s | ZjaeH | "Thankful" State of Xie | |
| Kor. | Sa (사) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sha | ||||||||||||||||||
| Can. | Tsia | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Saa, Sese, Sia | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Shieh | ||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | 22 | 宋 | Sòng | Sung4 | Sung3 | Sung | Sòng Sàng (K, T) |
Song | Sung | Song Soong |
Sūng | Viet. | Tống | State of Song | |||||
| Kor. | Song (송) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Soong | ||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | 26 | 唐 | Táng | T'ang2 | Tong4 | Tong | Tn̂g Tông (X, Z, K, T) |
Tng Tang |
Thòng | Tong Thong |
Thóng | Viet. | Đường | *N-rˤaŋ | Dang | Tang dynasty | |||
| Kor. | Dang (당) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | 35 | 許 | 许 | Xǔ | Hsü3 | Heoi2 | Hui Hooi |
Hoi | Khó͘ | Koh Khoh |
Hí | Hee | Hé | Viet. | Hái, Hứa | *qʰaʔ | XjoX | State of Xǔ ; To allow | |
| Kor. | Heo (허) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyo | ||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | 25 | 韓 | 韩 | Hán | Han2 | Hon4 | Hon | Hân | Hang | Hòn | Hon | Hón | Viet. | Hàn | *gˤar | Han | State of Han | ||
| Kor. | Han (한) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kan | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Hang | ||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | 27 | 馮 | 冯 | Féng | Feng2 | Fung4 | Fung | Fong | Pâng | Pang | Fùng Phùng |
Foong | Fūng | Viet. | Phùng | *Cə.bəŋ | Bjuwng | "Gallop" State of Feng | |
| Kor. | Pung (풍) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Hō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | 34 | 鄧 | 邓 | Dèng | Teng2 | Dang6 | Tang | Theng | Tēng (X, Z, K, T) Tèng (Q) |
Teng | Then | Ten Then |
Thèn | Viet. | Đặng | State of Deng | |||
| Kor. | Deung (등) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Deang | ||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | 32 | 曹 | Cáo | Ts'ao2 | Cou4 | Tso | Chaw | Chô (X, Z, K, T) Chô͘ (Q) |
Chow | Tshò Tshàu |
Cho Chaw |
Chhóu | Viet. | Tào | *N-tsˤu | Dzaw | State of Cao | ||
| Kor. | Jo (조) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | 39 | 彭 | Péng | P'eng2 | Pang4 | Pang | Banh | Phêⁿ (K) Phîⁿ (X, Q, T) Phêeⁿ (Z) |
Peh Phe |
Phàng | Phang | Pháng | Viet. | Bành | *C.bˤraŋ | Baeng | Descendant of Peng Zu | ||
| Kor. | Paeng (팽) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Hō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Khmer | Pay | ||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | 38 | 曾 | Zēng | Tseng1 | Zang1 | Tsang | Chang Dong |
Chan | Chan | Tsên | Chen | Chen | Viet. | Tăng | *tsˤəŋ | Tsong | State of Zeng ; Relationship between great-grandchildren and great-grandparent | ||
| Kor. | Jeung (증) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indon. | Tjan | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Tzeng | ||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | 30 | 蕭 | 肖 (萧) |
Xiāo | Hsiao1 | Siu1 | Siu | Sio | Siau (X, Z, K, T) Sio (X, Q, K, T) |
Seow Siau Siow |
Siâu | Siew Siaw |
Sieu | Viet. | Tiêu | *sˤiw | Sew | "Quiet" Kingdom of Xiao | |
| Kor. | So (소) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | 58 | 田 | Tián | T'ien2 | Tin4 | Tin | Chan | Tiân | Chan Chang |
Thièn | Thien Then |
Thién | Viet. | Điền | *lˤiŋ | Den | field, farmland | ||
| Kor. | Jeon (전) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ten | ||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | 29 | 董 | Dǒng | Tung3 | Dung2 | Tung | Tong | Táng Tóng (Z) |
Tong | Túng | Tung | Tûng | Viet. | Đổng | direct, supervise, mentor | ||||
| Kor. | Dong (동) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | 33 | 袁 | Yuán | Yüan2 | Jyun4 | Yuen | Wan | Oân | Wang | Yèn | Yen | Iōn | Viet. | Viên | *ɢʷan | Hjwon | a long robe | ||
| Kor. | Won (원) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | En | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Yan | ||||||||||||||||||
| 37 | 52 | 潘 | Pān | P'an1 | Pun1 | Poon | Pun | Phoaⁿ | Phua | Phân | Pan Phan |
Phon | Viet. | Phan | name of a river that flows into the Han | ||||
| Kor. | Ban (반) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Han | ||||||||||||||||||
| 38 | 28 | 于 | Yú | Yü2 | Jyu1 | Yue | U | Î (Z) Û (X) U (Q, K, T) |
Yee | Yî | Yee | Uī | Viet. | Vu | *ɢʷa | Hju | in, on, at; go to | ||
| Kor. | U (우) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | U | ||||||||||||||||||
| 39 | 43 | 蔣 | 蒋 | Jiǎng | Chiang3 | Zoeng2 | Tseung | Cheung | Chiúⁿ (X, Q, K, T) Chióⁿ (Z) |
Cheoh Chioh |
Tsiòng | Cheong | Chiông | Viet. | Tưởng | wild rice (Zizania latifolia) | |||
| Kor. | Jang (장) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | 44 | 蔡 | Cài | Ts'ai4 | Coi3 | Choi | Choy Tsoi Toy |
Chhoà | Chua | Chhai | Chai Choi |
Chhói | Viet. | Thái Sái |
*s.r̥ˤat-s | TshajH | State of Cai | ||
| Kor. | Chae (채) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sai | ||||||||||||||||||
| Can. | Chai | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Tsay | ||||||||||||||||||
| 41 | 51 | 余 | Yú | Yü2 | Jyu4 | Yu Yue |
U Yee |
Î (Z, K, T) Û (X, K, T) Îr (Q) |
Ee Eu |
Yì | Yee | Uī | Viet. | Dư | *la | Yo | extra, surplus | ||
| Kor. | Yeo (여) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Yo | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indon. | Ie, Iman, Oe | ||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | 53 | 杜 | Dù | Tu4 | Dou6 | To | Do Tou |
Tō͘ (X, Z, K, T) Tǒ͘ (Q) |
Toh | Thu | To Toh |
Thù | Viet. | Đỗ | To prevent[17] | ||||
| Kor. | Du (두) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | To | ||||||||||||||||||
| 43 | 49 | 葉 | 叶 | Yè | Yeh4 | Jip6 | Yip | Ip Yeap |
Ia̍p | Yap | Ya̍p | Yap | Iep | Viet. | Diệp | *lap | Yep | Leaf | |
| Kor. | Seob/Yeop (섭/엽) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Yō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Yee, Ee | ||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | 31 | 程 | Chéng | Ch'eng2 | Cing4 | Ching | Cheng | Thiâⁿ (X, Q, K, T) Thêeⁿ (Z) |
Thia | Chhàng Chhìn |
Chang Chin |
Tháng | Viet. | Trình | *C.lreŋ | Drjeng | rule, order, regulation, procedure, journey | ||
| Kor. | Jeong (정) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tei | ||||||||||||||||||
| 45 | 41 | 蘇 | 苏 | Sū | Su1 | Sou1 | So |
Sou | So͘ | Soh | Sû | Soo | Su | Viet. | Tô | *s.ŋˤa | Su | Come to | |
| Kor. | So (소) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | So | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Soo | ||||||||||||||||||
| 46 | 47 | 魏 | Wèi | Wei4 | Ngai6 | Ngai | Gūi (X, Z, K, T) Gùi (Q) |
Ngwee Ngui |
Ngui | Ngui Wee |
Ngùi | Viet. | Nguỵ Ngụy |
*N-qʰuj | Ngjw+j | State of Wei | |||
| Kor. | Wi (위) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Gi | ||||||||||||||||||
| 47 | 40 | 呂 | 吕 | Lǚ | Lü3 | Leoi5 | Lui | Loi | Lū (X, T) Lī (Z, K) Lǐr (Q) |
Lee Leu Ler Loo |
Lî | Lee | Liê | Viet. | Lữ Lã |
*raʔ | LjoX | A musical note | |
| Kor. | Yeo/Ryeo (여/려) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ryo | ||||||||||||||||||
| 48 | 46 | 丁 | Dīng | Ting1 | Ding1
Teng4 |
Ting | Ding |
Teng | Teng | Tén | Ten | Tiang | Viet. | Đinh | *tˤeŋ | Teng | Strong man | ||
| Kor. | Jeong (정) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tei | ||||||||||||||||||
| 49 | 59 | 任 | Rén | Jen4 | Jam6 | Yam | Iam Yum |
Jîm (Z, K) Lîm (X, Q) Līm (T) |
Jim | Ngim | Ngim Yim |
Nìm | Viet. | Nhiệm Nhậm |
*nəm-s | NyimH | Appoint | ||
| Kor. | Im (임) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Jin | ||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | 37 | 沈 | Shěn | Shen3 | Sam2 | Sum | Sam Shum |
Sím | Sim | Shím Sím |
Sim | Sím | Viet. | Thẩm Trầm |
*l̥əmʔ | SyimX | To sink | ||
| Kor. | Shim (심) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shin | ||||||||||||||||||
| 51 | 64 | 姚 | Yáo | Yao2 | Jiu4 | Yiu | Yeow Io Iu |
Iâu | Yeo | Yào | Yow | Iēu | Viet. | Diêu | Elegant | ||||
| Kor. | Yo (요) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Yō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 52 | 42 | 盧 | 卢 | Lú | Lu2 | Lou4 | Lo | Lou | Lô͘ | Loh | Lù | Loo | Lū | Viet. | Lư Lô |
Hut, cottage | |||
| Kor. | No/Ro (노/로) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ro | ||||||||||||||||||
| 53 | 60 | 姜 | Jiāng | Chiang1 | Goeng1 | Keung | Geung Keong |
Khiang (Z) Khiong (X, K, T) Khiuⁿ (Q) |
Kiang | Kiông | Keong | Kiong | Viet. | Khương | *C.qaŋ | Kjang | Ginger | ||
| Kor. | Kang (강) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 54 | 74 | 崔 | Cuī | Ts'ui1 | Ceoi1 | Chui | Choi | Chhui | Chui Chwee |
Tshûi | Chooi | Chhoi | Viet. | Thôi | *dzˤuj | Dzwoj | Towering[18] | ||
| Kor. | Choi (최) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sai | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Tseui | ||||||||||||||||||
| 55 | 56 | 鍾 | 钟 | Zhōng | Chung1 | Zung1 | Chung | Chong | Chiong Cheng (K, T) |
Cheng | Chûng Tsung |
Chong Chung |
Tung | Viet. | Chung | "Bell" State of Zhongli | |||
| Kor. | Jong (종) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 56 | 65 | 譚 | 谭 | Tán | T'an2 | Taam4 | Tam | Tom Ham Hom |
Thâm | Tham | Thàm | Tham | Thóm | Viet. | Đàm | "Talk" State of Tan | |||
| Kor. | Dam (담) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tan | ||||||||||||||||||
| 57 | 70 | 陸 | 陆 | Lù | Lu4 | Luk6 | Luk | Lok | Lio̍k | Loke Lek |
Liu̍k | Luk | Liuk | Viet. | Lục | *ruk | Ljuwk | Land | |
| Kor. | Yuk/Ryuk (육/륙) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Riku | ||||||||||||||||||
| 58 | 57 | 汪 | Wāng | Wang1 | Wong1 | Wong | Ong (X, Q, K, T) Óng (Z) |
Wang | Vong | Wong | Uong | Viet. | Uông | *qʷˤaŋ | 'Wang | Sea | |||
| Kor. | Wang (왕) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 59 | 61 | 范 | Fàn | Fan4 | Faan6 | Fan | Hoān (X, Z, K, T) Hoǎn (Q)Hwan |
Huang
Hoan Hwan |
Fam | Fam
Hoan Hwan |
Fàn | Viet. | Phạm | *bomʔ | BjomX | Example | |||
| Kor. | Beom (범) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Han | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60 | 69 | 金 | Jīn | King1 | Gam1 | Kam | Gum | Kim | Kim | Kîm | Kim | Kim | Viet. | Kim | *kəm | Kim | "Gold" | ||
| Kor. | Kim (김) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kin | ||||||||||||||||||
| 61 | 63 | 石 | Shí | Shih2 | Sek6 | Sek Shek |
Seac Seak |
Chio̍h | Chioh Cheoh |
Sha̍k Sak |
Shak | Sak | Viet. | Thạch | *dak | Dzyek | "Stone" | ||
| Kor. | Seok (석) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Seki | ||||||||||||||||||
| 62 | 66 | 廖 | Liào | Liao4 | Liu6 | Liu | Lew Leow Liew Lio |
Liāu (X, Z, K, T) Liàu (Q) |
Leow Liau Liow |
Liau | Liew Liau |
Lièu | Viet. | Liêu Liệu |
|||||
| Kor. | Ryo (료) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ryō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 63 | 45 | 賈 | 贾 | Jiǎ | Chia3 | Gaa2 | Ka | Ga | Ká (X, Q, K, T) Kée (Z) |
Kia | Ká | Ka | Kâ | Viet. | Giả | *C.qˤ<r>aʔ-s | KaeH | "Merchant" | |
| Kor. | Ga (가) Go (고) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ka | ||||||||||||||||||
| 64 | 55 | 夏 | Xià | Hsia2 | Haa6 | Ha | Hē (K, T) Hā (X, K, T) Hà (Q) Hēe (Z) |
Hah Hay |
Ha | Ha | Hà | Viet. | Hạ | "Summer" Xia Dynasty | |||||
| Kor. | Ha (하) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ka | ||||||||||||||||||
| 65 | 韋 | 韦 | Wéi | Wei2 | Wai4 | Wai | Vai | Ûi (X, Q, K, T) Úi (Z) |
Wee | Vúi Vì |
Wooi Wee |
Uī | Viet. | Vi | Soft Leather | ||||
| Kor. | Wi (위) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | I | ||||||||||||||||||
| 66 | 36 | 傅 | 付 (傅) |
Fù | Fu4 | Fu6 | Fu Foo |
Pò͘ | Poh | Fu | Fu | Fù | Viet. | Phó | *pa-s | PjuH | Teacher | ||
| Kor. | Bu (부) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Fu | ||||||||||||||||||
| 67 | 62 | 方 | Fāng | Fang1 | Fong1 | Fong | Hong (X, Q, K, T) Png (X, Q, K, T) Puiⁿ (Z) |
Pung | Fông | Fong | Fong | Viet. | Phương | *C.paŋ | Pjang | Square | |||
| Kor. | Bang (방) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Hō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | |||||||||||||||||||
| 68 | 73 | 白 | Bái | Pai2 | Baak6 | Pak | Bak | Pe̍h Pe̍k (Z) |
Peh | Pha̍k | Pak Phak |
Phak | Viet. | Bạch | *bˤrak | Baek | "White" | ||
| Kor. | Baek (백) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Haku | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Bo | ||||||||||||||||||
| 69 | 67 | 鄒 | 邹 | Zōu | Tsou1 | Zau1 | Chow | Jao Chau |
Chau (K, T) Cho͘ (X, Z, K, T) Cho (Q) Che (Z) |
Chou Choh |
Tsêu | Chew Chiew |
Chiu | Viet. | Trâu | ||||
| Kor. | Chu (추) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shū | ||||||||||||||||||
| 70 | 84 | 孟 | Mèng | Meng4 | Maang6 | Mang | Bēng (X, Z, K, T) Bèng (Q) |
Meng | Men | Mang | Màng | Viet. | Mạnh | *mˤraŋ-s | MaengH | First, Eminent | |||
| Kor. | Maeng (맹) Mang (망) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Mō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 71 | 68 | 熊 | Xióng | Hsiung2 | Hung4 | Hung | Hong | Hîm | Him | Yùng | Yoong | Hiūng | Viet. | Hùng | "Bear" | ||||
| Kor. | Ung (웅) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Yū | ||||||||||||||||||
| 72 | 78 | 秦 | Qín | Ch'in2 | Ceon4 | Chun | Tseun Tseon Chon |
Chîn | Ching | Tshìn | Chin | Chhín | Viet. | Tần | *dzin | Dzin | Qin Dynasty | ||
| Kor. | Jin (진) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shin | ||||||||||||||||||
| 73 | 77 | 邱 | Qiū1 | Ch'iu1 | Jau1 | Yau | Iao Iau |
Khu | Khoo | Khiû Hiû |
Hew Khew |
Khiu | Viet. | Khâu | Hills | ||||
| Kor. | Koo (구) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyū | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mal. | Hew, Hiew Chiew | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Chiou | ||||||||||||||||||
| 74 | 79 | 江 | Jiāng | Chiang1 | Gong1 | Kong | Kang | Kang | Kông | Kong | Kong | Viet. | Giang | *kˤroŋ | Kaewng | River | |||
| Kor. | Gang (강) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Kiang | ||||||||||||||||||
| 75 | 91 | 尹 | Yǐn | Yin3 | Wan5 | Wan | Ún (K, T) Ín (X, Q, Z) |
Un Eun Eung |
Yún | Yoon | Ín | Viet. | Doãn | *m-qurʔ | YwinX | Administer | |||
| Kor. | Yun (윤) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | In | ||||||||||||||||||
| 76 | 48 | 薛 | Xuē | Hsüeh1 | Sit3 | Sit | Sih | Siet | Set | Siot | Viet. | Tiết | Wormwood | ||||||
| Kor. | Seol (설) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Setsu | ||||||||||||||||||
| 77 | 50 | 閻 | 闫 (阎) |
Yán | Yen2 | Jim4 | Yim | Im | Giâm | Ngiam | Ngiàm | Ngiam Yam |
Iēm | Viet. | Diêm | Extremely cruel | |||
| Kor. | Yeom (염) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | En | ||||||||||||||||||
| 78 | 87 | 段 | Duàn | Tuan4 | Dyun6 | Tuen | Tun | Toān (X, Z, K, T) Toàn (Q) |
Tng Teung |
Thon | Ton Thon |
Thòn | Viet. | Đoàn | Section, part | ||||
| Kor. | Dan (단) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Dan | ||||||||||||||||||
| 79 | 88 | 雷 | Léi | Lei2 | Leoi4 | Lui | Loi | Lûi | Lui | Lùi | Looi Lui |
Lōi | Viet. | Lôi | *C.rˤuj | Lwoj | "Thunder" | ||
| Kor. | Roe (뢰) Noe (뇌) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Rai | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hoisan | Louie, Louis | ||||||||||||||||||
| 80 | 82 | 侯 | Hóu | Hou2 | Hau4 | Hau | Hao | Hô͘ (X, Z) Hâu (Q, K, T) Kâu (X, Q, Z) |
Hoh | Hèu | Hew | Héu | Viet. | Hầu | Marquis | ||||
| Kor. | Hu (후, 혜) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 81 | 85 | 龍 | 龙 | Lóng | Lung2 | Lung4 | Lung Loong |
Long | Lêng (K, T) Liông |
Leng | Liùng | Loong | Liūng | Viet. | Long | "Dragon" | |||
| Kor. | Yong/Ryong (용/룡) Rong (롱) Nong (농) Bang (방) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ryō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 82 | 80 | 史 | Shǐ | Shih3 | Si2 | Sze | Si | Sú (X, Z, K, T) Sái (X, Q) Sír (Q) |
Ser Seu Sze |
Sṳ́ | Soo Sze |
Sî | Viet. | Sử | History | ||||
| Kor. | Sa (사) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shi | ||||||||||||||||||
| 83 | 陶 | Táo | T'ao2 | Tou4 | Tou
To |
Tow | Tô (X, Z, K, T) Tô͘ (Q) Thô (Q) |
Tow | Thàu Thò |
Tao Tow |
Thóu | Viet. | Đào | Pleased | |||||
| Kor. | Do (도) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 84 | 93 | 黎 | Lí | Li2 | Lai4 | Lai | Lê | Loy Loi |
Lì Lài |
Lee Lai |
Lī | Viet. | Lê | Multitude | |||||
| Kor. | Yeo/Ryeo (여/려) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Rei | ||||||||||||||||||
| 85 | 97 | 賀 | 贺 | Hè | Hê4 Ho4 |
Ho6 | Ho | Hō (X, Z, K, T) Hò (Q) |
Hor | Ho Fo |
Ho | Hò | Viet. | Hạ | Congratulate | ||||
| Kor. | Ha (하) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ka | ||||||||||||||||||
| 86 | 81 | 顧 | 顾 | Gù | Ku4 | Gu3 | Ku | Goo Gu Khoo |
Kò͘ | Koh | Ku | Koo | Kū | Viet. | Cố | ||||
| Kor. | Go (고) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ko | ||||||||||||||||||
| 87 | 76 | 毛 | Máo | Mao2 | Mou4 | Mo | Mou | Mô͘ | Mor | Mô Mâu |
Mo Mao |
Mōu | Viet. | Mao | "Fur, Hair" | ||||
| Kor. | Mo (모) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Bō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 88 | 71 | 郝 | Hǎo | Hao3 | Kok3 | Kok | Hok | Hak | Khok | Hok | Viet. | Hác | |||||||
| Kor. | Hak (학) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kaku | ||||||||||||||||||
| 89 | 99 | 龔 | 龚 | Gōng | Kung1 | Gung1 | Kung | Kwong | Kéng (X, Q, K, T) Kiong (Z) |
Kiûng | Kong | Kiung | Viet. | Cung | Give, Present | ||||
| Kor. | Gong (공) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 90 | 83 | 邵 | Shào | Shao4 | Siu6 | Shiu | Shaw Sio |
Siō (X, K, T) Siāu (Z, K, T) Siàu (Q) |
Seow Sioh |
Shau Sau |
Shao | Sèu | Viet. | Thiệu | Pottery | ||||
| Kor. | So (소) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 91 | 86 | 萬 | 万 | Wàn | Wan4 | Maan6 | Man | Meng | Bān (X, Z, K, T) Bàn (Q) |
Buang | Van | Wan Man |
Màn | Viet. | Vạn | Ten thousand | |||
| Kor. | Man (만) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Ban | ||||||||||||||||||
| 92 | 89 | 錢 | 钱 | Qián | Ch'ien2 | Cin4 | Chin | Chee | Chîⁿ | Chee | Tshièn | Chen | Chhién | Viet. | Tiền | Money | |||
| Kor. | Jeon (전) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Sen | ||||||||||||||||||
| 93 | 嚴 | 严 | Yán | Yen2 | Jim4 | Yim | Im | Giâm | Ngiam | Ngiàm | Yam | Ngiēm | Viet. | Nghiêm | Tight, strict | ||||
| Kor. | Eom (엄) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Gen | ||||||||||||||||||
| 94 | 覃 | Tán / Qín | T'an2 | Taam4 | Tam | Thâm | Thàm | Thóm | Viet. | Tán | *N-r[a]mʔ | YemX | Extensive, spread to | ||||||
| Kor. | Dam (담) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tan | ||||||||||||||||||
| 95 | 95 | 武 | Wǔ | Wu3 | Mou5 | Mo | Mou | Bú | Boo | Vú | Moo Woo |
Mú | Viet. | Vũ Võ |
*maʔ | MjuX | Military | ||
| Kor. | Mu (무) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Bu | ||||||||||||||||||
| 96 | 54 | 戴 | Dài | Tai4 | Daai3 | Tai | Tè (X, Z, K, T) Tèr (Q) |
Tai | Tai | Tai | Thài | Viet. | Đái Đới |
*Cə.tˤək-s | TojH | Support, wear | |||
| Kor. | Dae (대) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tai | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phil. | Te | ||||||||||||||||||
| 97 | 莫 | Mò | Mo4 | Mok6 | Mok | Bo̍h (K, T) Bo̍k |
Mok | Mo̍k | Mok | Mok | Viet. | Mạc | *mˤak | Mak | Not | ||||
| Kor. | Mo (모) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Baku | ||||||||||||||||||
| 98 | 72 | 孔 | Kǒng | K'ung3 | Hung2 | Hung | Khóng | Kong Khong |
Khúng | Koong Khoong |
Khúng | Viet. | Khổng | *kʰˤoŋʔ | KhuwngX | Hole, opening | |||
| Kor. | Kong (공) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 99 | 向 | Xiàng | Hsiang4 | Heung3 | Heung | Hiòng (X, Q, K, T) Hiàng (Z) |
Hiang | Hióng | Hiòng | Viet. | Hưởng | *qʰaŋ-s *n̥aŋʔ-s |
XjangH | Direction | |||||
| Kor. | Hyang (향) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 100 | 90 | 湯 | 汤 | Tāng | T'ang1 | Tong1 | Tong | Thng | Tng Teung |
Thông | Thong Tong |
Thong | Viet. | Thang | *l̥ˤaŋ | Thang | Boiling water, soup | ||
| Kor. | |||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Tō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 75 | 康 | Kāng | Kang1 | Hong1 | Hong | Khng | Kang Khang |
Không | Khong Kong |
Khong | Viet. | Khang | *k-l̥ˤaŋ | Khang | Healthy | ||||
| Kor. | Gang (강) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 92 | 易 | Yì | I4 | Yi6 Yik6 |
E̍k (X, Z, K, T) Ia̍k (Q) |
Ek | Yit | Iak | Viet. | Dịch | *lek-s | YeH | Exchange, easy | ||||||
| Kor. | Yee (이) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Eki, I | ||||||||||||||||||
| 94 | 常 | Cháng | Ch'ang2 | Soeng4 | Sheung | Siông (X, Q, K, T) Siâng (Z) |
Sioh Seoh |
Sòng | Song | Sōng | Viet. | Thường | *daŋ | Dzyang | Common, often | ||||
| Kor. | Sang (상) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Shō | ||||||||||||||||||
| Misc. | Sōng, Thōng | ||||||||||||||||||
| 96 | 喬 | 乔 | Qiáo | Ch'iao2 | Kiu4 | Kiu | Kiâu | Keow Kiao |
Khiàu | Kiew Khiew |
Khiéu | Viet. | Kiều | *N-kaw | Gjew | Tall | |||
| Kor. | Kyo (교) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Kyō | ||||||||||||||||||
| 98 | 賴 | 赖 | Lài | Lai4 | Laai6 | Lay | Lai | Lōa (X, Z, K, T) Lòa (Q) |
Nai | Lai | Lài | Lài | Viet. | Lại | *rˤat-s | LajH | Rely on | ||
| Kor. | Roe (뢰) Noe (뇌) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Rai | ||||||||||||||||||
| 100 | 文 | Wén | Wen2 | Man4 | Man Mon |
Bûn | Boon | Vùn | Voon | Mūn | Viet. | Văn | *mən | Mjun | Words, script, writing | ||||
| Kor. | Moon (문) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jap. | Bun | ||||||||||||||||||
- Notes
- Other surveys
- 2006 multi-year survey and study conducted by Yuan Yida, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of Sciences's Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, using a sample size of 296 million spread across 1,110 counties and cities and recording around 4,100 surnames.[19]
- 1990: Ji Yuwen Publishing House, based on a sample size of 174,900.
- 1987 study conducted by Yuan Yida with a sample size of 570,000.
- 1977 study published by Li Dongming, a Chinese historian, as "Surname" (《姓》) in Dongfang Magazine.
Taiwan
According to a comprehensive survey of residential permits released by the Taiwanese Ministry of the Interior's Department of Population in 2016, Taiwan has only 1,503 surnames.[6] The top ten surnames in Taiwan accounted for 52.77% of the general population, and the top 100 accounted for 96.56%.
| Rank | Character | Romanizations | % of total pop. | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Mainland (2007) |
Mandarin | Taiwanese | Hakka | Cantonese | Other | ||||||||
| Trad. | Simp. | Wade | Pinyin | POJ | Other | PFS | Other | Jyutping | HK | Other | ||||
| 1 | 5 | 陳 | 陈 | Ch'en2 | Chén | Tân | Tan | Chin | Thin | Can4 | Chan | Chin | Ting | 11.14% |
| 2 | 19 | 林 | Lin2 | Lín | Lîm | Lim, Liem | Lim | Lim | Lam4 | Lam | Lum | 8.31% | ||
| 3 | 7 | 黃 | 黄 | Huang2 | Huáng | Ng | Eng, Ung Wee, Oei Ooi, Uy Bong |
Vòng | Wong | Wong4 | Wong | Wang Vang |
6.05% | |
| 4 | 3 | 張 | 张 | Chang1 | Zhāng | Tiu | Teo, Teoh Tio, Thio Tiew |
Chông | Chong | Zoeng1 | Cheung | Chong Cheong |
Tiong | 5.27% |
| 5 | 2 | 李 | Li3 | Lǐ | Lí | Lee Lie Dee |
Lí | Lee | Lei5 | Lee Li |
Ly Lei |
5.13% | ||
| 6 | 1 | 王 | Wang2 | Wáng | Ông | Heng | Vòng | Wong | Wong4 | Wong | Vang | 4.11% | ||
| 7 | 9 | 吳 | 吴 | Wu2 | Wú | Gô• Ngô• |
Goh, Gouw | Ǹg | Ng | Ng4 | Ng | Ung Eng |
Woo | 4.04% |
| 8 | 4 | 劉 | 刘 | Liu2 | Liú | Lâu | Low Lao, Lauw |
Liù | Liew | Lau4 | Lau | Lao Lou |
Lieu Liou |
3.16% |
| 9 | 40 | 蔡 | Ts'ai4 | Cài | Chhoà | Chua, Choa Tjoa |
Chhai | Chai Choi |
Coi3 | Choi | Choy Tsoi Toy |
Tsay | 2.91% | |
| 10 | 6 | 楊 | 杨 | Yang2 | Yáng | Iûⁿ | Eaw Yeo, Yeoh Yong Joe, Yo |
Yòng | Yong Yeong |
Joeng4 | Yeung | Yeong Ieong |
Young | 2.66% |
Other common surnames in Taiwan are listed by rank below. This report is based on the 2016 study. The ranking in the PRC (based on the 2007 study) is listed in the parenthesis. The Wade–Giles romanization is also listed first in the brackets, and the Hanyu Pinyin romanization is listed second in the brackets.
- 許 (traditional Chinese) / 许 (simplified Chinese) (26) [Hsü3, Xǔ]
- 鄭 / 郑 (21) [Cheng4, Zhèng]
- 謝 / 谢 (23) [Hsieh4, Xiè]
- 洪 (above 100) [Hung2, Hóng]
- 郭 (16) [Kuo1, Guō]
- 邱 (73) [Ch'iu1, Qiū]
- 曾 (32) [Tseng1, Zēng]
- 廖 (62) [Liao4, Liào]
- 賴 / 赖 (above 100) [Lai4, Lài]
- 徐 (11) [Hsü2, Xú]
- 周 (10) [Chou1, Zhōu]
- 葉 / 叶 (43) [Yeh4, Yè]
- 蘇 / 苏 (45) [Su1, Sū]
- 莊 / 庄 (above 100) [Zhuang1, Zhuāng]
- 呂 / 吕 (47) [Lü3, Lǚ]
- 江 (74) [Chiang1, Jiāng]
- 何 (17) [Hê2 or Ho2, Hé]
- 蕭 / 萧 (33) [Hsiao1, Xiāo]
- 羅 / 罗 (20) [Lo2, Luó]
- 高 (18) [Kao1, Gāo]
- Other surveys
- 1994–2011: The American researcher Chih-Hao Tsai has compiled unauthoritative annual surveys of the most common surnames on Taiwan[20] based on published lists of all successful applicants taking Taiwan's Joint College Entrance Exam.[21] The test was mandatory for college entrance until 2002 and is still quite common, with more than a hundred thousand successful applicants a year and a pass rate for all test takers between 60 and 90%.[21]
Canada
Statistics Canada has not released a list of common surnames for any of its recent censuses, but much of the Canadian Chinese population is clustered in Metro Vancouver and Greater Victoria in British Columbia and the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area and the Ottawa-Gatineau Area in Ontario, as well as in some emerging major clusters, such as the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor in Alberta, Montreal, and the Communauté métropolitaine de Québec (Quebec Community Metropolitan Area) in Quebec.
Ontario
A 2010 study by Baiju Shah & al data-mined the Registered Persons Database of Canadian health card recipients in the province of Ontario for a particularly Chinese-Canadian name list. Ignoring potentially non-Chinese spellings such as Lee (49,898 total),[22]: Table 1 they found that the most common Chinese names in Ontario were:[22]
| Rank | Name | Total Number | Character(s) | Romanization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trad. | Simp. | ||||
| 1 | Wong | 34,567 | 王 | Wáng, Wong | |
| 黃 | 黄 | Huáng, Hwang, Wang, Whang, Wong | |||
| 汪 | Wāng, Wong | ||||
| 2 | Chan | 32,692 | 陳 | 陈 | Chan, Chén |
| 3 | Li | 27,608 | 李 | Ly, Lee, Lei, Lǐ | |
| 黎 | Lai, Ly, Lee, Lei, Lí | ||||
| 4 | Chen | 25,618 | 陳 | 陈 | Chan, Chén |
| 5 | Wang | 22,548 | 王 | Wáng, Wong | |
| 汪 | Wāng, Wong | ||||
| 6 | Liu | 18,784 | 劉 | 刘 | Lau, Liew, Liú, Low |
| 廖 | Lau, Lew, Liào, Lieu, Liew, Liu | ||||
| 7 | Zhang | 18,003 | 張 | 张 | Chang, Chong, Chung, Cheung, Teo, Zhāng, Zheung |
| 8 | Lam | 15,910 | 林 | Lam, Lín | |
| 藍 | 蓝 | Lán | |||
| 9 | Leung | 13,696 | 梁 | Leung, Liáng | |
| 10 | Ho | 12,830 | 何 | Hé, Ho | |
| 賀 | 贺 | Hè, Ho | |||
Indonesia
Nearly as large is the Chinese Indonesian community. The 2010 Indonesian census reported more than 8.8 million self-identified Chinese, making up 3.7% of the general population.[23] Just as in Thailand, though, previous legislation (in this case, 127/U/Kep/12/1966) had banned ethnic Chinese surnames throughout the country. This law was abolished after the removal of Suharto, but Chinese names remain a mix of Indonesian, pinyin, and Dutch-influenced Hokkien.
Malaysia
During the 2010 Malaysian Census, approximately 6,960,000 Malaysians – self-identified as Chinese.[24] They are among the few Malaysians who have a continuous surname, as most Malaysians go by patronymics instead.
Singapore
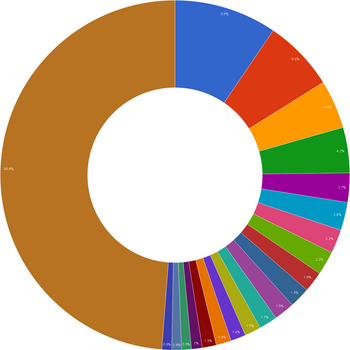
| Tan (9.5%) Lim (6.6%) Lee (4.5%) Ng (4.2%) Ong (2.7%) Wong (2.6%) Goh (2.2%) | Chua (2.2%) Chan (1.9%) Koh (1.9%) Teo (1.9%) Ang (1.7%) Yeo (1.5%) Tay (1.4%) | Chong (0.9%) Chia/Seah (0.9%) Other (48.8%) |
Ethnic Chinese make up almost three-fourths (2009) of Singapore's resident population of nearly four million (2011).
According to Statistics Singapore, as of the year 2000, the most common Chinese Singaporean names were:[25]
- Do take note that the 7th most common surname in China, 趙/赵, is extremely rare in Singapore.
- The surname list is not accurate, as the English surnames may actually have many variants not listed above. E.g. The 16th surname 'Low' can be 劉/刘, 廖,卢,or 羅/罗 in Chinese. The 1st surname Tan (陳/陈)is also a pinyin romanisation for the rare surname 谈。
Thailand
The largest Chinese diaspora community in the world are the Chinese Thais (or Sino-Thais), who make up 12–14%[26][27] of the total Thai population. However, very few of the Chinese Thais have Chinese surnames, after the 1913 Surname Act that required the adoption of Thai surnames in order to enjoy Thai citizenship. Moreover, the same law requires that those possessing the same surname be related, meaning that immigrant Chinese may not adopt the surname of their clansmen unless they can show actual kinship.
United States
The 2010 US Census found 3,794,673 self-identified Chinese Americans and 230,382 self-identified Taiwanese Americans,[28] up from 2,734,841 Chinese Americans and 144,795 Taiwanese Americans in 2000.[29]
Although the Chinese make up the largest segment of America's Asian and Pacific Islander population,[30] the most common Chinese-derived surname during the 2000 census was not itself Chinese but the Vietnamese Nguyễn (Chinese: 阮, Ruǎn).[2]
During the 2000 census, the 10 most common Chinese American names were:[31]
| Rank | Name | Ethnicity [32] |
Total Number (2000 census; API only) |
Character(s) | Pinyin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among API |
Across All Names |
Trad. | Simp. | ||||
| 2 | 24 | Lee | Chinese | 229,200 | 李 | Lǐ | |
| Korean | 黎 | Lí | |||||
| 6 | 262 | Chen | Chinese | 100,700 | 陳 | 陈 | Chén |
| 7 | 279 | Wong | Chinese (Cantonese) |
88,000 | 王 | Wáng | |
| 黃 | 黄 | Huáng | |||||
| 汪 | Wāng | ||||||
| 9 | 399 | Yang | Chinese (Mandarin) |
69,000 | 楊 | 杨 | Yáng |
| 10 | 440 | Wang | Chinese | 63,800 | 王 | Wáng | |
| 汪 | Wāng | ||||||
| 11 | 426 | Chang | Chinese | 62,900 | 張 | 张 | Zhāng |
| 常 | Cháng | ||||||
| 12 | 461 | Chan | Chinese (Cantonese) |
59,800 | 陳 | 陈 | Chén |
| 14 | 521 | Li | Chinese | 55,700 | 李 | Lǐ | |
| 黎 | Lí | ||||||
| 17 | 626 | Lin | Chinese | 47,000 | 林 | Lín | |
| 18 | 652 | Liu | Chinese | 45,500 | 劉 | 刘 | Liú |
| 廖 | Liào | ||||||
- Other surveys
- 2002: study by Matthew Falkenstein, data-mining the 2000 US Census for a particularly Asian & Pacific Islander name list,[33] omitting those like Lee that are common among other ethnicities
- 2000: study by Diane Lauderdale, et al., data-mining Social Security card applications by persons born abroad before 1941 for a particularly Chinese-American name list[32]
See also
References
- ^ Xinhua Net. "我国汉族公民最长姓名达15字 公安部:起名不规范会有不便 [My Country's Han Citizens' Longest Name Reaches 15 Characters]". 12 Dec 2007. Accessed 16 Mar 2012. Template:Zh icon
- ^ a b c United States Census Bureau. "Genealogy Data: Frequently Occurring Surnames from Census 2000". 27 Sept 2011. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.
- ^ a b Word, David L. & al. "Demographic Aspects of Surnames from Census 2000". 26 Jun 2001. Accessed 3 Feb 2012.
- ^ Prest, Kevin. "X三Y四: Similar Chinese Idioms (Chengyu)". 4 Mar 2011. Accessed 5 Apr 2012.
- ^ a b c "公安部统计:'王'成中国第一大姓 有9288万人 [Public Security Bureau Statistics: 'Wang' Found China's #1 'Big Family', Includes 92.88m People]." 24 Apr 2007. Accessed 27 Mar 2012.Template:Zh icon
- ^ a b 全國姓名統計分析. Ministry of the Interior, R.O.C. (Taiwan). 2016. ISBN 9789860503043.
- ^ McFarlan, Donald. 1990 Guinness Book of World Records. Sterling Pub. Co., 2001. ISBN 189205101X.
- ^ Beijing News. "一个“张伟”找到29万人 Archived 2007-09-14 at the Wayback Machine [One Name 'Zhang Wei' Covers 290,000 People]". 26 Jul 2007. Accessed 16 Mar 2012. Template:Zh icon
- ^ People's Daily Online. "China issues first set of stamps of Chinese family names". 19 Nov 2004. Accessed 28 Mar 2012.
- ^ 挑灯看剑 踏雪寻梅. "新'百家姓'图腾,快来看看您的尊姓啥模样 [The New Hundred Family Surnames's Totems: Quick, Come Look at Your Honorable Surname's Picture]". 12 Dec 2011. Accessed 28 Mar 2012. Template:Zh icon
- ^ Badan Pusat Statistik. "Population of Indonesia by Province 1971, 1980, 1990, 1995 , 2000 and 2010 Archived 2011-07-18 at the Wayback Machine". 2009. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.
- ^ Lafraniere, Sharon (21 April 2009). "Name Not on Our List? Change It, China Says". The New York Times.
- ^ Baxter, Wm. H. & Sagart, Laurent. "Baxter–Sagart Old Chinese Reconstruction". Archived from the original on 2012-04-25.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) (1.93 MB). 2011. Accessed 17 March 2013. - ^ 周长楫; 王建设; 陈荣翰; 林美治; 郭锦标, eds. (2006). Minnan Fangyan Da Cidian (in Chinese) (1st ed.). Fuzhou City: Fujian People's Publishing House. ISBN 7-211-03896-9.
- ^ Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwan Minnan (in traditional Chinese). Ministry of Education, R.O.C. [1]. Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- ^ a b c d "教育部異體字字典" [Dictionary of Chinese Character Variants].
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.zdic.net/z/1b/js/675C.htm
- ^ "%E5%B4%94 | Definition | Mandarin Chinese Pinyin English Dictionary | Yabla Chinese". chinese.yabla.com. Retrieved 2016-08-23.
- ^ The results of this survey were previously published at the National Citizen Identity Information Center's website at "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-04-21. Retrieved 2015-05-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). However, the link is now dead. - ^ Tsai, Chih-Hao. "Common Chinese Names". 8 Aug 2011. Accessed 30 Mar 2012.
- ^ a b Tsai, Chih-Hao. "A List of Chinese Names". 8 Aug 2011. Accessed 30 Mar 2012.
- ^ a b Shah, B. R.; Chiu, M.; Amin, S.; Ramani, M.; Sadry, S.; Tu, J. V. (2010). "Surname lists to identify South Asian and Chinese ethnicity from secondary data in Ontario, Canada: A validation study". BMC Medical Research Methodology. 10: 42. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-10-42. PMC 2877682. PMID 20470433.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Statistics Indonesia. 2010 Census. In "Racism remains for Chinese – Indonesians". The Jakarta Post. 2012-01-22. Retrieved 2012-02-18.
- ^ "Population and Housing Census, Malaysia 2010 (2010 Census)". Malaysia: Department of Statistics, Malaysia. 2010. Archived from the original on 2011-08-24. Retrieved 4 Apr 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Statistics Singapore. "Popular Chinese Surnames in Singapore".
- ^ US State Department. "Background Note: Thailand". 3 Jan 2012. Accessed 4 Apr 2012.
- ^ US Central Intelligence Agency. The World Factbook. "Thailand". 20 Mar 2012. Accessed 4 Apr 2012.
- ^ United States Census Bureau. "QT-P8. Race Reporting for the Asian Population by Selected Categories: 2010 2010. Census Summary File 1". 2010. Accessed 3 Apr 2012.
- ^ United States Census Bureau. "The Asian Population: 2000". Feb 2002. Accessed 3 Apr 2012.
- ^ United States Census Bureau. "Census 2000: Chinese Largest Asian Group in the United States". 4 Mar 2002. Accessed 29 Mar 2012.
- ^ Other popular Asian & Pacific Islander names are the Vietnamese names Nguyen (#1), Tran (#5), Le (#8), and Pham (#13); the Korean names Kim (#3) and Park (#15); and the Indian names Patel (#4) and Singh (#16).
- ^ a b Lauderdale, Diane S.; et al. (2000). "Asian American ethnic identification by surname" (PDF). Population Research & Policy Review. 19: 283–300..
- ^ Falkenstein, Matthew R. "The Asian & Pacific Islander surname list: as developed from Census 2000". Joint Statistical Meetings 2002. (New York), 2002.
External links
- Lin Yutang's Chinese-English Dictionary of Modern Usage, hosted at the Chinese University of Hong Kong. (~700 surnames)
- Netor's Ten-Thousand Families Template:Zh icon
- 中國姓氏人口排序 [China's Surname Population Rankings], lists of the most popular surnames under the Song, Yuan, and Ming dynasties Template:Zh icon
