Federal subjects of Russia
 |
|---|
Russia is a federation which, since March 1, 2008, consists of 83 federal subjects (Russian: субъект федерации, subyekt federatsii).[1] They are also known as the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. In 1993, when the Constitution of Russia was adopted, there were 89 federal subjects listed. By 2008, the number of federal subjects had been decreased to 83 because of several mergers.
The federal subjects are of equal federal rights in the sense that they have equal representation—two delegates each—in the Federation Council (upper house of the Federal Assembly). They do, however, differ in the degree of autonomy they enjoy.
Federal subjects should not be confused with Federal districts of Russia which are much larger and each encompass many federal subjects. There are 83 federal subjects in the Russian Federation; while there are only 8 federal districts.
Terminology
This section possibly contains original research. (January 2012) |
The official government translation of the Constitution of Russia in Article 5 states:[2] "1. The Russian Federation shall consist of republics, krays, oblasts, cities of federal significance, an autonomous oblast and autonomous okrugs, which shall have equal rights as constituent entities of the Russian Federation."
The term was also one of several discussed during the 49th annual American Translators Association conference in Orlando, in which Tom Fennel, a freelancer, gave an opinion that the term "constituent entity of the Russian Federation" is preferred to "subject".[3] This recommendation is also shared by Tamara Nekrasova, Head of Translation Department, Goltsblat BLP, who in her "Traps & Mishaps in Legal Translation" presentation in Paris stated that "constituent entity of the Russian Federation is more appropriate than subject of the Russian Federation (subject would be OK for a monarchy)".[4] The term is also used in the UN documents.[citation needed] Other academic sources use the term "subject".[citation needed]
Types
 |
Each federal subject belongs to one of the following types:
| 21 republics (Russian: республика, respublika) — nominally autonomous, each has its own constitution and legislature; is represented by the federal government in international affairs; is meant to be home to a specific ethnic minority. | |
| 46 oblasts (provinces; Russian: область, oblast') — most common type of federal subjects with federally appointed governor and locally elected legislature. Commonly named after their administrative centers. | |
| 9 krais (territories; Russian: край, kray)—essentially the same as oblasts. The title "territory" is historic, originally given because they were once considered frontier regions. | |
| 1 autonomous oblast (autonomous province; Russian: автономная область, avtonomnaya oblast')—the only autonomous oblast is the Jewish Autonomous Oblast | |
| 4 autonomous okrugs (autonomous districts; Russian: автономный округ, avtonomny okrug) — with substantial or predominant ethnic minority. | |
| 2 federal cities (Russian: город федерального значения, gorod federal'nogo znacheniya) — major cities that function as separate regions. |
List of federal subjects
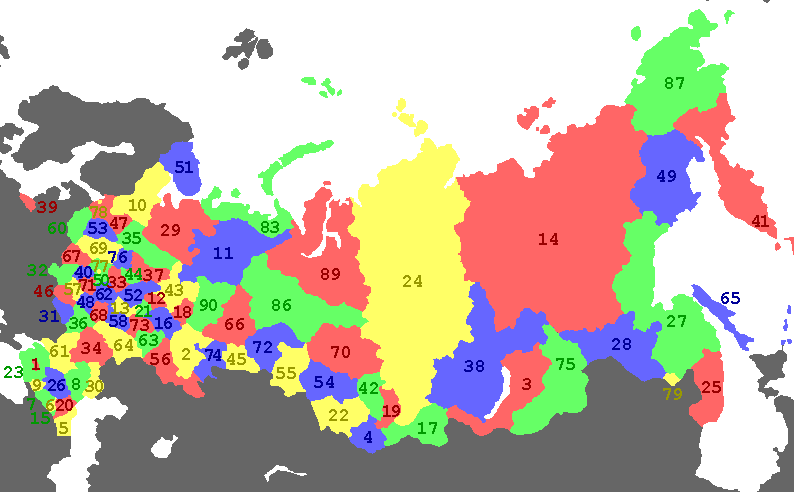
The subjects have both numerical codes and two- or three-letter ISO 3166-2:RU codes. The numerical codes span from 01 to 92, although nine of them (41, 59, 75, 80, 81, 82, 84, 85, and 88) are no longer in use after mergers.
Template:List of federal subjects of Russia
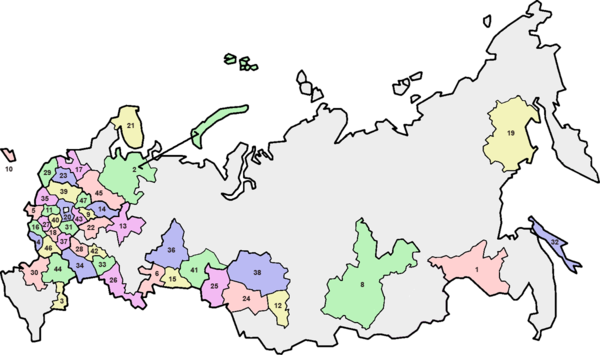
Oblasts
There are 46 oblasts (Russian: область; "provinces").
|
1. Amur |
17. Leningrad |
33. Samara |
Krais
There are 9 krais (Russian: край; territories).
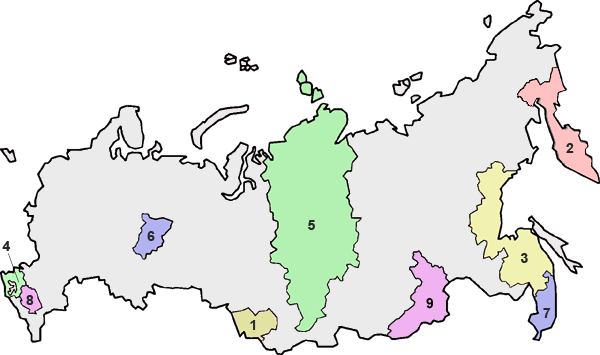
- Altai Krai
- Kamchatka Krai
- Khabarovsk Krai
- Krasnodar Krai
- Krasnoyarsk Krai
- Perm Krai
- Primorsky Krai
- Stavropol Krai
- Zabaykalsky Krai
Federal cities
There are 2 federal cities: Moscow and Saint Petersburg.
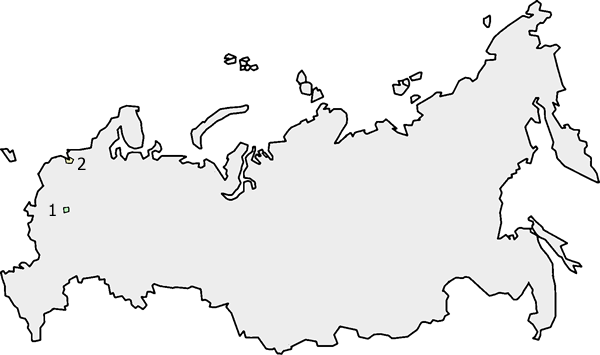
| Map # | Code | ISO Code | Name | Flag | Coat of arms | Federal district | Economic region | Area (km²)[5] | Population[6] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77 | MOW | Moscow | Central | Central | 1,100 | 10,382,754 | ||
| 2 | 78 | SPE | Saint Petersburg | Northwestern | Northwestern | 1,439 | 4,662,547 |
Autonomous oblast
There is one autonomous oblast, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast.

Mergers

Starting in 2005, some of the federal subjects were merged into larger territories. The merging process was finished on March 1, 2008. No new mergers have been planned since March 2008.
| Original territories | Original codes | New code | Date of referendum | Date of merger | Merger |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 1a | 59 (1), 81 (1a) | 90 | December 7, 2003 | December 1, 2005 | Perm Oblast (1) + Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug (1a) → Perm Krai |
| 2, 2a, 2b | 24 (2), 88 (2a), 84 (2b) | 24 | April 17, 2005 | January 1, 2007 | Krasnoyarsk Krai (2) + Evenk Autonomous Okrug (2a) + Taymyr Autonomous Okrug (2b) → Krasnoyarsk Krai |
| 3, 3a | 41 (3), 82 (3a) | 91 | October 23, 2005 | July 1, 2007 | Kamchatka Oblast (3) + Koryak Autonomous Okrug (3a) → Kamchatka Krai |
| 4, 4a | 38 (4), 85 (4a) | 38 | April 16, 2006 | January 1, 2008 | Irkutsk Oblast (4) + Ust-Orda Buryat Autonomous Okrug (4a) → Irkutsk Oblast |
| 5, 5a | 75 (5), 80 (5a) | 92 | March 11, 2007 | March 1, 2008 | Chita Oblast (5) + Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug (5a) → Zabaykalsky Krai |
Further proposals for mergers
The following merger proposals have been made in recent years; most have since become inactive.
| Proposals | Federal subjects | Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6, 6a | Arkhangelsk Oblast + Nenets Autonomous Okrug = Pomorsky Krai | 
|

| ||||
| 7, 7a, 7b | Khabarovsk Krai + Jewish Autonomous Oblast + Amur Oblast = Amur Krai | 
|

|
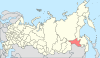
| |||
| 8, 8a | Magadan Oblast + Chukotka Autonomous Okrug = Magadan Krai | 
|
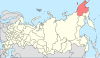
| ||||
| 9, 9a, 9b | Irkutsk Oblast + Buryat Republic + Zabaykalsky Krai = Baykalsky Krai | 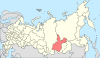
|
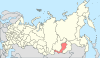
|

| |||
| 10, 10a, 10b | Tyumen Oblast + Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug + Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug = Tyumen Krai | 
|

|
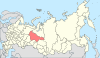
| |||
| 11, 11a, 11b | Novosibirsk Oblast + Omsk Oblast + Tomsk Oblast = Novosibirsk Krai | 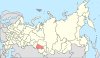
|

|

| |||
| 12, 12a, 12b | Kemerovo Oblast + Altai Republic + Altai Krai = Altai Krai | 
|
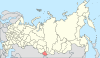
|
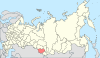
| |||
| 13 | St. Petersburg + Leningrad Oblast = St. Petersburg Oblast | 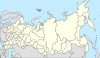
|
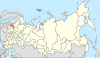
| ||||
| 14 | Moscow + Moscow Oblast = Moscow Oblast | 
|
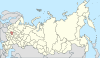
| ||||
| 15, 15a | Yaroslavl Oblast + Kostroma Oblast = Yaroslavl Krai | 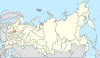
|

| ||||
| 16, 16a | Novgorod Oblast + Pskov Oblast = Novgorod Krai | 
|

| ||||
| 17, 17a | Krasnodar Krai + Republic of Adygea = Krasnodar Krai | 
|

| ||||
| 18, 18a | Republic of Ingushetia + Chechen Republic = Checheno-Ingushetia | 
|

| ||||
See also
- Subdivisions of Russia
- Federal districts of Russia
- Economic regions of Russia
- History of the administrative division of Russia
- Flags of the federal subjects of Russia
- List of heads of federal subjects of Russia
- List of Russian federal subjects by GRP
References
- ^ Constitution, Article 65
- ^ http://www.government.ru/eng/gov/base/54.html
- ^ http://www.ata-divisions.org/SLD/slavfile/winter-2009.pdf
- ^ http://eulita.eu/sites/default/files/Tammy_presentation.pdf
- ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации[[Category:Articles containing Russian-language text]] (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help) - ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек[[Category:Articles containing Russian-language text]] (Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban localities, rural localities—administrative centers, and rural localities with population of over 3,000)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2008-06-23.
{{cite web}}: URL–wikilink conflict (help)
Sources
- 12 декабря 1993 г. «Конституция Российской Федерации», в ред. Федерального конституционного закона №7-ФКЗ от 30 декабря 2008 г. Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Российская газета", №237, 25 декабря 1993 г. (December 12, 1993 Constitution of the Russian Federation, as amended by the Federal Constitutional Law #7-FKZ of December 30, 2008. Effective as of the official publication date.).
