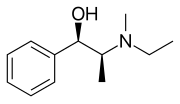
Etafedrine
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by DMacks (talk | contribs) at 04:58, 17 June 2020 (Remove malformatted |molecular_weight= when infobox can autocalculate it, per Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Pharmacology#Molecular weights in drugboxes (via WP:JWB)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.218 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H19NO |
| Molar mass | 193.290 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Etafedrine (INN) or ethylephedrine is a long-acting bronchodilator and has the brand name Nethaprin. It was previously commercially available as both the free base and as the hydrochloride salt from Sanofi-Aventis (now Sanofi) but is now no longer marketed.
Pharmacology
Unlike ephedrine and tyramine, etafedrine does not induce the release of epinephrine or norepinephrine and instead acts as a selective β2 adrenoreceptor agonist, thereby mediating its bronchodilator effects.[1]
See also
References
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
| Adamantanes | |
|---|---|
| Adenosine antagonists | |
| Alkylamines | |
| Ampakines | |
| Arylcyclohexylamines | |
| Benzazepines | |
| Cathinones |
|
| Cholinergics |
|
| Convulsants | |
| Eugeroics | |
| Oxazolines | |
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Phenylmorpholines | |
| Piperazines | |
| Piperidines |
|
| Pyrrolidines | |
| Racetams | |
| Tropanes |
|
| Tryptamines | |
| Others |
|
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
