List of countries by Human Development Index: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [pending revision] |
→Complete list of countries: per source |
|||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
| 26 || {{steady}} ||style="text-align:left"| {{flag|Singapore}} || 0.866 || {{increase}} 0.002 |
| 26 || {{steady}} ||style="text-align:left"| {{flag|Singapore}} || 0.866 || {{increase}} 0.002 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 27 || |
| 27 || {{steady}} ||style="text-align:left"| {{flag|Czech Republic}} || 0.865 || {{increase}} 0.002 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| 28 || {{steady}} ||style="text-align:left"| {{flag|United Kingdom}} || 0.863 || {{increase}} 0.001 |
| 28 || {{steady}} ||style="text-align:left"| {{flag|United Kingdom}} || 0.863 || {{increase}} 0.001 |
||
Revision as of 18:54, 17 February 2012
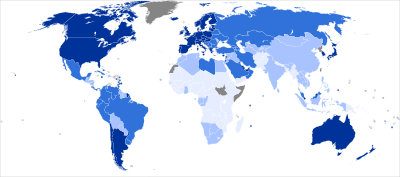
Very High | Low |
High | Data unavailable |
Medium |

| 0.900 and over 0.850–0.899 0.800–0.849 0.750–0.799 0.700–0.749 | 0.650–0.699 0.600–0.649 0.550–0.599 0.500–0.549 0.450–0.499 | 0.400–0.449 0.350–0.399 0.300–0.349 under 0.300 Data unavailable |
This is a list of all countries by Human Development Index as included in a United Nations Development Programme's Human Development Report. The latest report was released on 2 November 2011 and compiled on the basis of estimates for 2011. It covers 185 member states of the United Nations (out of 193), along with Hong Kong (of the People's Republic of China), and the Palestinian territories; 8 UN member states are not included due to lack of data. The average HDI of regions of the World and groups of countries are also included for comparison.
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure of life expectancy, literacy, education and standards of living for countries worldwide. It is a standard means of measuring well-being, especially child welfare. It is used to distinguish whether the country is a developed, a developing or an under-developed country, and also to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life. The index was developed in 1990 by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq[2] and Indian economist Amartya Sen.[3]
Countries fall into four broad human development categories, each of which comprises 47 countries: Very High Human Development, High Human Development, Medium Human Development and Low Human Development (46 countries in this category).
Due to the new methodology adopted since the 2010 Human Development Report, its HDI figures appear lower than the HDI figures in previous reports.
From 2007 to 2010, the first category was referred to as developed countries, and the last three are all grouped in developing countries. The original "high human development" category has been split into two as above in the report for 2007.
Some older groupings (high/medium/low income countries) have been removed that were based on the gross domestic product (GDP) in purchasing power parity (PPP) per capita, and have been replaced by another index based on the gross national income (GNI) in purchasing power parity per capita.
The country with the largest decrease in HDI since 1998 is Zimbabwe, falling from 0.514 in 1998 to 0.140 in 2010. The country with the largest decrease since 2009 is Cape Verde, which decreased by 0.170.
Over half of the world's population live in countries with "medium human development" (51%), while less than a fifth (18%) populate countries falling in the "low human development" category. Countries with "high" to "very high" human development account for less than a third of the world's total population (30%).
Complete list of countries
 = increase.
= increase. = steady.
= steady. = decrease.
= decrease.- Similar HDI values in the current list do not lead to ranking ties, since the HDI rank is actually determined using HDI values to the sixth decimal point.
- The number in brackets represents the number of ranks the country has climbed (up or down) relative to new 2011 data for 2010 (as indicated in the new 2011 report, p. 131).
Very high human development
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
High human development
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Medium human development
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Low human development
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
List of countries by continent
Africa
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Americas
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asia and Oceania
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Europe & Central Asia
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
List of countries by non-continental region
Arab League member states
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
European Union
Average of all members: 0.853
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
East Asia and the Pacific
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Latin America
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Middle East and North Africa
|
10 highest HDIs
|
10 lowest HDIs
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
HDI by regions & groups
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Countries missing from latest report
UN member states (latest UNDP data)
|
Non-UN members (not calculated by the UNDP)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- American Human Development Project
- Happy Planet Index
- List of African countries by Human Development Index
- List of Argentine provinces by Human Development Index
- List of Australian states and territories by HDI
- List of Brazilian states by Human Development Index
- List of Chilean regions by Human Development Index
- List of Chinese administrative divisions by Human Development Index
- List of countries by Human Development Index/Former reports
- List of countries by inequality-adjusted HDI
- List of Indian states and territories by Human Development Index
- List of Indonesian provinces by HDI
- List of Mexican states by Human Development Index
- List of Pakistani Districts by Human Development Index
- List of Philippine provinces by Human Development Index
- List of Russian federal subjects by HDI
- List of sovereign states in Europe by Human Development Index
- List of Thailand provinces by Human Development Index
- List of U.S. states by HDI
- List of Venezuelan states by human development index
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe statistics
- Satisfaction with Life Index
Notes
- ^ Somalia's last inclusion in the HDI ranking was in the 1996 report (1993 data).
- ^ The UN does not recognize the Republic of China (Taiwan) as a sovereign state. The HDI report does not include Taiwan as part of the People's Republic of China when calculating China's figures (see [1]). The ROC's government calculated its HDI to be 0.868, based on 2010 new methodology of UNDP for calculating 2010 HDIs.[11]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag "Human Development Report 2011 - Human development statistical annex" (PDF). HDRO (Human Development Report Office United Nations Development Programme. pp. 127–130. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- ^ "History of the Human Development Report". United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ^ "The Human Development concept". UNDP. 2010. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
- ^ a b "2011 Human Development Report". United Nations Development Programme. p. 151. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- ^ "The State of Human Development" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 1998. Retrieved 26 March 2009.
- ^ "Human Development Report: Somalia 2001" (PDF). 2001. p. 198. Retrieved 26 March 2009. [dead link]
- ^ "Puerto Rico (United States)". United Nations Environment Programme. 2 March 1998. Retrieved 26 March 2009.. [citation needed].
- ^ a b c d e f "Les défis de la croissance calédonienne, on page 13" (PDF) (in French). CEROM - INSEE. Retrieved 10 December 2008.
- ^ "Greenland (Denmark)". United Nations Environment Programme. 2 March 1998. Retrieved 26 March 2009.. [citation needed].
- ^ The UN did not calculate the HDI of Macau. The government of Macau calculates its own HDI. If it were included in the UN's HDI figures as of 2007, Macau would rank 23rd or 24th (tying either Singapore or Hong Kong). "Macao in Figures 2010". Statistics and Census Service, Macau SAR. 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
- ^ "2010中華民國人類發展指數 (HDI)" (pdf) (in Chinese). Directorate General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics, Executive Yuan, R.O.C. 2010. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^ "Human Development Report - Kosovo 2010" (PDF). UNDP. 2010. p. 100. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- ^ "L'Indice de Développement Humain : Une Évaluation pour la réunion" (PDF) (in French). Laboratoire d’Economie Appliquée au Développement (LEAD) Université du Sud Toulon-Var. Retrieved 10 December 2008.[dead link]
External links
- Human Development Report 2011
- Archive of Previous global reports.
- HDI 2011 Index (the first column).
- Data challenges in estimating the HDI: The cases of Cuba, Palau and the Occupied Palestinian Territory.
