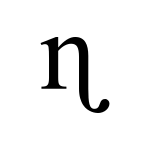Voiced retroflex nasal
Appearance
| Voiced retroflex nasal | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ɳ | |||
| IPA Number | 117 | ||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ɳ | ||
| Unicode (hex) | U+0273 | ||
| X-SAMPA | n` | ||
| Braille | |||
| |||
The retroflex nasal is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɳ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is n`. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA symbol is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of an en (the letter used for the corresponding alveolar consonant). It is similar to ⟨ɲ⟩, the letter for the palatal nasal, which has a leftward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of the left stem, and to ⟨ŋ⟩, the letter for the velar nasal, which has a leftward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of the right stem.
Features
Features of the retroflex nasal:
- Its manner of articulation is occlusive, which means it is produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract. Because the consonant is also nasal, the blocked airflow is redirected through the nose.
- Its place of articulation is retroflex, which prototypically means it is articulated subapical (with the tip of the tongue curled up), but more generally, it means that it is postalveolar without being palatalized. That is, besides the prototypical subapical articulation, the tongue can be apical (pointed) or, in some fricatives, laminal (flat).
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is a nasal consonant, which means air is allowed to escape through the nose, either exclusively (nasal stops) or in addition to through the mouth.
- Because the sound is not produced with airflow over the tongue, the central–lateral dichotomy does not apply.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Occurrence
| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enindhilyagwa | yingarna | [jiŋaɳa] | 'snake' | ||
| Hindi | [[[Devanāgarī|गणेश]]] Error: {{Lang}}: script: deva not supported for code: hi (help) | [ɡəɳeʃ] | 'Ganesha' | See Hindi phonology | |
| Kannada | [[[Kannada script|ಅಣೆ]]] Error: {{Lang}}: script: knda not supported for code: kn (help) | [ʌɳe] | 'dam' | ||
| Khanty | Eastern dialects | еңә | [eɳə] | 'large' | |
| Some northern dialects | |||||
| Malayalam[1] | അണ | [aɳə] | 'jaw' | ||
| Marathi | बाण | [baːɳ] | 'arrow' | See Marathi phonology | |
| Marshallese | [Ņadikdik] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ɳˠɑrʲiɯɡɯirʲiɯk] | 'Knox Atoll' | ||
| Norwegian | [[[Norwegian alphabet|garn]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | 'yarn' | See Norwegian phonology | ||
| Oriya | ବଣି | [bɔɳi] | 'old' | ||
| Pashto | اتڼ/Ataṇ | 'Attan' | |||
| Punjabi | ਪੁਰਾਣਾ / پُراڻا | [pʊraːɳaː] | 'old' | ||
| Swedish[2] | [[[Swedish alphabet|garn]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | 'yarn' | See Swedish phonology | ||
| Tamil[3] | அணல் | [aɳal] | 'neck' | See Tamil phonology | |
| Telugu | [[[Telugu script|ఒణ్ఢు]]] Error: {{Lang}}: script: telu not supported for code: te (help) | [oɳɖu] | 'cook' | ||
| Vietnamese[4] | [[[Vietnamese alphabet|bạn trả]]] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | [ɓaɳ˧ˀ˨ʔ ʈa˧˩˧] | 'you pay' | Allophone of /n/ before /ʈ/. See Vietnamese phonology | |
See also
References
- ^ Ladefoged (2005:165)
- ^ Eliasson (1986:278–279)
- ^ Keane (2004:111)
- ^ Thompson (1959:458–461)
Bibliography
- Eliasson, Stig (1986), "Sandhi in Peninsular Scandinavian", in Anderson, Henning (ed.), Sandhi Phenomena in the Languages of Europe, Berlin: de Gruyter, pp. 271–300
- Keane, Elinor (2004), "Tamil", Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 34 (1): 111–116, doi:10.1017/S0025100304001549
- Ladefoged, Peter (2005), Vowels and Consonants (Second ed.), Blackwell
- Thompson, Laurence (1959), "Saigon phonemics", Language, 35 (3): 454–476, doi:10.2307/411232, JSTOR 411232